A/P 1 Lab 2 Bones
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
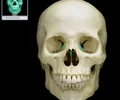
ethmoid bone
forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
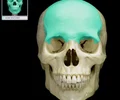
frontal bone
bone that forms the forehead
glabella
A single bony prominence of the frontal bone located between the superciliary arches in the inferior part of the frontal bone above the root of the nose.
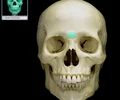
interior nasal concha
inferior turbinate; each forms part of the lateral walls of the nasal cavities; improves the airflow through the nasal cavity
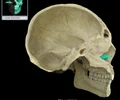
infraorbital foramen
opening under the orbit carrying the infraorbital nerves and blood vessels the the nasal region
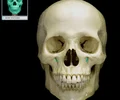
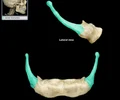
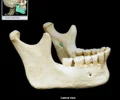
mandible
lower jaw bone
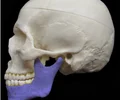
mandibular teeth
teeth of the lower jaw
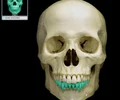
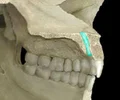
maxillary teeth
line the edge of upper jaw; keeps prey in mouth
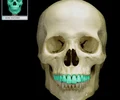
maxilla
upper jaw
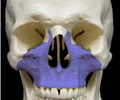
mental foramen
mandible
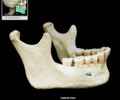
middle nasal concha
the middle thin, spongy, bony plate with curved margins, part of the ethmoidal labyrinth, projecting from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and separating the superior meatus from the middle meatus;
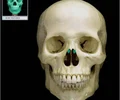
orbit
The eye socket, made up of the maxilla and zygoma.
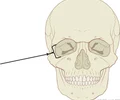
parietal bone
either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
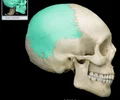
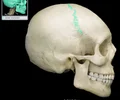
sphenoid bone
forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit
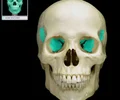
temporal bone
bone that forms parts of the side of the skull and floor of the cranial activity. There is a right and left temporal bone.
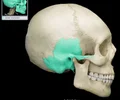
vomer
nasal septum
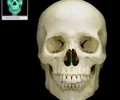
zygomatic bone
the arch of bone beneath the eye that forms the prominence of the cheek
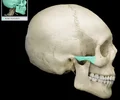
lambdoid suture
between parietal bones and occipital bone
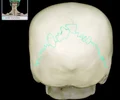
occipital bone
back of head
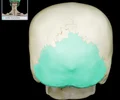
sagittal suture
between the two parietal bones
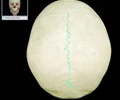
sutural bone
irregular bone within a cranial suture
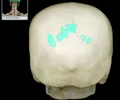
anterior nasal spine
a sharp projection of the maxilla located at the anterior and inferior portion of the nasal cavity
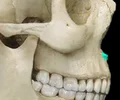
body of mandible
the horizontal portion of the lower jaw
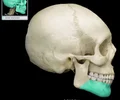
condylar process of mandible
thickened upward projection from posterior margin of mandibular ramus
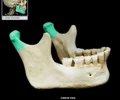
coronoid process of mandible
flattened upward projection from the anterior margin of the mandibular ramus
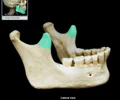
external acoustic meatus
Canal leading to eardrum and middle ear
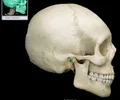
external occpital protuberance
prominent elevation on external surface; provides attachment for nuchal ligament
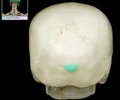
fossa for lacrimal sac
Shallow depression that contains lacrimal sac Continuous inferiorly with nasolacrimal duct Comment: Lacrimal sac, which collects lacrimal (tear) fluid from lacrimal canaliculi, is continuous inferiorly with nasolacrimal duct that leads to inferior nasal meatus
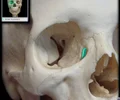
greater wing of sphenoid bone
paired, lateral projections; forms part of middle cranial fossa and lateral aspect of skull (temple)

head of mandible
the rounded end of the condyloid process of the mandible; articulates with mandibular fossa (temporal bone) to form temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
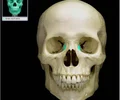
lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts
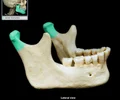
mandibular notch
between mandibular condyle and coronoid processes; broad notch along superior border of mandibular ramus; aka mandibular incisure
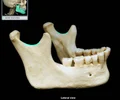
mastoid process of temporal bone
round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear; provides attachment for splenius capitis, sternocleidomastoid, and posterior digastric muscles
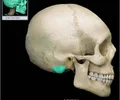
orbital plate of ethmoid bone
This portion of the Ethmoid bone is its lateral border and forms part of the orbit.
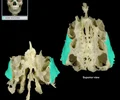
ramus of mandible
vertical portion of the lower jaw that communicates with the skull
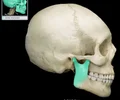
squamous part of temporal bone
large flat bone posterior to the sphenoid bone and inferior to the parietal bone
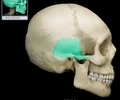
squamous suture
Between parietal and temporal bones
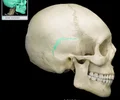
styloid process of temporal bone
pole-like process extending downward from the temporal bone on each side of the skull
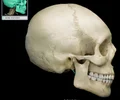
zygomatic arch
Bony arch formed by zygomatic bone (temporal process) and temporal bone (zygomatic process) Posterior and inferior to lateral margin of orbit Palpable where cheek and temple meet Provides attachment for masseter muscle
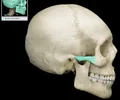
zygomatic process of temporal bone
extension from the temporal bone that forms the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch
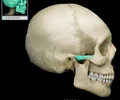
angle of mandible
a bony angle formed by the junction of the posterior edge of the ramus of the mandible and the inferior surface of the body of the mandible; marks widest part of lower 1/3 of face.
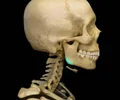
cribiform plate
superior surface of the ethmoid; perforated by a foramina which allows passage of the olfactory nerves, which provide sense of smell
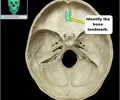
crista galli
Of the ethmoid bone, triangular process that projects superiorly from cribiform plate of ethmoid bone, where the membranes of the brain are attached
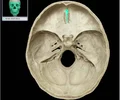
foramen magnum
A large opening at the base of the skull through which the brain connects to the spinal cord.
frontal sinus
cavity within the frontal bone
Paired, mucous membrane-lined cavity
One of paranasal air sinuses
Drains into middle nasal meatus via frontonasal duct
Common site of sinus infection
Contributes to voice resonance
Paranasal sinuses include: frontal, maxillary, and sphenoidal sinuses, and ethmoidal cells (sinus)
Hamulus of medial pterygoid plate
hook around which the tensor veli palatini muscle passes to the soft palate
incisive canal
paired short canals, transmits terminations of greater palatine artery and nasopalatine nerve
inferior nasal concha
shelf like projection of bone, located on each side of the nasal septum, attached to the lateral wall of the nasal cavity; increase epithelial surface area and create turbulence in the inspired air
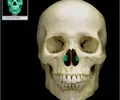
internal acoustic meatus
Bony canal that connects posterior cranial fossa to inner ear cavity Facial (CN VII) and vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) nerves traverse meatus
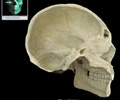
lateral pterygoid plate
Point of origin for internal and external pterygoid muscles.
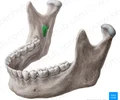
lingula of mandible
Thin, posteriorly-directed bony projection
Provides attachment for sphenomandibular ligament
Landmark for inferior alveolar nerve block in dentistry
mandibular foramen
Opens into mandibular canal Partially obscured by thin shelf of bone, the lingula Conducts nerves and vessels (inferior alveolar) for lower teeth and skin of chin
medial pterygoid plate
sharp process that medially and inferiorly projects from the sphenoid
mylohyoid line
bony ridge located along the inner (medial) surface of the mandibular body
palatine bone
L-shaped bone
Forms posterior portion of hard palate
perpendicular plate of ethmoid
Thin, vertical projection of ethmoid in nasal cavity Forms superior part of nasal septum Articulates with vomer and nasal septal cartilage
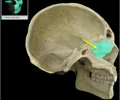
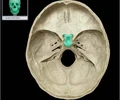
sella turcica
depression in the sphenoid bone where the pituitary gland is located
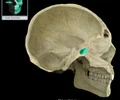
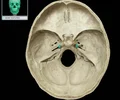
sphenoid sinus
found deep within the skull behind the Ethmoid sinuses. They are small cavities approximately the size of a large grape. The left and right ., sit next to each other and are separated by a thin plate of bone (septum).
foramen lacerum
Irregularly shaped opening formed by sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones Superior opening (middle cranial fossa) Inferior opening (base of skull) Inferior opening is closed in living subjects by fibrocartilage Internal carotid artery enters posterior wall and ascends into middle cranial fossa
foramen ovale
phenoid bone (greater wing)
Oval-shaped hole
Superior opening in middle cranial fossa
Inferior opening in infratemporal fossa
Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (CN V3) passes through this opening
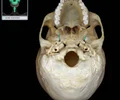
foramen spinosum
Round hole Superior opening in middle cranial fossa Inferior opening in infratemporal fossa Middle meningeal artery passes through this opening
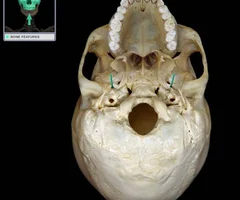
jugular foramen
Irregularly-shaped opening
Superior opening (posterior cranial fossa)
Inferior opening (base of skull)
Posterior to external opening of carotid canal
Traversed by internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), and accessory nerve (CN XI
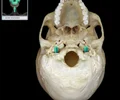
mandibular fossa
the depression in the temporal bone into which the condyle of the mandible fits
occipital condyle
ridges on left and right of foramen magnum
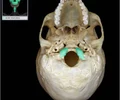
opening of carotid canal
Opening in base of skull Transmits internal carotid artery and carotid plexus of sympathetic nerves from neck to carotid canal and cranial cavity Superior opening of canal is into foramen lacerum
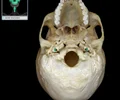
stylomastoid foramen
Between styloid and mastoid processes Small opening in tympanic part of temporal bone Transmits facial nerve (CN VII) and stylomastoid artery
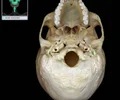
temporal process of zygomatic bone
short extension from the zygomatic bone that forms the anterior portion of the zygomatic arch
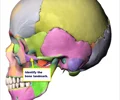
body of sphenoid bone
Cube-shaped part with central concavity (sella turcica) for pituitary gland
Articulates with ethmoid bone (anterior), greater wing (lateral), and occipital bone (posterior)
Contains sphenoidal sinuses (paranasal sinuses)
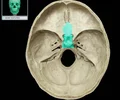
dorsum sellae
Square projection Posterior part of sella turcica Has paired, posterior clinoid processes Forms posterior wall of hypophysial fossa
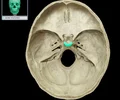
foramen rotundum
most medial of the 3 foramen Horizontal canal Connects middle cranial fossa with pterygopalatine fossa Transmits maxillary (CN V2) nerve
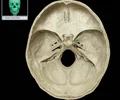
hypoglossal canal
Short canal through occipital bone near foramen magnum External opening on medial aspect of occipital condyle Traversed by hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
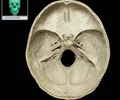
lesser wing of sphenoid bone
One of two side wings extending from the body of the sphenoid bone
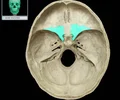
optic canal
allows the optic nerve to pass to the eye
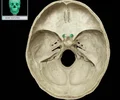
petrous part of temporal bone
raised area on internal surface of cranial vault which encloses structures of middle and inner ear
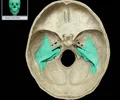
superior orbital fissure
Oblique fissure Bordered by body, greater wing, and lesser wing of sphenoid, and frontal bone (orbital surface) Connects orbit with middle cranial fossa Transmits oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), and abducens (CN VI) nerves, branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1), and ophthalmic veins
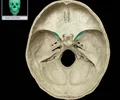
anterior ethmoidal foramen
Small foramen in suture between orbital plate of ethmoid bone and orbital surface of frontal bone Connects orbit with ethmoidal sinuses and nasal cavity Transmits anterior ethmoidal nerve, artery, and vein
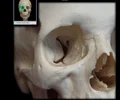
inferior orbital fissure
fissure in the orbit floor between maxilla and greater wing of sphenoid
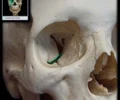
infraorbital canal
Canal in floor of orbit Continuous posteriorly with infraorbital groove Opens anteriorly through infraorbital foramen Transmits infraorbital nerve, artery, and vein
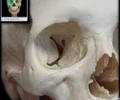
nasal bone
bridge of nose
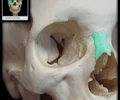
orbital part of lesser wing of sphenoid bone
Posterior part of roof of orbit Upper boundary of superior orbital fissure Has orbital opening of optic canal Optic canal transmits optic nerve and ophthalmic artery
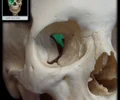
orbital process of palatine bone
Superolaterally directed process Minor contribution to orbital floor Orbital floor formed by maxilla (orbital surface), zygomatic bone (orbital surface), and palatine bone (orbital process)
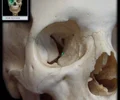
orbital surface of frontal bone
Internal surface on upper part of eye orbit
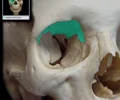
orbital surface of greater wing of sphenoid bone
Location: Sphenoid bone (greater wing) Orbit (lateral wall) Description: Smooth, quadrilateral bony surface Forms posterior part of lateral wall of orbit Contributes to superior orbital fissure Contributes to inferior orbital fissure
Comment: Lateral orbital wall formed by greater wing of sphenoid (orbital surface) and zygomatic bone (orbital surface) Superior orbital fissure formed by body, greater wing, and lesser wing of sphenoid, and frontal bone (orbital surface) Superior orbital fissure transmits ophthalmic (CN V1), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), and abducens (CN VI) nerves, and ophthalmic veins Inferior orbital fissure formed by maxilla (orbital surface), greater wing of sphenoid (orbital surface), zygomatic bone (orbital surface), and orbital process of palatine bone Inferior orbital fissure transmits maxillary nerve (CN V2) and accompanying vessels, and a connection between inferior ophthalmic vein and pterygoid venous plexus (in infratemporal fossa)
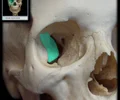
orbital surface of maxilla
forms part of the inferior surface of the orbit, located inferior and lateral to the lacrimal bones
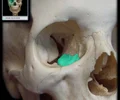
orbital surface of zygomatic bone
forms lateral eye orbit
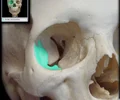
supraorbital notch
an incomplete supraorbital foramen
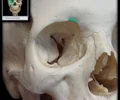
ethmoidal cells
Paired, thin-walled, mucous membrane-lined cavities
Clustered into anterior, middle, and posterior cells
One of paranasal air sinuses
Also known as:Ethmoidal air cells, Ethmoid sinus
Posterior ethmoidal cells open into superior nasal meatus
Anterior and middle ethmoidal cells open into middle nasal meatus
Paranasal sinuses include: frontal, maxillary, and sphenoidal sinuses, and ethmoidal cells (sinus)
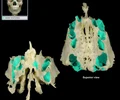
orbital plate of ethnoid bone
Thin-walled, smooth lateral surface of ethmoid
Forms large part of medial wall of orbit
Covers middle and posterior ethmoidal air cells
supraorbital margin
The superior rim of the eye socket located on the frontal bone.
alveolar process of mandible
upper border of the mandibular body that contains the lower teeth
angle of mandible
The lower posterior of the ramus
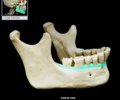
maxillary sinus
largest paranasl sinus; pyramidal; on cheek bone lateral to nasal bone Drains into middle nasal meatus Common site of sinus infection Contributes to voice resonance Paranasal sinuses include: frontal, maxillary, and sphenoidal sinuses, and ethmoidal cells (sinus)
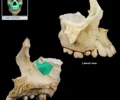
palatine process of maxilla
The portion of the maxillary bone that forms most of the hard palate. It consists of 2 pieces of bone that grow and fuse at the midline during the fetal stage.

hypophysial fossa
depression in the sella turcica where the saddle dips, contains pituitary gland, aka pituitary fossa

medial pterygoid plate
paired, flattened bony projections of the sphenoid bone located on the inferior skull medial to the lateral pterygoid plate; form the posterior portion of the nasal cavity lateral wall
Connects pterygopalatine fossa with foramen lacerum
Conducts nerve and vessels of pterygoid canal
mastoid part of temporal bone
Mastoid process is inferior, conical projection
Contains mastoid air cells and antrum Internal surface has groove for sigmoid dural venous sinus
Provides attachment for occipitalis, sternocleidomastoid, splenius capitis, and longissimus muscles Mastoid and petrous parts of temporal bone sometimes combined as petromastoid part
Spread of bacterial infection from tympanic cavity of middle ear to mastoid air cells and antrum called mastoiditis

body of hyloid bone
Hyoid bone (anterior) Central portion Anterior surface is convex Posterior surface is smooth and separated from epiglottis by loose connective tissue Provides attachment for suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles

greater horn of hyoid bone
Paired, posteriorly-directed projections
Provides attachment for middle pharyngeal constrictor, hyoglossus, thyrohyoid, and stylohyoid muscles, digastric tendon (via fibrous loop), and thyrohyoid membrane
Also known as:
Greater cornu