hematology
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
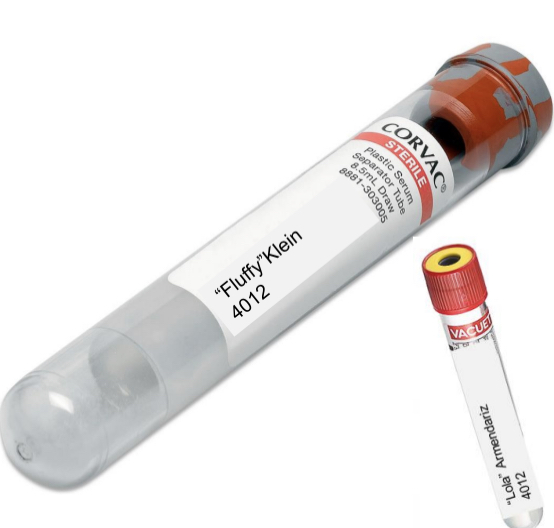
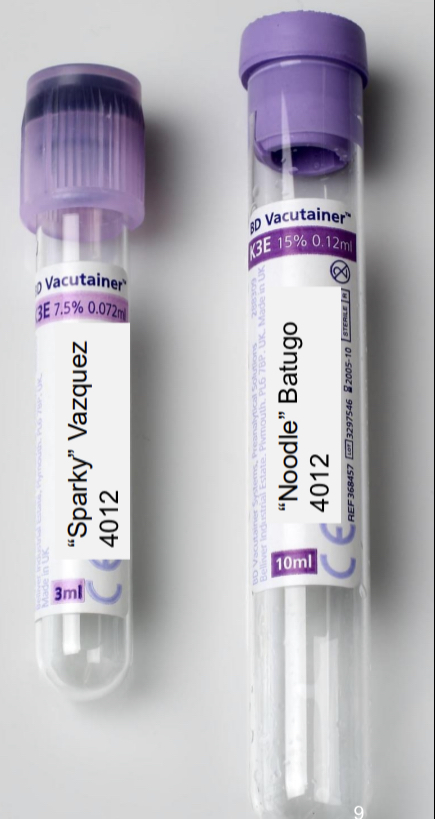
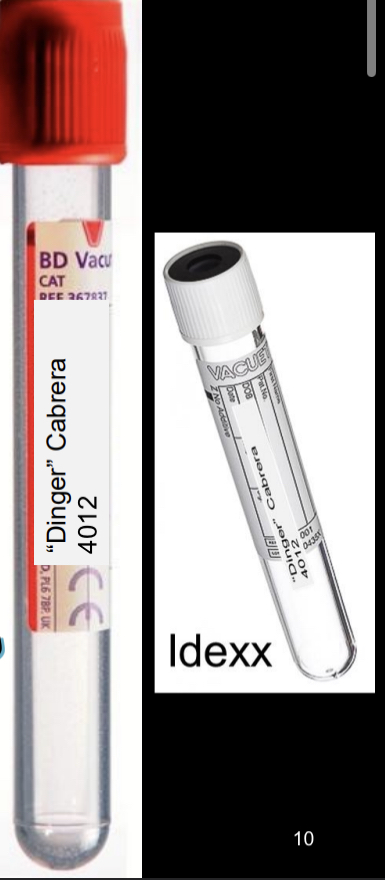

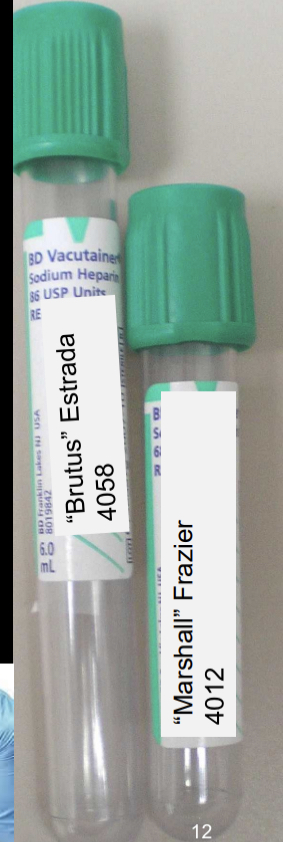
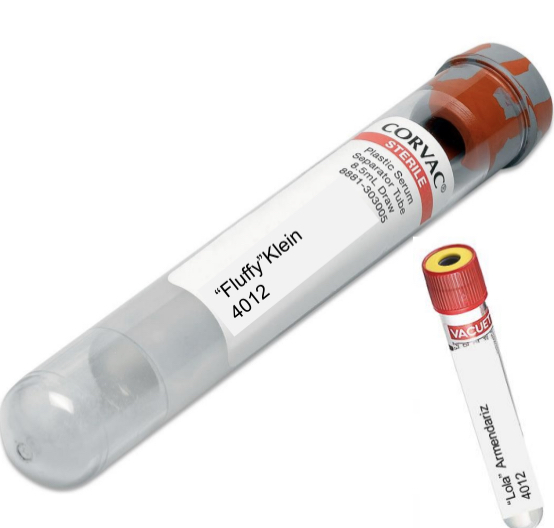
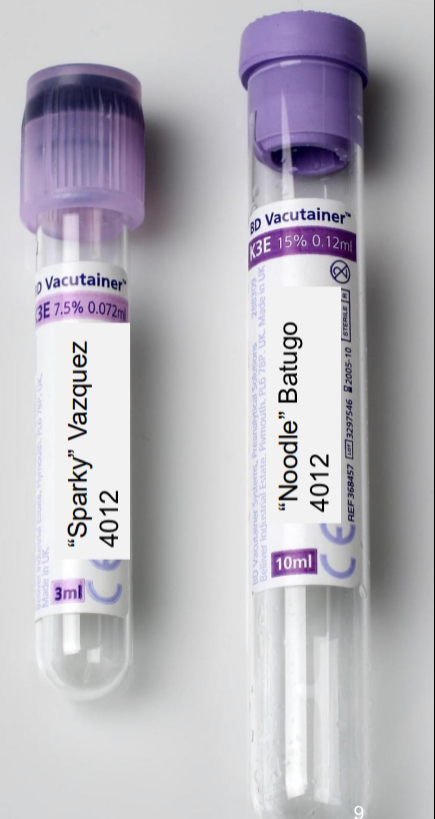
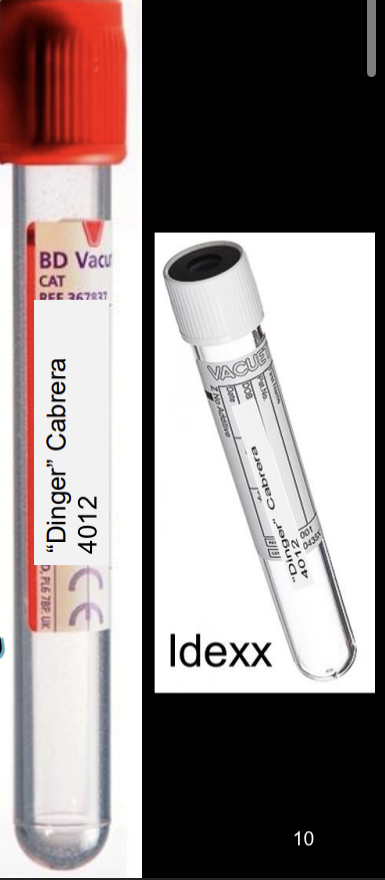

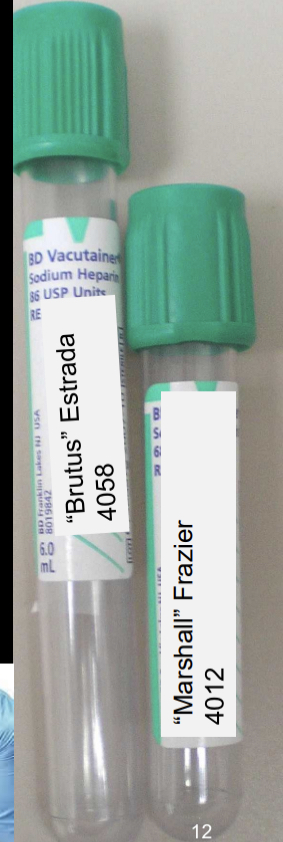
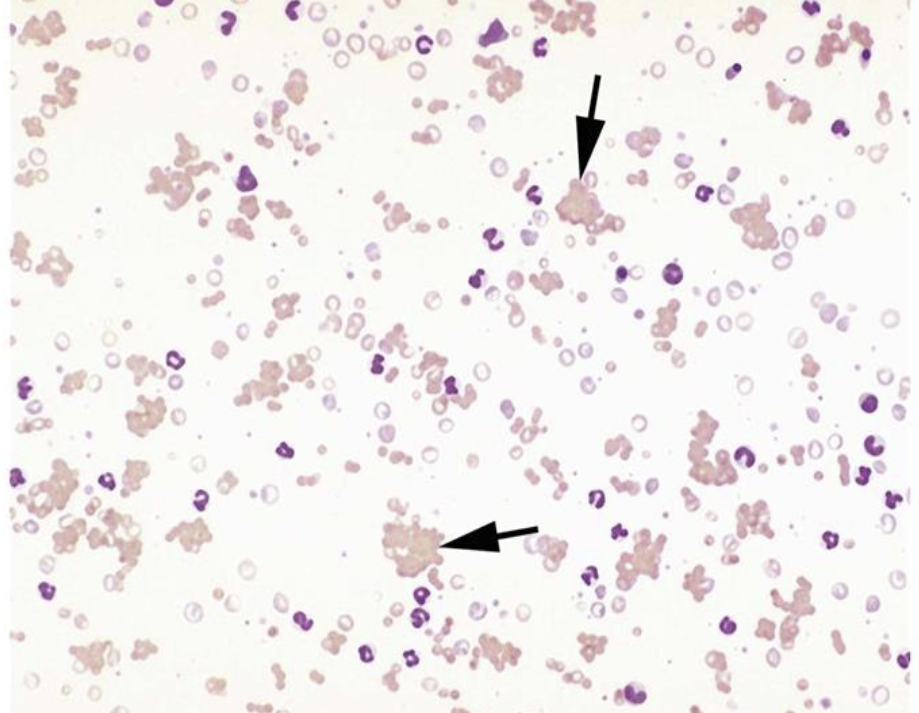
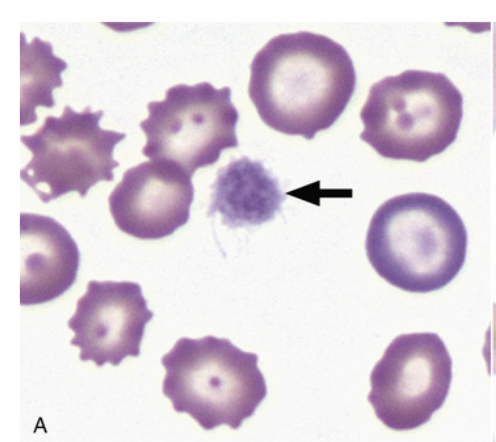
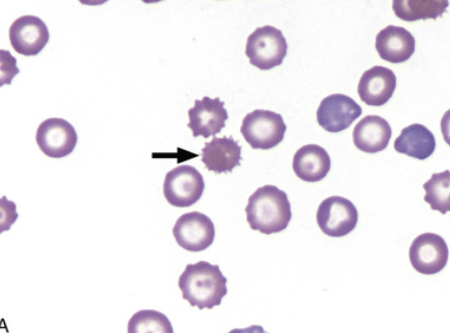
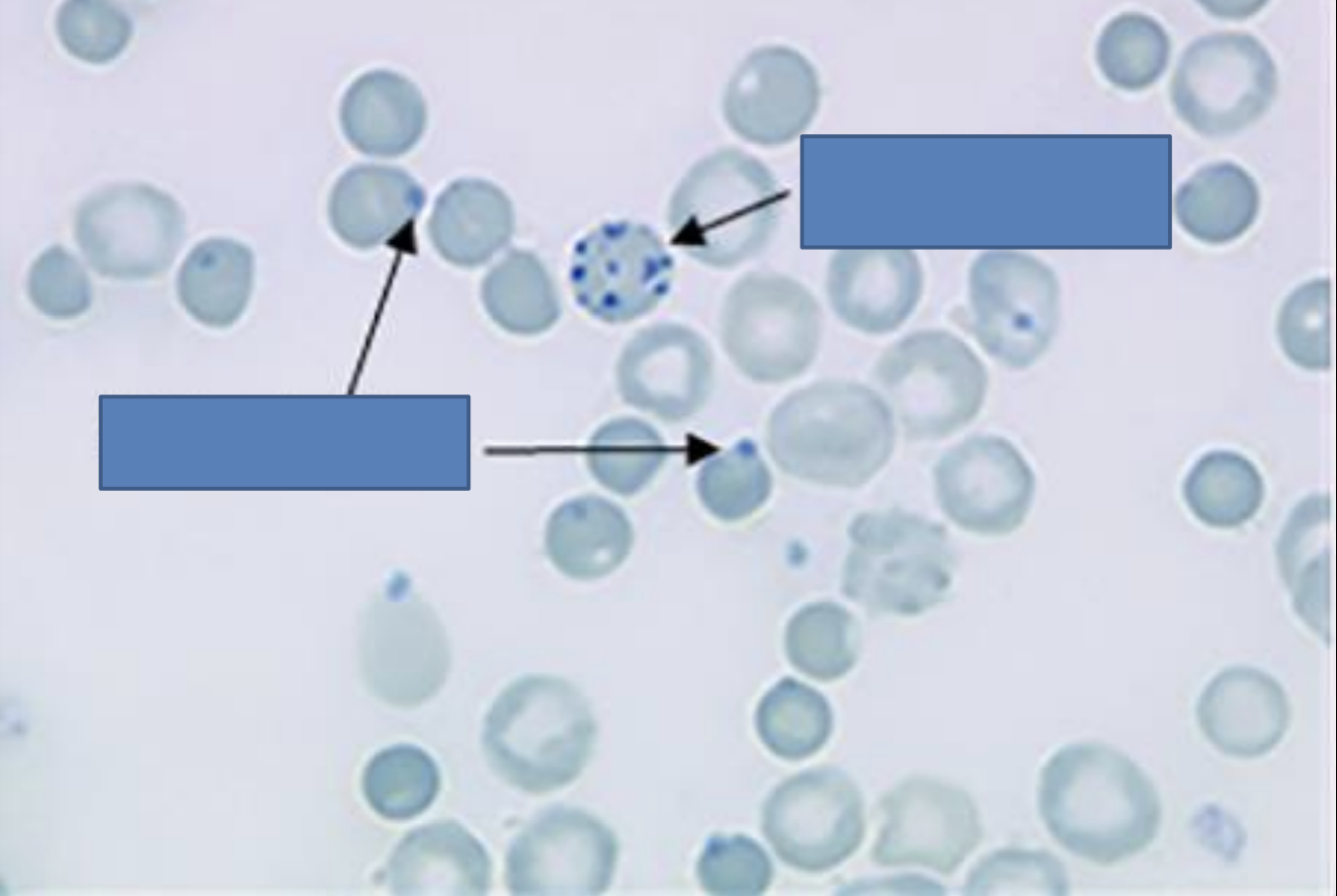
type B
type AB
packed RBCs
fresh frozen plasma
platelet-rich plasma
alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
is more “liver” specific than other enzymes like AST and can also be interpreted in conjunction with CPK levels to differentiate between liver and muscle sources that are “leaking” this enzyme.
aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT)
alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
albumin
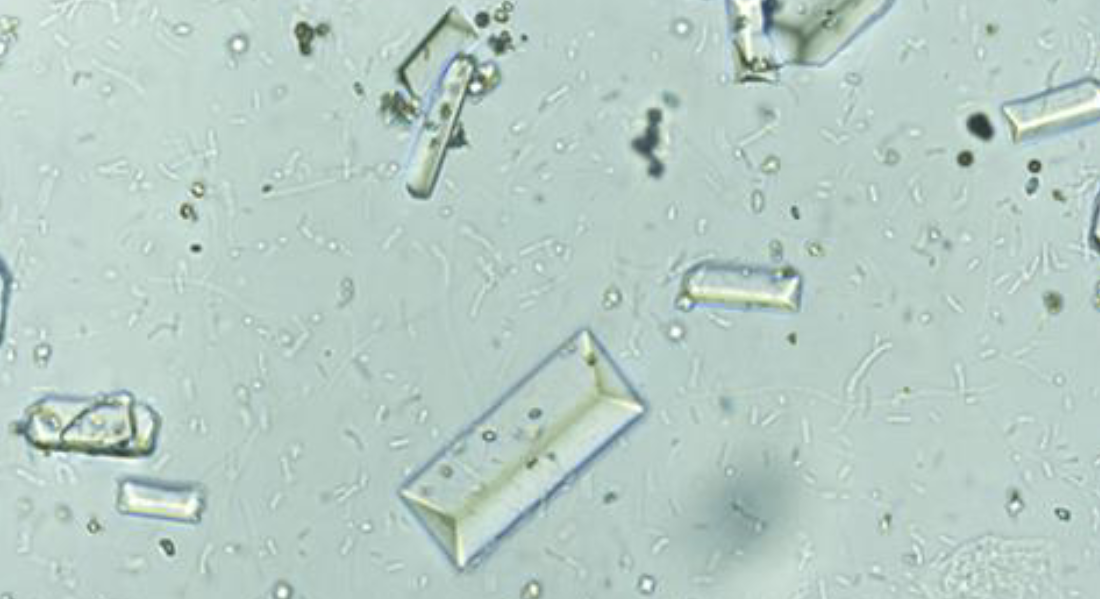
what type of crystal is this
struvite (magnesium-ammonium-phosphate )
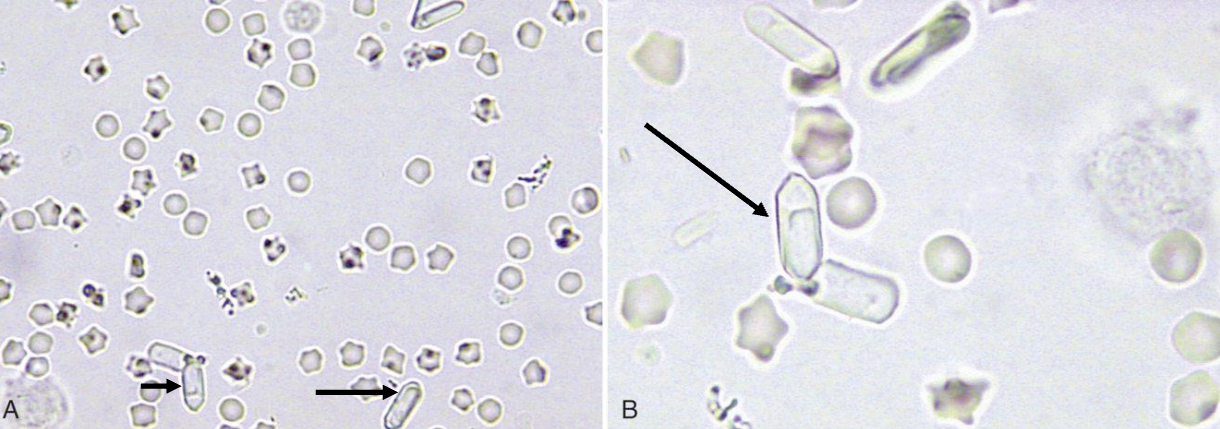
what type of crystal is this
calcium oxalate monohydrate
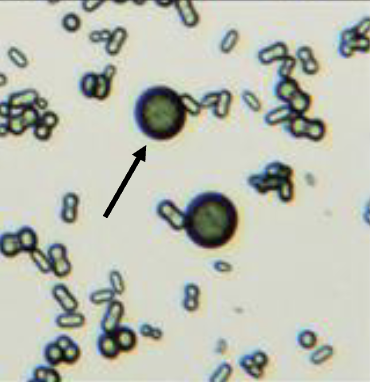
what type of crystal is this
calcium carbonate
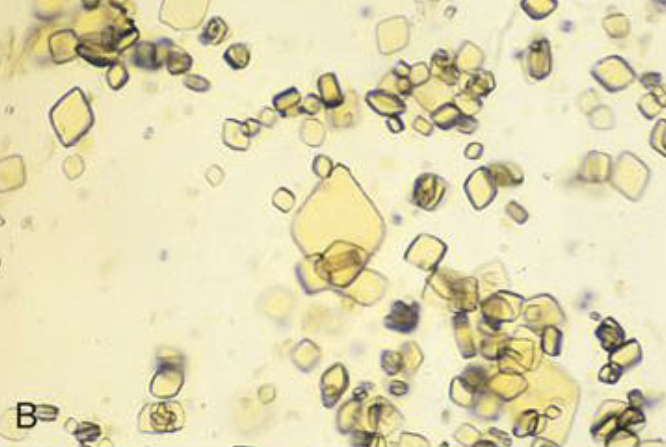
what type of crystal is this
uric acid crystals
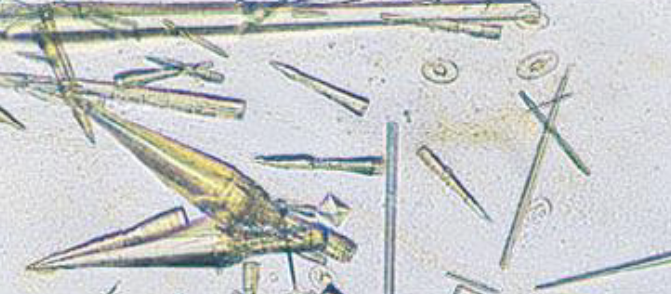
what type of crystal is this
sodium urate crystals
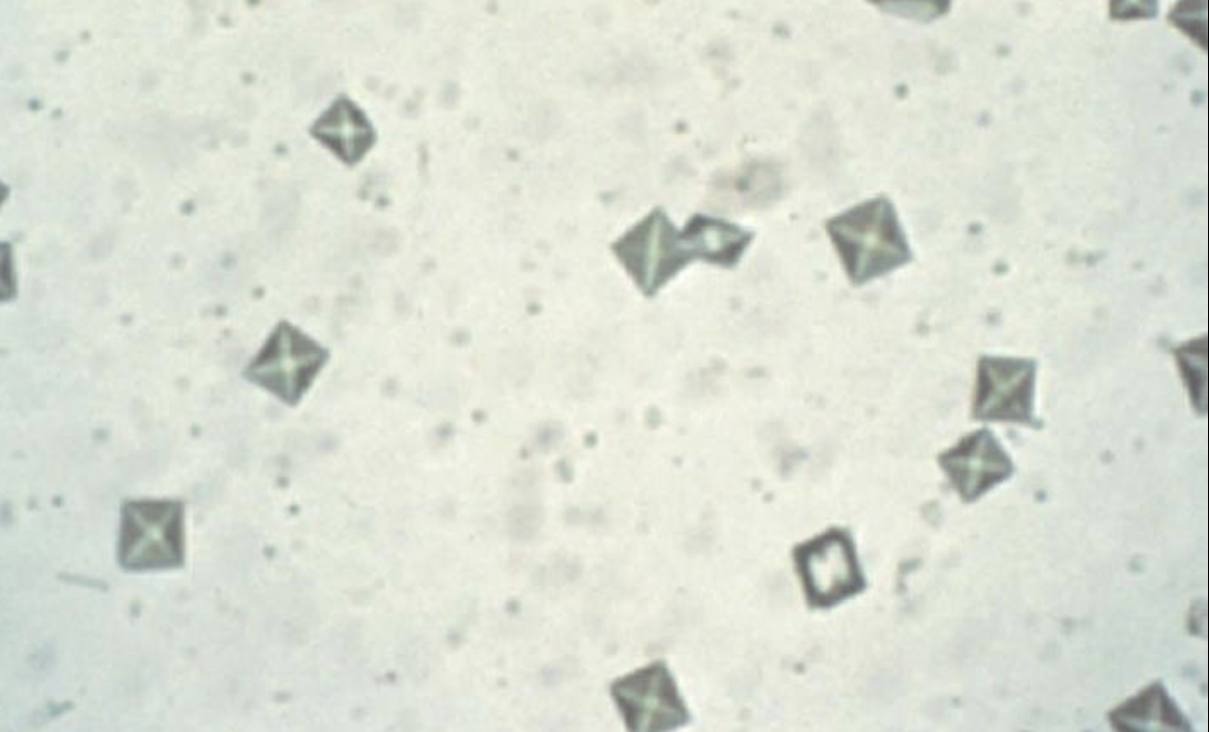
what type of crystal is this
calcium oxalate dihydrate
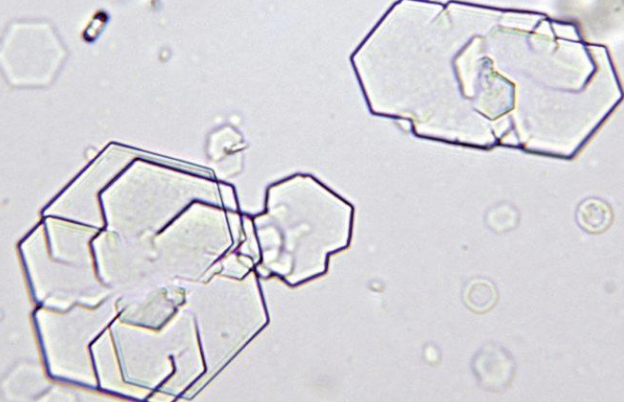

what type of crystal is this
cystine crystals
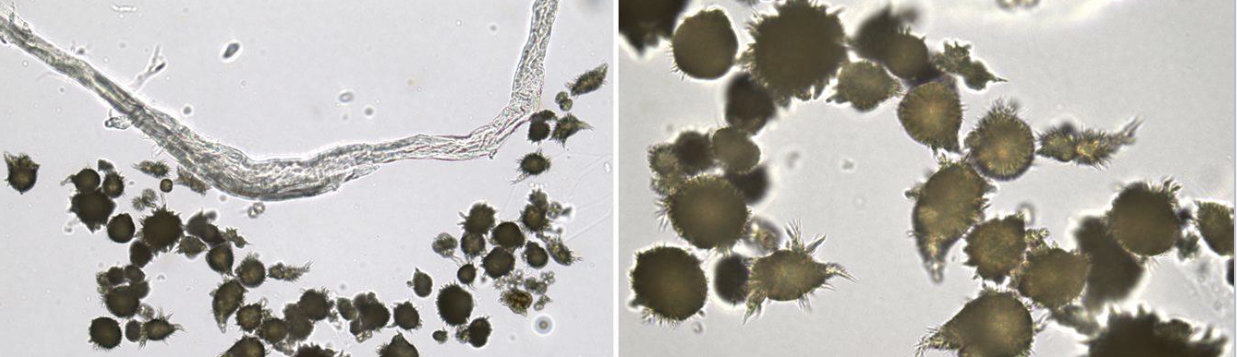
what type of crystal is this
ammonium biurate
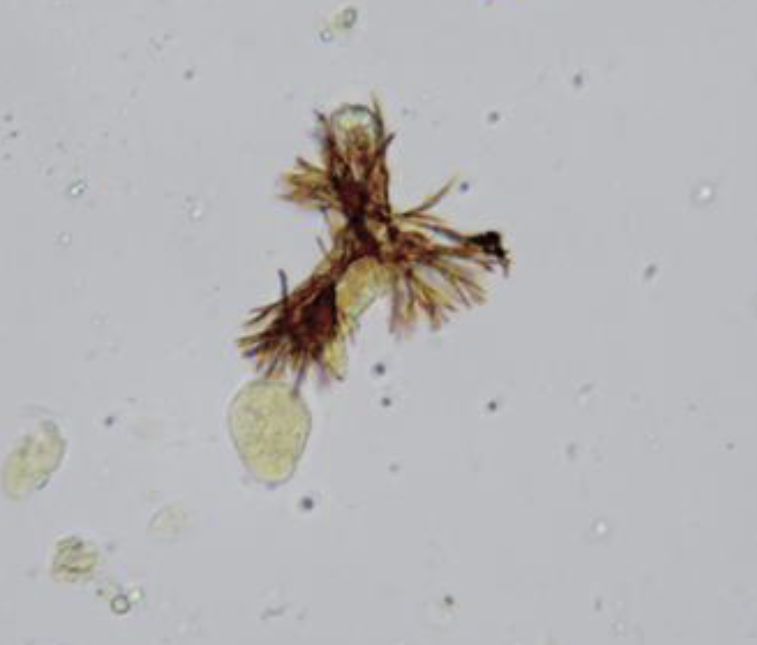
what type of crystal is this
bilirubin
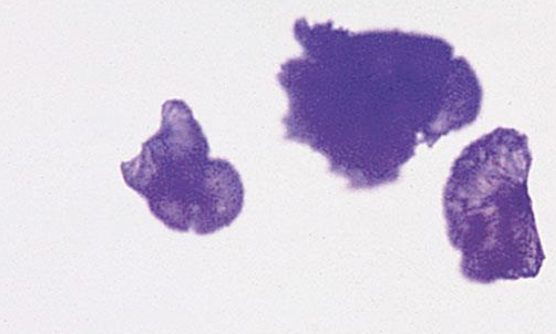
what type of crystal is this
tyrosine crystals
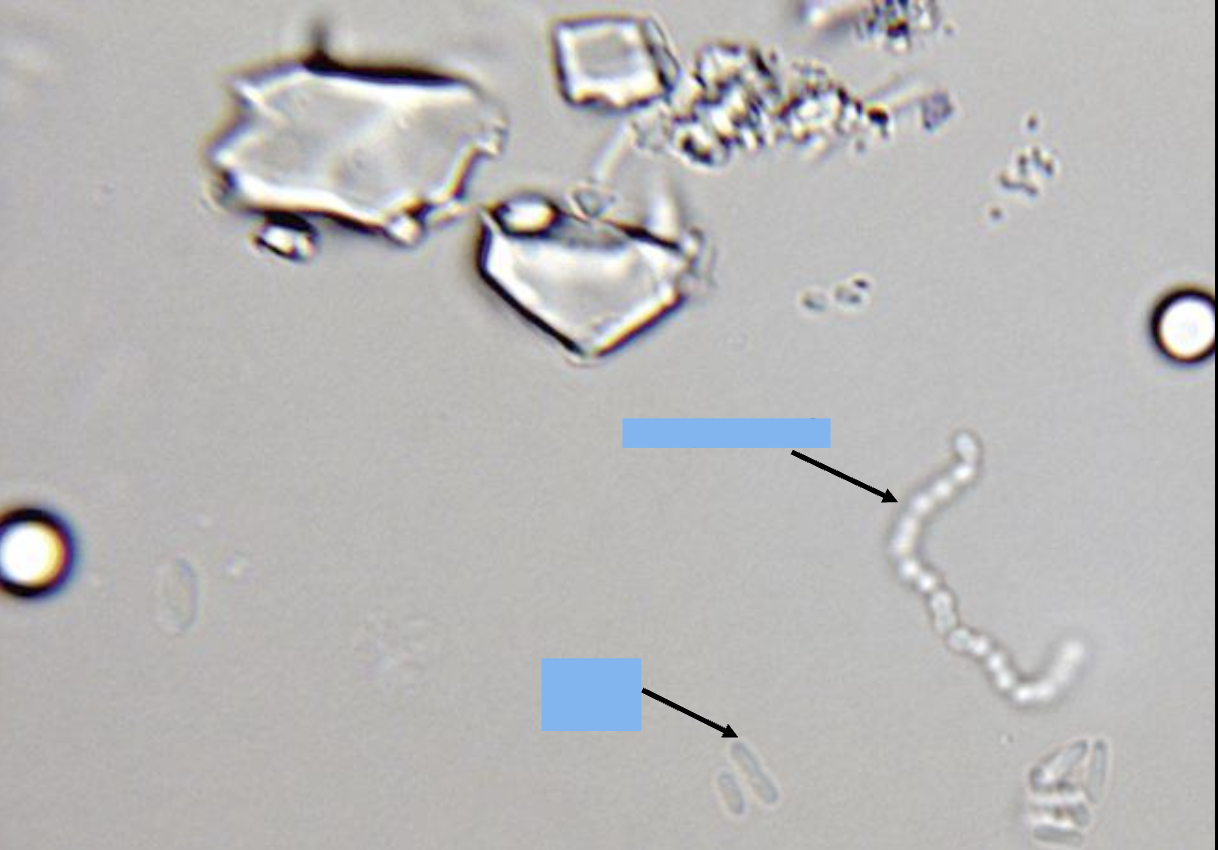
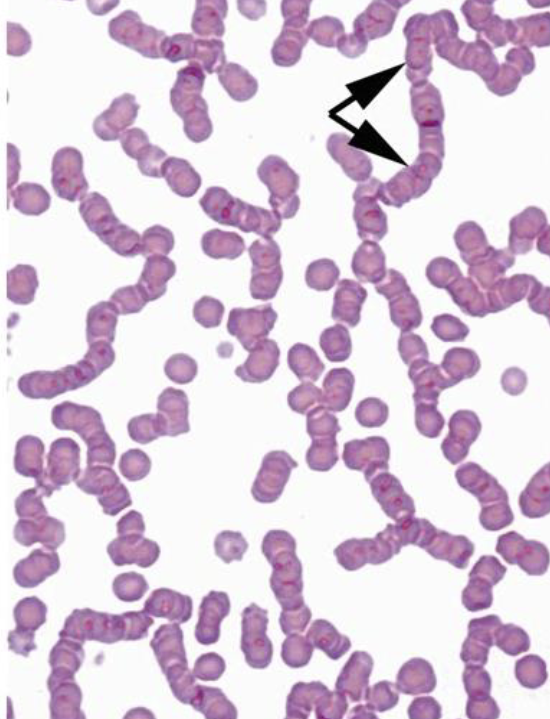
what is the top arrow pointing at
streptococci
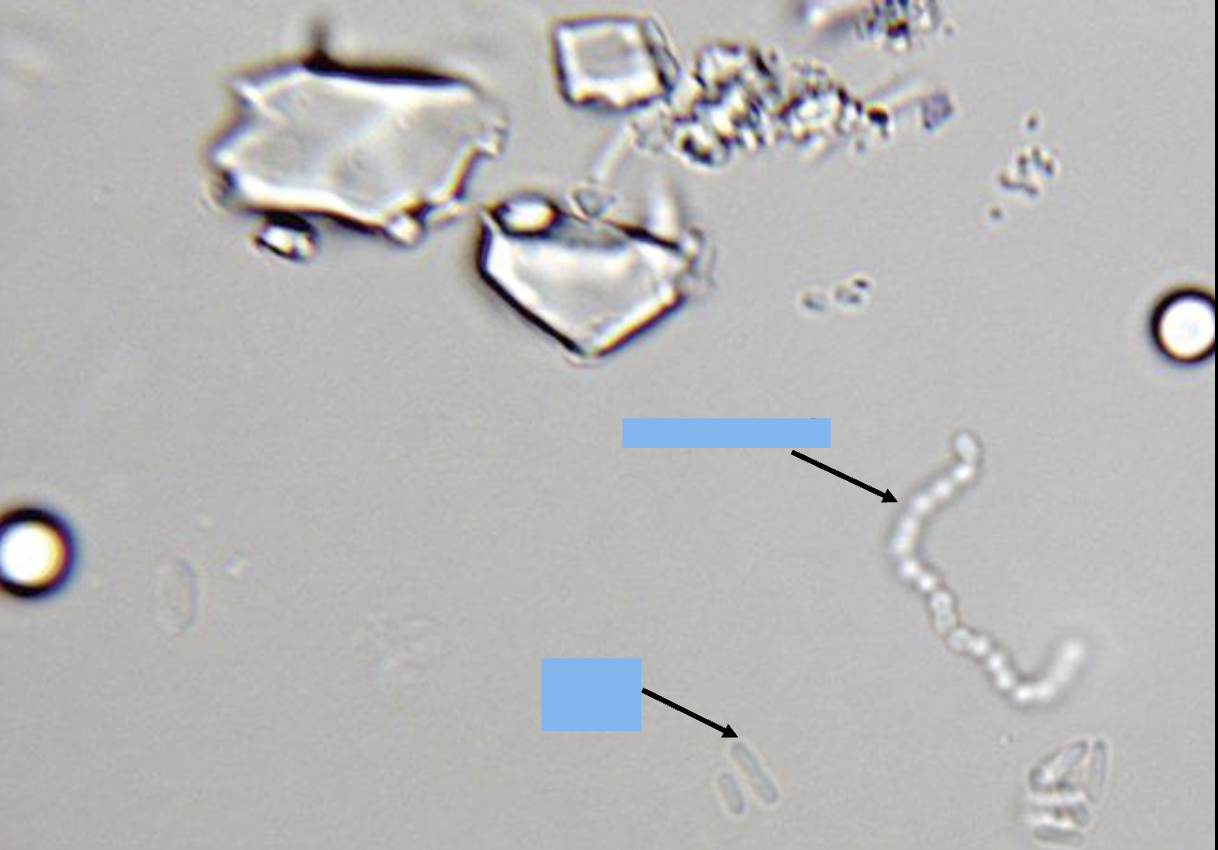
what is the bottom arrow pointing at
bacilli (rods)
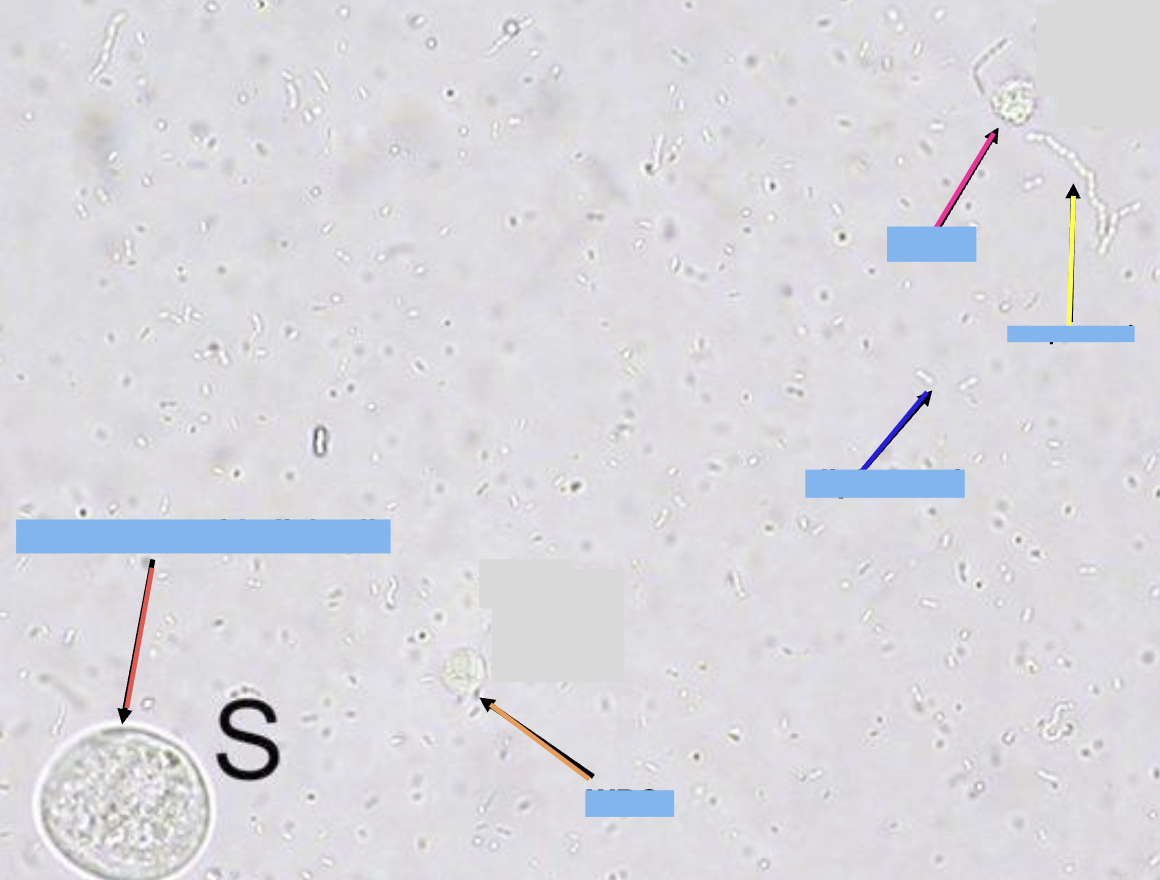
what is the orange and pink arrow pointing at
white blood cells WBC
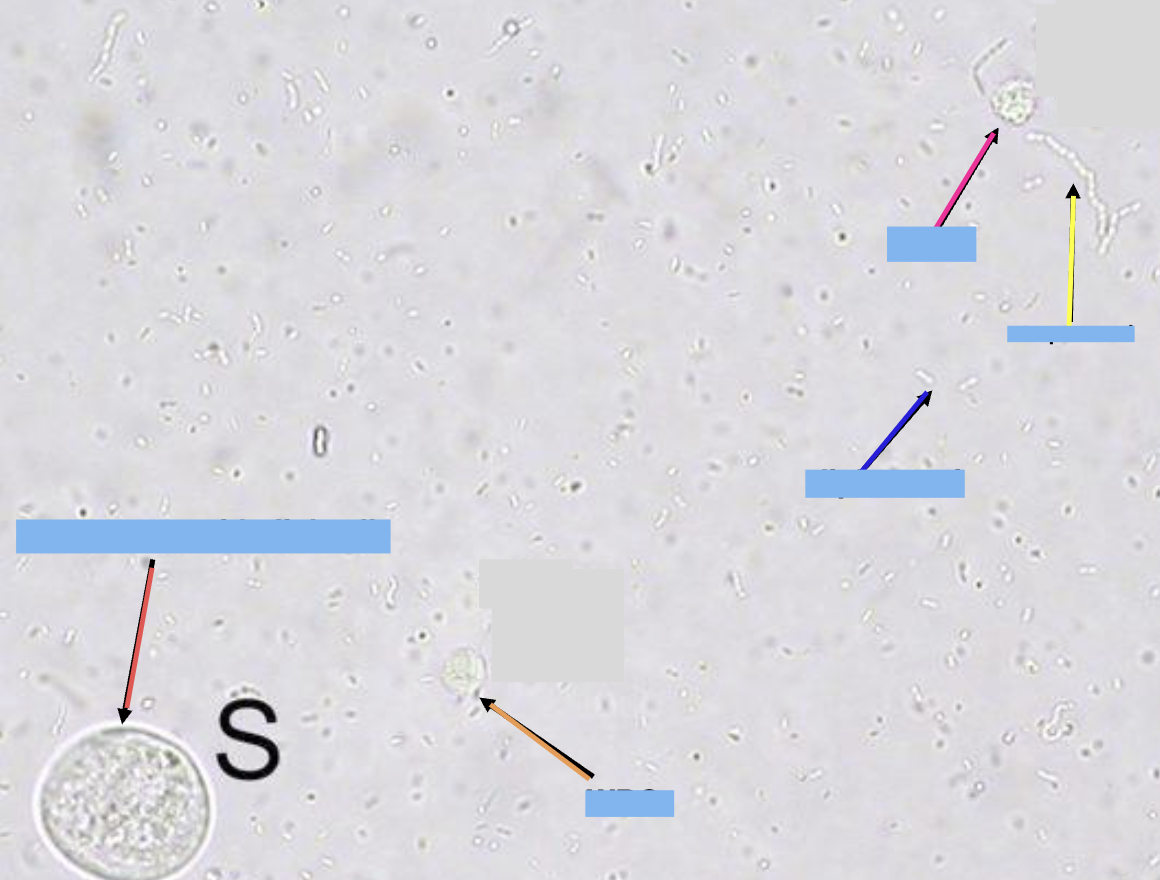
what is the red arrow pointing at
squamous epithelial cell
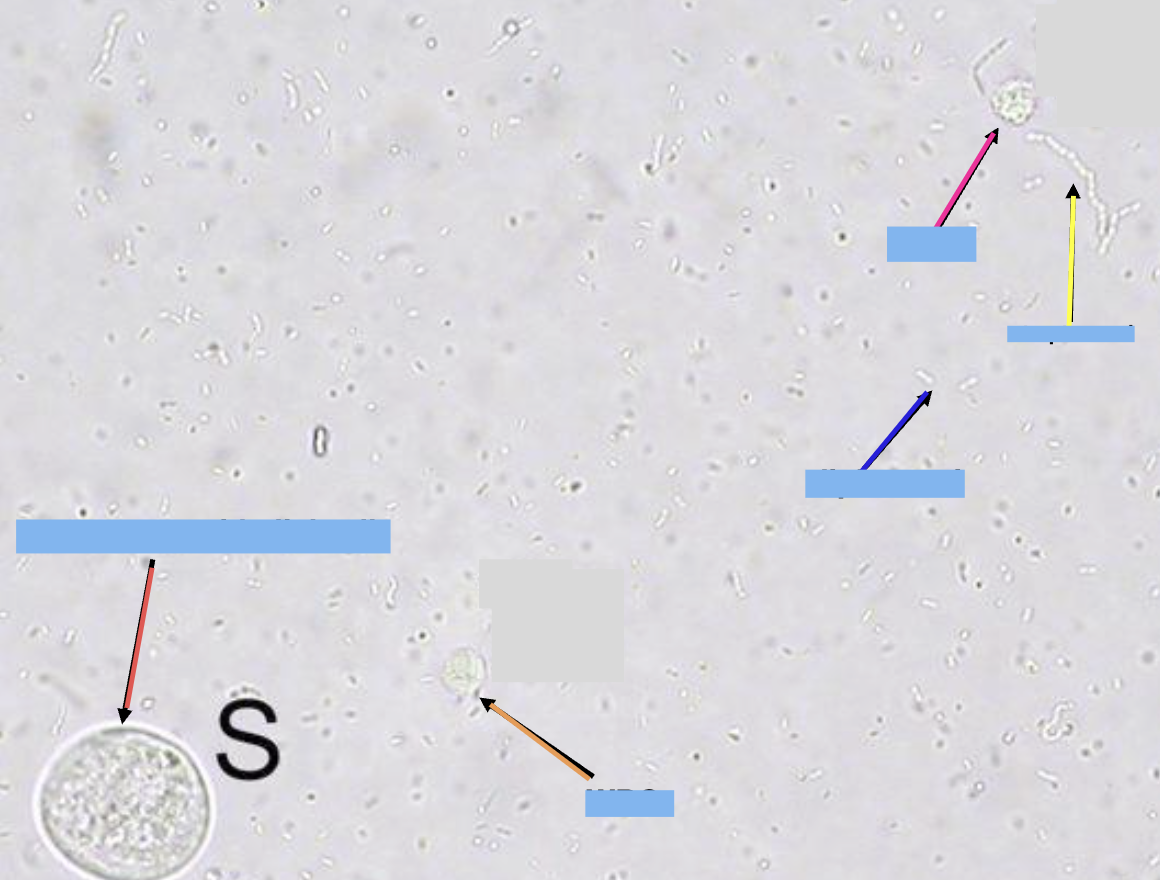
what is the yellow arrow pointing at
streptococci
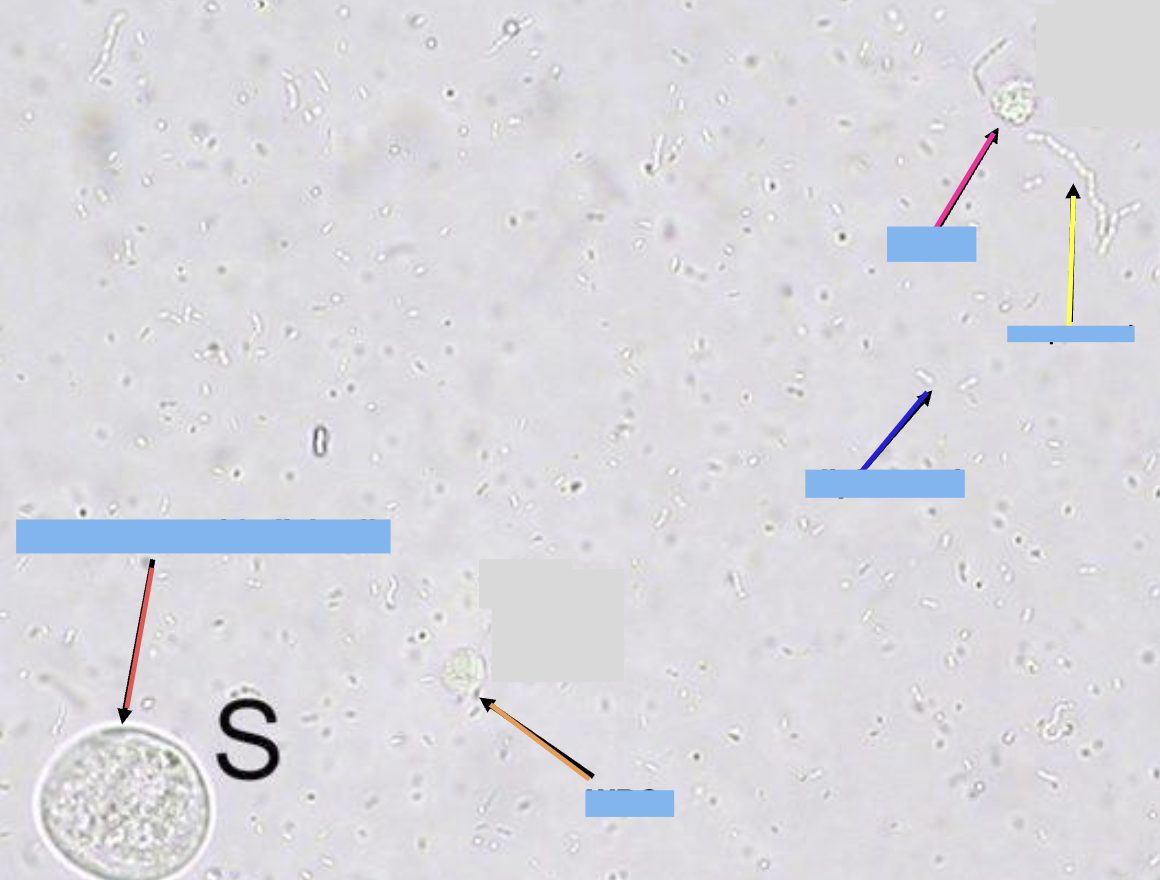
what is the dark blue arrow pointing at
diplococci
polyuria
excessive or increased urine formation (volume)
oliguria
decreased urine formation
pollakiuria
frequent urination in small amounts
anuria
no urine produced or absence of urine
enuria
Urinary incontinence only at night, usually when the patient is sleeping or extremely relaxed.