OB Chapter 3: Genetics, Conception, and Reproductive System
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Genes
Formed by DNA and Proteins
Genotype
A persons genetic makeup
phenotype
The way in which these genes are outwardly expressed in physical traits
Advances in genetics
the study of heredity
focuses on single genes
genomics
study of genes and their function and related to technology
focuses on all genes
Recessive Genes
genetic disease and disorders are related defective__________
Autosomal-recessive
One defective gene carries disorders but doesn’t mean person has disorder
Ex. Sickle Cell, Cystic Fibrosis, Thalassemia, Tay-Sachs Disease
Autosomal- Dominant
one or both genes in pair carry defect
Huntington’s
Xeroderma Pigmentation
X-linked inheritance
X chromosome is mutated gene
Male child mutated x chromosome will have disorders ( recessive→ dominant)
Male children Y chromosome → father to son only
Female children mutated X chromosome→ no disease
Ex. hemophilia
Genomic Medicine
Medical discipline using genomic information about patient to provide clinical care and outcomes.
Newborn screenings for inherited diseases
cell - free circulating DNA (biomarker factor)
pharmacogenetics
drug therapy for genetic disease
Genetic Testing
used to identify individuals who carry gene mutation when there is family history of genetic disorder
→ detect changes in embryos
ex. downs syndrome, hemophilia, Tay-sach’s disease
Risk factors of genetic disorders
Pregnant mother who is over 35 y/o has a little boy and uncle with downs syndrome.
Teratogens
drugs, viruses, and infections that can cause birth defects or death to fetus.
What is teratogenic exposure based on?
length, amount and when exposure occurs
When is the fetus most vulnerable to teratogens?
8 weeks of gestation during organogenesis
Examples of drug teratogens
alcohol
ace inhibitors
Carbamazepine (anticonvulsants)
cocaine
warfarin→ abortions and hemorrhaging
Examples of viral teratogens
Chicken pox
Rubella
Syphilis
Toxoplasmosis
Zika
Cytomegalovirus
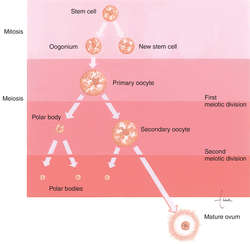
oogenesis
Anterior pituitary gland secretes FSH hormone which causes the growth of follicles that secrete estrogen that causes the maturing of the ovum
Conception
fertilization of the egg within the outer third of the fallopian tubes
→ oocyte to zygote
mature ovum enters fallopian tube
sperm travels to fallopian tubes
ovum is fertilization
Where is sperm and maturated at?
epididymis
what hormones does the functional layer of the uterus secrete?
estrogen and progesterone which thickens wall
follicular phase
from first day of mensuration + 12-14 days after
Graafian follicle
__________matures due to LH & FSH hormone which produces estrogen
Estrogen peaks
What action causes ovulation to begin which release oocyte
Proliferation phase
Occurs after mensuration and ends with ovulation
endometrium becomes thicker
Hint: part of the endometrial cycle
secretory phase
Occurs after ovulation and ends with mensuration
progesterone secreted from corpus luteum
Hint: part of the endometrial cycle
what is the purpose of glycogen being released from the corpus luteum?
Energy source for blastocyst
What week should all organs of the fetus be formed ?
week 8
The heart is formed by week ___ of gestation and begins to beat by week ___.
three; four
12 weeks ( 9cm/45g)
RBC produced in the liver, plate infusion, sex can be identified, eyelids are fused closed, FHR can be heard with doppler.
16 weeks ( 14cm/200g)
Lanugo on head, Meconium in intestine, teeth begins to form, sucking motions are made w/ the mouth skin transparent
20 weeks (20cm/450g)
Lanugo covers entire body, vernix caseosa covers the body, nails are formed, brown fat begins to develop
24 weeks (30cm/820g)
alveoli form in the lungs and begin to produce surfactant, footprints and fingerprints are forming, respiratory movement detected
28 weeks (37cm/1300g)
eyelids are open, adipose tissue develops rapidly. the respiratory system has developed to a point where gas exchange is possible but lungs are not fully mature.
32 weeks (42cm/2100g)
bones are fully developed. lungs are maturing increased amounts of adipose tissue.
36 weeks (47cm/2900g)
Lanugo begins to disappear. labia majoria and minora are equally prominent. testes are in upper portion of scrotum.
40 weeks (51cm/ 3400g)
fetus is considered full term at 38 weeks all organs and system are fully developed.
what prevents mothers and baby’s blood from mixing?
placenta membranes
placenta, Fetal waste products and CO2 if transferred from fetal blood to _____________ by diffusion
maternal sinuses
glucose, amino acids, and o2 transferred from the maternal blood sinuses by _________
Active transport
what is the functions of progesterone?
facilitates implantation
decreases uterine contractility
what are the functions of estrogen?
enlargement of the breast and uterus
maturing of graafian follicle
what is the function of hcg hormone?
stimulates the corpus luteum so it will continue to secrete estrogen and progesterone until placenta is mature
rises rapidly during first trimester
assessed in pregnancy tests.
what does the HPL (human placental lactogen)functions?
promotes fetal growth by regulating available glucose and stimulates breast development in preparation for lactation
At what week is the placenta fully functional?
8-10 weeks
The __________ inner membrane is developed from embryoblast and its outer membrane is formed by trophoblast. _____________ provides a sterile environment for the fetus.
amniotic sac
what is formed by the amniotic membrane during the first trimester but then if formed by the fetal kidneys during the second and third trimester?
amniotic fluid
what are the functions of amniotic fluid1?
cushions the fetus from sudden movement
prevents fetus to adhere to amniotic membranes
allows fetal freedom of movement
provides consistent thermal environment
polyhydramnios
excess amount of amniotic fluid
risk facto for chromosomal, GI, cardiac, neural tube
Oligohydramnios
decreased amount of amniotic fluid
risk facto for congenital renal problems
the umbilical cord connect the fetus to the placenta and consist of two ________ umbilical vessel and one umbilical _______.
arteries; vein
if there is only one umbilical vein and artery what is the fetus more at risk for ?
cardiac and vascular defects
umbilical arteries carry _________ blood and umbilical veins carry blood
Unoxygenated; oxygenated
How is infertility defined / diagnosed?
inability of conceive after 12 months of unpretected sex.
Male causative factors for infertility include
endocrine issues
pituitary disease
hypothalamic disease
decreased levels of LH, FSH and testosterone
sperm antibodies that react against sperm causing a decrease in sperm motility
blocked structures of the male reproductive system
erectile dysfunction
gonadotoxins include
Drugs ( chemotheraputics, calcium channel blockers, alcohol and heroin)
Infections and viruses ( STI’s, mumps, prostatitis
systemic illness
Prolonged heat exposure to the testes( hot tubs, tight underwear, frequent cycling)
pesticides
radiation
what are the female factors that can lead to infertility
ovulatory dysfunction
hormonal imbalances
hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
high levels of prolactin
menopause before 40
damage to fallopian tubes (related to Pelvic inflammatory disease(PID) or endometriosis
cervical surgeries (cryotherapy)
risk factor for infertility for women include
autoimmune disorders
diabetes
eating disorders / malnutrition
alcohol
excessive exercising
obesity
older age
gonadotoxin therapy
diagnostic test for infertility include
STI screenings
Hormone test
semen analysis
detecting LH surge
Ovarian reserve testing
a nurse is taking care of a male patient who is at risk for infertility. what information should she be aware of regarding the semen analysis?
abstain from masturbating 2-3 days
specimens must be collected with in an hour and taken to facility
semen analysis includes the checking the volume, concentration, motility and morphology of sperm.
treatment for infertility includes
Male
hormone therapy
lifestyle changes
corticosteroids
antibodies to clear infections '
repair hernias
Female
lifestyle changes
drug therapy → letrozole, injectable gonadotropins, GnRH pump, bromocriptine and Clomiphene Citrate (clomid)→ stimulates the release of LH FSH to promote ovulation
Artificial insemination
Sperm that has been removed from semen is deposited directly into the cervix or uterus using a plastic catheter
The sample is collected by masturbation then sperm are separated from the semen and prepared for insemination. Sperm can be from partner or donor.
Reasons for procedure:
poor cervical mucus production due to previous surgery of the cervix
anti-sperm antibodies
decreased amount of sperm
decreased sperm motility.
Testicular sperm aspiration
Sperm are aspirated or extracted directly from the testicles then it is microinjected into the harvested eggs of the female partner.→ intra-cytoplasmic injection.
had an unsuccessful vasectomy reversal
have an absence of vas deferens
have an extremely low sperm count or no sperm in their ejaculated semen.
IVF
oocytes are harvested and fertilization occurs outside the female body in a laboratory.
Zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT)
zygote is placed into the fallopian tube via laparoscopy 1 day after the oocyte is retrieved from the woman and IVF is used
Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
In GIFT, sperm and oocytes are mixed outside the woman’s body and then placed into the fallopian tube via laparoscopy. Fertilization takes place inside the fallopian tube.
This procedure is used when there has been (1) a history of failed infertility treatment for anovulation, (2) unexplained infertility, and (3) low sperm count.
ET
ET is when, through IVF, an embryo is placed in the uterine cavity via a catheter.
Example of fertility condition in which this procedure is used is when the fallopian tubes are blocked