5- sinonasal pathology
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
3 skin conditions of the nose caused by UV radiation
solar (actinic) keratosis
basal cell carcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
clinical presentation of solar (actinic) keratosis
scaly plaques on face, lip, ears, scalp, neck, arms, etc
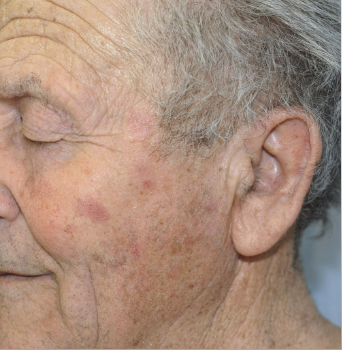
basal cell carcinoma is caused by a mutation of what
PTCH1 → loss of function
T/F: basal cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes
true
treatment for basal cell carcinoma
local excision
3 skin conditions of the nose caused by inflammation
lupus erythematosus
rosacea
rhinophyma
clinical presentation of lupus erythematosus
discoid rash: erythematous raised patches w/ adherent keratotic scaling + follicular plugging
malar rash: fixed erythema, flat/raised, over malar eminences
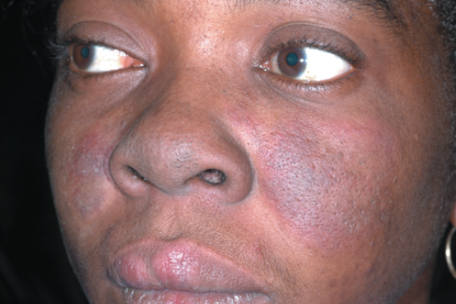
lupus erythematosus is exacerbated by
UV light
4 stages of rosacea
pre-rosacea: flushing episodes
mild: persistent erythema + telangiectasia (visible blood vessels)
moderate: pustules + papules
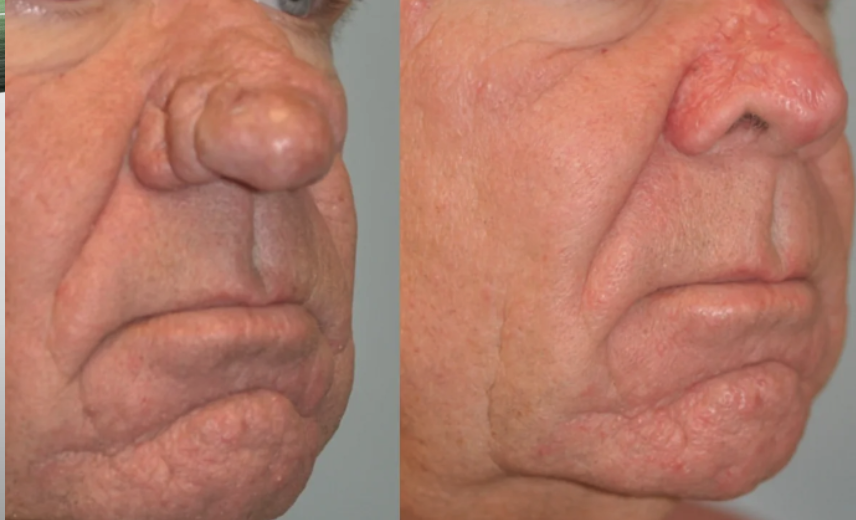
severe: rhinophyma (permanent thickening of nasal skin by erythematous papules + prominent follicles)
rosacea affects men or women more
women
which form of rosacea is common in men
rhinophyma
rhinophyma is associated w/
hypertrophy of sebaceous glands + follicular plugging by keratotic debris
what’s rhinitis
inflammation of nasal cavity
3 types of rhinitis
infectious (common cold): caused by adeno-, echo-, rhinoviruses
allergic
chronic: repeated attack of acute rhinitis from allergy or microbial
what’s sinusitis
inflammation of paranasal sinuses
what’s rhinosinusitis
inflammation of nasal cavity + paranasal sinuses
clinical presentation of nasal polyps
smooth surfaced
semi-transparent
ovoid shaped
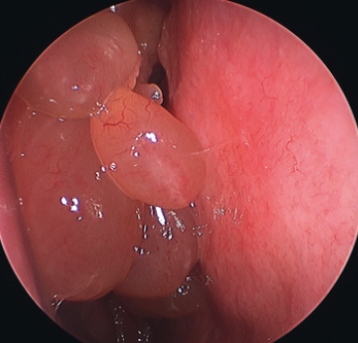
histopathology presentation of nasal polyps
immense edema
scattered chronic inflammatory cells: mainly plasma or eosinophils
nasal polyps are most often associated w/ what condition
allergic rhinosinusitis
5 possible causes of nasal polyps
infections
asthma
aspirin intolerance
cystic fibrosis
diabetes
what’s epistaxis
nosebleed
8 possible causes of epistaxis
Trauma
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)
Hypertension
Thrombocytopenia
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Sarcoidosis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis)
Hemangioma
what’s anosmia
loss of smell
4 possible obstructive causes of anosmia
rhinitis
sinusitis
nasal polyps
tumors
2 possible sensorineural causes of anosmia
trauma
tumors
2 types of maxillary sinusitis
acute
chronic
acute maxillary sinusitis usually comes after
acute or chronic rhinitis
acute maxillary sinusitis can be caused by what dental condition
periapical infection
acute maxillary sinusitis can lead to severe infections of
ethmoid + frontal sinuses, brain meninges
drainage for acute maxillary sinusitis must occur at
ostia
chronic maxillary sinusitis is caused by
recurring episodes of acute sinusitis or symptomatic disease lasting longer than 3 months
failure of acute inflamed sinus to drain
chronic maxillary sinusitis can be mistaken for
painful, abscessed tooth
T/F: chronic maxillary sinusitis can be caused by fungal infection
true
4 benign tumors of nose/paranasal sinuses
squamous papilloma
fungiform + inverted papillomas
hemangioma (vascular malformation)
nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
which benign tumor of nose/paranasal sinuses can have malignant transformation
fungiform + inverted papillomas
which benign tumor of nose/paranasal sinuses present w/ epistaxis
hemangioma (vascular malformation) + nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
which benign tumor of nose/paranasal sinuses exclusively affects young men
nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
malignant tumor of paranasal sinuses
squamous cell carcinoma, often affects maxillary sinus
malignant tumor of nasopharynx
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
nasopharyngeal carcinoma is caused by
Epstein-barr virus
nasopharyngeal carcinoma is prevalent in which countries
China, Southeast Asia, East Africa
3 clinical signs of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
nasal obstruction
epistaxis
cervical lymph node metastasis
3 risk factors for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
smoking
salted fish
pickled food
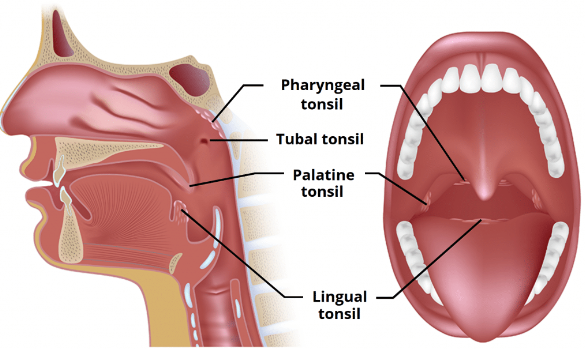
what’s Waldeyer’s ring
ring containing the 4 structures:
palatine tonsils
nasopharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
lingual tonsils
tubal tonsils (eustachian)
4 pathological conditions of the oropharynx
viral + bacterial infections: cold, flu, mono (from EBV)
reactive lymphoid hyperplasia
pharyngitis: mild + severe
tonsilitis
what’s the most common cause of tonsillar enlargement
reactive lymphoid hyperplasia
complications of severe pharyngitis + tonsillitis
peritonsillar abscess “quinsy”
acute rheumatic fever
acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
severe pharyngitis + tonsillitis can accompany which conditions
beta-hemolytic streptococcal + adenovirus infection
diphtheria presents w/
pseudomembrane produced on soft palate + pharynx
fever
malaise
sore throat
neck swelling
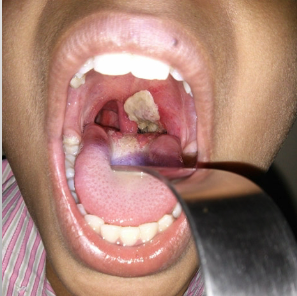
diphtheria is usually found in individuals that have had contact w/
farm animals or dairy products
4 pathologies of the larynx
laryngitis
allergy + toxin damage
reactive nodules
benign/malignant tumors
4 types of laryngitis
acute: inhalation of irritant, allergy rxn, common cold
diphtheria: produces exotoxins + pseudomembrane
tuberculosis: from infected, coughed up sputum
croup (laryngotracheobronchitis): from parainfluenza virus
which type of laryngitis affects children
croup (laryngotracheobronchitis)
which type of laryngitis presents w/ hoarseness + temporary loss of voice
acute
which type of laryngitis presents w/ harsh persistent cough
croup (laryngotracheobronchitis)
how is the larynx damaged via allergic rxn
type 1 hypersensitivity rxn → angioedema, can be life-threatening
how is the larynx damaged via toxins
acute toxic laryngitis: via toxic fumes
chronic toxic laryngitis: via cigarettes, premalignant
polyps can be found where in the larynx
true vocal cords
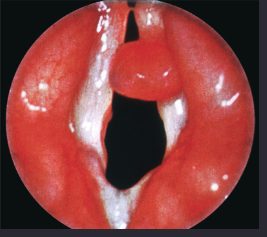
polyps on the true vocal cords can cause
hoarseness
clinical presentation of polyps on the true vocal cords
unilateral
smooth + round
sessile + pedunculated
clinical presentation of singer’s nodules
bilateral lesions on true vocal cords
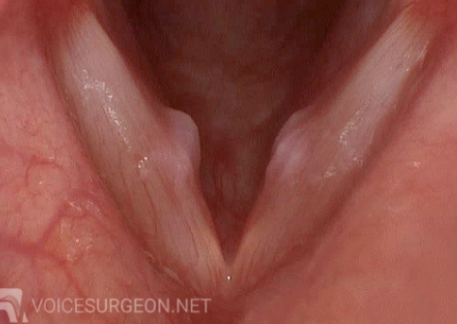
2 treatment options for singer’s nodules
voice/speech therapy
behavior modification
benign tumor of larynx
squamous papilloma, caused by HPV
squamous papilloma of larynx occurs where
true vocal cords
squamous papilloma of larynx presentation in adults vs. children
adults: solitary mass
children: multiple masses, known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis or juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis
recurrent respiratory papillomatosis or juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis can extend from larynx to the
trachea
recurrent respiratory papillomatosis or juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis is caused by
HPV 6 + 11
malignant tumor of larynx
laryngeal carcinoma, usually squamous cell carcinoma
laryngeal carcinoma affects men or women more
men
best prognosis of laryngeal carcinoma involves which part of the larynx
true vocal cords
metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma can occur from
area of supraglottis (usually to cervical lymph nodes)
4 risk factors of laryngeal carcinoma
chronic cigarette smoking
HPV
alcohol
asbestos exposure