Midterm #2
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Modern Principles of Economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how responsive the quantity demanded is to a change in price
Perfectly Elastic and Perfectly Inelastic Demand Curve
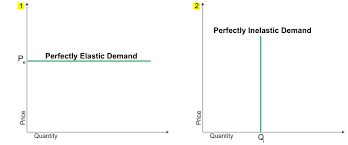
What are some factors that determine if demand becomes more inelastic?
Fewer Substitutes
Short Run (Less Time)
Categories of Product i.e., orange soda
Necessities
Small Part of budget
What are some factors that determine if demand becomes more elastic?
More Substitutes
Long Run (More Time)
Specific Brand i.e., Fanta
Luxuries
Large Part of Budget
How do you calculate elasticity of demand?
* Elasticity of demand is always negative.
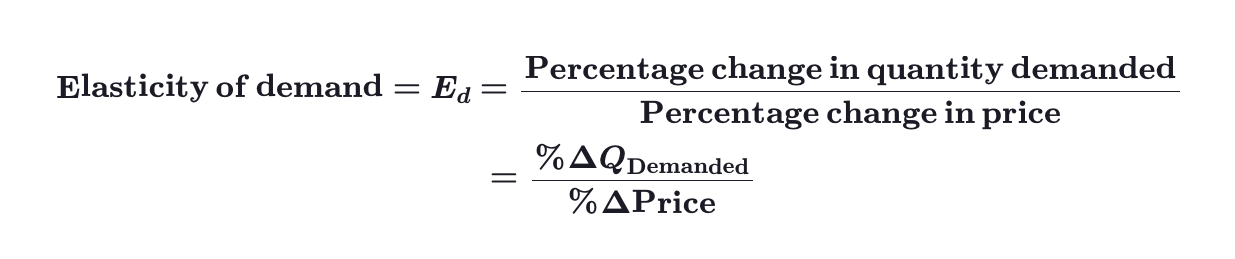
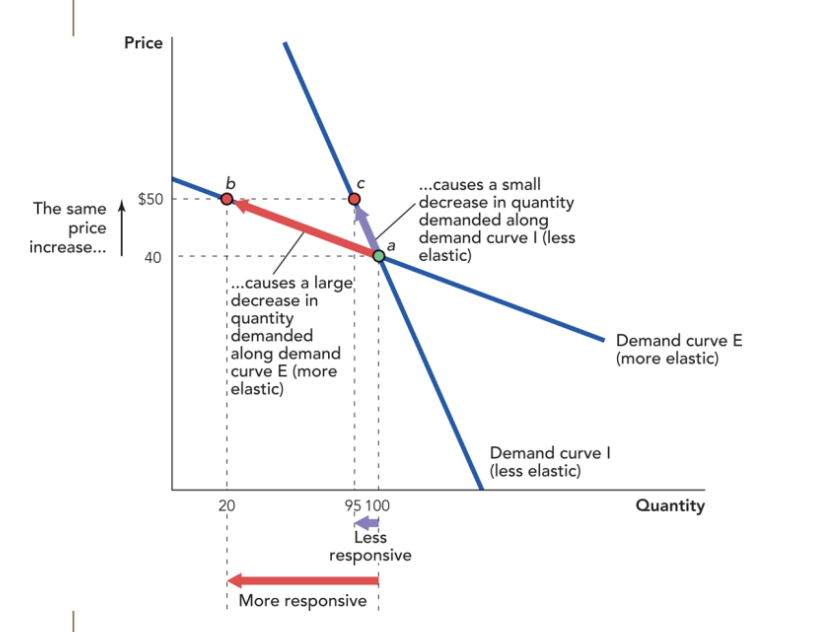
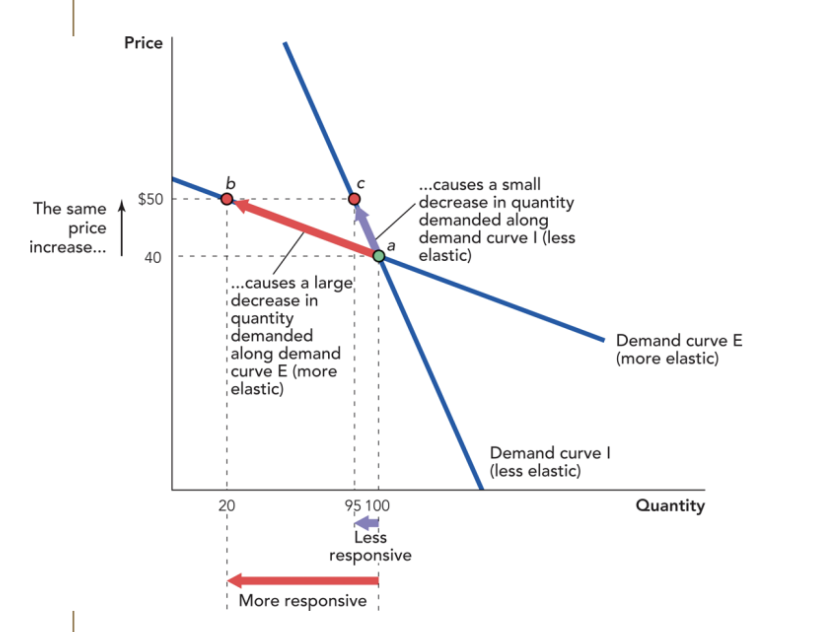
Is Demand Curve I or Demand Curve E more elastic and explain why.
Demand Curve E is more elastic than Demand Curve I because it is flatter and closer to being a horizontal line than Demand Curve I. Demand Curve E is also more responsive to a change in price than Demand Curve I, which is the exact definition of elasticity.
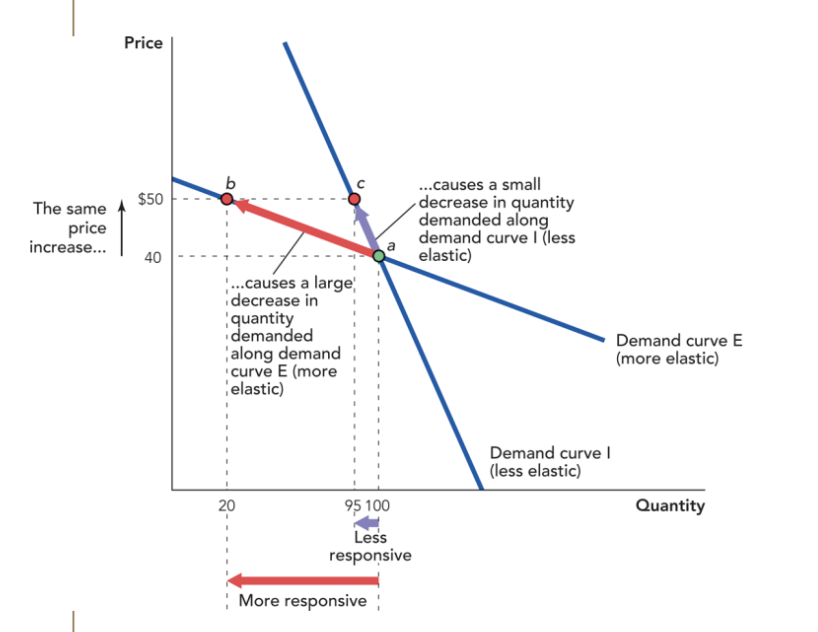
Calculate the ED of Demand Curve I.
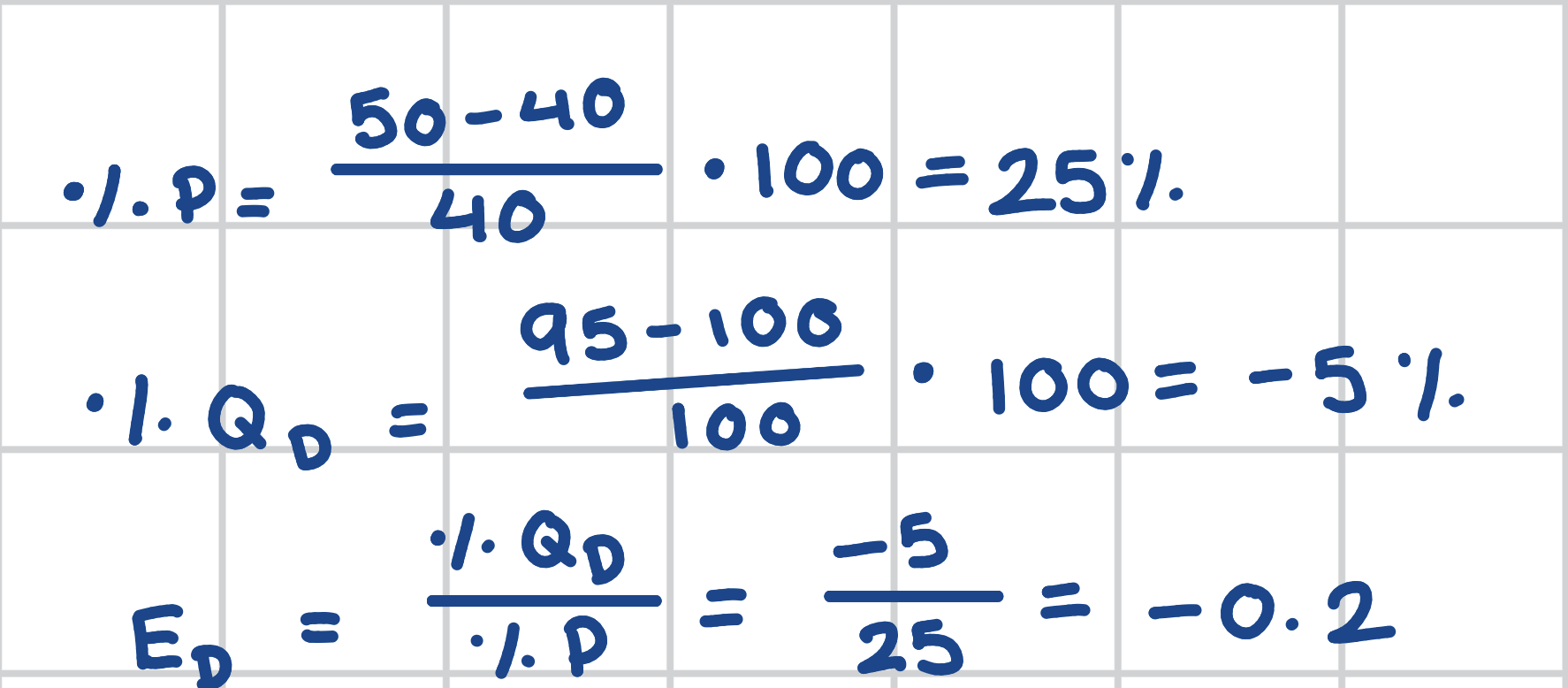
Calculate the ED of Demand Curve E.
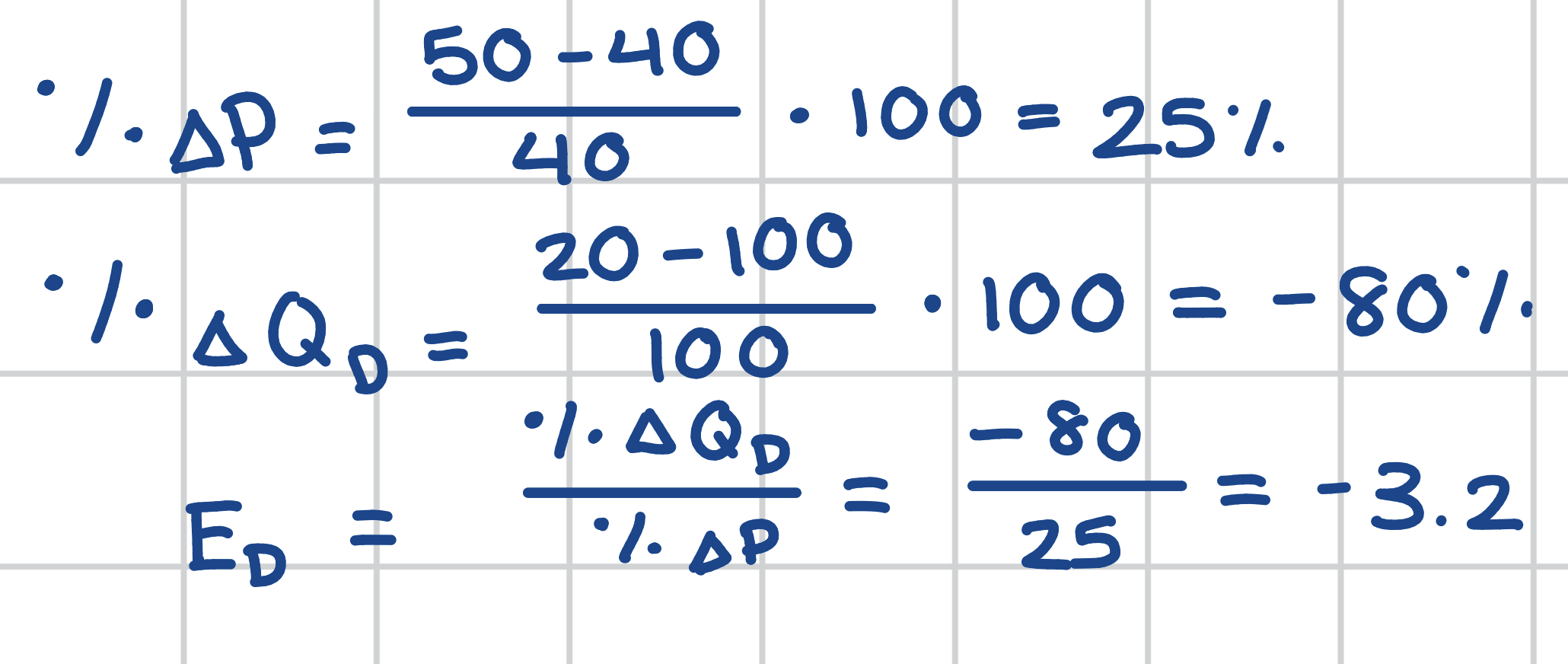
If the absolute value of the elasticity of a demand curve is less than 1, then what does this tell us about the demand curve?
The demand curve is inelastic.
If the absolute value of the elasticity of a demand curve is greater than 1, then what does this tell us about the demand curve?
The demand curve is elastic.
Unit Elastic
When the absolute value of the elasticity is exactly equal to 1
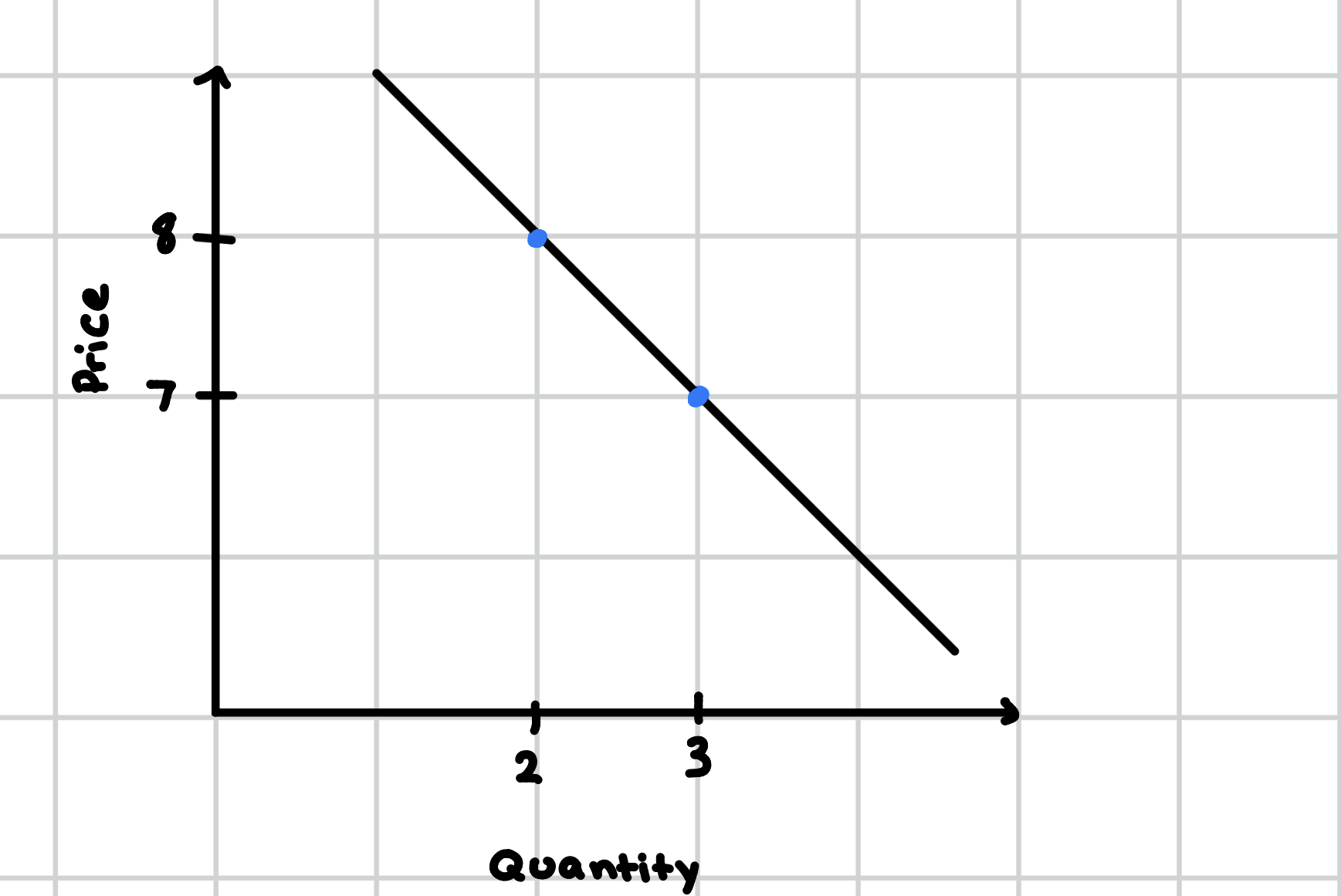
How do you calculate ED using the midpoint method?
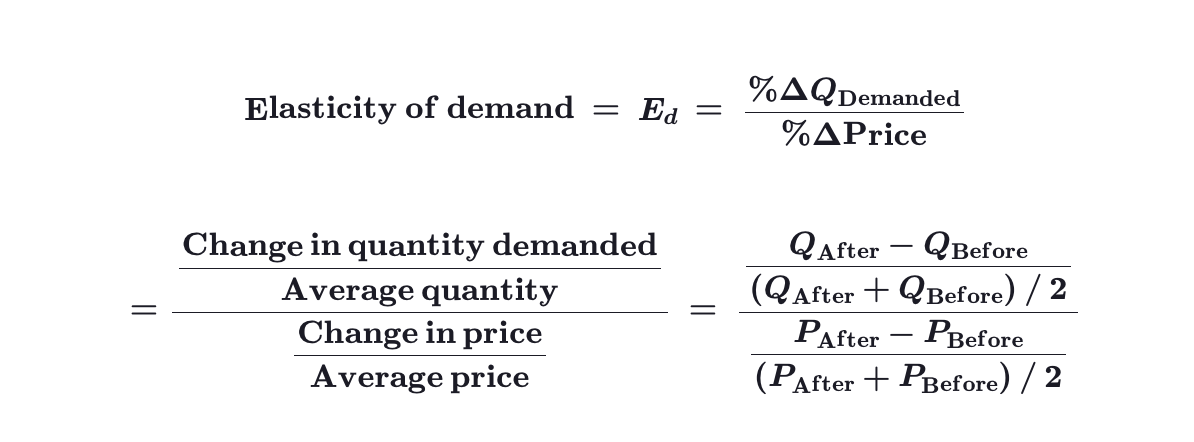
Calculate ED using the midpoint method.
How do you calculate revenue?
Revenue = Price x Quantity
When the demand curve is inelastic (ED < 1), price and revenue _________.
Move together
When the demand curve is elastic (ED > 1), price and revenue _________.
Move in opposite directions
When the demand curve is elastic (ED = 1), when price changes, revenue _________.
Stays the same
Elasticity of Supply
A measure of how responsive the quantity supplied is to a change in price
When is the supply curve inelastic?
Difficult to increase production at constant unit cost
Large share of market for inputs
Global supply
Short run
When is the supply curve elastic?
Easy to increase the supply (production at constant unit cost)
Small share of market for inputs
Local supply
Long run
How to calculate elasticity of supply?
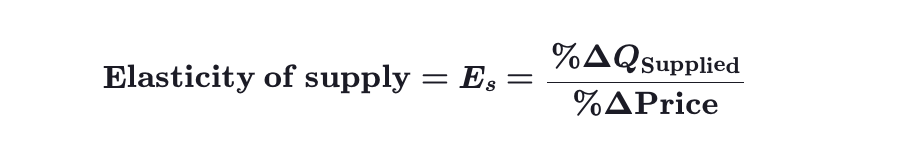
How to calculate elasticity of supply using the midpoint method?
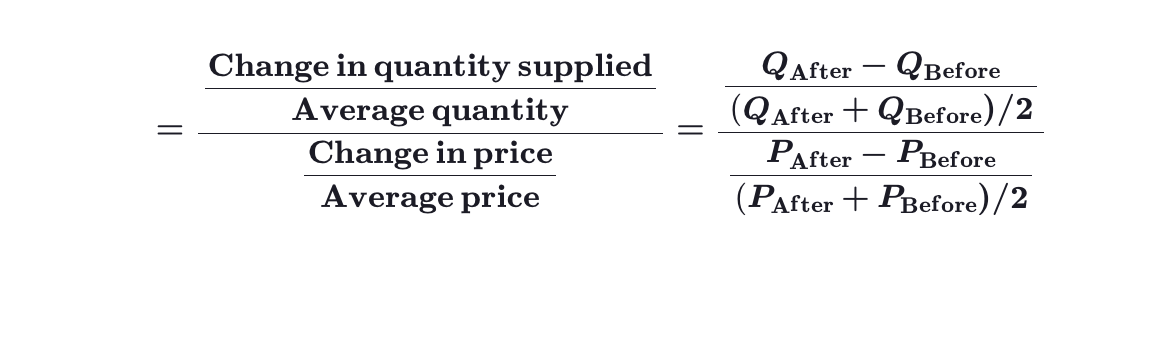
What are the three most important things to remember about commodity tax?
Who ultimately pays the tax does not depend on who writes the check to the government
Who ultimately pays the tax does depend on the relative elasticities of demand and supply
Commodity taxation raises revenue and creates deadweight loss (i.e., reduces the gains from trade)
How do you calculate tax?
Tax = Price paid by buyers - Price received by sellers
When the demand curve is more elastic, the ________ pay more of the taxes.
Sellers/Producers
When the demand curve is more ________, the buyers/demanders pay more of the taxes.
Inelastic
How do you calculate how much the consumers pay of the tax?
(Price demanders pay - Equilibrium price without tax)/Tax
How do you calculate how much the producers pay of the tax?
(Price suppliers receive - Price without tax)/Tax
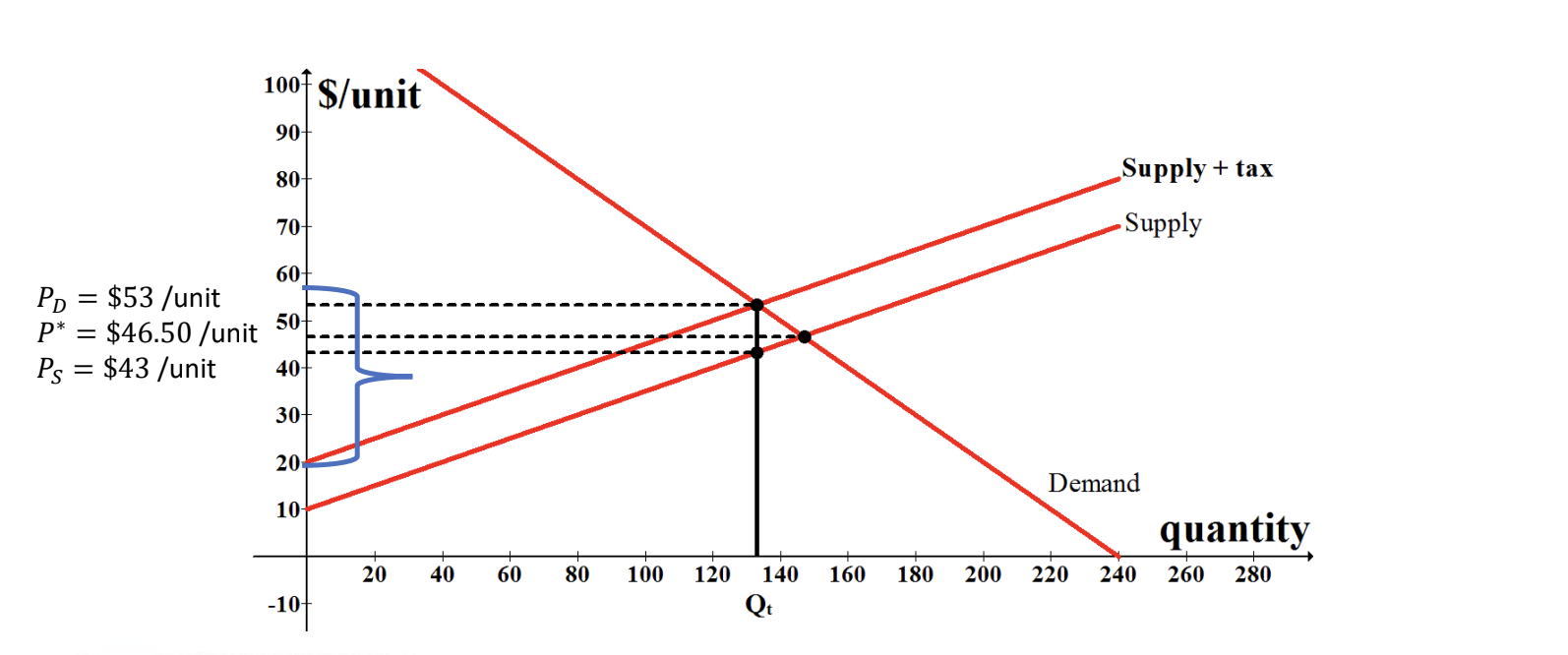
Calculate how much tax both the consumers and producers pay.
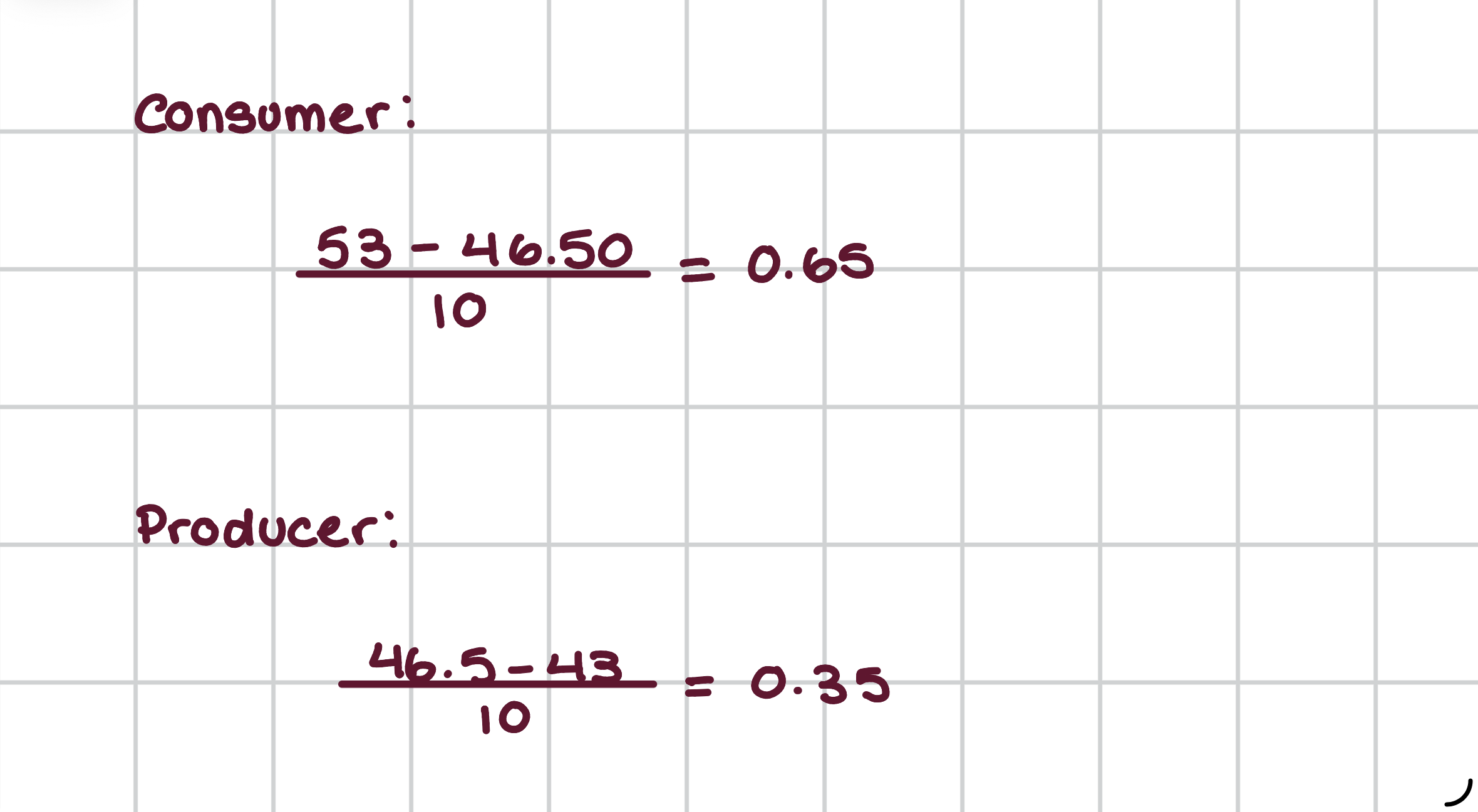
Deadweight Loss
Reduction in the total surplus caused by a market distortion or inefficiency
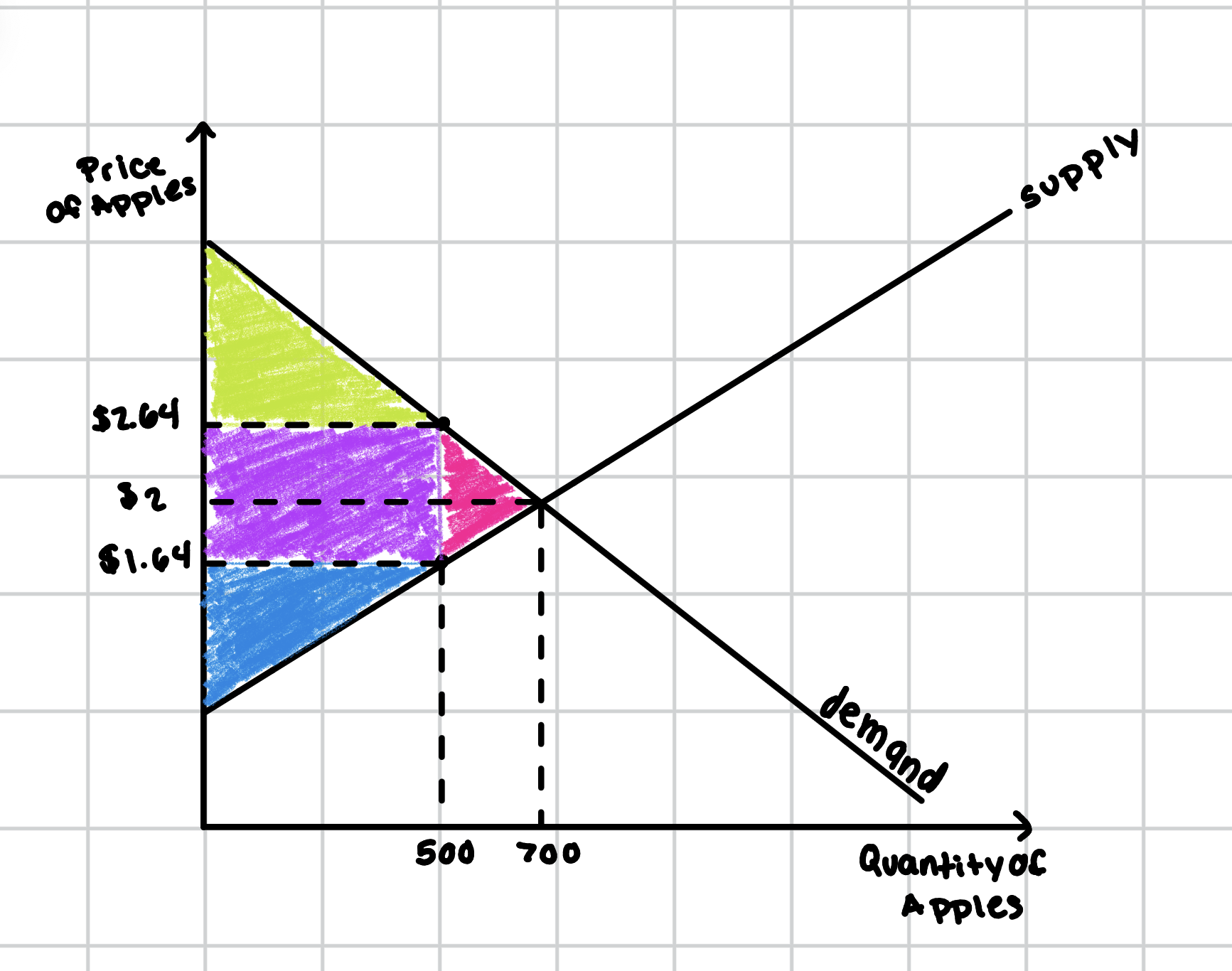
Label all the parts of the graph.
Light Green - Consumer Surplus
Purple - Tax Revenue
Blue - Producer Surplus
Pink - Deadweight Loss
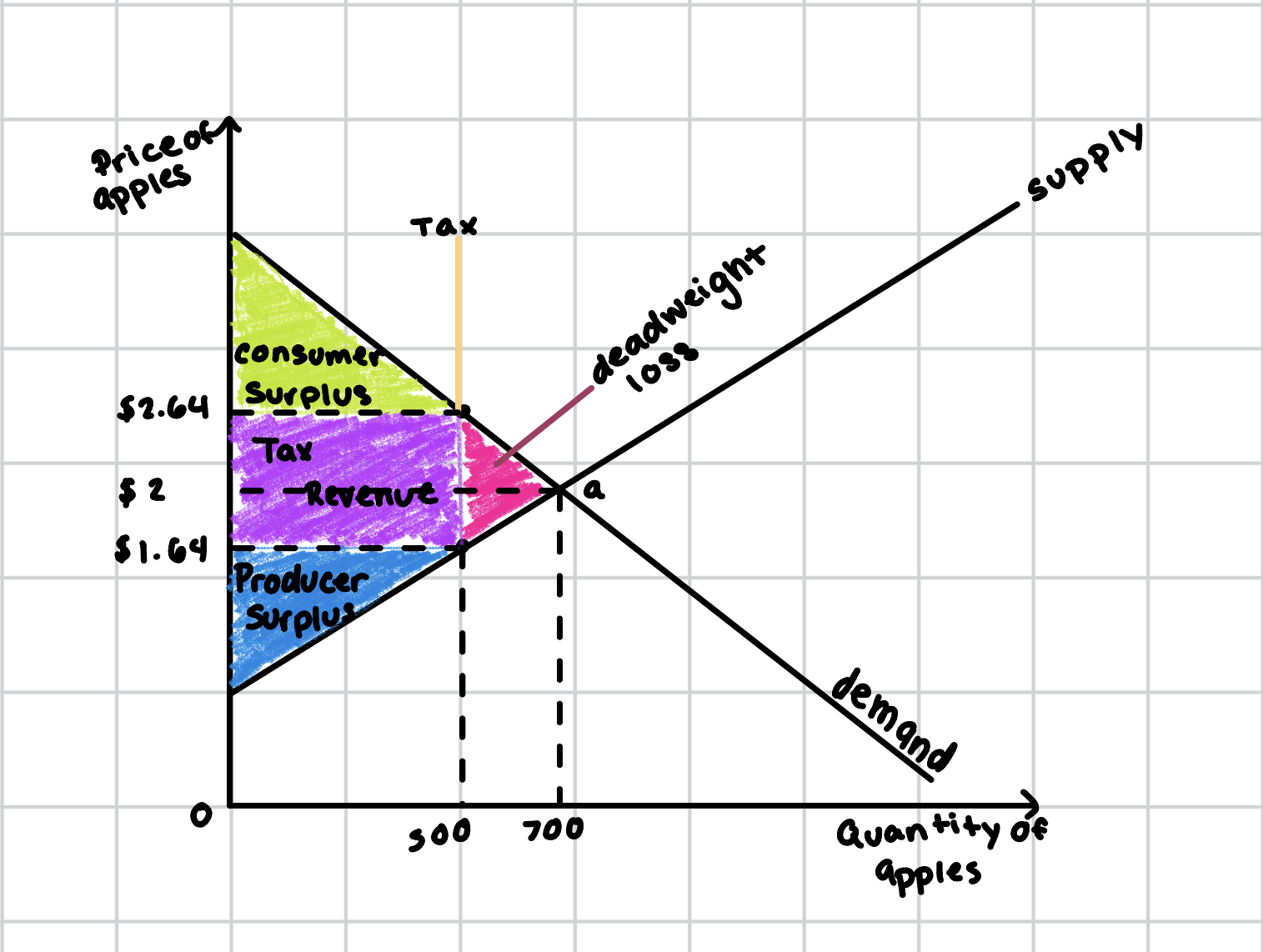
How do you calculate dead weight loss?
½ (Q* - Qt)T
When the demand curve is more elastic, deadweight loss …
Increases
Subsidy
Reverse tax, where the government gives money to producers or consumers to purchase a product
What are the three most important things to remember about subsidies?
Who gets the subsidy does not depend on who gets the check from the government
Who benefits from a subsidy does depend on the relative elasticities of demand and supply
Subsidies must be paid for by taxpayers and they create inefficient increases in trade (deadweight loss)
How do you calculate a subsidy?
Subsidy = Price received by sellers - Price paid by buyers
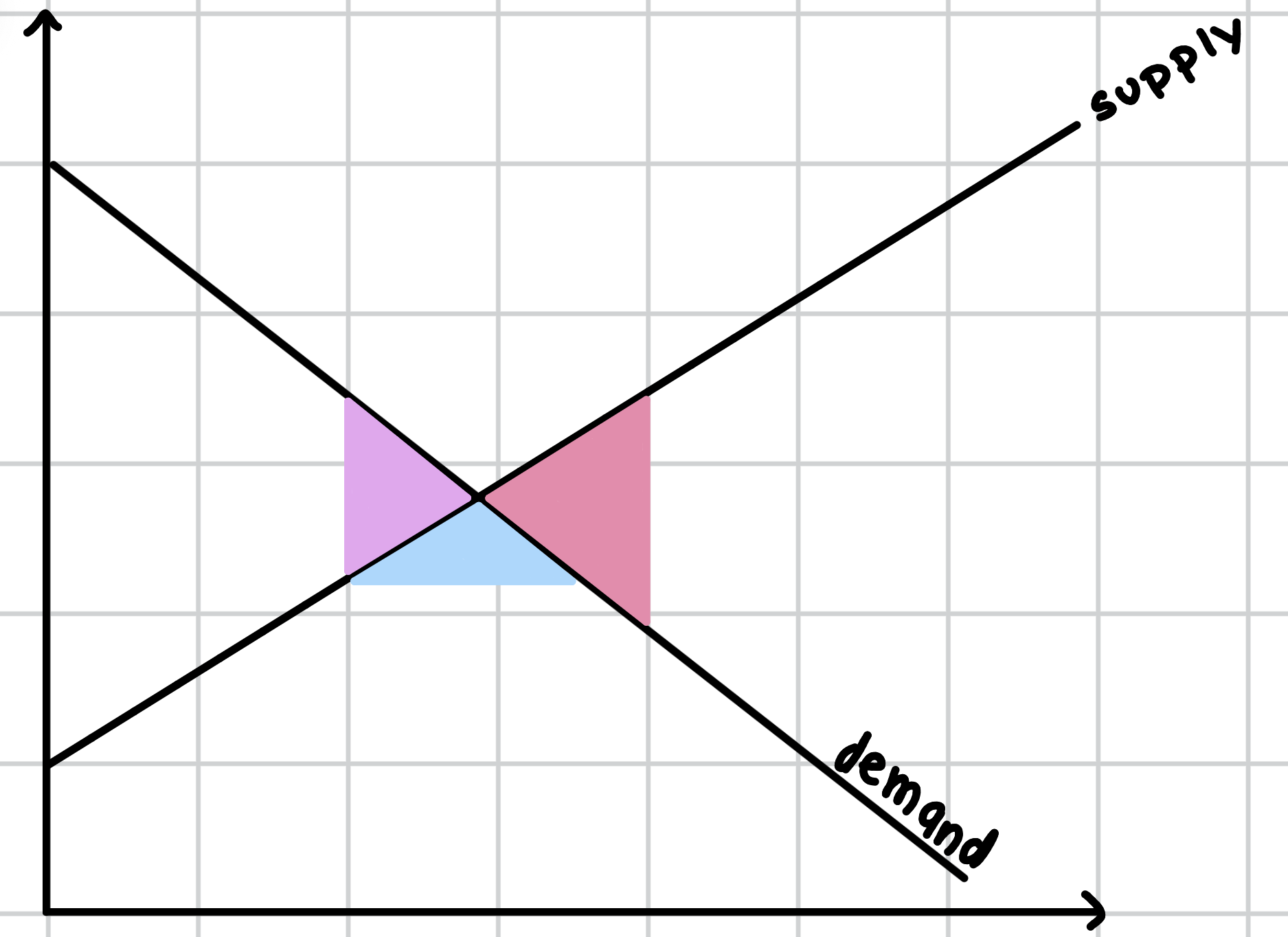
Which part of the graph represents a subsidy?
Pink
Price Ceiling
Maximum price allowed by law
What are the effects of price ceilings?
Shortages
Reductions in product quality
Wasteful lines and other search costs
A loss of gains from trade (Deadweight Loss)
A misallocation of resources
Shortage
When prices are held below the market price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied
Rent Control
Price Ceiling on rental housing
Arguments for Price Ceiling
Discipline monopolies
The public
Creates affordable housing (but there are better ways to do this like housing vouchers)
Price Floors
A minimum price allowed by law
What are the effects of price floors?
Surpluses
Lost gains from trade (Deadweight Loss)
Wasteful increases in quality
A misallocation of resources
Minimum wages creates ________.
Unemployment
If minimum wage rises, will that increase or decrease the demand for the average union workers’ labor? Why?
If the minimum wage rises, that will increase the demand for the average union worker’s labor because the competition (unskilled labor) is getting priced out of the market.

Identify what the colors represent.
Pink - Total Value of Wasted Time
Purple - Lost Consumer Surplus
Blue - Lost Producer Surplus
Lost Consumer Surplus + Lost Producer Surplus = ?
Total Deadweight Lost
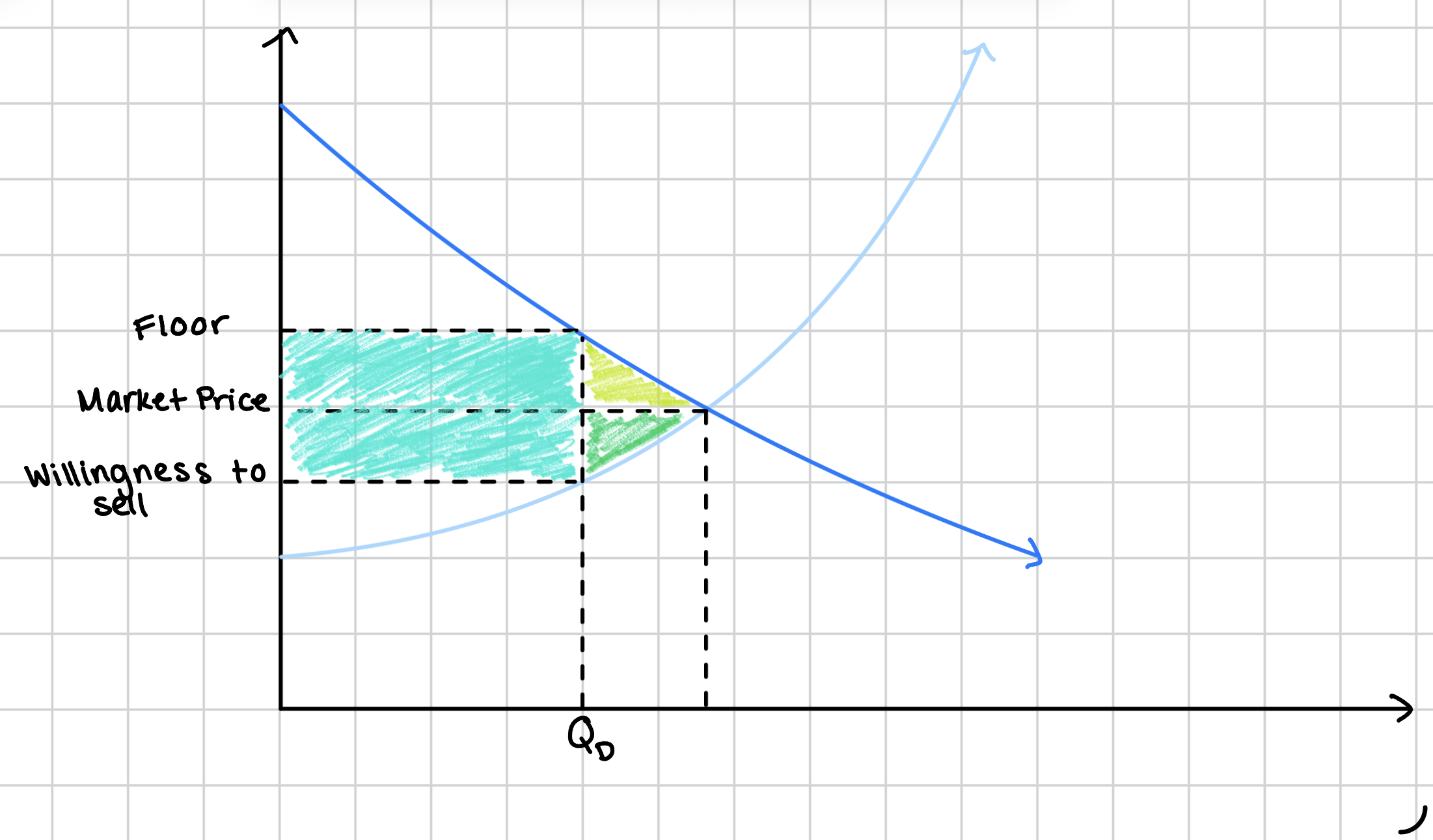
Identify what the colors represent. Where would the surplus be represented?
Teal - Total Value of Wasted Time
Light Green - Lost Consumer Surplus
Dark Green - Lost Producer Surplus

Identify what the colors represent.
Pink - Loss due to random allocation
Green - Total Consumer Surplus under Random Allocation
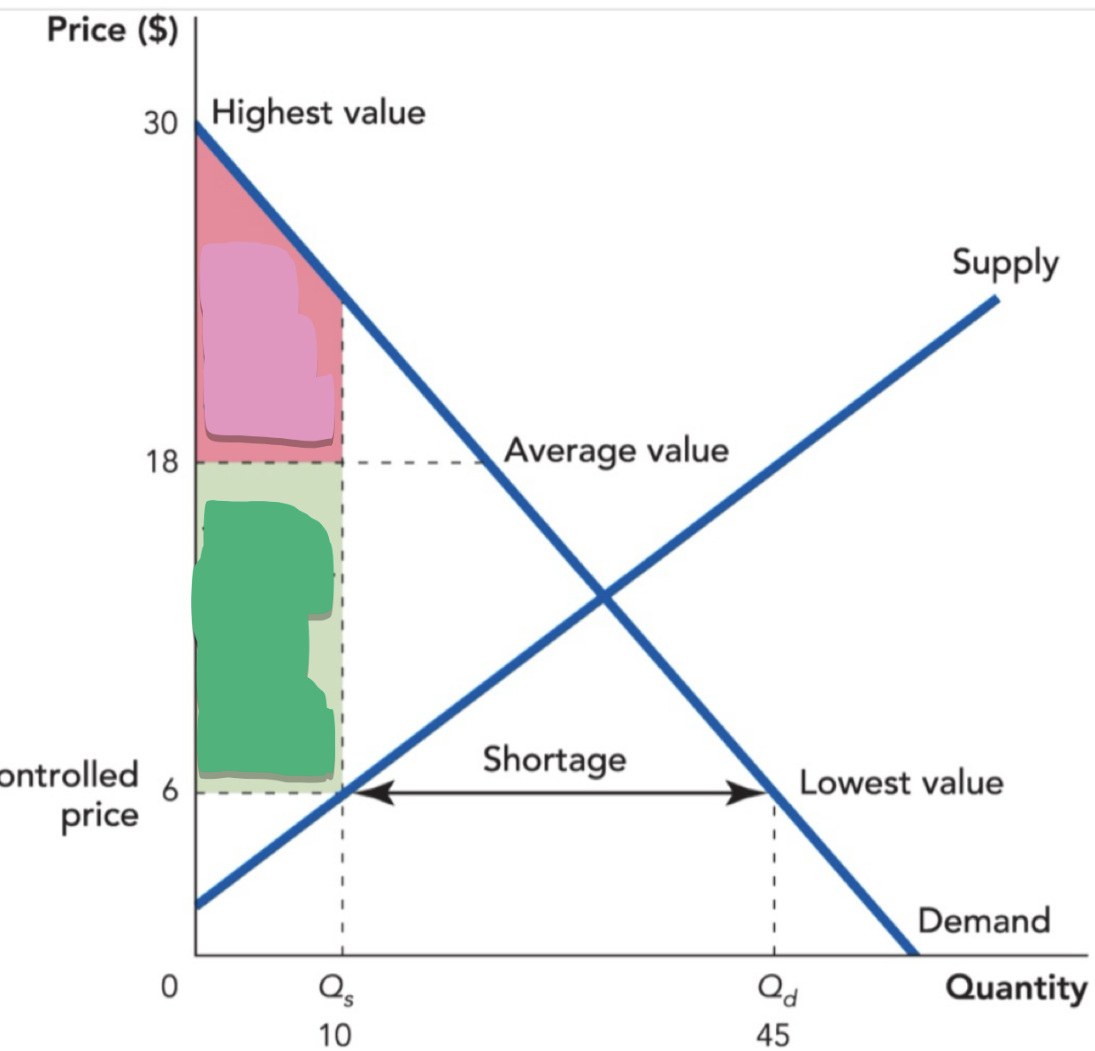
How do you calculate the average value?
Average Value = ½ (30 + 6) = $18
Blat
Using one’s connections to get favors
Give an example of blat.
A manager of a radio factory trades the manager of a beed factory a radio in exchange for beef.
_______ are not only incentives, but also signals to producers to make more or less of a certain good and if consumers should buy more of a certain good.
Prices
Great Economic Problem
How to arrange our scare resources to satisfy as many of our wants as possible
Central Planning
An economic system where a government or single authority makes all key decisions about the production and distribution of goods and services
Why does centralized planning fail?
Lack of information and incentives
Decentralized Planning
Strategy that transfers authority, decision-making, and resources from a central body to lower-level or local entities, such as local governments or individual departments (Capitalism)
An example of central planning is ___________; an example of decentralized planning is ______________.
USSR; United States
Speculation
The attempt to profit future from price price change