Plant Reproduction and Life Cycle Overview
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Flower
Reproductive structure producing gametes and seeds.
Gametes
Haploid cells involved in sexual reproduction.
Seeds
Embryo with nutrient stores in a protective coat.
Fruits
Develop from flowers, containing seeds.
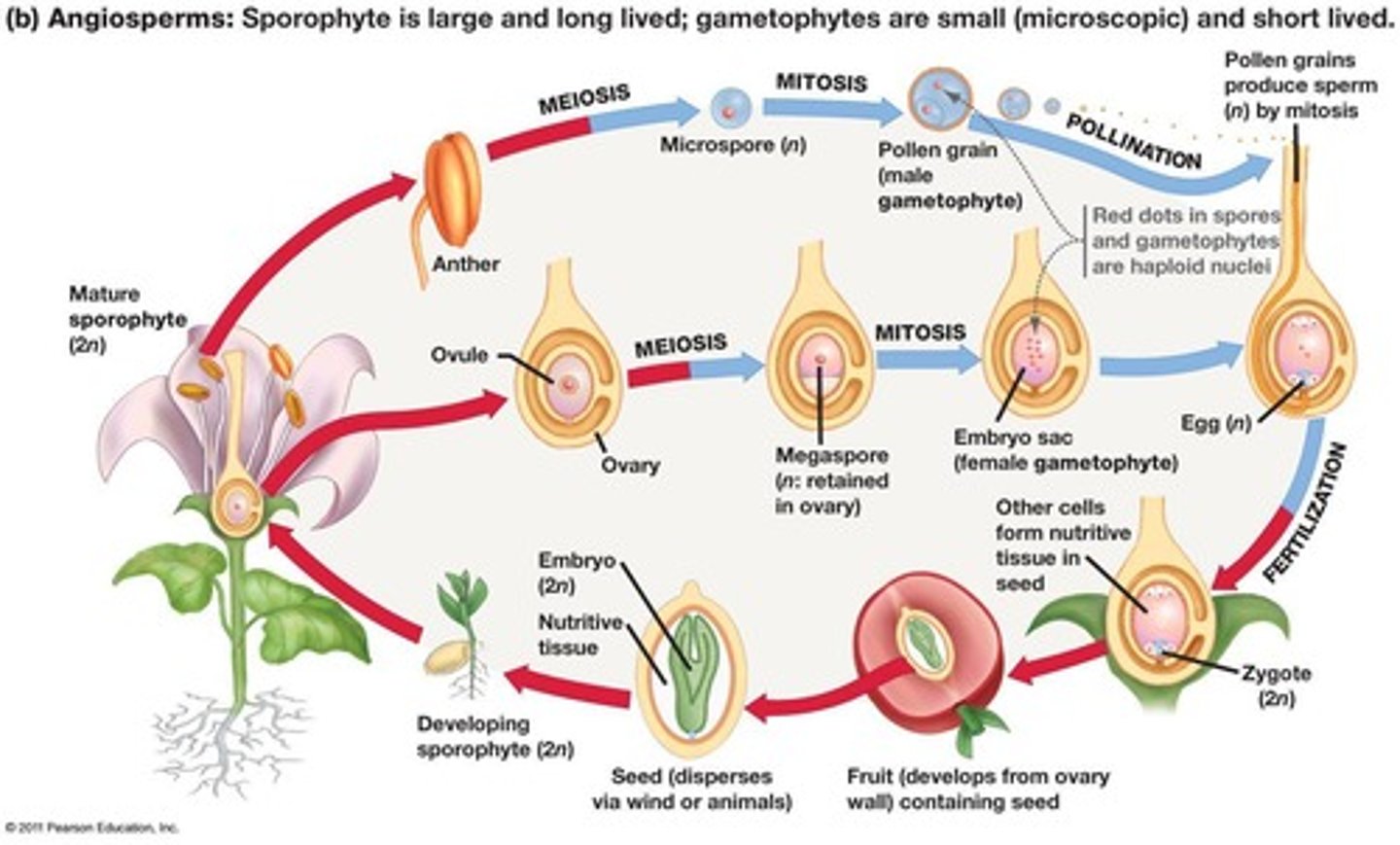
Sexual Reproduction
Involves meiosis and fertilization for offspring.
Meiosis
Nuclear division reducing chromosome number by half.
Fertilization
Fusion of haploid gametes forming a diploid zygote.
Sporophyte
Diploid phase of land plant life cycle.
Gametophyte
Haploid phase of land plant life cycle.
Alternation of Generations
Life cycle with alternating diploid and haploid forms.
Spores
Haploid cells growing into adult individuals.
Sporangia
Structures where meiosis produces haploid spores.
Mitosis
Cell division producing genetically identical cells.
Zygote
Diploid cell formed from fertilized gametes.
Asexual Reproduction
Production of clones without fertilization.
Clones
Genetically identical copies of the parent plant.
Vegetative Reproduction
Cloning new plants from adult parts.
Runners
Horizontal stems producing new plants at nodes.
Rhizomes
Underground stems that produce new shoots.
Apomixis
Asexual embryo development in ovule.

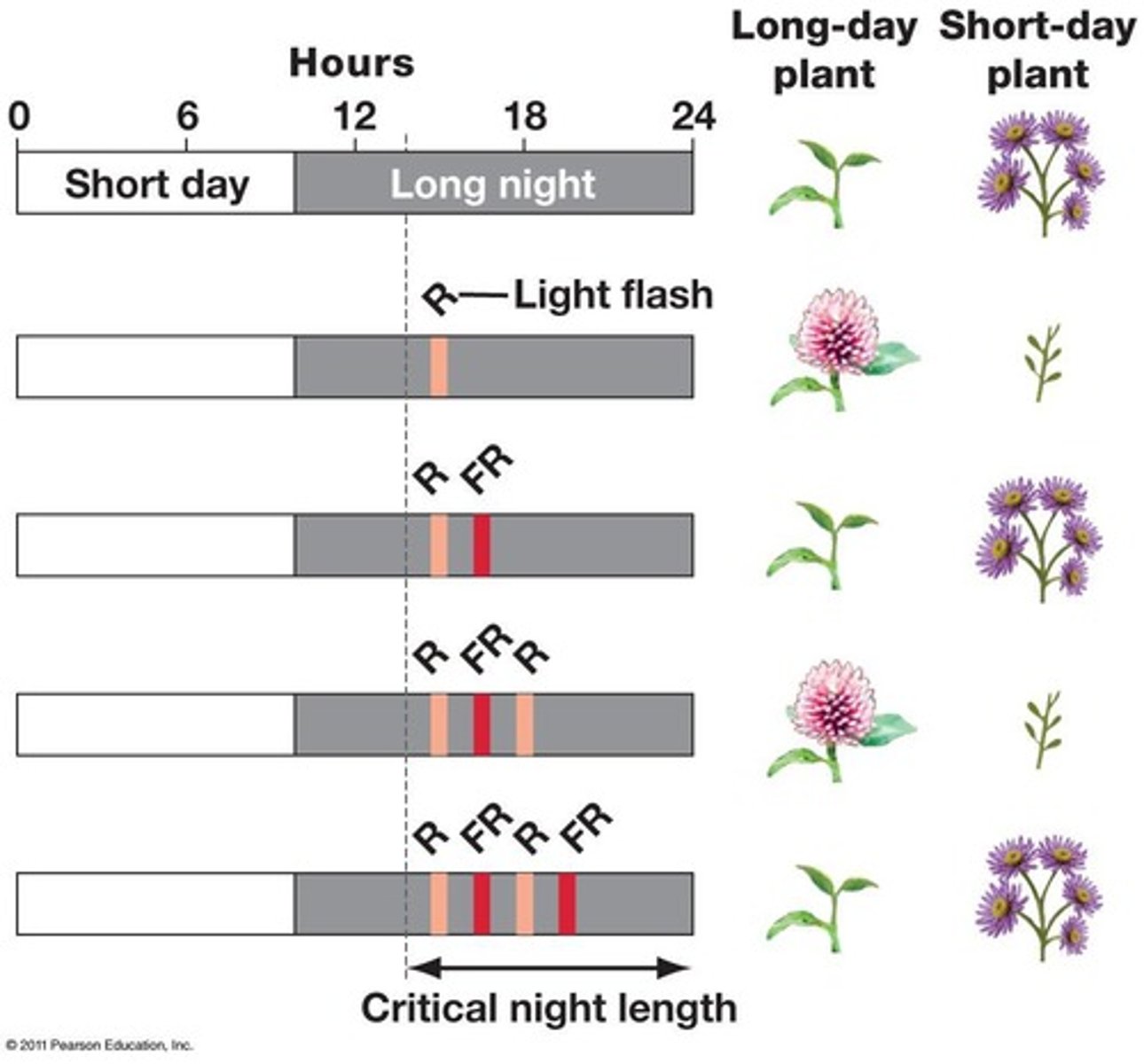
Photoperiodism
Plant response based on day and night lengths.
Photoperiod
Relative lengths of day and night.
Floral Meristem
Apical meristem developing into flower structures.
Long-day plants
Bloom in midsummer with longest days.
Short-day plants
Bloom in spring or fall with shortest days.
Day-neutral plants
Flower regardless of photoperiod.
Phytochrome
Plant pigment involved in photoperiod response.
CONSTANS (CO)
Gene expression triggered by clock proteins.
Florigen
Hypothetical flowering hormone from leaves.
Calyx
Group of sepals protecting flower buds.
Corolla
Group of petals attracting pollinators.
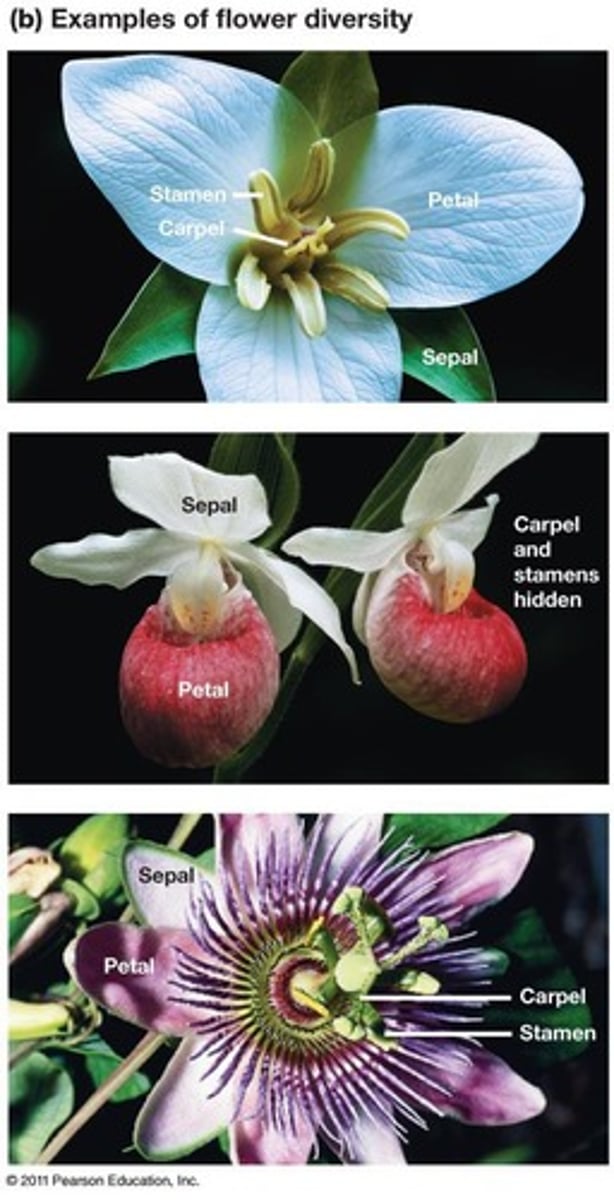
Stamens
Male reproductive structures producing pollen.
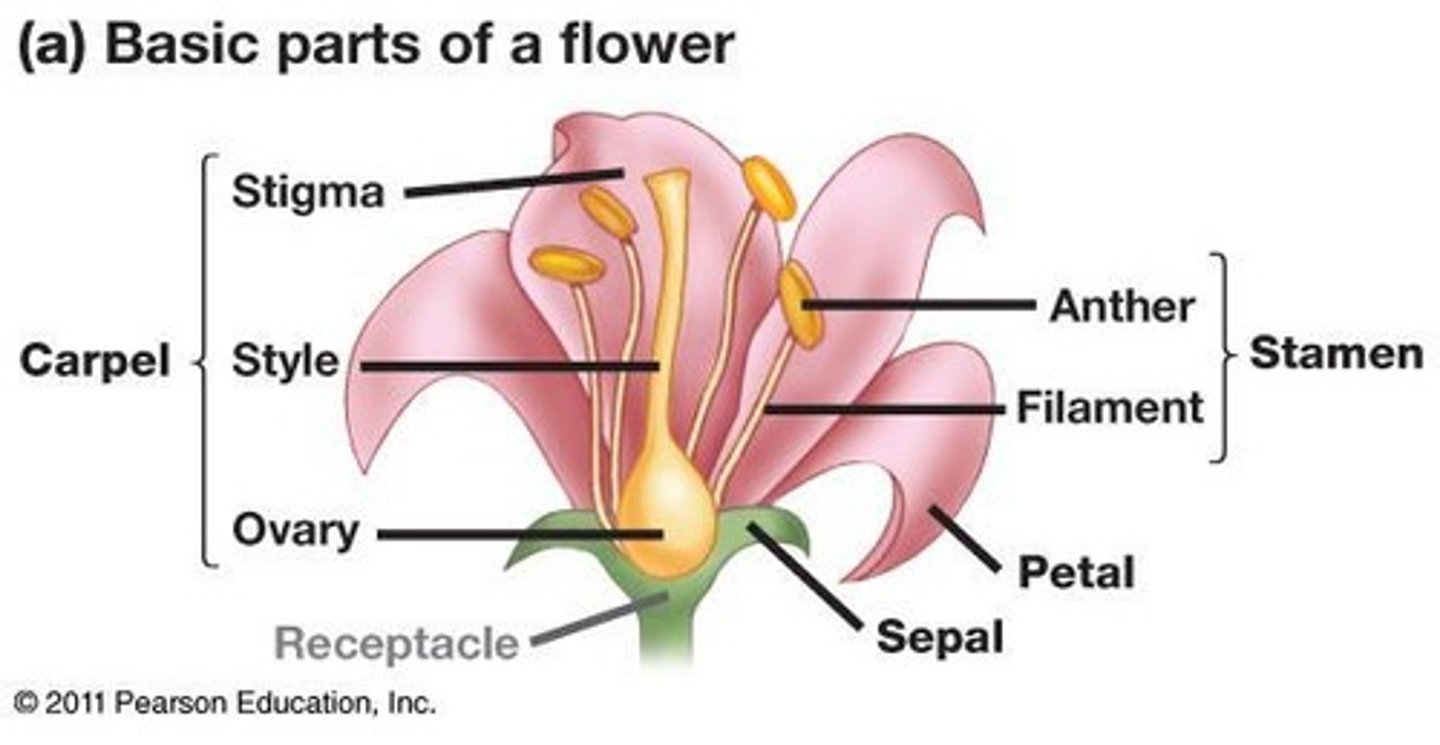
Anthers
Pollen-producing organs on stamens.
Filament
Stalk supporting the anther in stamens.
Carpels
Female reproductive structures producing ovules.
Stigma
Moist tip of carpel receiving pollen.
Style
Slender stalk connecting stigma and ovary.
Ovary
Base of carpel containing ovules.
Perfect flowers
Contain both stamens and carpels.
Imperfect flowers
Contain either stamens or carpels only.
Monoecious plants
Have both stamen and carpel flowers.
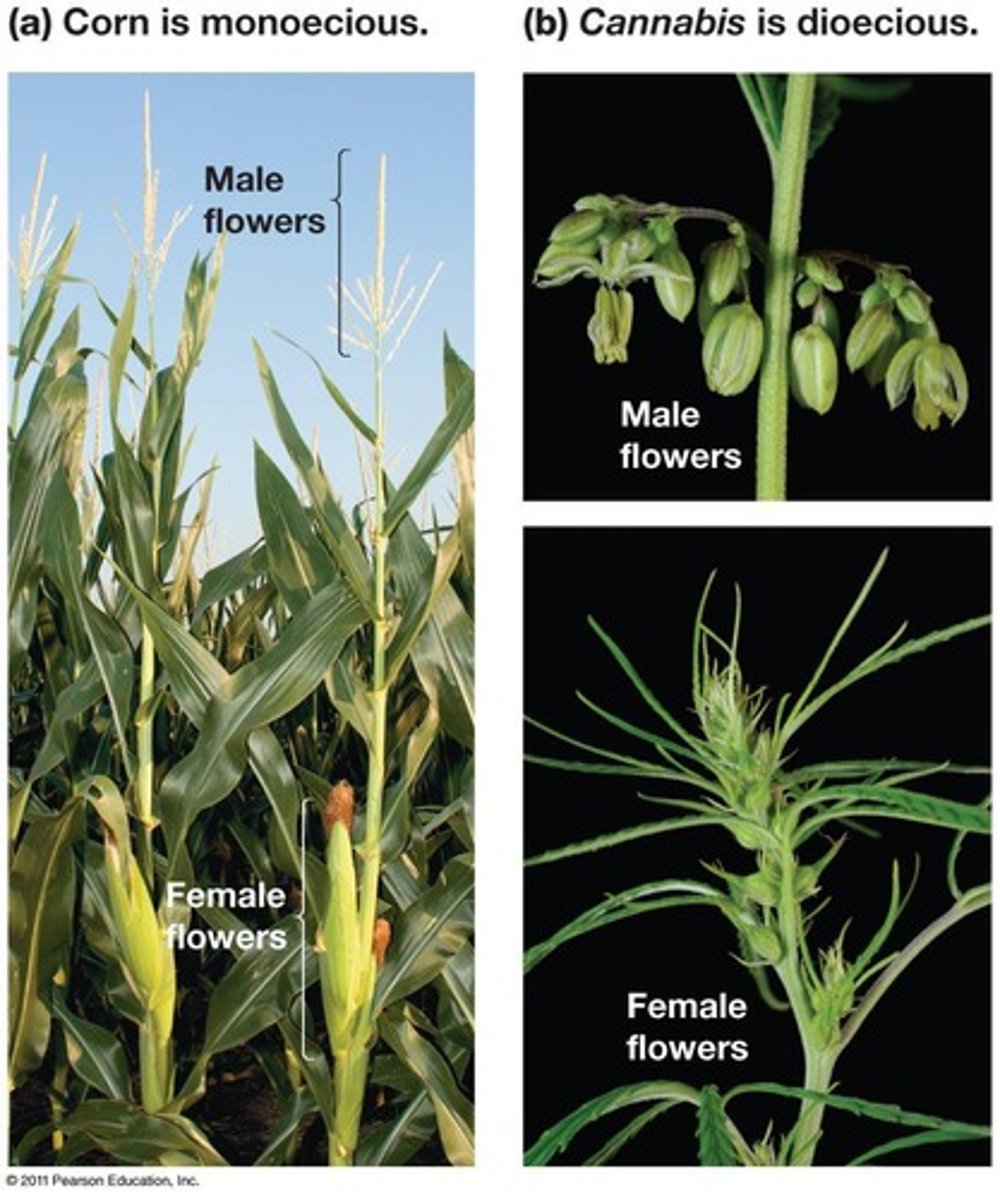
Dioecious plants
Have either stamen or carpel flowers.
Megasporocyte
Diploid cell dividing to form megaspores.
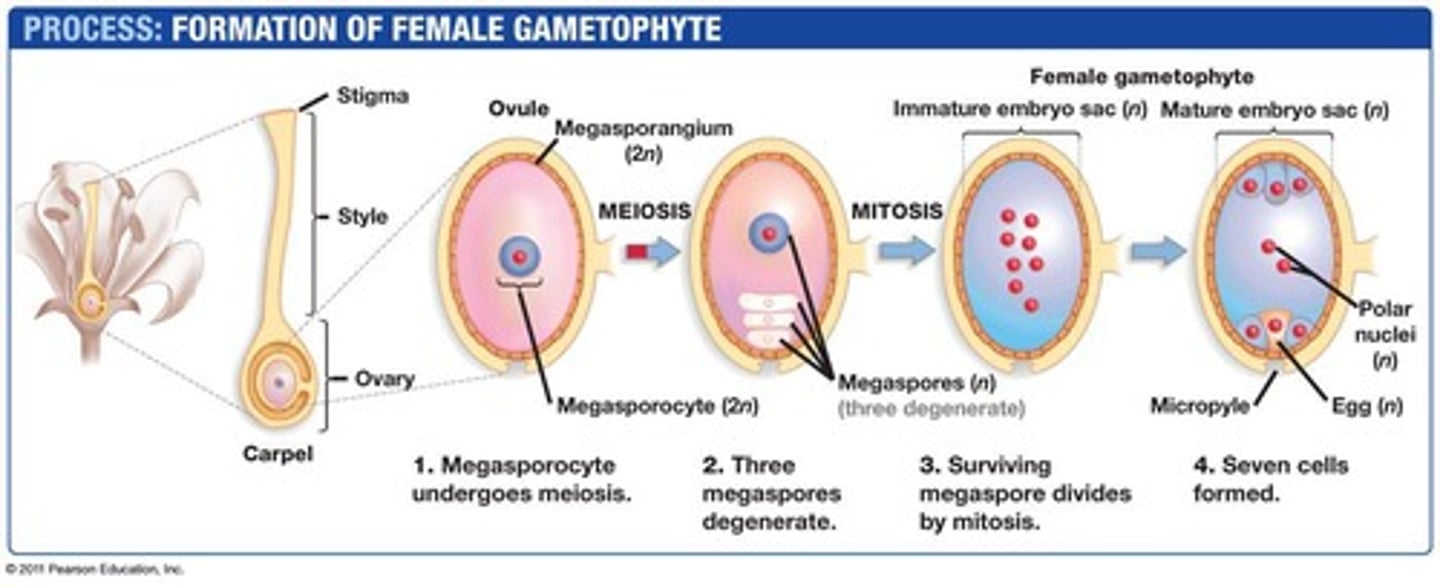
Embryo sac
Multicellular haploid gametophyte from megaspore.
Micropyle
Opening to the ovule for pollen entry.
Haploid nuclei
Nuclei in embryo sac segregating during development.
Ovules
Structures in ovary containing female gametophytes.
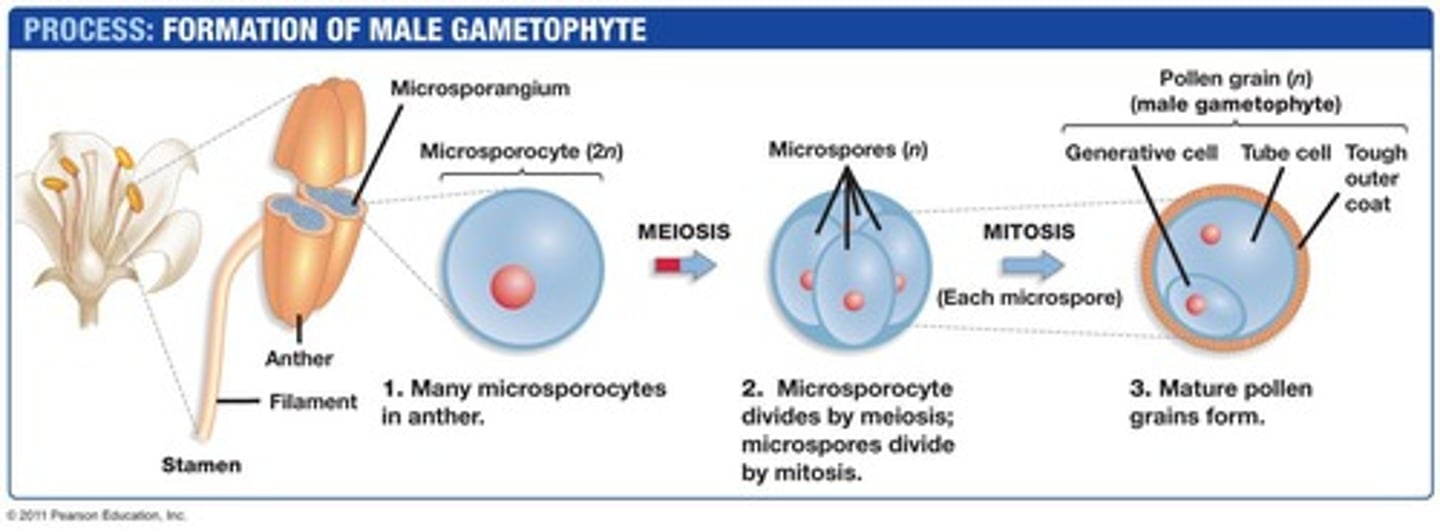
Microsporangia
Structures in anthers containing diploid microsporocytes.
Microsporocytes
Diploid cells that undergo meiosis to form microspores.
Microspores
Haploid cells produced from microsporocytes via meiosis.
Pollen Grain
Haploid, immature male gametophyte with two nuclei.
Male Gametophyte
Develops from microspores, produces sperm after maturation.
Generative Cell
Cell in male gametophyte that produces sperm cells.
Tube Cell
Larger cell in pollen grain aiding in fertilization.
Pollination
Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma.
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg forming a diploid zygote.
Self-fertilization
Sperm and egg from the same individual combine.
Outcrossing
Sperm and egg from different individuals combine.
Cross-pollination
Pollen transfer between different individuals.
Inbreeding Depression
Reduced biological fitness from mating between closely related individuals.
Temporal Avoidance
Male and female gametophytes mature at different times.
Spatial Avoidance
Physical separation of anthers and stigma in flowers.
Molecular Matching
Blocking pollination if pollen and stigma proteins match.
Mutualism
Mutually beneficial relationship between pollinators and plants.
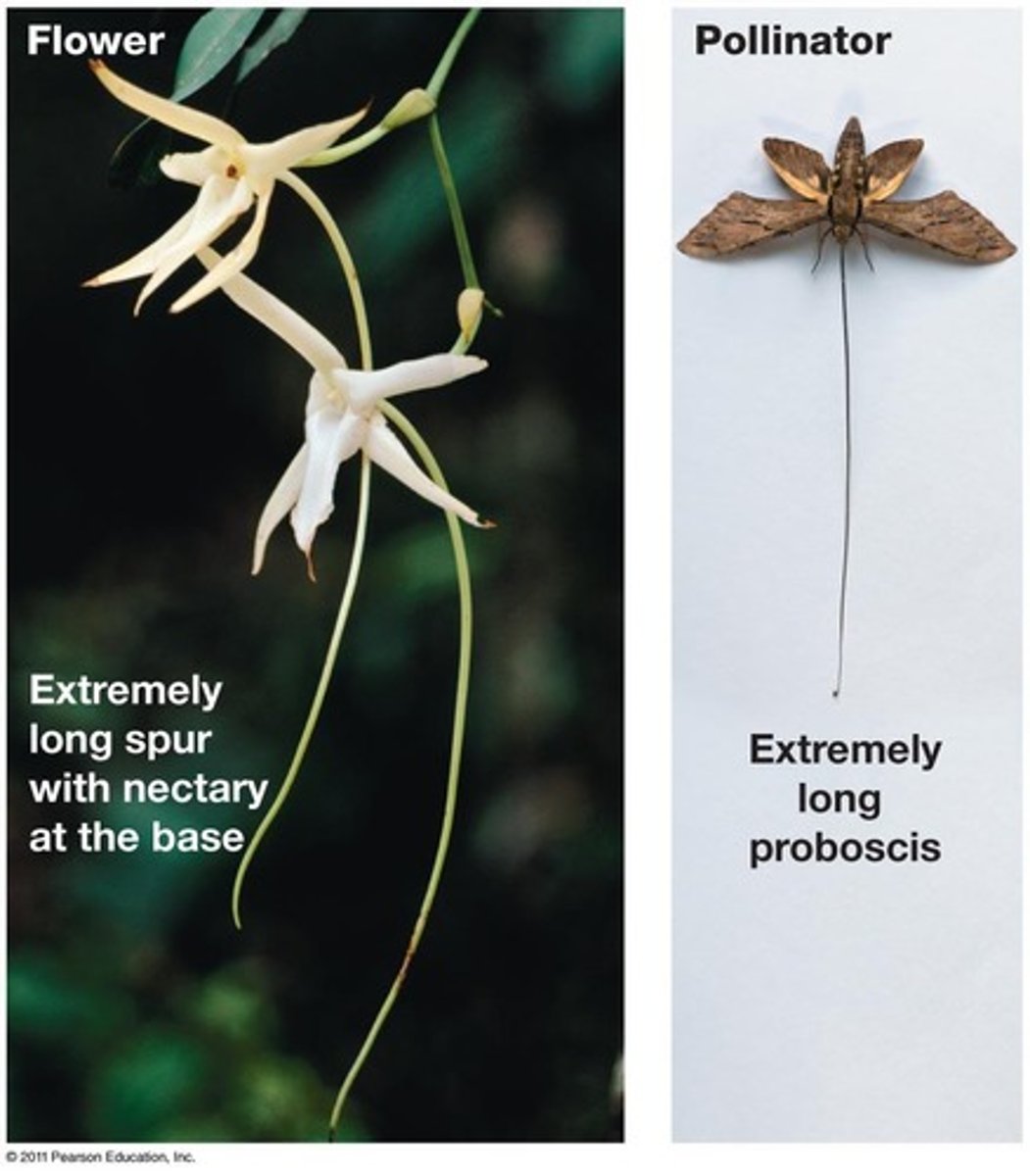

Pollination Syndromes
Correlations between flower structure and pollinator traits.
Coevolution
Adaptation of flowers and pollinators enhancing pollination efficiency.
Wind-pollinated Species
Produce many pollen grains, rely on wind for pollination.
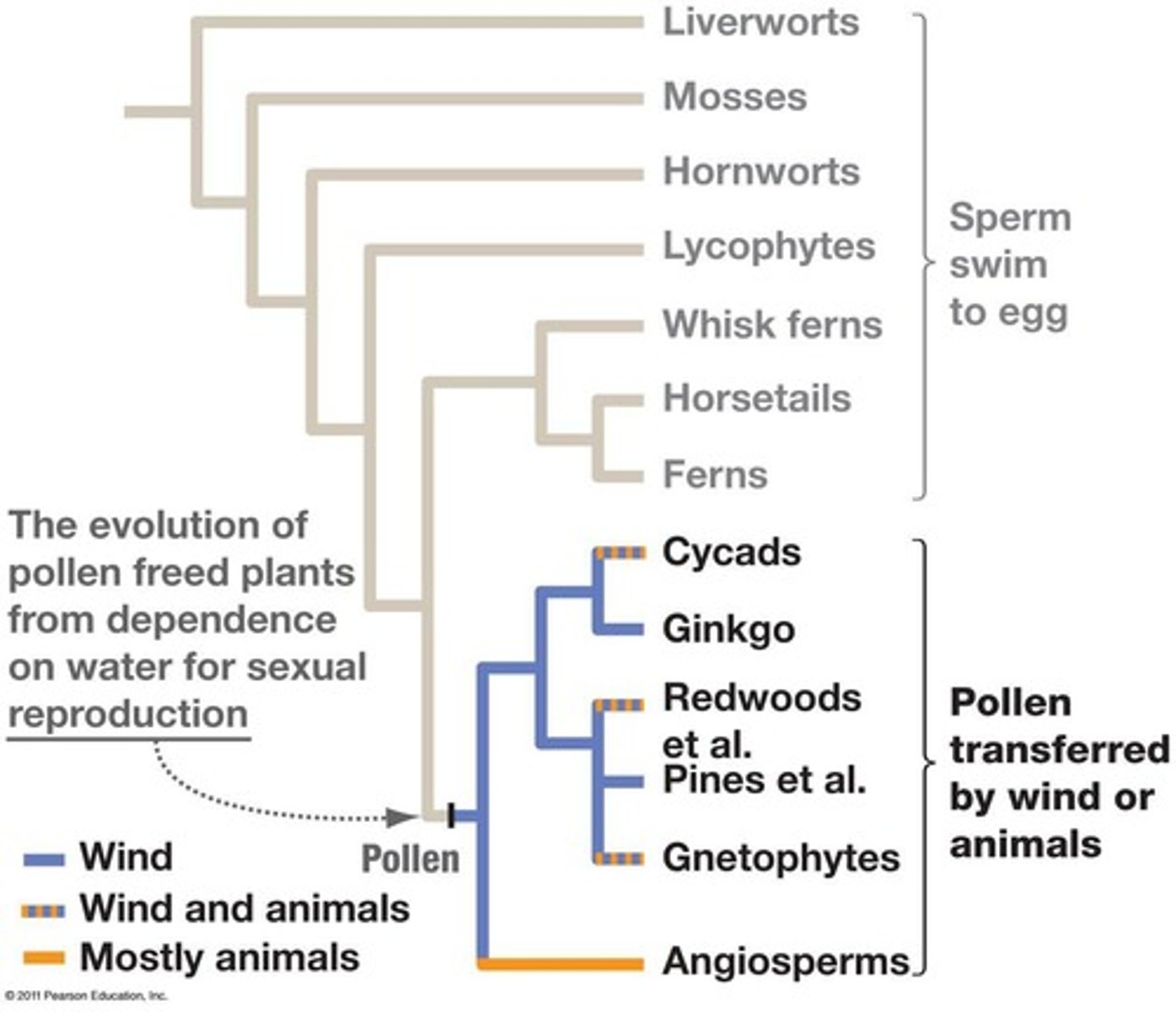
Animal-pollinated Species
Make fewer pollen grains, attract animals for pollination.
Insect Pollination
Enhances sexual reproduction efficiency and species formation.

Dioecious Species
Plants with separate male and female individuals.
Alpine skypilot
Plant with distinct flower traits based on habitat.
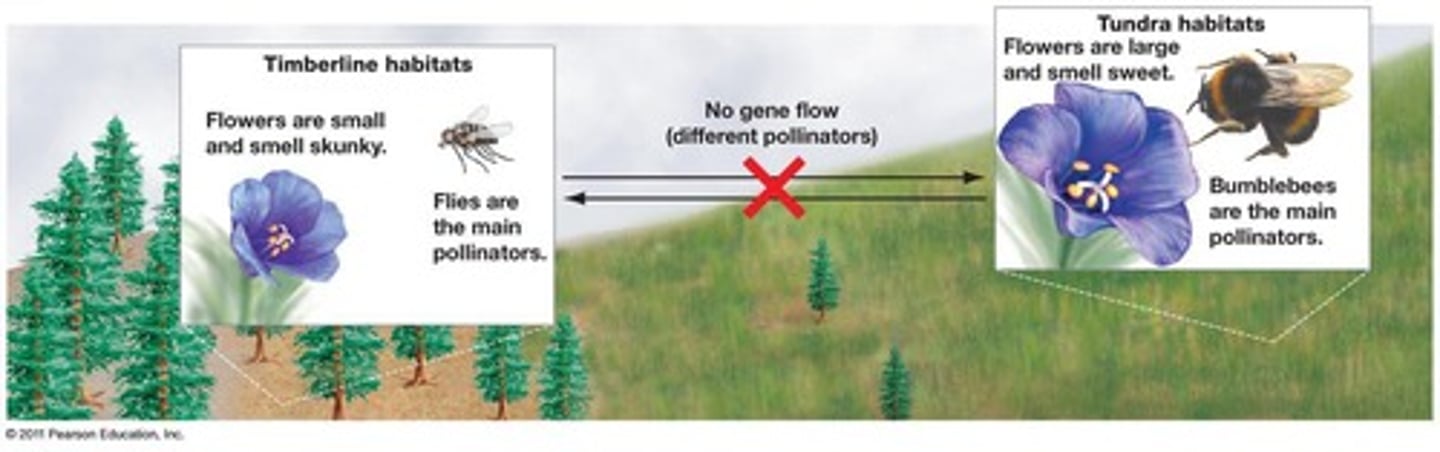
Speciation
Formation of new species through evolutionary processes.
Gene flow
Transfer of genetic material between populations.
Pollination
Transfer of pollen from male to female reproductive structures.
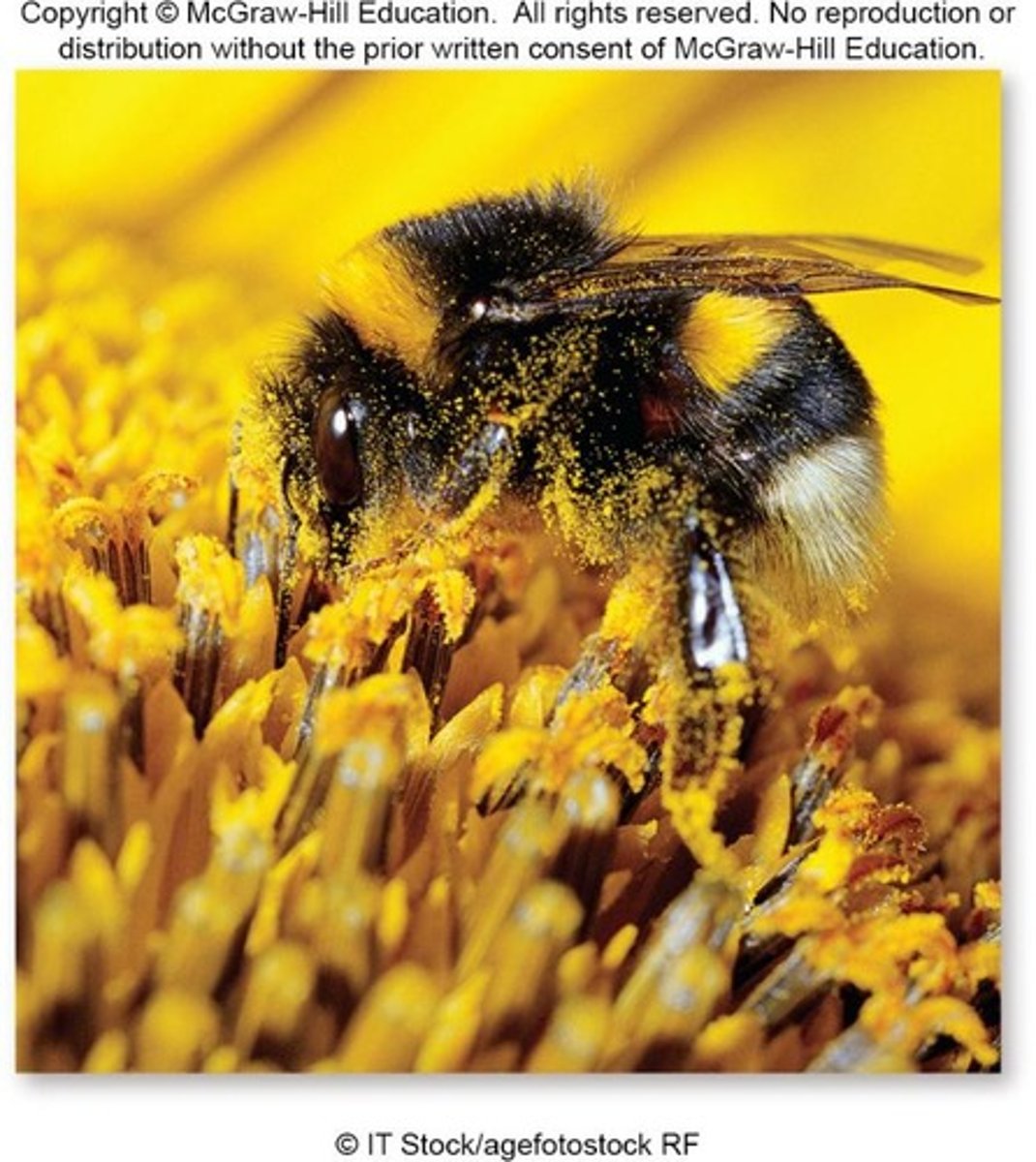
Insect pollinators
Insects that facilitate pollination by visiting flowers.
Bee pollination
Bees prefer yellow or blue flowers with nectar.
Butterfly pollination
Flowers visited by butterflies have flat landing platforms.
Moth pollination
Moth-pollinated flowers are often white and heavily scented.
Bird pollination
Birds prefer flowers with high nectar and red color.
Wind pollination
Pollination method using wind, often odorless flowers.
Fertilization
Fusion of sperm and egg to form a zygote.
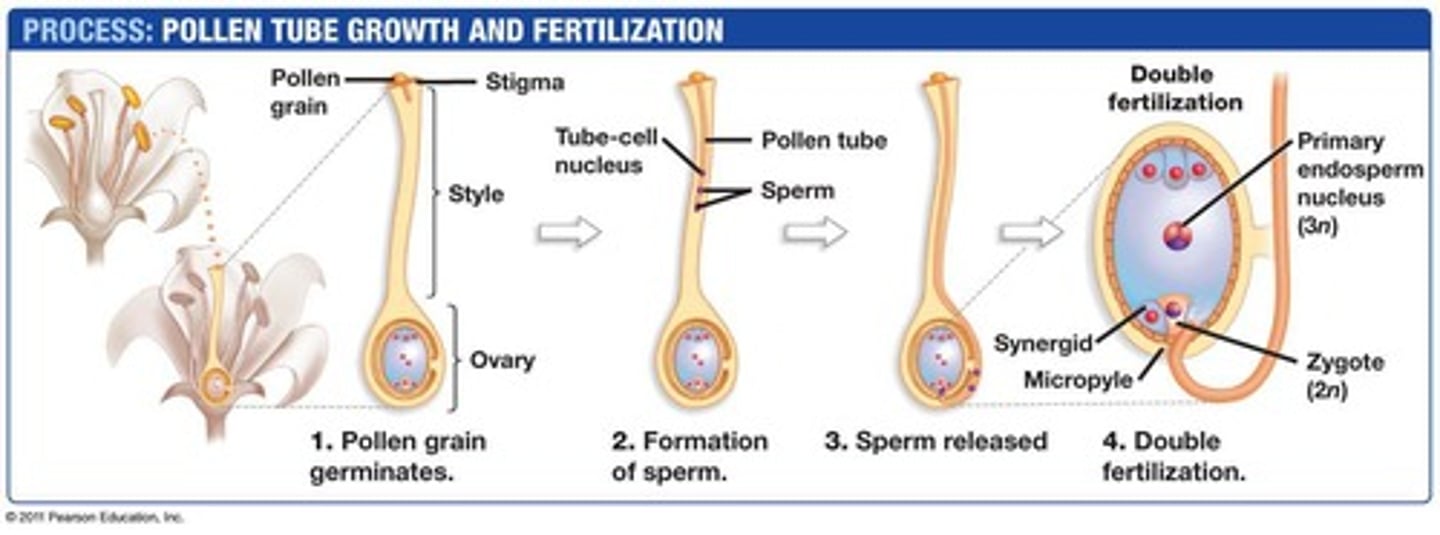
Double fertilization
Two fertilization events in angiosperms producing zygote and endosperm.
Primary endosperm nucleus
Triploid cell formed during double fertilization.
Endosperm
Nutrient-storing tissue for developing embryo.
Seed development
Process of seed maturation after fertilization.
Seed coat
Protective outer layer surrounding the seed.
Mature seed
Contains embryo, endosperm, and seed coat.
Embryogenesis
Development process from zygote to multicellular embryo.
Pollen tube
Structure that delivers sperm to the ovule.
Sporophyte
Diploid phase in the plant life cycle.
Ovule
Structure that develops into a seed after fertilization.
Fruit
Mature ovary enclosing seeds for protection.
Nectaries
Flower parts that produce nectar to attract pollinators.
Basal Cell
Divides to form root tip and suspensor.
Suspensor
Transports nutrients from parent to embryo.
Terminal Cell
Forms cell mass for embryo development.
Protoderm
Exterior layer forming the plant's epidermis.
Ground Meristem
Forms ground tissue inside protoderm.
Procambium
Develops into vascular tissue in embryo.
Cotyledons
Seed leaves that store nutrients for seedlings.