A&P of Speech Final
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Skeletal Structure
Maxilla (upper jaw and most of the hard palate)
Mandible (lower jaw)
Frontal bone
Zygomatic bone
Sphenoid bone
Temporal bone
Parietal bone
Styloid process
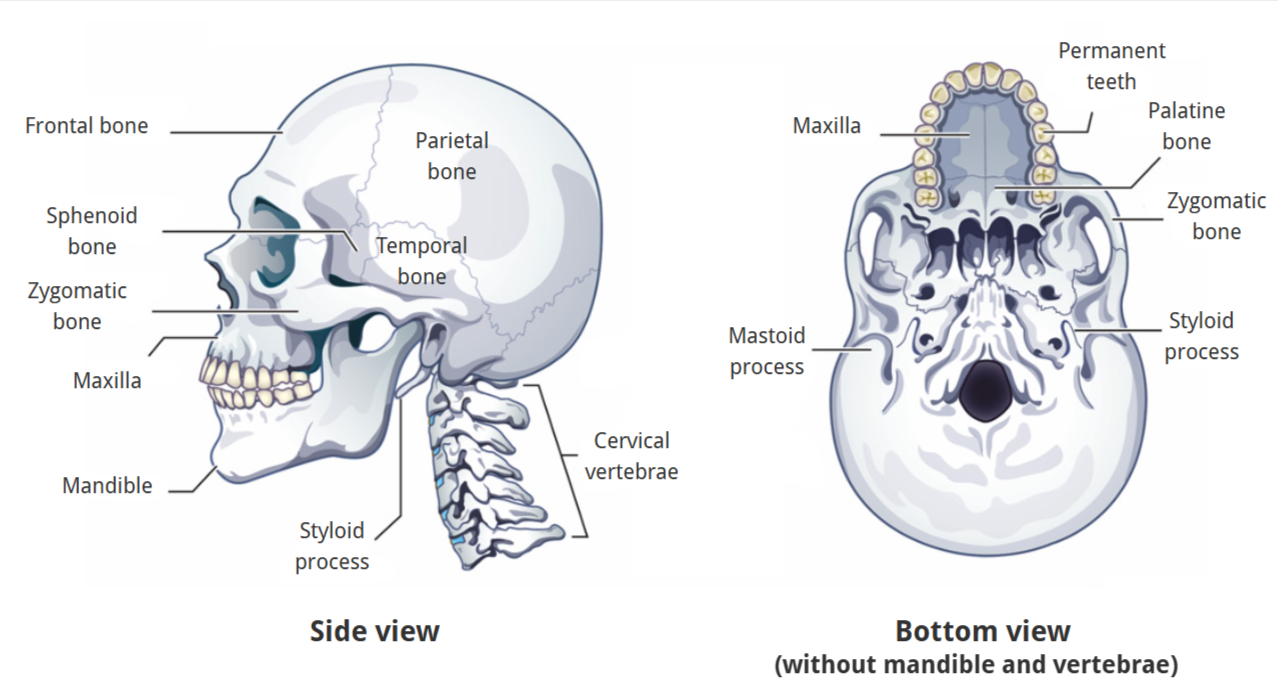
Skeletal Structure of Maxilla
alveolar process
nasal notch
facial surface
body of maxilla
permanent teeth
palatine process of maxilla
horizontal process of palatine bone
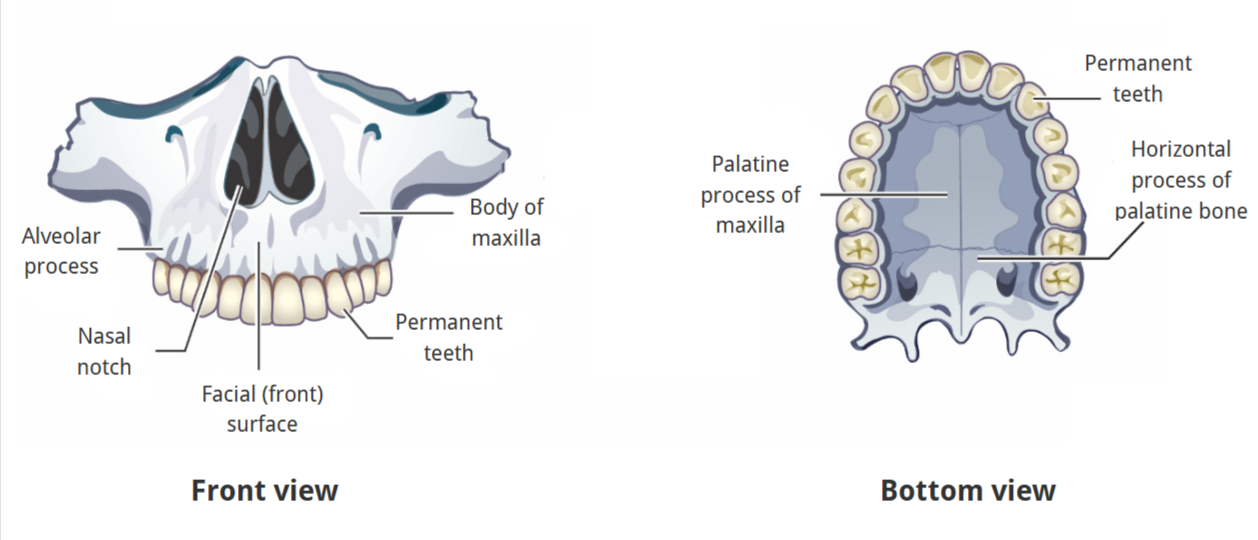
Skeletal Structure of Mandible
alveolar process
ramus
coronoid process
condylar process
body
teeth
Teeth Types
Incisors: front 2 (on each side)
Canines: 3rd tooth (on each side)
Premolars: 4 & 5th teeth
Molars: back 3 teeth
***ICPM
First teeth are developed around…?
4-6 months
teeth are important for speech
Molars
Developed later compared to many other teeth
1st usually at age 6
2nd age 12
3rd (wisdom teeth) age 18
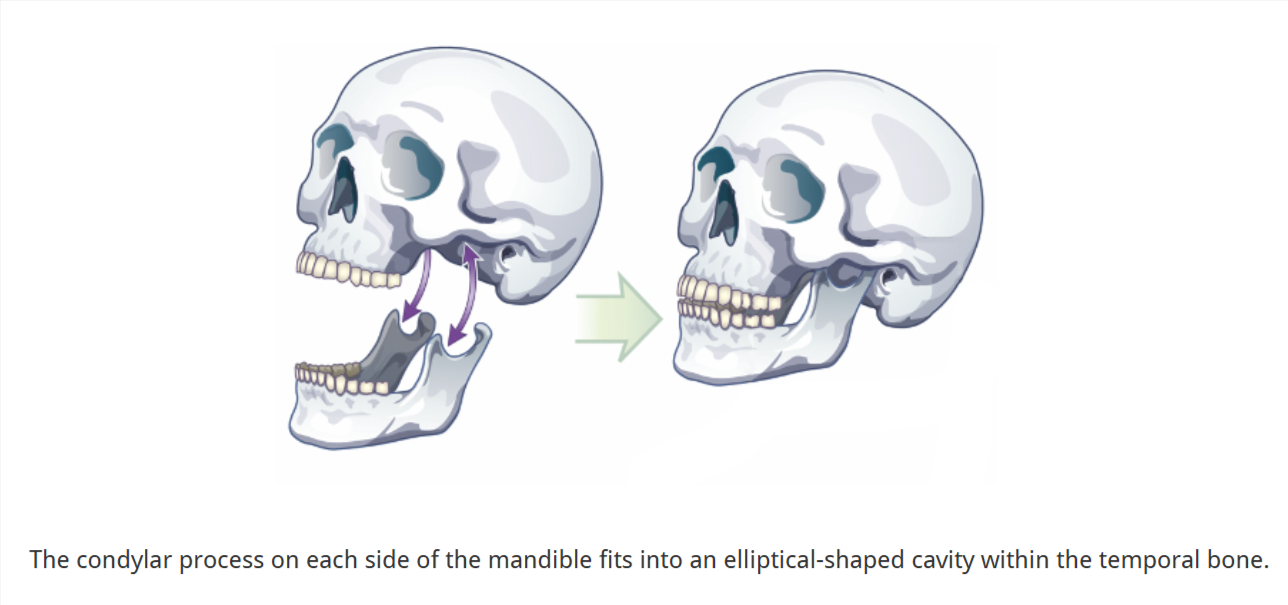
What forms the Temporomandibular Joints (TMJ)?
The mandible articulating (attaching) with the left and right temporal bones
Each TMJ is a condyloid joint
egg-shaped condylar head fits into an elliptical cavity in the temporal bone
articular surfaces of the condyle and temporal bone are covered with fibrocartilage (prevents wear and tear)
3 Temporomandibular Ligaments
Temporomandibular ligament
Sphenomandibular ligament
Stylomandibular ligament
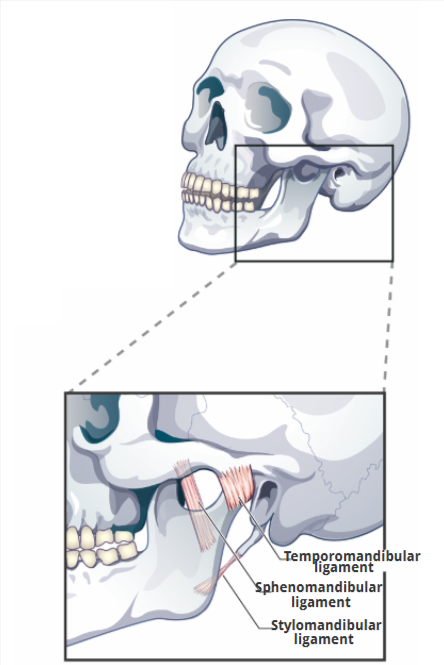
Temporomandibular ligament
limits downward and backward displacement of the condyle
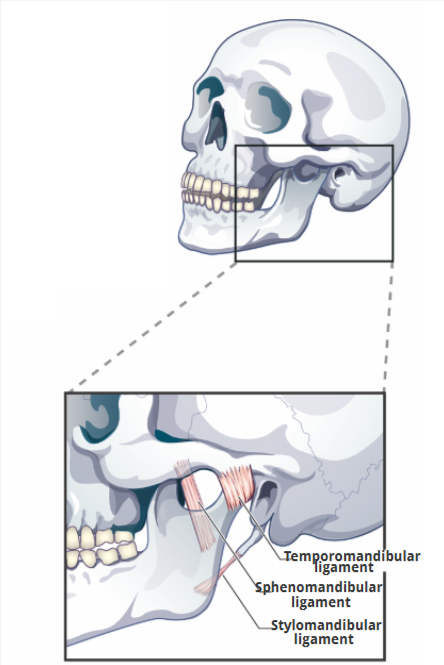
Sphenomandibular ligament
limits downward and backward displacement of the mandible
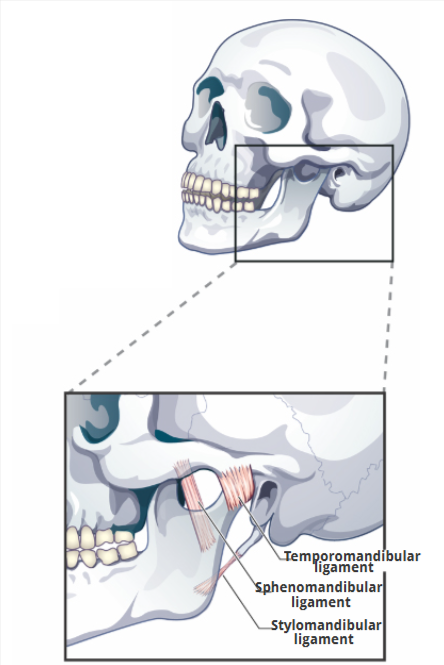
Stylomandibular ligament
limits downward and forward displacement of the mandible
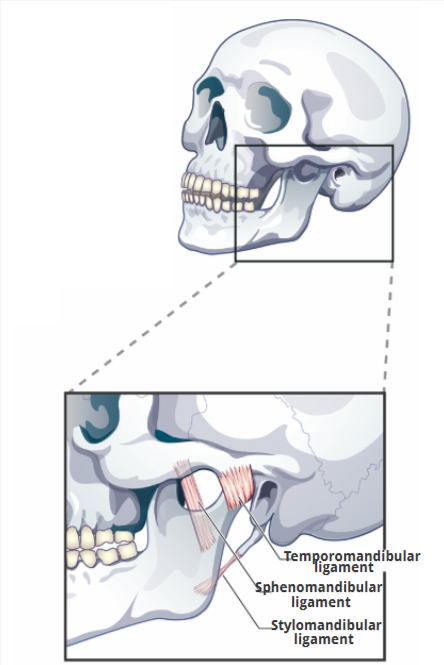
Occlusion
relationship btwn maxillary and mandibular teeth when they come together for chewing or when at rest/bones are attached and tightly closed
Movements of the mandible
Lowers and raises
Forward and back
Side to side
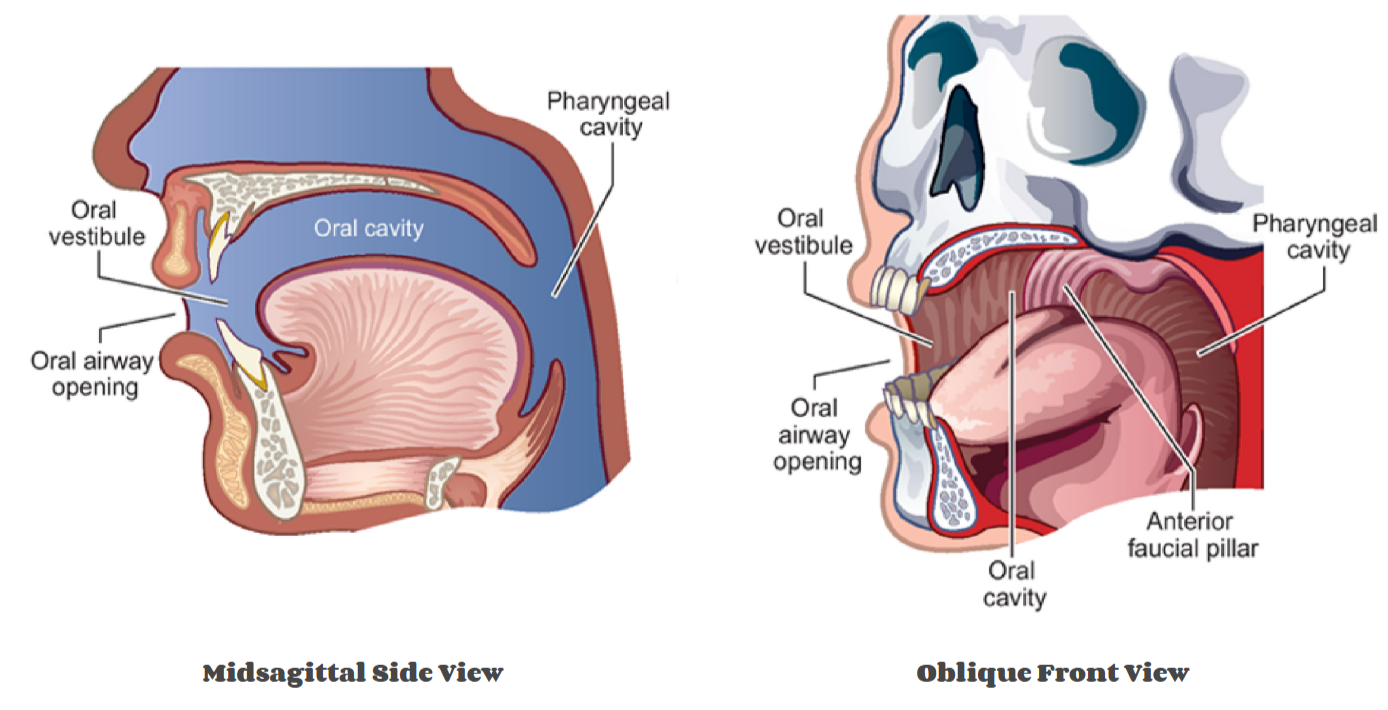
pharyngeal-oral apparatus cavities (2)
oral cavity
buccal cavity
Oral Cavity
Bounded by:
Front and sides: lips, teeth, and alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible.
Top: hard palate and velum (soft palate).
Bottom: floor of the mouth, mostly made up of tongue
Back: anterior faucial pillars (palatoglossal arches) — the tissue just behind the most posterior molars.
oral vestibule is the front entry to the oral cavity
tongue = most prominent feature
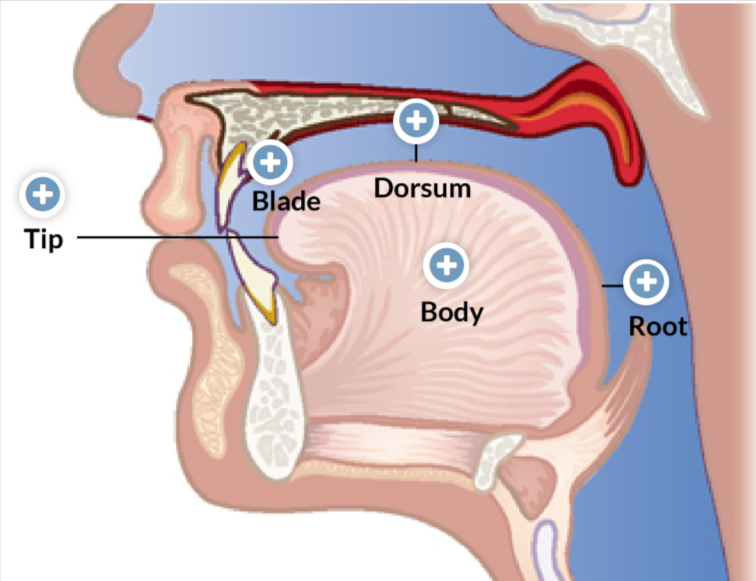
5 primary functional/anatomical subdivisions of Tongue
Tip: located nearest the front teeth when the tongue is at rest
Blade: surface region that lies behind the tip and below the alveolar ridge of the maxilla and the anterior hard palate
Dorsum: lies behind the blade and below the posterior hard palate and velum.
Root: faces the back of the pharynx and front of the epiglottis.
Body: central mass underlying the 4 other regions
Buccal Cavity
on the sides of the oral cavity, btwn teeth and cheeks
Newborns have cheek pads that:
Limit buccal space
Help direct liquids down the middle of the oral cavity for safer swallowing
As cheek pads are lost in early childhood:
The buccal space enlarges.
Increased buccal space and neuromuscular development allows for:
More precise articulation.
Mastication (chewing) of more complex food textures
post-swallow aspiration risk
Food can collect in the buccal spaces
Oral Membranes
Inside of the mouth (except tongue, hard palate, and gums): lined with shiny squamous epithelium
Masticatory mucosa: covers the gums and hard palate
surface of the tongue: covered with specialized mucosa
Inside of the mouth (except tongue, hard palate, and gums) is lined with shiny squamous epithelium that:
Produces surface liquid to keep the mouth moist
Provides comfort and allows for smooth, rapid movement during speech
Masticatory mucosa covers the gums and hard palate:
Has collagen subflooring that makes the epithelium firmly attached to bone.
The surface of the tongue is covered with specialized mucosa that contains:
Taste buds.
Sensory nerve endings for temp and pressure detection.
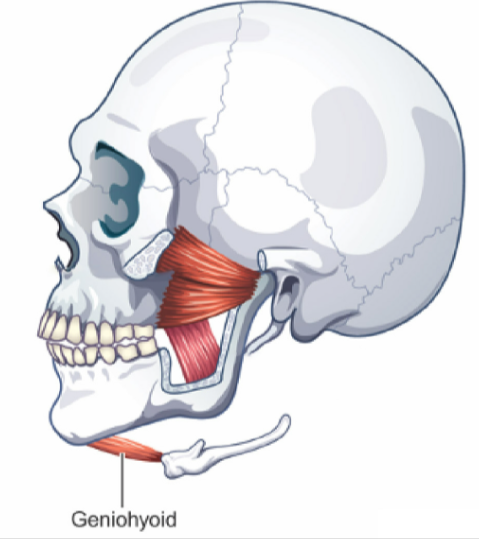
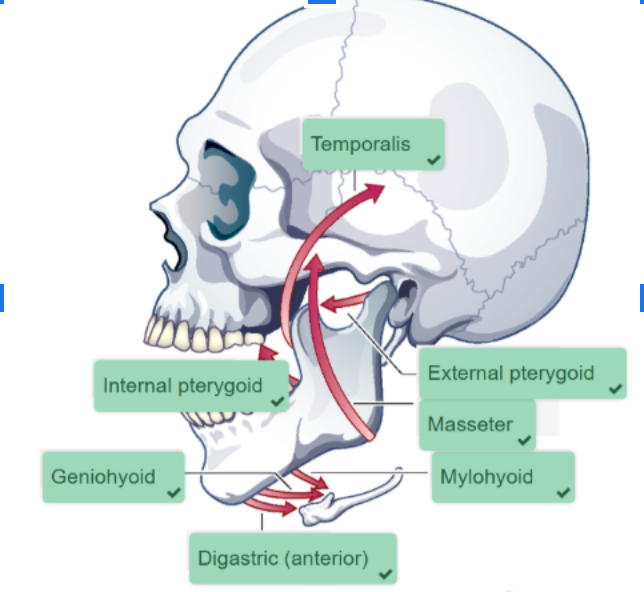
Muscles of the Mandible (7)
Masseter
Temporalis
Internal (Medial) Pterygoid
External (Lateral) Pterygoid
Digastric
Mylohyoid
Geniohyoid
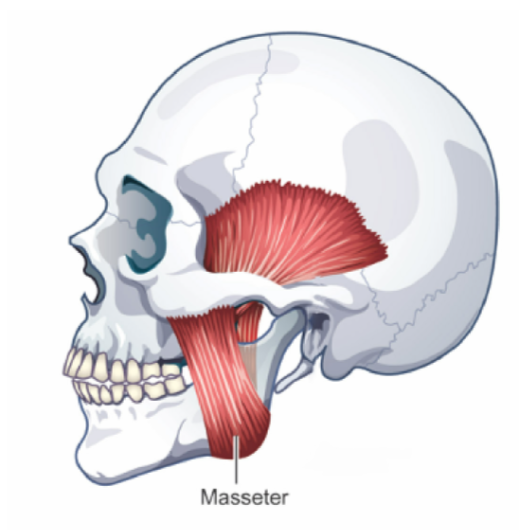
Masseter
ELEVATES (closes) and RETRACTS Mandible
muscle covering the outer surface of the mandibular ramus
Has two layers
outer (larger)
inner (smaller)
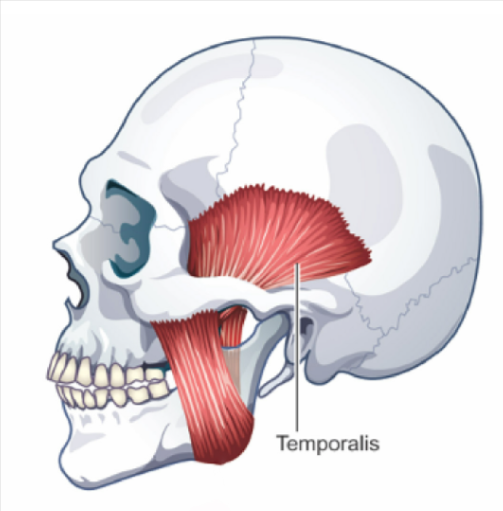
Temporalis
ELEVATES (closes) and RETRACTS Mandible
muscle that covers much of the side of the cranium (temporal bone)
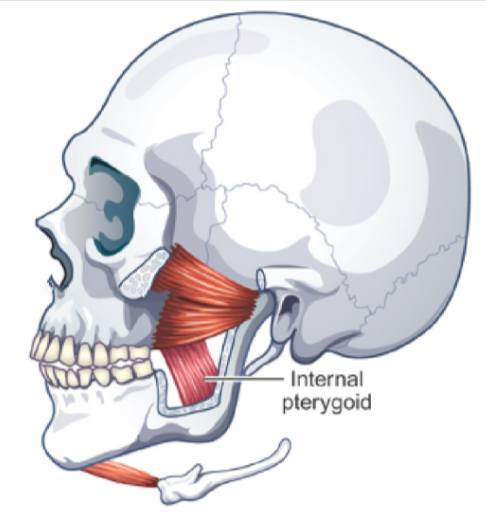
Internal Pterygoid
ELEVATES (closes) mandible
one-sided contraction = jaw moves toward opposite side (helps w/ chewing)
parallel to the masseter
together, they form a muscular sling that surrounds the angle of the mandible, strapping the ramus of the mandible to the skull
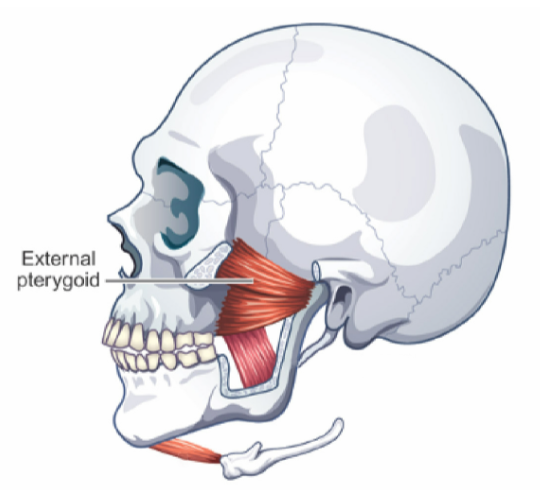
External Pterygoid
Slides condyle DOWN and FORWARD (helps open jaw and protrude it)
one sided contraction = chin area moves toward opposite side (helps w/ chewing)
smaller muscle of the mandible
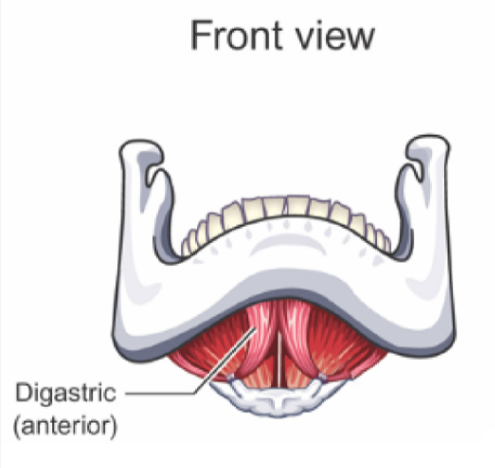
Digastric
LOWERS Mandible (opens mouth) and ELEVATES hyoid bone and larynx
Not directly attached to hyoid bone
similar to Mylohyoid and Geniohyoid
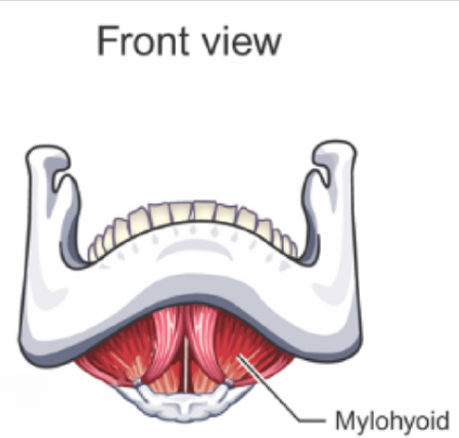
Mylohyoid
LOWERS mandible (opens mouth) and ELEVATES hyoid bone and larynx
Connected to lower structure of mandible
similar to Digastric and Geniohyoid
Geniohyoid
LOWERS mandible (opens mouth) and ELEVATES hyoid bone and larynx
Connected to lower structure of mandible
similar to Digastric and Mylohyoid
Muscles of the Mandible
complete
Movements of the Mandibular Muscles
Elevation and depression
Protrusion and retraction
Lateral movement
Muscles of the Tongue