Latitude and Longitude/Maps
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Why should Geography matter?
international relationships are constantly and rapidly shifting
to better understand how globalization affects you
to be better-informed players on the “world-stage” (geographically literate)
How do places effect you?
The unique characteristics of a place yields development of new technology and culture; places are also settings for social interaction
Why is earth not a perfect sphere?
Because it has a geoidal bulge at the equator
Geoidal Bulge
The earth’s equatorial diameter is greater than its polar diameter
What is the latitude and longitude grid system used for?
To locate places on the surface of the earth
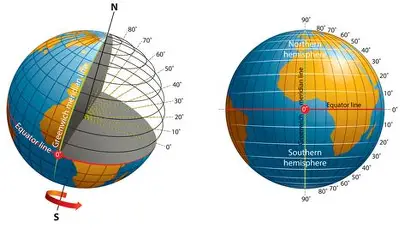
Parallels of Latitude
parallel lines on the earth the run East-West, measured North or South of the equator
What degrees does latitude start and end with?
0 (at the equator) - 90 (North or South poles)
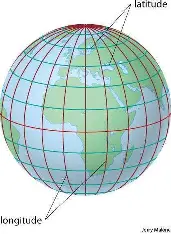
Meridians of Longitude
non-parallel lines on the earth that run North-South, measured East or West of the Prime Meridian
What degrees does longitude start and end with?
0 (at the Prime Meridian) to 180 (at the International Date LIne)
How are the degrees of latitude and longitude divided?
By minutes and seconds
How do you write earth coordinates?
Latitude, Longitude
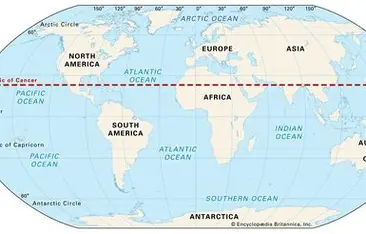
Tropic of Cancer
23.5 degrees North
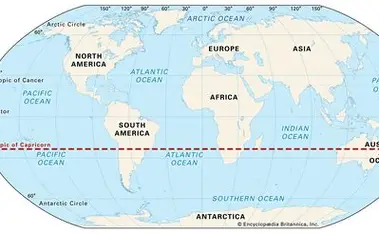
Tropic of Capricorn
23.5 degrees South
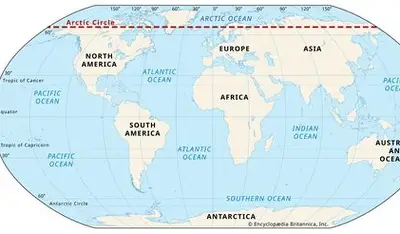
Arctic Circle
66.5 degrees North
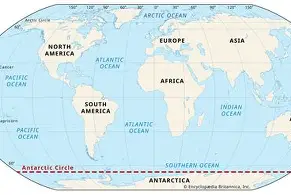
Antarctic Circle
66.5 degrees South
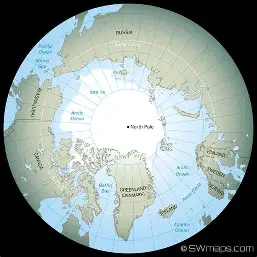
North Pole
90 degrees North
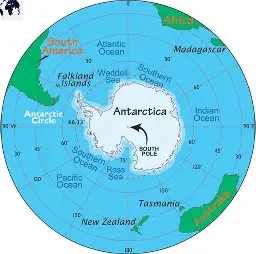
South Pole
90 degrees South
International Date Line
180 degrees
What are time zones determined by?
The Earth’s rotation and the Meridians of Longitude
How many degrees of longitude is one time zone?
15 degrees
Greenwich Mean Time
the local time in London, England (Greenwich)
How do you determine the difference in time (zones) between 2 locations?
By taking the difference in longitude and dividing it by 15
Transferring the globe onto a flat surface often causes…
distortion of the physical size and shape of the earth
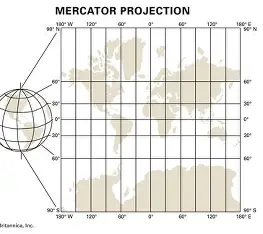
Mercator projection
the most commonly used map projection
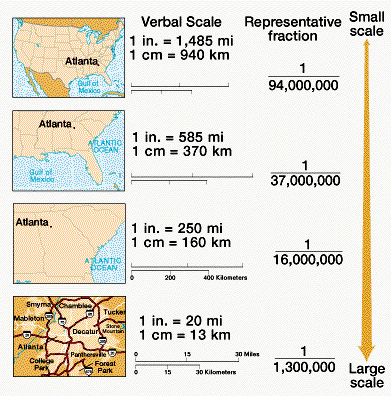
Scale
the ratio of distance on a map to the actual distance on the group
How is scale shown on a map?
Written scale, representative fraction, or a graphic (bar) scale
Example of a written scale
one-inch equals four miles
Example of a representative fraction scale
1:24,000 inches
Large-scale map
shoes a small area of the Earth’s surface is more detail
Small scale map
shows a large area of the Earth’s surface with less detail
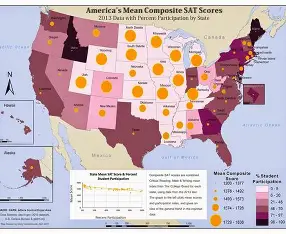
Thematic Maps
shows the distribution of phenomena (climate, language, boundaries) to show relationships between places or diffusion
Spatial Distribution
The arrangement of landscape on a feature being studied
What do geographers’ study about spatial distribution?
Why it is the way that it is and what causes it
Three properties of spatial distribution
Density, Concentration, Patterm
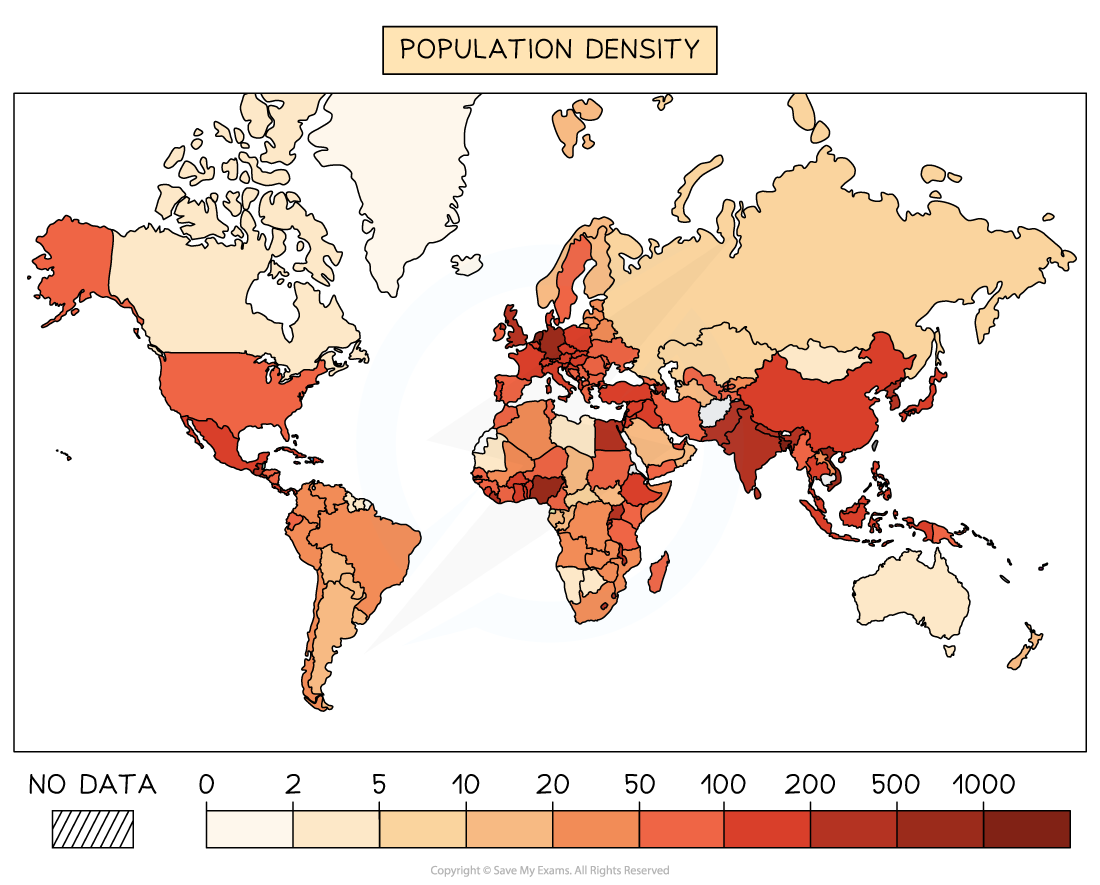
Density
frequency with which a feature/phenomenon occurs within a given area

Concentration
how the arrangement of a feature or phenomenon is spread over a unit of area
Pattern
the geometric arrangement of a feature across the landscape
Absolute Space
mathematical construct described through points, lines, areas, planes, and configurations (lat and long)
Relative space
nature and degree of connectivity between locations (down the street)
Types of Relative Space
Topological, Socioeconomic, Cultural
Topological space
degree of connectivity of people and places (routes of a subway system)
Socioeconomic space
how spatial relationships are fixed through measures of time, cost, profit, and production (measuring the inequalities among places or regions)
Cultural Space
space of people with common ties, the places, territories and settings which carry special meaning ( your neighborhood, country)
Cognitive Space
a person’s values, feelings, beliefs, and perceptions about a place or region
Mental Map
the image in your mind of a particular, area, place, or route; involves your environmental perception, your memories of a place or route