Final Orgo Lab
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
1
New cards
Spectroscopy
Is the branch of science that studies the interaction between light and matter. It is mainly used for structure determination
2
New cards
Principle of Spectroscopy
Measuring the response of molecules after absorbing a certain amount of energy.
3
New cards
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic Radiation has wave-like & particle-Like properties
4
New cards
Infrared Spectroscopy “IR”
The functional groups present or absent
5
New cards
Ultraviolet-Visible Spectrometry “UV-VIS”
Conjugated Systems
6
New cards
Identification of Functional Groups by IR (How does it work???)
• Stretching of bonds is a change of state “length”. \n • Each change of state requires a specific amount of energy. \n • This amount of energy is equal to the difference in energy between the two states “energy gap” \n • Each bond has its own specific energy gap. \n • We irradiate the molecule with light having all frequencies (energy) and then we determine which one \n “frequency” is missing. \n • The missing frequency was absorbed by the molecule.
7
New cards
Jones Oxidation
Oxidizes primary & secondary alcohols and aldehydes (turns **Blue Green)**

8
New cards
Lucas Test
It is used to differentiate between primary, secondary & tertiary alcohols
\
The reagents used are HCl with ZnCl2
\
Primary- NR
Secondary-turbid solution in a couple of minutes
Tertiary-turbid solution quickly
\
The reagents used are HCl with ZnCl2
\
Primary- NR
Secondary-turbid solution in a couple of minutes
Tertiary-turbid solution quickly
9
New cards
Ferric Chloride Test
• It is used to test for phenols.
• Phenol forms **red-blue-violet** complex with Fe(III)
• Phenol forms **red-blue-violet** complex with Fe(III)
10
New cards
Derivative Test
• Convert aldehydes and ketones into other derivatives.
• 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine & semicarbazone
• They convert liquid **aldehydes and ketones into solids**.
• 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine & semicarbazone
• They convert liquid **aldehydes and ketones into solids**.
11
New cards
Tollen’s Test
• It is used to test for **aldehydes**
• The reagents used are AgNO3 and HO-
• The aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
• Ag(I) is reduced to **Ag (silver mirror)**
\
• The reagents used are AgNO3 and HO-
• The aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
• Ag(I) is reduced to **Ag (silver mirror)**
\
12
New cards
Iodoform Test
• Test for presence of **methyl ketones**
• Reagents used are iodine (I2) and (HO-)
• It gives a carboxylate and Iodoform (ICl3) **(yellow precipitate)**
• Reagents used are iodine (I2) and (HO-)
• It gives a carboxylate and Iodoform (ICl3) **(yellow precipitate)**
13
New cards
Bromine Test
• Test for presence of double or triple bonds
• Reagents used are iodine (Br2) (red color)
• Bromine adds to the double bond or triple bonds and since it is consumed the **red color disappears**
\
• Reagents used are iodine (Br2) (red color)
• Bromine adds to the double bond or triple bonds and since it is consumed the **red color disappears**
\

14
New cards
Permanganate Test
• Test for presence of double or triple bonds
• Reagents used are KMnO4 & HO- (purple color)
• It adds two hydroxyl groups to the double bond
• Since the permanganate is consumed **the color disappears**
\
• Reagents used are KMnO4 & HO- (purple color)
• It adds two hydroxyl groups to the double bond
• Since the permanganate is consumed **the color disappears**
\
15
New cards
Atomic size
As atomic size decreases, the bond length decreases and the wavenumber increases.
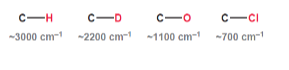
16
New cards
AS bond length decreases,
wavenumber INCREASES
17
New cards
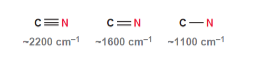
Bond Strength
As bond strength increases, the wavenumber increases
18
New cards
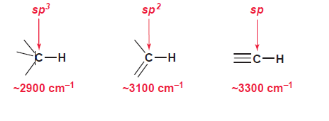
Effect of Hybridization
19
New cards
Effect of Resonance
Resonance decreases the wavenumber
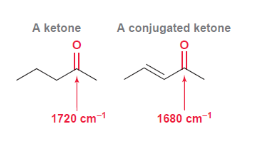
20
New cards
Intensity
As bond polarity increases, the signal intensity increases
21
New cards
Effect of Hydrogen Bonding “Alcohols”
•Concentrated alcohols (too many H-Bonds) will have a broad signal
• Diluted alcohols give narrower signals
• Diluted alcohols give narrower signals
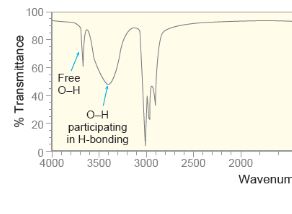
22
New cards
IR Single Bonds
appear below 1500 cm-1
23
New cards
IR Double bonds
appear between 1600-1850 cm-1
24
New cards
IR Triple Bonds
appear between 2100-2300 cm-1
25
New cards
X-H (O-H, N-H, C-H)bonds
appear between 2700-4000 cm-1
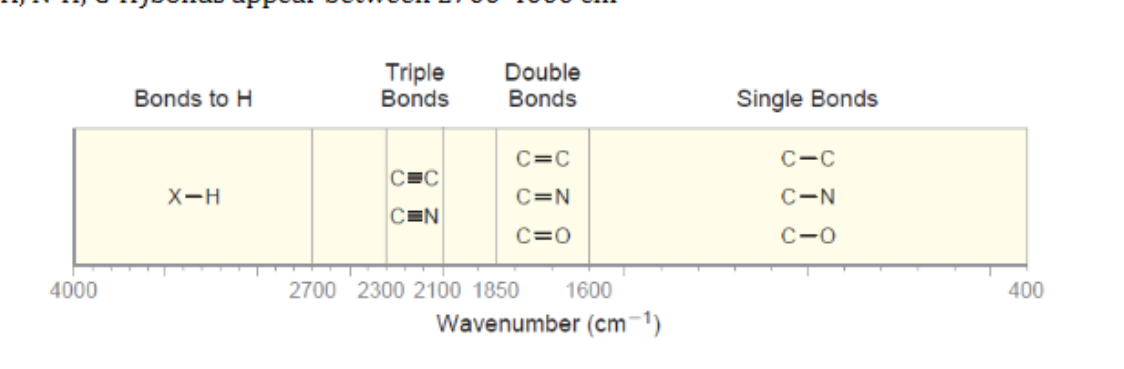
26
New cards
Carboxylic acid IR
27
New cards
Alkene
* note the peaks between 1600-1850
* to conform a C=C-H bond, there should be a small peak at 3100
* to conform a C=C-H bond, there should be a small peak at 3100
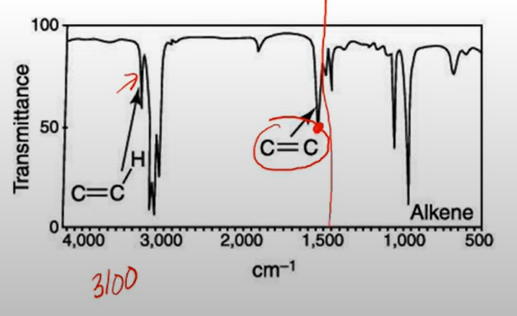
28
New cards
Alkyne
* note peaks around 2100-2300
* C(triple)C-H will have peak at 3300
* C(triple)C-H will have peak at 3300
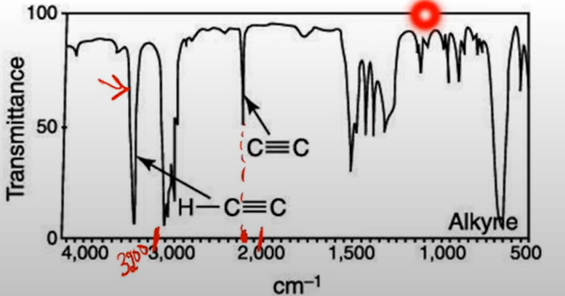
29
New cards
Alcohol
* Board band around 3200-3600
30
New cards
Primary Amine
* two short peaks after 3000
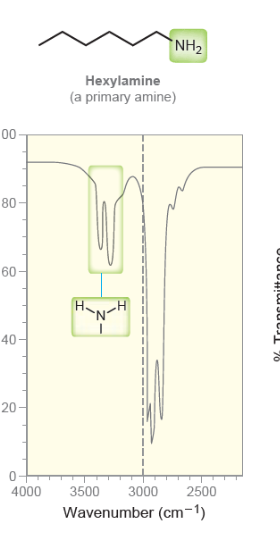
31
New cards
Secondary Amine
* one peak after 3000
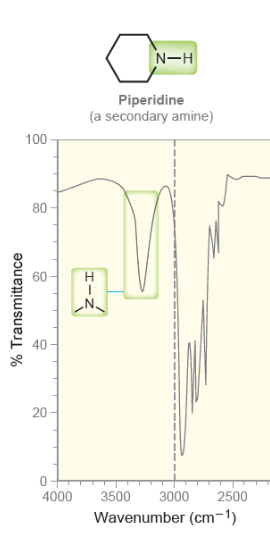
32
New cards
Conjugation ==
lower wavenumber 1750 to 1680
33
New cards
IR tips
Hint: Tetrasubstituted alkenes and internal alkynes have no signals in the designated regions.
34
New cards
As conjugation increases
gap decreases, λmax increases
35
New cards
Woodward Fieser rules: base line
**217 nm**
36
New cards
Woodward Fieser rules: each extra double bond
add 30 for each
37
New cards
Woodward Fieser rules: auxochromic alkyl group
add 5 for each
38
New cards
Woodward Fieser rules: each exocyclic double bond
add 5 for each
one carbon of the double is in a defined ring and the other carbon of the double bond is not
one carbon of the double is in a defined ring and the other carbon of the double bond is not
39
New cards
Woodward Fieser rules: homoannular diene
add 39
40
New cards
Which of the following is the least soluble in water?
A. Alcohols
B. Secondary Amines
C. Primary Amines
D. Carboxylic acids
A. Alcohols
B. Secondary Amines
C. Primary Amines
D. Carboxylic acids
B. Secondary Amines
41
New cards
Dehydration of cyclohexanol follows:
A. Markovnikov’s Rule
B. Zaitsev’s Rule
C. Evelyn Effect
D. Hallalov Rule
A. Markovnikov’s Rule
B. Zaitsev’s Rule
C. Evelyn Effect
D. Hallalov Rule
B. Zaitsev’s Rule
42
New cards
In the dehydration mechanism, the first step is:
A. Formation of the carbocation
B. Protonation of the “OH” group
C. Loss of a proton
D. Rearrangement
A. Formation of the carbocation
B. Protonation of the “OH” group
C. Loss of a proton
D. Rearrangement
Protonation of the “OH” group
43
New cards
Dehydration reaction is done in a distillation apparatus:
A. The alkene is toxic
B. To push the equilibrium to the right
C. To push the equilibrium to the left
D. To condense the reactants back
A. The alkene is toxic
B. To push the equilibrium to the right
C. To push the equilibrium to the left
D. To condense the reactants back
B. To push the equilibrium to the right
44
New cards
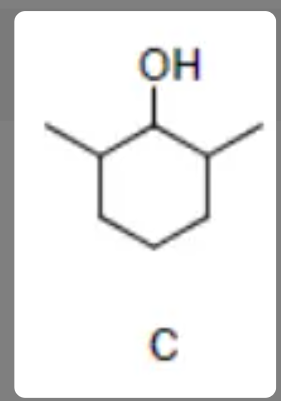
Draw the product of the dehydration reaction of
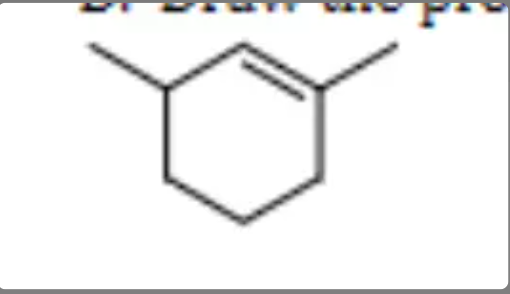
45
New cards
SN1 reactions
\-Unimolecular
\-polar protic solvents
\-carbocation
\-tertiary and secondary halides
\-AgNO3 in ethanol
\-SN1 depends on ALKYL HALIDE
\-polar protic solvents
\-carbocation
\-tertiary and secondary halides
\-AgNO3 in ethanol
\-SN1 depends on ALKYL HALIDE
46
New cards
SN2 reactions
\-Bimolecular
\- polar aprotic solvents
\-primary and secondary halides
\-NaI in acetone
\-SN2 depends on BOTH ALKYL HALIDE AND NUCLEOPHILE
\- polar aprotic solvents
\-primary and secondary halides
\-NaI in acetone
\-SN2 depends on BOTH ALKYL HALIDE AND NUCLEOPHILE
47
New cards
Zaitzev’s rule
an elimination reaction the major product is the more stable alkene with the more highly substituted double bond
48
New cards
Markovnikov’s rule
When HZ is added to unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen will add to the carbon with the most number of hydrogens
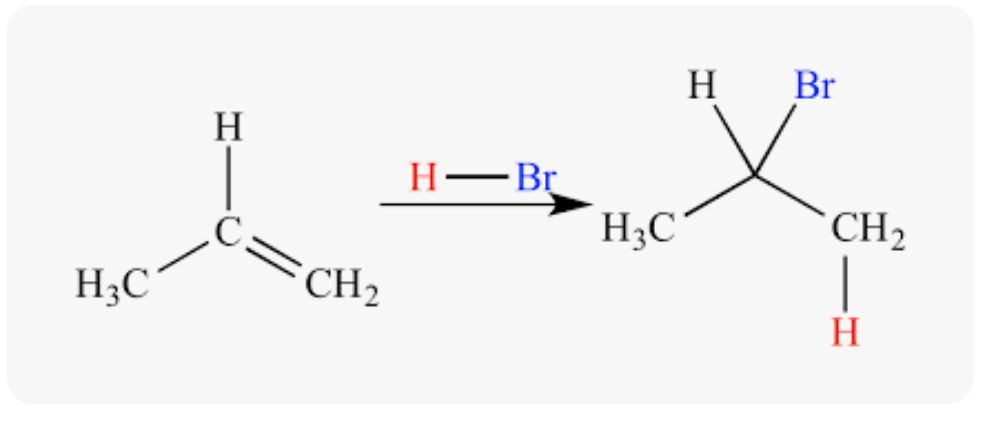
49
New cards
E1 mechanism
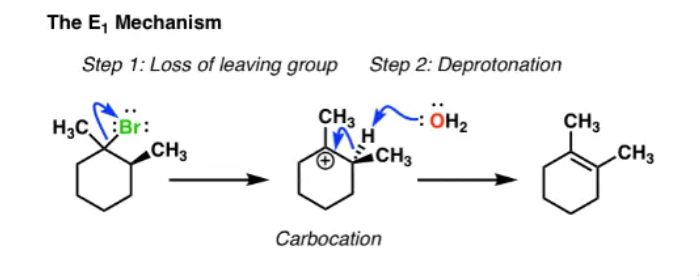
50
New cards
E2 mechanism
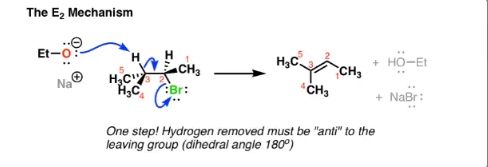
51
New cards
Evelyn effect
the product composition changes during the course of the reaction
\
Its hypothesized that the reason is because of the starting mixture of cis- and trans- isomers
\
Its hypothesized that the reason is because of the starting mixture of cis- and trans- isomers
52
New cards
What equipment is used in fractional distillation?
Vigreux column
53
New cards
Mass Spectrometry
It is used to detect the molecular weight and molecular formula
54
New cards
Ionization
Bombard molecule with a high energy electron beam to eject an electron and form a radical cation
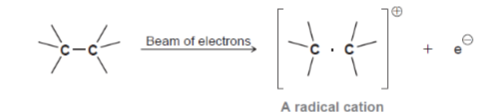
55
New cards
Radical Cation
Also called, molecular ion or the parent ion and it has a mass equal to that of the original \n compound. Radical cations are unstable and rapidly fragment into smaller ions and radicals.
56
New cards
base peak
highest peak
57
New cards
molecular ion
its weight is equal to the molecular weight of the compound
58
New cards
base peak does not always equal
the molecular ion peak
59
New cards
Nitrogen Rule
• Odd Molecular weight = Odd number of nitrogen \n atoms \n • Even Molecular weight = No nitrogen or even number \n of nitrogen atoms.
60
New cards
Bromine in mass spec
Will have a 1:1 ratio
61
New cards
Chlorine in mass spec
Will have a 3:1 ratio
62
New cards
Analysis (M+1)+. Peak
Intensity (M+1) = (# of carbons x (% abundance) x Intensity \[M\]) / 100
63
New cards
In our reduction experiment, hydrogen has two roles
making the catalyst and reducing the trans cinnamic acid
64
New cards
A Grignard reagent is
* a carbon nucleophile
* made from alkyl halide and Mg
* cannot react with water if we want a successful Grignard reaction
* \
* made from alkyl halide and Mg
* cannot react with water if we want a successful Grignard reaction
* \
65
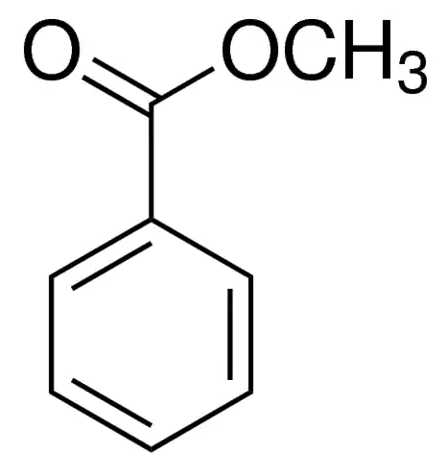
New cards
Methyl benzoate