Weather Briefing - Final Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
Automated Surface Observation System
What does A.S.O.S stand for?
2
New cards
6 hours, November to March (Cold months)
What is the time difference between UTC and CST and what months is it in effect?
3
New cards
5 hours, March to November (Warm months)
What is the time difference between UTC and CDT and what months is it in effect?
4
New cards
Displays wind shear, providing important information about storm motion, supercells/multicells, and cell splitting.
What does a hodograph provide us with?
5
New cards
Surface, 1000mb, 925mb, 850mb, 700mb, 500mb, 400mb, 300mb, 250mb, 200mb, 150mb, 100mb
What are the mandatory levels?
6
New cards
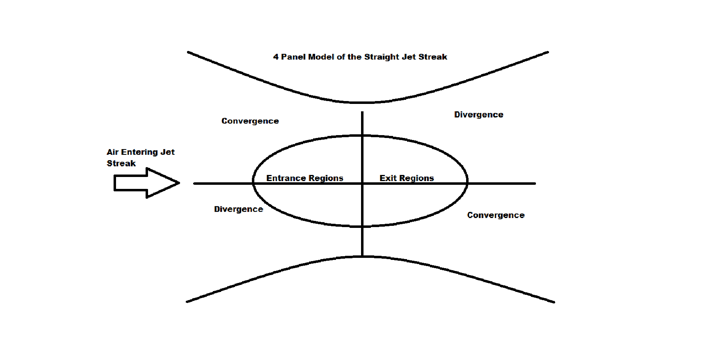
\
Jet Streak Model
7
New cards
Around 500mb
What is the level of non-divergence?
8
New cards
Wind blows from a region of cold air to a region of warmer. Occurs on the backside of a low. Produces a sinking motion. Associated with subsidence and clear sky.
Describe CAA (Cold Air Advection)
9
New cards
Wind blows from a region of warm air to a region of cooler air air. Occurs ahead of a low. Produces an upward motion. Associated with cloud formation and precip.
Describe WAA (Warm Air Advection)
10
New cards
Low thickness corresponds to cold air and high thickness implies warm air.
Which is larger, 1000-500mb thickness in warm air or cold air?
11
New cards
lines of equal atmospheric pressure
What is an isobar?
12
New cards
lines of equal temperature
What is an isotherm?
13
New cards
lines of equal wind speed
What is an isotach?
14
New cards
This is the area between the troposphere and the atratosphere. Characterized by temperatures that stop decreasing and remain steady before increasing in the stratosphere. Usually at the 200mb level.
What is the tropopause and where is it usually located?
15
New cards
when the air temperature increases with height.
What is an inversion?
16
New cards
4-9 degrees Celcius per kilometer
What is the moist adiabatic lapse rate?
17
New cards
9.8 degrees Celcius per kilometer
What is the dry adiabatic lapse rate?
18
New cards
Look for WAA and CAA, LLJ
What to look for at 850mb?
19
New cards
Look for areas of significant moisture, vertical velocity
What to look for at 700mb?
20
New cards
Look for areas of positive/negative vorticity, ridges/troughs
What to look for at 500mb?
21
New cards
Locating the jet stream, upper level divergence
What to look for at 250mb?
22
New cards
Look for fronts, highs/lows, and their respective strengths
What to look for at surface level?
23
New cards
Ratio of the mass of water vapor to the mass of dry air in a sample of moist air
Mixing Ratio
24
New cards
The mixing ratio that a parcel of air would have if it were saturated
Saturation Mixing Ratio
25
New cards
The temperature that a parcel of dry air would have if it were brought dry adiabatically from its original position to a pressure of 1000 mb.
Potential Temperature
26
New cards
The part of the total atmospheric pressure that is contributed by water vapor
Vapor Pressure
27
New cards
the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor
Dewpoint Temperature
28
New cards
the ratio of the amount of water vapor in a parcel to the amount of water vapor that the parcel could hold if it were saturated
Relative Humidity
29
New cards
the ratio of water vapor to dry air in a particular mass (mositure content)
Specific Humidity
30
New cards
the temperature that a moist air parcel would have if all water vapor in it were condensed out at constant pressure and adiabatically
Equivalent Temperature
31
New cards
the temperature a parcel at a specific pressure level and temperature would have if it were raised to 0mb, condensing all moisture from the parcel, and then lowered to 1000mb
Equivalent potential temperature
32
New cards
the height to which a parcel of air, if heated sufficiently, from below will rise adiabatically until it is just saturated. This is the height of the base of cumuliform clouds produced by surface heating
Convective Condensation Level (CCL)
33
New cards
the surface temperature that must be reached to start formation of convection clouds by surface heating
Convective Temperature
34
New cards
the height at which a parcel of air becomes saturated when it's lifted dry-adiabatically
Lifting Condensation Level
35
New cards
height at which a parcel of air that is lifted dry OR moist adiabatically becomes less dense (warmer) than the surrounding air
Level of Free Convection
36
New cards
the max energy available on an ascending air parcel. this is often called positive area, which is proportional to the amount of kinetic energy the parcel can gain from the environment
Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE)
37
New cards
the energy needed to lift an air parcel vertically and pseudo-adiabatically from its originating level to its level of free convection
Convective Inhibition (CIN)
38
New cards
the height where the temp. of a positively buoyant parcel of air becomes equal to the surrounding atmosphere and above this level the parcel becomes negatively buoyant
Equilibrium Level
39
New cards
When the winds go in a clockwise direction from the surface.
What is veering?
40
New cards
When the winds go in a counterclockwise direction from the surface
What is backing?
41
New cards
From the dewpoint curve, follow a saturation mixing ratio line upward. From the temperature curve follow a dry adiabat line upward. Where these lines intersect is the LCL.
How do you find the Lifted Condensation Level (LCL)?
42
New cards
From the LCL, proceed upward along a moist adiabat until you intersect the temperature curve. The intersection is the LFC.
How do you find the Level of Free convection?
43
New cards
From the temperature curve at the given pressure level follow the dry adiabat line that intersects the temperature curve down to 1000mb. The temperature value at this intersection is the potential temperature.
How do you find the potential temperature?