Negative Externalities
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
What are negative externalities of production?
Often created during the production of a good/service
The market is failing due to over-provision of these goods/services as only the private costs are considered by the producers and not the external costs
If the external costs were considered, the supply would decrease and they would be sold at a higher price
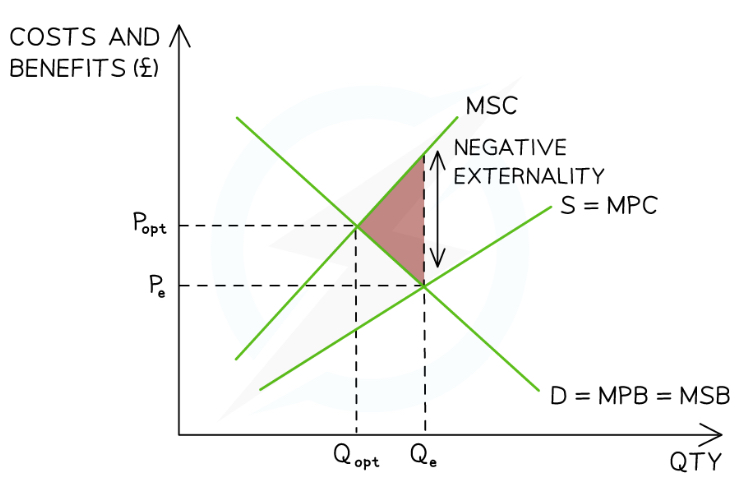
What diagram shows negative externalities of production?
The marginal social benefit (MSB) is assumed to be equal to the marginal private benefit (MPB) as the focus is on the producer side of the market
The free-market equilibrium can be seen at PeQe. This is where the MPC = MSB
The larger the external costs in production, the larger the gap between the MPC and the marginal social cost (MSC)
The optimum allocation of resources from society’s point of view, would generate an equilibrium where MSB = MSC
This can be found at PoptQopt
There is no market failure at this equilibrium
The free market is failing due to over-provision of this good/service equal to Qe-Qopt
The factors of production used to manufacture this over-provision represent a welfare loss to society (pink triangle)
To be socially efficient, fewer factors of production should be allocated to producing this good/service
What are negative externalities of consumption?
Often created during the consumption of a good/service
The market is failing due to over-consumption of these goods/services as only the private costs are considered by the consumers and not the external costs
If the external costs were considered, demand would decrease and they would be sold at a lower price
What diagram shows negative externalities of consumption?