PSYC 178: Industrial and Organizational Psychology Lecture Review
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the main focus of I-O psychology?
The application of psychological principles, theory, and research to the work setting.
What was the outcome of the Brown v. Board of Education case in 1954?
It ruled that separate educational facilities are inherently unequal.
What are the three fields of I-O Psychology?
Personnel psychology, organizational psychology, and human factors.
What is the purpose of the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology (SIOP)?
To promote the application of I-O psychology to workplace issues.
What is “HWP” in the context of I-O psychology?
Humanitarian work psychology, focusing on workplace issues in humanitarian settings.
What does the concept of emotional intelligence encompass?
The ability to recognize one's own and others' emotions and use that information to guide thinking and behavior.
What are the common areas of concentration for I-O psychologists?
Selection, training, organizational development, career planning, and performance measurement.
What does the “Hawthorne effect” describe?
Changes in behavior resulting from awareness of being observed. This happened because of observations being made in a factory.
What is the main distinction between “speed” and “power” tests in assessments?
Speed tests have strict time limits, while power tests do not.
What does “incremental validity” refer to?
The value added of a new predictor to an existing selection system.
What are the Big Five personality traits in the workplace?
Conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, emotional stability, and openness to experience.
What is the primary criticism of personality testing in hiring?
Candidates may fake responses to improve their scores.
What is the role of '“biodata” in the assessment process?
Collecting past employment history, education, and experiences to predict future performance. There are questions of ethicality to this method.
What does “construct-related validity” assess?
It gathers evidence to support decisions about psychological constructs being measured.
What are typical methods used for assessing individual differences?
Cognitive ability tests, personality tests, and work sample tests.
Why is emotional intelligence considered valuable in the workplace?
It is linked to better mental health and job performance.
What is the significance of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in I-O psychology?
It prohibits employment discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
What recent trends are influencing the field of I-O psychology?
Technological advancements, AI integration, and shifts in workplace dynamics due to remote working.
What is the difference between Alpha army and Beta army tests?
Alpha tests verbal intelligence while Beta tests non-verbal intelligence..
What is revery obsession?
A state of mind resulting from mind-numbing, repetitive, and laborious work that resulted in higher level of stress, depression, and lower level of productivity.
What are the 4 requirements for IO psychology to be?
relevant
useful
needs to think bigger (applicable to real world issues)
grounded in scientific method
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical cultures?
Horizontal cultures minimize distances between individuals, while Vertical cultures accept & depend on distances between individuals. (individualism/collectivism)
What is science?
Approach that involves the understanding, prediction, and control of some phenomenon of interest
What makes a theory “good”?
Offer novel insights, Are interesting, Are focused, Are relevant to important topics, Provide explanations and Are practical.
Difference between non-experimental and quasi-experimetal research?
Non-experimental work doesn’t manipulate or assign different variable while quasi-experimental research doesn’t involve random assignment at all.
What does “triangulation” mean?
Examining converging information from different sources (qualitative and quantitative research).
What is the difference between experimental and statistical control?
Experimental control eliminates influences that could make results less reliable or harder to interpret (i.e.confounds), while Statistical control’s techniques are used to control for the influence of certain variables (e.g., ANCOVA)
What is the difference between Type I and Type II error in data?
Type I (false positive) is claiming there is a difference when there isn’t, and Type II (false negative) is saying there is no difference when there is
What are the three measures of central tendency?
Mean (average)
Mode (most frequent)
Median (50% percentile)
When describing a score distribution, what do the 3 measure of central tendency do to the data?
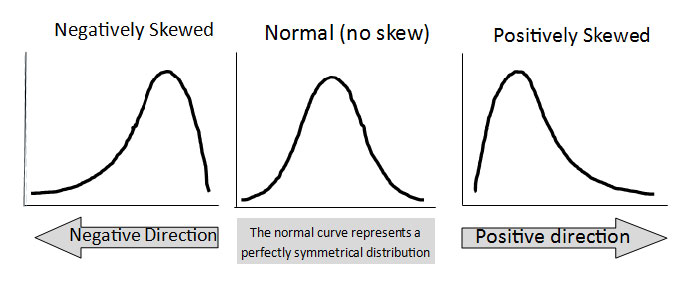
Mean is affected by high or low scores, median is not.
Mean pulls in direction of skew
– Positive skew (skewed to the right)
– Negative skew (skewed to the left)
What is statistical significance?
Defined in terms of a probability statement (e.g., p = .03). Threshold for significance is often set at .05 or lower.
In scatterplots, what are positive and negative correlations?
Positive correlation → As one variable increases, other variable also increases & vice versa
Negative correlation → As one variable increases, other variable decreases & vice versa
What is meta-analysis?
Statistical method for combining results from many studies to draw a general conclusion
What is micro, meso, and macro research?
Micro-research: study of individual
behavior
Macro-research: study of collective
behavior
Meso-research: study of interaction of
individual and collective behavior
What is Generalizability theory?
Simultaneously considers all types of error in reliability estimates
Error could be due to:
» Time/occasion
» Individual
» Rater
» item
What is criterion-related criterion?
Correlate a test score (predictor) with a performance measure; resulting correlation often called a validity coefficient
What is construct validity?
Demonstrates that content of selection procedure represents adequate sample of important work behaviors & activities or worker KSAOs defined by job analysis
What are the 2 main contributions to varieties in individual differences?
Cognitive ability & the g-ocentric model (tendency to understand and predict the behavior or workers simply by examining “g”)
g = intelligence
What does Carroll’s hierarchical model of intelligence suggest?
That there are 3 levels to intellligence
G
Broad Abilities
Specific abilities
What are some examples of Fleishmen’s psychomotor abilities?
Arm-hand steadiness, Response orientation, Manual dexterity, Rate control, and Reaction time
what are some examples of cognitive ability tests?
Wonderlic Personality Test and General Aptitude Test Battery
What are two examples of integrity tests?
Overt Integrity Test: Asks questions directly about past honesty behavior (stealing, etc.) as well as attitudes toward various behaviors (employee theft, etc.)
Personality Based Integrity Test: infers honesty and integrity from questions dealing with broad personality constructs (conscientiousness, reliability, and social responsibility)
What is graphology vs polygraph?
Graphology: Assumes traits can be assessed from various characteristics of a person’s handwriting
Polygraph: Machine that measures person’s physiological reactions & signals deception