Adv. Biology Chapter 5; Cell Division and Growth
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/63
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
Why do cells divide?
stay small, repair and replace, embryonic development, reproduction method
2
New cards
What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction?
asexual-one parent; sexual-two parents
3
New cards
What type of reproduction is genetically identical?
asexual
4
New cards
What type of reproduction is genetically different?
sexual
5
New cards
What type of reproduction is quicker?
asexual
6
New cards
What type of reproduction is slower?
sexual
7
New cards
What type of reproduction uses less energy?
asexual
8
New cards
What type of reproduction uses more energy?
sexual
9
New cards
What is the the advantage sexual reproduction has over asexual reproduction?
species can adapt in a changing environment
10
New cards
What are chromosomes?
DNA and histone (protein)
11
New cards
What is histone?
protein
12
New cards
What type of cell has one circular chromosome?
prokaryotic
13
New cards
What type of cell has multiple chromosomes?
eukaryotic
14
New cards
What type of cell is easier to divide?
prokaryotic
15
New cards
What type of cell is harder to divide?
eukaryotic
16
New cards
What type of cell has binary fission?
prokaryotic
17
New cards
What is the first step of interphase?
G1
18
New cards
What is the second step of interphase?
S
19
New cards
What is the third step of interphase?
G2
20
New cards
What happens in the G1 phase?
the cell grows
21
New cards
What happens in the S phase?
DNA replication
22
New cards
What happens in the G2 phase?
the cell prepares for mitosis
23
New cards
What are the 5 parts of cell division?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
24
New cards
What happens in mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
25
New cards
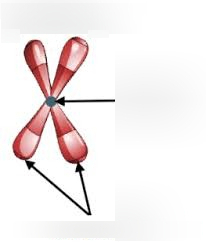
What is the arrow in the middle pointing to? The bottom arrows?
centromere; sister chromatids
26
New cards
What are the two parts of cell division?
mitosis; cytokinesis
27
New cards
What does mitosis do?
makes two from one
28
New cards
What is the result of cell division?
daughter cells are genetically identical; have the same number of chromosomes as parent
29
New cards
What happens in prophase?
nuclear membrane dissolves, chromosomes condense )( , mitotic spindle appears
30
New cards
What happens in metaphase?
chromosomes line up in the middle of cell (single file)
31
New cards
What happens in anaphase?
chromosomes move away from middle, sister chromosomes break apart
32
New cards
What happens in telophase?
nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes begin to unravel, mitotic spindle dissolves
33
New cards
How do animal and plant cells differ when dividing?
animal cells "pinch inward" before dividing
34
New cards
What are checkpoints?
safety measures in a cell that control how fast a cell divides
35
New cards
What is checked during a checkpoint?
proper growth, DNA replication, spindle fiber formation; DNA errors
36
New cards
What is cancer?
uncontrolled division of cells
37
New cards
What is cancer commonly mistaken for?
virus or bacteria
38
New cards
What is a tumor?
mass of cells
39
New cards
What is apoptosis?
programmed cell suicide
40
New cards
What type of tumor is not harmful and slow dividing?
benign
41
New cards
What type of tumor is harmful, fast dividing, and spreads to other organs?
malignant
42
New cards
What does metastasize mean?
spread
43
New cards
What are ways you can get cancer?
inherit, UV, tobacco, pollutants
44
New cards
What are carcinogens?
cancer causing agents (usually chemical)
45
New cards
What phase do centromeres divide and chromosomes move toward respective poles?
anaphase
46
New cards
What phase do chromatin condense to form chromosomes?
prophase
47
New cards
In a chromosome pair connected by a centromere, what is each individual chromosome called?
chromatid
48
New cards
What are the two parts of cell division?
mitosis and cytokinesis
49
New cards
What structure forms in prophase along which the chromosomes move?
spindle fiber
50
New cards
What is the last phase in which chromatids are together?
metaphase
51
New cards
What phase is characterized by non-dividing cell?
interphase
52
New cards
What structure is produced when protein fibers radiate from centrioles?
spindle fibers
53
New cards
What forms across the center of a plant cell near the end of telophase?
cell plate
54
New cards
What is the period of cell growth and development between mitotic divisions?
interphase
55
New cards
What is cell differentiation?
process of stem cell becoming specialized
56
New cards
What is a problem with cell division?
can cause cancer
57
New cards
What is a positive about cell division?
stem cell therapy
58
New cards
What are the 2 types of stem cells?
embryonic, adult
59
New cards
What are sources of embryonic stem cells?
umbilical chords, IVF
60
New cards
What are sources of adult stem cells?
skin, bone marrow, nasal cavity, liver
61
New cards
What does pluripotent mean?
change into any type of cell
62
New cards
Which type of cell comes from fetus and is pluripotent?
embryonic stem cell
63
New cards
What type of cell comes from adults and isn't pluripotent?
adult
64
New cards
What does induced pluripotent stem cell (IPS) mean?
adult cell reprogrammed to be an embryonic stem cell