Sociological Perspective of Society
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Structural Functionalism
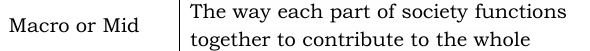
Conflict Theory
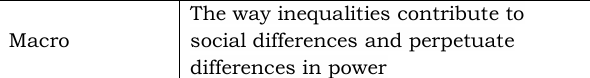
Symbolic Interactionism
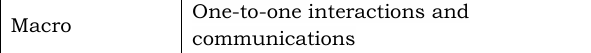
Structural-functional theory
Also called functionalism, sees society as a structure with interrelated parts designed to meet the biological and social needs of the individuals in that society.
Hebert Spencer
Functionalism grew out of the writings of English philosopher and biologist, ___________ (1820–1903), who saw similarities between society and the human body. He argued that just as the various organs of the body work together to keep the body functioning, the various parts of society work together to keep society functioning
Émile Durkheim
Another early sociologist, applied Spencer’s theory to explain how societies change and survive over time. He believed that society is a complex system of interrelated and interdependent parts that work together to maintain stability, and that society is held together by shared values, languages, and symbols.
Social Facts
Are the laws, morals, values, religious beliefs, customs, fashions, rituals, and all of the cultural rules that govern social life
social solidarity
Social ties within a group
Robert Merton
Pointed out that social processes often have many functions.
Manifest functions
Are the consequences of a social process that are sought or anticipated
Latent Functions
Are the unsought consequences of a social process
Dysfunctions
Social processes that have undesirable consequences for the operation of society are called _________.
Conflict Theory
Looks at society as a competition for limited resources.
bourgeoisie
Capitalist
proletariat
Workers
False consciousness
Marx’s term for the proletarian’s inability to see her real position within the class system, a mis-recognition that is complicated by the control that the bourgeoisie often exerts over the media outlets that disseminate and normalize information.
Class Conciousness
A common group identity as exploited proletarians and potential revolutionaries.
Max Weber
Agreed with some of Marx’s main ideas, but also believed that in addition to economic inequalities, there were inequalities of political power and social structure that caused conflict.
Ida B. Wells
Articulated the conflict perspective when she theorized a connection between an increase in lynching and an increase in black socio-economic mobility in the United States from the late 1800s into the mid-20th century.
W.E.B. DuBois
Examined race in the U.S. and in U.S. colonies from a conflict perspective, and emphasized the importance of a reserve labor force, made up of black men. Race conflict paradigms will be examined later in the course in the module devoted to race and ethnicity.
Symbolic Interactionist Theory
A micro-level theory that focuses on meanings attached to human interaction, both verbal and non-verbal, and to symbols.
looking-glass self
Describe how a person’s self of self grows out of interactions with others, and he proposed a threefold process for this development: 1) we see how others react to us,
2) we interpret that reaction (typically as positive or negative) and
3) we develop a sense of self based on those interpretations.
Dramaturgical analysis
The focus on the importance of interaction in building a society led sociologists like Erving Goffman (1922–1982) to develop a technique called
Group

Aggregate
A simple collection of people who are in the same place at the same time without interacting with each other
Category
A simple collection of people who share distinctive characteristics (age, sex, race, income/social class, occupation, religion, political beliefs, ethnicity
Collectivity
Collection of people in a given place and time
Primary Groups

Secondary Groups

In-group
group with which the individual identifies and which gives him sense of belonging, solidarity, camaraderie, esprit de corps, and a protective attitude toward the other members.
The members are loyal to each other and share common norms, activities, goals and background.
Out-group
viewed as outsiders by the in-group;
Any member of the in-group has insufficient contact with the members of the out-group
Members of the in-group have feelings of strangeness, dislikes, avoidance, antagonism, indifference and even hatred toward it.
Reference Group
Group that is significant to us as models even though we ourselves may not be a part of the group.
Is one which an individual does not only have a high regard for but one after which he or she patterns his/her life
Its central aspect is self-identification rather than actual membership
Formal Group Boundaries
Groups in which duties and privileges are clearly defined and expectations are prescribed, independent of the person who happens to occupy a given position -
Individual roles are explicitly designed as president, v-president, secretary, and treasurer -
With constitution or set of by-laws
Informal Group Boundaries
rises spontaneously out of the interactions of two or more people
They are unplanned, have no explicit rules for membership, and do not have specific objectives to be attained
The members exchange confidences, share a feeling of intimacy and acquire a sense of belongingness.