geography coasts revision
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
depositional landforms
the process where a transporting agent loses energy and drops sediment
a beach as dynamic equilibium
sediment erodes from the beach during a storm and with constructive waves
sediment deposited offshore
waves forced to break out sea. energy is dissipated and reduces erosion of beach
after storm, constructive waves return / redistribute sediment from the offshore bar back to the beach
sections of the coastal zone (…shore)
inshore - between the point where waves meet on the Low Water Mark
foreshore - are between high water mark and low water mark
nearshore - are in the LWM and where waves begin to break
backshore - area beyond the HWM and landward limit of marine activity

sediment cells
a stretch of coastline within which the process of erosion, transportation and deposition operate, and the movement of sediment is largely self-contained
sources of sediment in sediment cells
Marine organisms (coral, shells etc)
Weathering an mass movement
Rivers and estuaries
Offshore currents, waves, tides etc
Longshore currents
Cliff erosion
marine process - erosion
hydraulic action - wave power hits cliffs, loosening interior of joints. cavitation is similar but involves the effervesce of rocks to create a mini explosion
wave quarrying / pounding - high ernertgy waves hit the cliff, it can remove large chunks of rock in ojne go through vibration
corrasion / abrasion - when high energy waves carry pebbles which then hit the cliff face, chipping away fragments when the wave breaks.
solution – weak carbonic acid in seawater dissolves rock at the coastline and breaks it down (particular if it contains calcium carbonate e.g. limestone and chalk)
attrition – rocks and boulders loosened from the coastline are ground, smoothing and rounding the boulders to become pebbles, which become shingle, which become sand
sub-aerial processes - weathering
salt weathering - salt evaporates living crystals which expand in rocks widening cracks
wetting / drying - rock asborbs and release moisture as tides rise and fall leading to a loss of interconnectedness
freeze-thaw action - sub zero air causes water in rocks to freeze and expand
chemical solution – minerals in coastal rocks are dissolved by chemicals in sea water and acid rainfall
biological weathering – plant roots enlarge rock fissures, nesting marine organisms and birds that drill into the rock such as the piddock
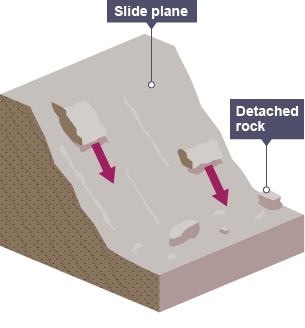
mass movement: rock fall
loose fragments of rock breaks of a cliff face and fall onto the beach, creating talus / scree at the base of the cliff
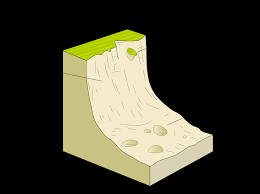
mass movement: landslide
blocks of rock become dethatched from the cliff face and slide down, occurs when bedding planes dip towards the sea
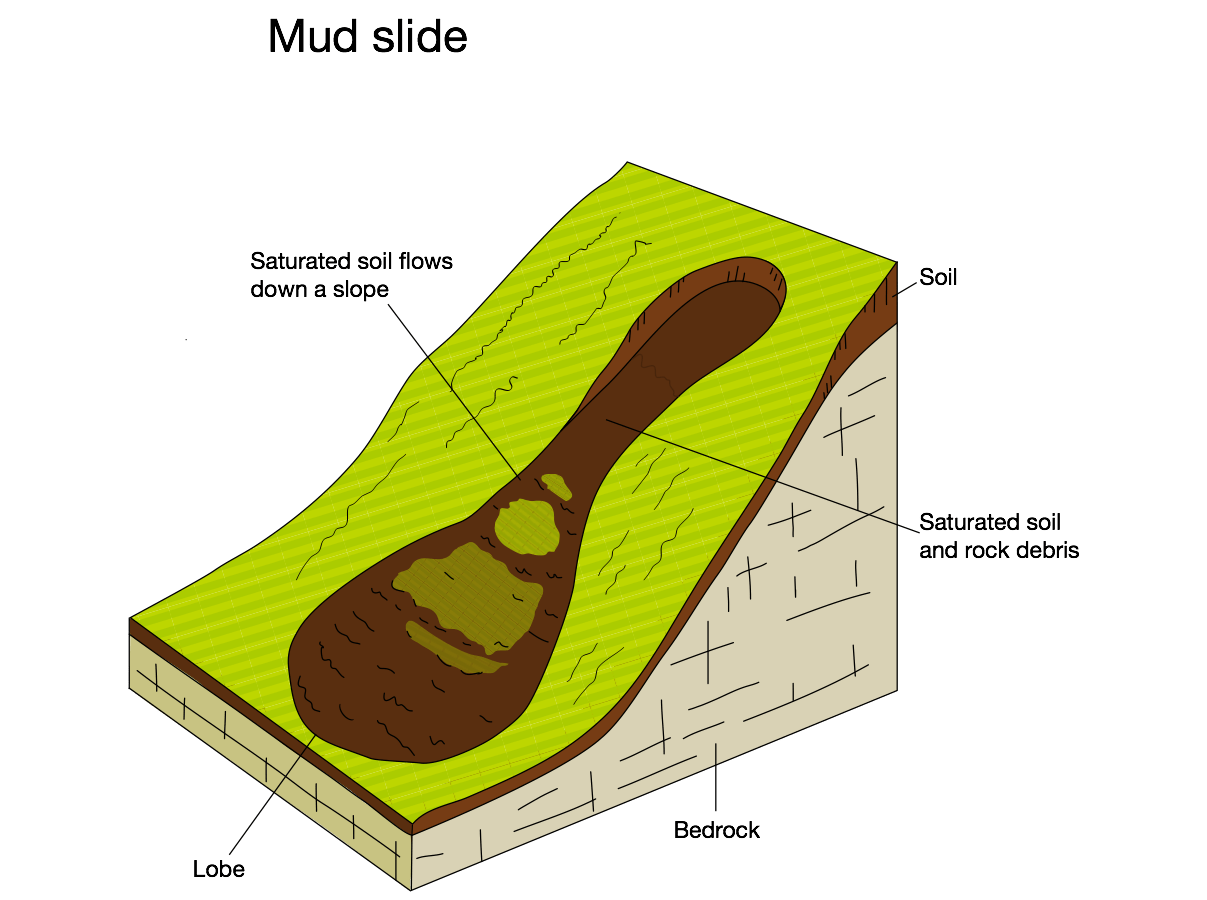
mass movement: mudflow
saturated soil and rock flows down a cliff face, happens after heavy rainfall on loosely consolidated cliffs
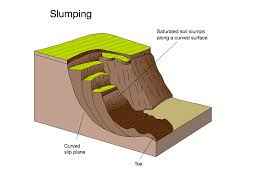
mass movement: rotational slip (slump) - mass movement
saturated soil and rocks slide down the cliff face with a rotational (curved movement)
creates a steep profile in the cliff
marine sediment transport processes:
suspension - fine material such as clay and sediment is carried by the sea
solution - dissolved minerals carried by the sea
traction - large boulders and pebbles are rolled along the sea bed
saltation: small stones, pebble and silt bounces along the sea bed
longshore drift process
the prevailing wind (most common wind direction causes waves to approach at an angle
when they hit thew beach, the swash it an an angle
when the wave runs out of energy, it will slope down the beach due to gravity
this will then continue across the coastline in the direction of the prevailing wind

arolian sediment transport processes
surface creep - large material rolled across the sand floor by the wind (similar to traction)
saltation - material bounced / hop across the sand floor
suspension - carrying sand particles in the air by strong wind or smaller pebbles
factors effecting erosion:
`wave strength - controlled by fetch and the wind speed . longer fetch creates more powerful waves with more erosive power
underwater topography
beaches - increase distance waves travel before it reaches cliffs and energy. headlands refract waves around them, reducing erosive power at one location while increasing another
weathering - creates weaknesses in rocks for erosion to exploit
human activity - dredging to remove material and coastal management reducing it
Fetch definition
the length of water surface over which the wind blows in a consistent direction
concordant and dicordant coastline
Concordant – contains layers of rock which run parallel to the coastline
Discordant – coastlines where layers of rock run perpendicular to the coastline
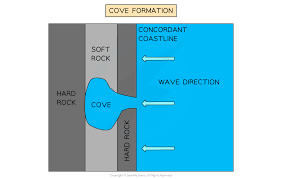
erosional formation: coves
on concordant coastlines
the more resistant band of rock is breached
erosion speeds up when it reaches the softer, les resistant rock behind which spreads laterally
once it reached the harder rock, erosion slows down
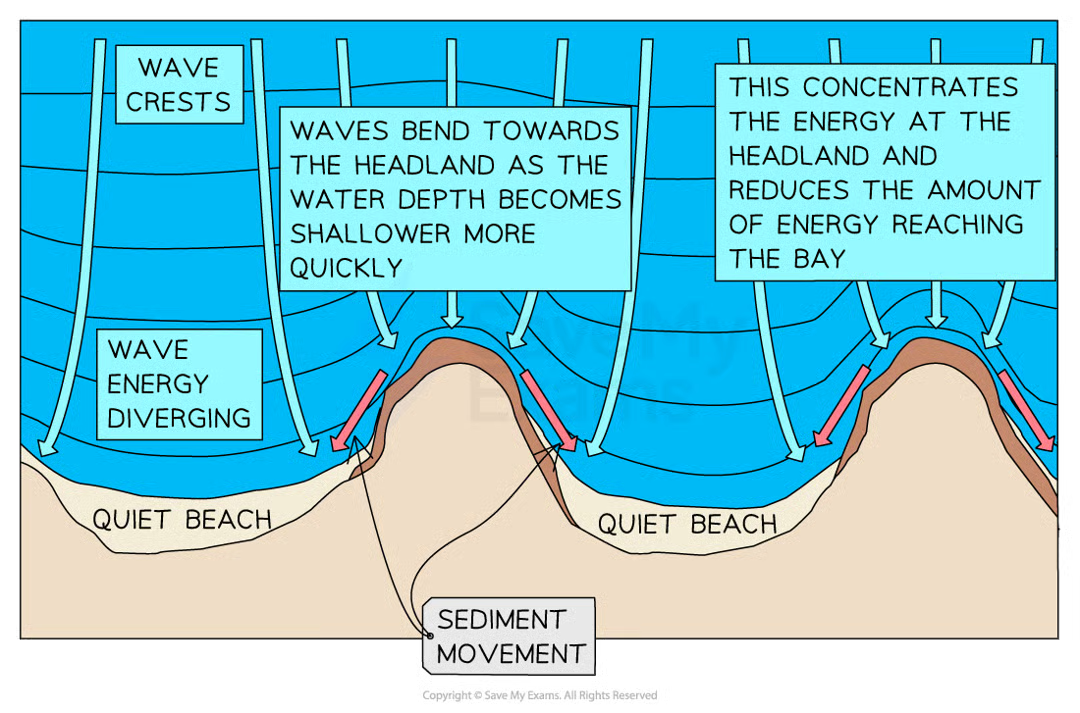
erosional formation: headlands and bays
more resistant rock erodes slowly, leaving rock sticking out to sea which is a headland
the less resistant rock erodes more quickly and retreats to form a bay
a beach develops here because the wave a constructive as well as the eroded soft rock being broken down by attrition
wave refraction is important as it concentrates wave energy on the headland, this encourages deposition int he bay, further developing the beach
High energy coastline example: Holderness coast
coastline located in East Yorkshire, spanning 50 miles from Flamborough in the noth to spurn pount in the town:
stakeholders - residents, farmers, business owners (gas terminal, seaside resort)
retrieved 40 metres in some areas
a.8 metres a year
fetch of 400km
ringborough farm - 1939 = 145 acres 2010 = 70 acres
geology - high energy coastlines have rocky coasts whcih cause the waves to dispurse, Flamborough however, has a soft geology coastline, made up of boulder clay and a glacial till , maiign it more likely to by rapdily eroded overtime due to it being more easily saturated, counter with it being a more fertile source.
coasts as a system
the system is in a constant state of dynamic equilibrium and can be seen as both an open system and a closed system
coasts as a system - positive and negative feedback
positive feedback:
waves eroding a cliff, releasing material which can abrade against the cliff, leading to more cliff erosion
negative feedback:
as the shore is eroded, material makes the wave cut platform wider, absorbing wave energy and reducing the impact at the base of the cliff
factors effecting the strength of wind on waves
fetch - the distance of open water the wind blows over
strength - how forceful the wind is
duration - how long it has been blowing
storm surges - intense increase in wavelength and speed
human - impermeable surfaces and energy from boats
tidal range and the characteristics of a coast
all tides have the same amount of time to reach their tidal range:
high tidal range - large difference in high and low tide e.g. Bristol Channel
Low tidal range - small difference e.g. the Mediterranean
types of waves - constructive wave
formed - calm local weather, short fetch
long wavelength, spilling waves
strong swash weak backshash
build up a gentle beach profile
types of waves - destructive
formed - local storms, strong winds, high fetch
short wavelength, plunging waves
weak swash, strong backwash
beach is lost and a steeper beach profile is likely in short term
wave refraction
changing the amount of energy reacing the shore on a small scale, concentrating energy at the headland and increases rates of erosion
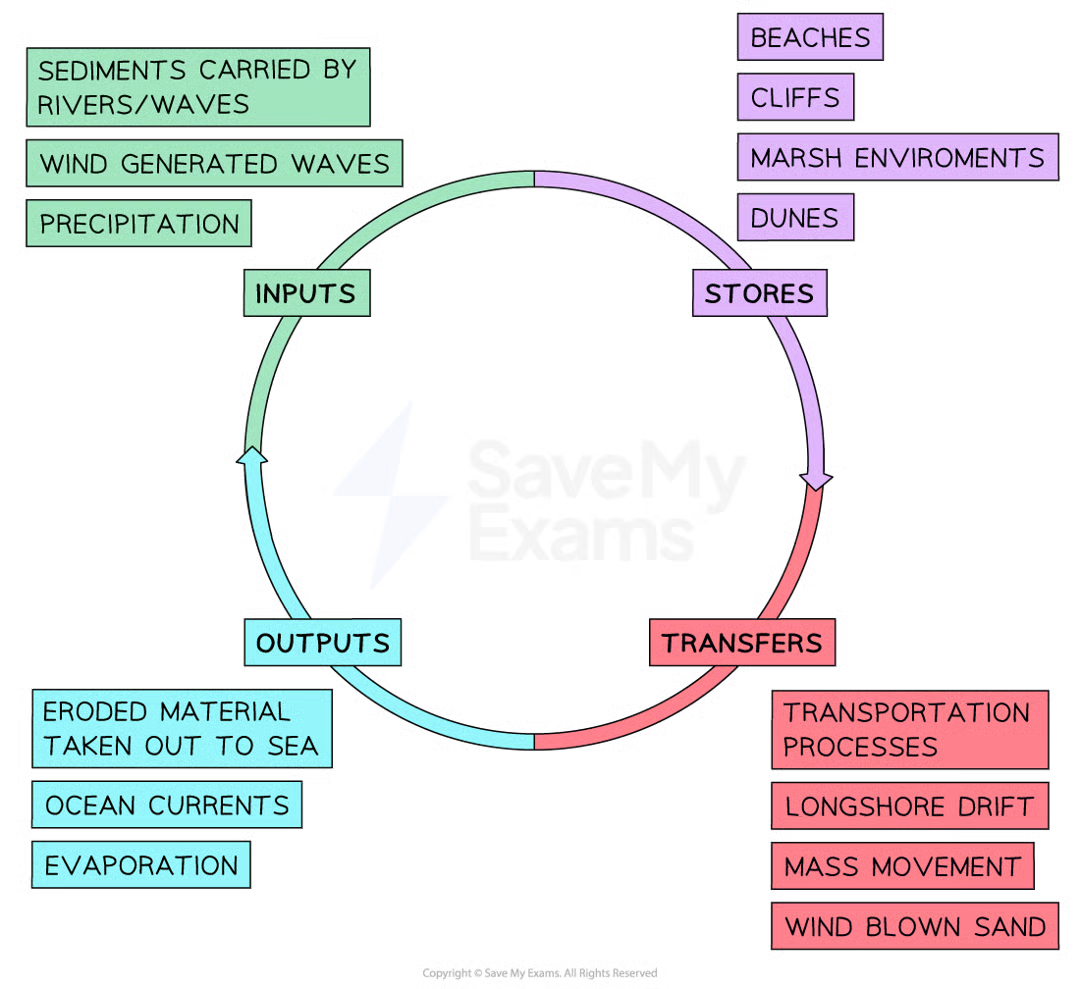
sediment cell
a section of coastline in which sediment is recycled but not added or lost. s
sources of sediment - rivers and cliff erosion
rivers:
hold the vast majority of coastal sediment, especially in high-rainfall environments
sediment is often deposited in river mouths and estuaries, where it is reworked by waves and tides
cliff erosion:
important in local areas of soft rock
sand and clay cliff erosion rates can be as high as 10m a year
sources of sediment - longshore drift and wind
longshore drift:
sediment is transported from one stretch of coastline (output) to another
this can change depening on sediment rates and wind speeds e.g. big or small pieces
Wind:
sand can be deposited in coastal region by wind, creating sand dunes at the coast
this depends on wind speed as well as proximity to sand
sources of sediment - glaciers and offshore sediment
glaciers
ice shelves carve (big chunks of ice breaking of a glacier) into the sea, depositing sediment trapped in ice
areas near the poles gain sediment from climate change
offshore
sediment offshore can be transferred into different coastal zones by waves and tides
in the UK at the end of the glacial perioid, sea levels rose, which led to sediment at southern coastlines to form landforms such as barriter beaches
sediment budget
the balance between the inputs and outputs of sediment in the system / sediment cell
the 3 main types of weathering
mechanical / physical - when rocks break up with no chemical changes
biological - rock breakdown due to organic activity
chemical - rock breakdown due to a chemical reaction
mechanical weathering - Freeze-thaw
when temperatures freeze below 0
water goes into the small cracks of rock
when the temperature is below 0, the water in the cracks become ice
the water expands as it freezes, creating forces on the surrounding rock, increasing crack size
this cycle continues until the fragment of rock breaks away completely
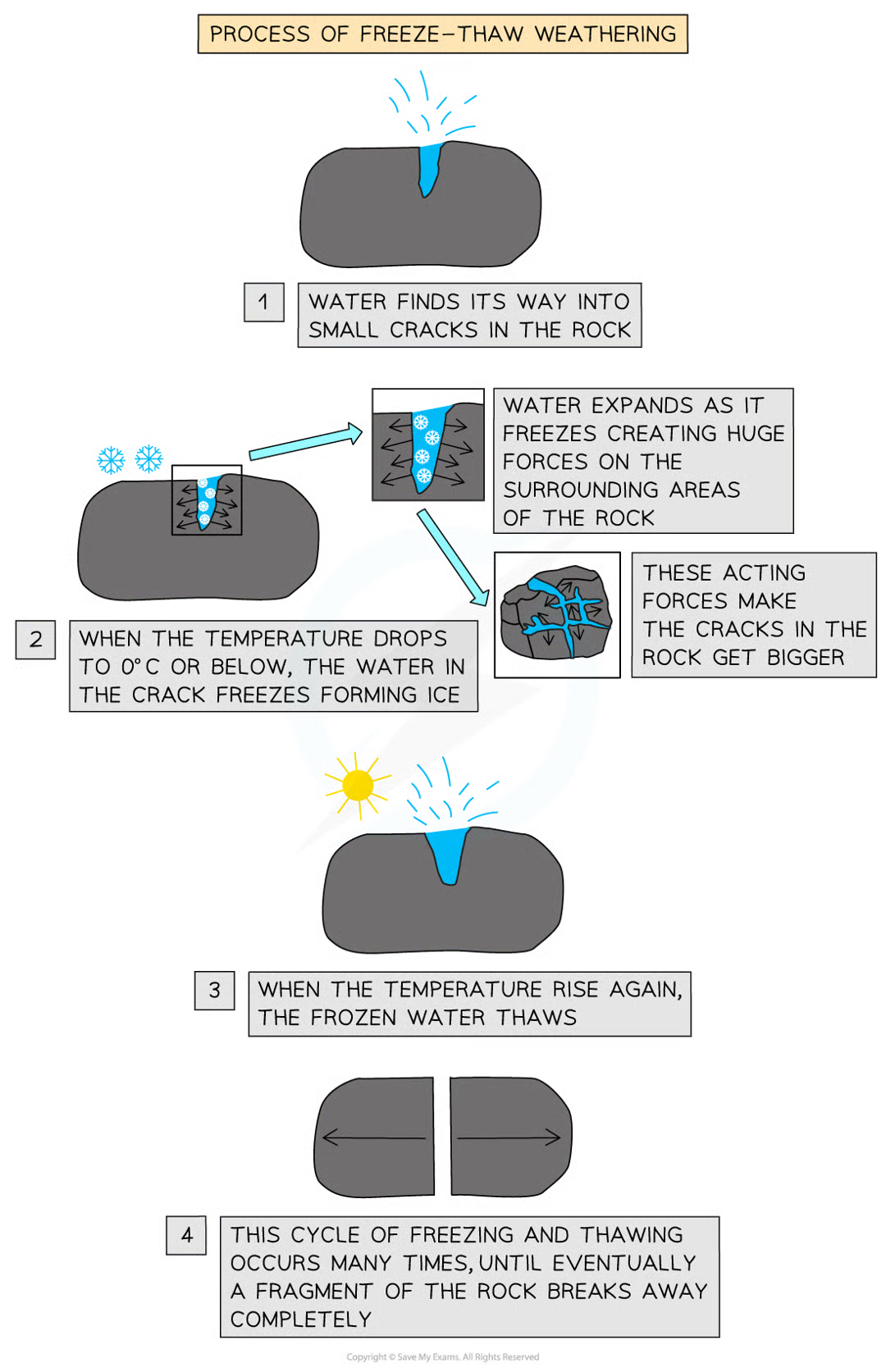
mechanical weathering - wetting and drying
similar to freeze-thaw
in warm climates, water doesn’t freeze, it just wets and dry’s which works the same way just without ice
often occurs in the inter-tidal zone
rocks expand when wet and contract when dry
mechanical weathering - salt crystallisation
this occues because the salt crystals are larger than the water molecules
this exerts pressure on the rock, causing it to break down
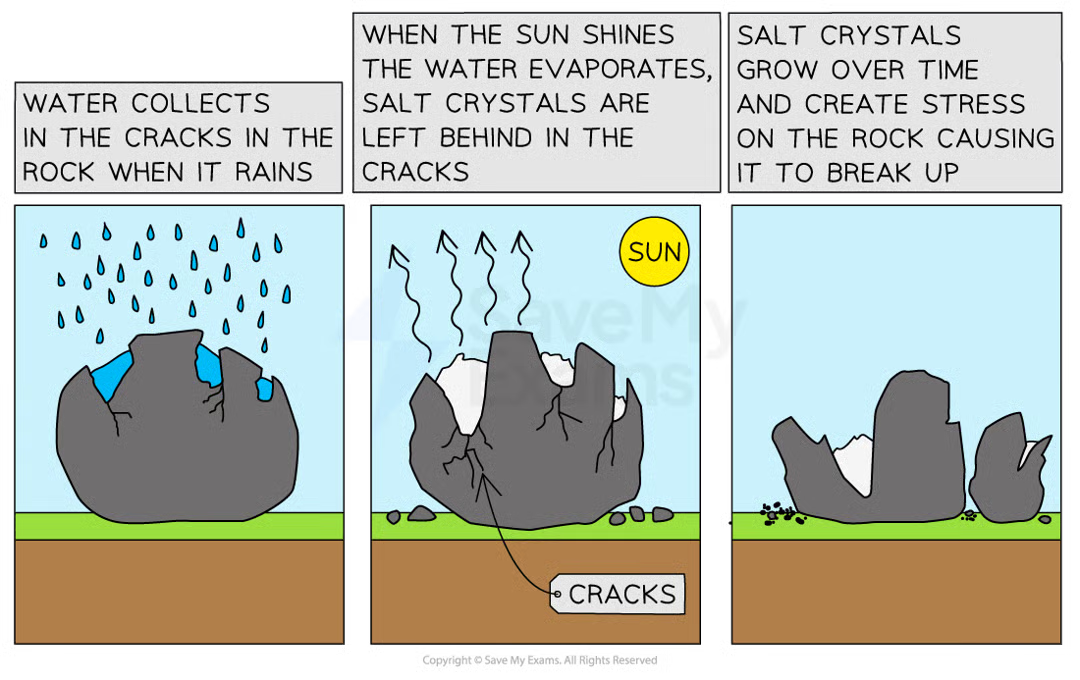
water collects in the cracks in the rock when it rains
when it is sunny, the water evaporates, salt crystals are left behind in the cracks
salt crystals grow over time and creates stress, causing the rock to break