Organelles
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
plasma membrane
structure: phospholipid bilayer containing cholesterol, proteins (integral and peripheral), and some carbohydrates (externally)
function: contains receptors for communication, forms intercellular connections, acts as physical barrier to enclose cell contents, regulates material movement into and out of the cell
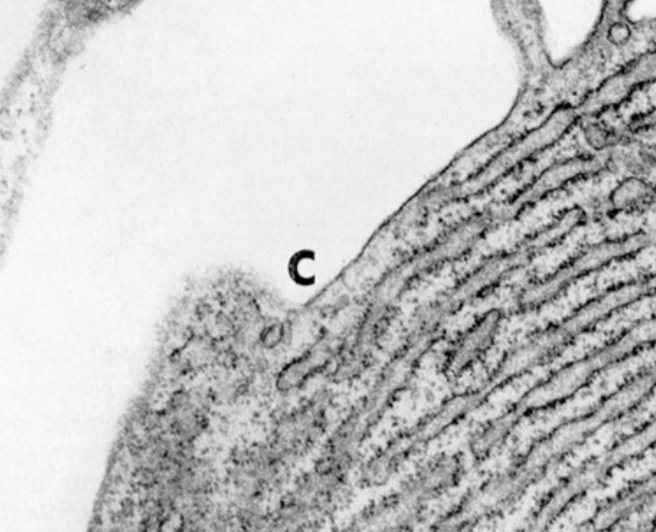
cytoplasm
structure: consists of cytosol (fluid portion) and organelles
function: place of many metabolic processes of the cell, stores nutrients and dissolved solutes
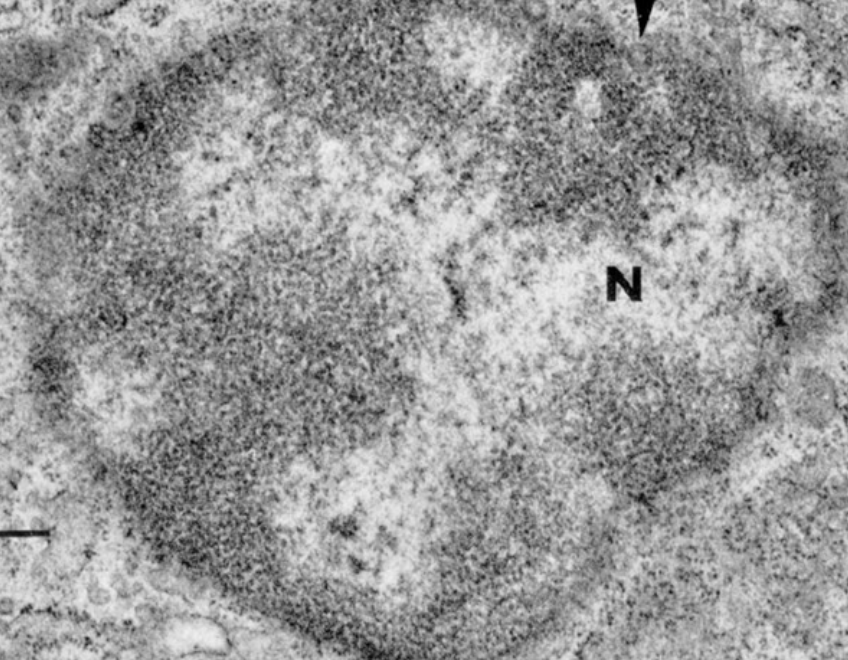
nucleus
structure: surrounded by double membrane nuclear envelope (each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer), contains nucleolus and chromatin within nucleoplasm (a fluid)
function: acts a cell control center, houses genetic information (DNA), site of ribosome subunit assembly
proteins
scattered within membrane and some are attached, others “float”
cholesterol
strengthens membrane
glycocalyx
carbohydrates that participate in cell to cell recognition
microvilli
increase membrane surface area for increased absorption or secretion
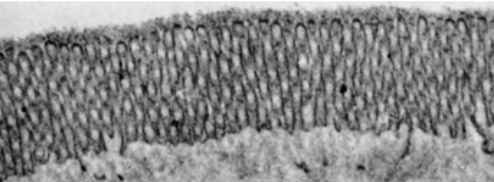
cilia
larger, hairlike projection (larger than microvilli) and move substances over cell surface
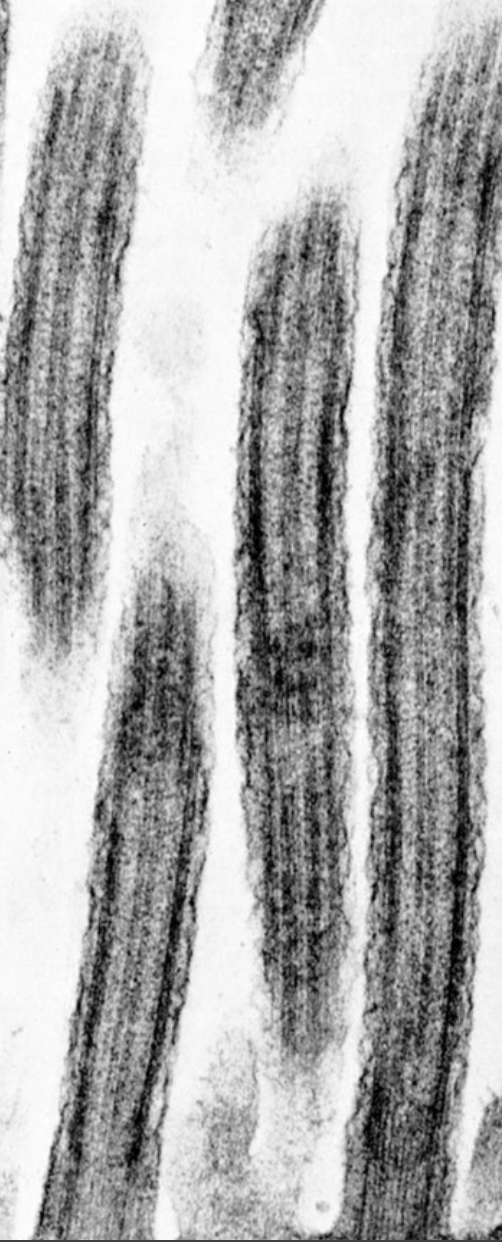
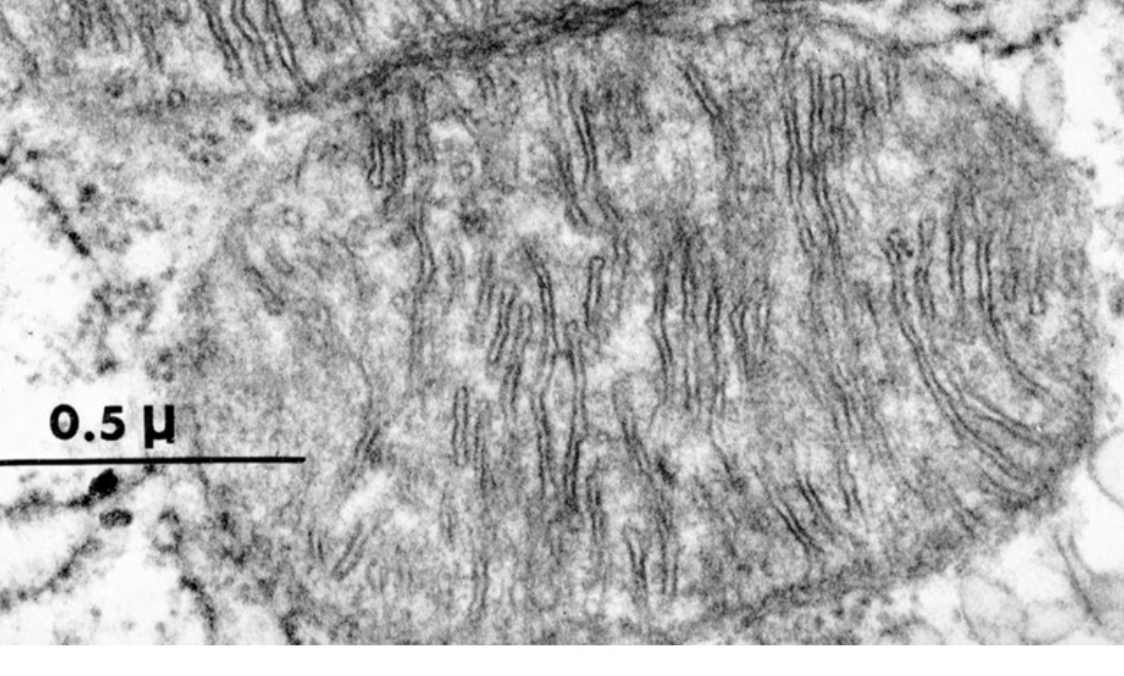
mitochondria
structure: double membrane structures with cristae, fluid matrix contents at center, contains its own DNA called mtDNA
function: make ATP and contain their own DNA inherited from oocyte (egg) because head of sperm contains no mitochondria
ribosomes
spherical structures involved in protein synthesis
free ribosomes
primarily make proteins for the cell itself

bound ribosomes
make proteins for plasma membrane or proteins to be exported outside cell
rough endoplasmic reticulum
has ribosomes on walls, synthesizes and distributes proteins
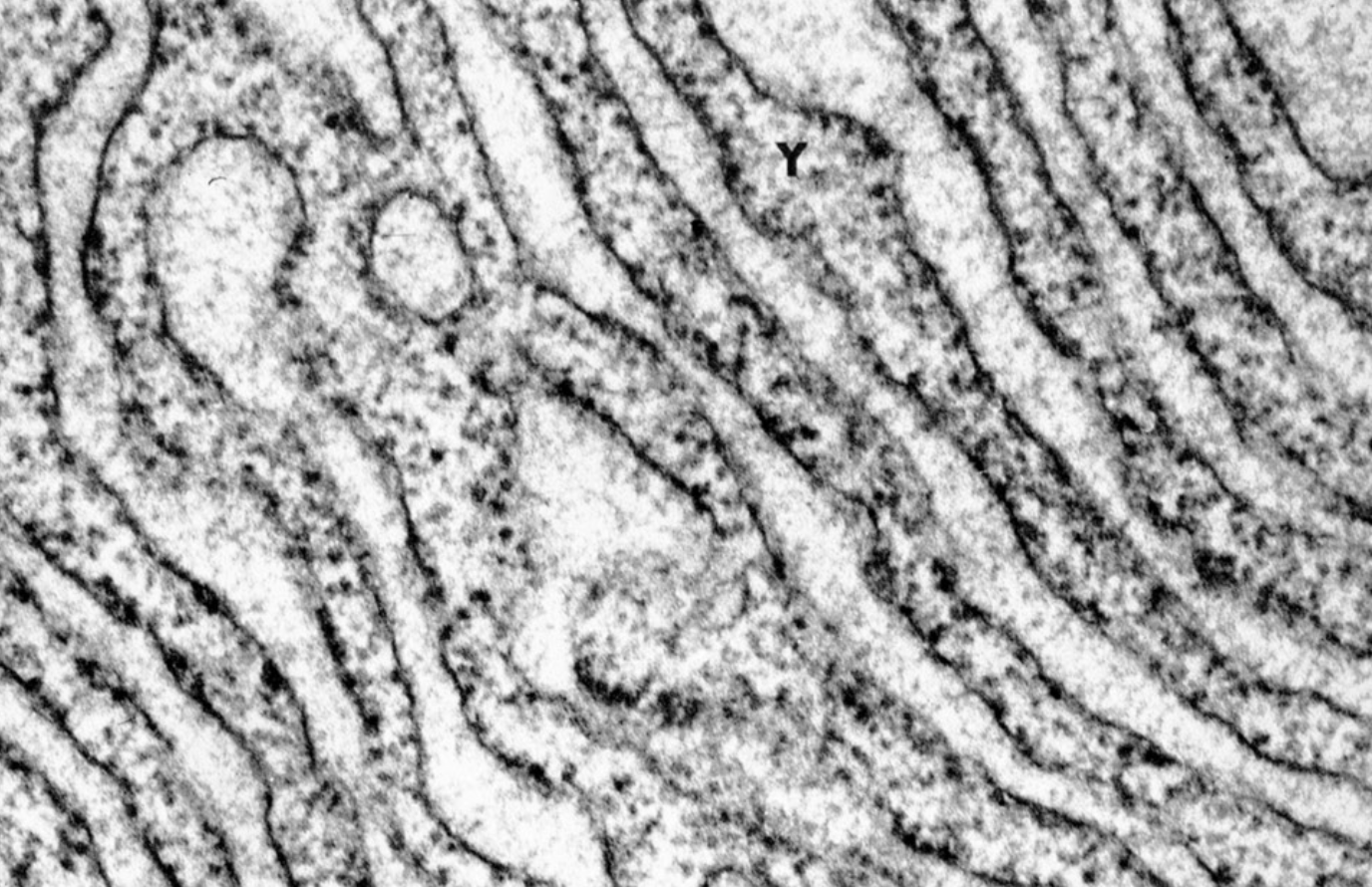
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
has no ribosomes, synthesizes lipids (especially steroid hormones), detoxifies drugs, alcohol, poisons
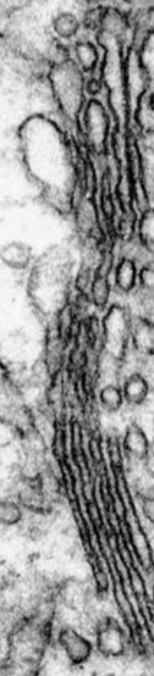
golgi apparatus
structure: flattened, smooth sacs with small “vesicles”
function: accepts, sorts, packages materials from rough ER, common in secretory cells
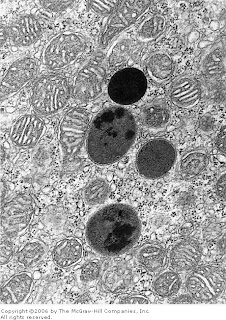
lysosomes
structure: spherical digestive enzymes
function: digest materials or microbes ingested by cell, remove old/damaged organelles, self destructs (autolyze)
Tay-Sachs disease (inherited disorder, lysosomal enzyme missing of dysfunction, buildup of waste in cells, including nerve cells)
centrioles
pair of rod-shaped structures involved in cell division
nucleolus
structure: spherical, dark-staining, dense granular region in the nucleus
function: synthesizes rRNA and assembles ribosome subunits