Anomie and Strain Theories in Criminology Lec #4
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Anomie
A state of normlessness in society.
Strain Theory
Theory explaining deviance through societal pressures.
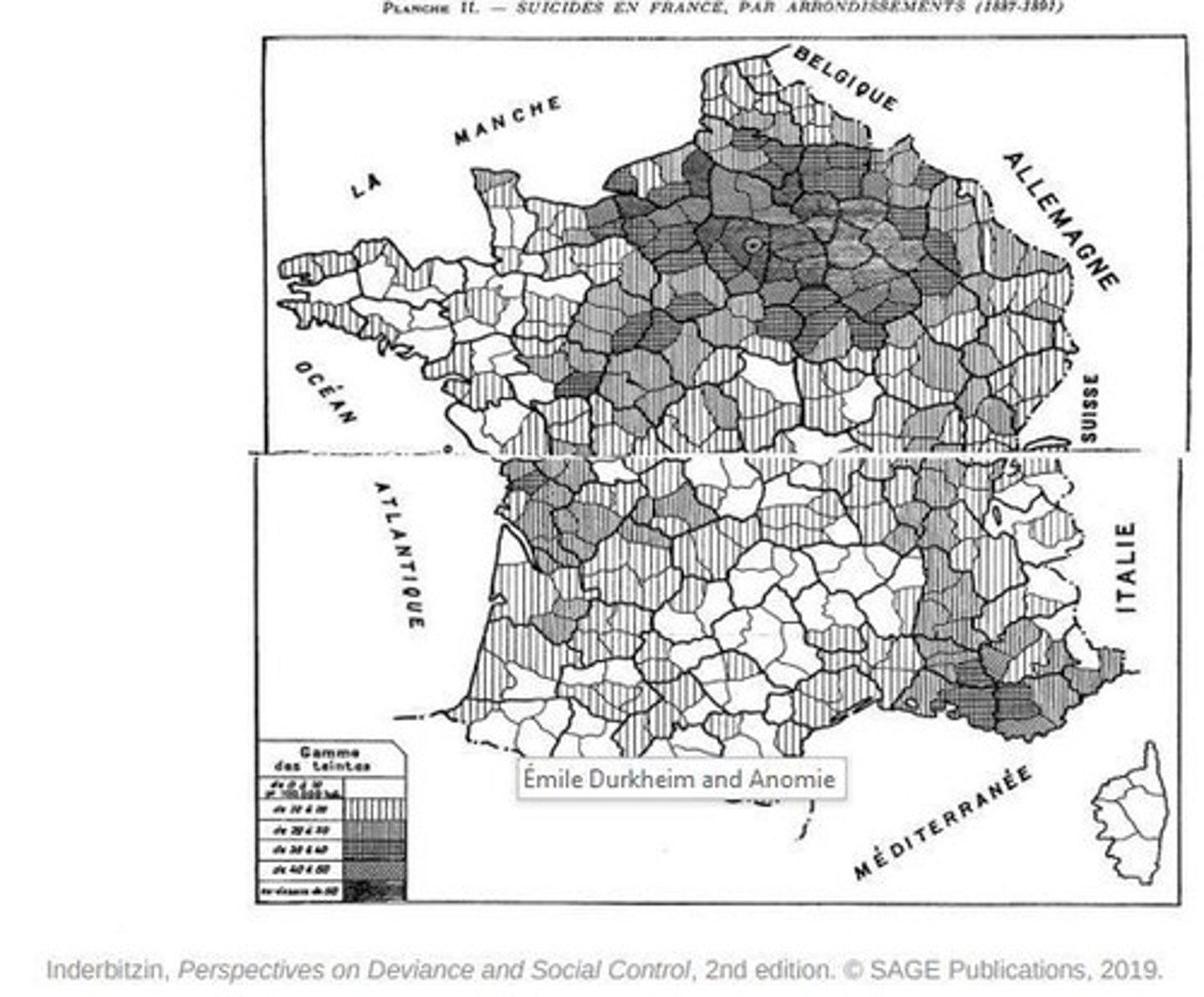
Durkheim's Anomie Theory
Crime offends collective conscience, evokes punishment.
Merton's Adaptations
Five responses to societal strain and anomie.
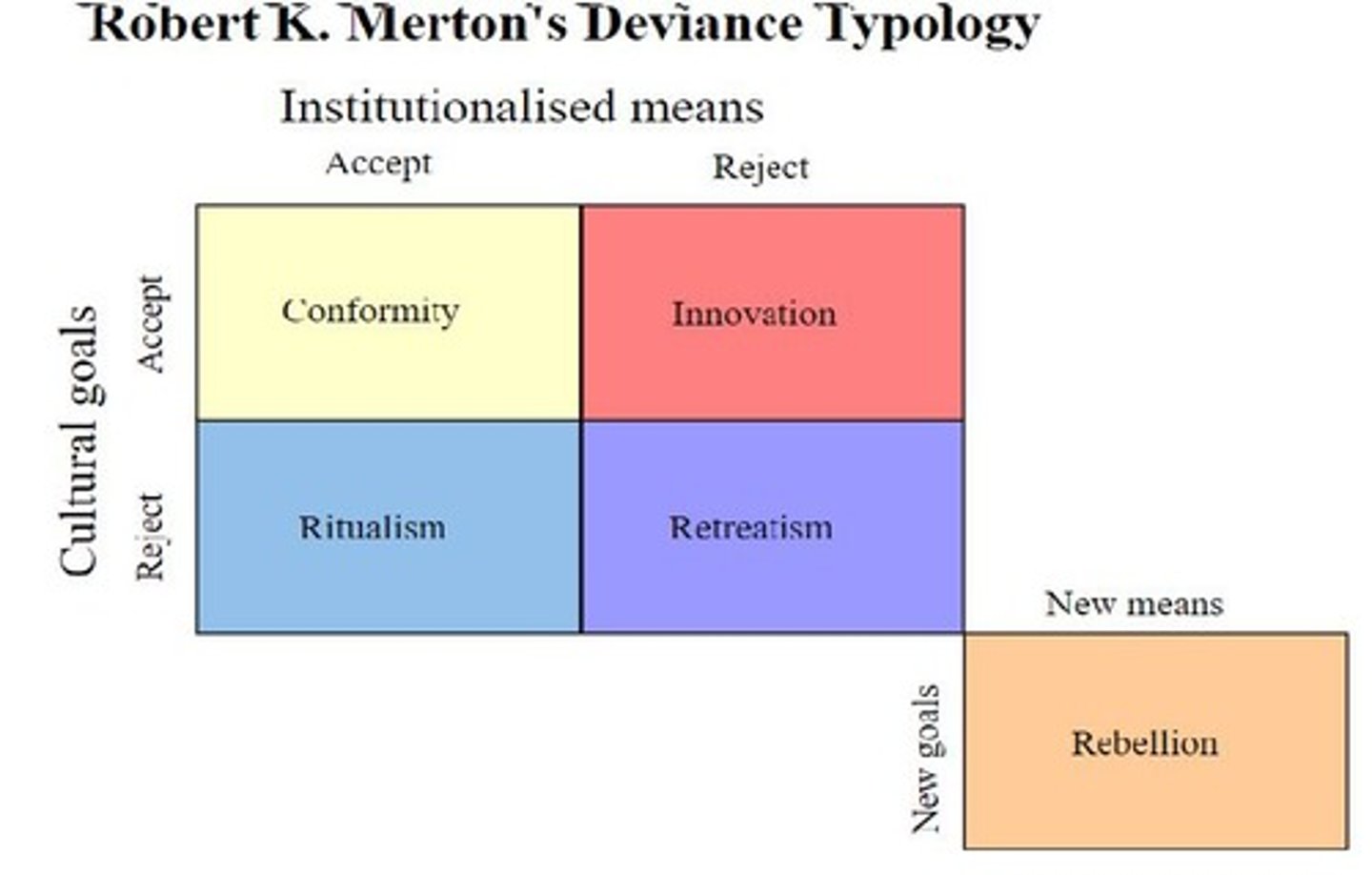
Conformity
Acceptance of goals and legitimate means.
Innovation
Acceptance of goals, but rejection of means.
Ritualism
Rejection of goals, acceptance of means.
Retreatism
Rejection of both goals and means.
Rebellion
Replacement of societal goals with new ones.
Status Frustration
Lower-class boys' response to middle-class standards.
Differential Opportunity Theory
Gang behavior based on illegal opportunity availability.
Criminal Subculture
Gangs in areas with organized crime opportunities.
Conflict Subculture
Gangs in disorganized communities with limited opportunities.
Retreatist Subculture
Isolation and drug use among double failures.
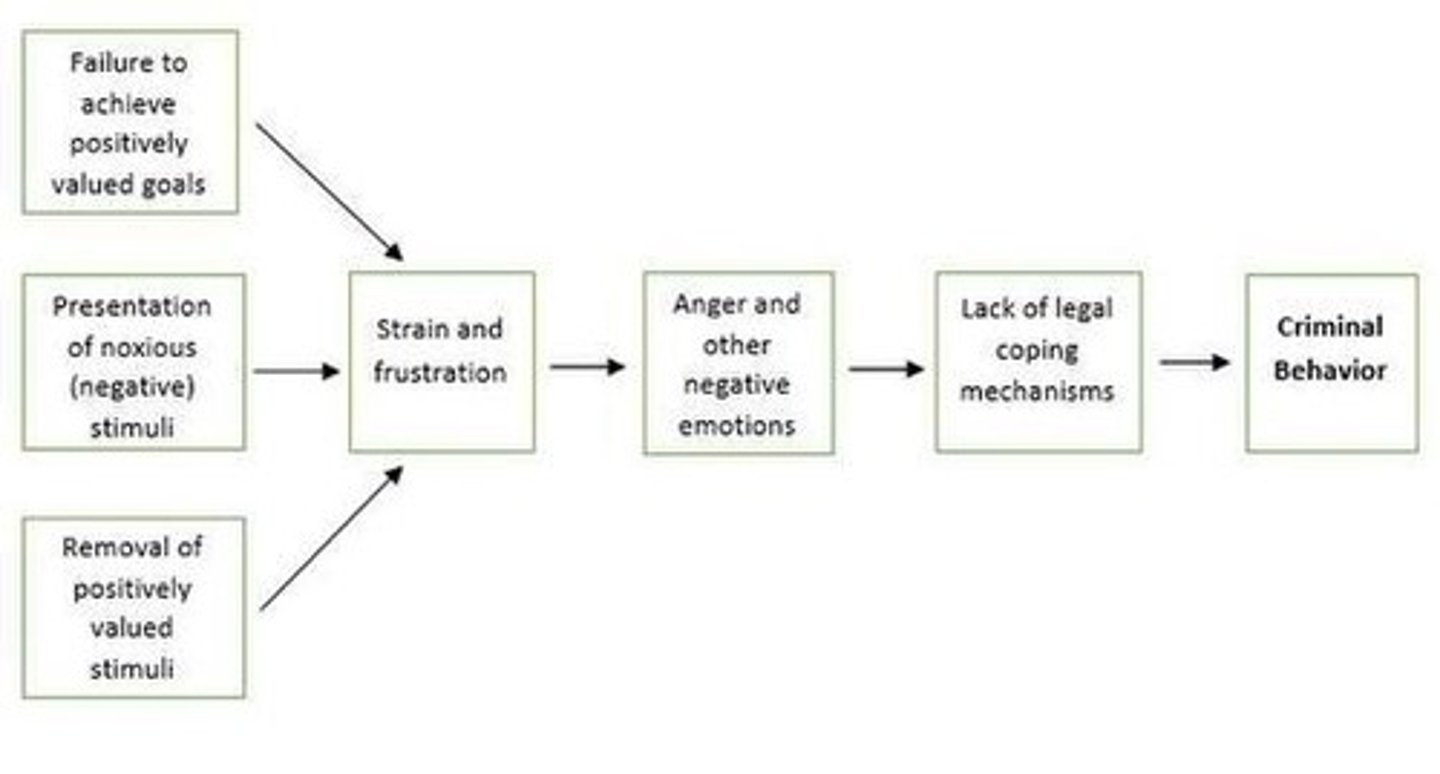
General Strain Theory
Focuses on multiple sources of strain affecting behavior.
Institutional Anomie Theory
Critiques American Dream's impact on societal values.
American Dream
Cultural belief in success through hard work.
Individualism
Emphasis on personal success and rivalry.
Universalism
Aspiration for success is widespread in society.
Measurement of Success
Success often quantified by financial achievement.
Collective Conscience
Shared beliefs and values in a society.
Social Structure
Framework of societal relationships and institutions.
Cultural Goals
Societal objectives that individuals strive to achieve.
Deviance
Behavior that violates societal norms.
Crime
Legally defined deviance punishable by law.
Collective Punishment
Punishment of individuals for group offenses.
Empirical Demonstration
Using data to show relationships in society.
Labelling Theory
Focus on societal reaction to deviance.
Research Limitations
Critiques of assumptions in strain theories.
Progressive Reforms
Changes aimed at addressing social inequalities.