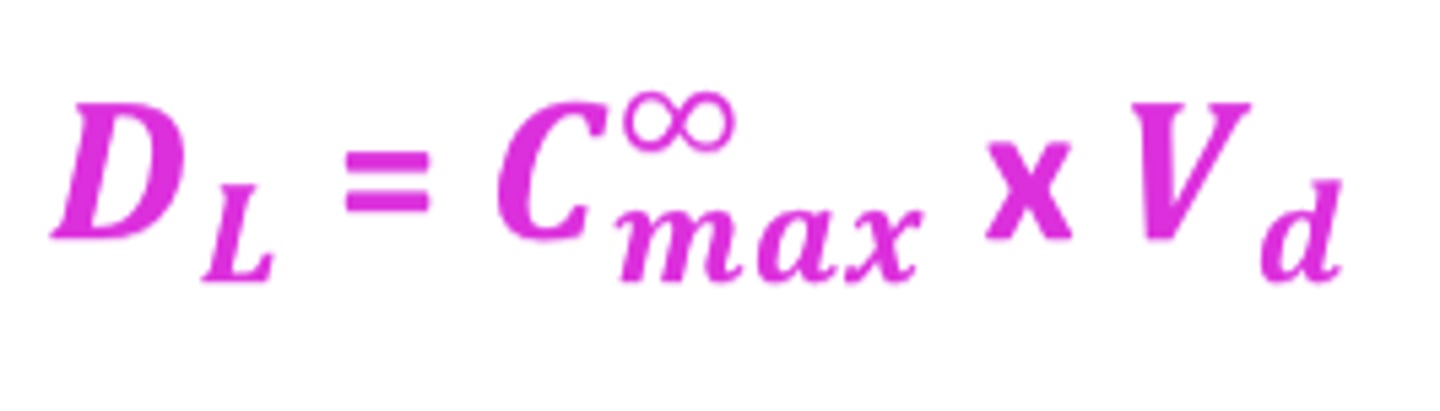Lecture 8: Multiple dose rate regiment
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Dosage regiment can be defined as...
the manner in which the drug is taken
In cases where a single dose may provide an effective treatment, but the duration of illness is longer than the therapeutic effect produced, drugs are required to...
required to be taken on a repetitive basis over a period of time
What does multiple dosing achieve and maintain?
drug concentration in plasma or at the site of action that are both safe and effective within the therapeutic window for the entire duration of therapy
Major questions for multiple dose therapy:
1. How much (dose)
2. How often (frequency of drug administration)
3. How long (duration of therapy)
Ex: a drug with a half-life of 6 is administered. After 48 hours all drug is eliminated and no ____________________ occurs
no accumulation
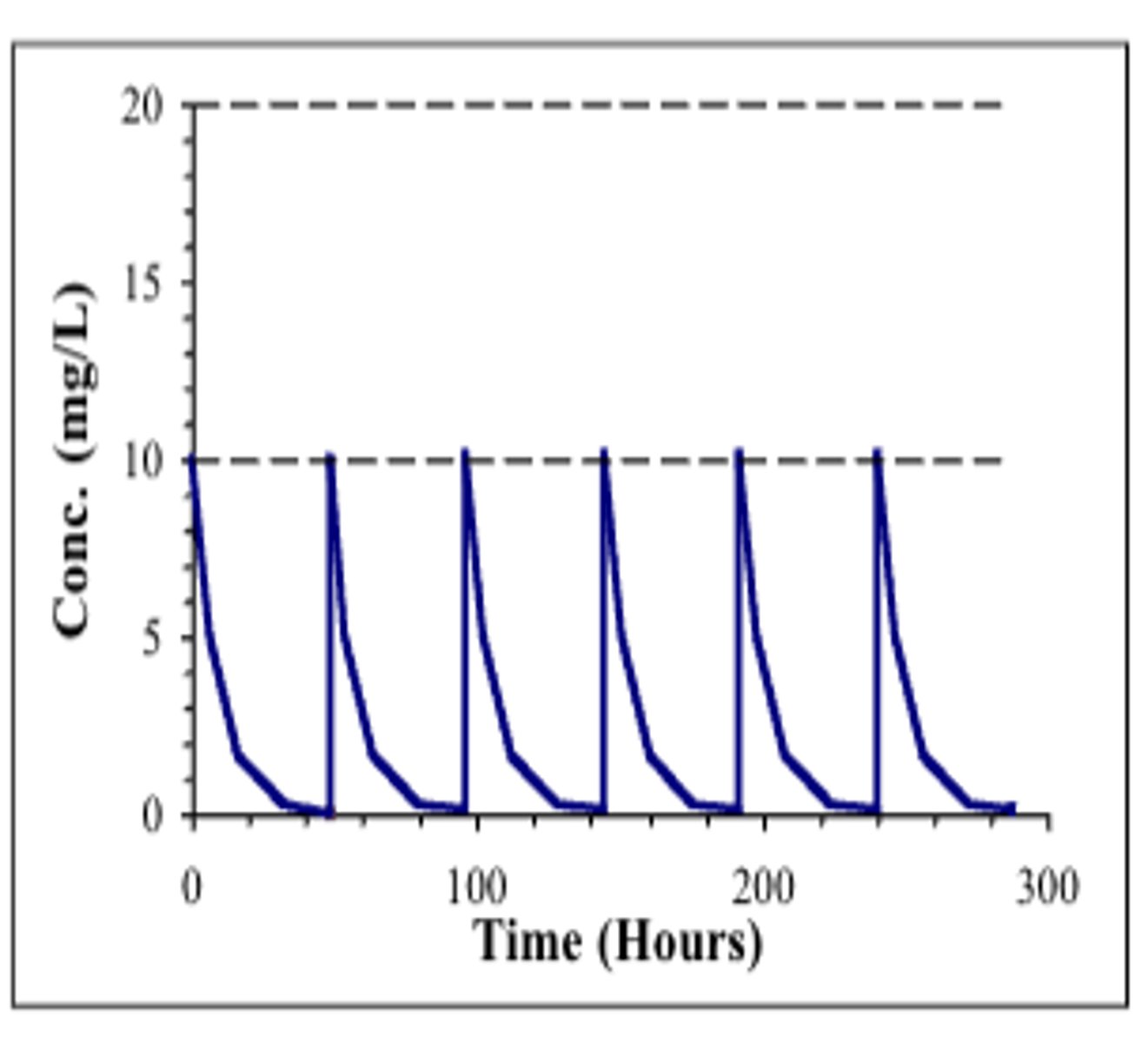
ex: for the same drug, if the next dose is administered 6 h (one half-life) after administration of the first dose, 50% of the drug from the 1st dose is still in the body and ___________________________ will occur when the next dose is given
significant accumulation
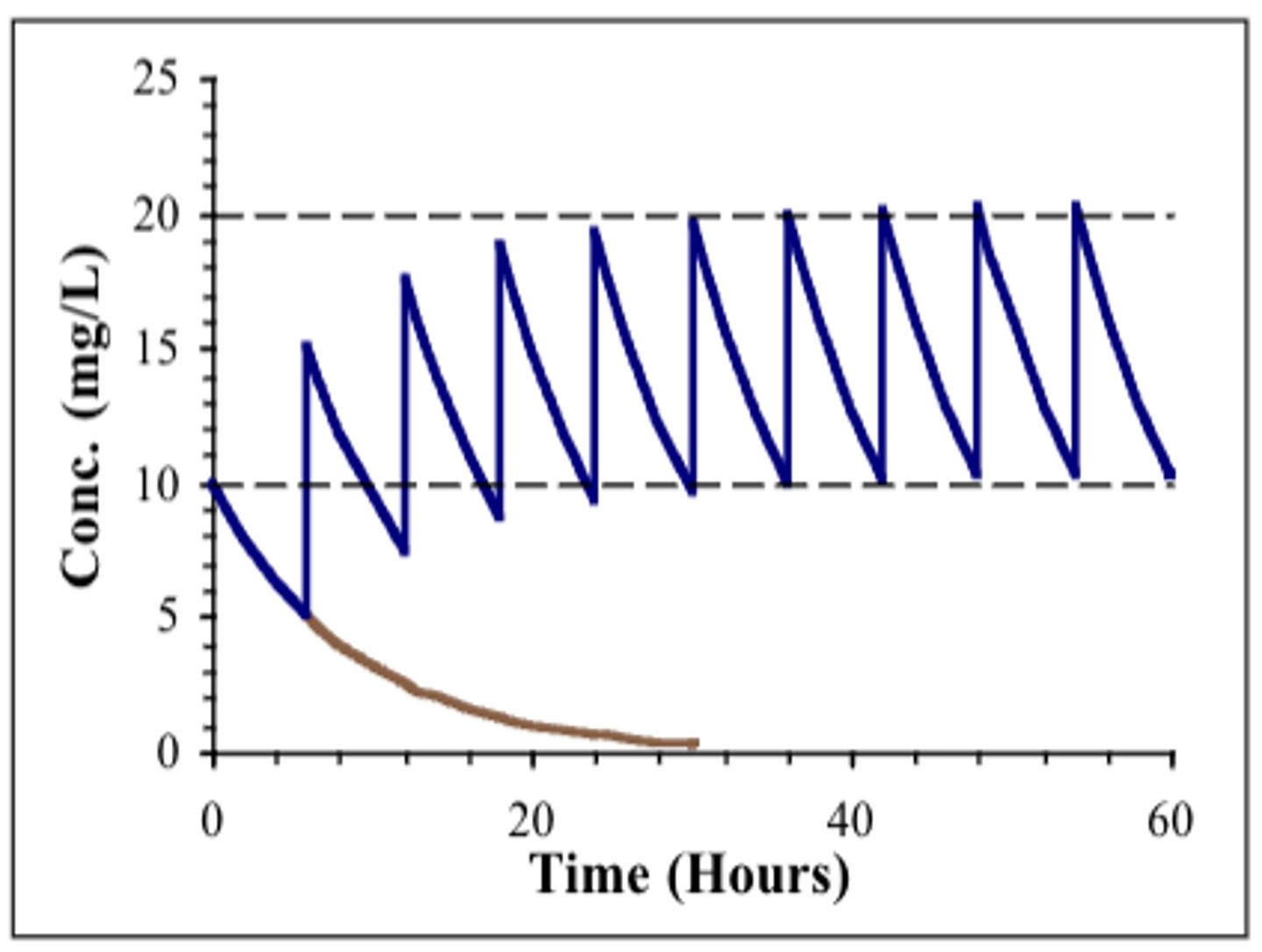
at some point after the start of the multiple dose regimen, the concentration of the drug.....
fluctuates between a constant max. and min.
- this is when the rate of input (dosing rate) becomes equal to the elimination rate = steady state
What is the extent of accumulation (Racc) dependent on?
t1/2 /𝜏
t1/2 =half-life (direct relationship)
!!!!! 𝜏 =dosing interval (indirect relationship)
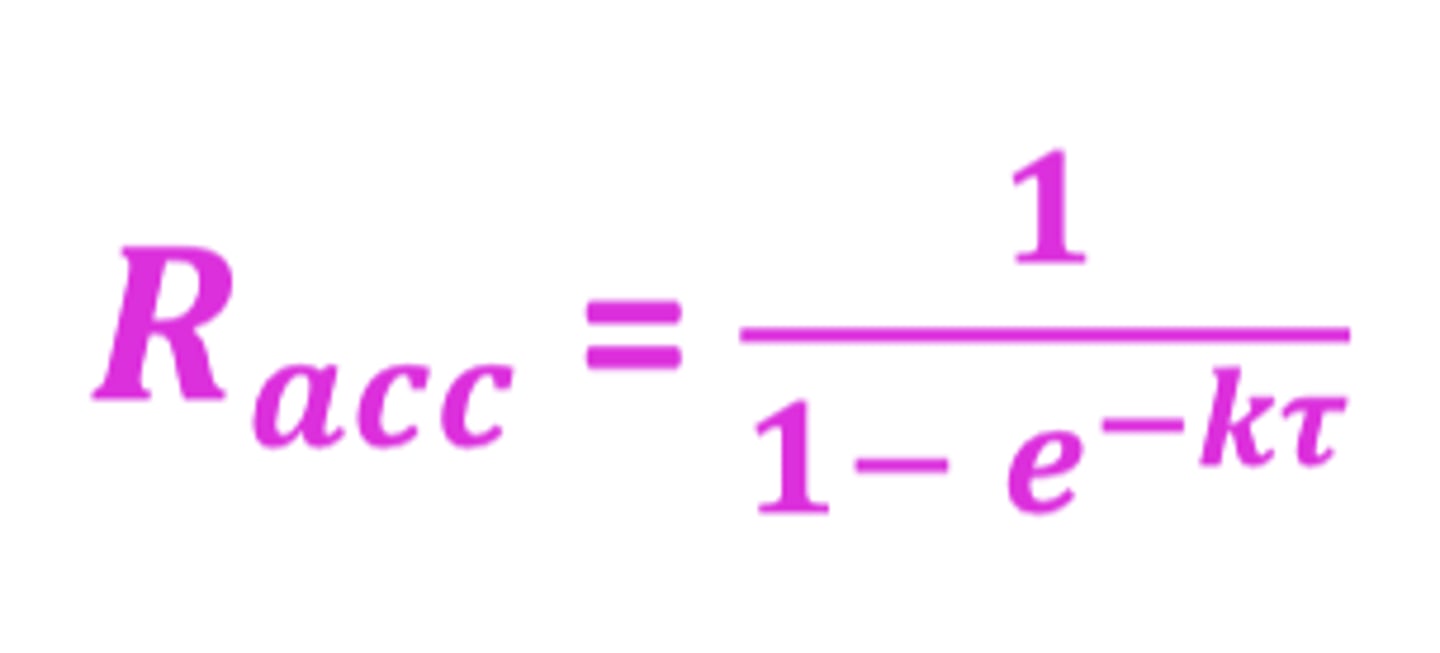
Formula for extent of accumulation (Racc)
t1/2 /𝜏
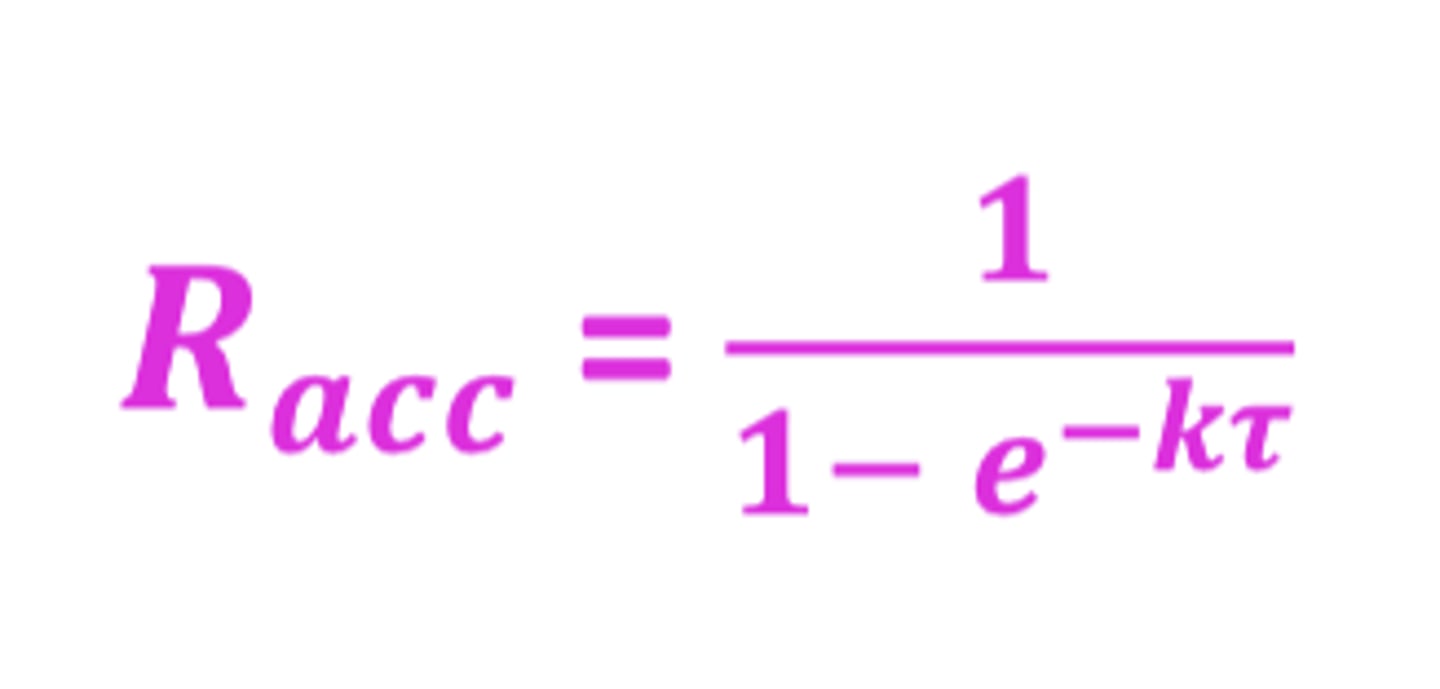
For some drugs such as Digoxin, ______________ is longer than ______________
- t1/2 (6 days)
- 𝜏 (1 day)
t1/2 /𝜏 > _______, resulting in significant _________________
- t1/2 /𝜏 >1
- significant accumulation
The plasma concentrations after multiple dosing gradually.....
increases after the first dose until a steady state is achieved
The concentrations at any time during the dosage interval at steady state are equal to....
the concentrations at the same time after the first dose multiplied by the accumulation factor
Formula for the conc. at steady state at time t=conc. after the 1st dose at time t x Racc

Formula for C at steady state at time 0 (immediately after drug administration)
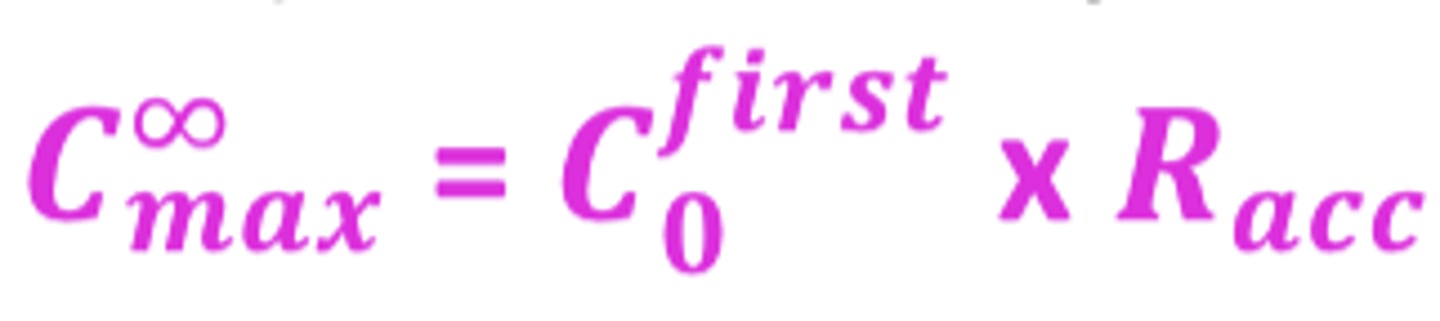
Formula for C at steady state at the end of interval (immediatly before drug administration)

Although the concentration fluctuates between Cmax and Cmin at steady state, one can determine the average conc. at steady state (Cav), a parameter similar to...
Css after constant infusion
Formula for Cav with
Cav = (dose/𝜏)/Cl
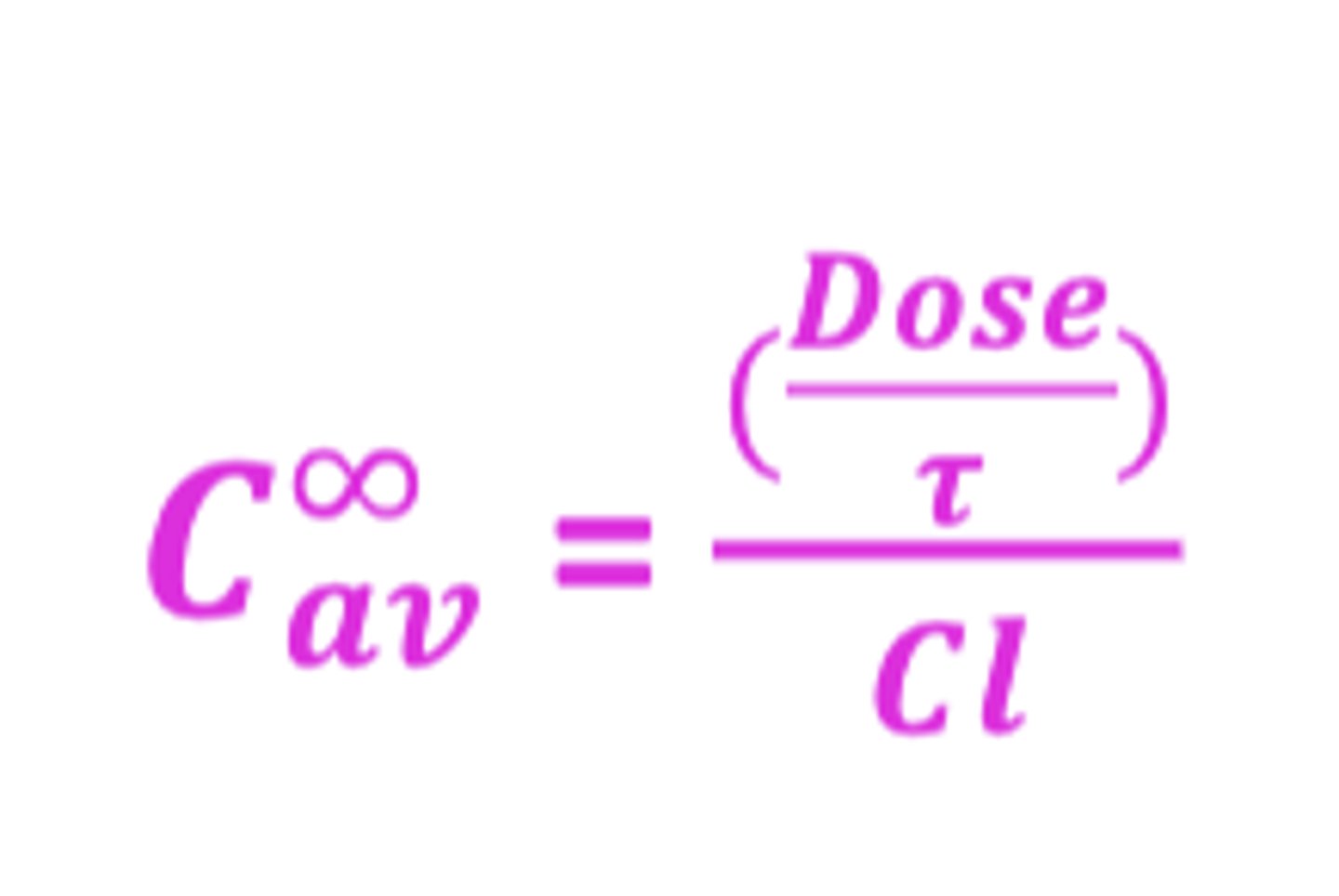
Dosing rate
Dose/𝜏
- the average rate of drug input for each dosage interval
The more universal equation applicable to all routes of administration (including PO) by including F (extent of BA)
Cav = F x (Dose/𝜏)/Cl
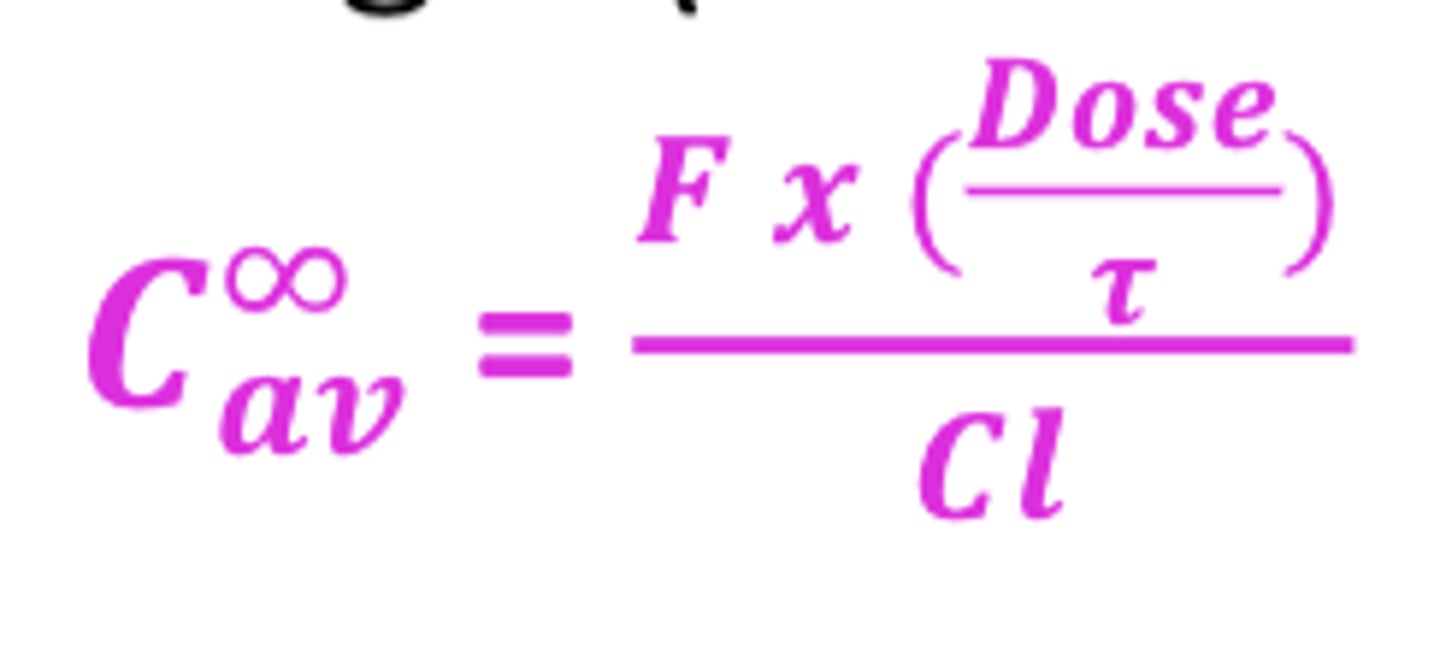
As opposed to IV infusion, steady state after multiple dosing does not mean....
constant concentration
- the concentration fluctuates between a maximum and minimum
What is the magnitude of decline of Cmax dependent on?
dependent on the time (dosage interval), 𝜏 and half-life (or rate constant of drug)
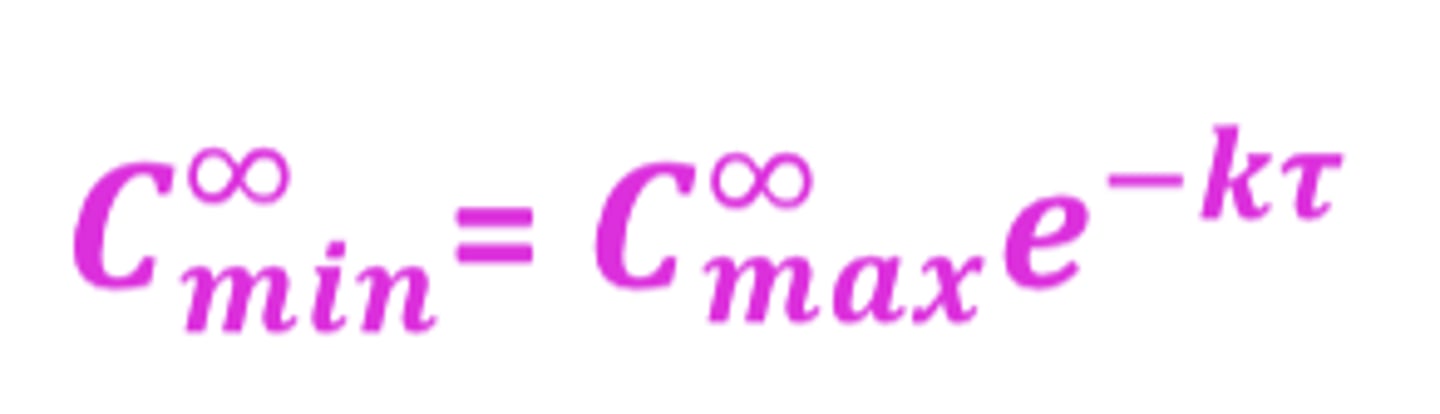
What do the fluctuations between the max and min concentrations at steady state depend on?
- on 𝜏 (direct relationship)
- half-life (inverse relationship
𝜏/t1/2
(opposite of dependency for Racc)
The formula to obtain accurate Cav from Cmax and Cmin
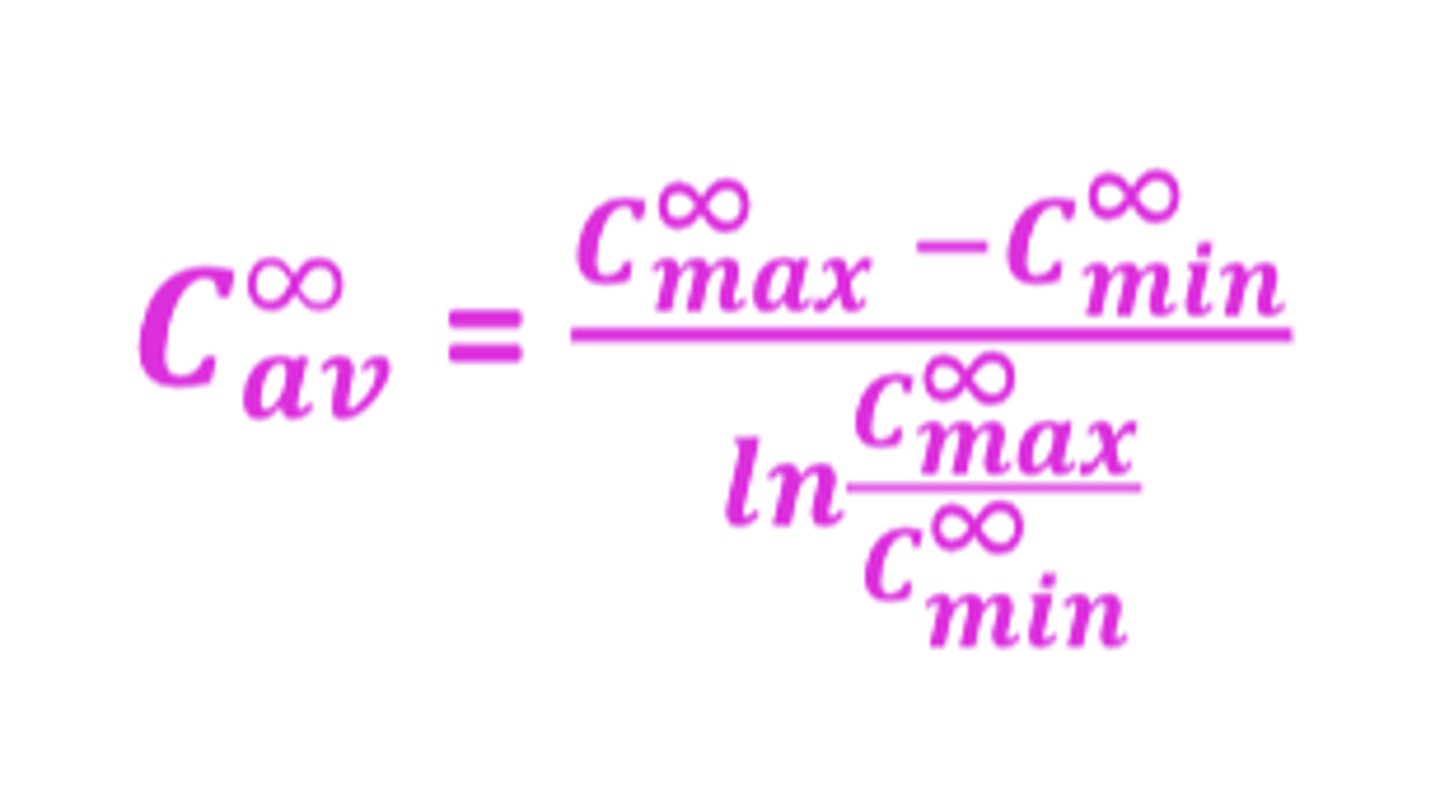
Loading dose
an initial dose of medication administered to rapidly achieve therapeutic levels
What is the purpose of the loading dose?
achieve the desired steady state concentration with the first dose and to maintain those concentrations with subsequent maintenance doses
Loading dose formula from maintenance dose and Racc
DL = DM x Racc
DL= loading dose
DM= maintenance dose
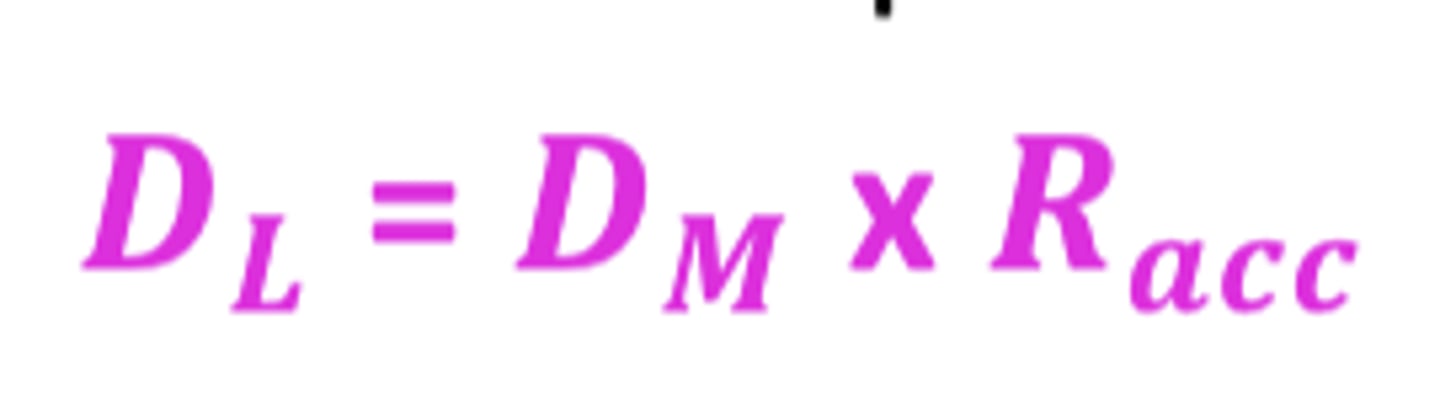
Loading dose formula from Cmax and Vd
DL = Cmax x Vd