531 Lec 35
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:08 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Understand the role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in anxiety.
Causes an increase in cortisol secretion to the adrenal cortex
2
New cards
Understand the influence of different areas of the brain on the HPA in anxiety.
amygdala goes off when there is a perceived threat, usually there’s a balancing event when that is not a real threat
\
hippocampus files events - can lead to perceiving memories as if they are happening now
\
hippocampus files events - can lead to perceiving memories as if they are happening now
3
New cards
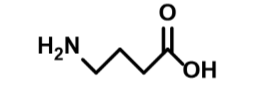
What molecule is this
GABA
4
New cards
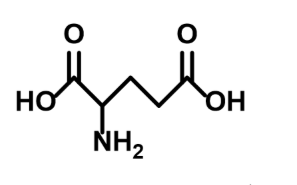
What molecule is this
Glutamate
5
New cards
Know the role of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the CNS.
Glutamate is an excitatory NT
\
\
GABA is an inhibitory NT(calming)
\
\
GABA is an inhibitory NT(calming)
6
New cards
Understand the GABA shunt, why it is relevant to our anxiety discussion, and the reactions and enzymes involved
GABA shunt reactions are responsible for the synthesis, conservation and metabolism of GABA
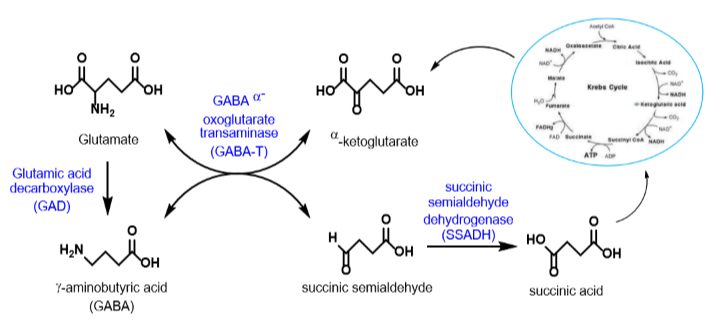
7
New cards
How is glutamate transported from glia cells without causing depolarization ?
1) Glutamate from the Glia cell gets converted into inert glutamine that can travel between Glia cells and presynaptic neurons so that we don’t have loose glutamate hanging around binding things
2)In the presynaptic neuron glutamine gets converted into glutamate then GABA then released into the synaptic cleft
2)In the presynaptic neuron glutamine gets converted into glutamate then GABA then released into the synaptic cleft
8
New cards
GABAa Receptors
Ionotropic- Ligand gated ion channels
Fast acting
Fast acting
9
New cards
GABAb Receptors
Metabotropic receptors
G protein coupled receptors
Slow acting
G protein coupled receptors
Slow acting
10
New cards
What do ionotropic receptor subunit subtypes do?
modulate the pharmacology of the receptor
11
New cards
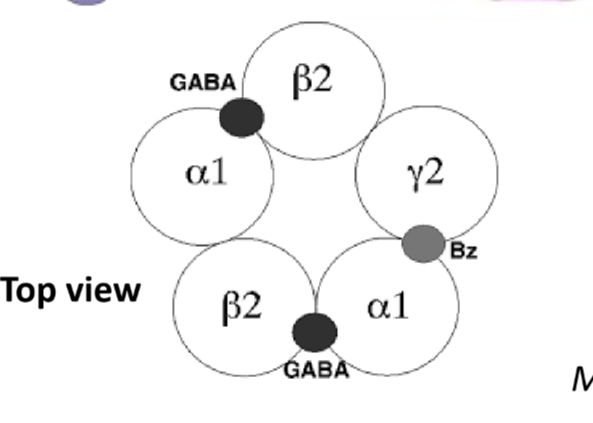
Know where GABA binds on each of its receptor types.
Gaba binds at the nexus at alpha 1 and beta 2 ( need 2 to bind)
12
New cards
Know what effect benzodiazepine binding has on chloride flux and what results.
Open the Cl Ion channel
Cl- flux stabilizes the membrane so it’s desensitized against stimuli
Cl- flux stabilizes the membrane so it’s desensitized against stimuli
13
New cards
baclofen
GABA-B receptor agonist
→ increased k+ flux, long lasting inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
→ reduced calcium influx, helps GABA autoreceptors inhibit presynaptic GABA release
→Suppress Adenylate cyclase activity→ decreases cAMP concentrations
→Activation of K+ channels through GABAb coupled G proteins inhibits neuron firing
→ increased k+ flux, long lasting inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
→ reduced calcium influx, helps GABA autoreceptors inhibit presynaptic GABA release
→Suppress Adenylate cyclase activity→ decreases cAMP concentrations
→Activation of K+ channels through GABAb coupled G proteins inhibits neuron firing
14
New cards
Know where Baclofen binds on its receptor
????????
15
New cards
Know the activity and side effect profile of benzodiazepines
Used as sedative hypnotics, muscle relaxants, anxiolytics, anticonvulsants
Nonselective with respects to alpha subunit
\
Side effects:
Sedation
Respiratory depressant depending on dose and duration
Anterograde amnesia
Withdrawal syndrome
Accumulation leads to tolerant
Potential for physical dependence with chronic use
Nearly all BZs cause dose-dependent behavioral changes
Nonselective with respects to alpha subunit
\
Side effects:
Sedation
Respiratory depressant depending on dose and duration
Anterograde amnesia
Withdrawal syndrome
Accumulation leads to tolerant
Potential for physical dependence with chronic use
Nearly all BZs cause dose-dependent behavioral changes
16
New cards
For what indications are benzodiazepines generally prescribed?
Sleep aids, Muscle relaxants, anxiolytics, anticonvulsants
17
New cards
Know what alpha subunits of GABA-A are associated with sedative vs anxiolytic effects.
alpha 2,3, and 5 subunits mediate anxiolytic and muscle relaxant properties
\
alpha 1 subunit mediate sedative effects
\
alpha 1 subunit mediate sedative effects
18
New cards
Know where and under what circumstances benzodiazepines bind on the GABA receptor.
Binds between alpha 1 and gamma 2 subunits of GABA ionotropic receptors
19
New cards
Know the general effect of an agonist at the GABA-A receptor.
Anticonvulsant (anti muscle spasms), anxiolytic, sleep aid, muscle relaxant
20
New cards
Know the general effect of an antagonist at the GABA-A receptor.
Convulsant (causing muscle contractions)
21
New cards
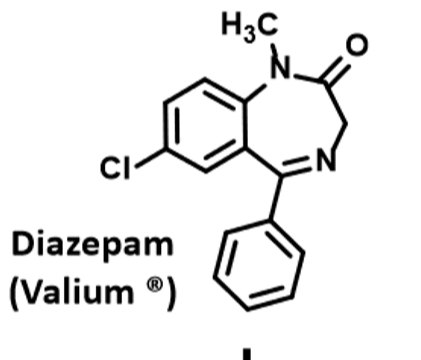
Diazepam (Valium)
Anxiolytic, Sedative, Muscle Relaxant, Anticonvulsant and Amnestic effects
Increased risk of abnormalities in preggo
Passes into breast milk
N alkylation
Metabolized to N-desmethyldiazepam
Increased risk of abnormalities in preggo
Passes into breast milk
N alkylation
Metabolized to N-desmethyldiazepam
22
New cards
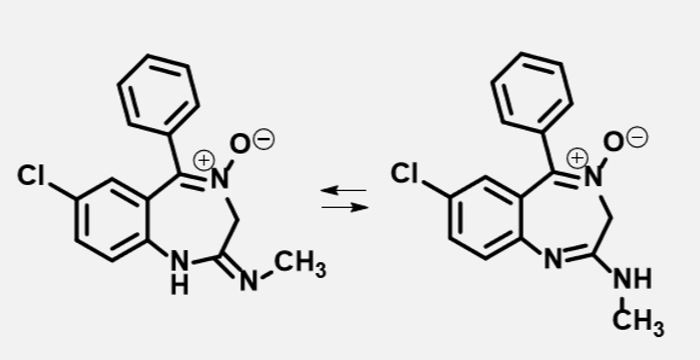
Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
Anxiolytic
Sedative properties
Oral tablets
Light sensitive
Metabolized to N-desmethyldiazepam
Sedative properties
Oral tablets
Light sensitive
Metabolized to N-desmethyldiazepam
23
New cards
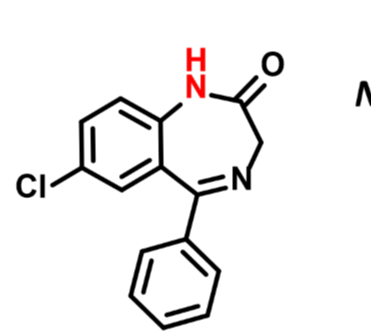
N-desmethyldiazepam
Active metabolite of Valium and Librium