marketing chapter 12
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
addressing competition and driving growth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
growth strategies
building your market share
developing committed customers and stakeholders
building a powerful brand
innovating new products, services, experiences
international expansion
acquisitions, mergers, alliances
building an outstanding reputation for social responsibility
partnering with gov and NGOs
growing the core
strengthening a brand's original, most profitable products or services
deepen penetration and add premium extensions
make premium products to achieve sustainable, focused growth
competitive strategies for market leaders
expanding total market demand: grow the overall market size
protecting market share: defend against competitors’ attacks
increasing market share: gain additional share within the market
expanding total market demand
new customers
more usage
protecting market share strategies
proactive marketing: take initiative to stay ahead of competitors
responsive anticipation: quickly react to emerging threats or opportunities
creative anticipation: innovate to foresee and shape future market trends
risks of increasing market share
high acquisition cost: buying share may cost more than it earns
antitrust risk: aggressive tactics (eg predatory pricing) can trigger regulation
high economic cost: heavy promos/ads reduce short-term profits
wrong marketing focus: spending on ineffective campaigns, or poor targeting waste resources
quality strain: rapid growth can hurt quality or service
market challenger strategies
a market challenger can attack the market leader, underfunded firms its own size, small local and regional firms, the status quo
choosing a general attack strategy
frontal attack: directly challenge a competitor’s strengths
flank attack: target competitor’s weak or underserved areas
encirclement attack: attack on multiple fronts at once
bypass attack: avoid competitor by moving into new markets or techs
guerrilla attacks: small, irregular attacks to harass competitors
market follower strategies
cloner: copies the leader’s products and marketing closely
imitator: copies some elements but adds differentiation
adapter: improves or adapts the leader’s products for new markets
market nicher strategies
focus on serving small, specialised segments that are overlooked by larger competitors, offering tailored products
firms with low shares of the total market can become highly profitable through smart niching
to be a leader in a small market
niche specialist roles
end-user specialist: focuses on a specific type of customer
vertical-level specialist: targets a particular stage in the supply chain
customer-size specialist: serves small, medium, or large customers exclusively
geographic specialist: focuses on a specific region or area
job-shop specialist: handles customized, small-batch, or specialized orders
channel specialist: concentrates on a particular distribution or retail channel
product life cycle marketing strats
a company’s positioning and differentiation strat must change as its product, market, and competitors change over the PLC
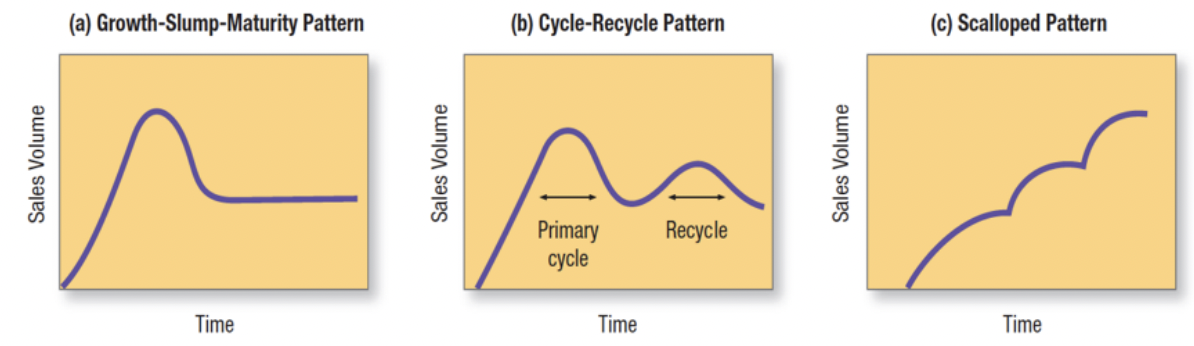
growth-slump-maturity pattern: standard PLC with growth, slowdown, and maturity stages
cycle-recycle pattern: product renewed or updated to start a new growth cycle
scalloped pattern: successive sales waves from adding new product features or targeting new segments
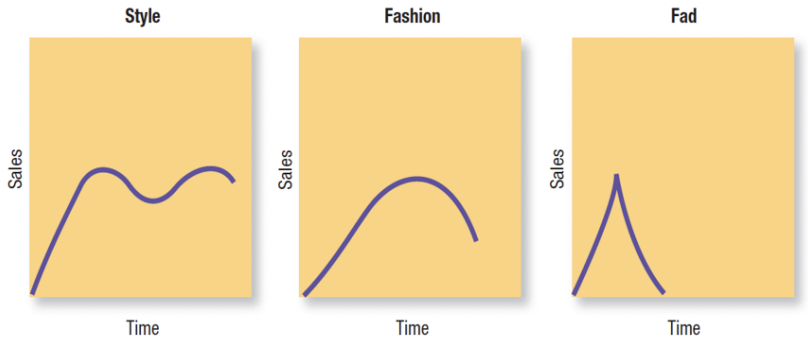
style, fashion, and fad life cycles
style LC: long-term pattern of adoption for a basic, enduring product design or way of doing things
fashion LC: medium-term trend adopted by many but eventually replaced by new fashions
fad LC: short-term craze with rapid adoption and equally rapid decline
marketing strats: pioneering
being the first to introduce a product, category, or innovation to a market
advantages
recall brand name
establish product class attributes
captures more uses in middle of market
gain first-mover advantage
disadvantages
imitators can surpass innovators
once leadership is lost, its rarely regained
marketing strat: growth stage
to sustain rapid market share growth now
improve product quality and add new features
add new models and flanker products
enter new market segments
increase distribution coverage and enter new distribution channels
shift from awareness and trial communications to preference and loyalty communications
lower prices to attract the next layer of price-sensitive buyers
marketing strats: maturity stage
market modification: find new users, segments, or uses for the product
product modification: improve quality, features, or style to renew interest
marketing program modification: adjust price, promotion, or distribution to boost sales
ways to increase sales volume: market modification
expand number of users
convert non-users
enter new market segments
attract competitors’ customers
increase usage rates among users
have consumers use the product on more occasions
have consumers use more of the products on each occasion
have consumers use the product in new ways
marketing strats: decline stage
eliminating weak products
harvesting: reduce marketing support and costs while continuing to sell the product for profit
divesting: withdraw the product entirely from the market or sell it off
marketing in a slow growth economy
explore upside of increasing investment
get closer to customers
review budget allocations
put forth compelling value proposition
fine tune brand and product offerings