PhysioEx Practical 1 - BSC2086L
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What is the resting membrane potential of a neuron caused by?
Na+ and K+
What alters the resting membrane potential?
Alterations to the ion concentration inside or outside the neuron
Why is there a greater resting membranepotential when the extracellular [K+] was increased compared to a similar decrease in extracellular
more passive K+ than passive Na+
What does decreasing extracellular Na+ concentration do to membrane potential
more negative
what does increasing extracellular K+ do to membrane potential
less negative
what happens when correct stimulus is applied
receptor will open or close membrane ion channels
Pacinian corpuscles respond to high to low amounts of ______.
Unresponsive to ____, _____, or _____
pressure
chemical, heat, light
Olfactory receptors respond to low to high amounts of _____ _____.
Unresponsive to _____, ______, ______.
chemical stimuli
heat, pressure, light
What do free nerve endings respond to?
heat, pressure
What needs to happen in order to generate action potential?
change in voltage
What does the membrane potential have to reach before action potential can be generated
threshold
What stimulus voltage causes action potential in the nerve?
20 and above
Why was there no decrease in magnitude of action potential
action potential is regenerated at each segment of axon
What happens during action potential propagation
an influx of Na+ into the axon triggers the depolarization of adjacent axon segments
What happens when axon segment is in refractory period
it cannot respond when it is depolarized to threshold
TTX is a sodium ____
antagonist
What happens when threshold voltage is reached
the activation gate opens, allowing Na + to enter the cell
What is it called when depolarization of the membrane does not elicit another action potential
refractory period
What is it called when an action potential can be generated as it required a greater depolarization than usual to reach threshold state
relative refractive period
Why does increasing voltage not have an effect on the nerve
you are within the absolute refractory period of the nerve
once an action potential is generated, it always has the same _____
magnitude
_____ of the action potential is not the same for all axons
speed
What can affect the speed of the action potential
myelinated axons, larger diameter axons
Which fibers have tje fastest action potential conduction speed?
Type A
Which fibers have small diameters and no myelination and therefore have the lowest action potential conduction speed
Type C
Which fibers have a medium diameter axons that have some myelination so they will have action potential conduction speeds that are in between the other fibers
Type B
What happens when action potential reaches axon terminal
voltage gated Ca2+ channels open
What happens if the extracellular fluid contains no Ca2+
neurotransmitters will not be released since exocytosis will not occur
What happens if extracellular concentration of Ca2+ is low?
will reduce the amount of neurotransmitter released since less exocytosis will occur
What happens if Mg2+ is added to extracellular fluid?
Mg 2+ will act as a calcium channel blocker.
What is propylthiouracil?
What does it do?
antithyroid medicine, inhibits the production of thyroxine;
makes it harder for the body to use iodine to make thyroid hormone
what is the experiment trying to prove?
...
What is the purpose of TSH? Thyroxine?
TSH - tests how much of the hormone is in your blood and how well your thyroid is working
Thyroxine - controls how much energy your body is using
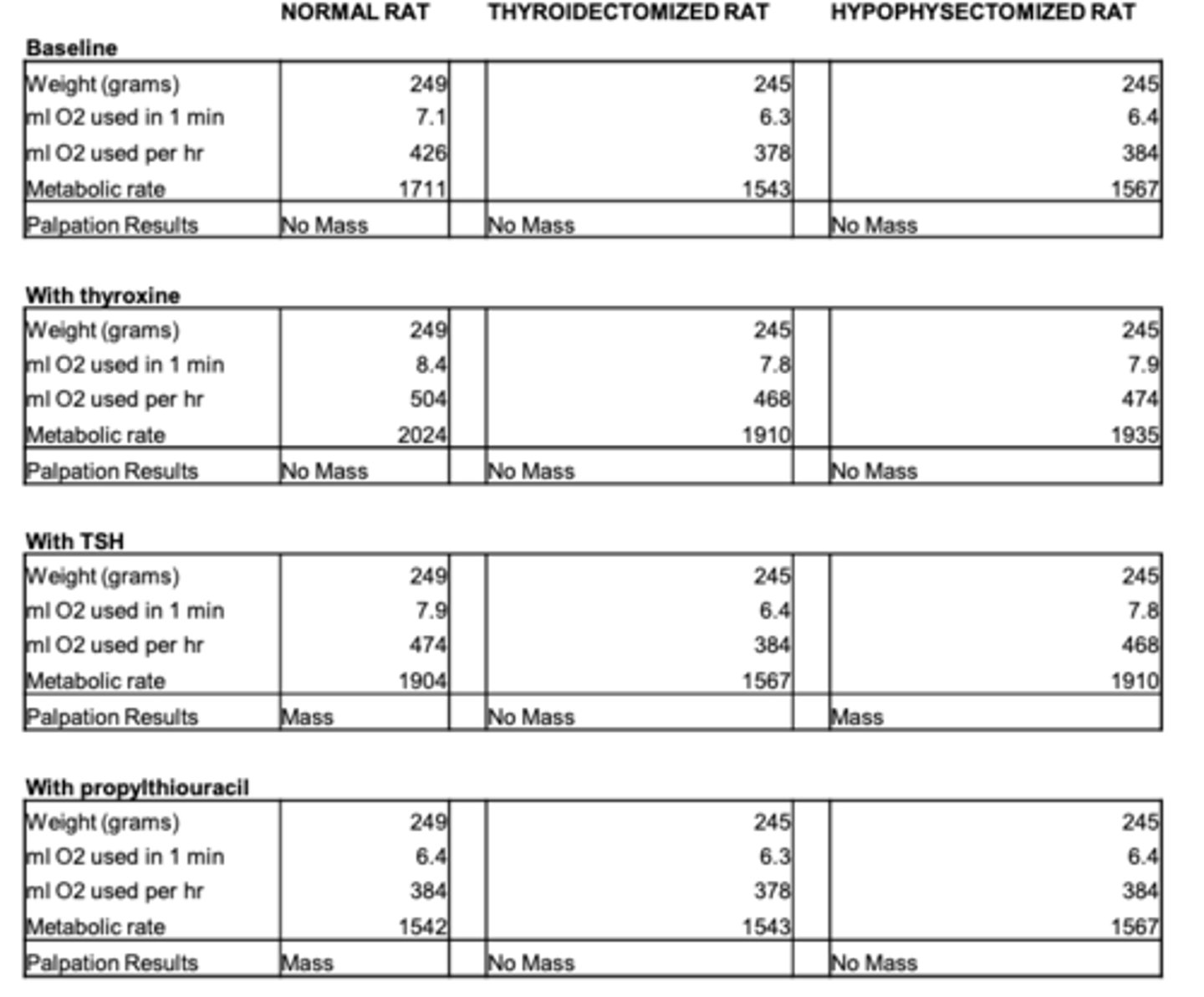
Whose metabolic rate was the highest?
normal rat
Why can't Tx rate produce thyroxine to increase metabolism
lacks a thyroid gland
Why can't hypox rat produce thyroxine
lacks pituitary gland
What happens with removal of pituitary gland?
all hormones are removed with the gland
What happens if thyroxine is injected in any of the rats?
an increase in metabolism compared to their base metabolic rat
What compensates for the lack of thyroid gland
thyroxine
What happens if TSH is injected to the normal and hypox rats
increase in metabolic rate compared to the baseline
Why doesn't metabolic rate increase for Tx rat after TSH injection
lacks thyroid gland for TSH to stimulate
normal rat - NA
Tx rat - lacks ____ gland
Hypox rat - lacks _____ gland
thyroid
pituitary
Why does TSH injection increase metabolic rate in hypox rat even though it lacks pituitary gland?
simulates the actions of a pituitary gland to cause thyroxine release from the thyroid gland which increases metabolism.
What is followed by the secretion of TRH in normal rat
increase in TSH secretion
Why doesn't TSH injection increase metabolic rate for Tx rat
lacks thyroid gland
What happens to metabolic rate in normal rat after injection of propylthiouracil? tx and hypox rat<
decreases;
no effect
Why is production of functional thyroid hormone prevented and it mimics a diet low in iodine
propylthiouracil (PTU) blocks the attachment of iodine to tyrosine
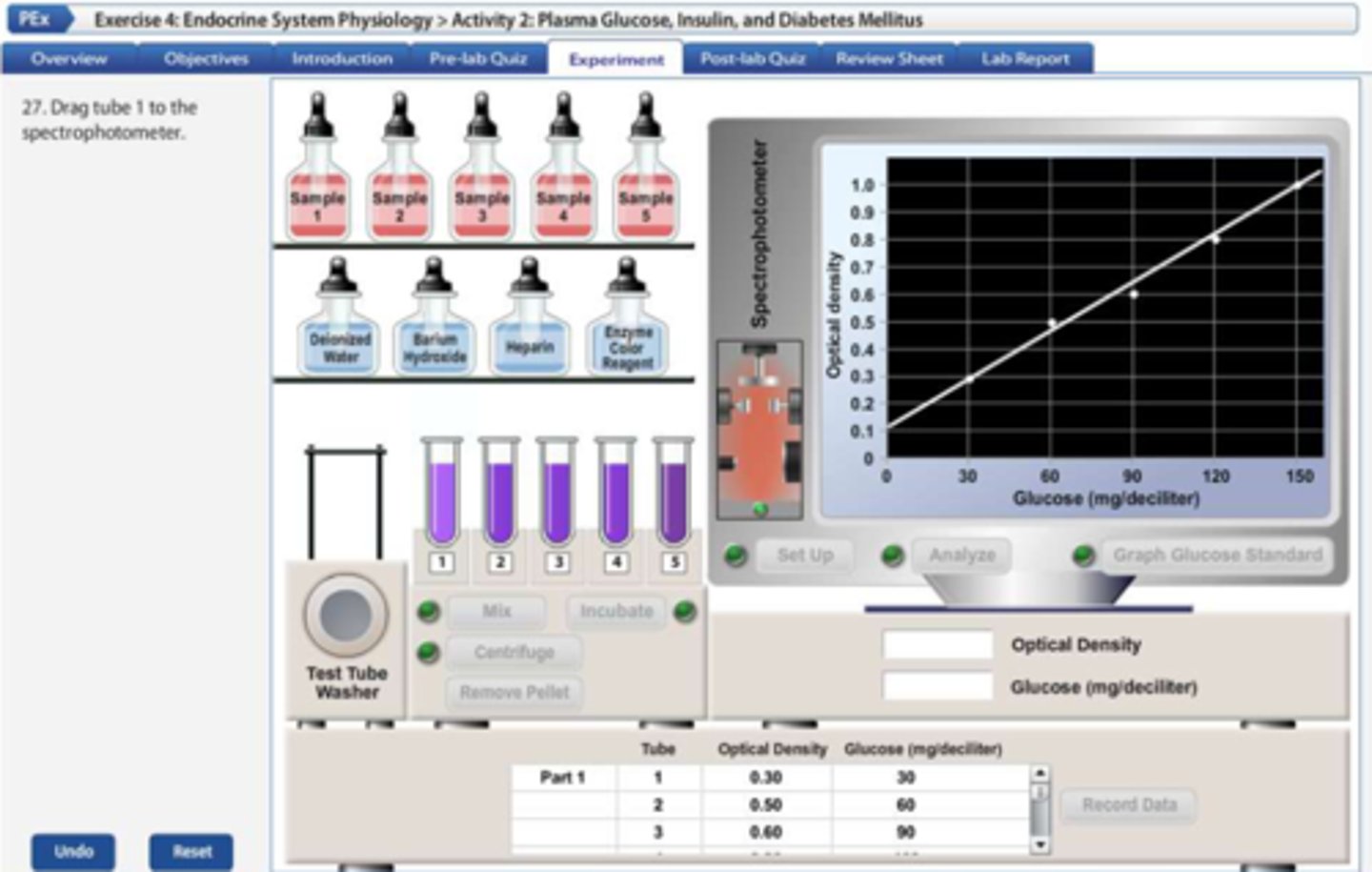
How to determine the unknown amount of glucose in a sample?
glucose standard graph
Since the optical density _______ proportionally as the amount of glucose ______, a straight line can be drawn from the optical density values.
increases; increases;
Where can blood be drawn from since there isn't a significant difference in the plasma glucose of blood in those locations?
finger or arm
What is the fasting plasma glucose of a normal person
less than 110 mg/dl
What FPG value indicates impairment of borderline impairment of insulin-mediated glucose uptake
between 110 and 126 mg/dl
What FPG value to be diagnosed with diabetes?
above 126
What diabetes occurs during pregnancy?
gestational
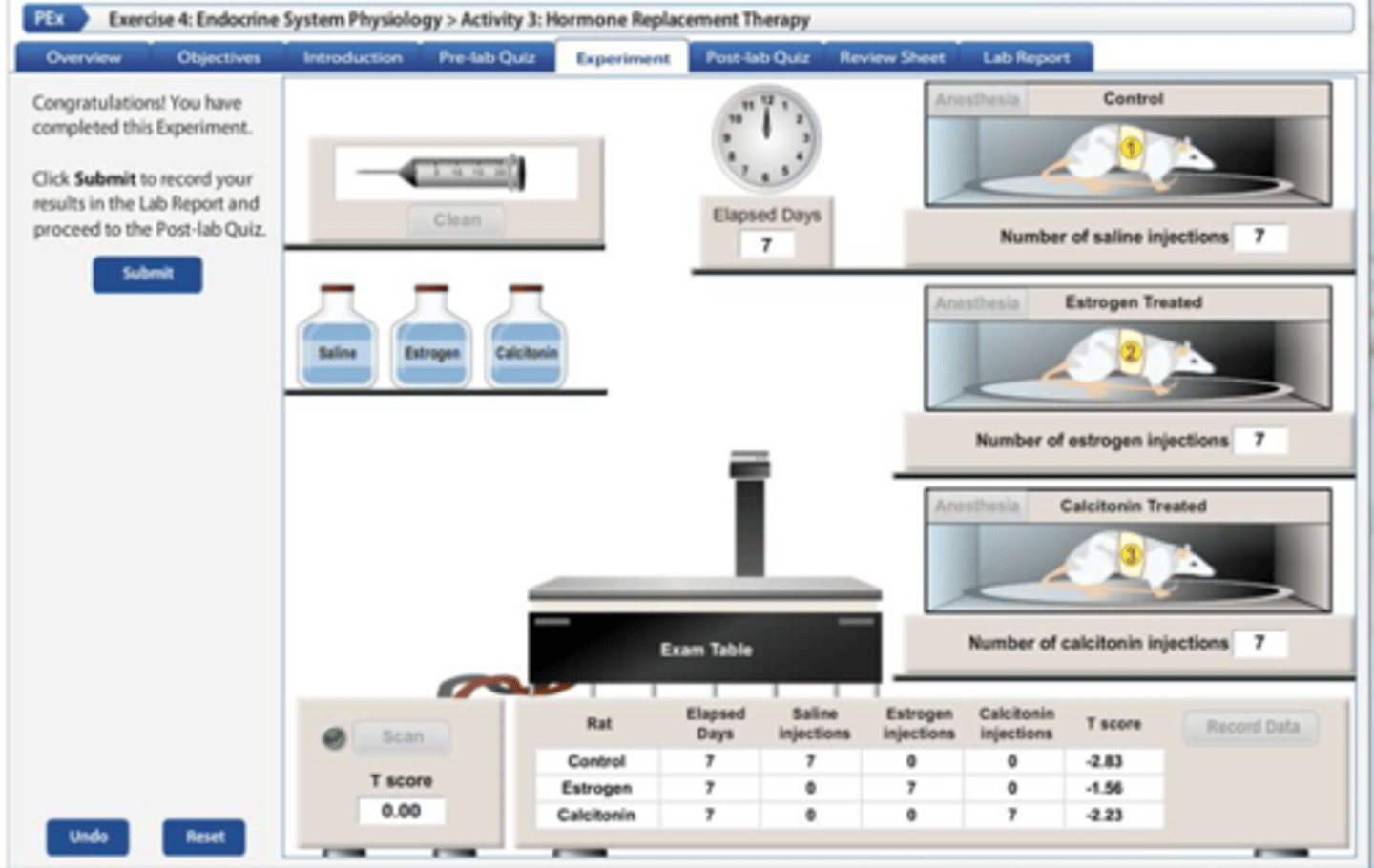
What is a T score
measurement of the mineral content of bone
Normal T score range-
Osteopenia-
Osteoporosis-
1 to -0.99
-1.0 to -2.49
-2.5 and below
what were ovariectomized rats used for in this experiment
stimulate menopause when the ovaries would stop producing estrogen
HRT with estrogen _______ the strength of the bone tissue and improved the rat's condition to osteopenia.
increased
What are the risks of HRT even though it increases bone density
increase risk of uterine/breast cancer, blood clots, and strokes
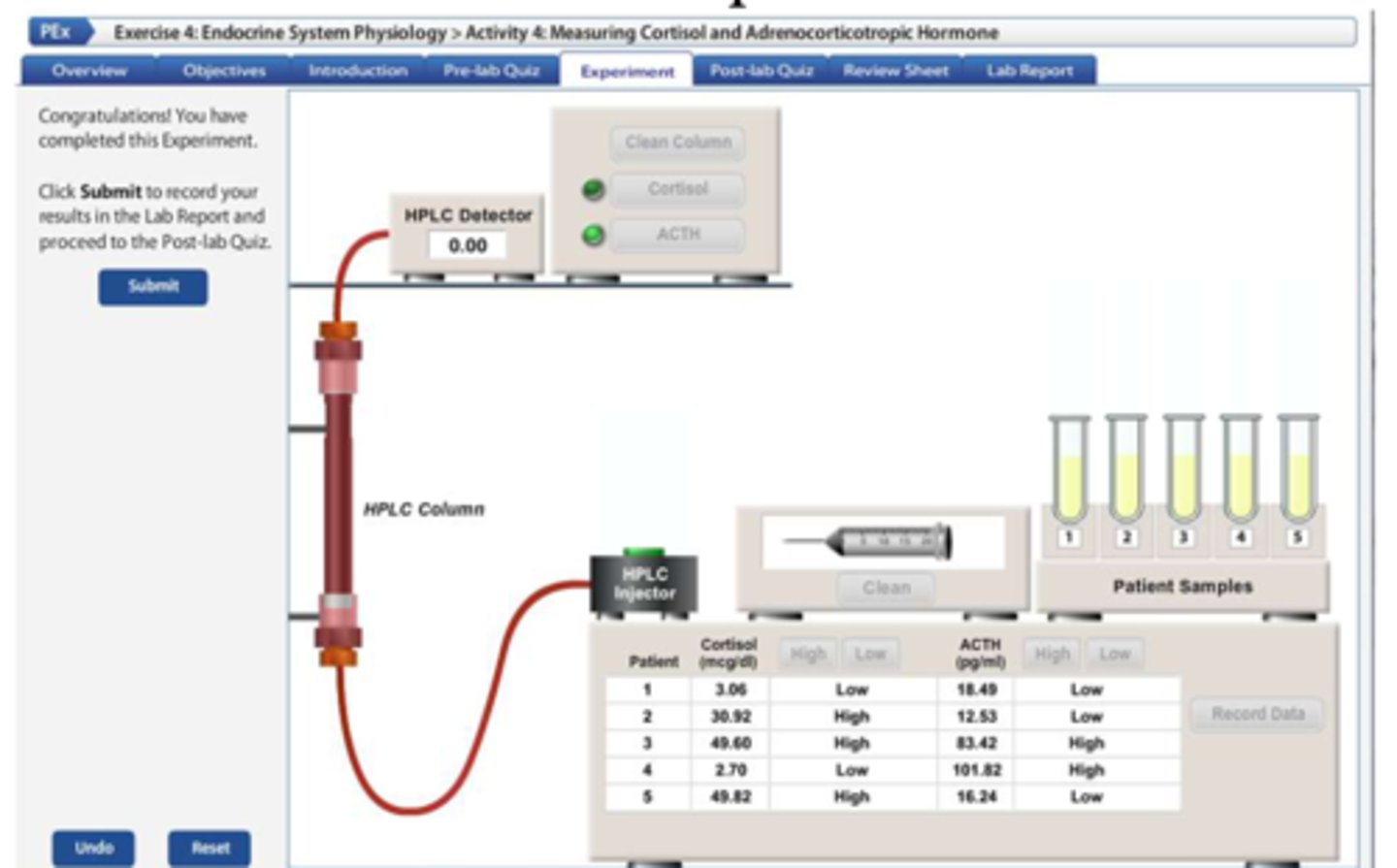
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
ACTH
stimulates the release of cortisol from the adrenal cortex
As cortisol levels rise, what can it inhibit?
the release ofCRH (from the hypothalamus) and ACTH (from the anterior pituitary)
Cushing's Syndrome
Increased blood levels of cortisol (hypercortisolism) caused by an adrenal gland tumor
Cushing's disease
hypercortisolism caused by an anterior pituitary tumor
What is the difference between Cushing's syndrome and disease?
syndrome - primary hypercortisolism caused by an adrenal gland tumor
disease - secondary hypercortisolism caused by a pituitary tumor
Addison's disease
Hypocortisolism because of destruction of the adrenal cortex
What happens in hypopituitarism
damage to the anterior pituitary causes secondary adrenal insufficiency
physioex4 activity 1 results
physioex4 activity 2 results
physioex4 activity 3 results
physioex4 activity 4 results
physioex11 activity 1 results
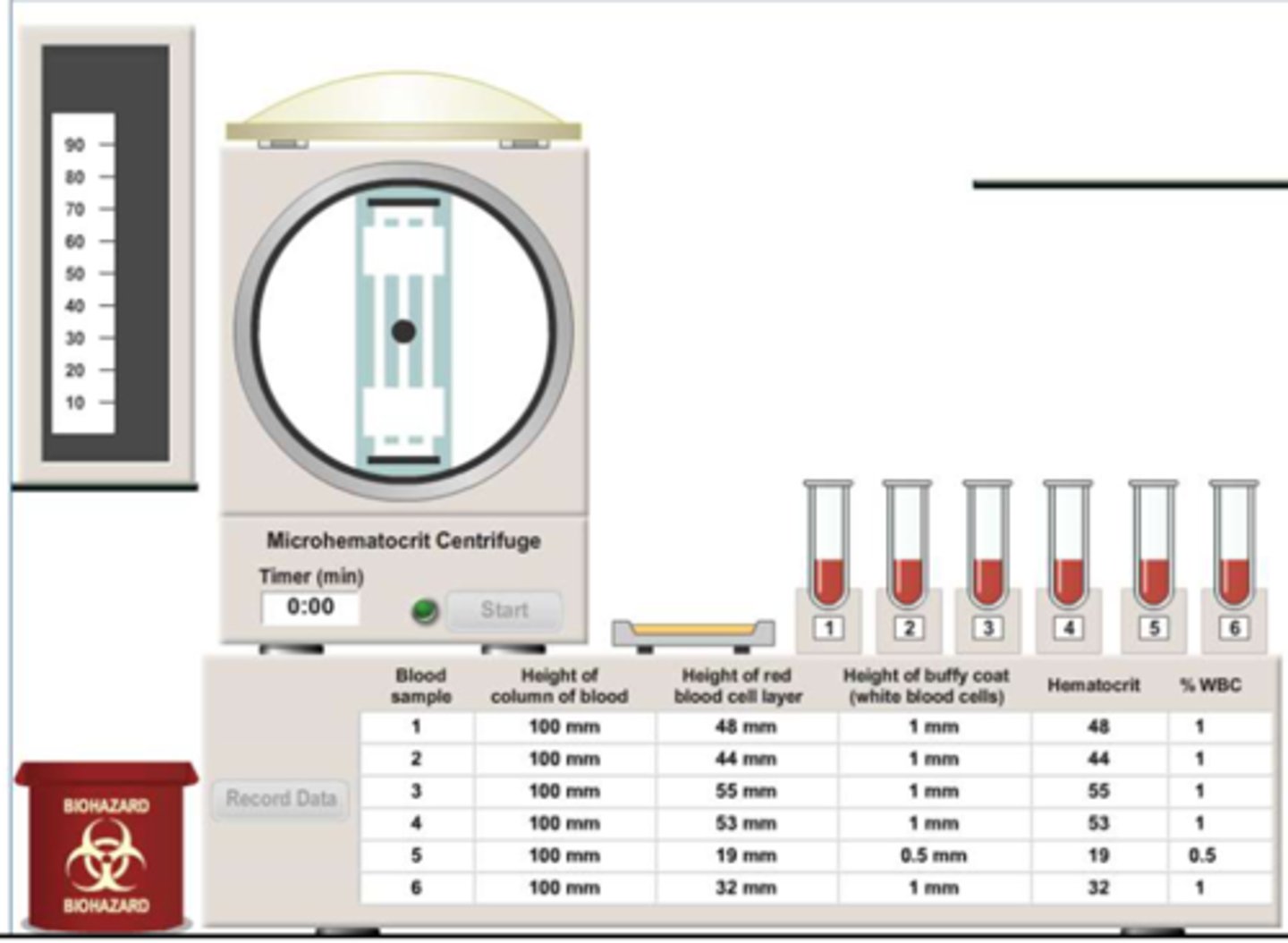

hematocrit
the height of the red blood cell layer divided by the total height of blood (packed cell volume divided by total blood volume)
Where are the heavier items (RBCs) in blood packed after cetrifugation?
the bottom
buffy coat
what is the layer of white blood cells above the RBCs called?
plasma
what is the liquid component above the buffy coat called?
erythropoietin (EPO)
what is RBC production stimulated by?
kidneys
what is EPO released from
low O2 content of blood or the sex hormone testosterone
what is EPO release triggered by
42-52% males
37-47% females
average hematocrit for males and females
Why is hematocrit higher in males?
more testosterone
What happens to RBC production at higher altitudes?
production increases
what does anemia cause
a reduction in erythrocyte population which reduces the hematocrit and oxygen transport in blood
physioex11 activity 2 results
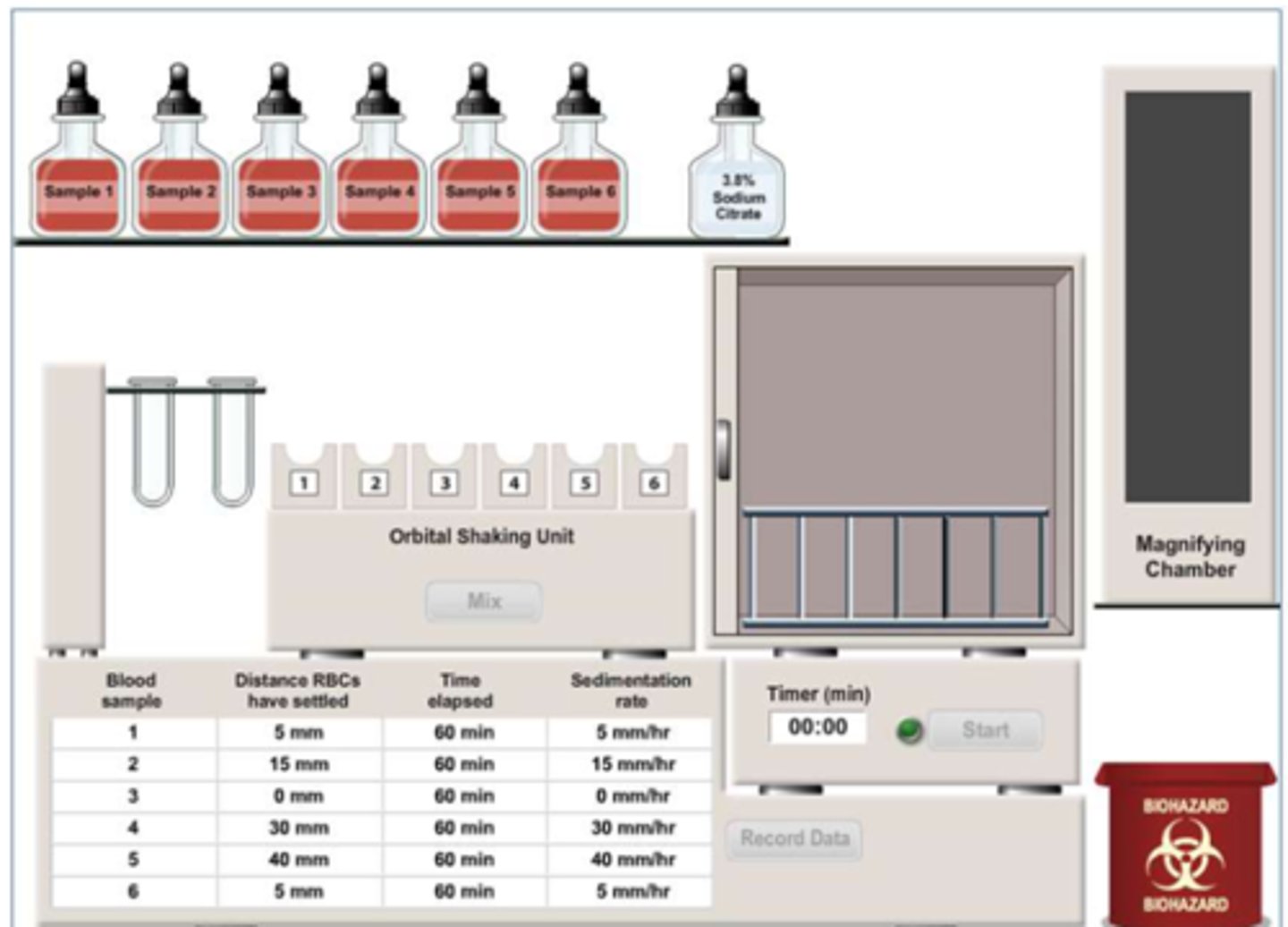
settling of RBCs is a _____ process in a normal person
slow
what does increased production of fibrinogen and immunoglobulin cause RBCs to do
clump together and/or stack up (rouleaux formation), making them heavier and settle faster
normal ESR
5 mm/hr
what diseases cause an increase in ESR
iron-deficiency anemia, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and acute pelvic inflammatory disease
Sickle Cell anemia vs iron deficiency
iron deficiency anemia shows an increased ESR, sickle cell anemia shows a lower ESR
why doesn't angina pectoris have no effect on the ESR
angina pectoris is not necessarily associated with a myocardial infarction
what does sickle cell anemia prevent
normal sedimentation
who has a higher sedimentation rate
menstruating females and people with iron deficiency
physioex11 activity 3 results

normal blood avg
12-18 g/100 ml
normal ratio of packed cell volume to hemoglobin
3:1
People live at higher altitudes, suffering from polycythemia, suffering from congestive heart failure, or suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will have _______ Hb levels
higher
People suffering from anemia, hyper thyroidism, cirrhosis of the liver, renal disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and severe hemorrhage (blood loss) will show a _______ in hemoglobin levels
decrease
physioex11 activity 4 results
what does red bone marrow produce
RBCs
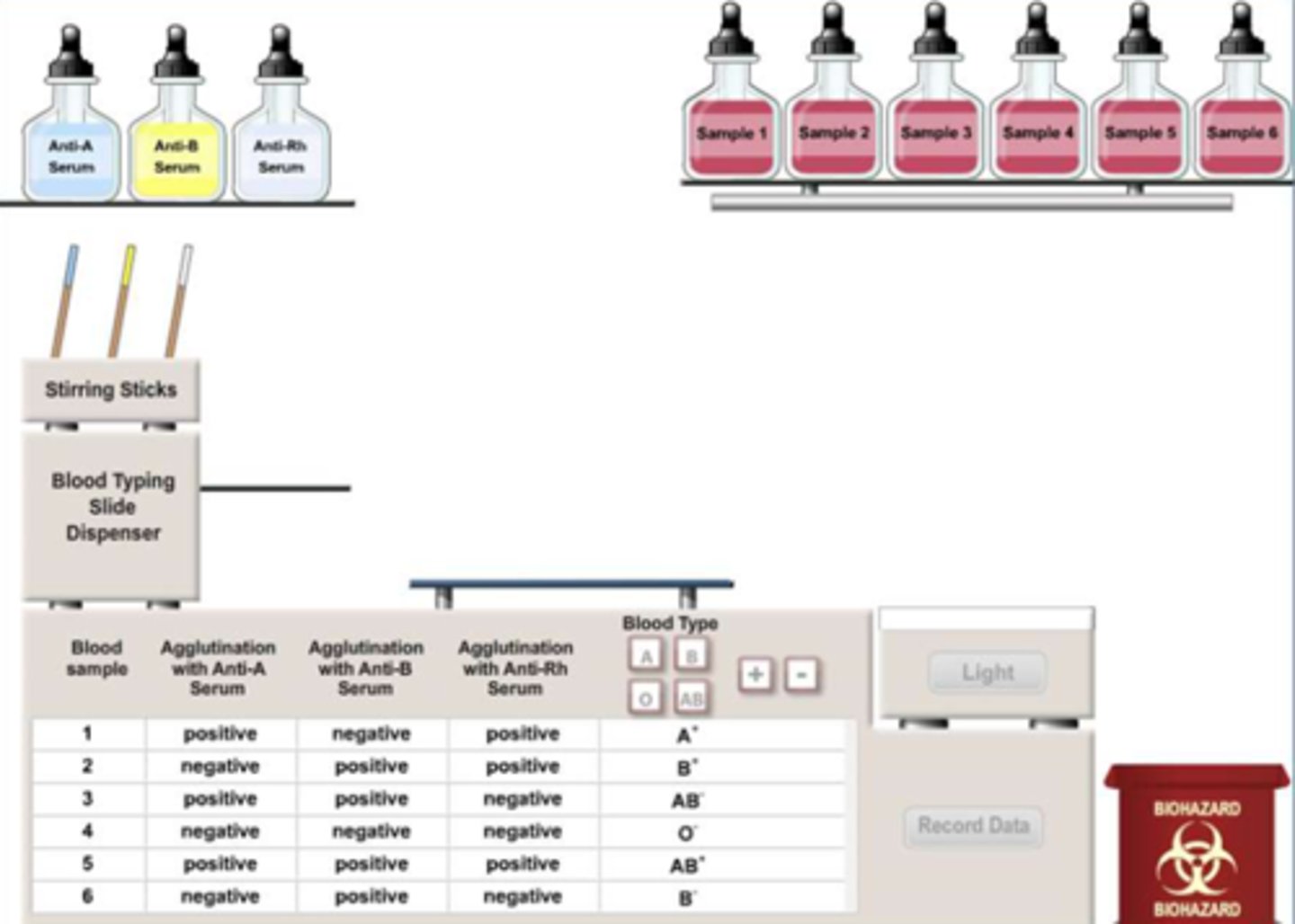
how to determine blood type
specific cell surface antigens on the plasma membrane of red blood cells