ESS Human Populations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Crude Birth Rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Crude Death Rate
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Immigration Rate
The number of new arrivals in a country in a given year per 1000 people.
Emigration Rate
The number of people leaving a country in a given year per 1000 people.
Total Fertility Rate
The average number of births per woman of childbearing age.
Life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical condition and if current factors remain unchanged.
Doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Natural Increase Rate
The difference between the number of births and the number of deaths
Anti-natalist policies
Government policies to reduce the number of births.
Pro-natalist policies
Government policies to increase the crude birth rate.
Demographic Transition Model
A model that describes the changing levels of births and deaths in a human population through different stages of development over time.
Dependency Ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force, which is an indicator of the economic burden on the working-age population
Population Momentum
Continued population growth that does not slow in response to growth reduction measures and even after fertility rates decline
Impacts of Human Population
climate change, resource scarcity, environmental degradation, and social and economic inequality (CRES).
Stage 1 of DTM
Pre-industrial : High birth and death rate, short life expectancy, slow population growth
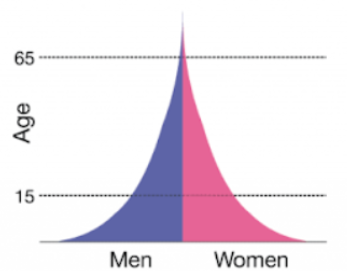
Stage 2 of DTM
Low income country : High birth rate, moderate death rate, medium life expectancy, rapid population growth
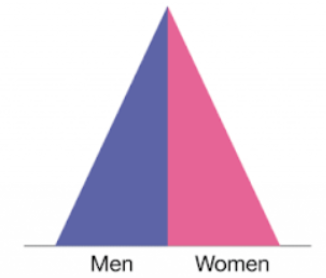
Stage 3 of DTM
Wealthier middle income country : Declining birth rate, low death rate, long life expectancy, slowing population growth
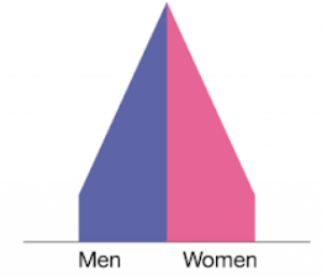
Stage 4 of DTM
High income country: Low birth and death rate, long life expectancy, stable population growth
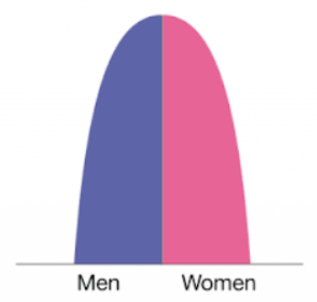
Stage 5 of DTM
High income country: Very low birth rate, low death rate, long life expectancy, shrinking population growth
Sudden onset events
Migration that happens quickly due to sudden, severe events like natural disasters or conflicts.
Slow onset events
Migration that occurs gradually over time due to factors like environmental degradation or economic changes - desertification, saltwater inundation
Environmental migration
Migration that occurs due to environmental events.
Direct population growth strategies
targets fertility (families) or immigration.
Indirect population growth strategies
targets socio-economic conditions such as poverty and education.
Population growth
Determined by fertility rate, death rate and migration rate