Histology Section
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
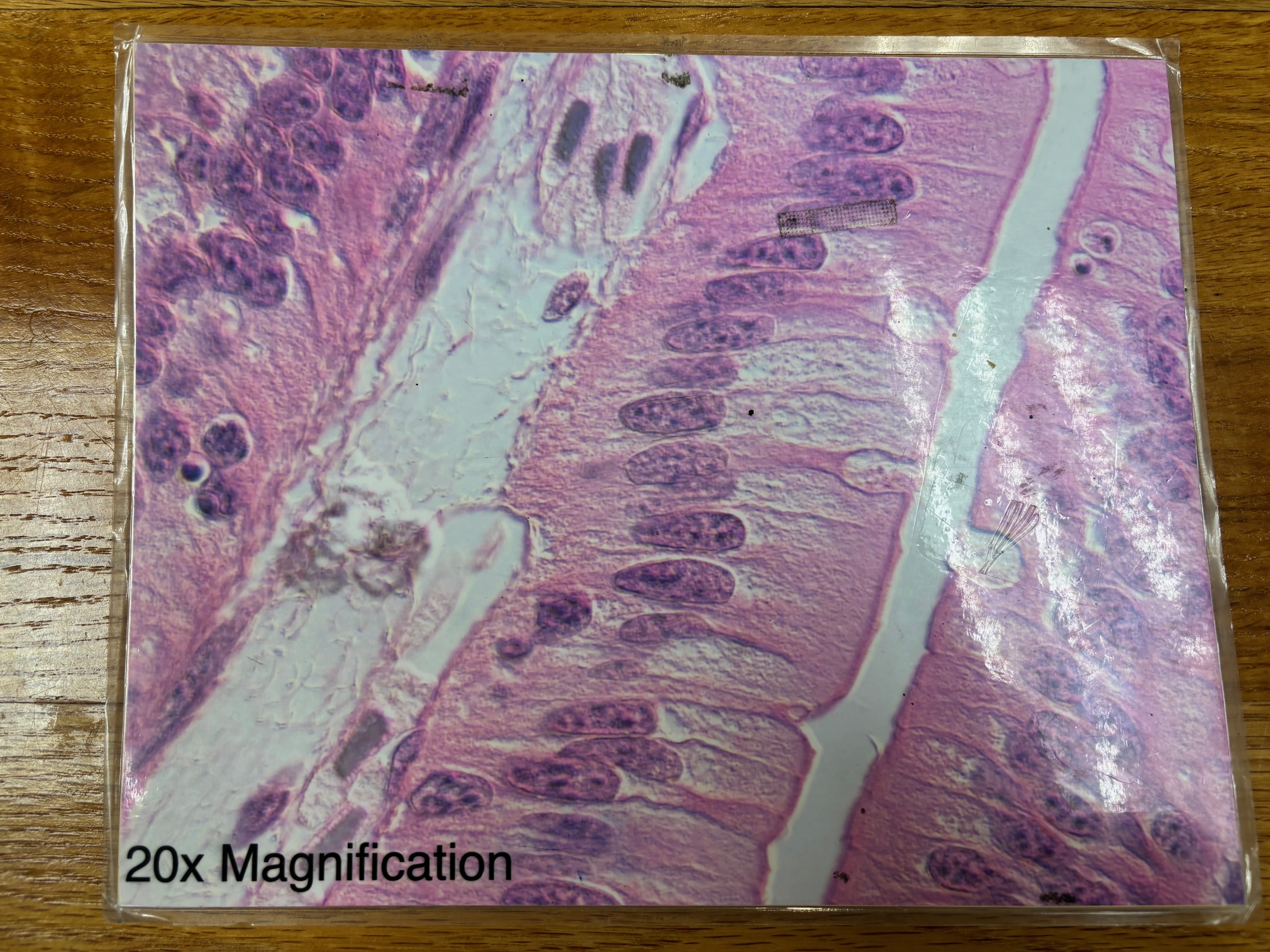
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
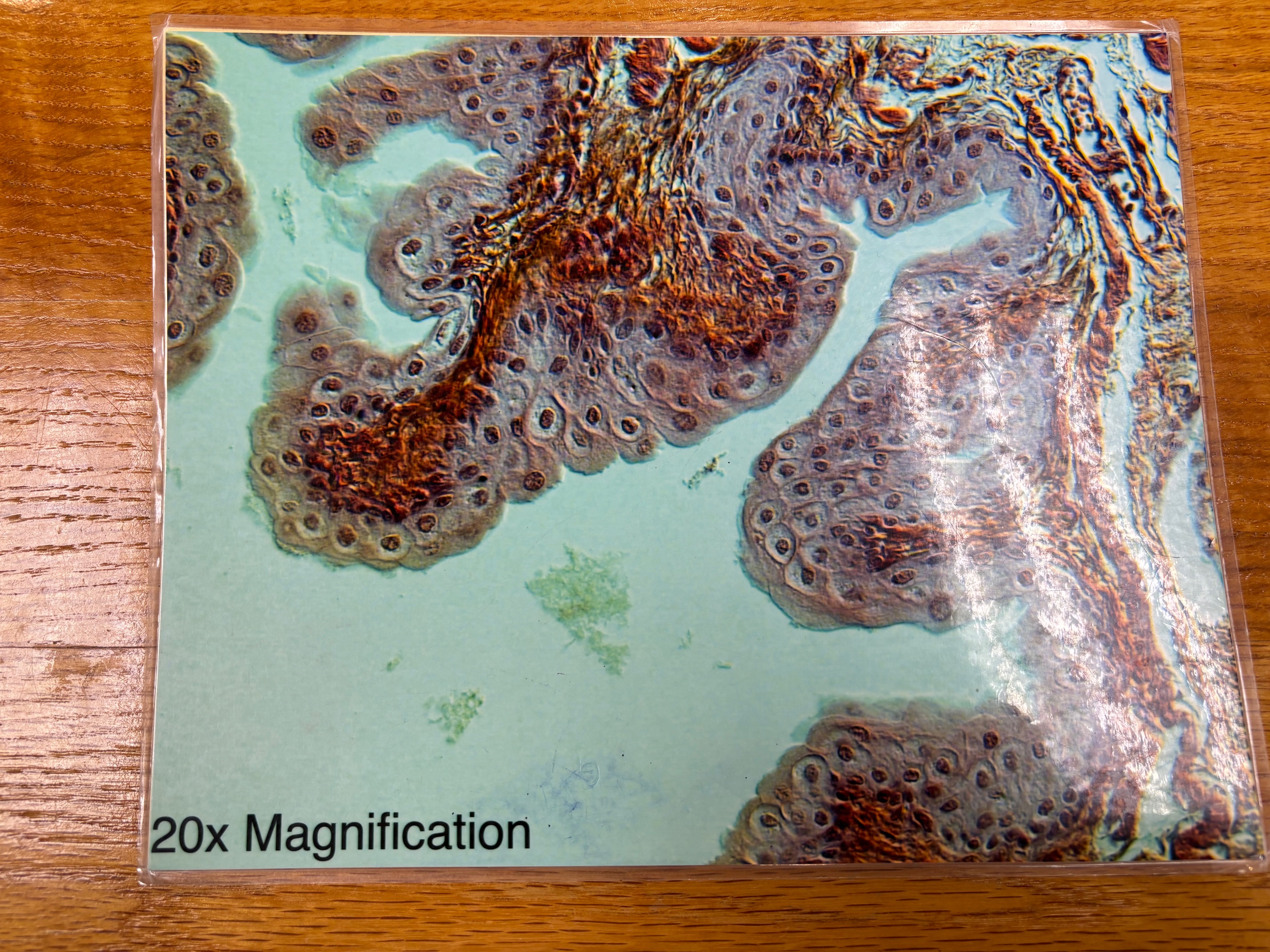
Transitional epithelium
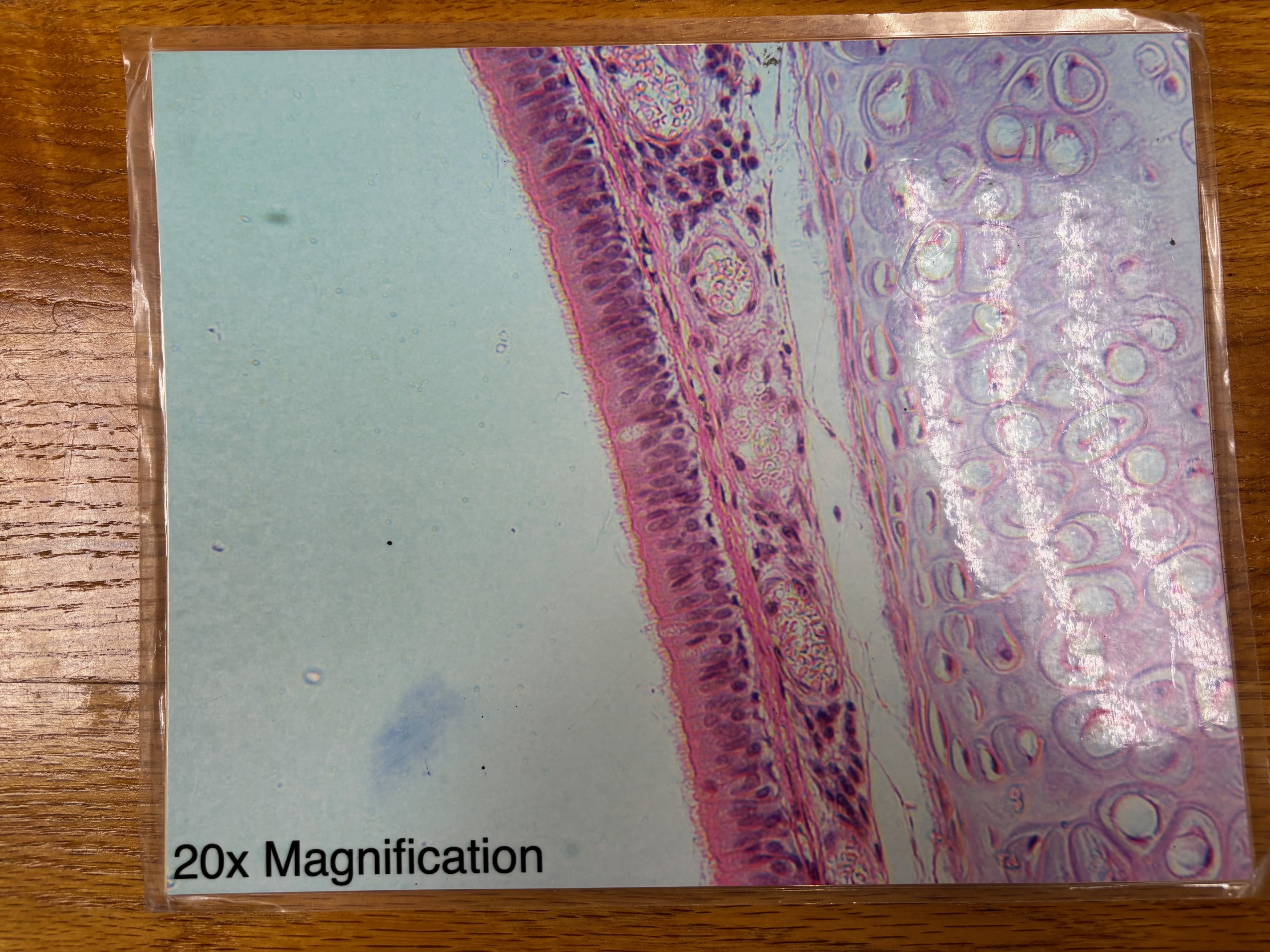
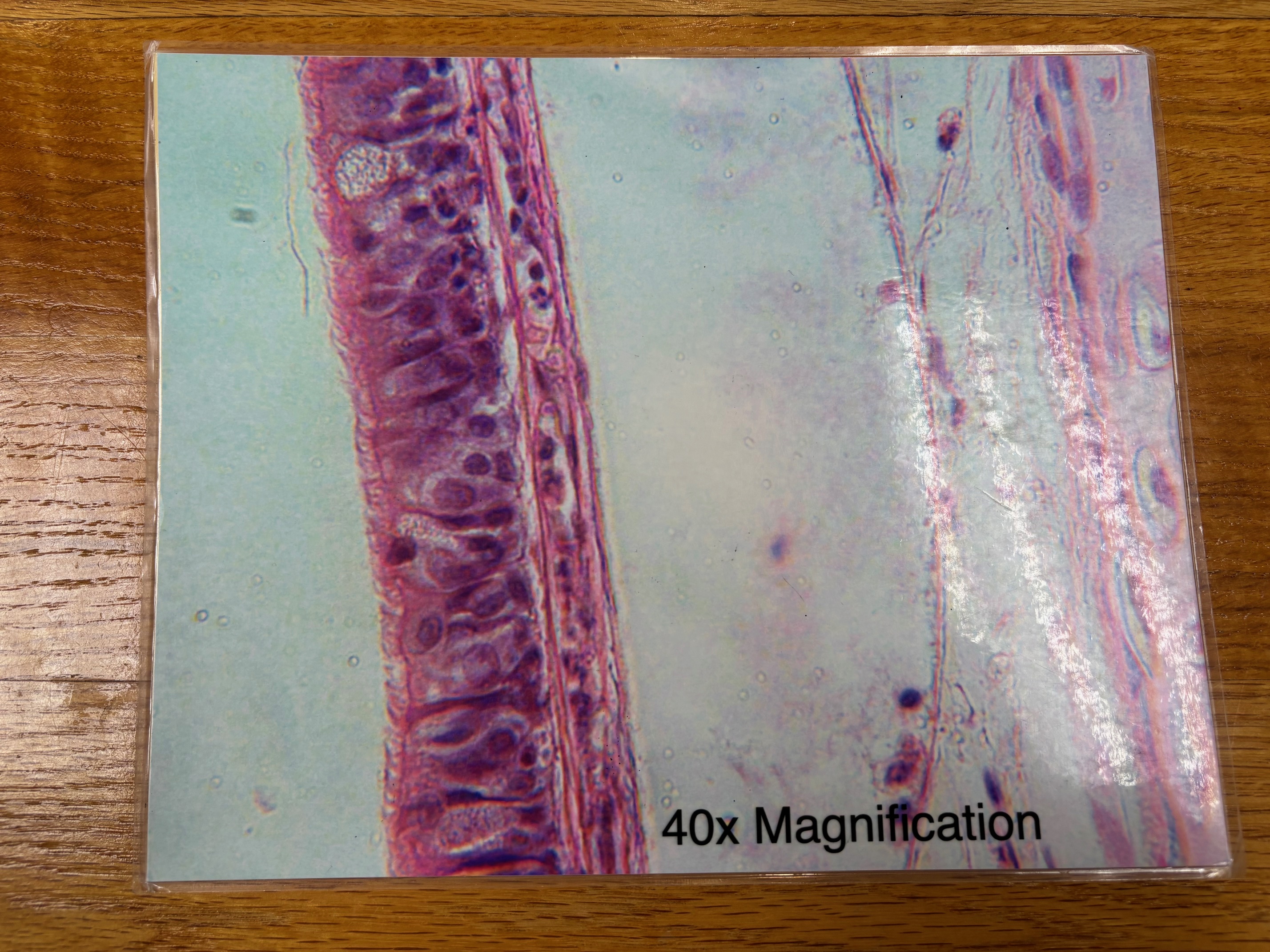
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
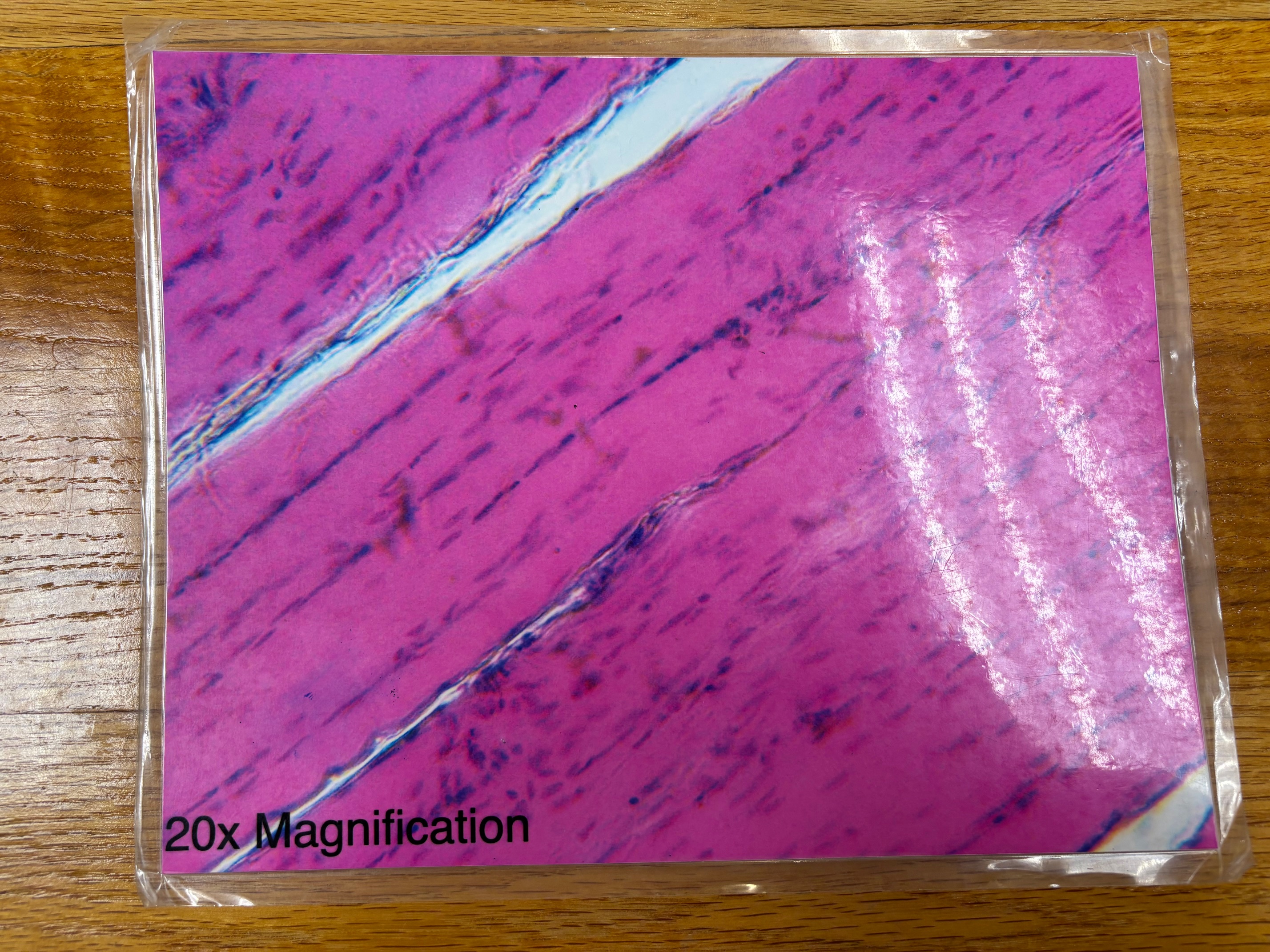
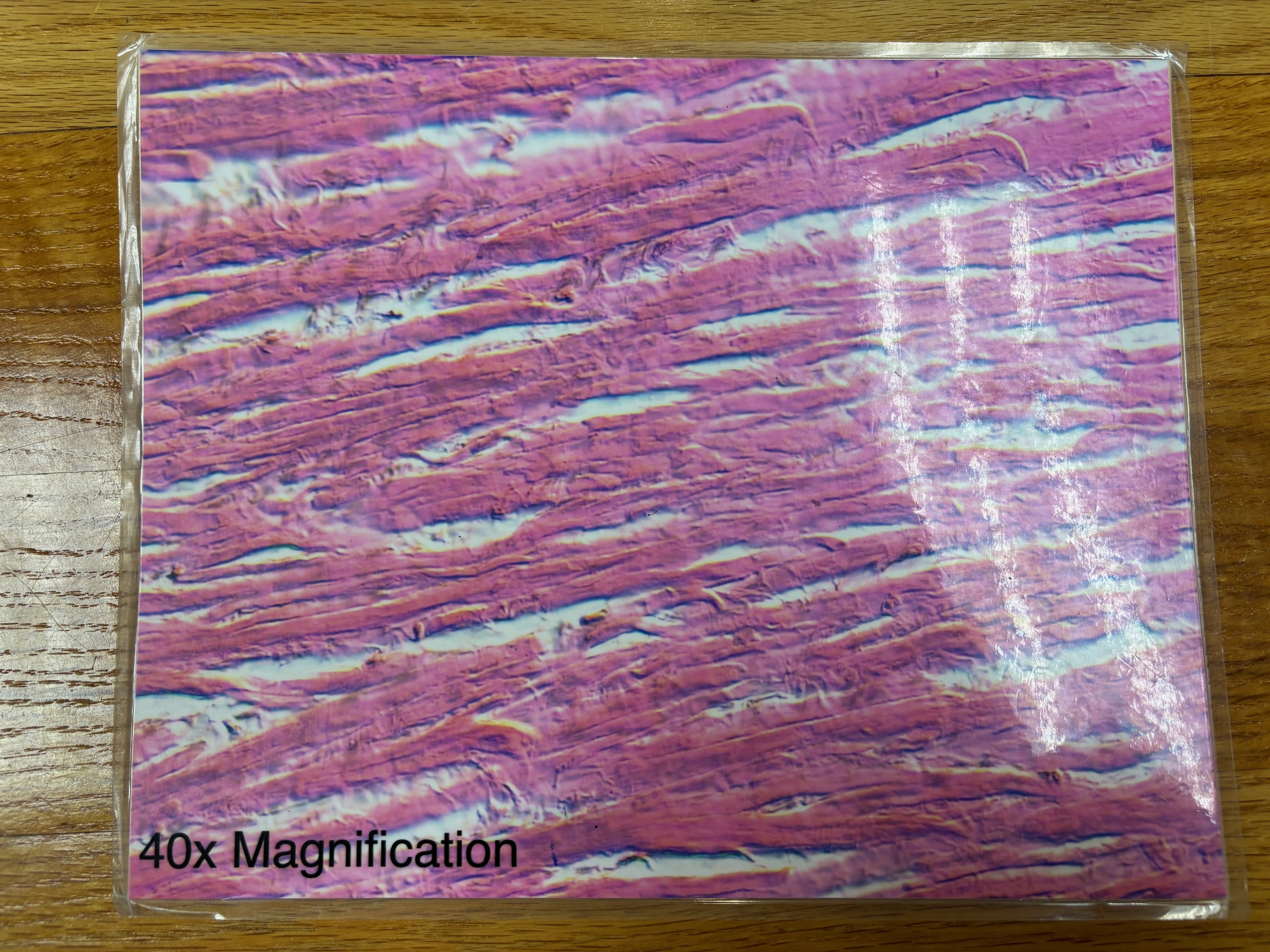
Dense regular connective tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue
remember striations, sarcomeres
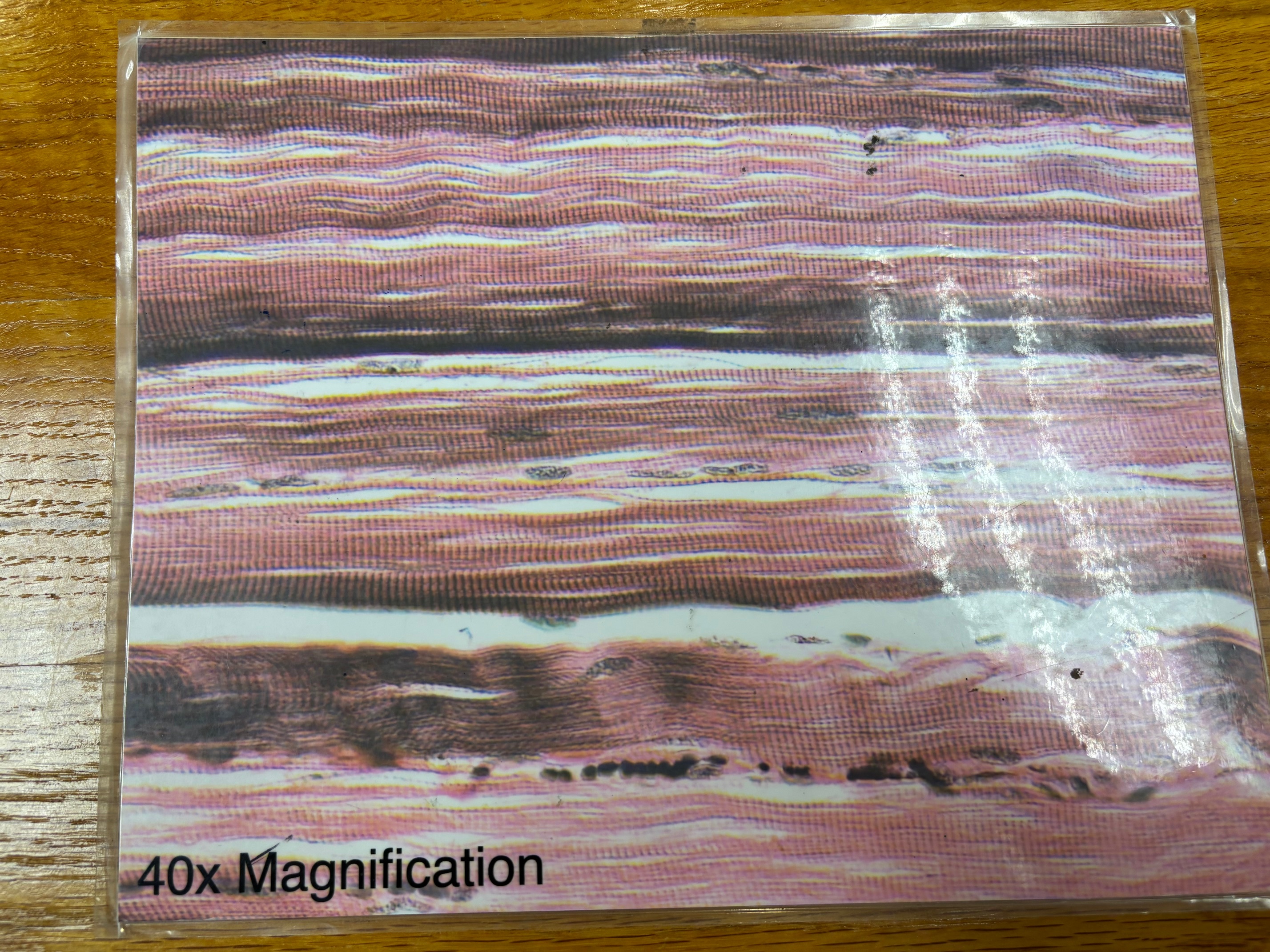

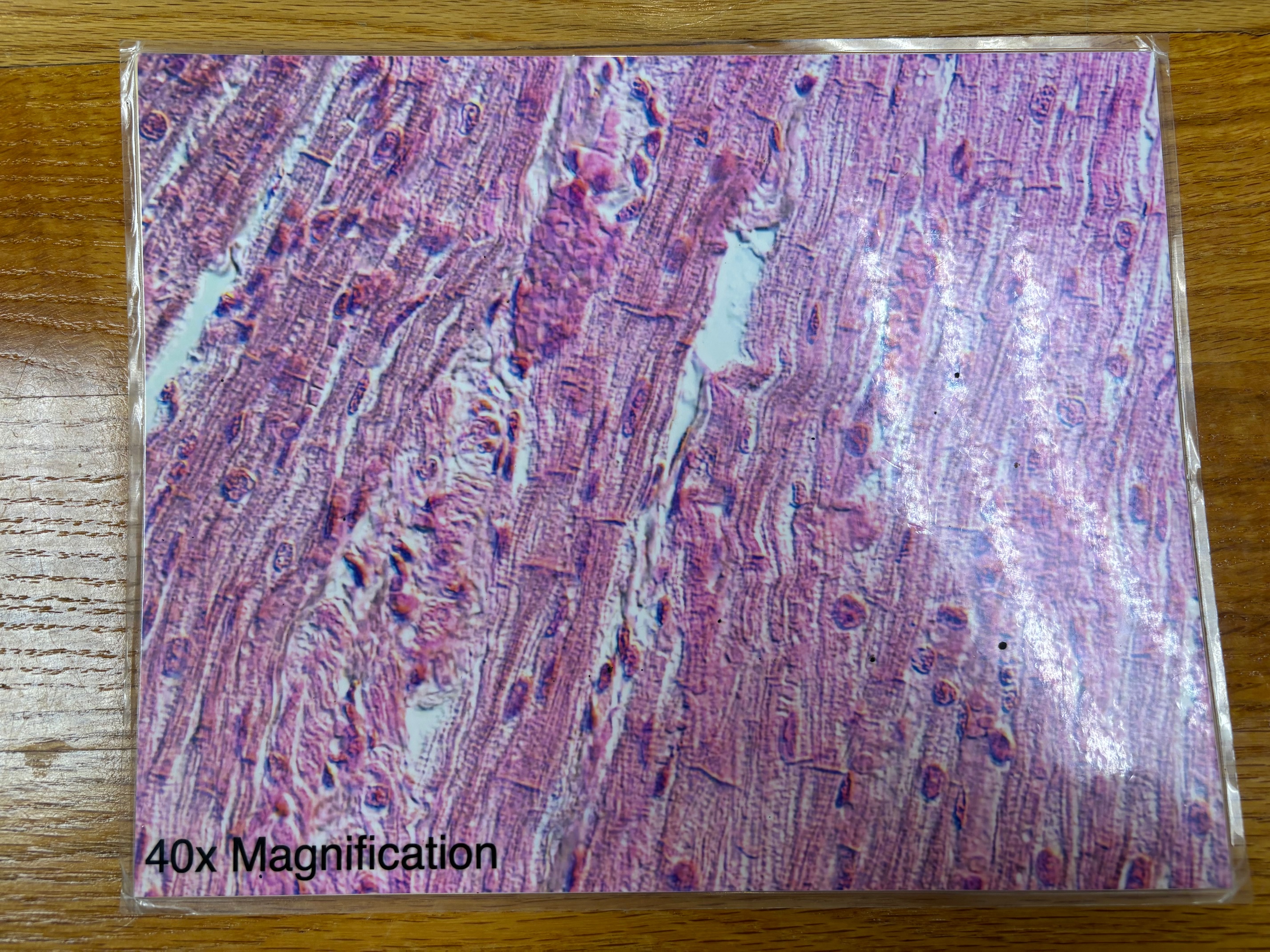
Cardiac muscle tissue
remember intercalated disks
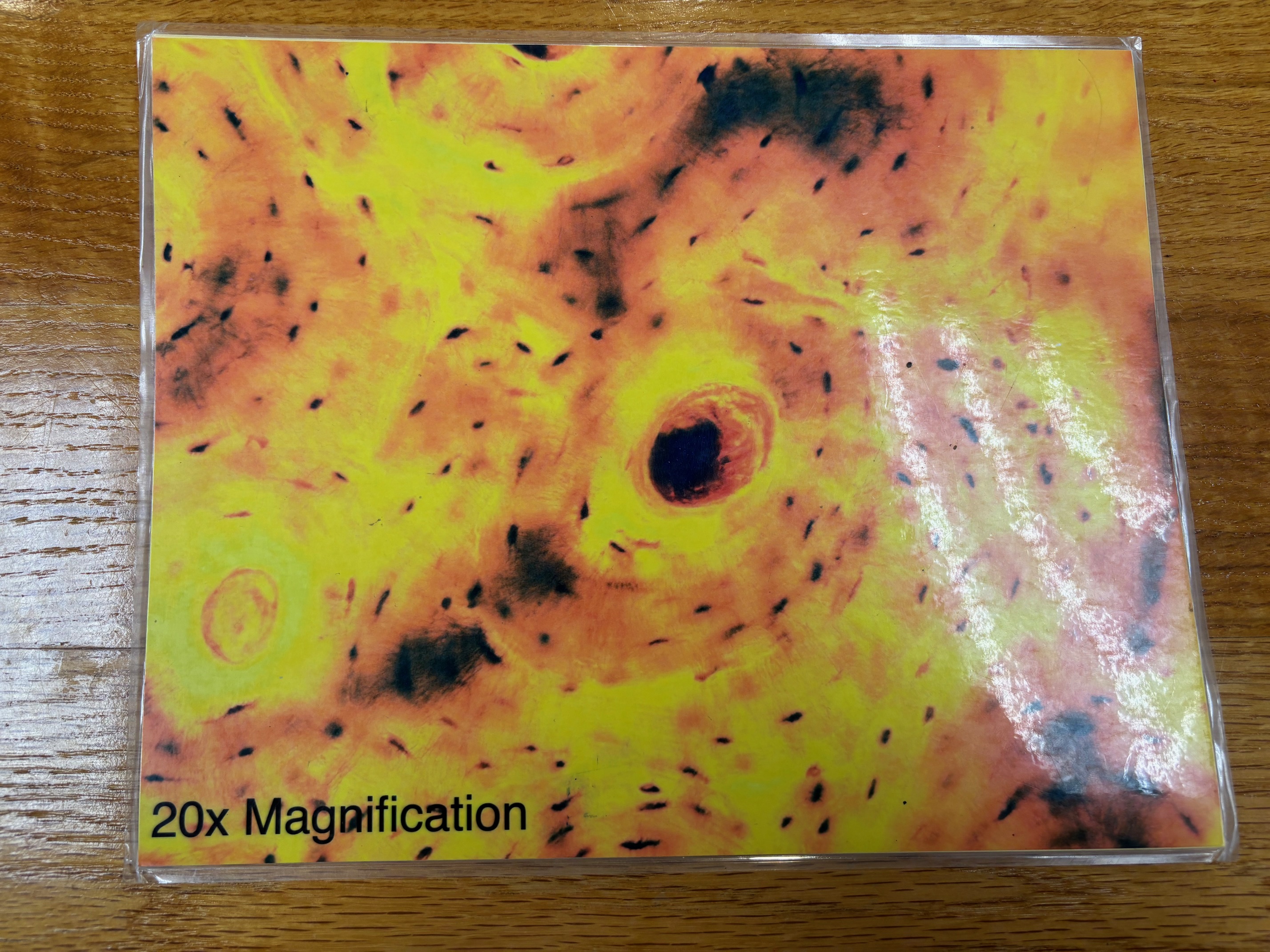
Bone tissue
Transitional epithelium
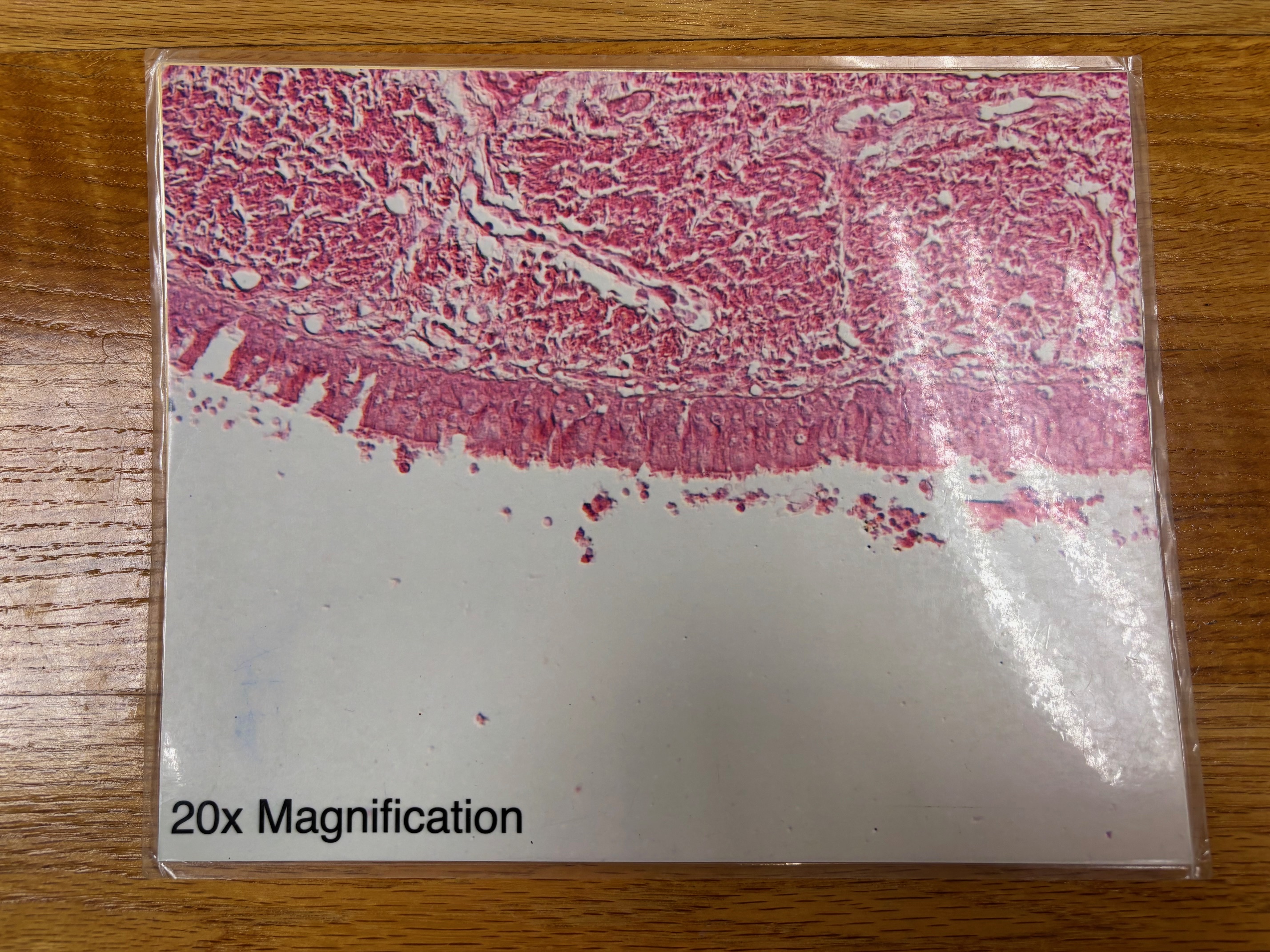
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
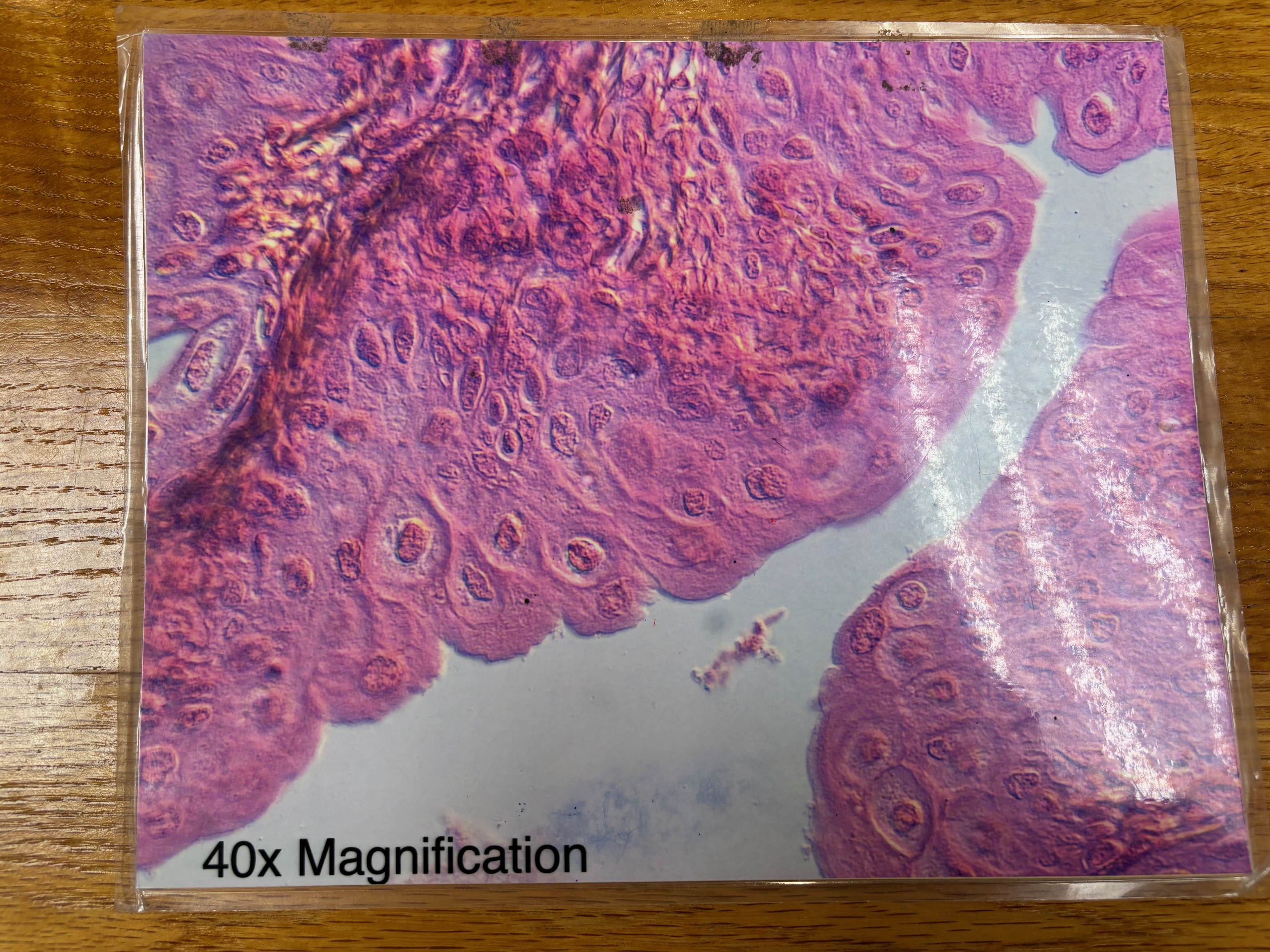
Stratified squamous epithelium
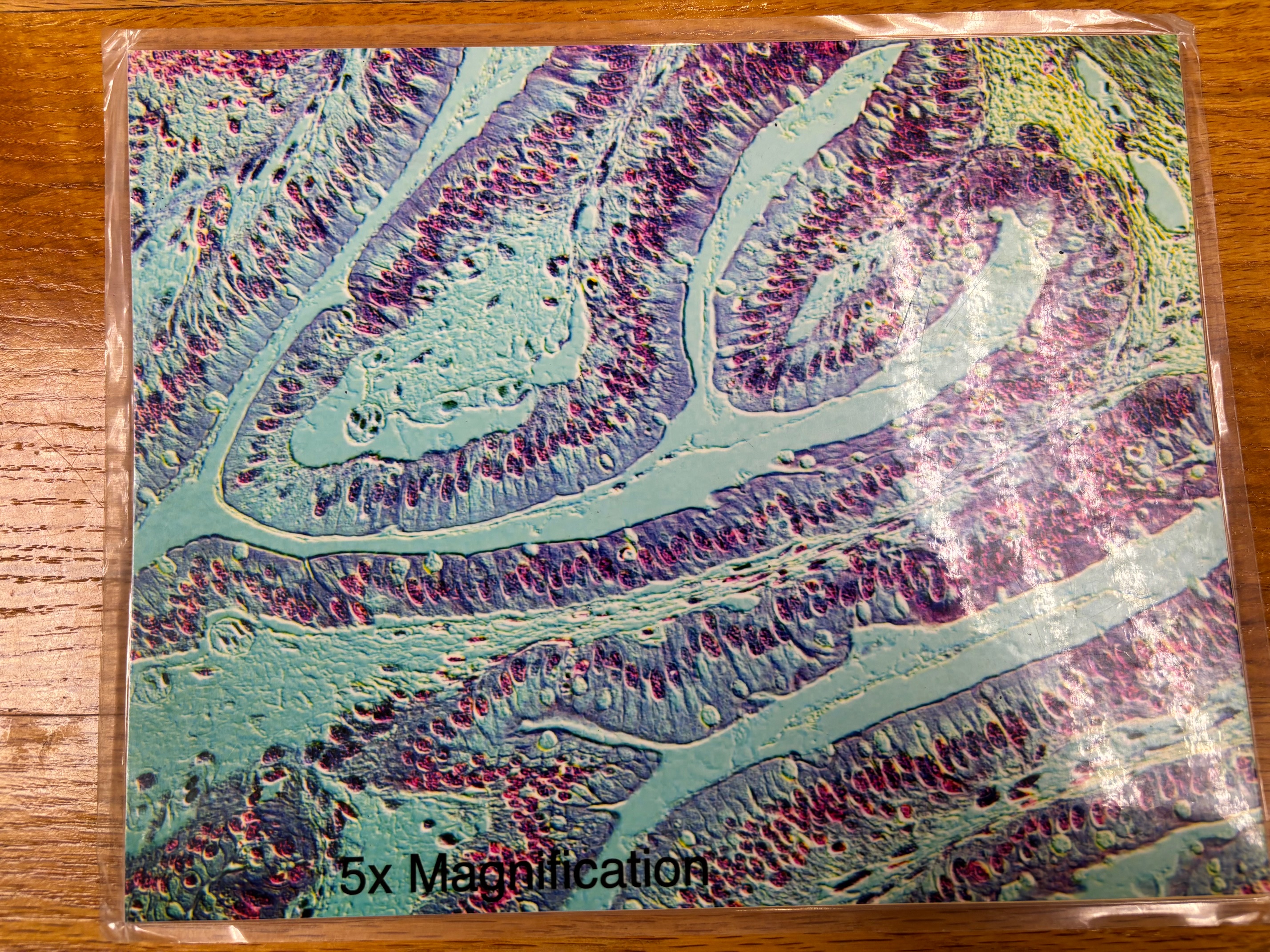
Simple columnar epithelium
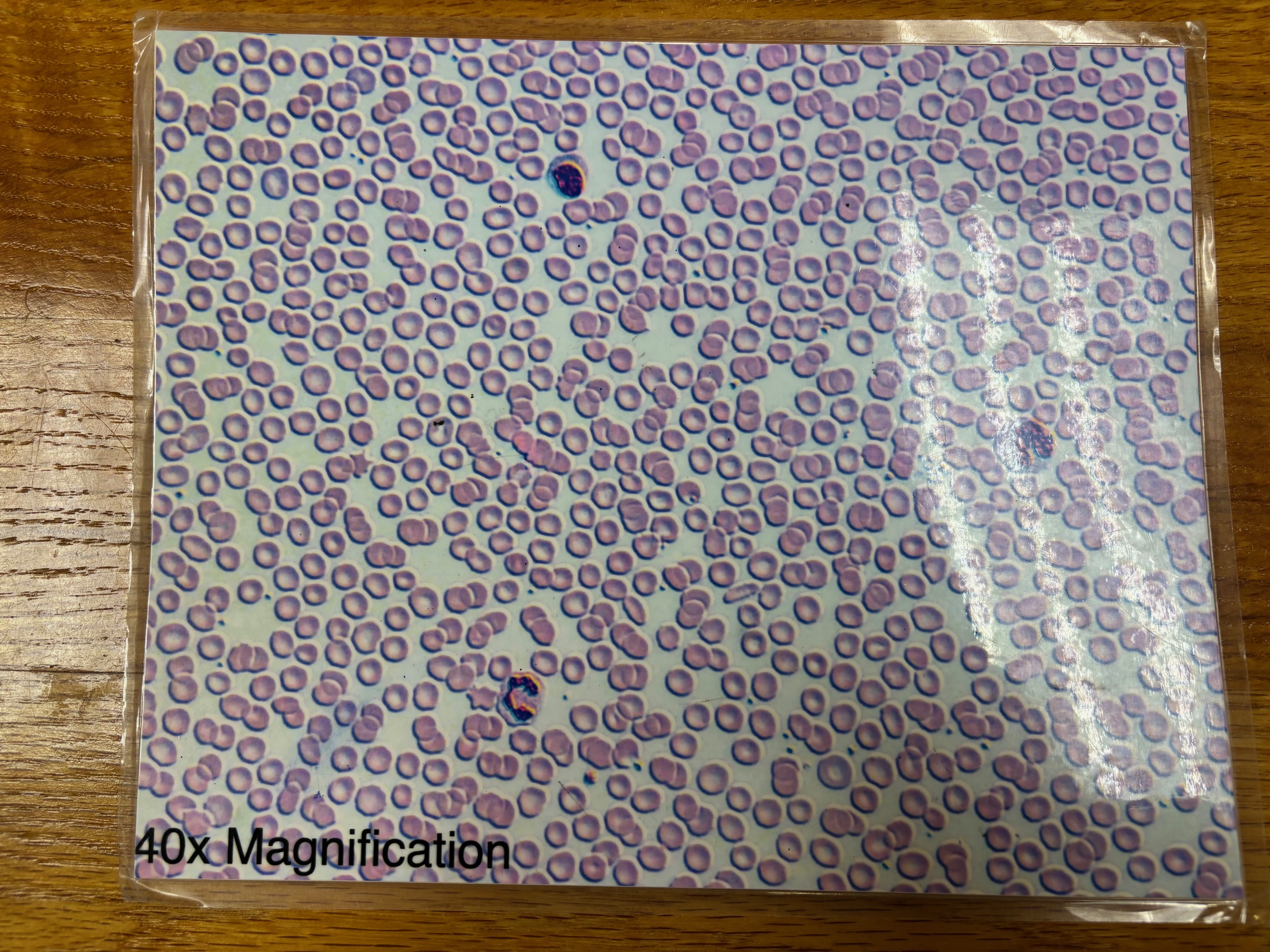
Blood connective tissue
Simple columnar epithelium
Hyaline cartilage connective tissue
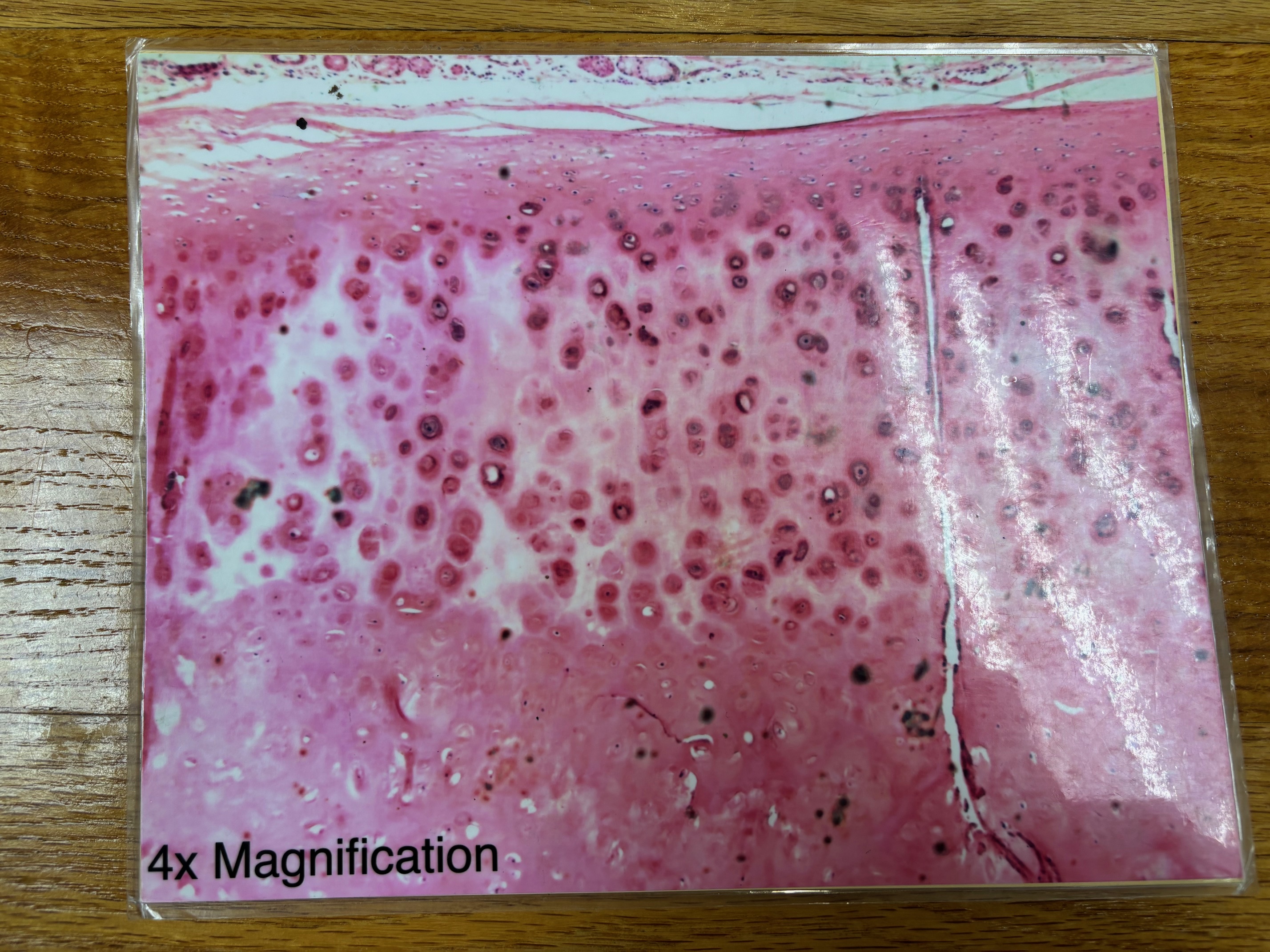
Simple cuboidal epithelium
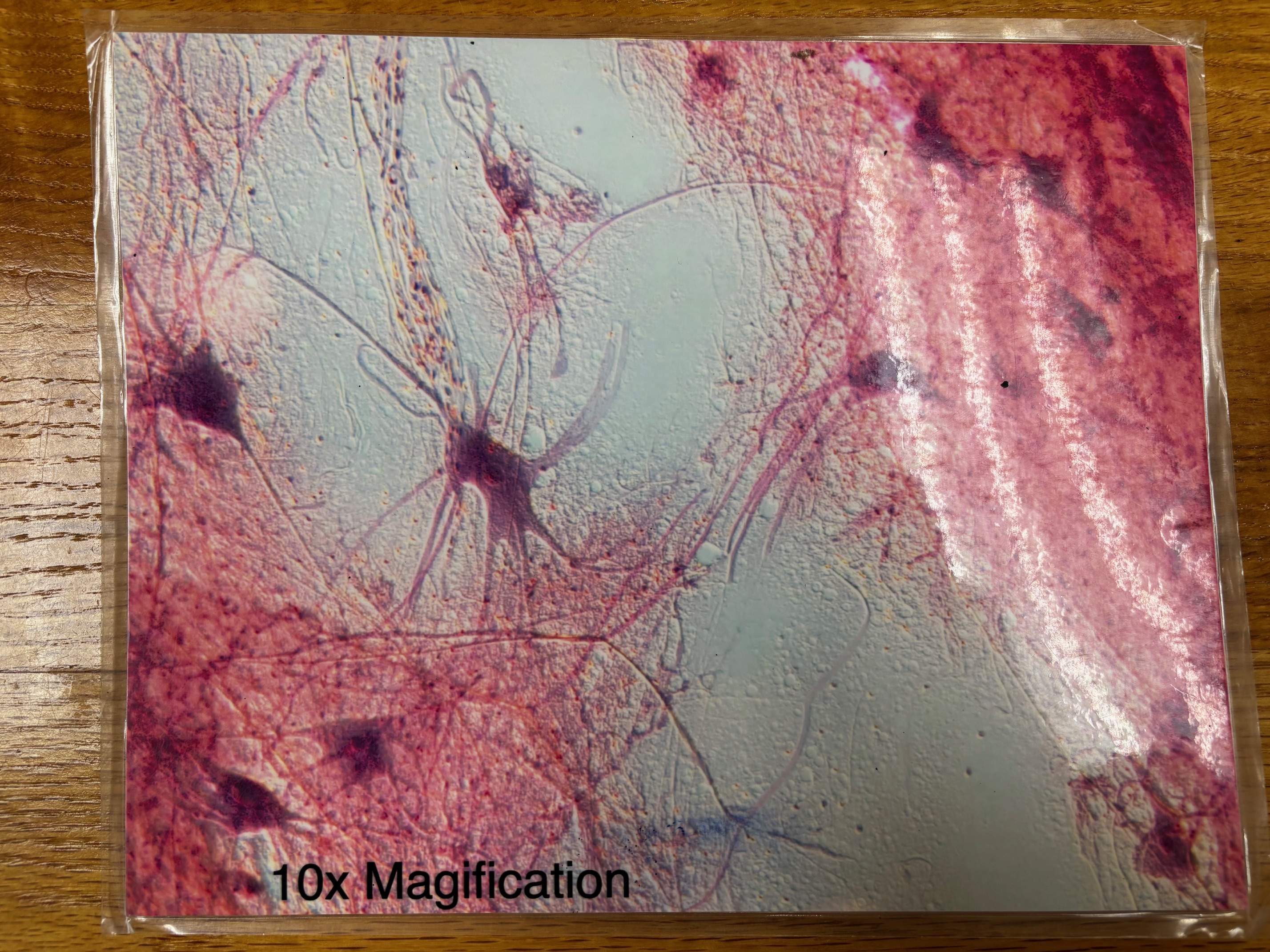
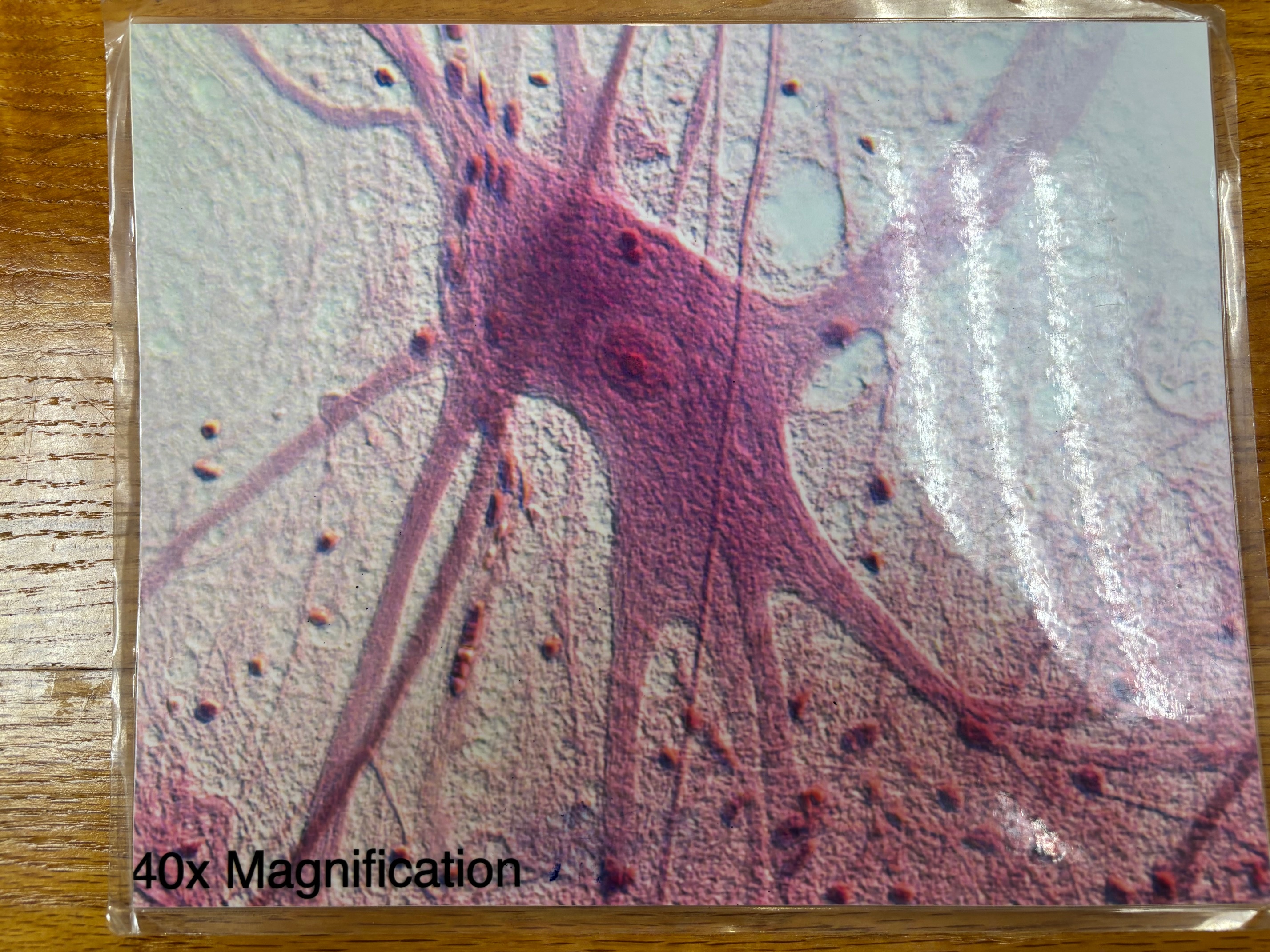
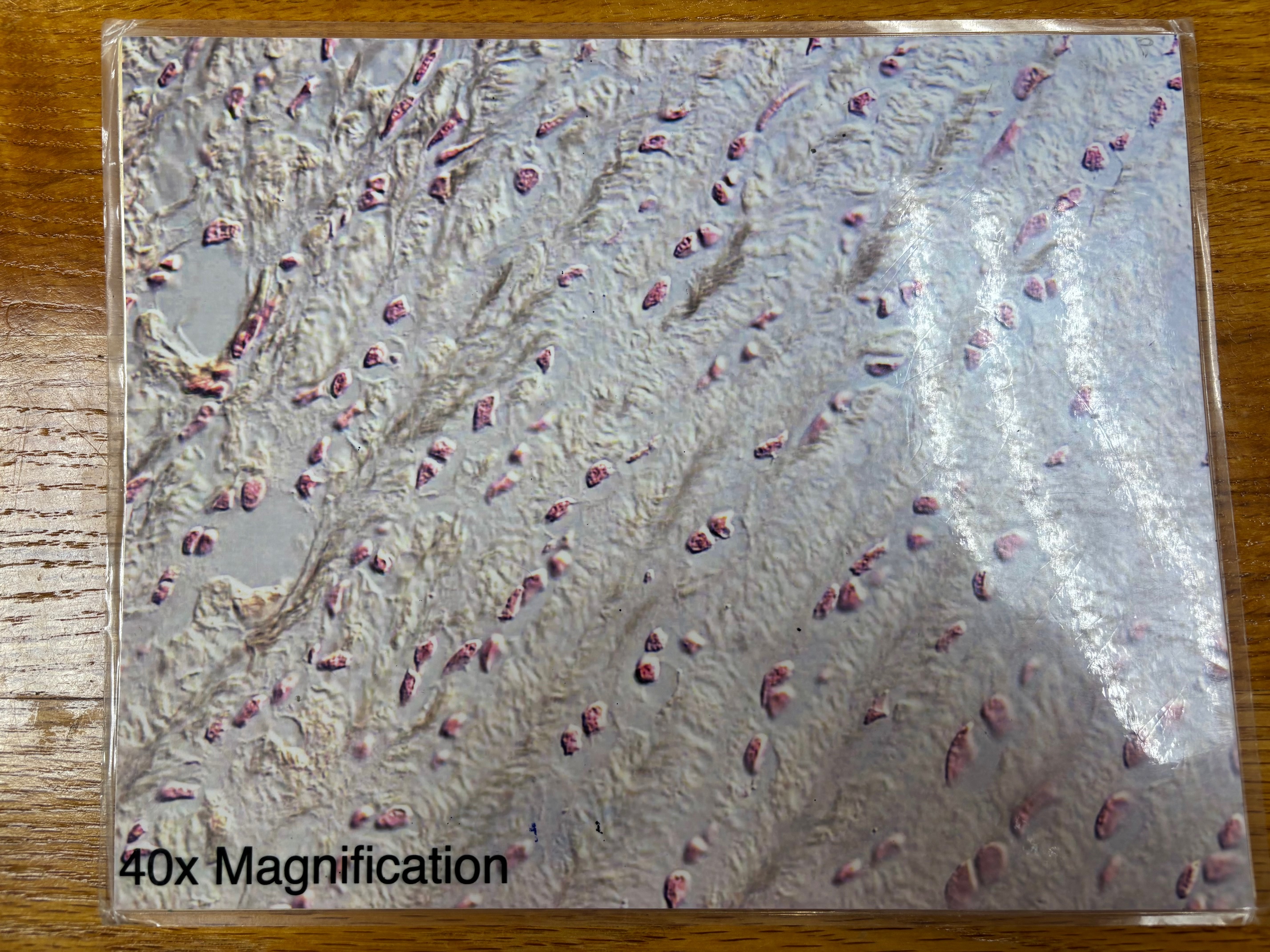
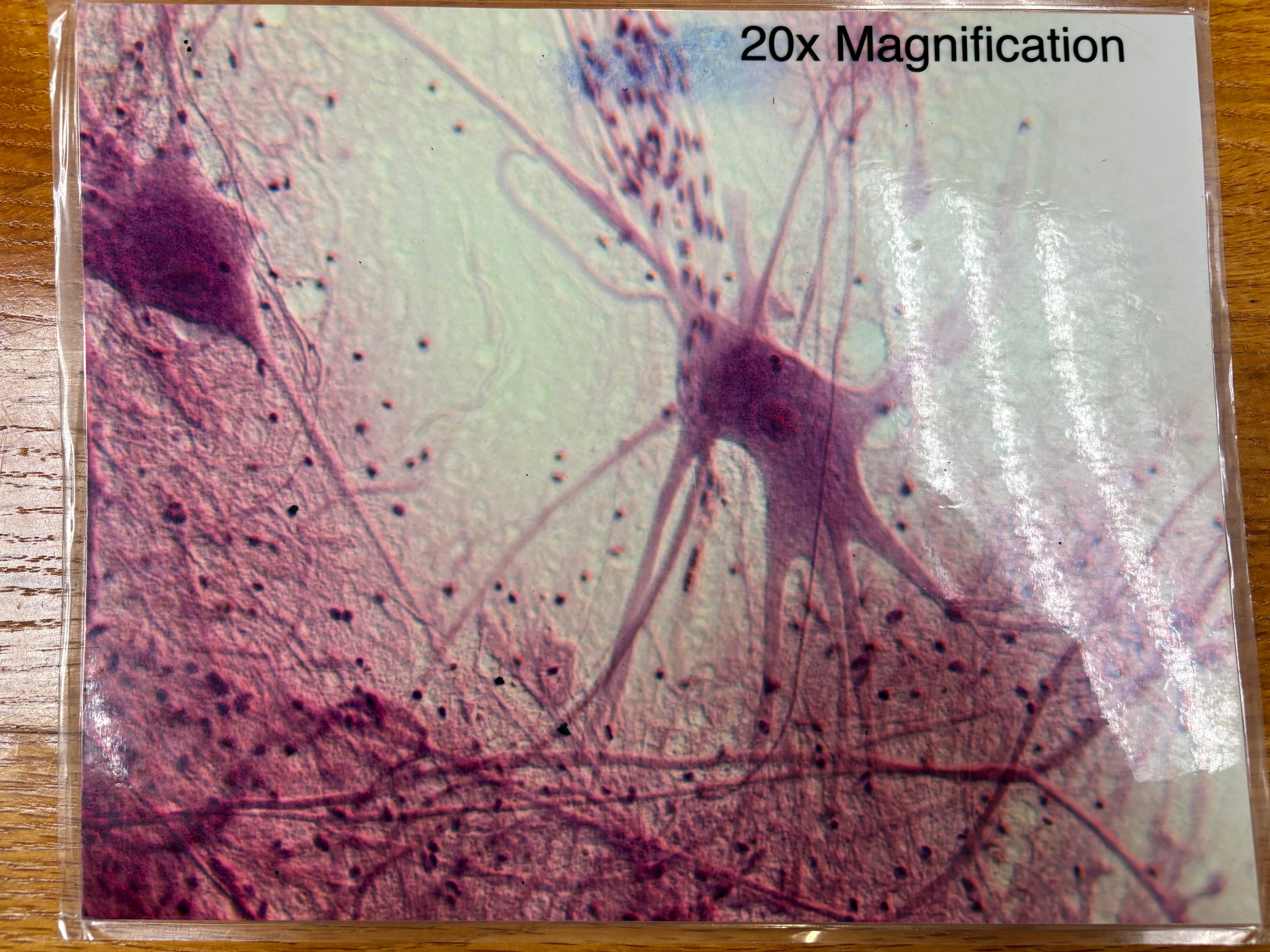
Nervous tissue
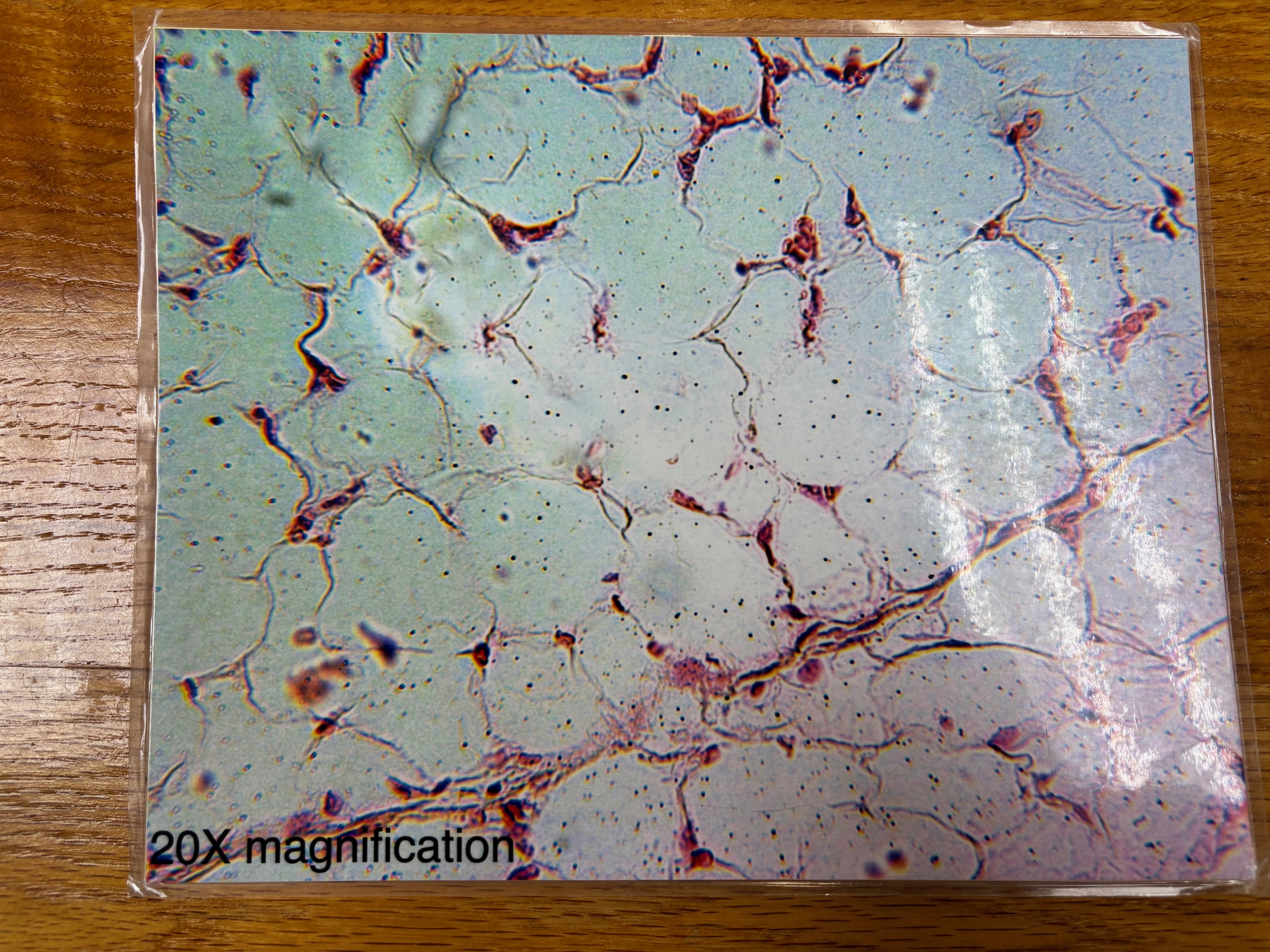
Adipose connective tissue
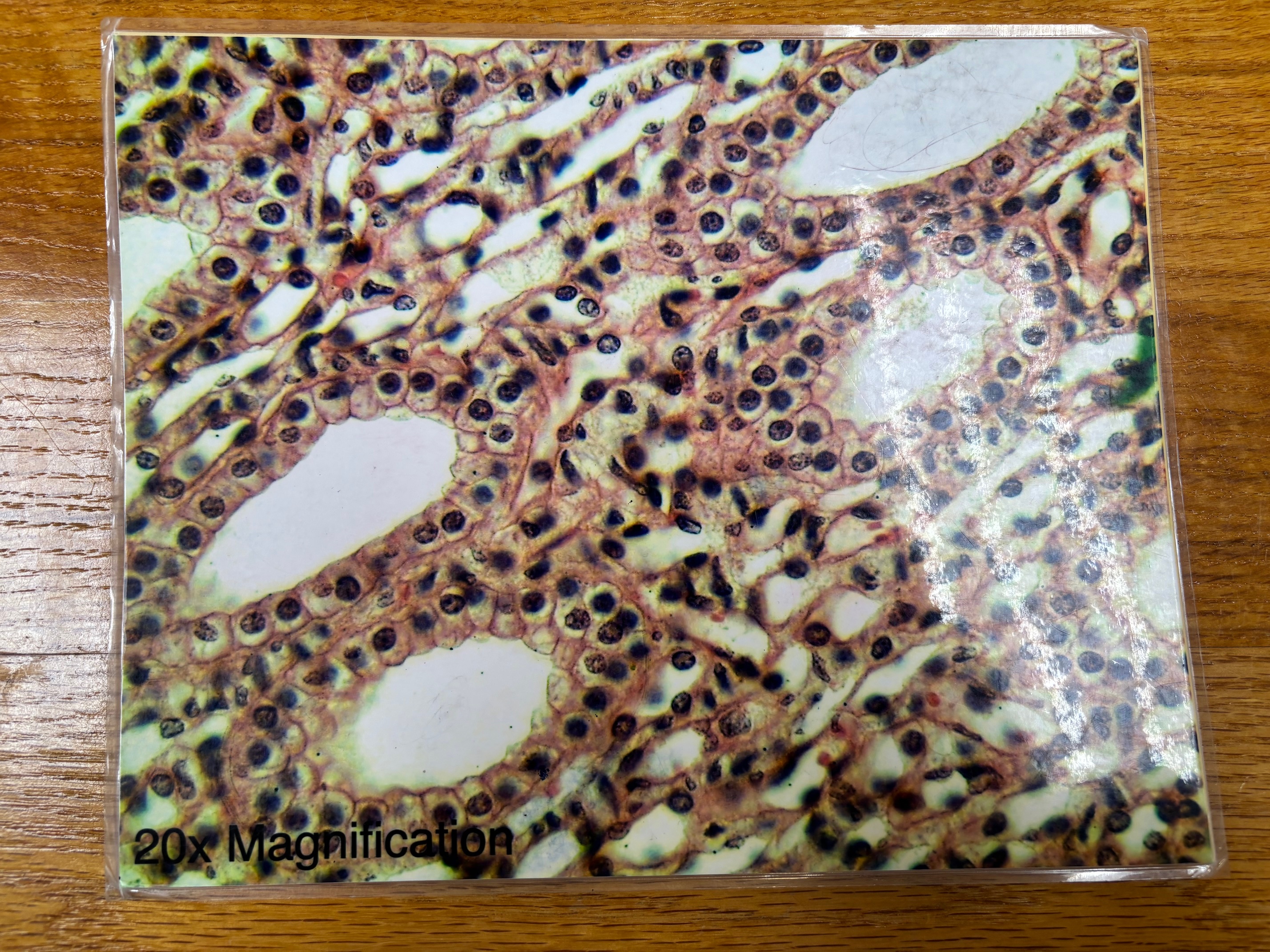
Simple cuboidal epithelium
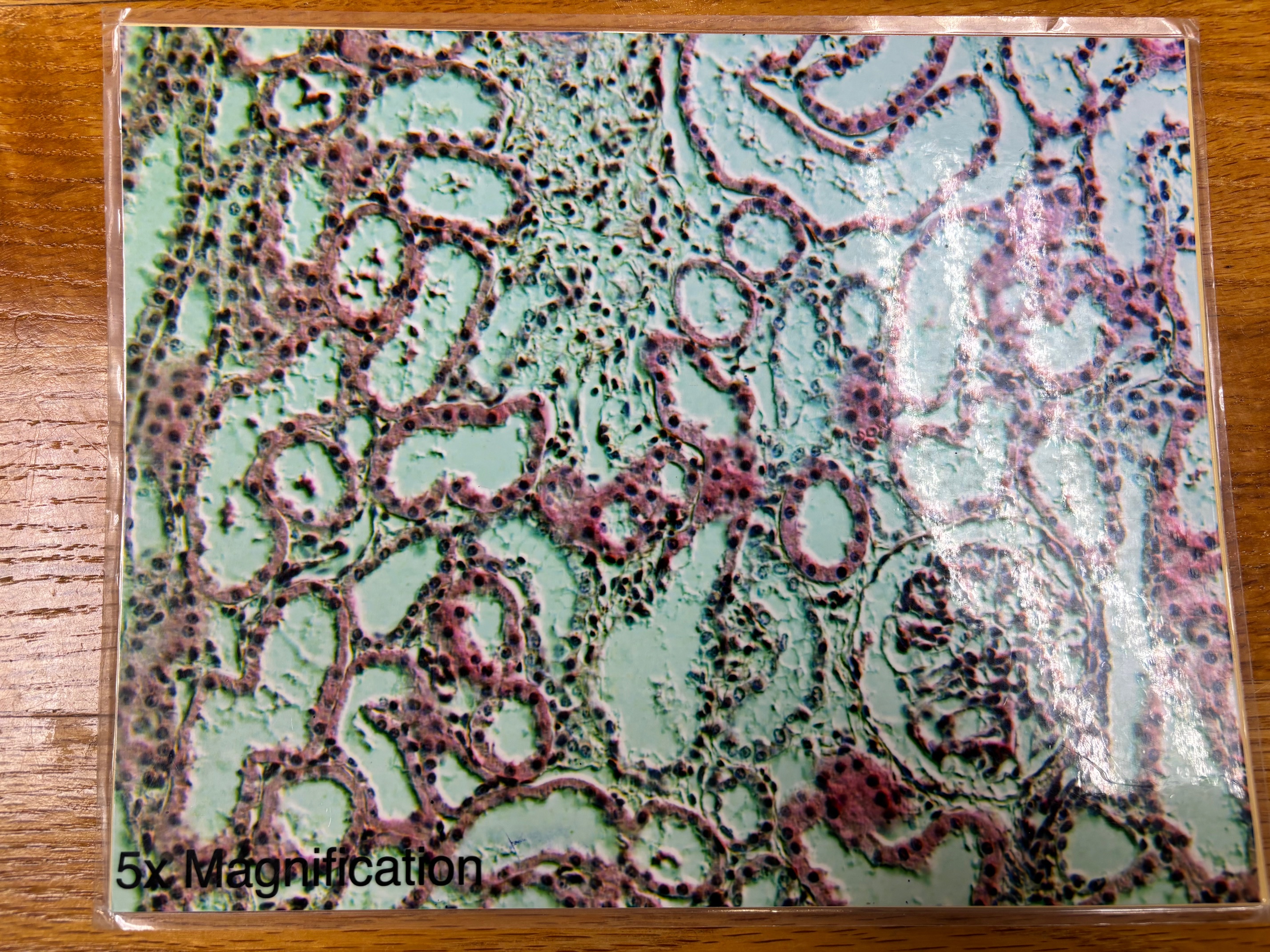

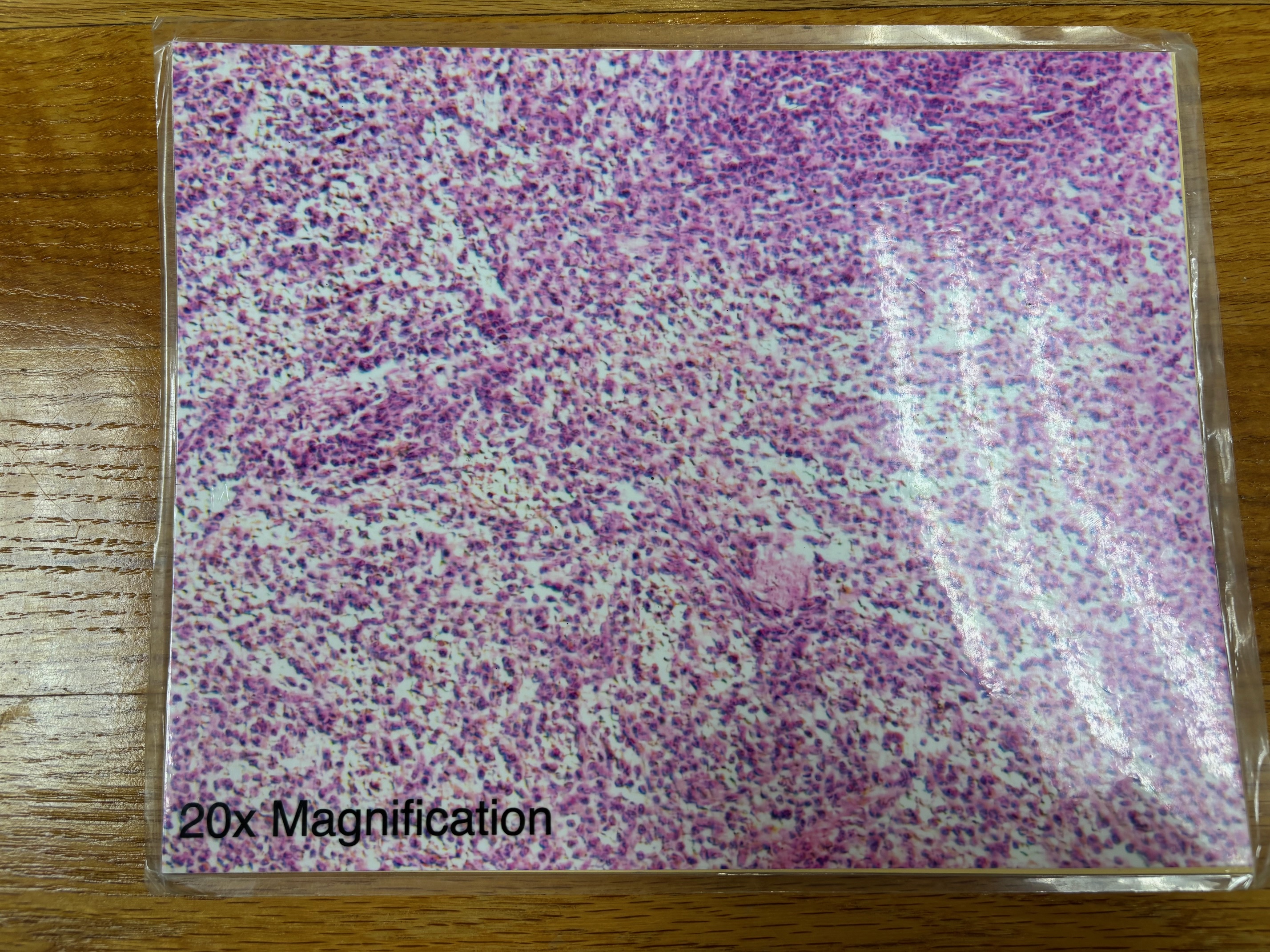
Reticular connective tissue
Areolar connective tissue

Elastic connective tissue
Dense regular connective tissue
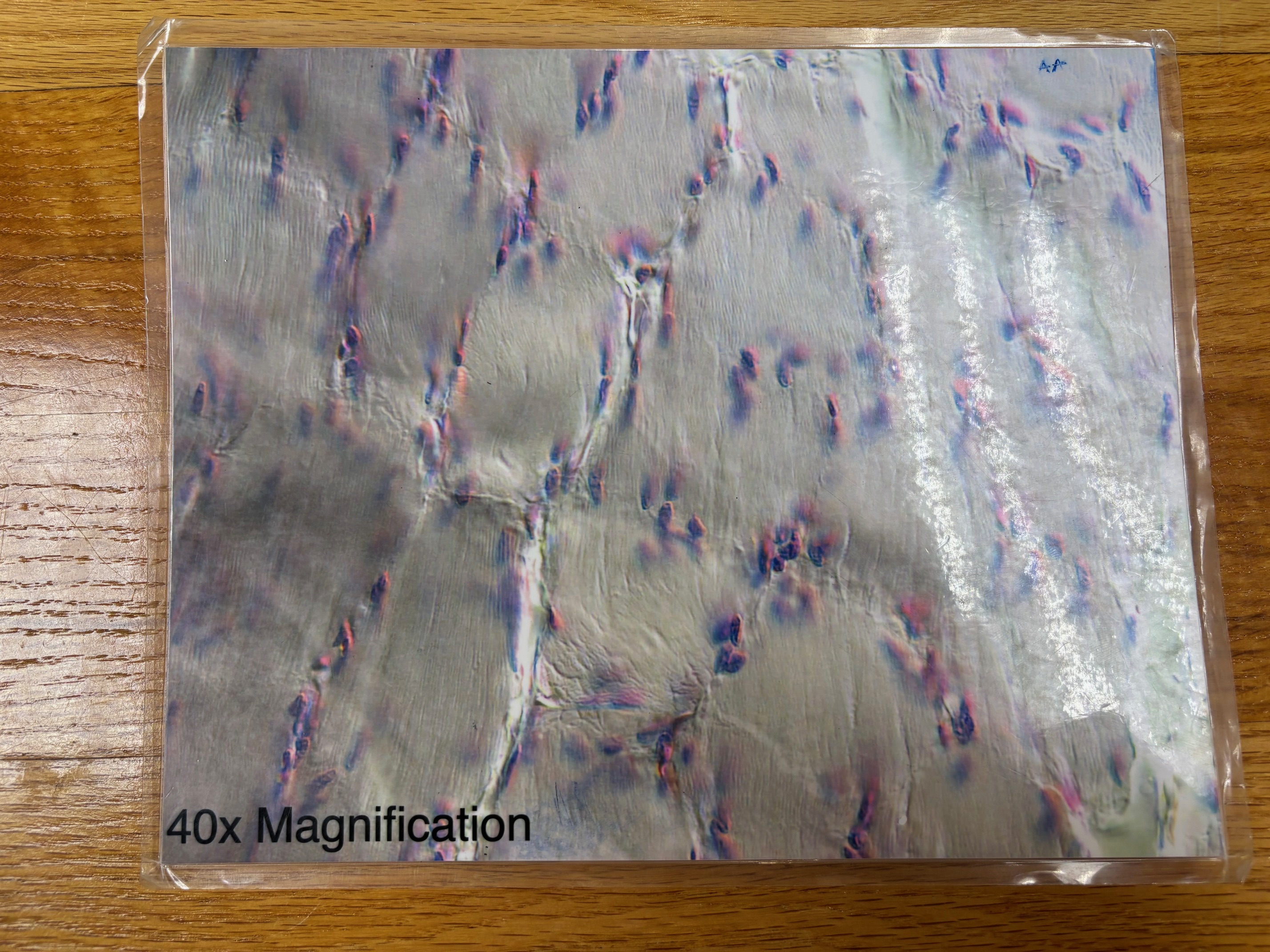

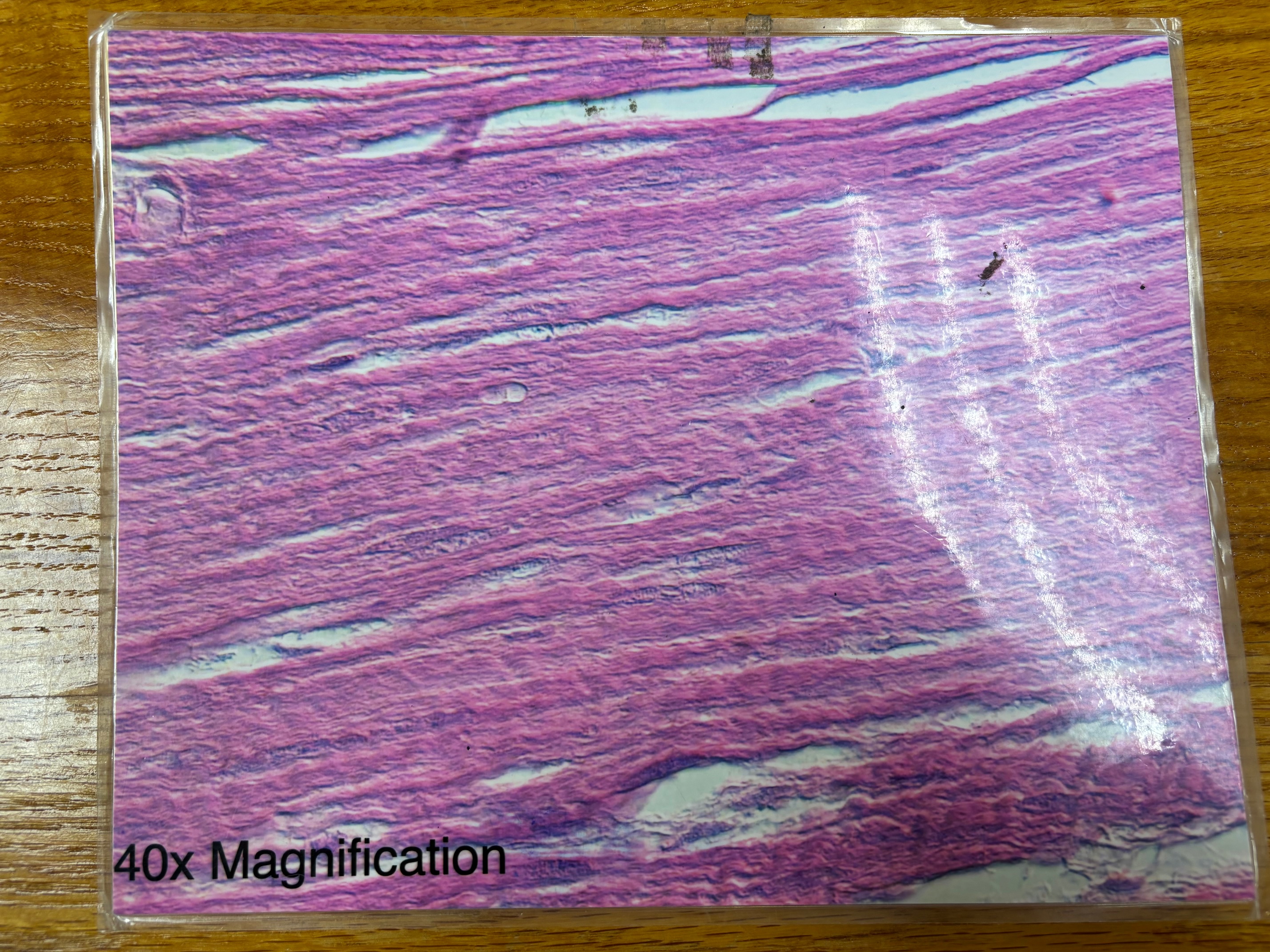
Dense regular connective tissue
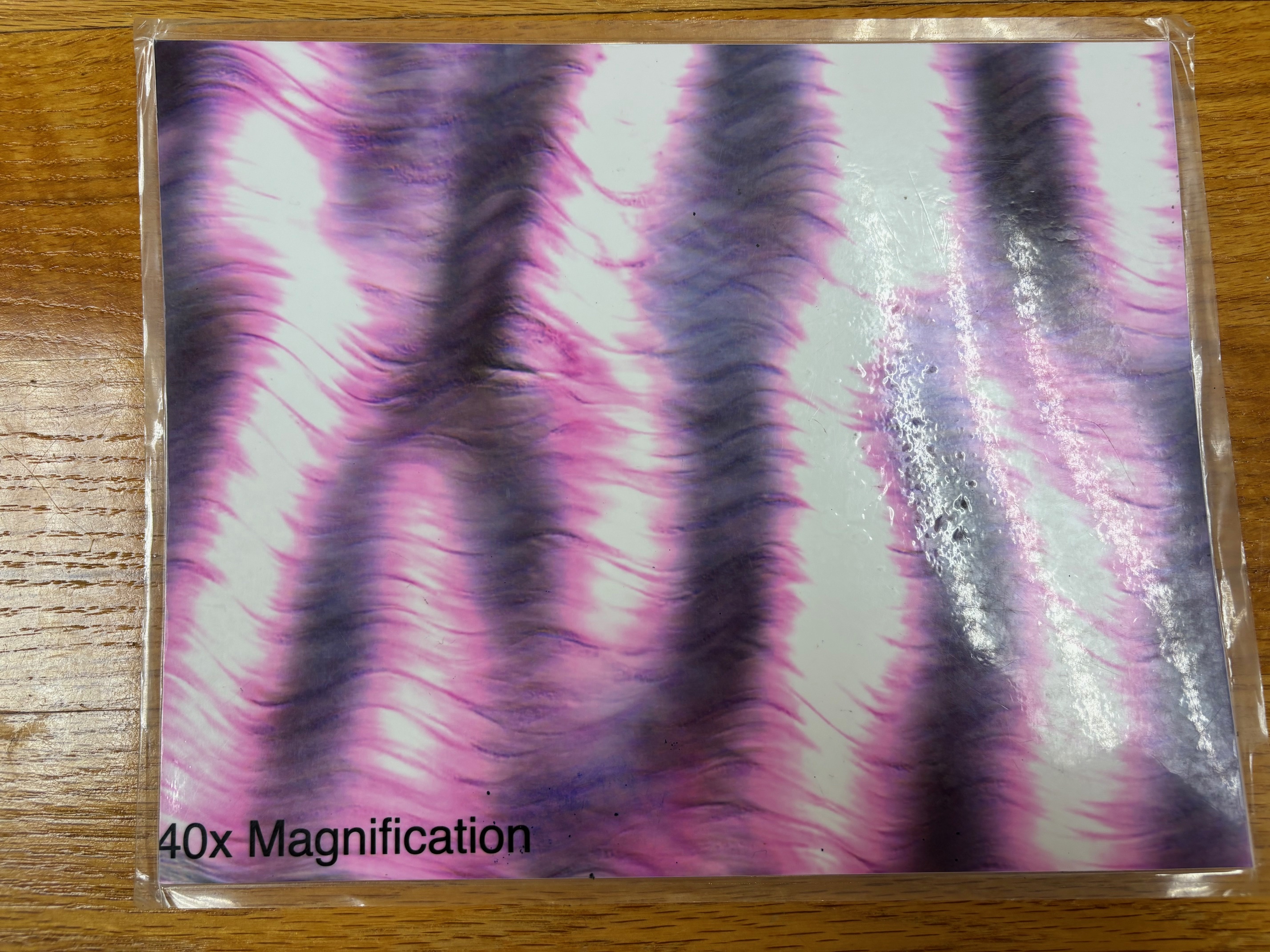

Smooth muscle tissue
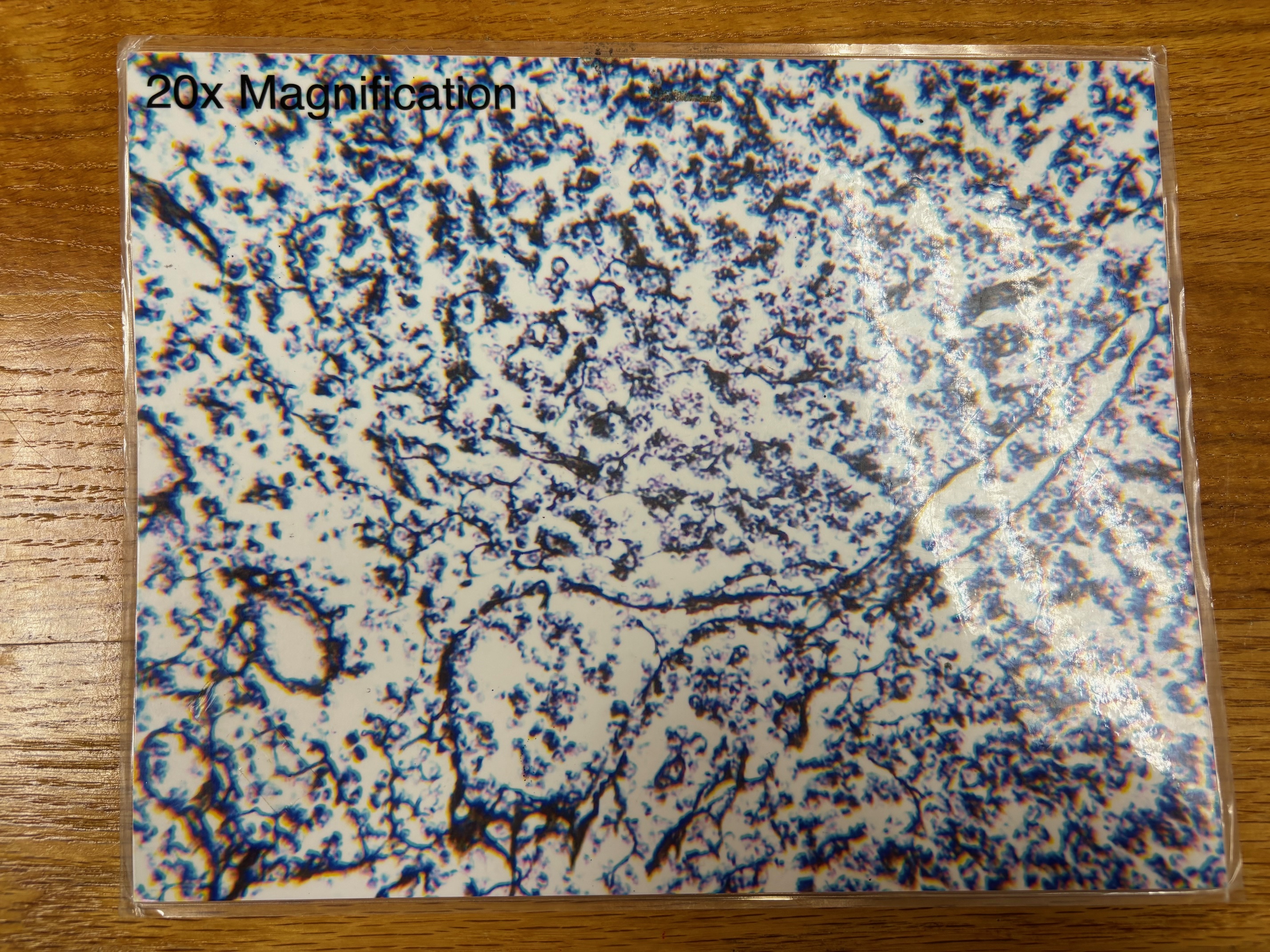
Reticular connective tissue
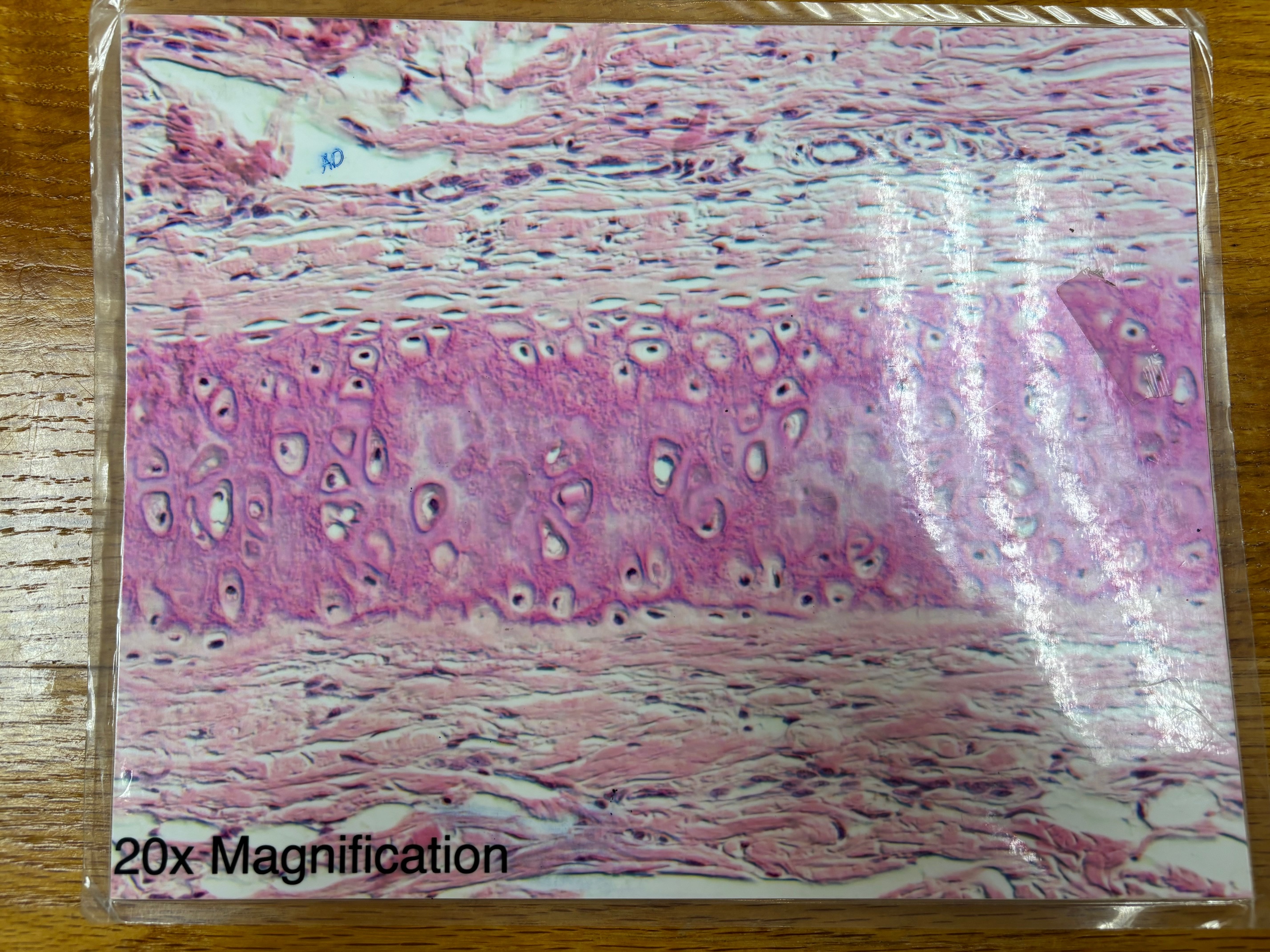
Elastic cartilage connective tissue
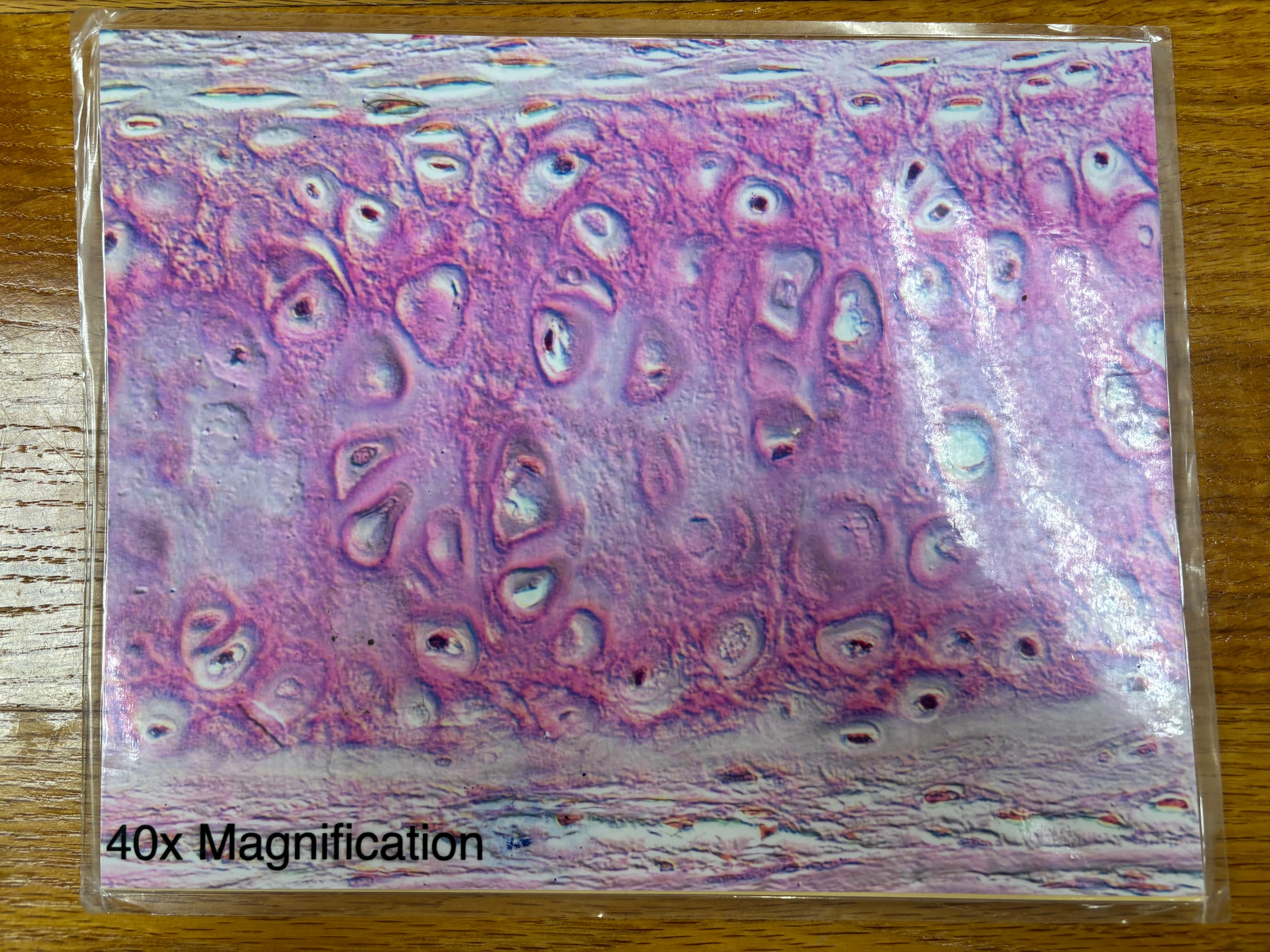
Nervous tissue
Dense irregular connective tissue
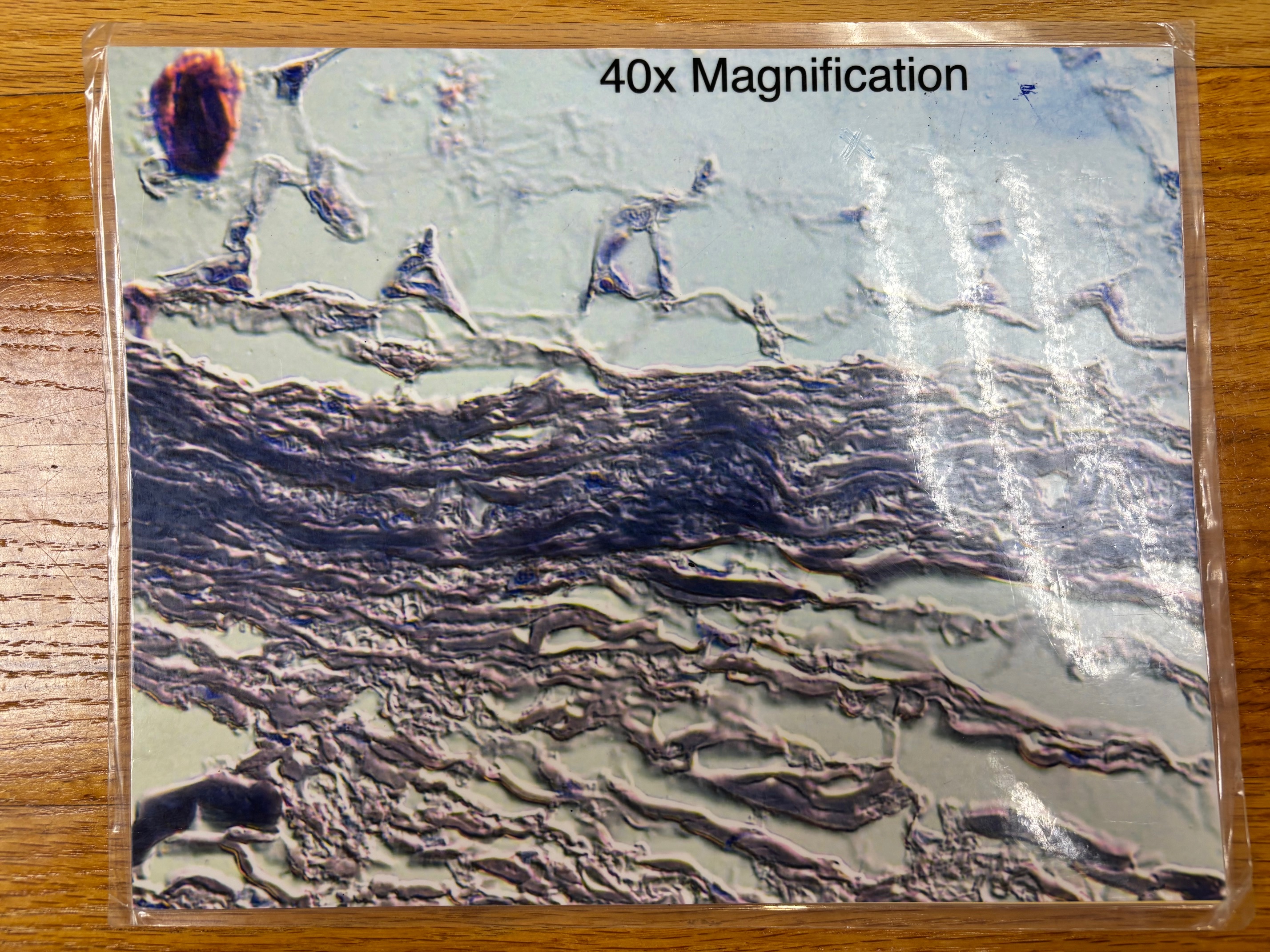

Fibrocartilage connective tissue
Elastic cartilage connective tissue
Nervous tissue
Hyaline cartilage connective tissue
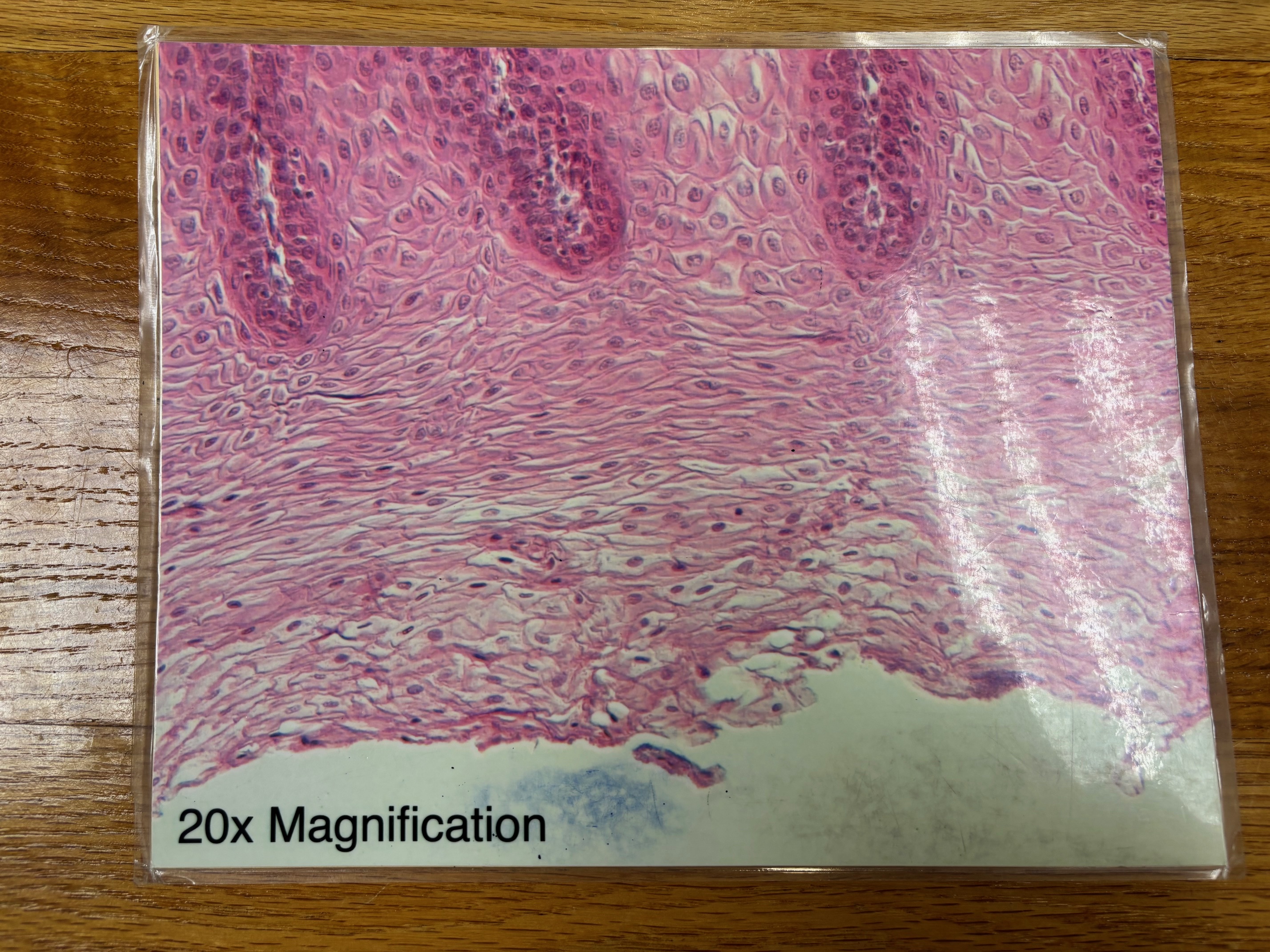
Thin skin
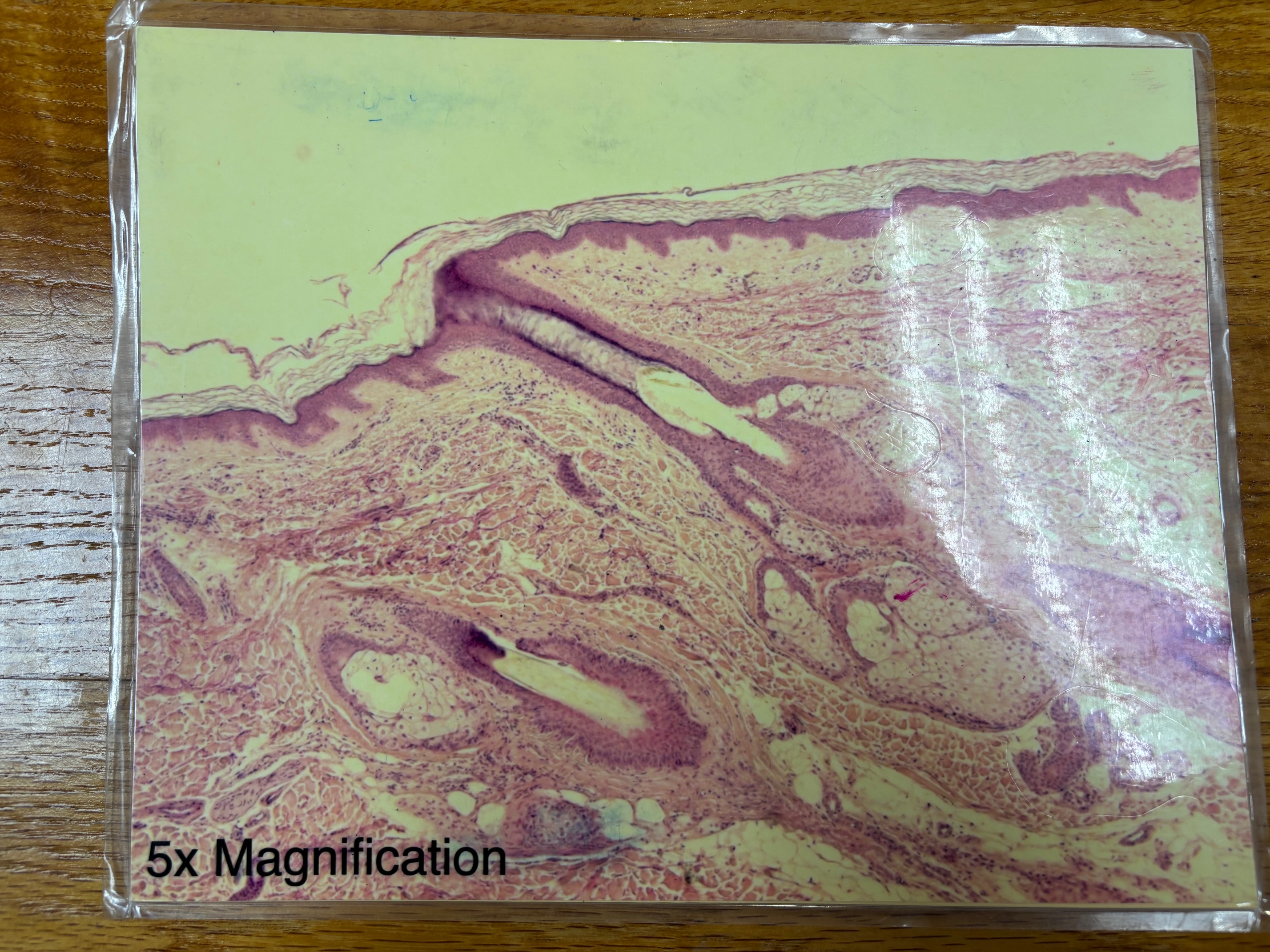
Thin skin

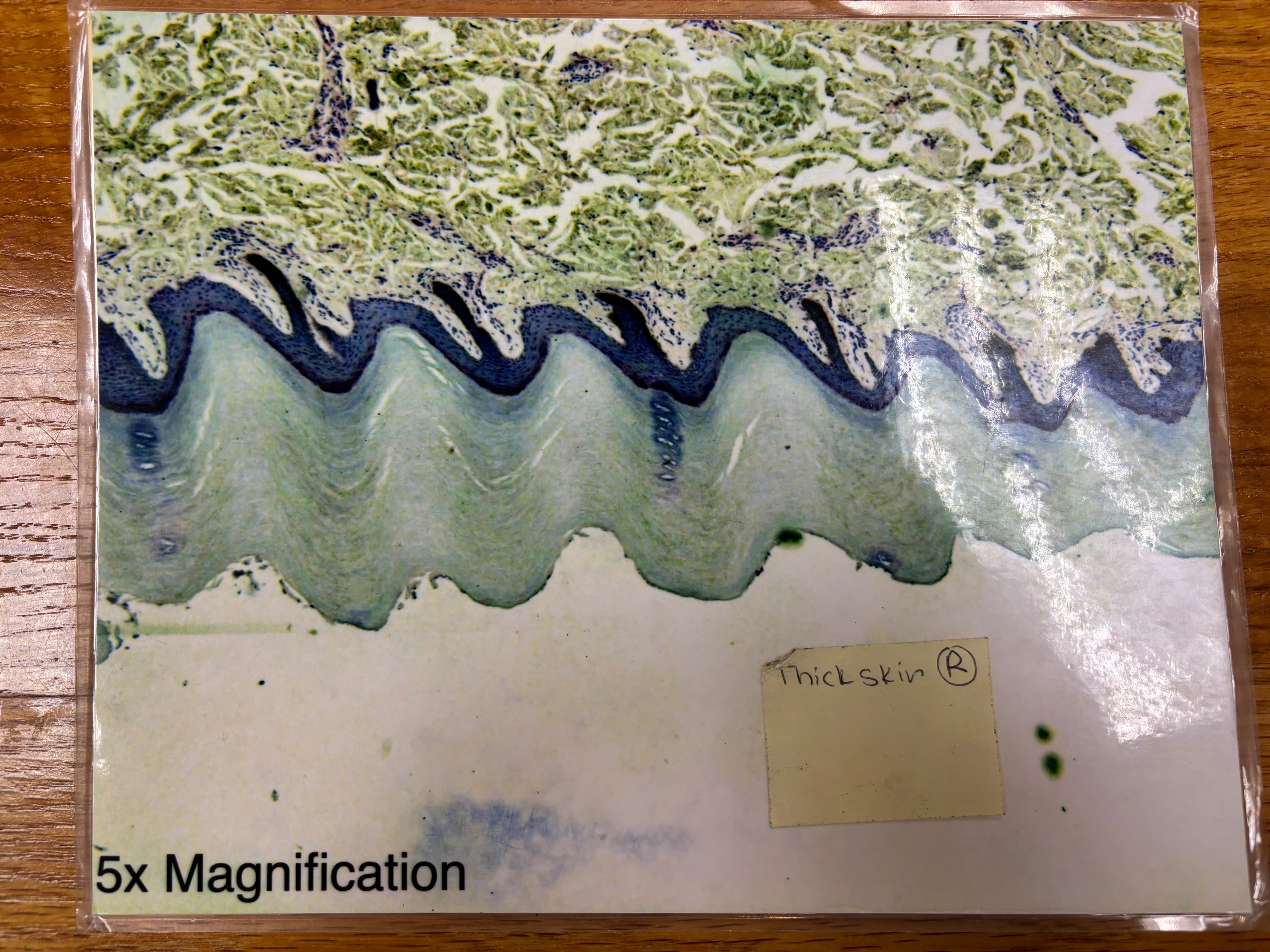
Thick skin
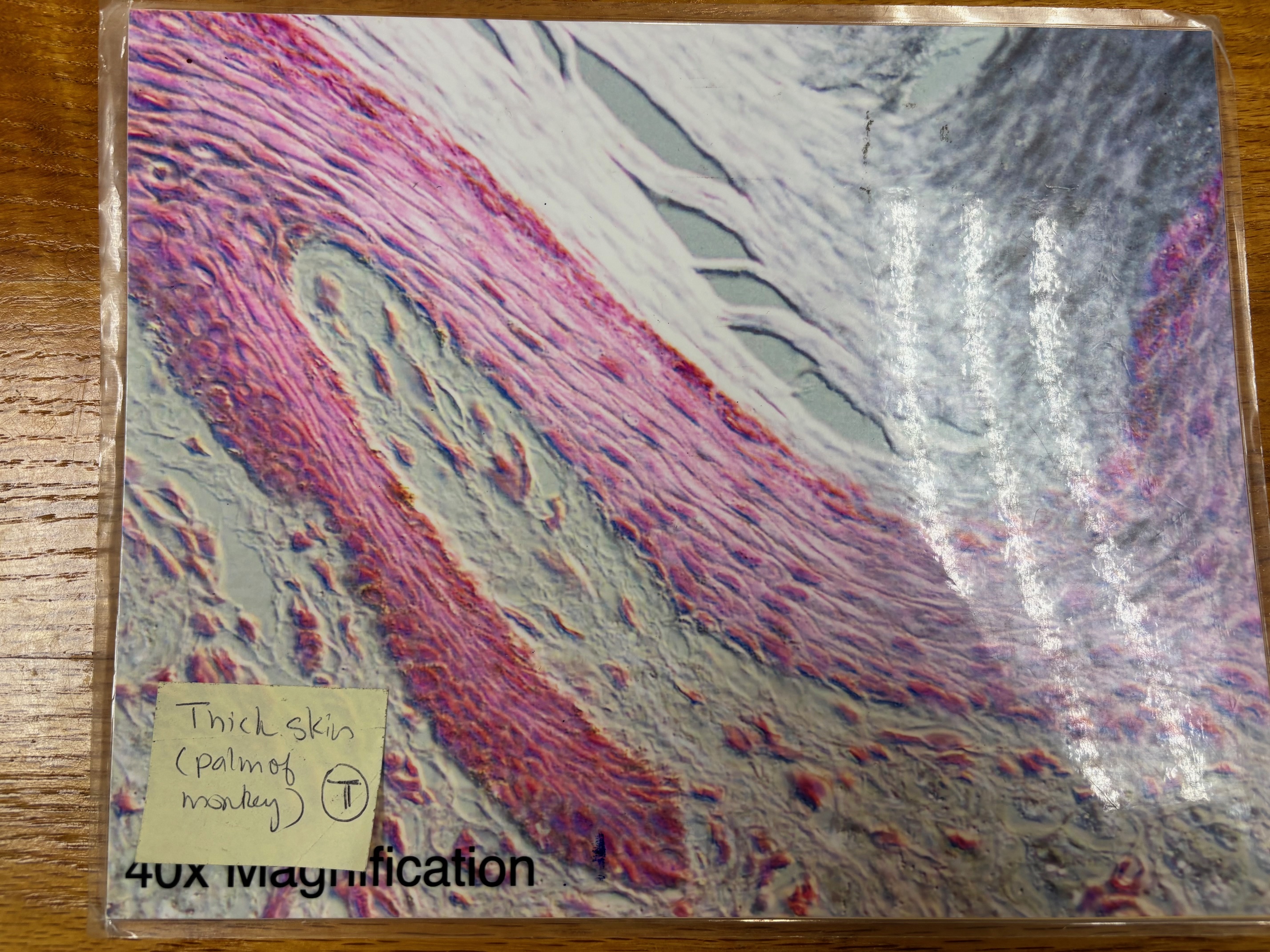
Thick skin

Simple squamous epithelium
simple squamous epithelium
Stratified columnar epithelium
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
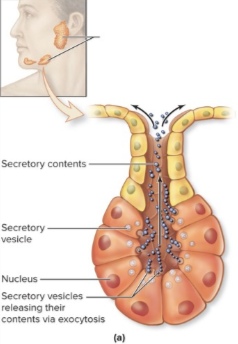
Endocrine - glandular epithelium
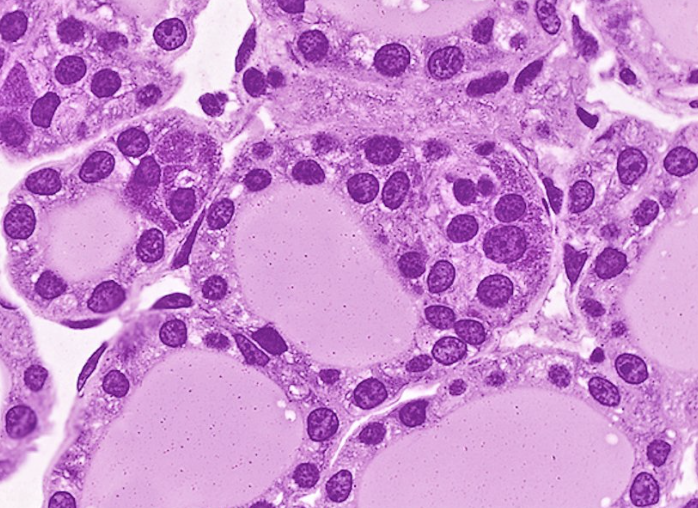
Holocrine - glandular epithelium
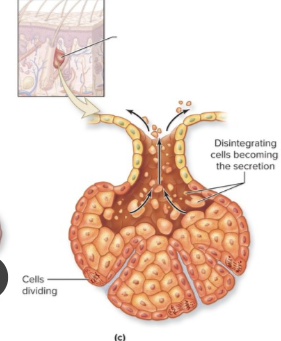
Merocrine - glandular epithelium
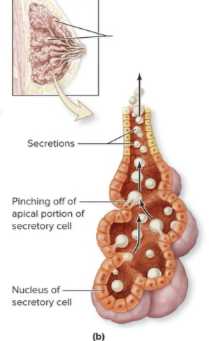
Apocrine - glandular epithelium
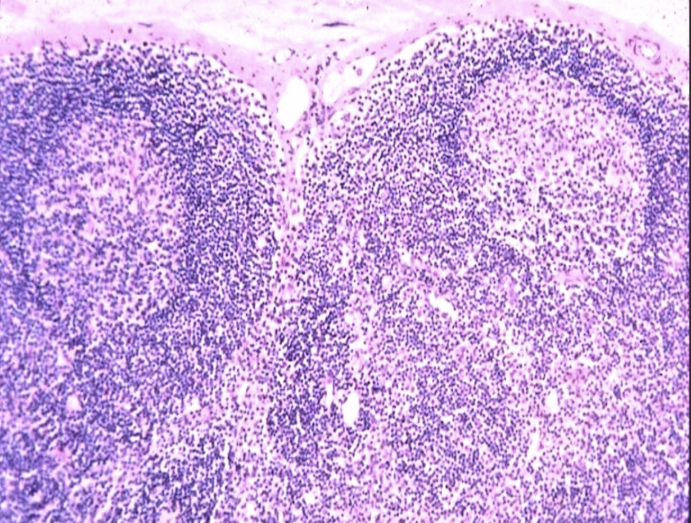
Lymph connective tissue
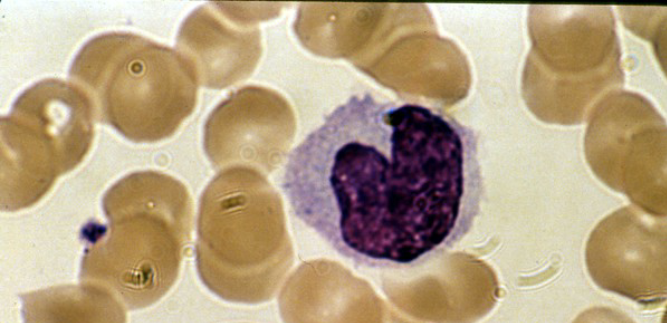
Blood: monocyte
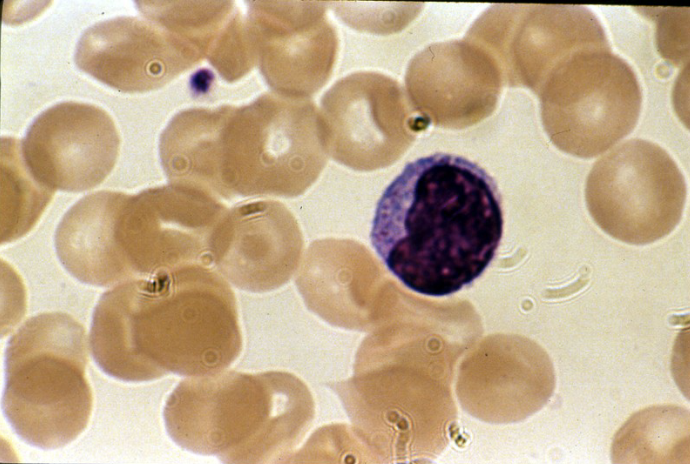
Blood: lymphocyte
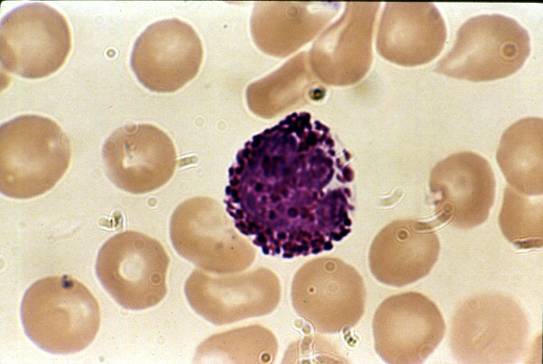
Blood: basophil
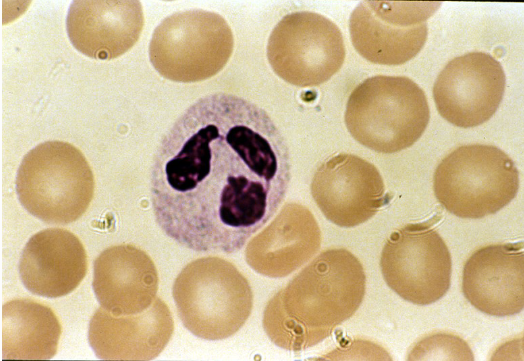
Blood: eosinophil
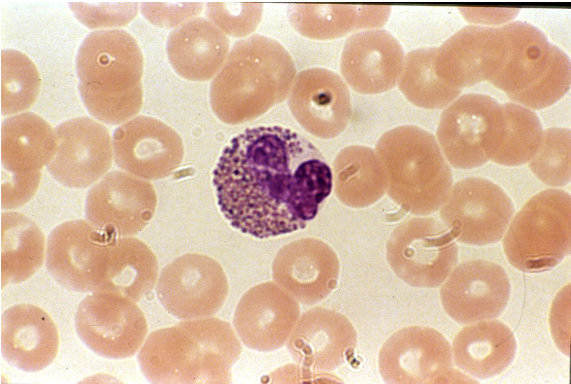
Blood: neutrophil
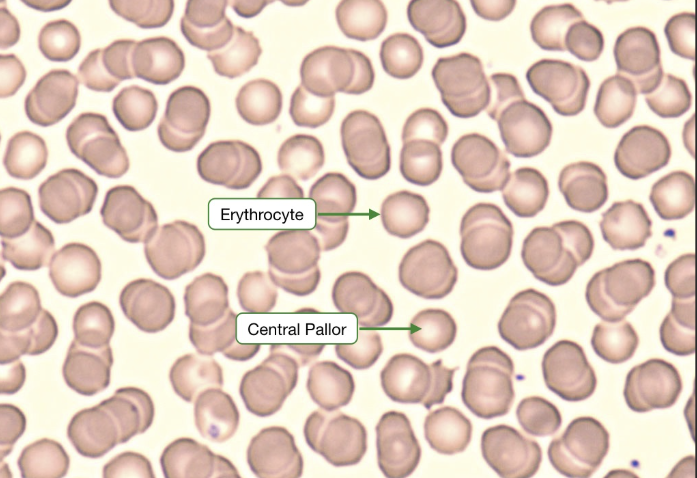
Blood: erythrocytes
basically, a red blood cell
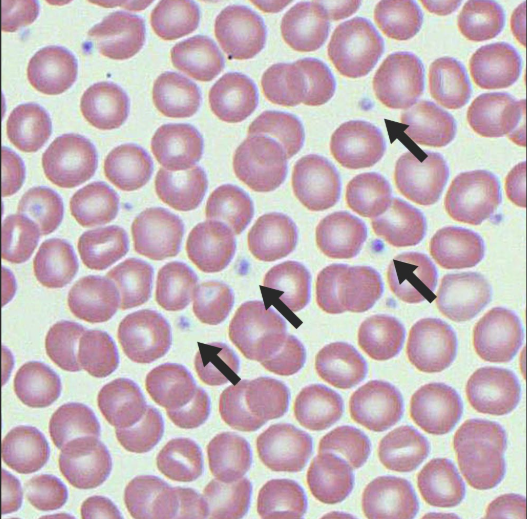
Blood: platelets
also called a thrombocyte
Simple squamous epithelium - location
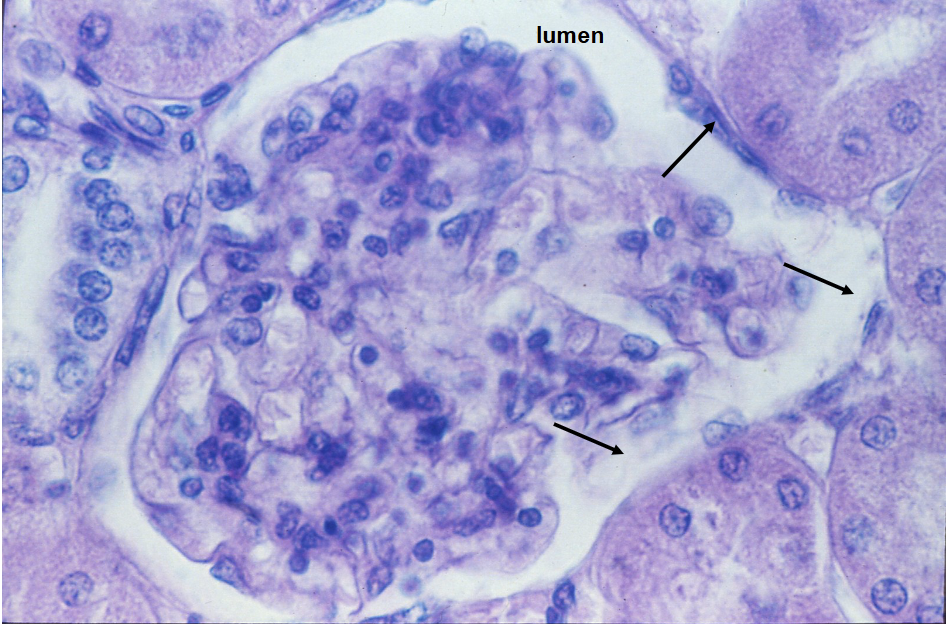
Kidney glomeruli; air sacs of lungs; lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels; serosae
Simple cuboidal epithelium - location
Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface
Simple columnar epithelium - location
Non-ciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
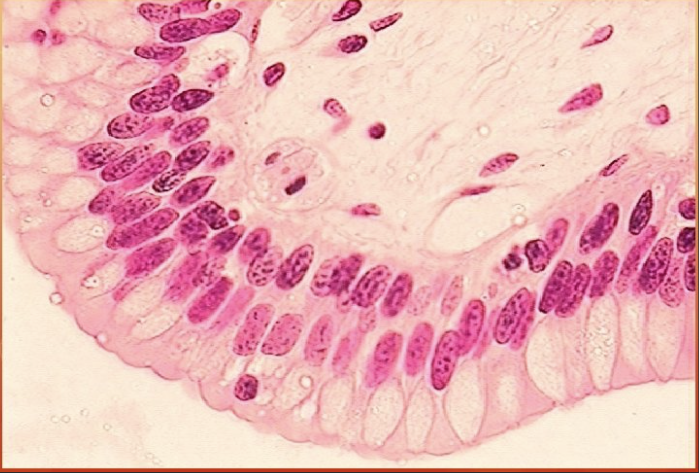
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium - location
Ciliated variety lines the trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract; non-ciliated type in males’ sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands
Stratified squamous epithelium - location
Nonkeratinized type forms the moist linings of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina; keratinized variety forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry epithelium
Stratified cuboidal epithelium - location
quite rare, mostly found in the ducts of some of the larger glands (sweat glands, mammary glands)
Stratified columnar epithelium - location
also, quite rare, small amounts are found in the pharynx, the male urethra, and lining some glandular ducts
Transitional epithelium - location
Lines the ureters, bladder, and part of the urethra
Areolar connective tissue - location
Widely distributed under epithelia of body, e.g., forms lamina propria of mucous membranes; packages organs; surrounds capillaries
Adipose connective tissue - location
Under skin in subcutaneous tissue; around kidneys and eyeballs; within abdomen; in breasts
Reticular connective tissue - location
Lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
Dense regular connective tissue - location
tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
Dense irregular connective tissue - location
Fibrous capsules of organs and of joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract
Elastic connective tissue - location
Walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with the vertebral column; within the walls of the bronchial tubes
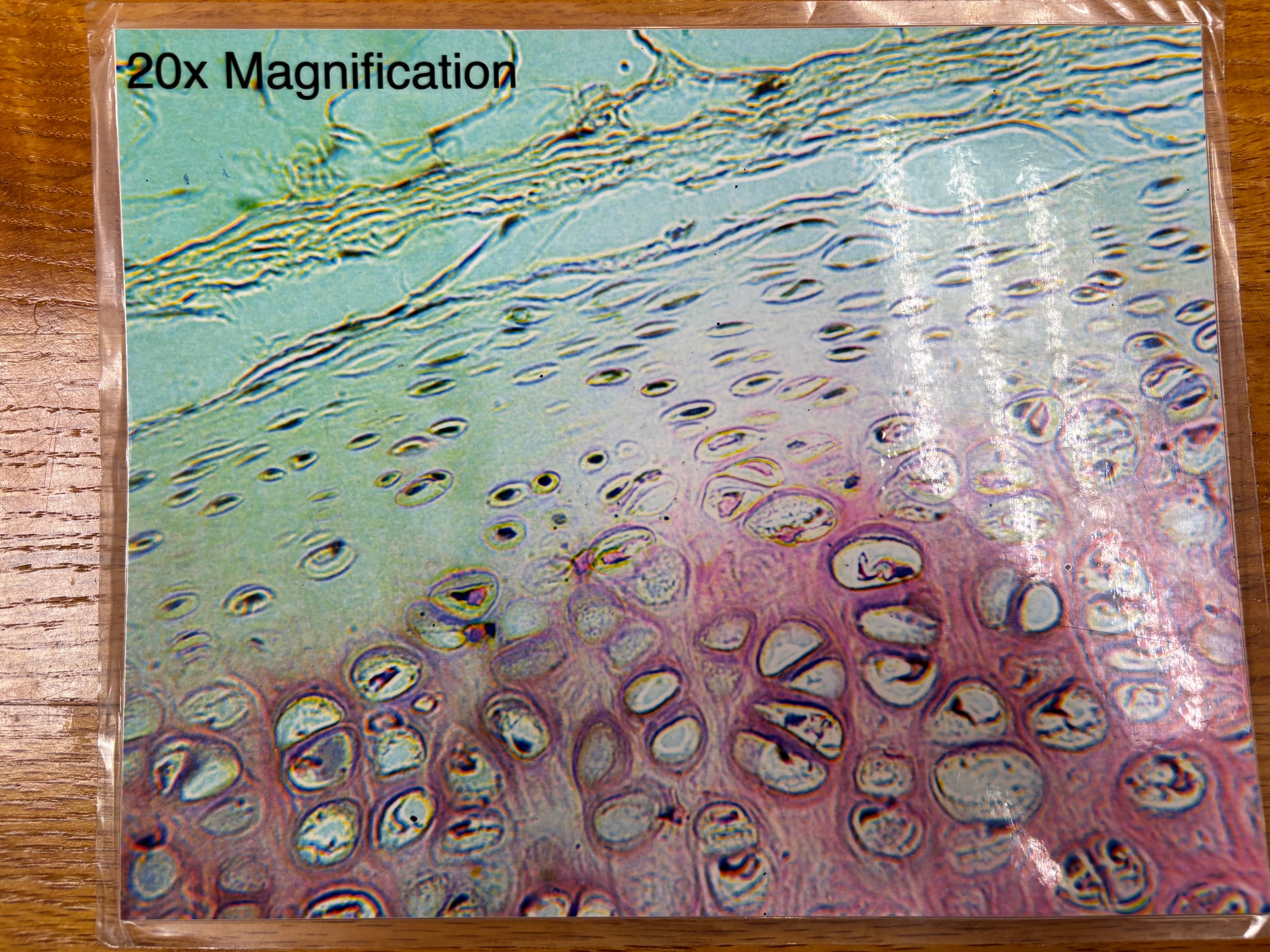
Hyaline cartilage connective tissue - location
Forms most of the embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms costal cartilages of the ribs; cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx
Elastic cartilage connective tissue - location
Supports the external ear (pinna); epiglottis
Fibrocartilage connective tissue - location
Intervertebral discs; pubic symphysis; discs of knee joint
Bone connective tissue - location
Supports and protects (by enclosing); provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
Blood connective tissue - location
contained within blood vessels
Lymph connective tissue - location
primarily located in lymph nodes, the spleen, the thymus, and throughout the mucosal linings of the body, playing a crucial role in the immune system.
Skeletal muscle tissue - location
In skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin
Cardiac muscle tissue - location
The walls of the heart
Smooth muscle tissue - location
Mostly in the walls of hollow organs