Gene expression
1/17
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Environmental factor –
something that affects organisms gene expression/phenotype. It does not change the genotype. Give example from question.
Mutagen
substance or environmental factor that changes genotype. ex uv light exposure can cause skin cancer.
Why is transcription important (purpose)?
The triplets on the DNA strand need to be made into codons on the mRNA so that the code to build the protein can leave the nucleus and enter the cytoplasm to reach the ribosome for translation. So mRNA carries the code for the correct sequence of amino acids to build the protein.
Why is translation important (purpose)?
Translation is important because it ensures that the mRNA is accurately read by the ribosome. The tRNA molecules, with their anticodons, recognize complementary codons on the mRNA and deliver the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome. This precise matching allows the amino acids to be assembled in the correct sequence, ensuring that the protein can fold and function correctly.
Describe tRNA and its function
tRNA has three unpaired bases called an anticodon. tRNA function is to carry a specific amino acid to the ribosome, and its anticodon which is complementary to a codon on the mRNA matches.
Transcription process
Enzyme RNA polymerase which reads DNA binds to the promotor and separates the DNA so it unwinds along a specific gene to be copied - h bonds break and the 2 DNA strands separate exposing bases.
RNA polymerase moves along the template strand building the mRNA molecule by joining free nucleotide bases using the complementary base pairing rule - except a pairs with u in mRNA.
when RNA polymerase reaches terminator sequence transcription is done - mRNA detaches and the 2 DNA strands rejoin.
Translation process
Start of translation, the edited and completed mRNA leaves the nucleus vis nuclear pores and travels to the ribosome joining at start codon AUG.
The ribosome then moves along the mRNA reading it in triplets/codons. tRNA molecule each carrying a specific amino acid and recognizing a complementary codon vie their anticodon bring amino acids to the ribosome.
peptide bonds form between adjacent amino acids creating a growing polypeptide chain. translation continues until stop codons UAG, UGA, UAA is reached. this signals to the ribosome to release the newly synthesized polypeptide chain which folds into a 3d shape becoming a functional protein.
Base substitution
A single nucleotide swapped which could result in a codon coding for a different amino acid (missense) or still code for the same amino acid (silent)
Silent mutation
A silent mutation is a base substitution where a single nucleotide base is swapped for another but the resulting triplet still codes for the same amino acid. This is due to the degeneracy in the genetic code leading to redundancy. There are 20 amino acids and 64 triplet codes, so some amino acids will have more than 1 triplet coding for it. So, if the mutation still has the same amino acid coded, the correct number of bases, start and stop codons haven’t been affected then the amino will fold correctly shape will be correct and protein will function correctly.
Missense mutation
If it is a missense mutation a single nucleotide base will be swapped resulting in a triplet coding for a different amino acid. (name it). The change in amino acid will result in the final protein folding incorrectly, thus altering shape and therefore protein cannot function correctly.
Nonsense mutation (stop codon)
A nonsense mutation is a base substitution where a single nuelcoetide base is swapped resulting in the amino acid being changed to a premature STOP codon, which will cause the amino acid sequence to be shorter/result in early termination of translation and fold incorrectly thus changing the shape. therefore protein will be unable to function.
Deletion/insertion mutation
in insertion and deletion mutation you get a frame shift mutation, meaning it changes the reading frame from the point mutation on the entire downstream part of the gene on the DNA. This affects the sequence of all triplets that follow. This results in early termination of protein synthesis when stop codon occurs. so no protein formed or with severely impaired biological function.
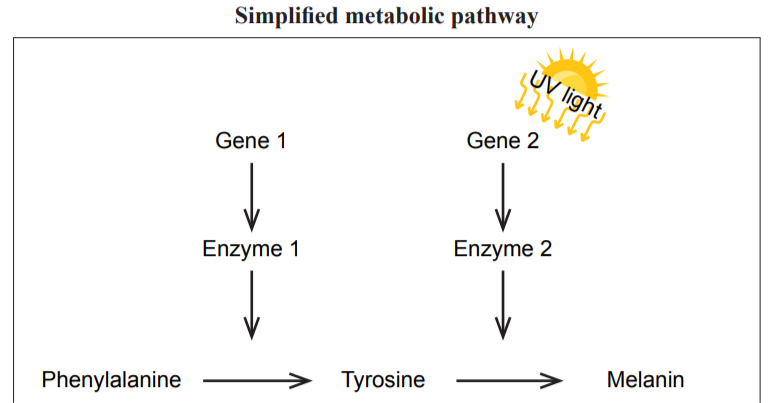
Metabolic pathways
A metabolic pathway is a series of enzyme controlled reactions where the product of one reaction is the substrate for the next. In a metabolic pathway, Gene 1 will code for enzyme 1 and each enzyme catalyzes one specific reaction due to its unique shape.
ex. melanin is produced when gene 1 codes for enzyme 1 converting phenylalanine into tyrosine. tyrosine is then used as the substrate for the next reaction where gene 2 codes for enzyme 2 to convert tyrosine into melanin.
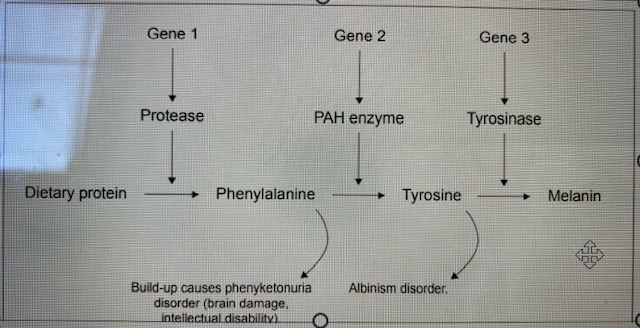
PKU metabolic pathway - REFER TO DIAGRAM
a person with PKU must stick to low protein diet their entire life as they have a mutation in their DNA - gene 2 - that codes for the PAH enzyme. This means they cannot produce this enzyme. As a result if person ingests protein this will be converted into phenylalanine by protease coded for by gene 1. However the phenylalanine cannot be converted into tyrosine and then into melanin so will build up in the body - even if all other enzymes in the pathway are working. However a person can avoid developing PKU by not eating protein. They do this by skipping out this part of the metabolic pathway by consuming foods containing tyrosine. Now no phenylalanine can build up, as there is no substrate or protein for protease to catalyze into phenylalanine, but tyrosine is still present so can be turned into melanin by enzyme tyrosinase.
How does a mutation affect protein in a pathway?
because each step of the pathway is controlled by an enzyme, which is a protein coded for by a gene ex. gene 1 codes for the tyrosinase enzyme, if there is a mutation in the gene/enzyme resulting in anon-functioning protein there will be a build up of the substrate and no product produced.
word equation for phenotype
Genotype + environment = phenotype
How does an environmental factor change the phenotype but not the genotype?
An environmental factor affects an organism phenotype, and does not change genotype. For example, royal jelly changes phenotype and not genotype as it is not a mutagen and therefore cannot change the genotype/DNA base sequence. Royal jelly interacts with the honey bees genotype to express different phenotypes, but DOES NOT CHANGE THE GENOTYPE. For example the genes for large ovaries are expressed with a diet of royal jelly, and NOT expressed with no jelly.
Define phenotype and genotype
Phenotype - physical appearance/traits/characteristics
Genotype - set of alleles that code for the expression of the phenotype/trait