Business Data Science Technologies Exam 1
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
information system
interrelated components working together to collect/process/store/disseminate info, has feedback mechanism to monitor/control operation
uses of info system
accomplish work-related tasks & everyday living activities, to analyze large amounts of data
competitive advantage benefits
generate more sales, achieves superior profit margins
how to gain competitive advantage
cost leadership, differentiation, focus, much effort to keep, managers identify/use info systems
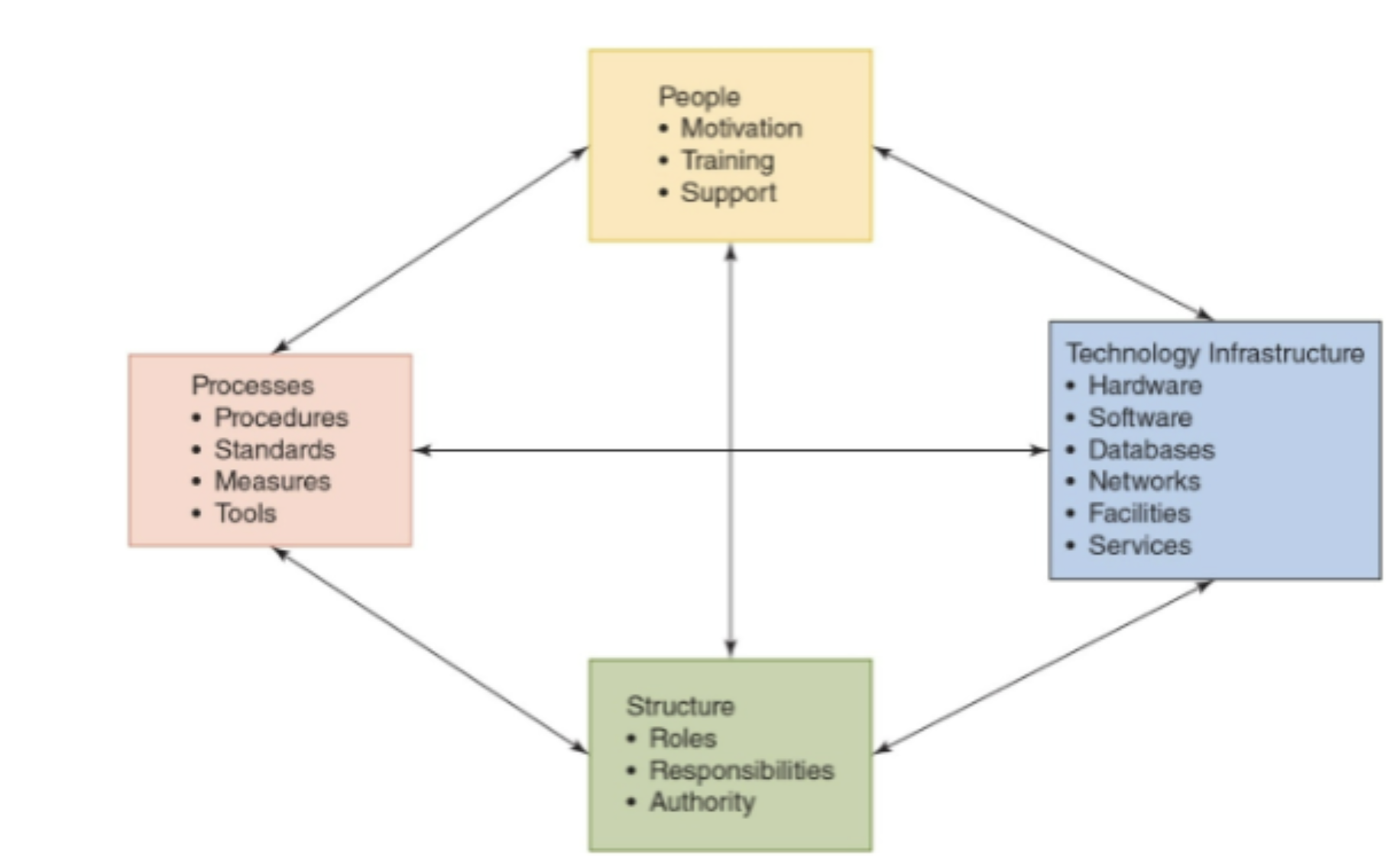
leavitt’s diamond
used to introduce new systems to workplace, highlights people, tech infrastructure, processes & structure
benefits of leavitt’s diamond
can lower stress, encourage teamwork, increase successful implementation
leavitt’s diamond: people
most important element, require training/understanding of need for info system, motivation to use, access to support if needed
leavitt’s diamond: tech infrastructure
hardware, software, databases, networks, facilities, must meet all users need, foundation of every computer-based info system
leavitt’s diamond: processes
structured set of related activities, input- add value- create output, how to achieve result, who does what when, what if went wrong
leavitt’s diamond: structure
defines relationships btw org. members, defines roles/responsibilities (often change w new info system)
Types of info systems
Personal info system, workgroup info system, enterprise info system, inter organizational IS
Personal IS
improves productivity of individual users in performing stand-alone tasks
workgroup IS
enables ppl to work together effectively
enterprise IS
facilitates organization-wide business needs
interorganizational IS
enables sharing of into across organizational boundaries
strategic planning
managerial process meant to identify initiatives/projects to achieve, must see everything is changing
benefits of strategic planning
give framework/clearly defined direction to guide decision making & effective use of org. resources, allows org to be productive, improves communication
IS strategic planning types
cost center/service provider, business partner/peer, game changer
Cost center/service provider
inward looking, control/reduce IS costs, improve IS operations/services, react to strategic plans of business units
business partner/peer
business focused, improve IS/business partnership, control IS costs, expand IS services, execute IS projects to support business plans
game changer
outward looking, drive business innovation, deliver new products/services, use IS to achieve competitive advantage
chief info officer
employ IS departmentequipment /personnel, achieve org. goals, understand finance/accounting/return on investment
software developer
creative mind behind computer programs, develop applications/operating systems, tests/debugs/upgrades software
IS security analyst
plans/designs/implements/maintains integrity of systems/data, analyzes security measures, creates security breach action plans
systems analyst
consults w management/users, defines scope of/requirements for new IS, brings business & IS together
programmer
converts program design into a working program
web developer
designs/maintains websites performance/capability
business analyst
improve company competitiveness /performance, evaluates/solve business issues, needs broad set of business skills
RAM- random access memory
instructions/data is temporarily stored (volatile), mounted directly on main circuit board, types: Static RAM, dynamic RAM, double data rate synchronous dynamic RAM
cache memory
high-speed memory, processor can access faster than main memory
read-only memory (ROM)
nonvolatile memory w permanent storage for data/instructions that don’t change
types of ROM: Programmable ROM (PROM)
holds data & instructions that can’t be changed
types of ROM: electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM)
user-modifiable ROM, can be erased/reprogrammed repeatedly
Classes of general-purpose computers
portable computers, non portable computers, systems used by multiple users
Portable computers (general)
small enough to easily carry, used by one user ex) phone, laptop, notebook, tablet
types of non portable single user computer (general)
thin clients, desktop computers, nettop computer, workstations
thin clients (non-portable general)
low cost, centrally managed computer, no attached drives for data storage
desktop computers(non-portable general)
highly versatile, single-user computer systems, sufficient power/ memory/ storage for most business tasks
nettop computer(non-portable general)
very small/inexpensive desktop computer, used for internet access/email/web-based access/document processing/audiovisual playback, only 1/10 power needed
workstations(non-portable general)
more powerful than personal computer, small enough for desktop, support engineering/technical users
server (general)
computer employed by many users to perform specific task, offers high scalability, ex) web server, enterprise server, file server
scalability
ability to increase processing capability of computer system so it can handle more users/data/transactionsm
mainframe computer
large, powerful computer, shared by dozens-hundreds of same time users connected through a network, uses backward compatibility
backward compatibility
key feature allowing current mainframes to run software from decades ago
supercomputer
special-purpose machines designed for applications needing extensive/rapid capabilities
operating systems
set of programs controlling computers hardware, interface w application software, task management
kernel
heart of OS controlling critical processes, ties OS components together, regulates other programs
server visualization
logically dividing a single physical server’s resources to create multiple logical servers
hypervisor
virtual server program that controls host processor and resources, allocated necessary resources to each virtual machine and ensures they don’t disrupt each other
types of application software
proprietary software, off the shelf software, software as a service, workgroup application software, enterprise application
proprietary software
one of a kind software designed for a specific application for individual company org, or person using it, can give competitive advantage
off-the-shelf software
produced by software vendors to address needs theater common across businesses, org, or individuals
software as a service
third party provider hosts applications , available from any computer/device, SaaS provider handles upgrades/patches, lower cost software licensing
workgroup application software
designed to support teamwork, location doesn’t matter
web based software
ideal for group use
personal application software
can extend into workgroup application arena
enterprise application
software for org-wide business needs, shares data w other enterprise application used in the org- consider $, installation, level of training needed, integration w other applications
end user license agreement (EULA)
legal agreement btw software manufacturer & user, stipulates terms of usage, types: single-user license, individual/multiuser licenses, network/multiuser licenses
open source software
often free/distributed w source code, available for study/change/improvement, may have hidden $, support issues
GNU General public license
protects open source software
network topology
shape/structure of a network, star network, bus network, mesh networks
star network
devices connect through a single central device called the hub node
bus network
devices connected to common backbone, serves as shared communications medium
mesh networks
multiple access points link a series of devices across a large area
network types
personal area network (PAN), local area network (LAN), metropolitan area network (MAN), wide area network (WAN)
personal area network (PAN)
type of network, connects devices close to one person
local area network (LAN)
type of network, connects systems/devices within small area
metropolitan area network (MAN)
type of network, connects suers and their computers in a geographical area spanning campus/city
wide area network (WAN)
type of network, connects large geographic regions
twisted-pair wire
copper wire used for phone service, widely available, limitations on speed/distance
coaxial cable
inner conductor wire surrounded by insulation, cleaner/faster transmission, more expensive
fiber-optic cable
many thin strands of glass bound together in sheathing, light beams transmit signals, smaller than coaxial, less distortion, high transmission rates, expensive
types of wireless transmission
wireless communication, near field communication, bluetooth, wifi
wireless communication- wireless transmission
transfer of info btw 2 or more points not connected by electrical conductor, sent within range of frequencies
near field communication (NFC)- wireless transmission
very short-range wireless connectivity tech
bluetooth- wireless transmission
devices connected over 10-30 ft at 2 Mbps
wi-fi
wireless network brand owned by wifi alliance, improves interoperability of wireless local area network products
IP address
32-bit # uniquely identifying computer, divided into 4 bytes
network interface card (NIC)
circuit board/card installed into hardware device, specific MAC address burned into NICS’s ROM
Switch- network hardware
keeps record of MAC address of all devices connected to it, determines port a frame of data should be directed to
router- network hardware
directs data packets to other networks until each packet reaches destinationr
outing- network hardware
use dynamic routing to move packets, may arrive at destination device out of order
internet
infrastructure on which web exists, computers/network hardware/software/ communications media, TCP/IP protocols
world wide web
server/client software, hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP), standards, markup languages combine to deliver info/services over internet
client/server architecture
many clients request/receive services from servers on networkd
main name system (DNS)
maps name ppl use to locate a website to IP address a computer uses to find website, uses URL
Uniform resource locator (URL)
web address specifying location of web page w letters/words mapping to IP address/location
search engine
enables user to find info on the web, specify keywords related to topic of interests
search engine optimization (SEO)
process for driving traffic to website, improves site’s ranking in search results
instant messaging
online/real time communication, btw 2/more ppl connected via internet
intranet
internal cormorant network using internet/WWW standards/products
extranet
built using web tech, links selected company intranet resources w customers/suppliers/other partners
virtual private network (VPN)
secure connection btw 2 internet points, encapsulates traffic w IP packets, sends packets via internet
types of attack perpetrators
careless insider, malicious employees, cybercriminal, hacktivist, lone wolf attacker, cyberterrorist
careless insider
insider who doesn’t follow org security policies allowing a cyberattack to happenl
malicious employees
insider who deliberately attempts to get access to/disrupt company’s IS & operations
cybercriminal
one who attacks computer system/network for financial gain
hacktivist
one who hacks computers/websites to promote political ideology
lone wolf attacker
one who violates computer/internet security maliciously for illegal personal gain
cyberterrorist
state-sponsored person/group who attempts to destroy infrastructure parts of gov’t/financial places/corporations/utilities/ emergency units