CHM 111 Chapter 2 Practice - Exam 1
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Periodic Table, Ions (Oxyanions/Polyatomic Ions), Nomenclature, Isotopes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
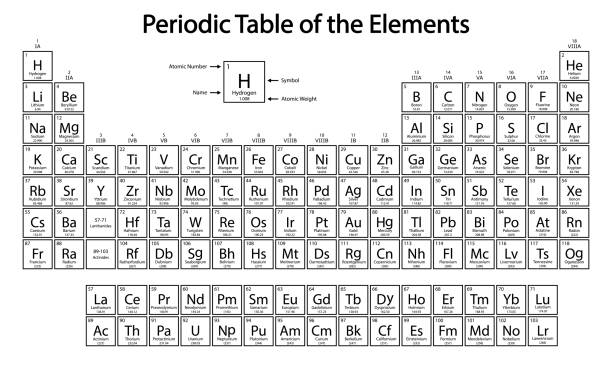
In order, what are the common names for groups 1, 2, 16, 17, and 18 of the periodic table?
Alkali metals, alkaline metals, chalcogenides, halogens (halides), and noble gases.
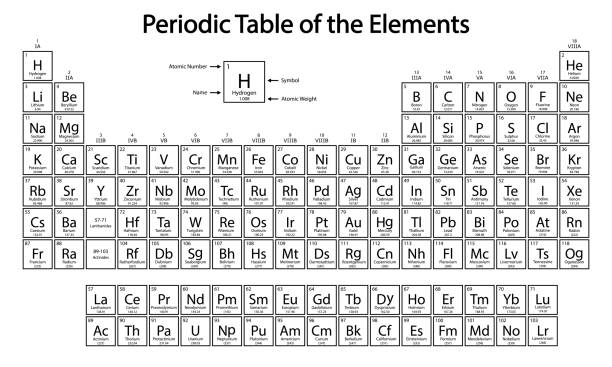
What elements on the periodic table are found as diatomic gases?
N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, H2
Empirical Formula
Simplest ratio of atoms present in a compound
Molecular Formula
Ratio of how many atoms of each element are in a compound
True or False
Cations form a positive charge.
True
True or False
Cations and anions are both ions.
True
True or False
Isotopes of the same element have the same number of neutrons and a different number of protons.
False
True or False
You can know the charge of a transition metal by simply looking at the periodic table.
False
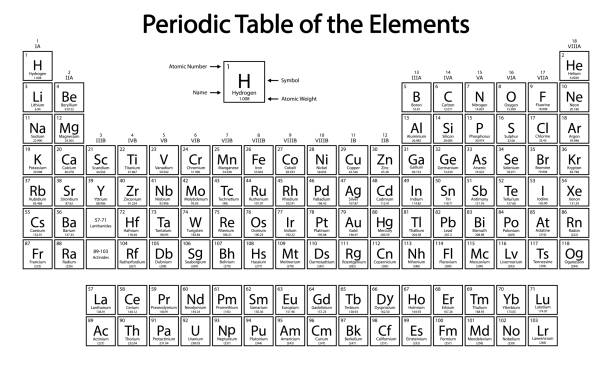
Which transition metals have a consistent charge?
Ag+, Zn2+,Al3+
Ammonium
NH4+
Chlorate
ClO3-
Nitrate
NO3-
Cyanide
CN-
Hydroxide
OH-
Sulfate
SO42-
Carbonate
CO32-
Phosphate
PO43-
When an acid’s original anion ends in “-ide”, the “hydro-” prefix is added and the “-ic” suffix is adopted. Name these acids: HCl, HBr, HCN.
Hydroclauric acid, hydrobromic acid, and hydrocyanic acid.
When an acid’s original anion ends in “-ate”, the “-ic” suffix is adopted. Name these acids: HNO3, HClO4, H3PO4.
Nitric acid, perchloric acid, phosphoric acid.
When an acid’s original anion ends in “-ite”, the “-ous” suffix is adopted. Name these acids: HNO2, HClO.
Nitrous acid, hypochlourous acid.
Neutral acids have all of their hydrogen. Ex: H2SO4. Acids that have lost a hydrogen use “molecule” form to list the number of hydrogen present. Name these acids: H2PO2-, HSO4-.
Dihydrogen phosphate, hydrogen sulfate.