1. DNA & RNA
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts in genetics, embryology, and personalized medicine, including DNA structure, replication, transcription, and translation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Chromosomes
Divided into 46 separate chromatin strands. Each pair of chromosomes contains a unique collection of genes and is characterised by a different length and a special pattern of stripe width.
Homologous Chromosome
One chromosome is donated by the father and the other by the mother
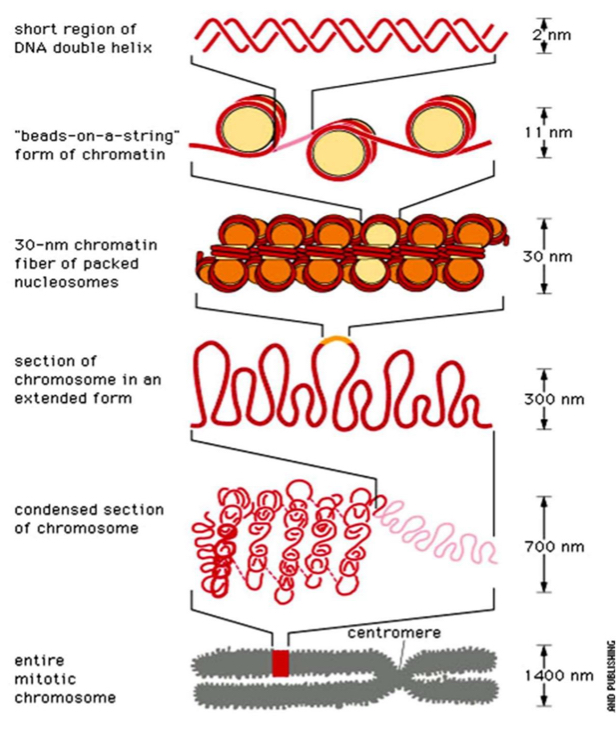
The Process of DNA molecule to chromosome
An efficient packaging system is needed because the length of of the DNA chainis much longer than the cell. DNA wraps around histones to form nucleosomes, which further coil and condense to create chromosomes.
Chromatin
The material that makes up chromosomes, consisting of DNA and proteins, which is less tightly packed than chromosomes.
Histones
Protiens used to form chromatin. Core (H2A, H2B, H3, H4) + H1
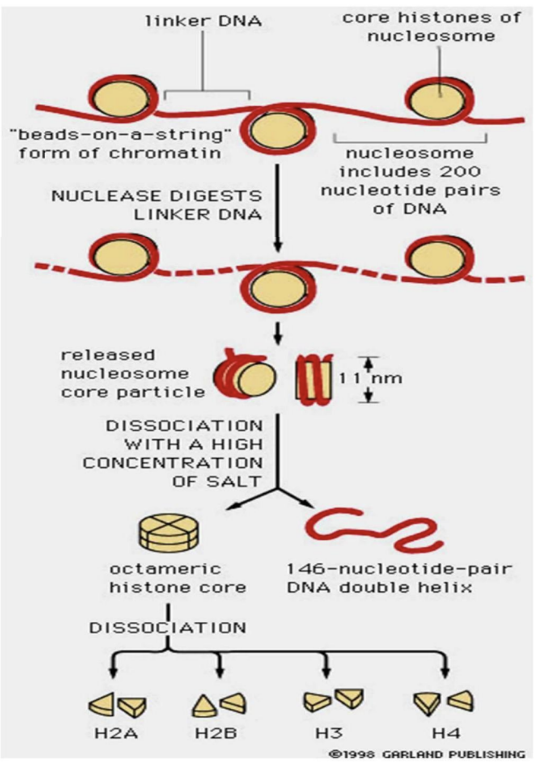
Nucleosome
A unit of DNA that consists of a short DNA strand, 146 bases long, wrapped around a histone cylinder.
DNA packaging
Not all done the same way, there are open and closed areas. More open areas are active and form proteins.
The Cell
The starting point. Most metabolic and biochemical processes occur within the cell.
The Nucleus
Control centre of the cell. Contains the chromosomes. The processes that occur are DNA replication and RNA transcription.
Nucleotides that make up DNA
Pymidines: Thymine (T), Cytosine (C); Purines: Adenine (A), Guanine (G).
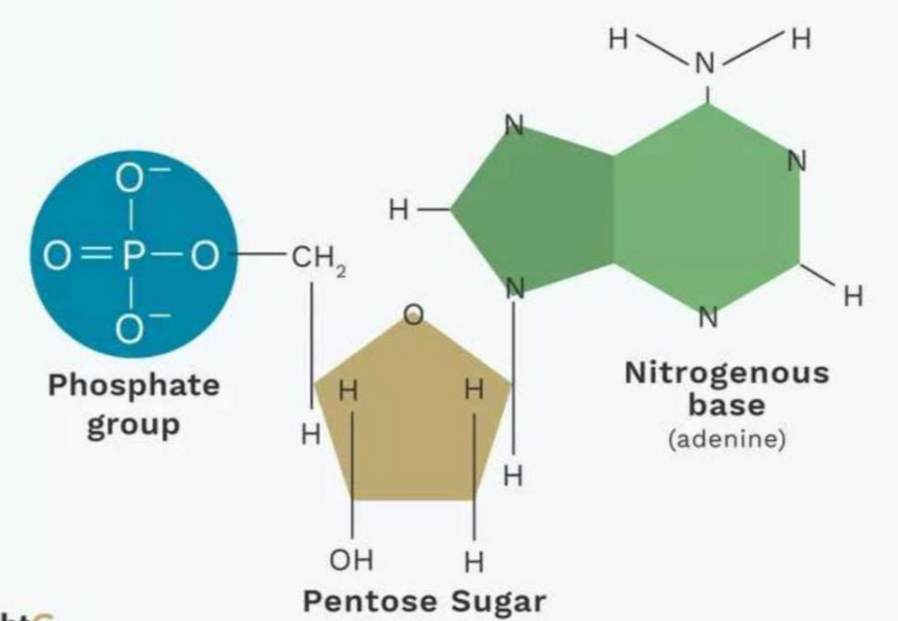
Nucleotide
The basic building blocks of DNA and RNA, consisting of a sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
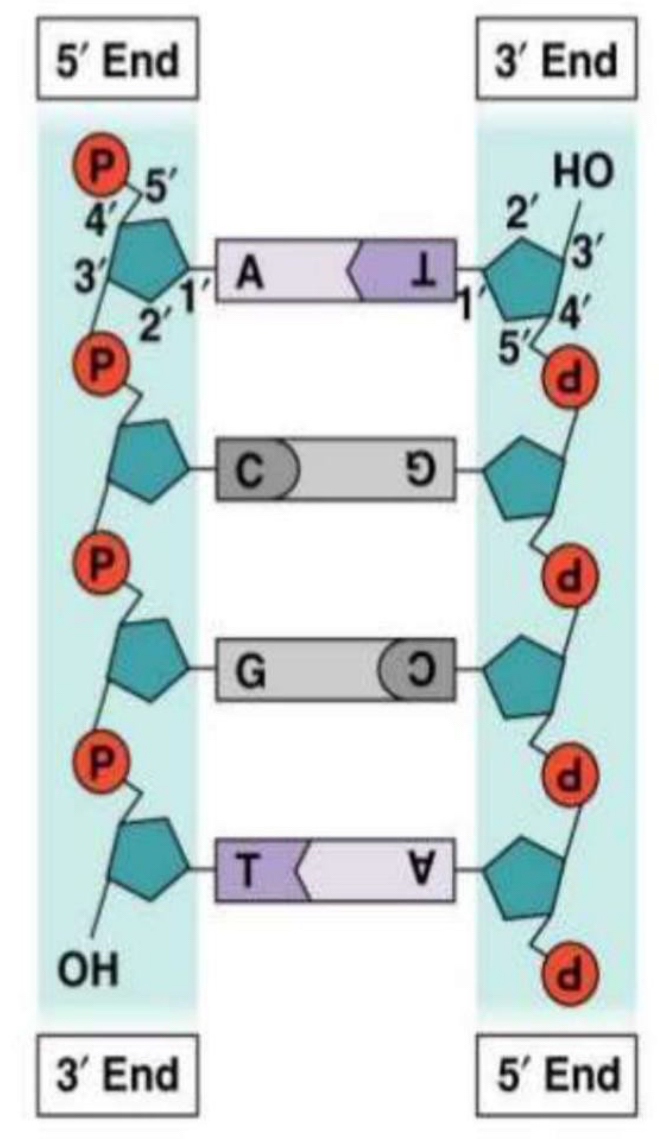
DNA Stucture
The molecular skeleton is made up of sugar, phosphate and the nitrogenous base.
The bond between adjacent nucleotides is called a phosphodiester bond.
The amount of adenine (A) is equal to the amount of thymine (T), and the same goes for Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G).
The two strands are antiparallel (antisense), running in opposite directions 5’ to 3’ one way and 3’ to 5’ the other.
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases: Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C)
Purines
Nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
How DNA chains are built
The nucelotides building blocks (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP) each has three phosphates attached.
When a new one comes in it connects to the 3’ OH (hydroxyl group) of the growing DNA strand
Two phosphates are removed, the “pyrophosphate” is the part that flies off, water is also a byproduct
The energy from this reation is used to form a strong covalent phosphodiester bond.
This bond links the sugar of one nucleotide to the phosphate of the next
The Link Between Two Strands
The helices are fomed by hydrogen bonds formed between complementary bases (A-T and C-G) holding the two strands of DNA together. A:T is two hyrogen bonds, G:C is three hyrogen bonds.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a growing chain.
Telomere
The region at the end of a chromosome that contains repeated sequences, protecting DNA from deterioration. It shortens with each cell division, playing a role in aging and cellular lifespan.
Semiconservative Replication
A method of DNA replication where each new DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one newly synthesized strand.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, a type of RNA that carries the genetic information from DNA to be translated into proteins.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
RNA Polymerase
The enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
Operon
A group of genes whose expression is regulated together in prokaryotes.
Amino Acid
The building blocks of proteins, coded for by codons in mRNA.
5' Cap
A modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5' end of a precursor mRNA molecule that assists in ribosome binding.
Intron
Non-coding segments of a gene that are removed during RNA processing.
Exon
Coding segments of a gene that are retained in the final mRNA after processing.
Peptidyl Transferase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds during protein synthesis.
Promoter
A region of DNA where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Translational Initiation Complex
The assembly of ribosomal subunits, mRNA, and the initiator tRNA to begin translation.
Spliceosome
A complex of proteins and RNA that facilitates the removal of introns from pre-mRNA.
Polyadenylation
The addition of a poly-A tail to the 3' end of mRNA, which protects it from degradation.