Quiz 9: Pharmacokinetics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What are three major causes of changes in pharmacokinetic parameters?
disease, natural physiological changes (age, organ function), and concomitant drug therapy
What primary PK parameters should be evaluated first when assessing drug interactions?
Clearance (CL), Volume of distribution (V), and Bioavailability (F)
Why must primary PK effects be evaluated before secondary PK parameters?
secondary parameters (half-life, k, steady-state concentration) depend on primary parameters
What physiologic variables affect absorption rate constant (ka)?
blood flow, gastric emptying, intestinal motility, and transporter expression
What are bioavailability (F) physiologic influences?
affected by gastric emptying, acid secretion, intestinal motility, hydrolytic enzymes, and first-pass effect
What physiologic factors affect hepatic clearance (CLH)?
hepatic blood flow, binding in blood, intrinsic enzyme and transporter activity
What physiologic factors affect renal clearance (CLR)?
renal blood flow, binding, active secretion, reabsorption, urine pH, urine flow, and GFR
What determines volume of distribution (V)?
binding in blood and tissues, body composition, tissue partitioning, and body size
What are 3 secondary PK parameters and their primary dependencies?
- t½ (dependent on V/CL)
- k (CL/V)
- fe (CLR/CL)
What is the formula for elimination half-life?
t½ = 0.693 × V/CL
What is the equation for average steady-state concentration following oral dosing?
Css = FD / (CL × τ)
What are the 4 mechanisms of pharmacokinetic drug interactions?
absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
What is the mechanism of absorption-related drug interactions?
altered absorption, first-pass metabolism, or inhibition of intestinal efflux transporters
What type of interaction is protein-binding displacement?
distribution interaction
What are 2 mechanisms of metabolism interactions?
competitive enzyme inhibition and enzyme induction
What transporters influence excretion interactions?
efflux transporters (PGP) in renal tubules or biliary system
What happens when doxycycline is co-administered with antacids?
reduced absorption and lower bioavailability
What causes reduced doxycycline absorption with antacids?
chelation of drug in intestinal lumen, preventing absorption
What are 3 sites where first-pass metabolism may occurs?
gut lumen, gut wall, and liver
What enzyme is highly expressed in intestine and liver and involved in many interactions?
CYP3A4
What are examples of CYP3A4 inhibitors?
ketoconazole, erythromycin, diltiazem
What are examples of CYP3A4 inducers?
barbiturates and oral contraceptives
What is the result of CYP3A4 inhibition during absorption?
increased bioavailability and plasma concentration
What two systems work together in gut for drug interactions?
CYP3A4 metabolism and P-glycoprotein efflux
How does lovastatin increase verapamil bioavailability?
inhibits intestinal PGP, allowing more drug absorption
How can fruit juices affect intestinal interactions?
inhibit influx transporters (OATP), decreasing absorption
What is indicated when CLR >> fu × GFR?
active secretion is occurring
How does probenecid affect antibiotic renal clearance?
blocks tubular secretion, decreasing CLR and increasing AUC
What happens to AUC and t½ when probenecid inhibits secretion?
both increase due to reduced clearance
In hepatic clearance, what is the equation for CLH using the well-stirred model?
CLH = (Q × fu × CLint) / (Q + fu × CLint)
What are the determinants of intrinsic clearance (CLint)?
Vmax (enzyme capacity) and Km (enzyme affinity)
For low clearance drugs, what is CLH approximately equal to?
CLH ≈ fu × CLint
For high clearance drugs, what parameter does CLH approximate?
Blood flow (Q)
Why is unbound drug concentration (Css,u) clinically important?
only free drug is pharmacologically active
How is Css,u calculated for IV infusion?
Css,u = (fu × k0) / CL
In a low clearance drug, what happens when protein binding decreases (fu ↑)?
total Css decreases, but Css,u remains unchanged
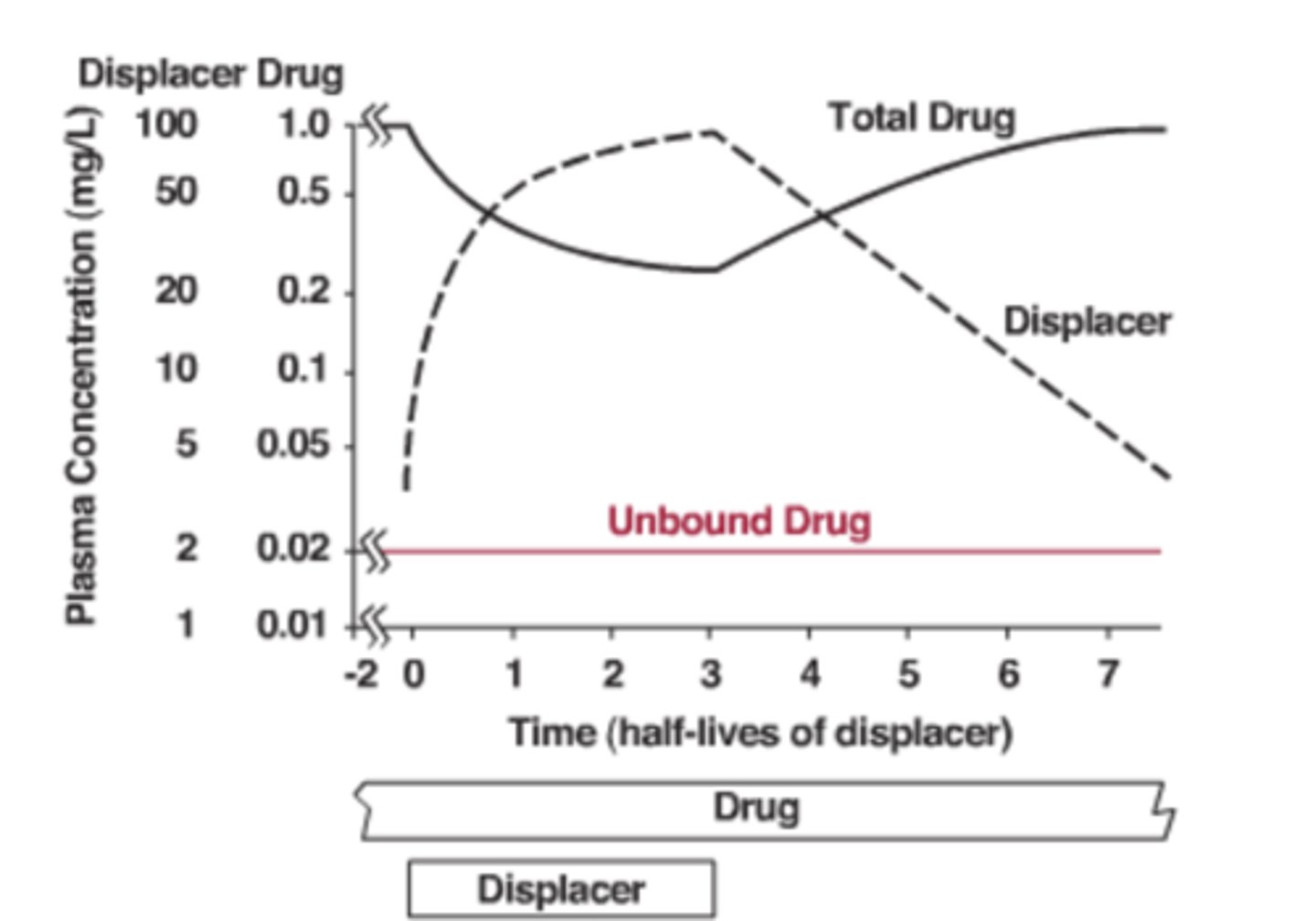
Why should dosing NOT be changed when fu increases for low-clearance drugs?
active (unbound) drug concentration remains unchanged
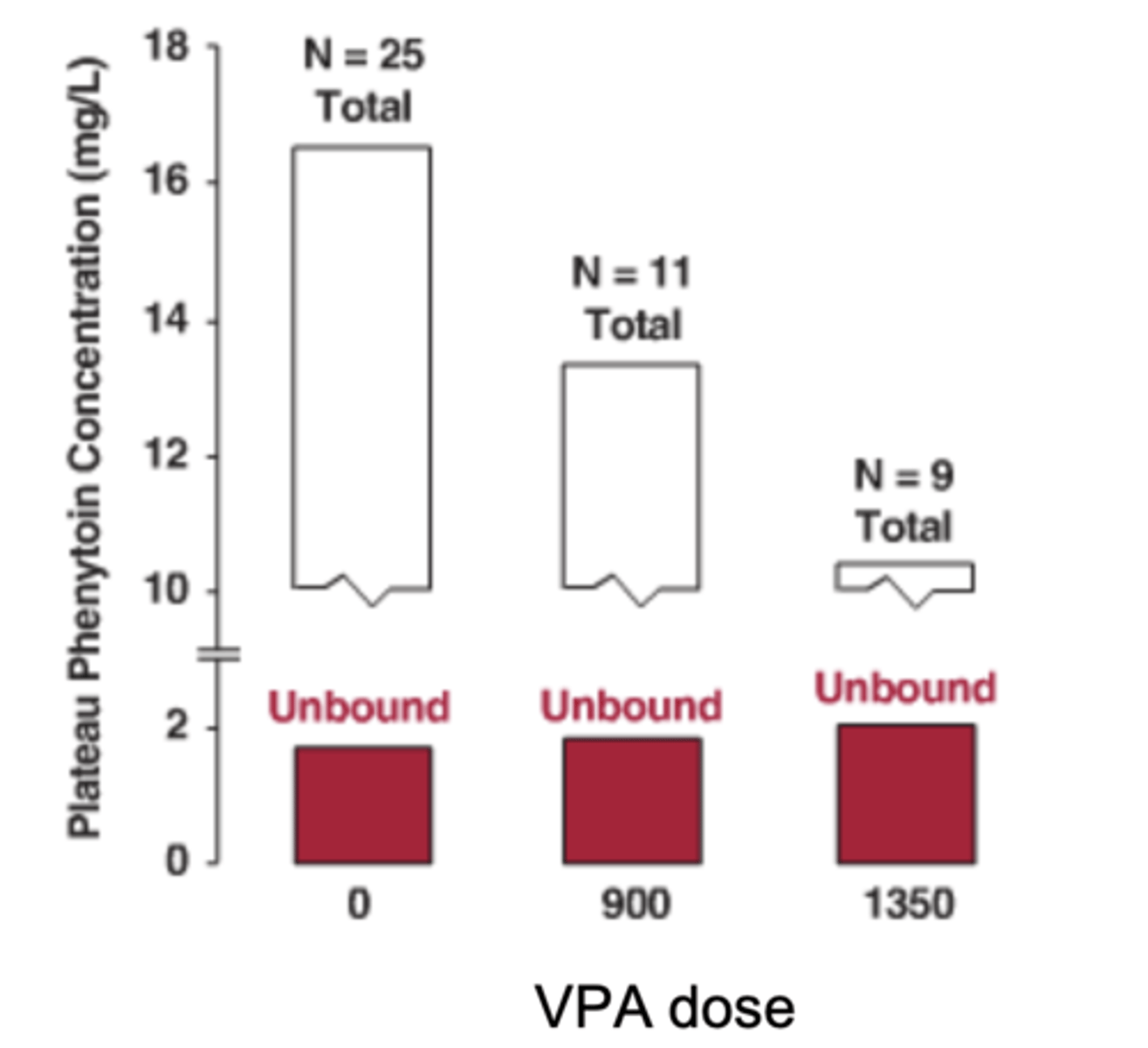
What example demonstrates protein-binding displacement without dosing change?
phenytoin + valproic acid interaction
What happens to Css and Css,u when intrinsic clearance increases (enzyme induction) for low-clearance drugs?
Css and Css,u both decrease
What happens to t½ when CLint increases (induction) in low clearance drugs?
half-life decreases
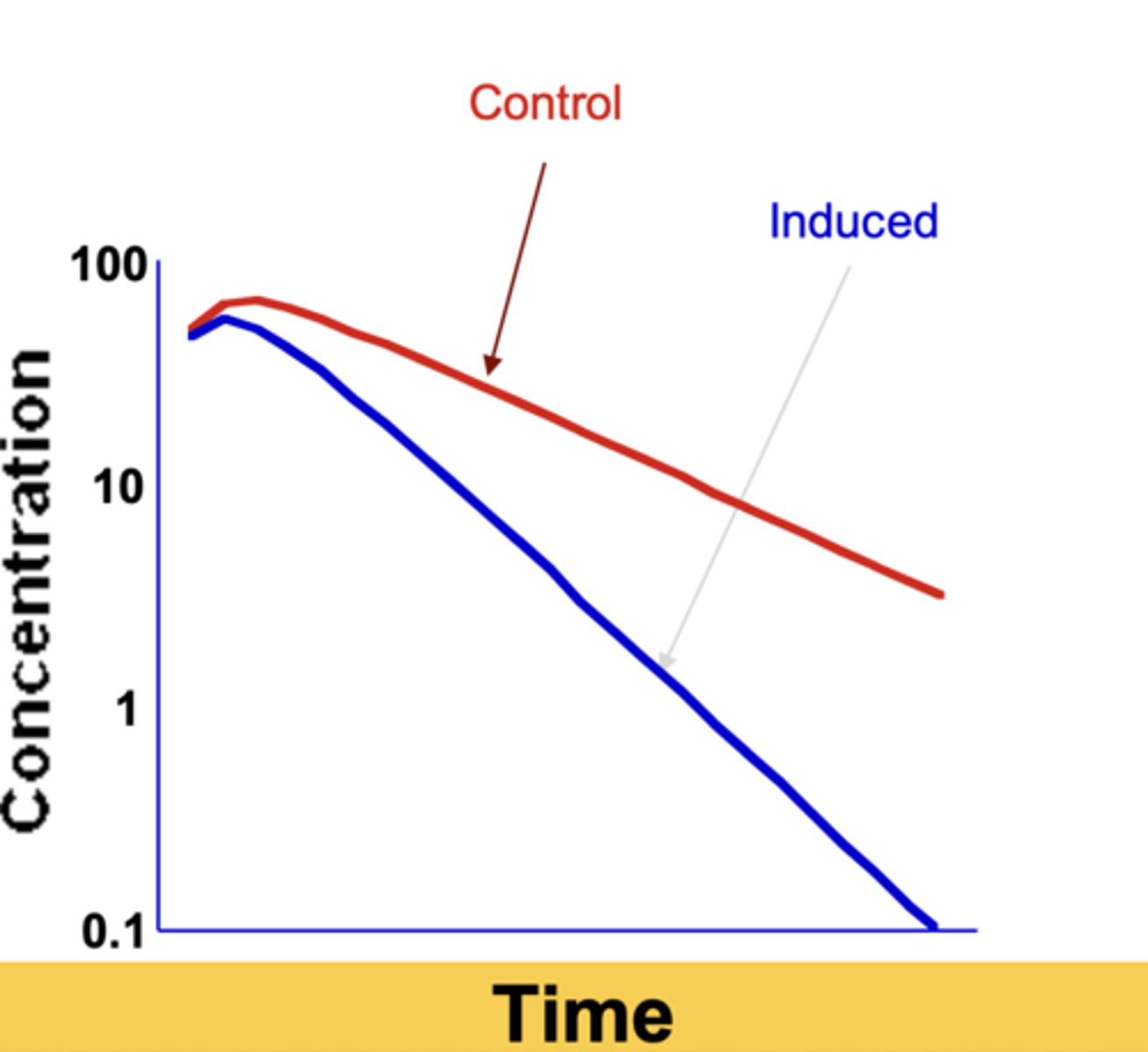
Which parameter primarily increases during enzyme induction?
Vmax (more enzyme produced)
What causes CLint to increase during induction?
increased enzyme synthesis (higher R), not change in kt
What happens to drug levels when an inducer is discontinued?
drug concentration gradually returns to baseline
What are the effects of enzyme inhibition (low clearance drug)?
CL decreases, AUC increases, t½ increases
How does enzyme inhibition affect Css,u compared to induction?
Css,u increases due to reduced CL
What determines time-course of inhibition effects?
inhibitor's own half-life
For high clearance drugs, what controls clearance?
hepatic blood flow (Q), not CLint or fu
Why does induction of CLint have minimal effect on CL for high clearance drugs?
CLH is flow-limited (already near max)
What parameter is impacted most for high-clearance drugs when CLint increases?
bioavailability decreases (greater first-pass extraction)
What happens to F when extraction ratio increases from 0.9 to 0.95?
F decreases from 0.1 to 0.05 (50% drop)
What happens to AUC PO when bioavailability decreases for high clearance drugs?
AUC decreases due to lower F
How does decreasing hepatic blood flow affect high clearance drugs?
CLH decreases, AUC increases, t½ increases
In oral dosing of high clearance drugs, why may AUC not change when Q decreases?
reduced bioavailability offsets reduced clearance
What is an example of blood-flow based interaction?
propranolol reducing lidocaine clearance via lowered hepatic flow
What formula explains tissue binding's role in volume of distribution?
Vss = Vp + (fu/fu,t) × VT
How does increased fu affect V?
more free drug available to enter tissues → increased V
How does increased fu,t change V?
more unbound in tissue moves to plasma → lower V.
Which drug interactions affect V most?
those involving protein binding shifts or tissue partitioning
What is the final clinical step after evaluating PK effects of an interaction?
decide whether to adjust the dose or dosing interval
What is the most important determinant of dosing changes due to interactions?
change in unbound steady-state concentration (Css,u)