Overview of Sensory Receptors and the Eye
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Sensory receptor
A sensory receptor is a structure that functions to receive sensory stimuli and generate an electrical neuronal signal.
Exteroceptors
Exteroceptors are receptors that receive stimuli from the external environment.
Interoreceptors
Interoreceptors are receptors that receive stimuli from the internal environment (like organs).
Proprioceptors
Proprioceptors receive information about the relative stretch of muscles and tendons in order to understand where the body parts are in space.
Thermoreceptor
A type of sensory receptor that responds to temperature changes.
Photoreceptor
A type of sensory receptor that responds to light.
Chemoreceptor
A type of sensory receptor that responds to chemical stimuli.
Baroreceptor
A type of sensory receptor that responds to changes in pressure.
Nociceptor
A type of sensory receptor that responds to pain stimuli.
Mechanoreceptor
A type of sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion.
General sense receptor
A type of sensory receptor that detects general sensations such as pain, temperature, and touch.
Special sense receptor
A type of sensory receptor that is specialized for specific senses such as vision, hearing, taste, and smell.
Tactile receptor
Receptors that respond to touch and pressure, including tactile (Merkel) discs and lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles.
Olfactory epithelium
The tissue in the nasal cavity that contains olfactory receptor cells responsible for the sense of smell.
Olfactory receptor cell
A type of sensory receptor cell that detects odor molecules.
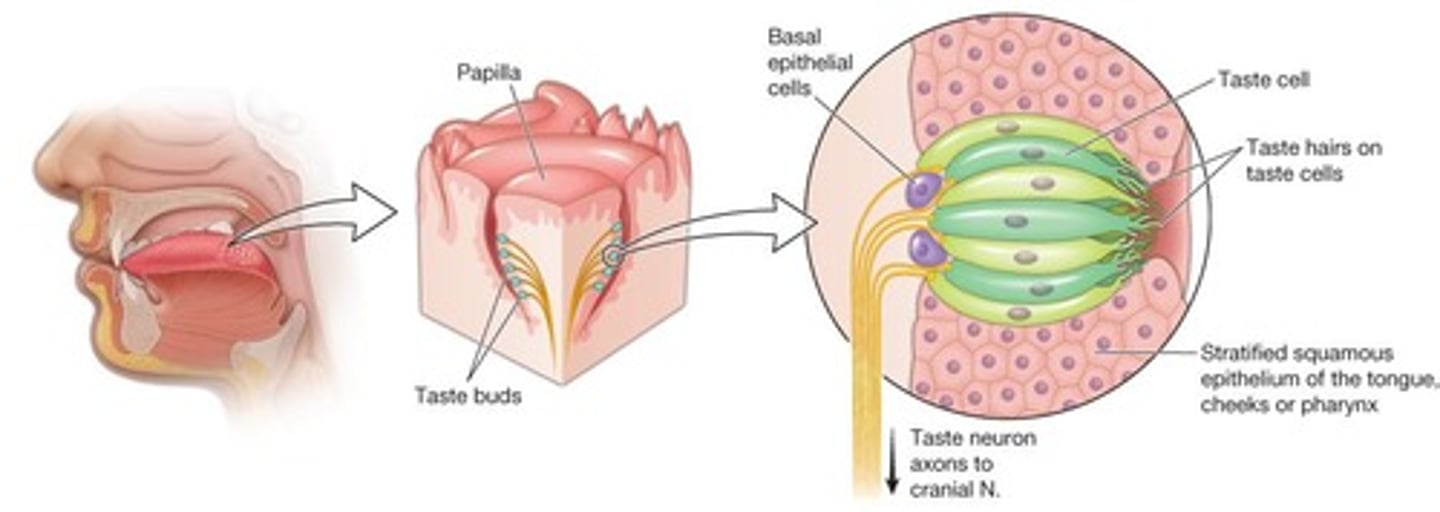
Taste buds
Structures on the tongue that contain gustatory receptor cells responsible for the sense of taste.
Gustatory receptor cell
A type of sensory receptor cell that detects taste stimuli.
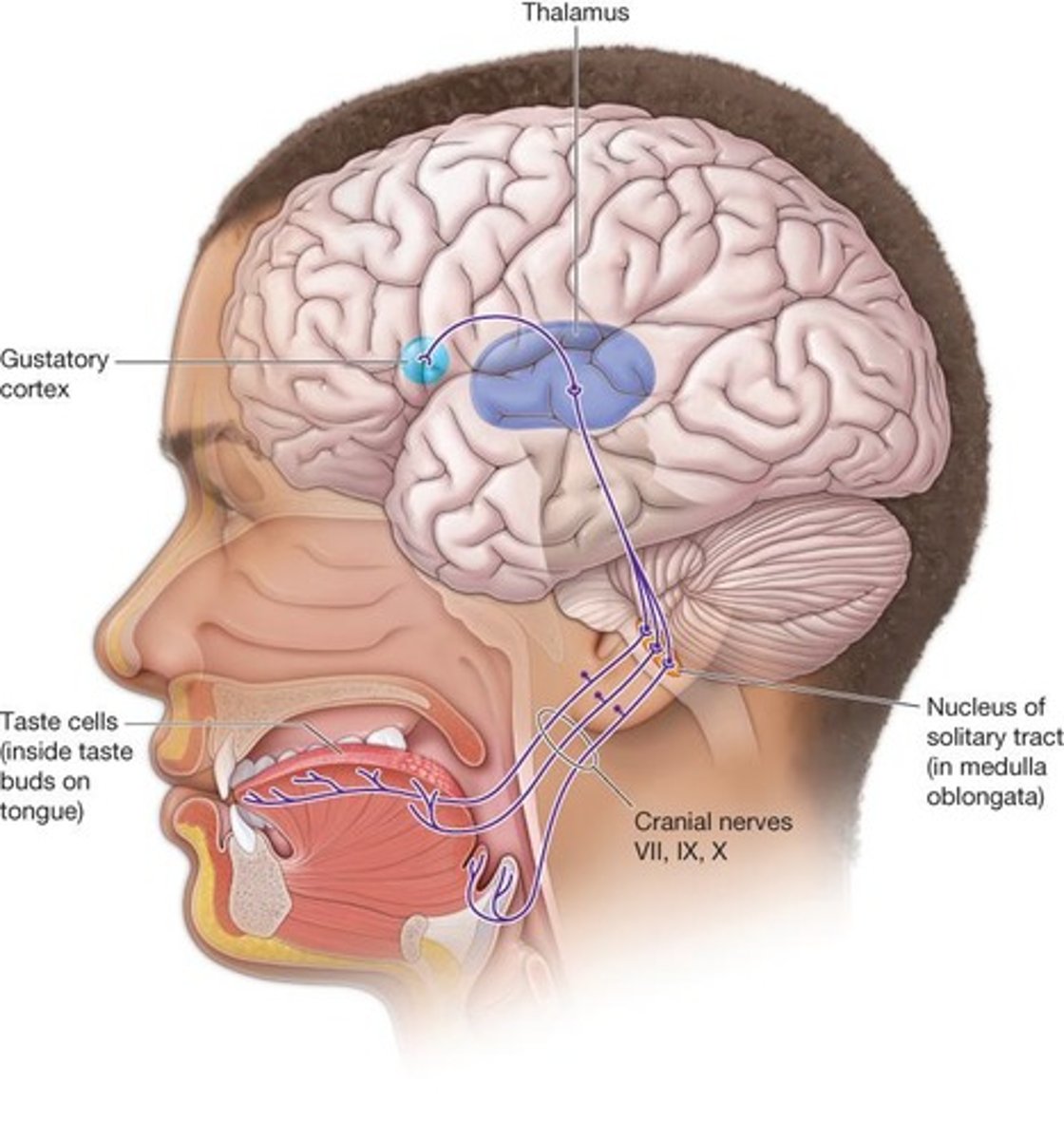
Cranial nerves for taste
Nerves that transmit taste information from the tongue to the brain.
Outer ear
The external part of the ear that collects sound waves.
Middle ear
The cavity that contains the ossicles and transmits sound vibrations to the inner ear.
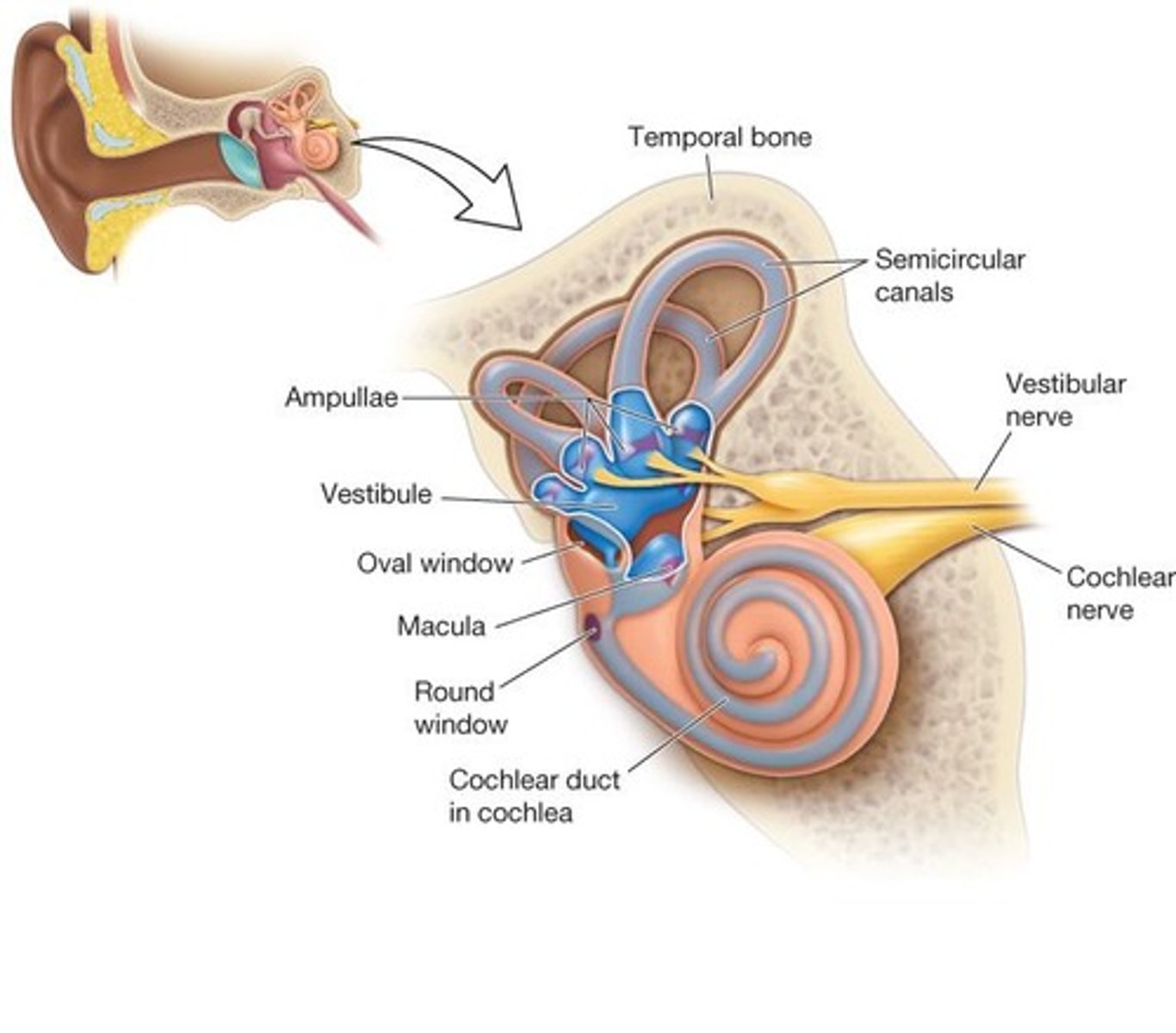
Inner ear
The part of the ear that contains the cochlea and vestibular system, responsible for hearing and balance.
Cochlea
A spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear that contains the sensory organ for hearing.
Spiral organ (of Corti)
The sensory structure within the cochlea that contains hair cells responsible for converting sound vibrations into nerve impulses.
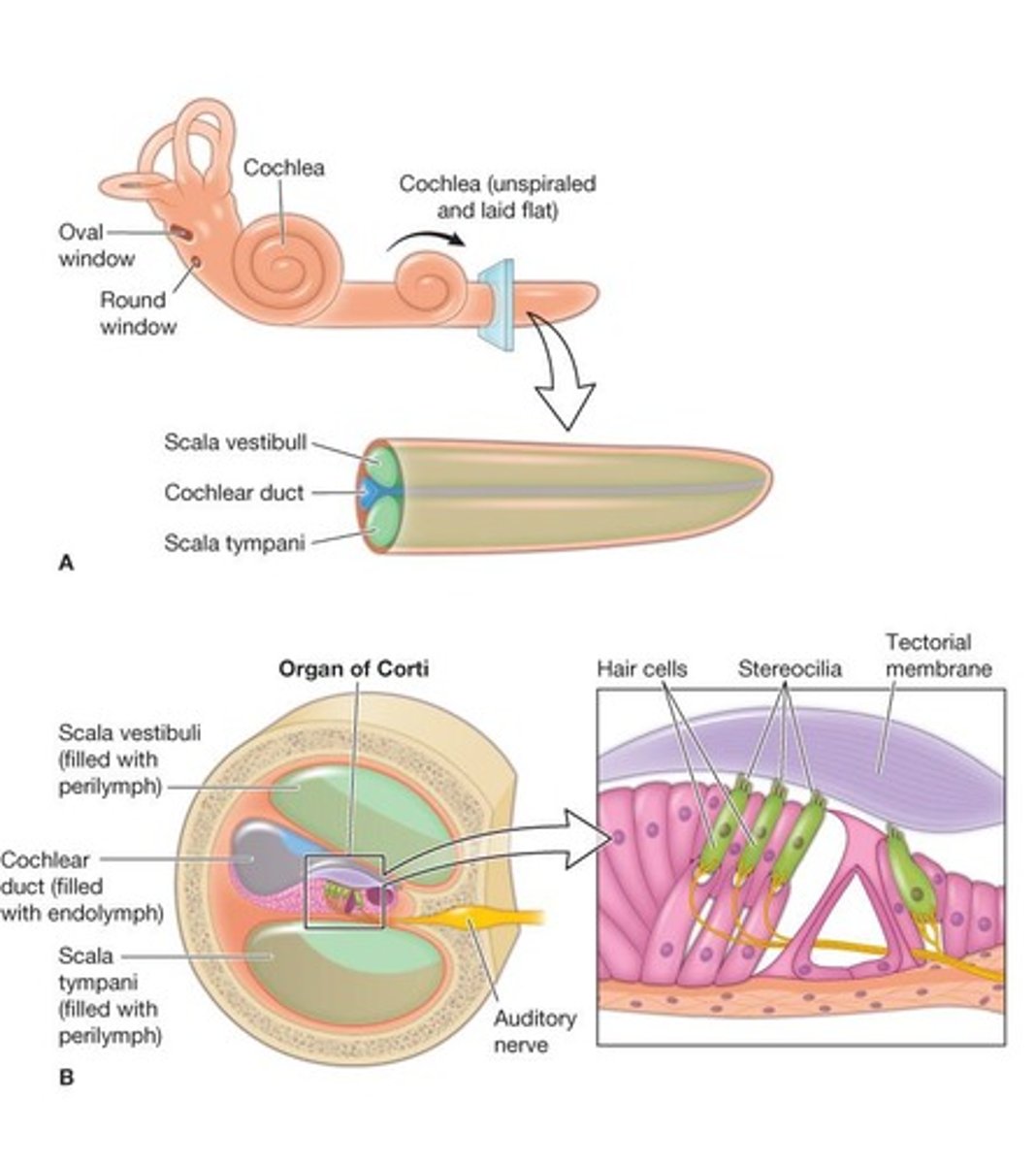
Scala vestibuli
The vestibular duct of the cochlea that conducts sound waves.
Scala tympani
The tympanic duct of the cochlea that conducts sound waves.
Thermoreceptors
temperature receptors
Photoreceptors
receive photons of light
Chemoreceptors
bind chemicals
Baroreceptors
detect pressure changes
Nociceptors
pain receptors
Mechanoreceptors
detect touch, vibration, stretch, etc
General senses
all over the body
Special senses
limited to the head
General senses
dendritic ends of neurons
Special senses
dedicated specialized receptor cells
General senses
touch, pain, vibration, stretch, itch
Special senses
smell, equilibrium, hearing, vision, taste
Tactile receptors
e.g., tactile [Merkel] disc and lamellated [Pacinian] corpuscle
Tears
produced for crying
Pupil
widens or narrows in response to light availability
Sympathetic nervous system
widens the pupil
Anterior and posterior cavities of the eye
associated with humors
Lens
role in vision
Retina components
e.g., optic disc, macula lutea, fovea centralis, rods, cones
Path of light
passes through the eye to the retina, refracted by structures
Rods and cones
functions and locations
Olfactory epithelium
location and structure
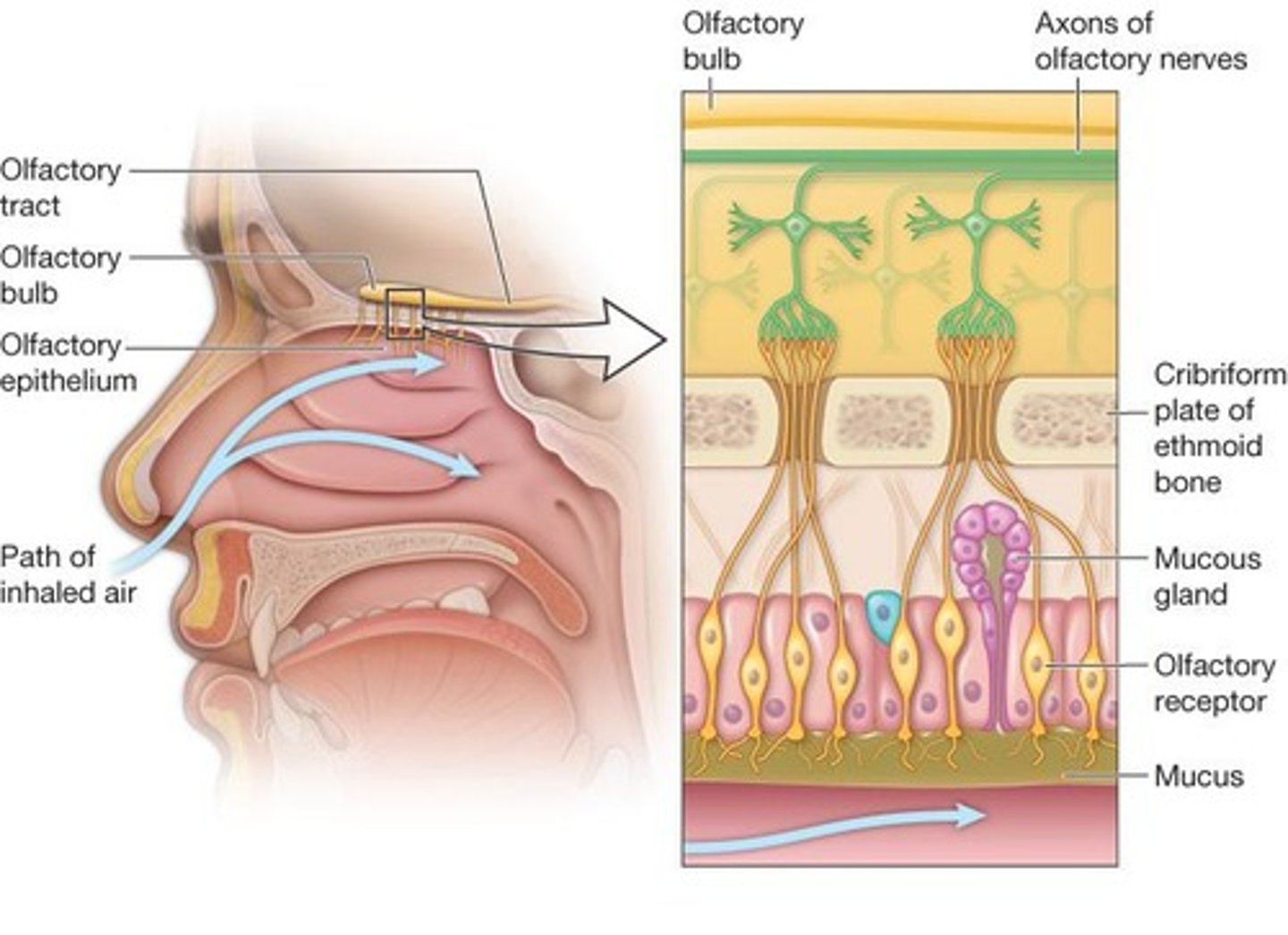
Path of olfaction
from olfactory receptors to the brain
Taste buds
location and structure
Cranial nerves
transmit taste information from the tongue to the brain
External ear structures
e.g., elastic cartilage
Middle ear structures
identify components
Inner ear components
Vestibule, Semicircular canals, Cochlea
Auditory processing
occurs in the temporal lobe