UNIT 4- PLATES-TIDES
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
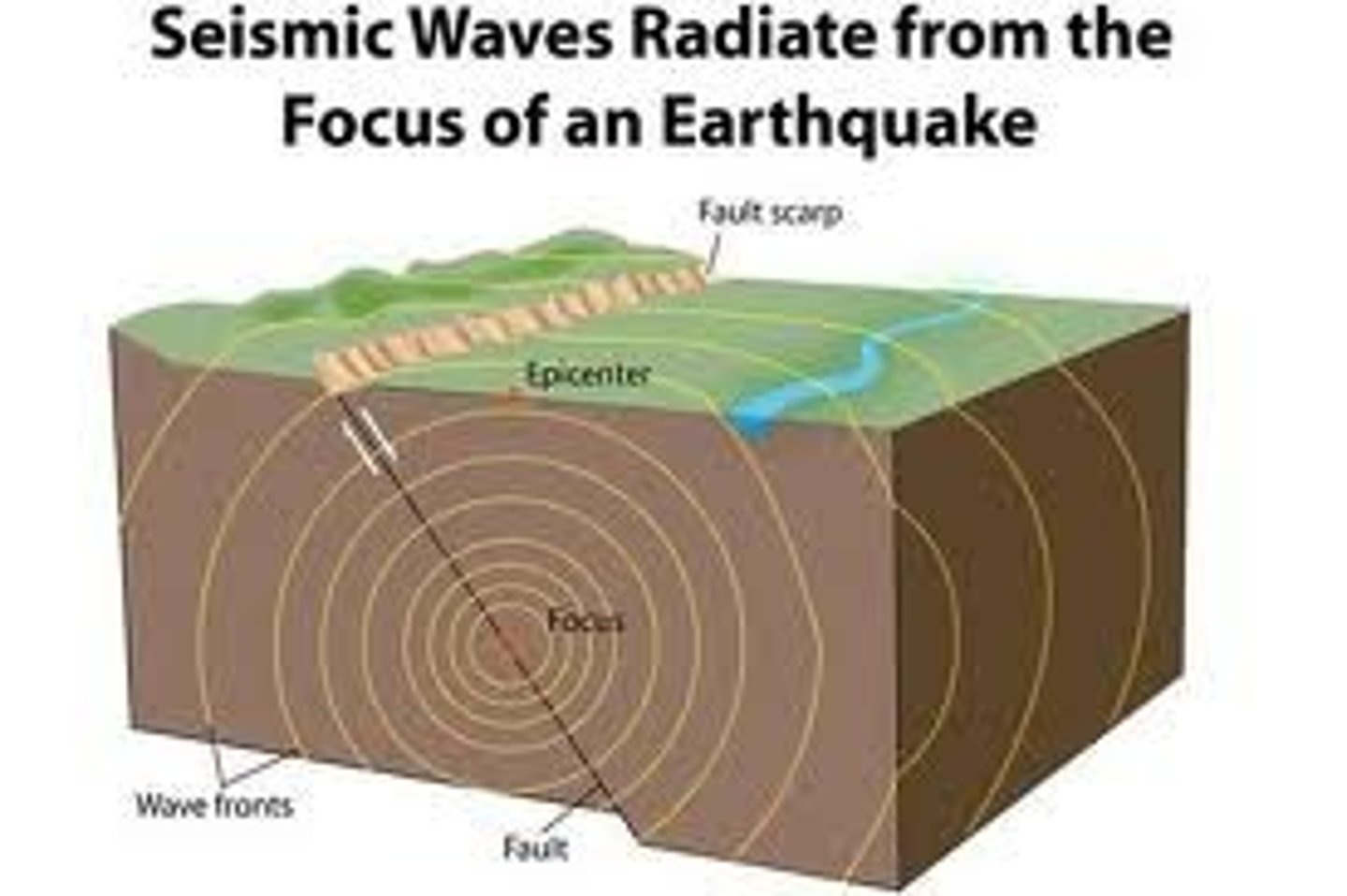
earthquake
The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface.
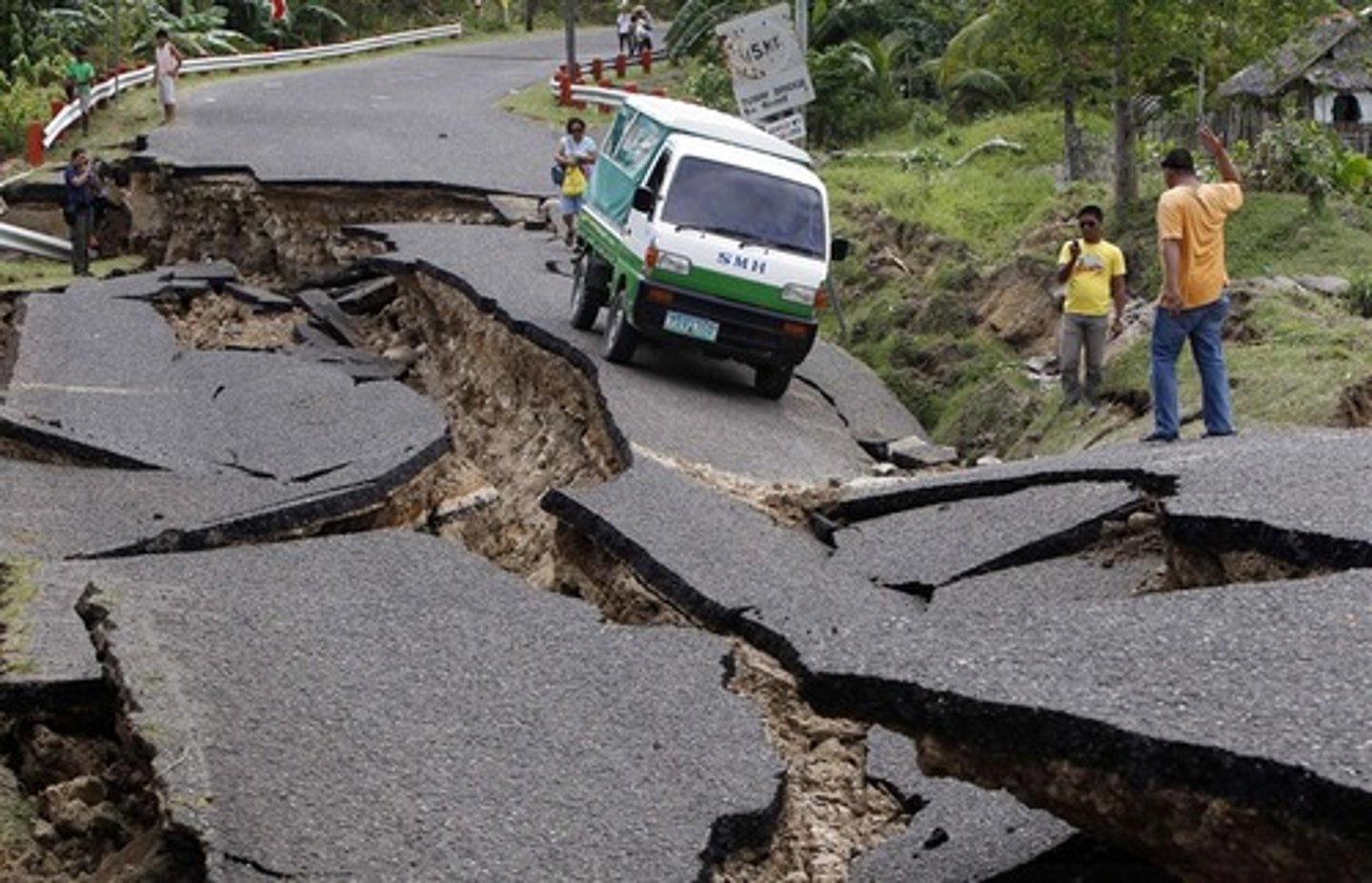

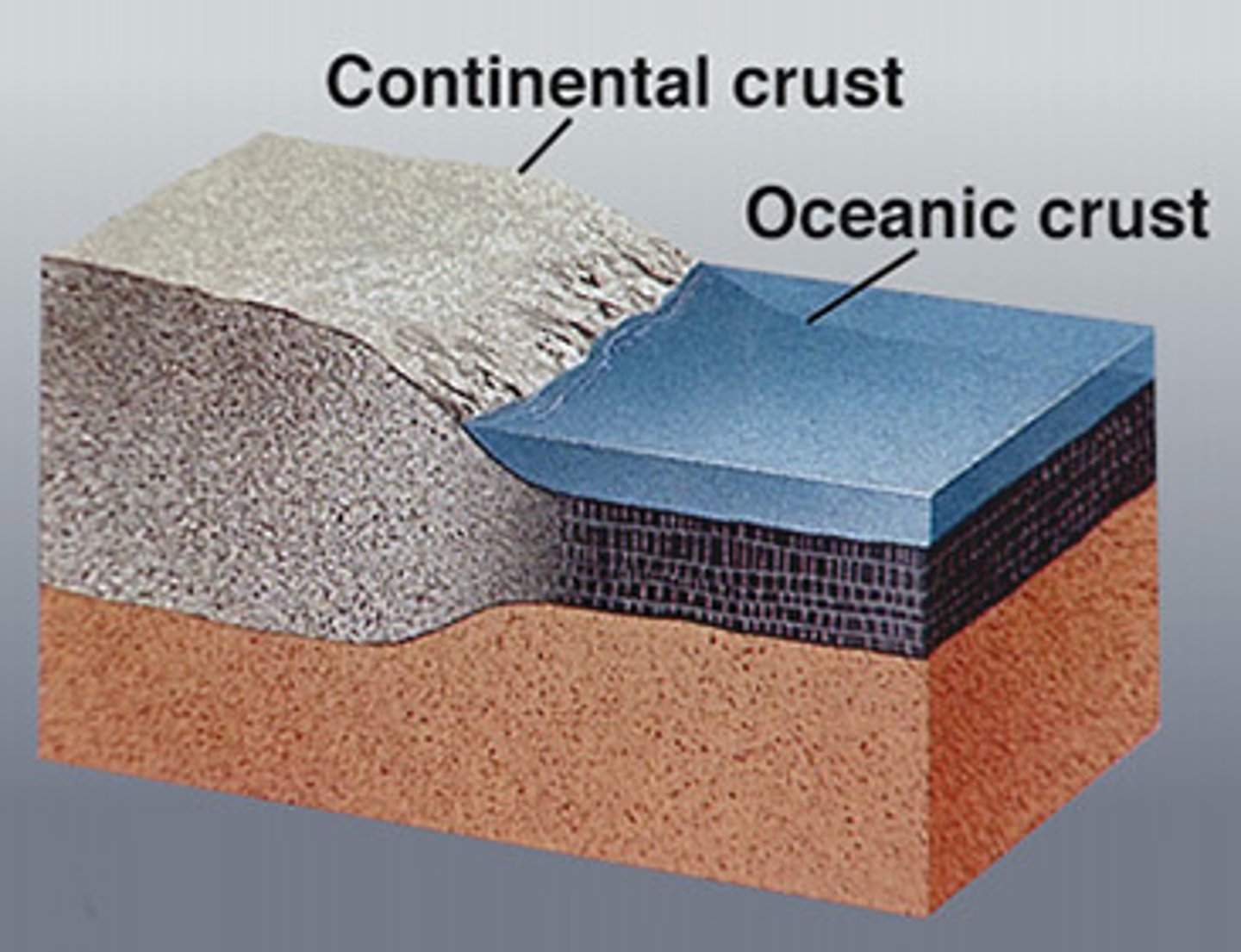
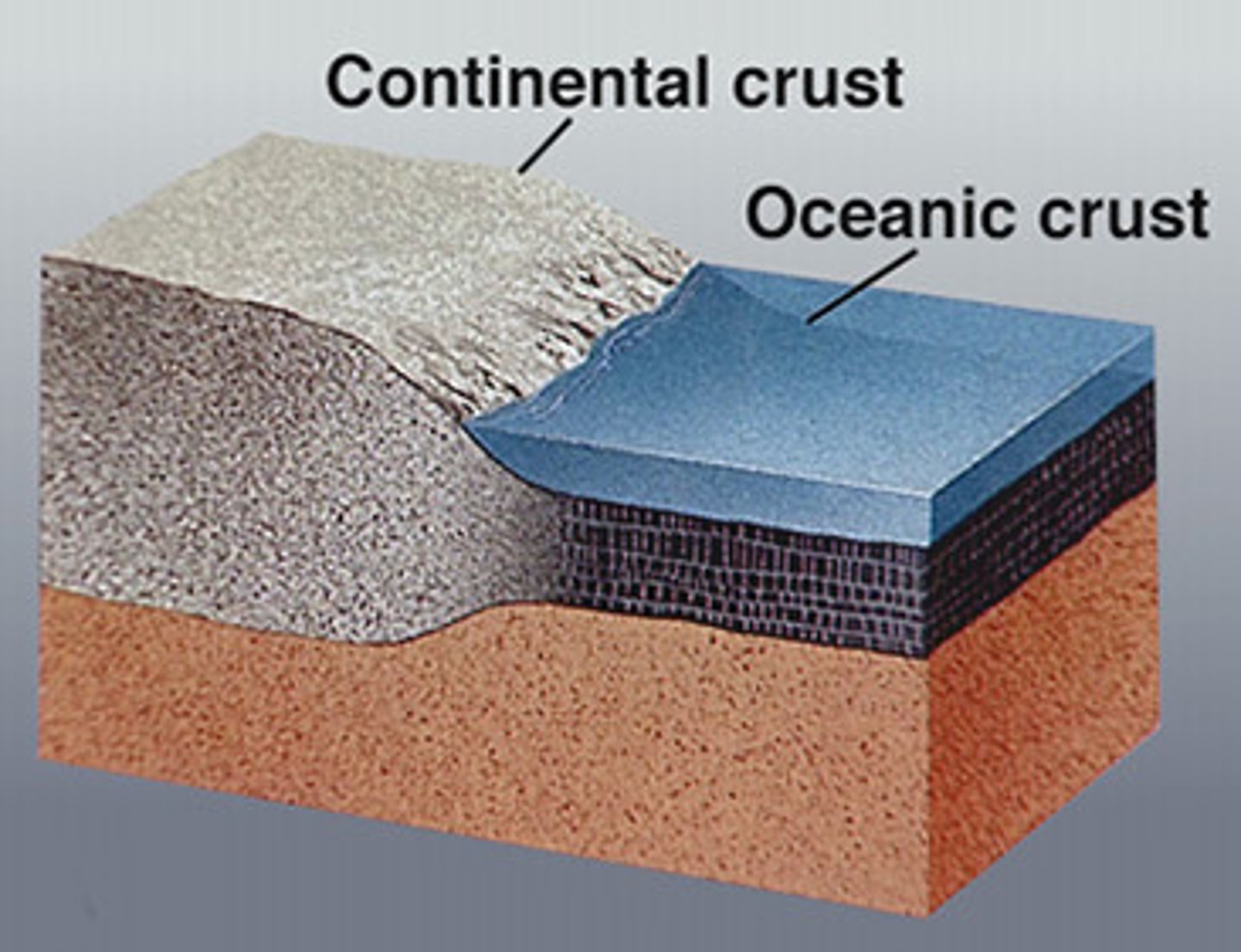
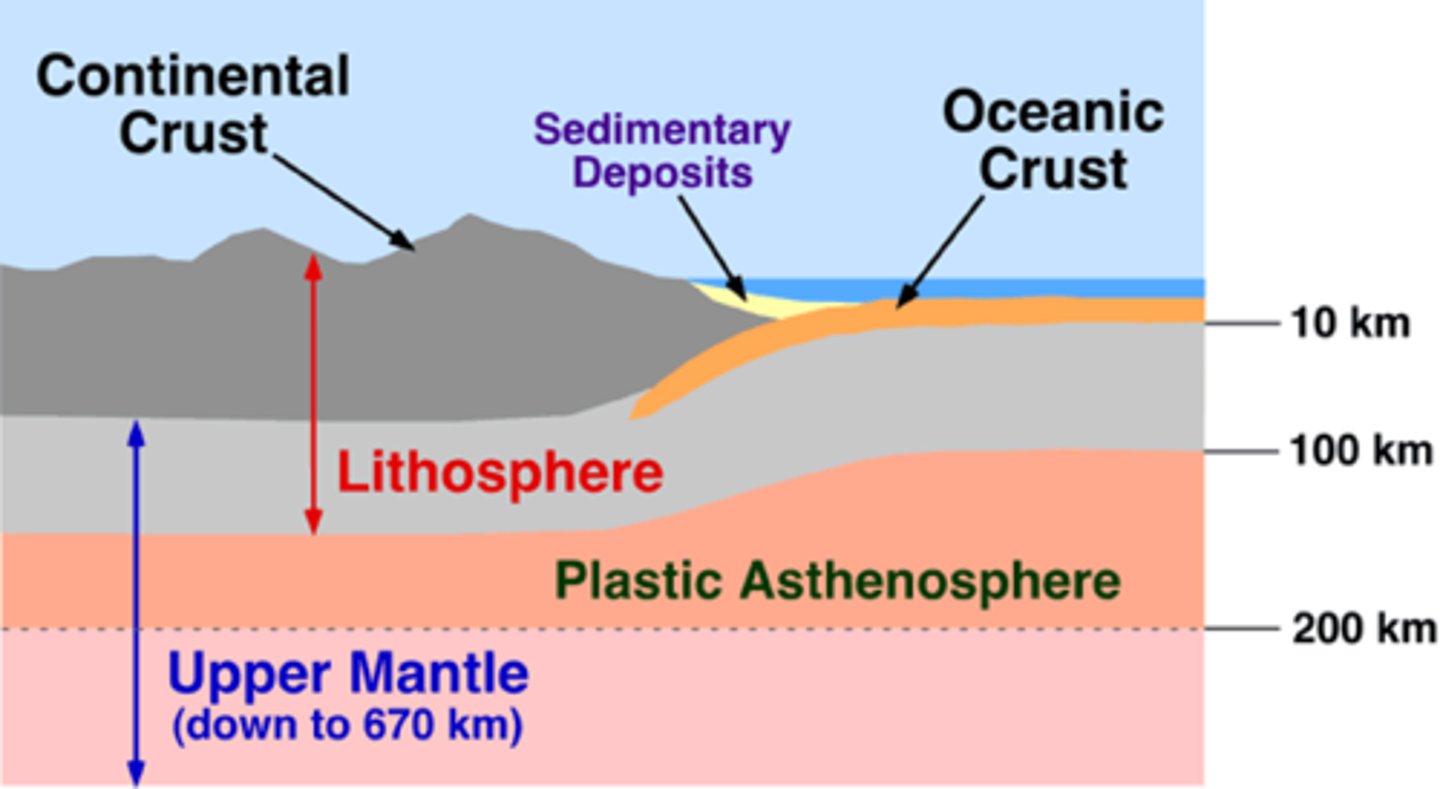
continental crust
The portion of the earth's crust that primarily contains granite, is less dense than oceanic crust, and is 20-50 km thick
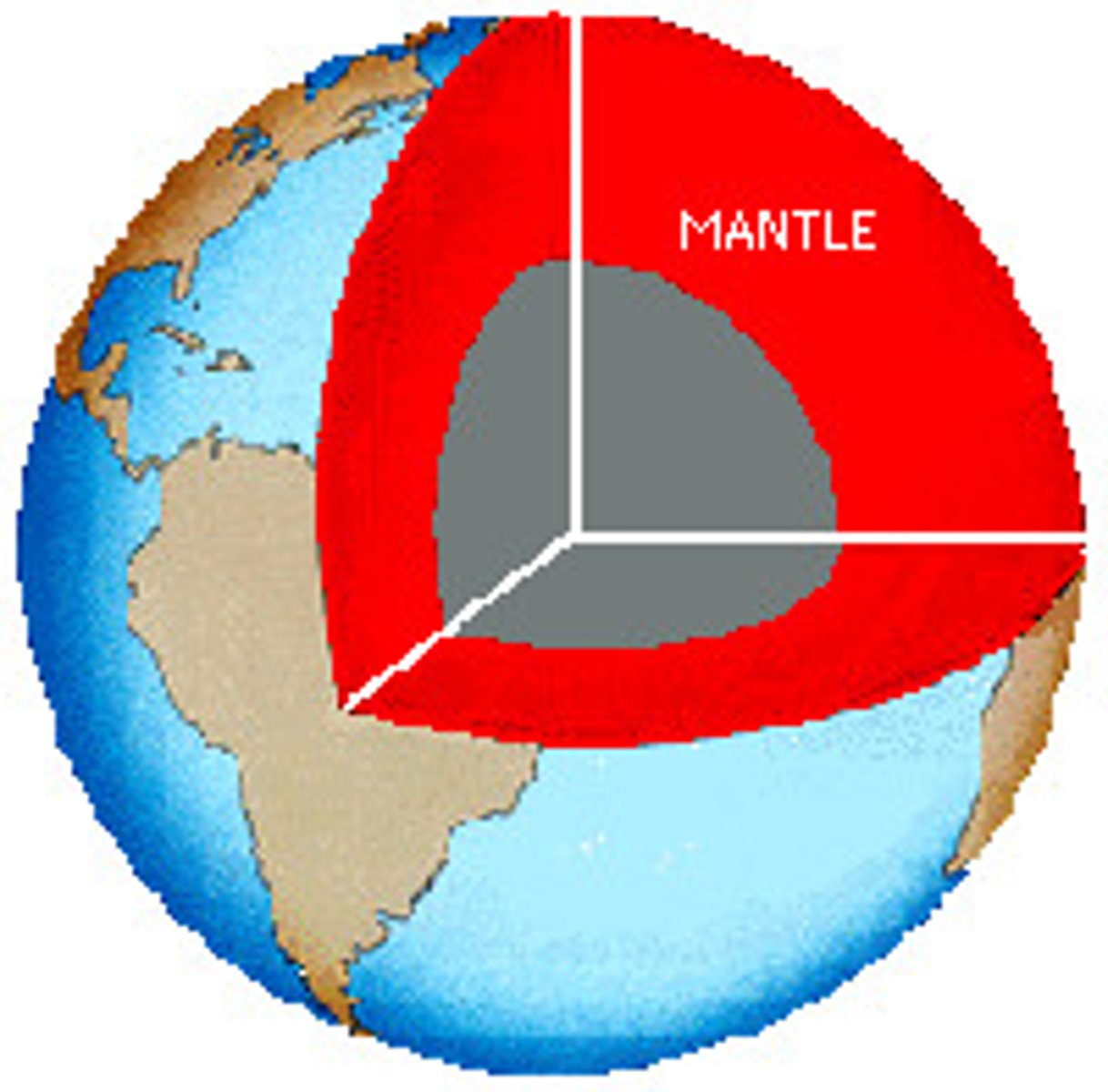
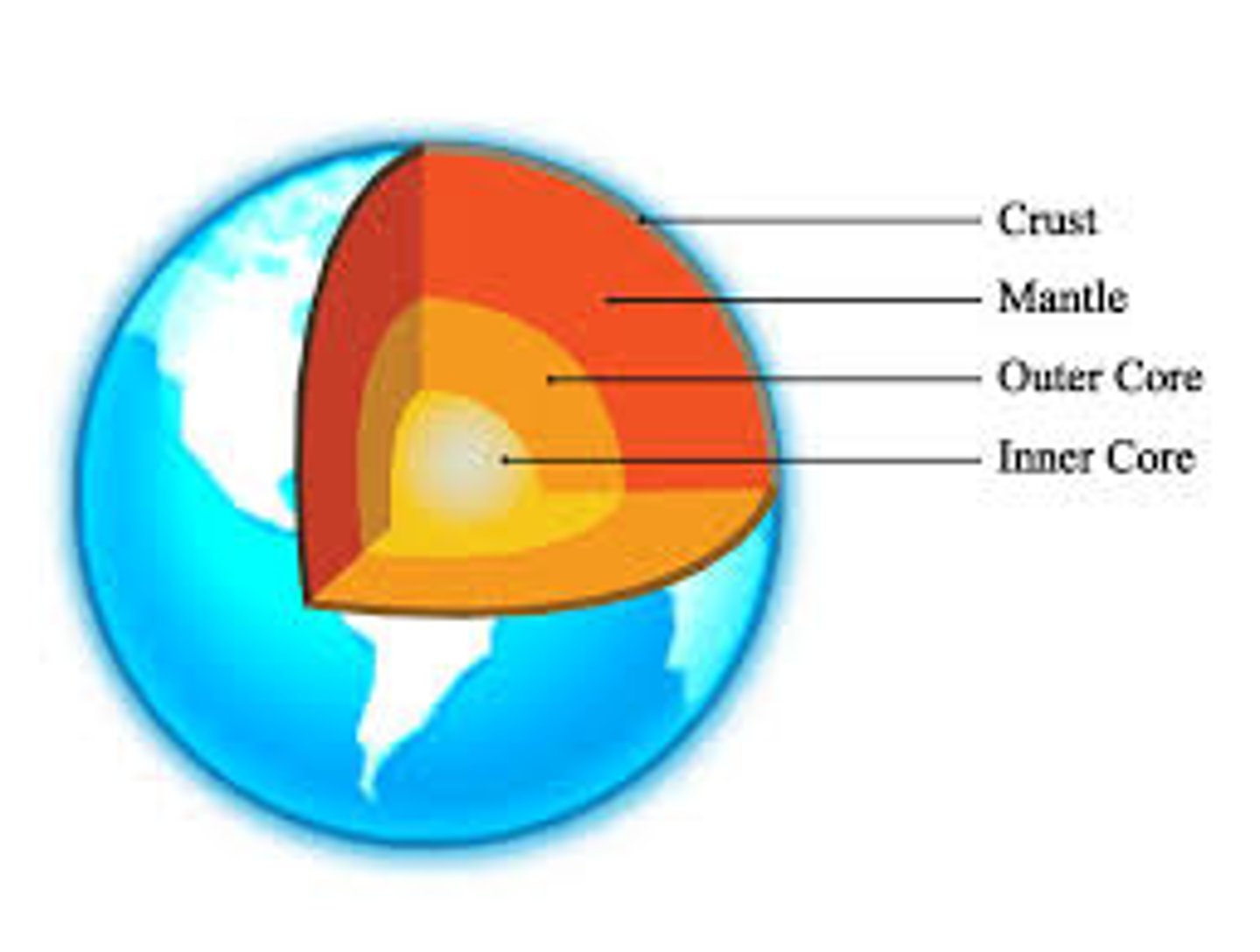
Mantle
The layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core.
core
The central part of the earth below the mantle
seismic
relating to earthquakes
oceanic crust
the portion of Earth's crust that is usually below the oceans and not associated with continental areas, thinner and higher in density that continental crust and basaltic rather than granitic in composition
Continental Drift Theory
Alfred Wegener believed landmasses of Earth once fit together to form single landmass called "Pangaea"; landmasses "drifted" to where they are today; theory disregarded due to lack of evidence
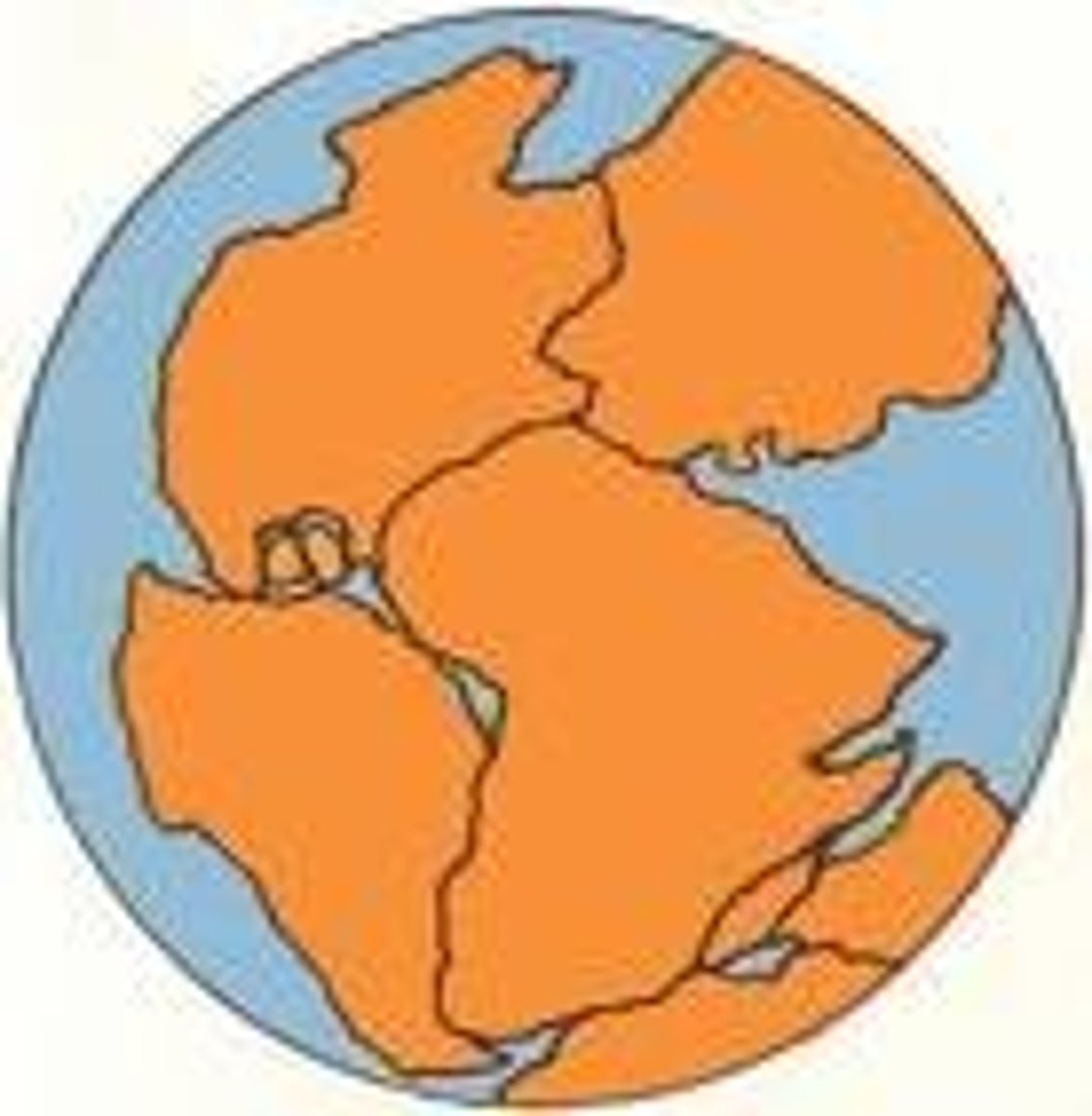
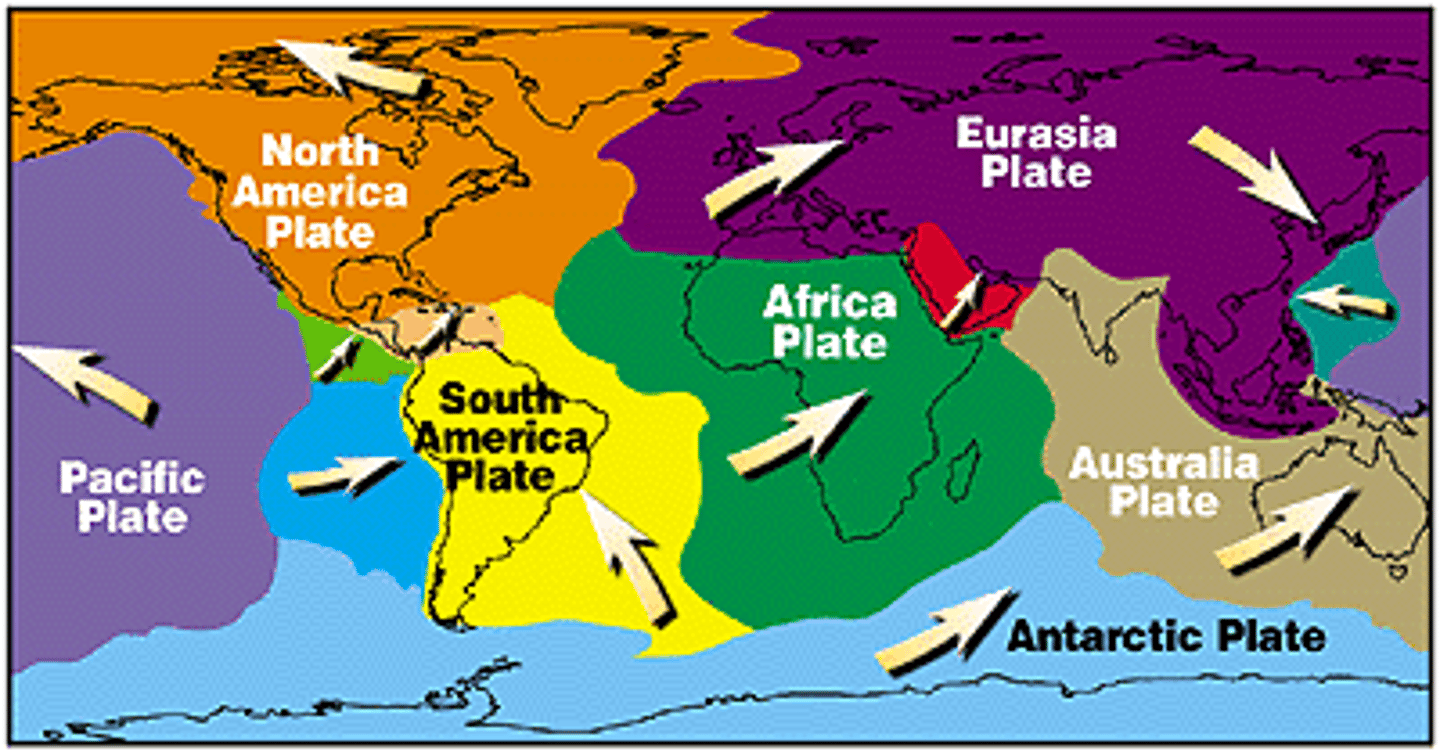
plate tectonics
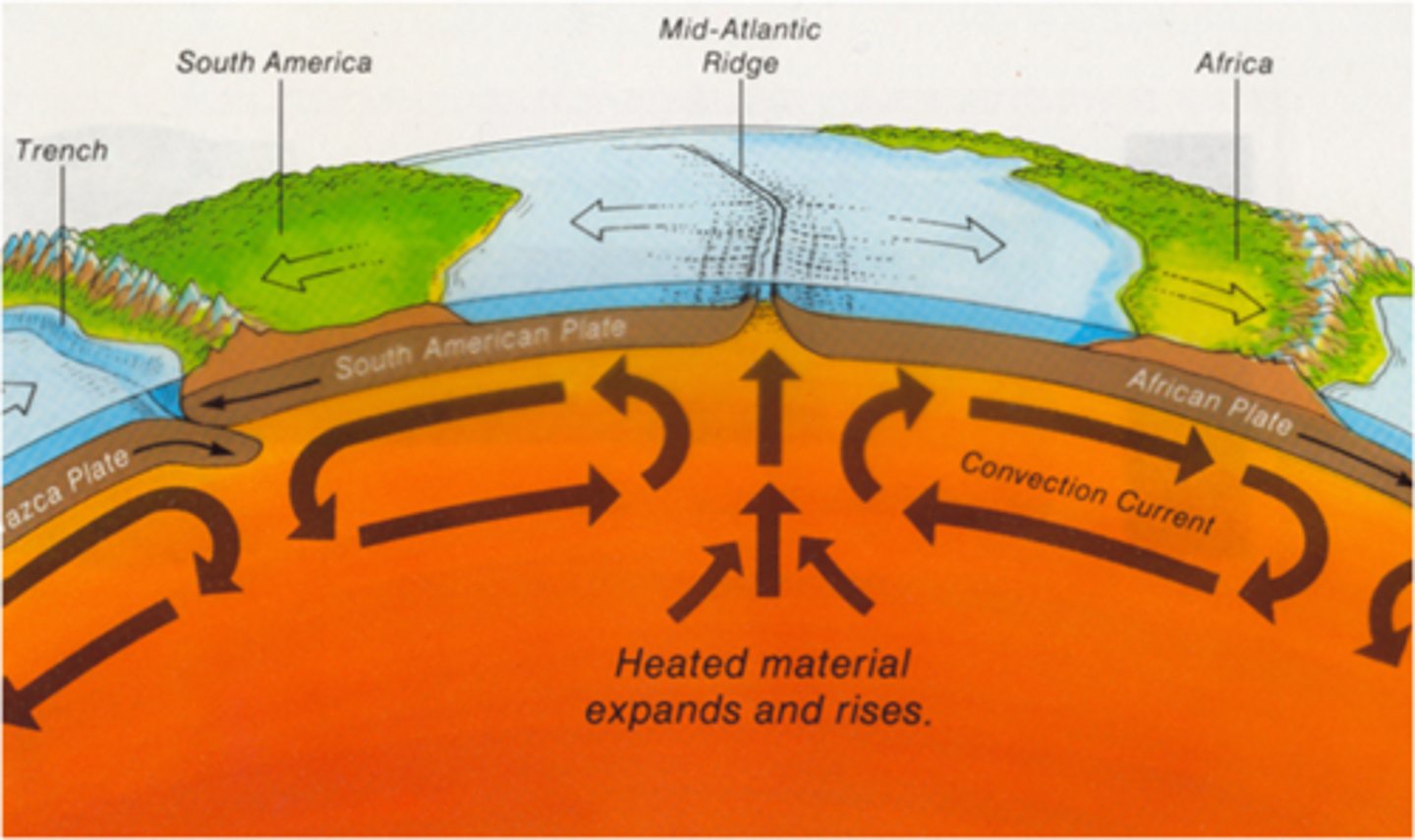
The theory that pieces of Earth's lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle.
Lithosphere
the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
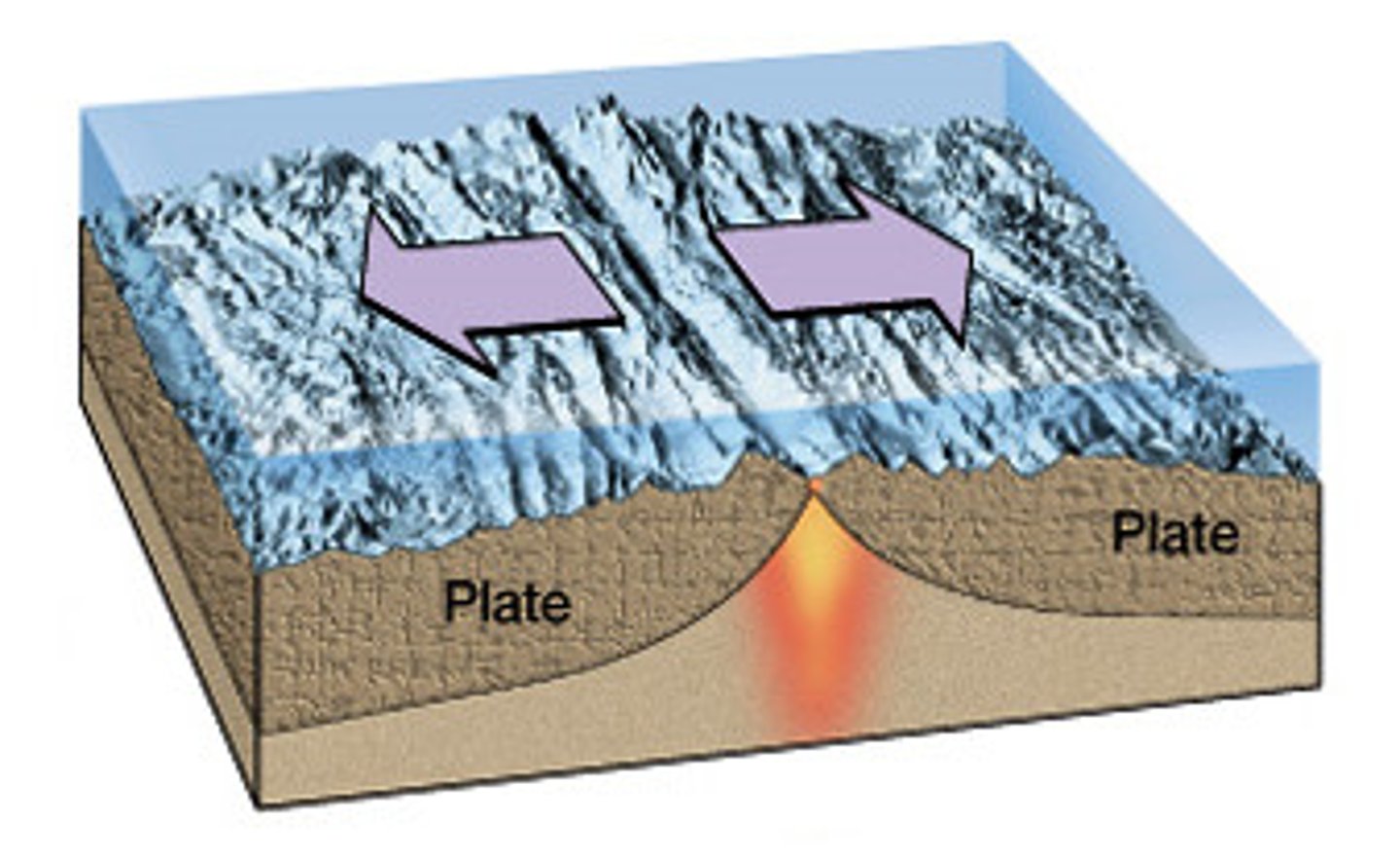
mid-ocean ridge
An undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary.

MAGNETIC STRIPES
provide evidence of sea floor spreading when they show the reversal of magnetic fields
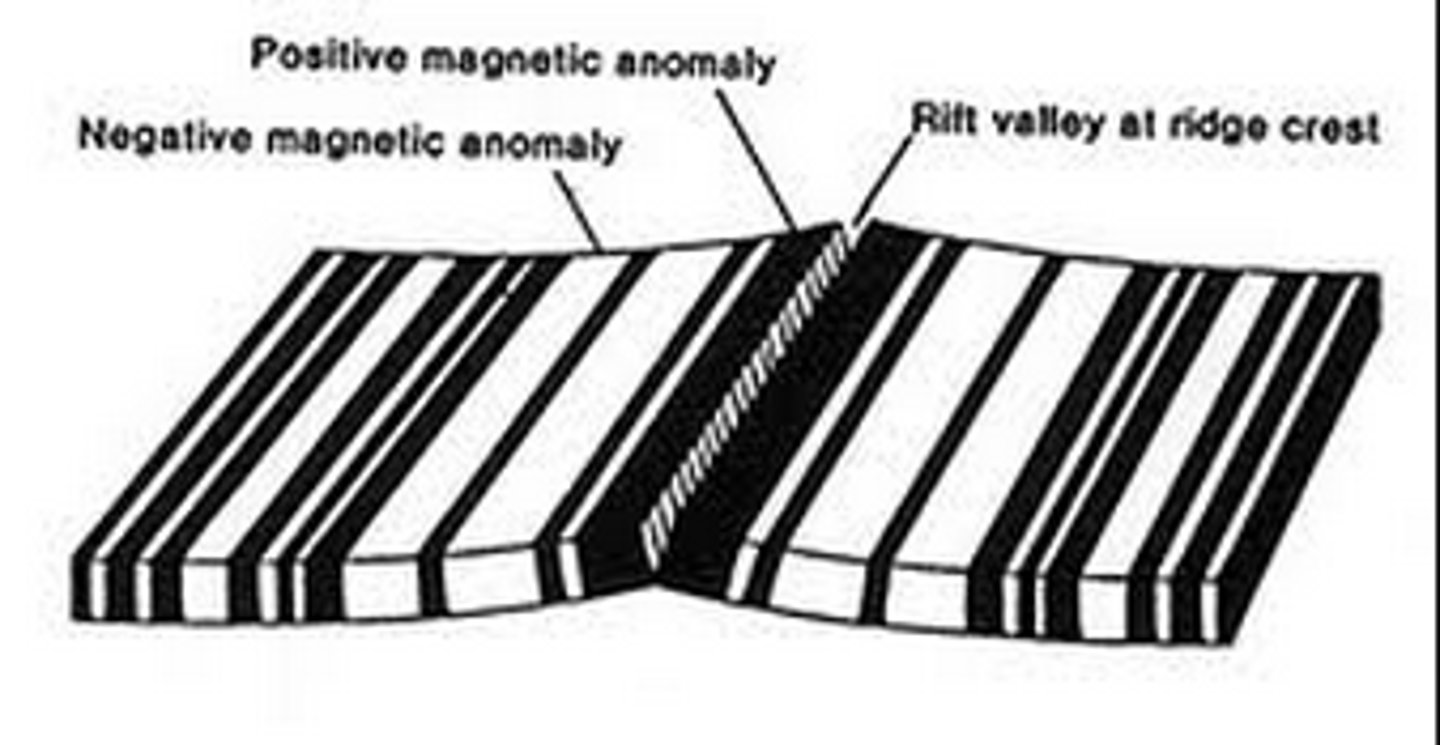
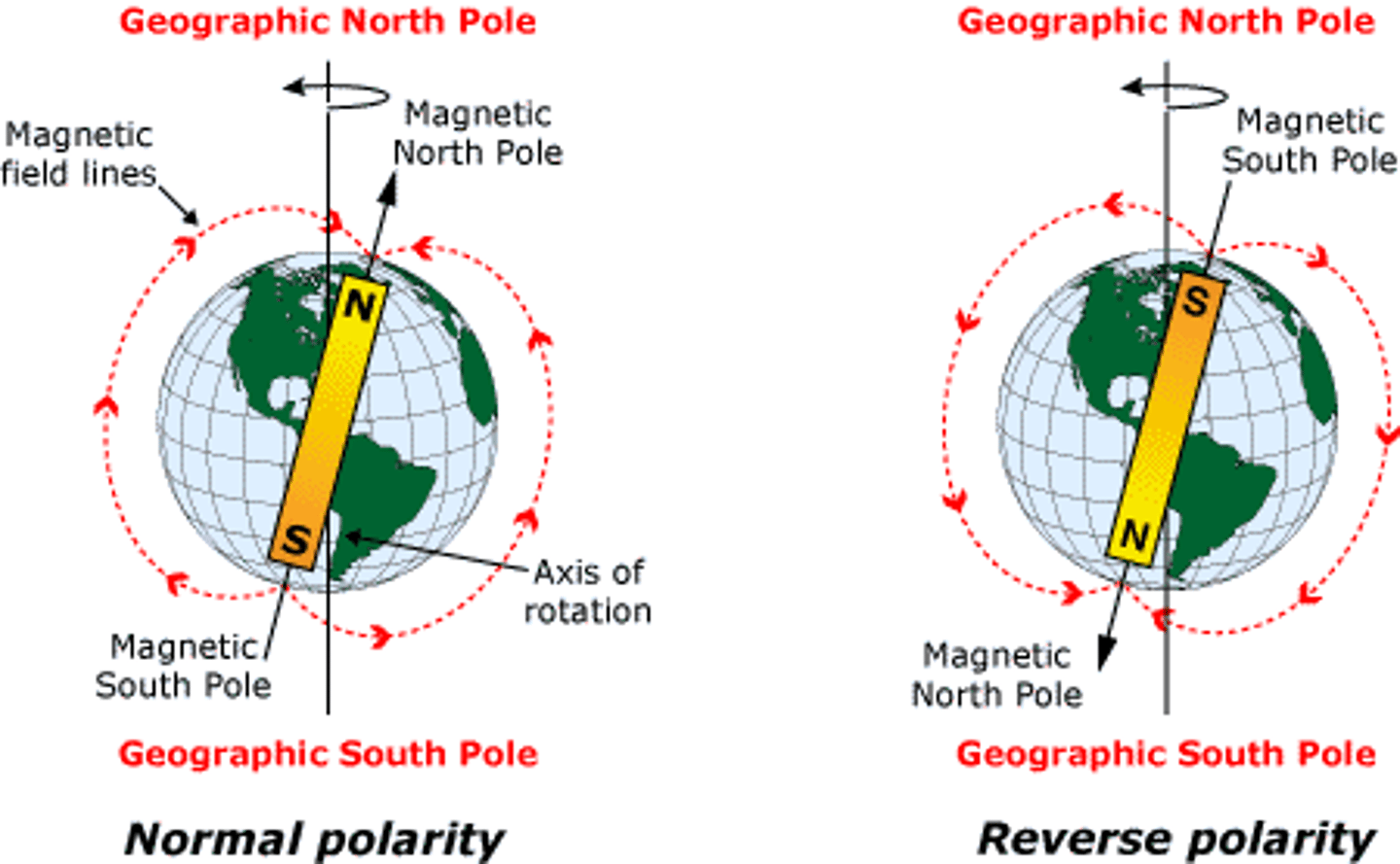
Polarity
A lack of electrical symmetry in a molecule. Charge differences on opposite ends of a structure.
Magnetite
magnetic

divergent boundary
The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other
convergent boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates collide, come together, or crash into each other.
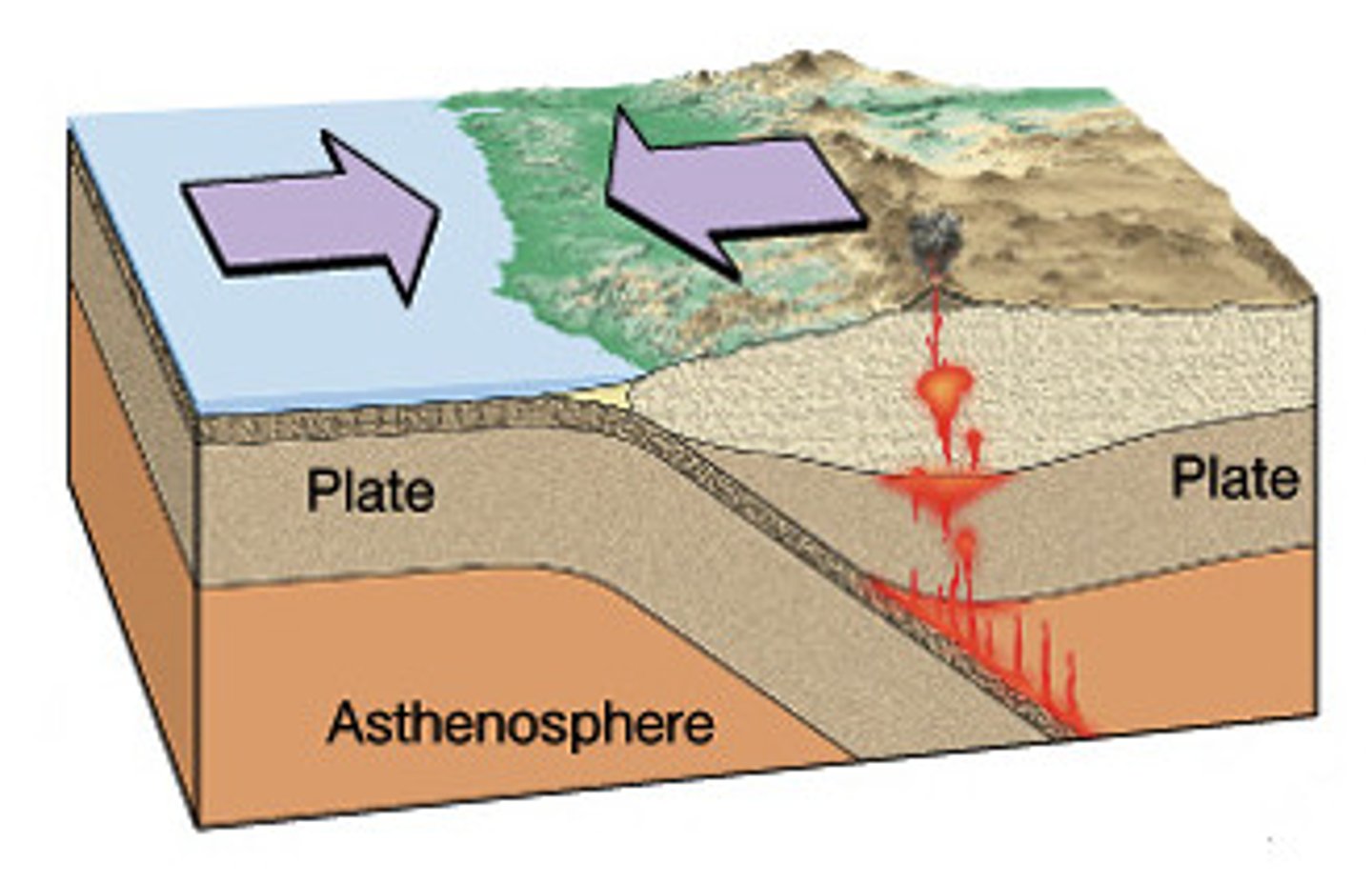
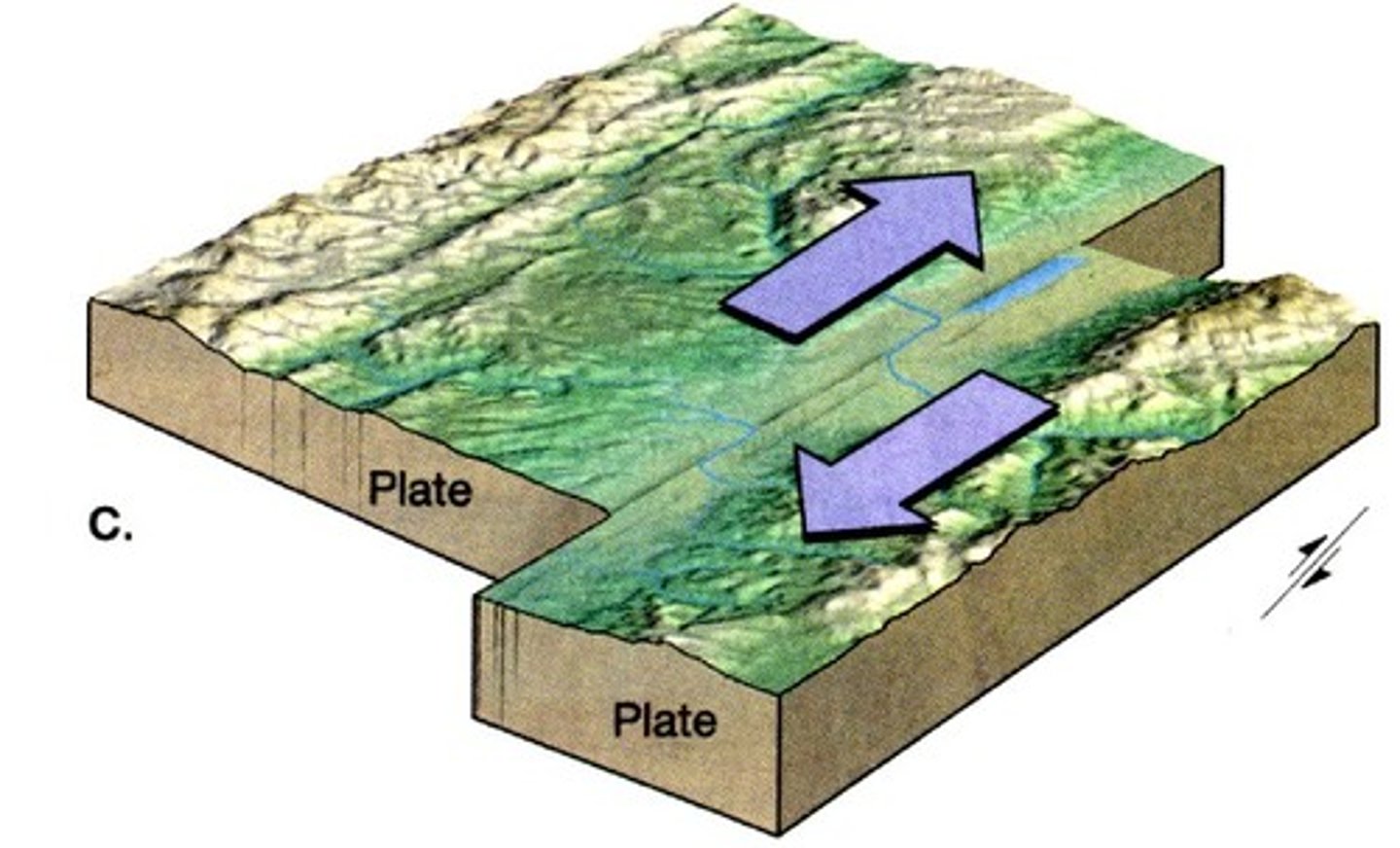
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
convection currents in the mantle
What drives plate movement?
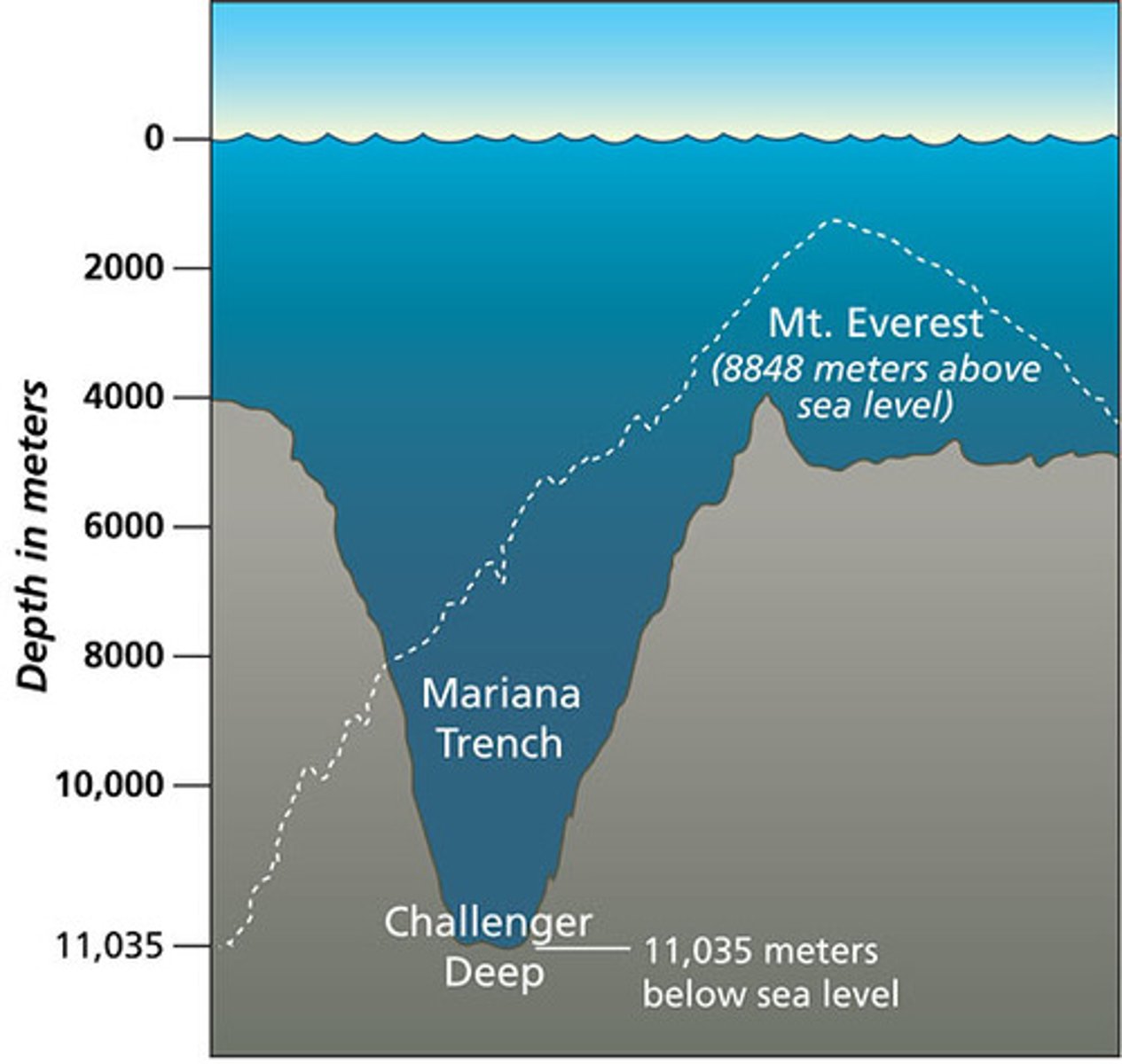
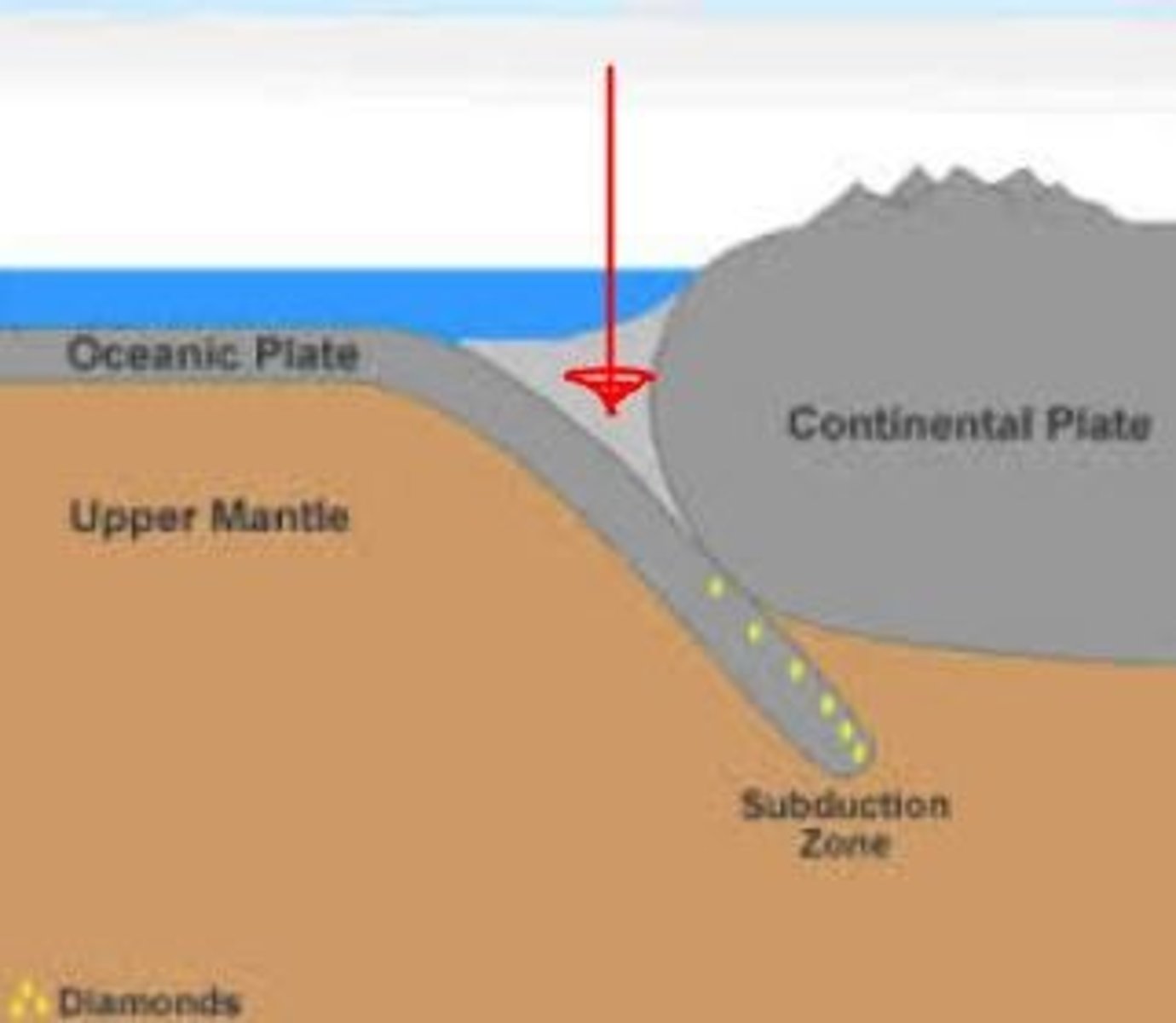
Mariana Trench
The location of the deepest trench on earth made from two oceanic crusts converging.
subduction zone
The region where oceanic plates sink down into the asthenosphere.
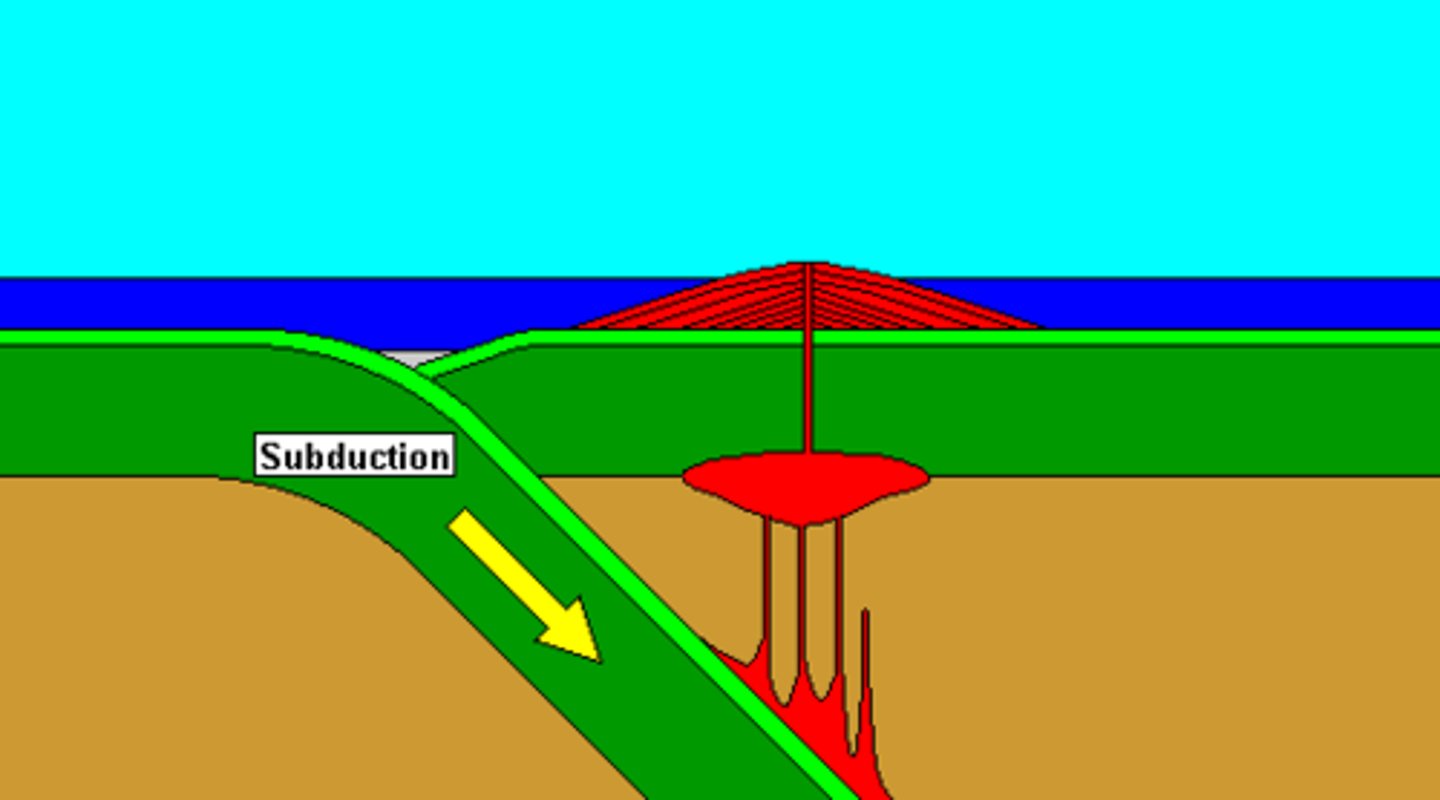
trench
extremely deep areas in the ocean that are created by a subducting plate
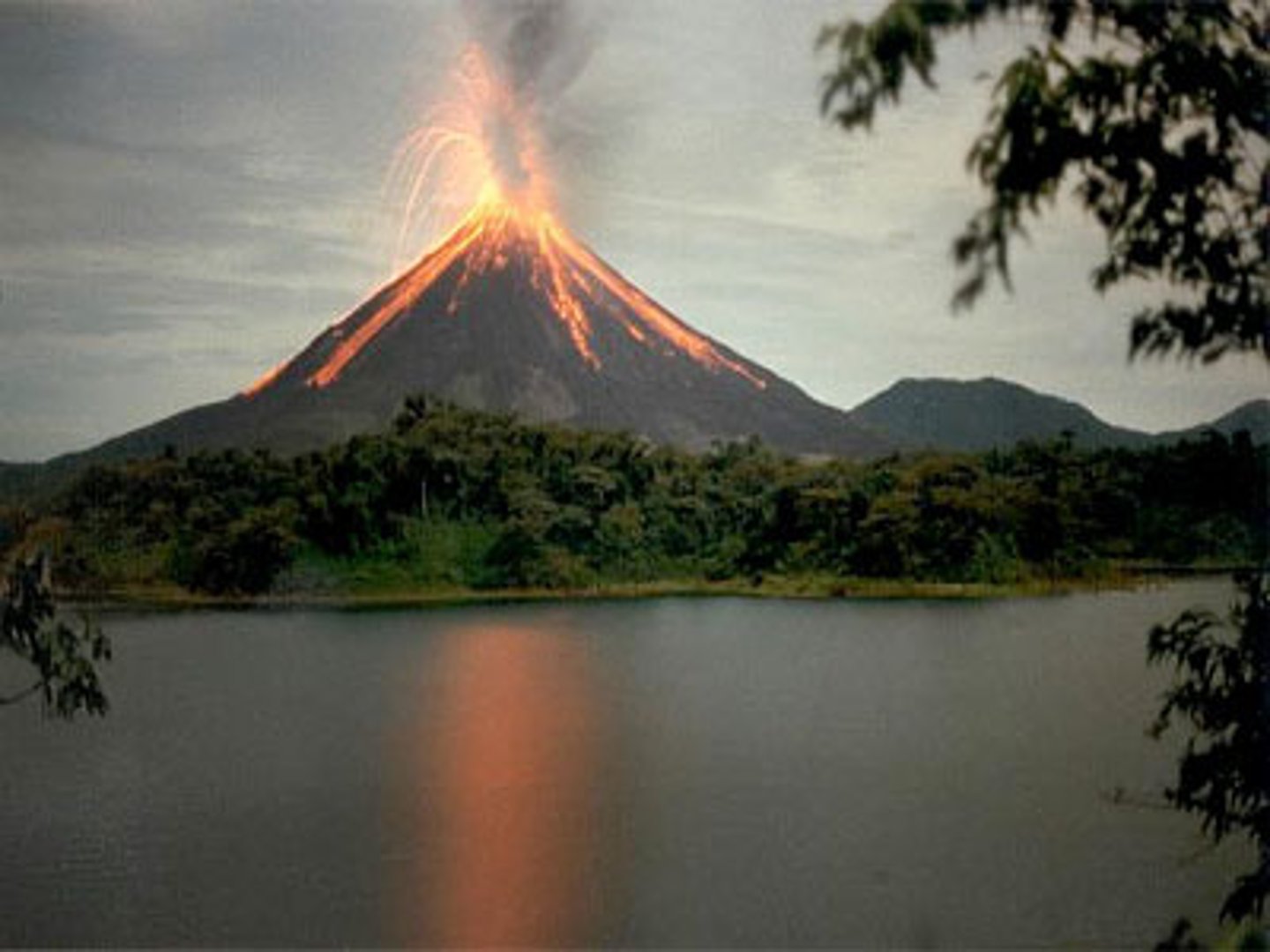
volcano
A vent or fissure in the Earth's surface through which magma and gases are expelled

Tsunami
a long high sea wave caused by an earthquake, submarine landslide, or other disturbance.
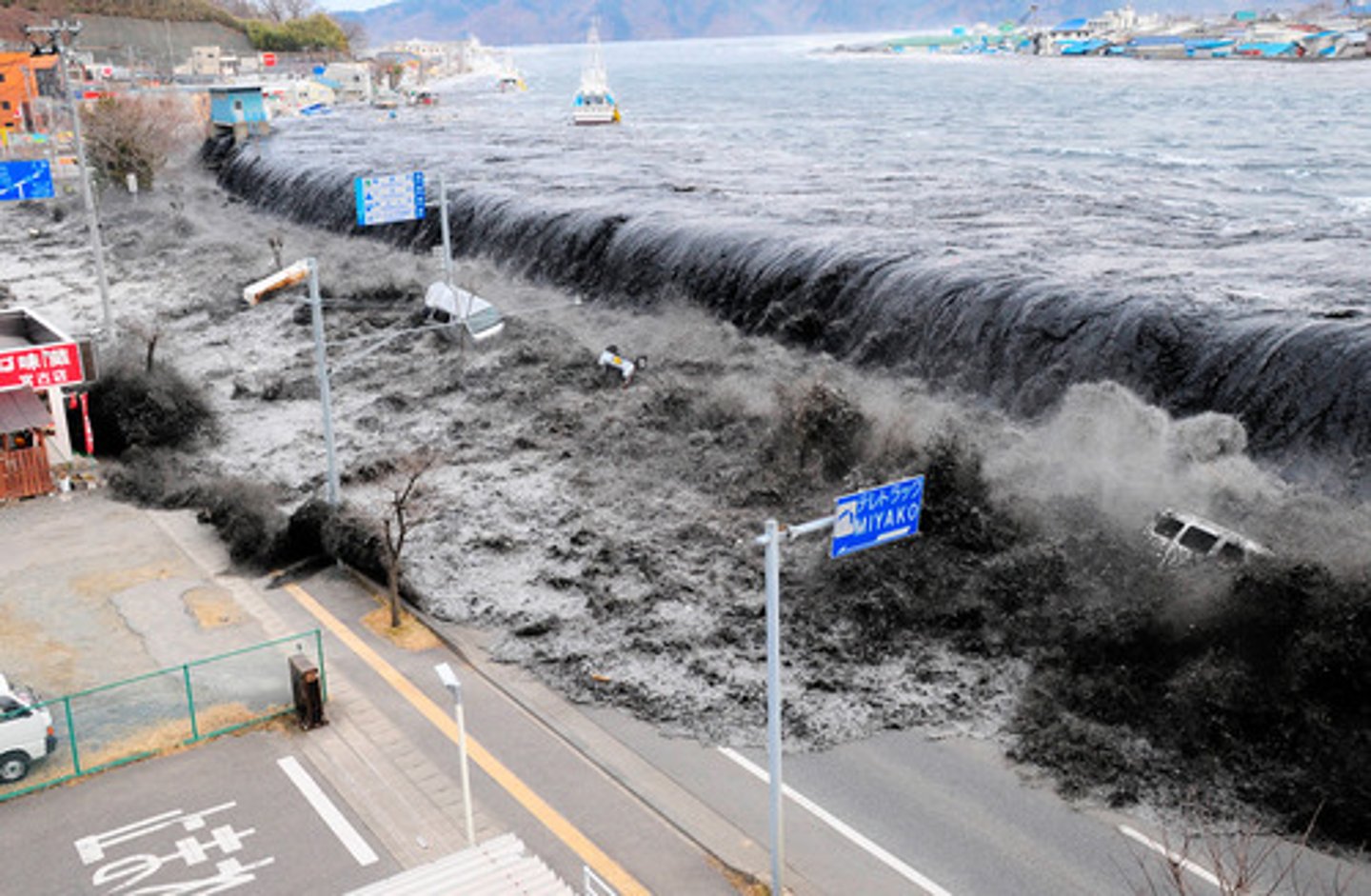

hydrothermal vents
spots on the ocean floor where hot gases and minerals escape from earth's interior into the water

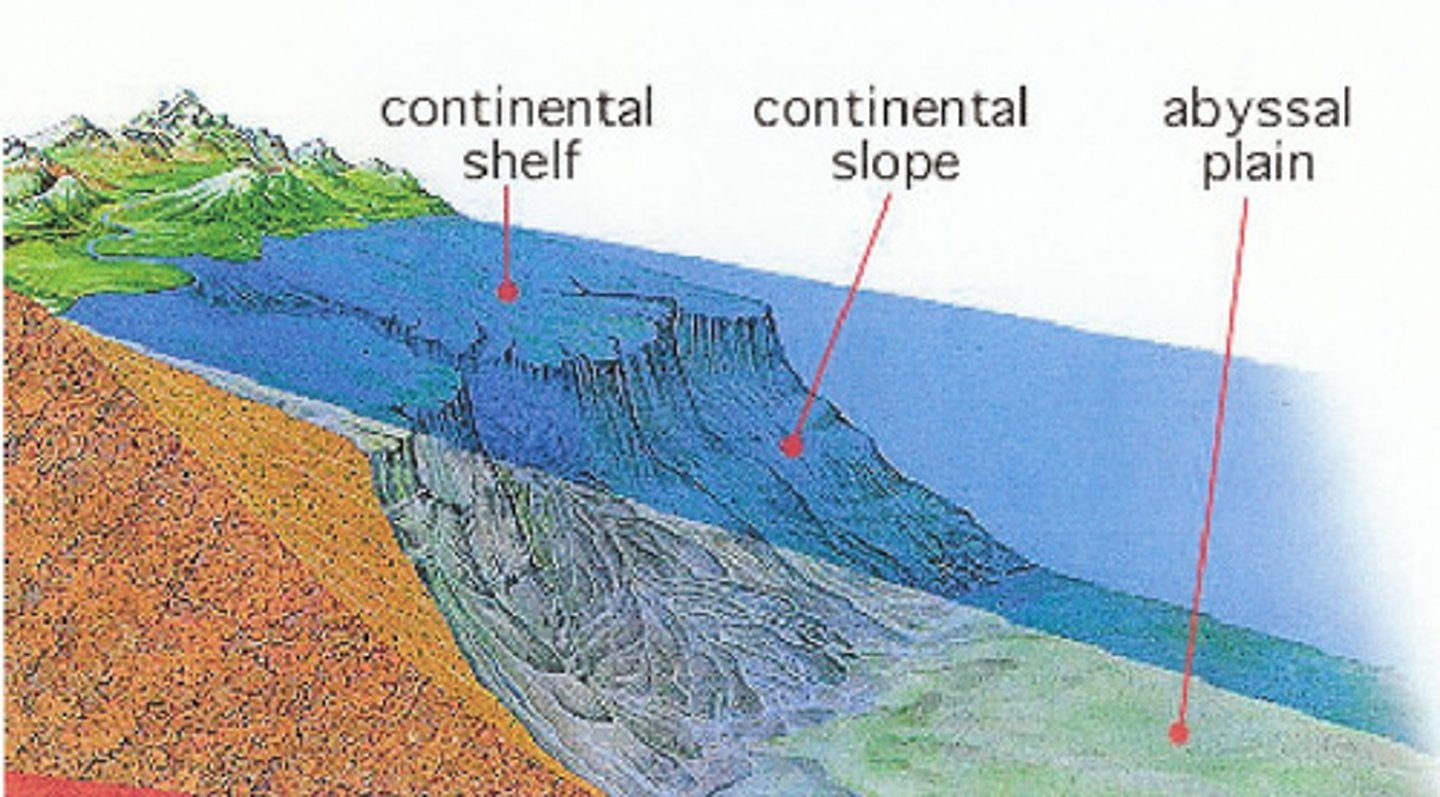
abyssal plain
very level area of the deep-ocean floor, usually lying at the foot of the continental rise
tide
The periodic rise and fall of the level of water in the ocean
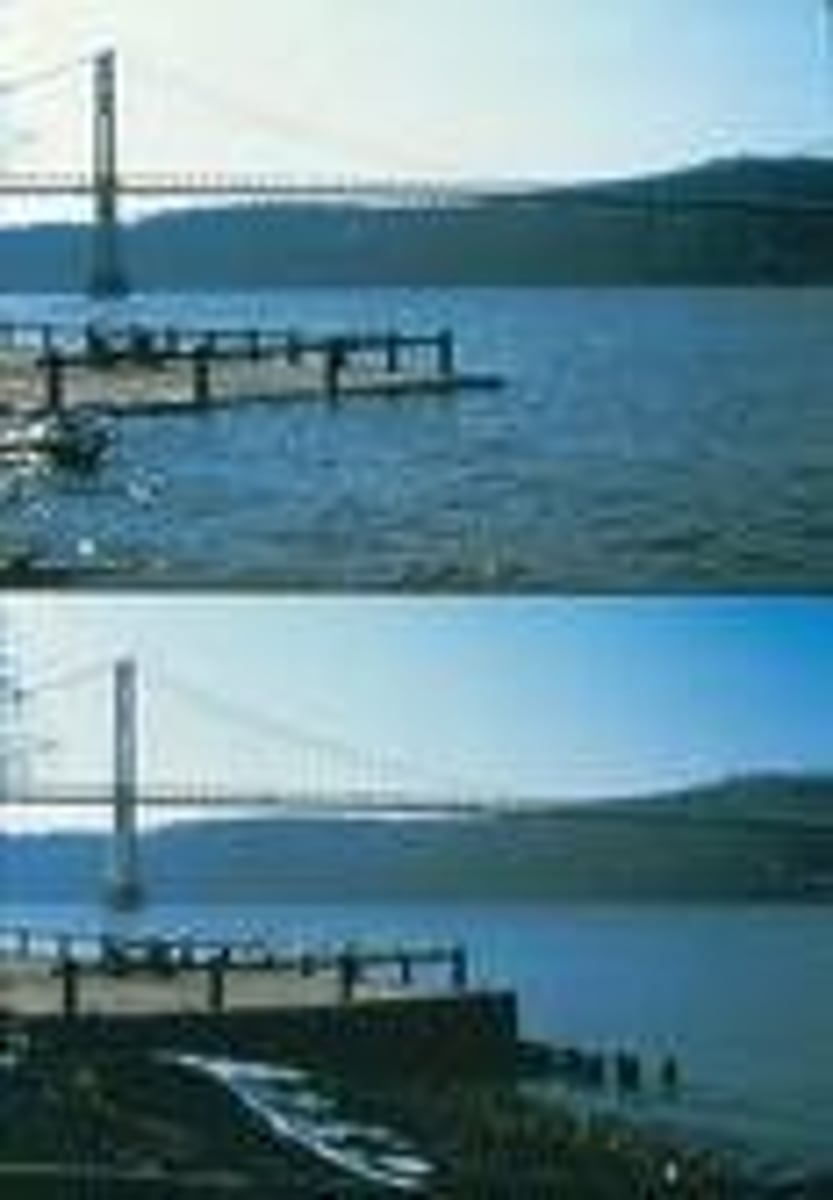

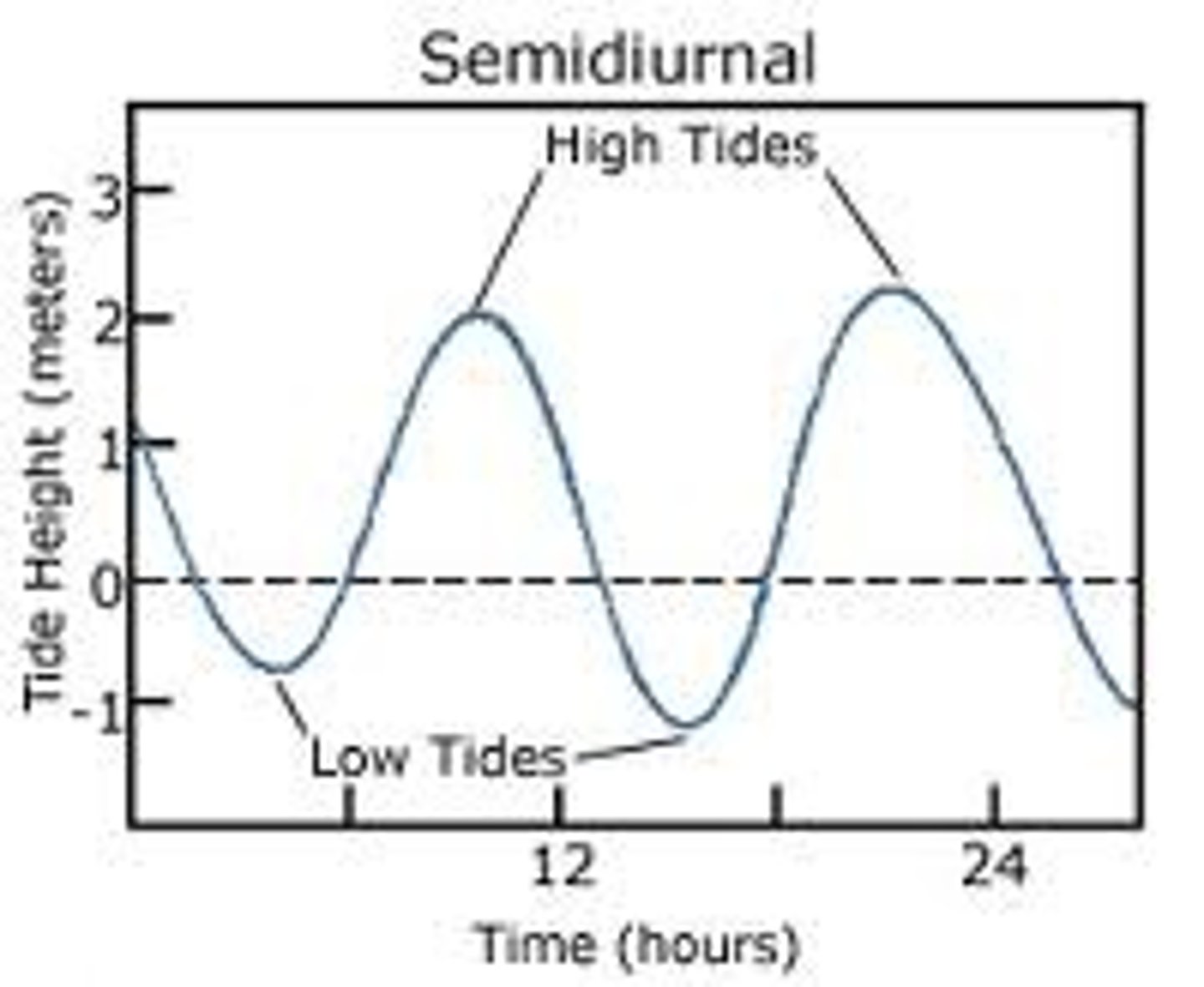
semi-diurnal tide
A tidal cycle of two high tides and two low tides each lunar day, with the high tides of nearly equal height.
diurnal tide
A tidal cycle of one high tide and one low tide per day.

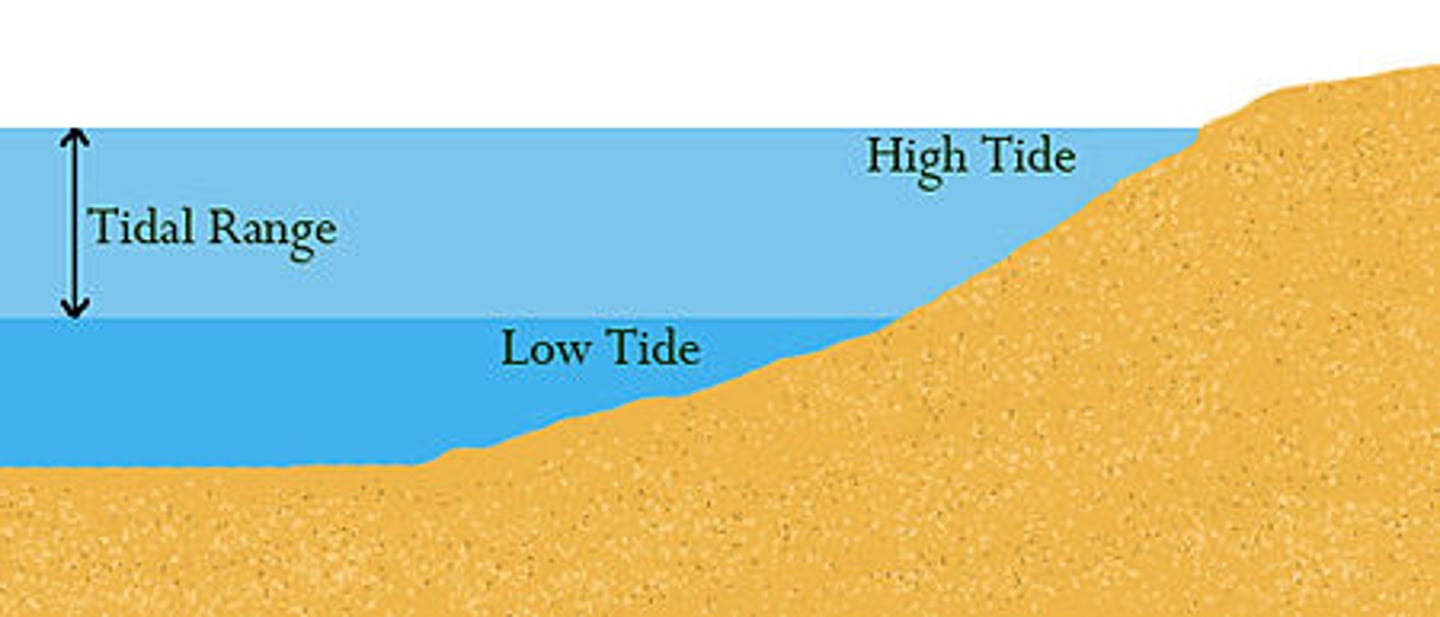
tidal range
The difference in levels of ocean water at high tide and low tide
Tidal surge
the coastal flooding of an abnormally high seawater level associated with low pressure weather systems; also called a storm surge

spring tide
a tide just after a new or full moon, when there is the greatest difference between high and low water.
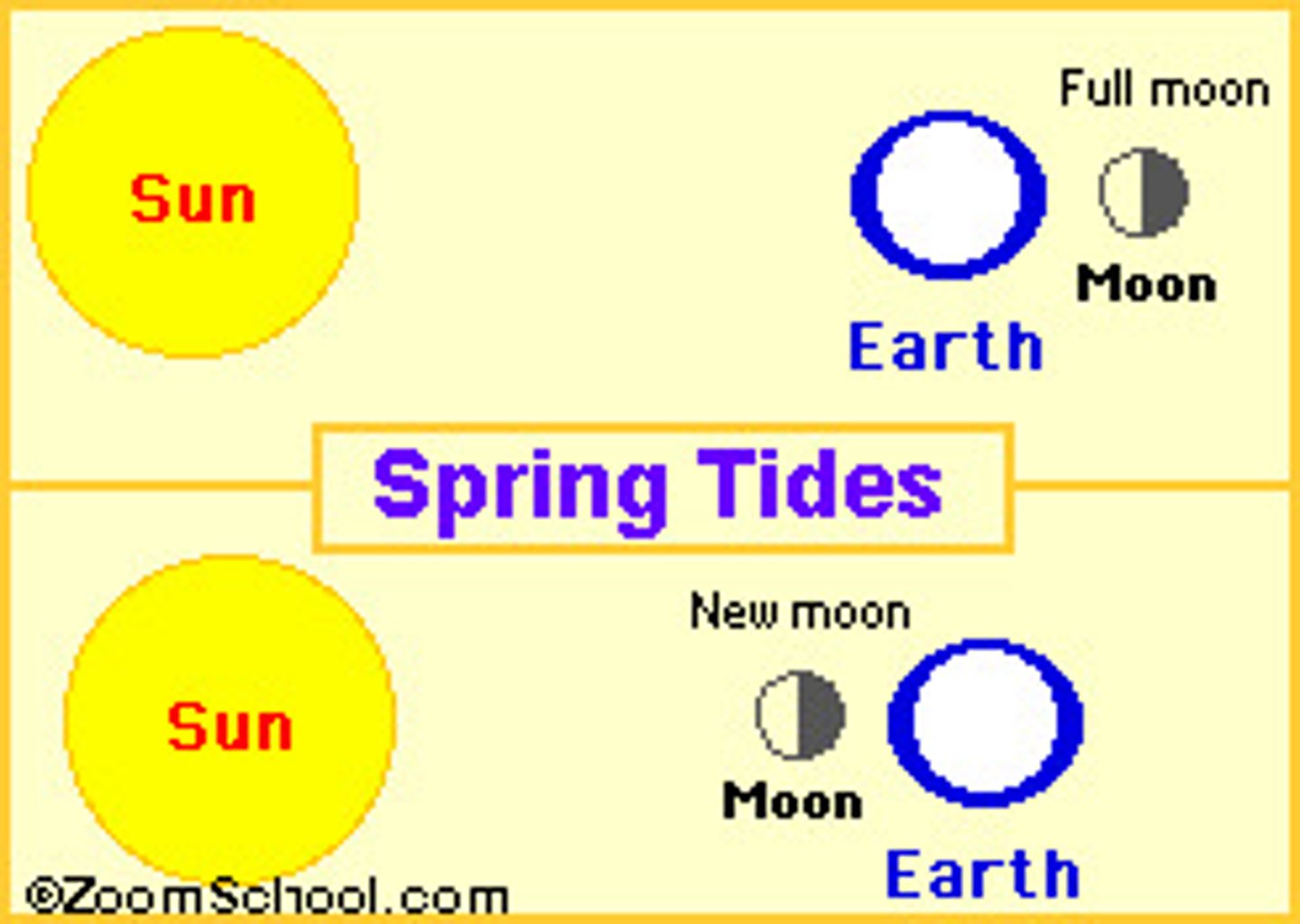
Neap tides are
about 20 percent lower than the average tide. Happen when the sun and the moon are at right angel
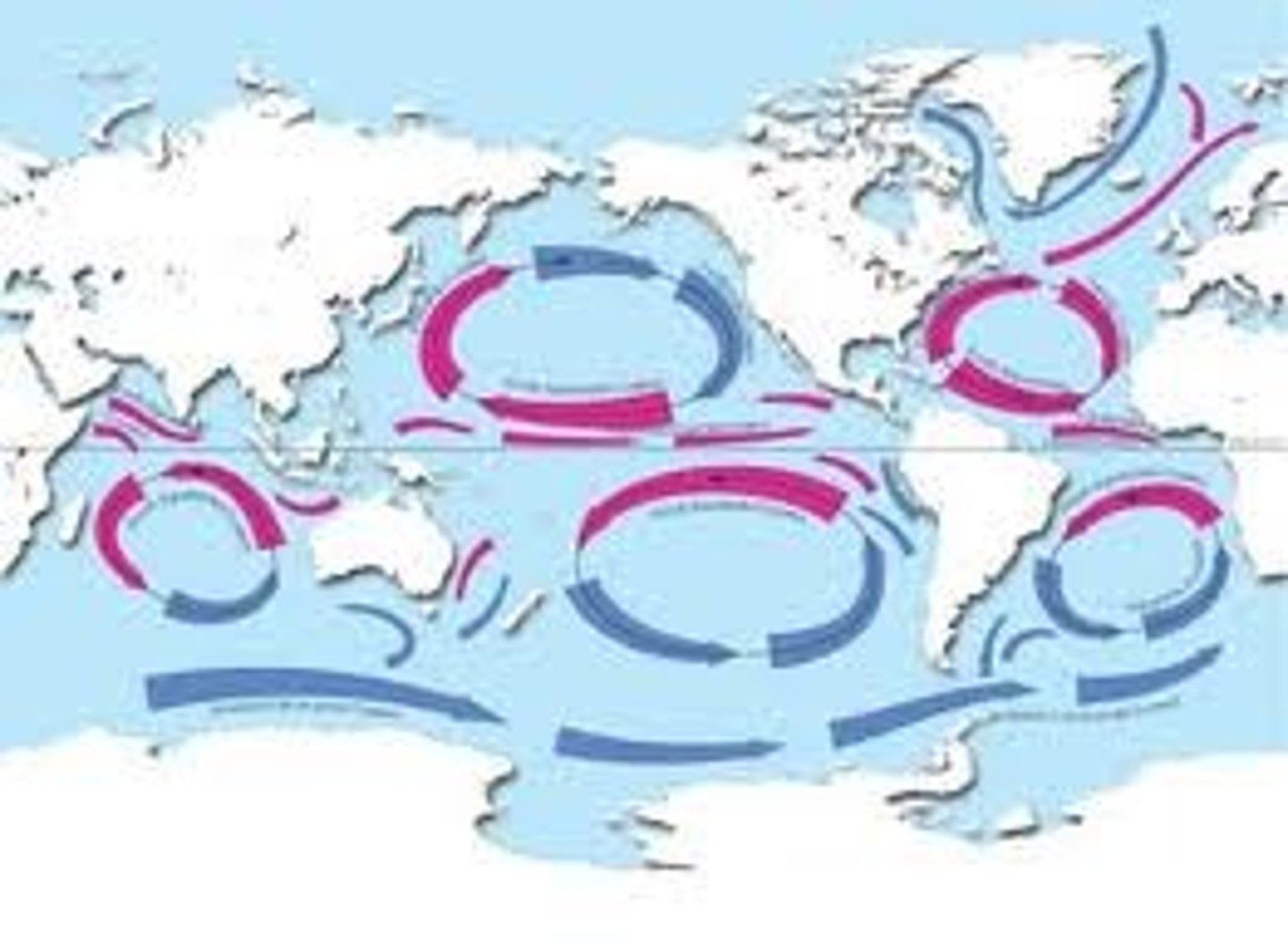
current
A large stream of moving water that flows through the oceans
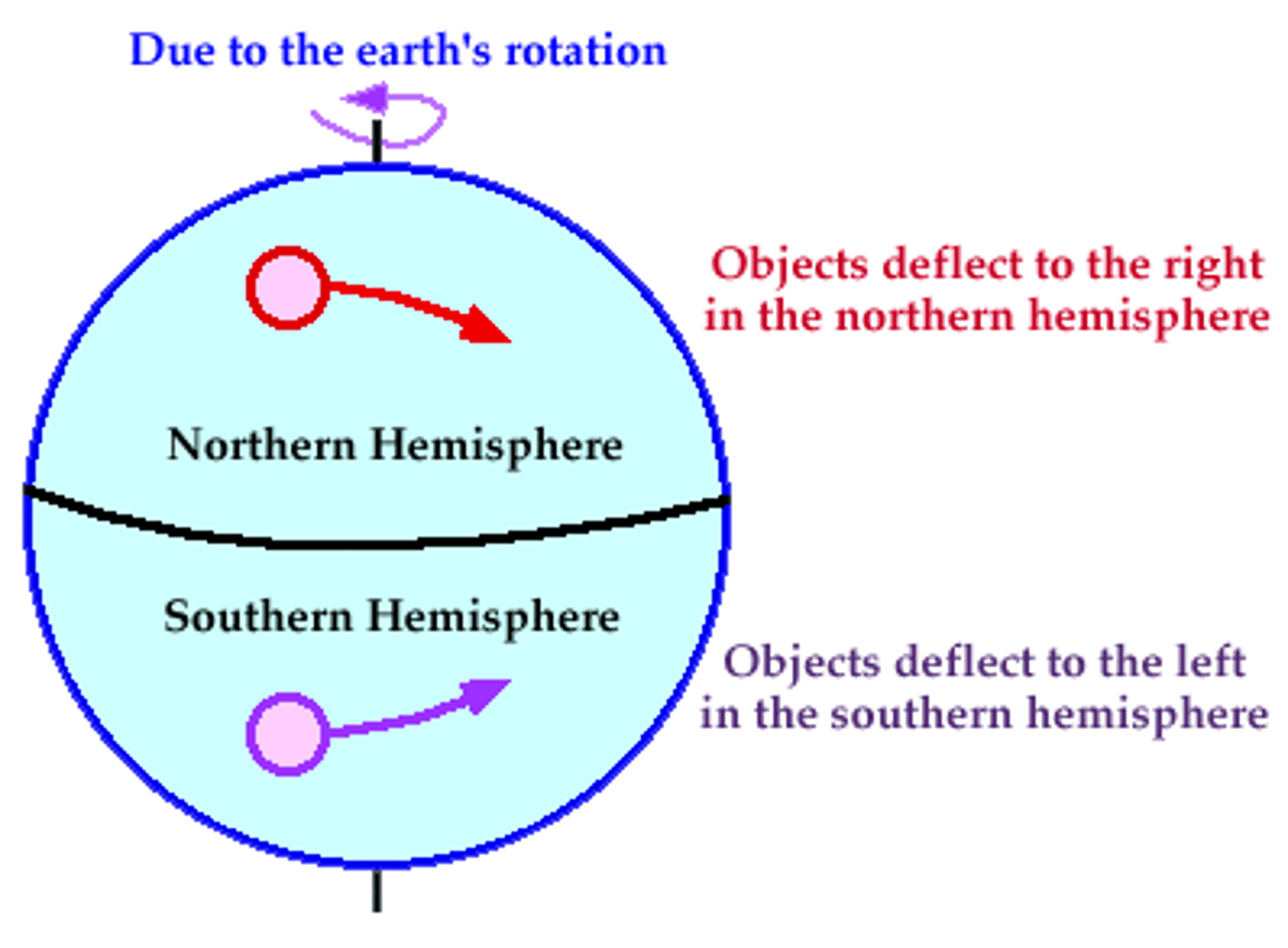
Coriolis effect
Causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere due to Earth's hemisphere.
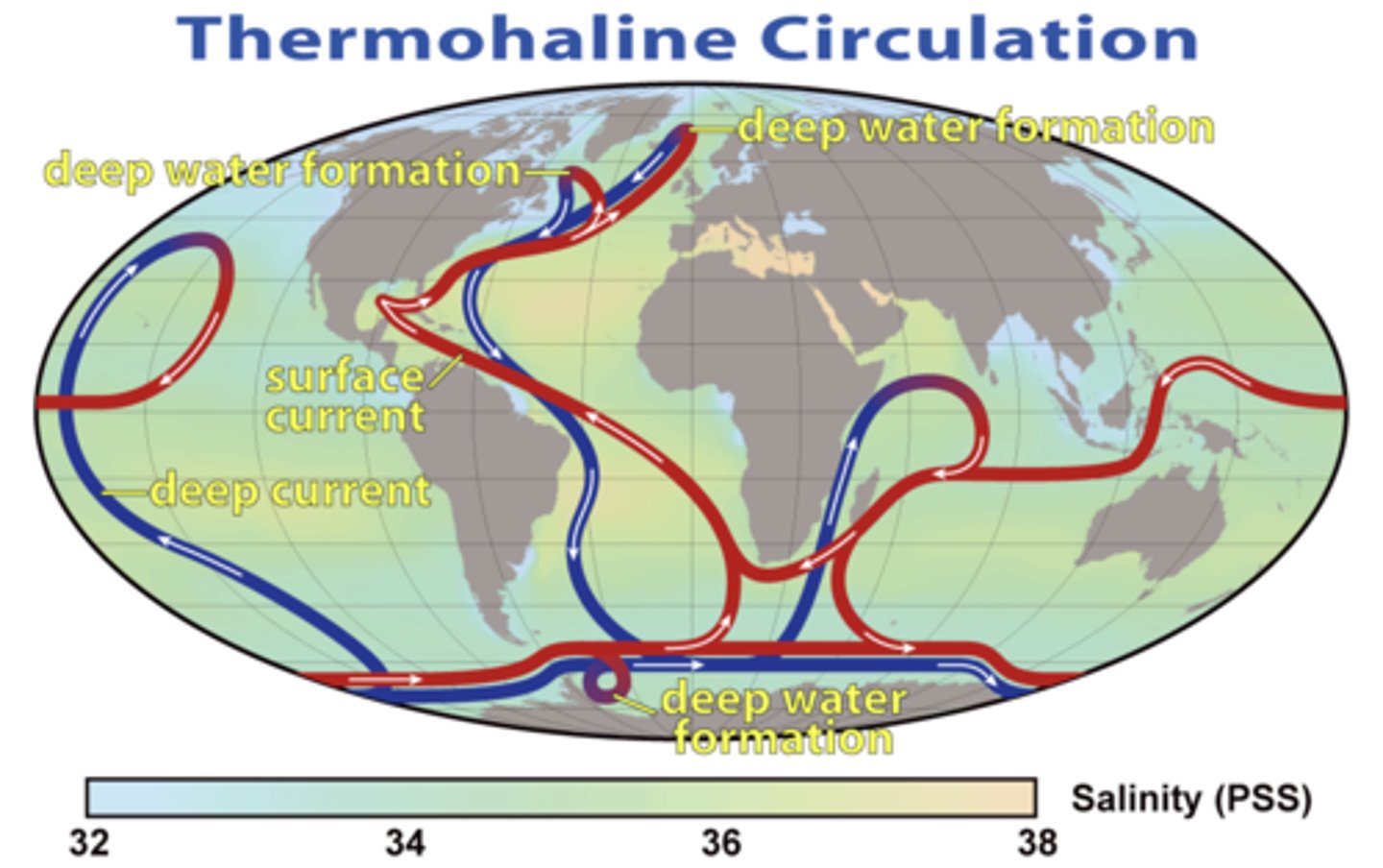
thermohaline circulation
water circulation produced by differences in temperature and/or salinity (and therefore density)
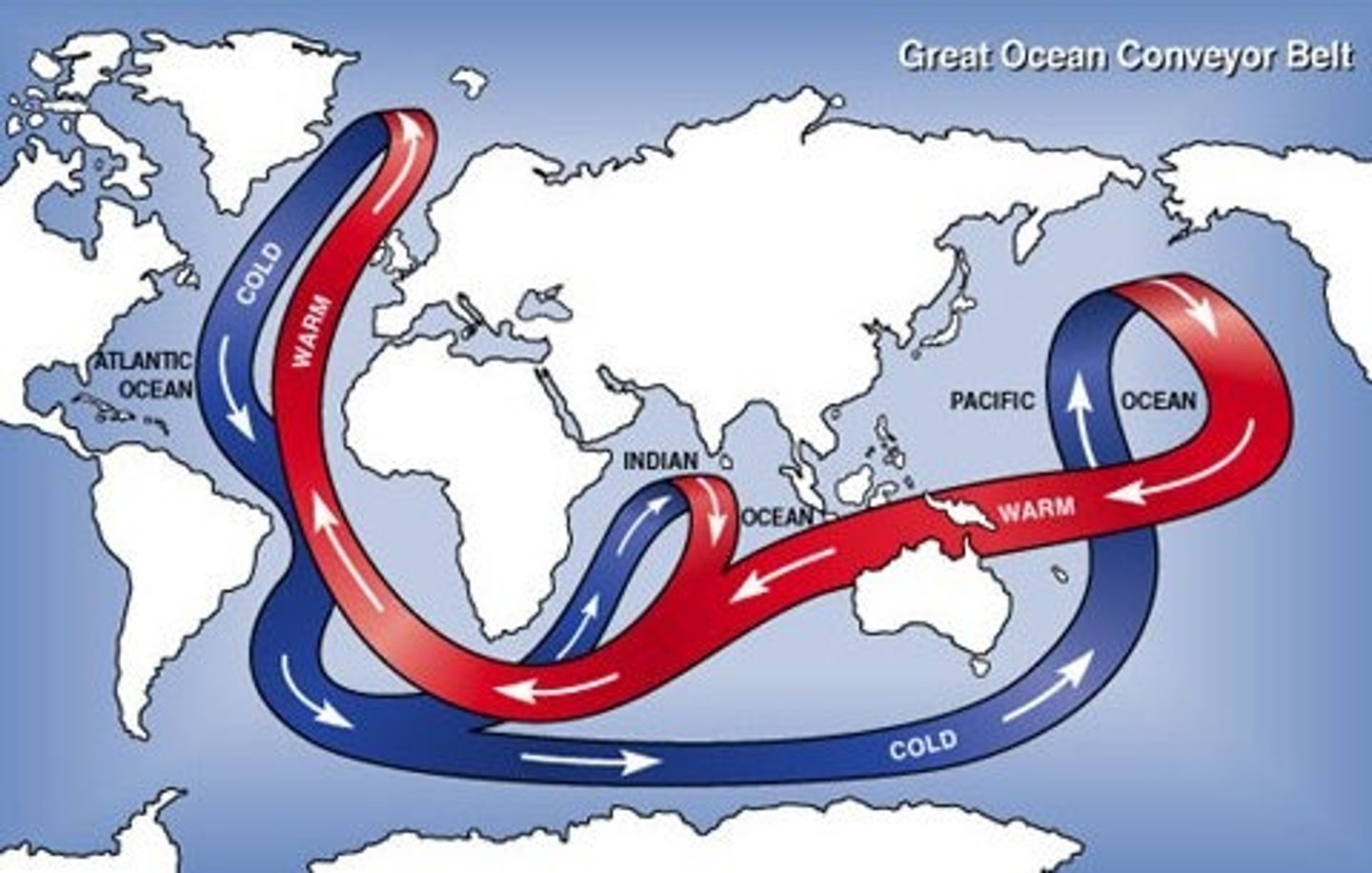
global ocean conveyor belt
a constantly moving system of deep-ocean circulation driven by temperature and salinity
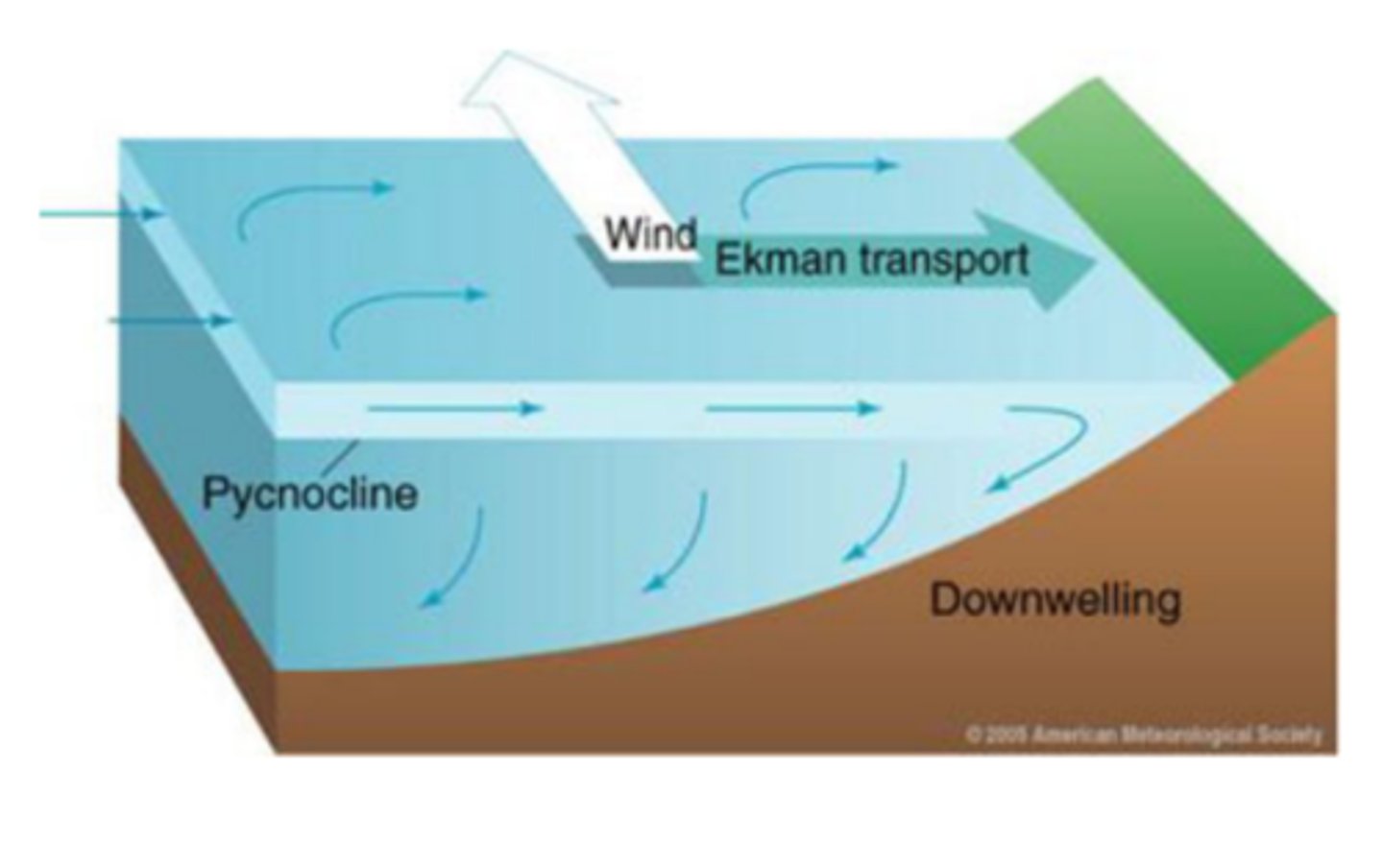
Downwelling
is the movement of water from the surface to greater depths
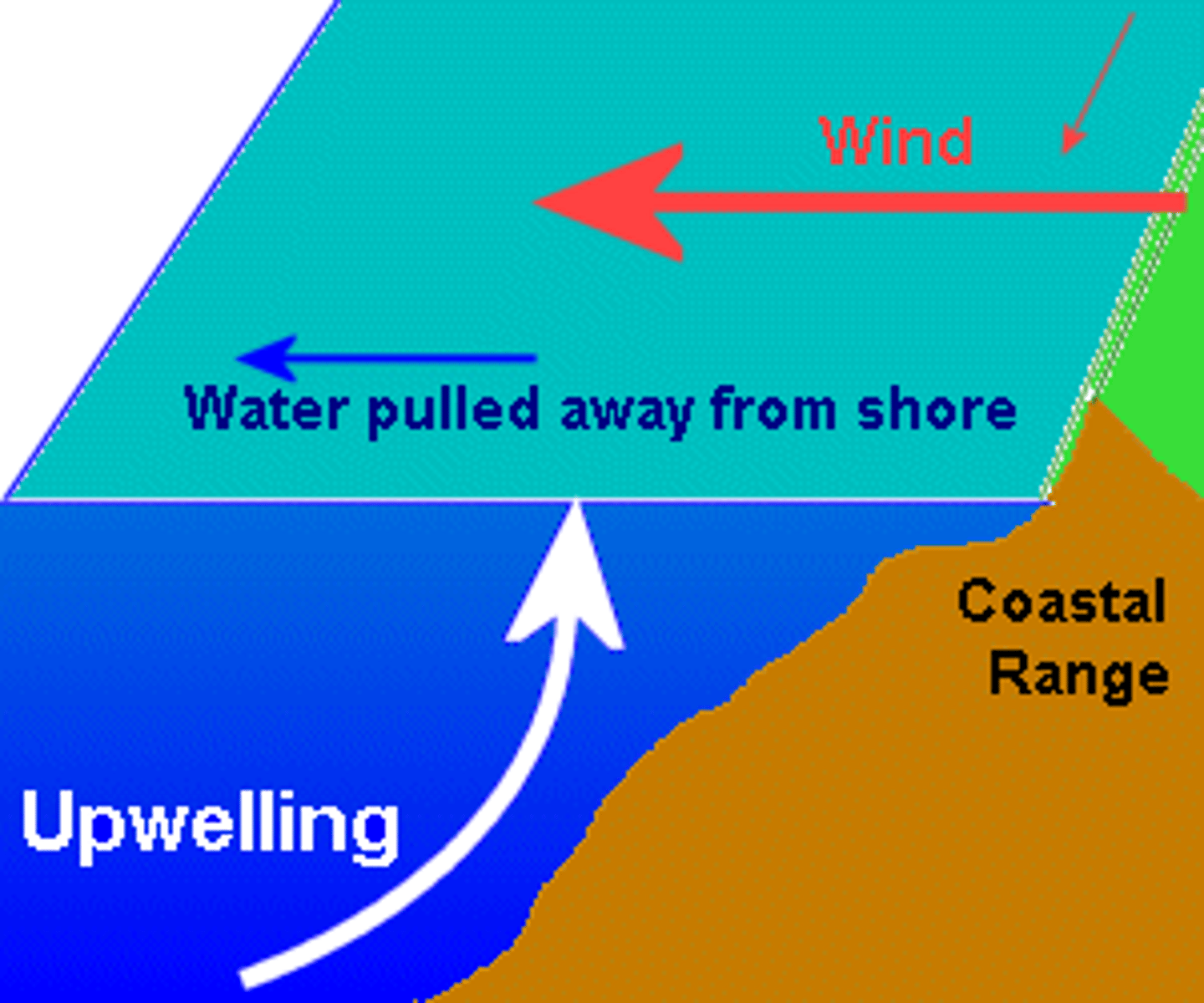
Upwelling
the upward movement of ocean water toward the surface as a result of diverging currents
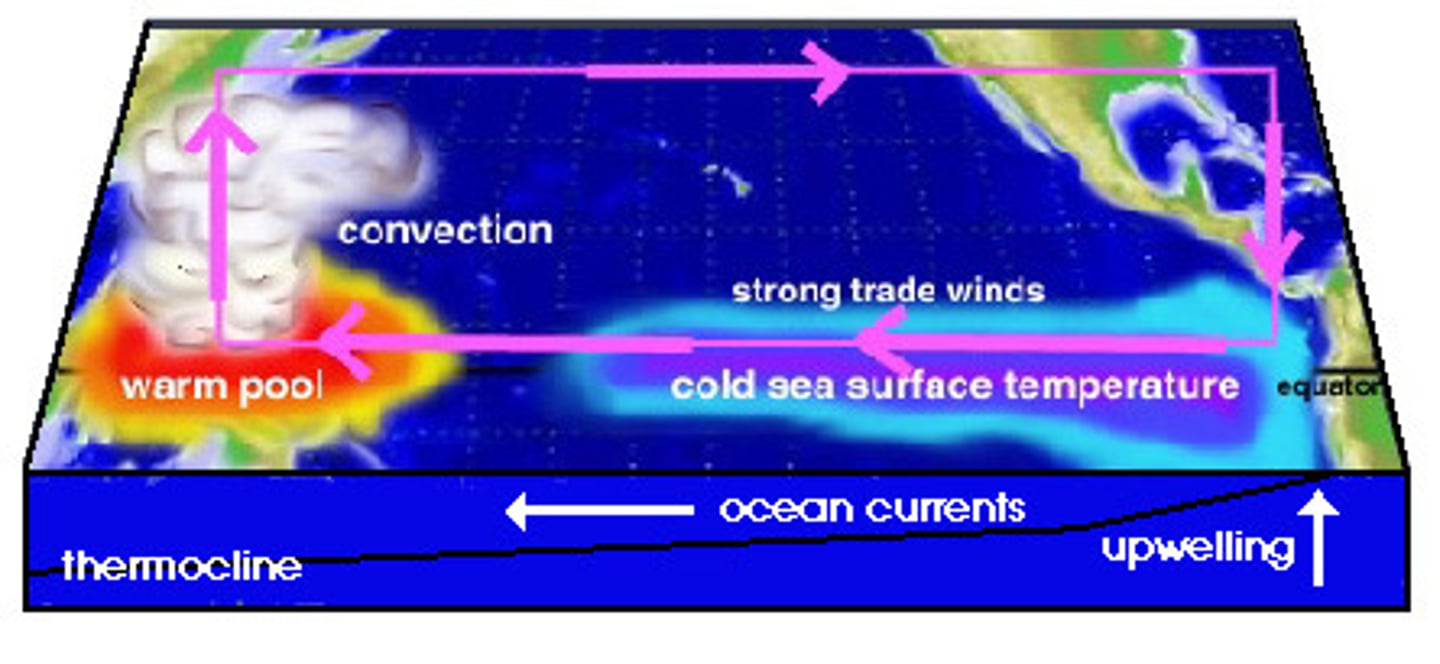
El Nino
A warm ocean current that flows along the coast of Peru every seven to fourteen years
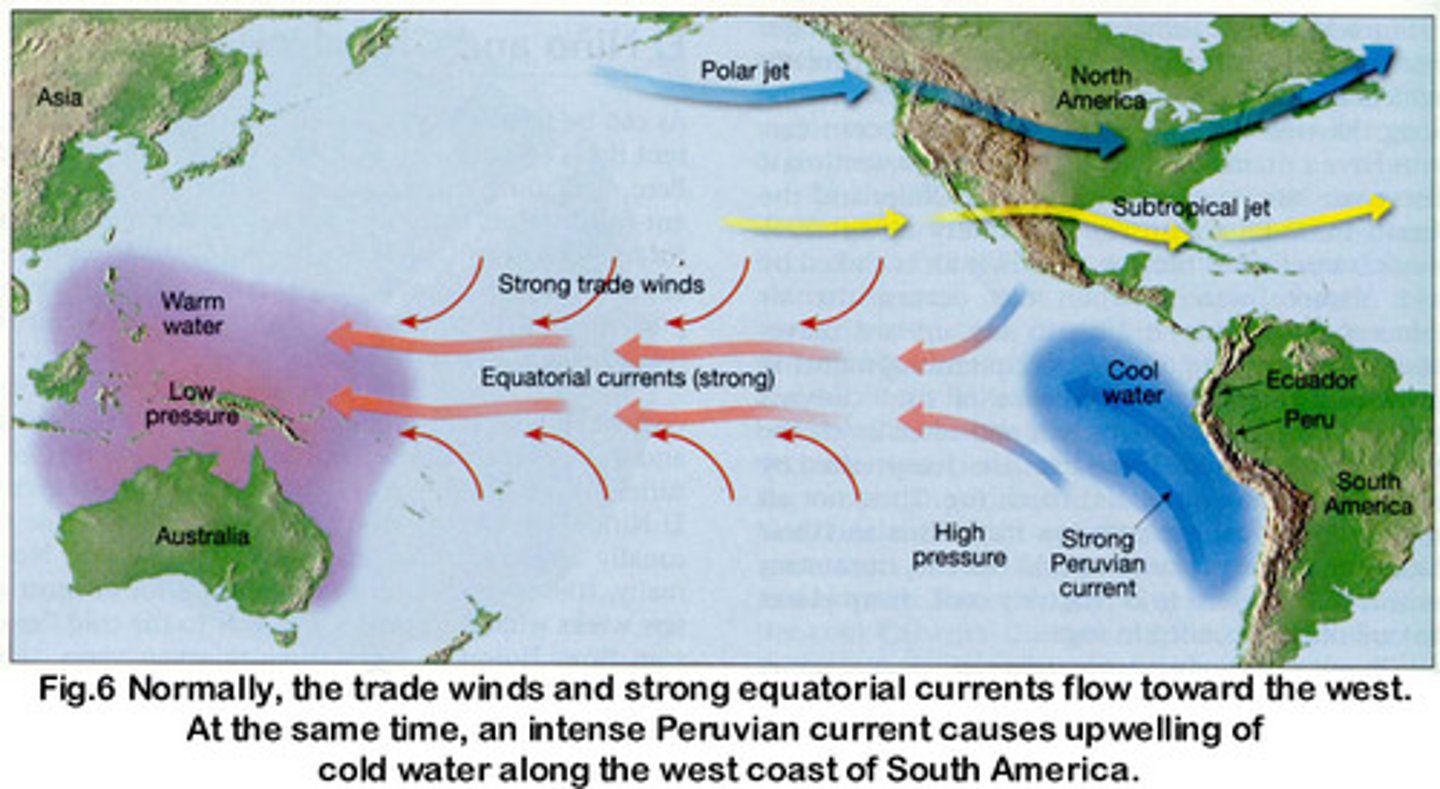
La Nina
A cooling of the ocean surface off the western coast of South America, occurring periodically every 4 to 12 years and affecting Pacific and other weather patterns.
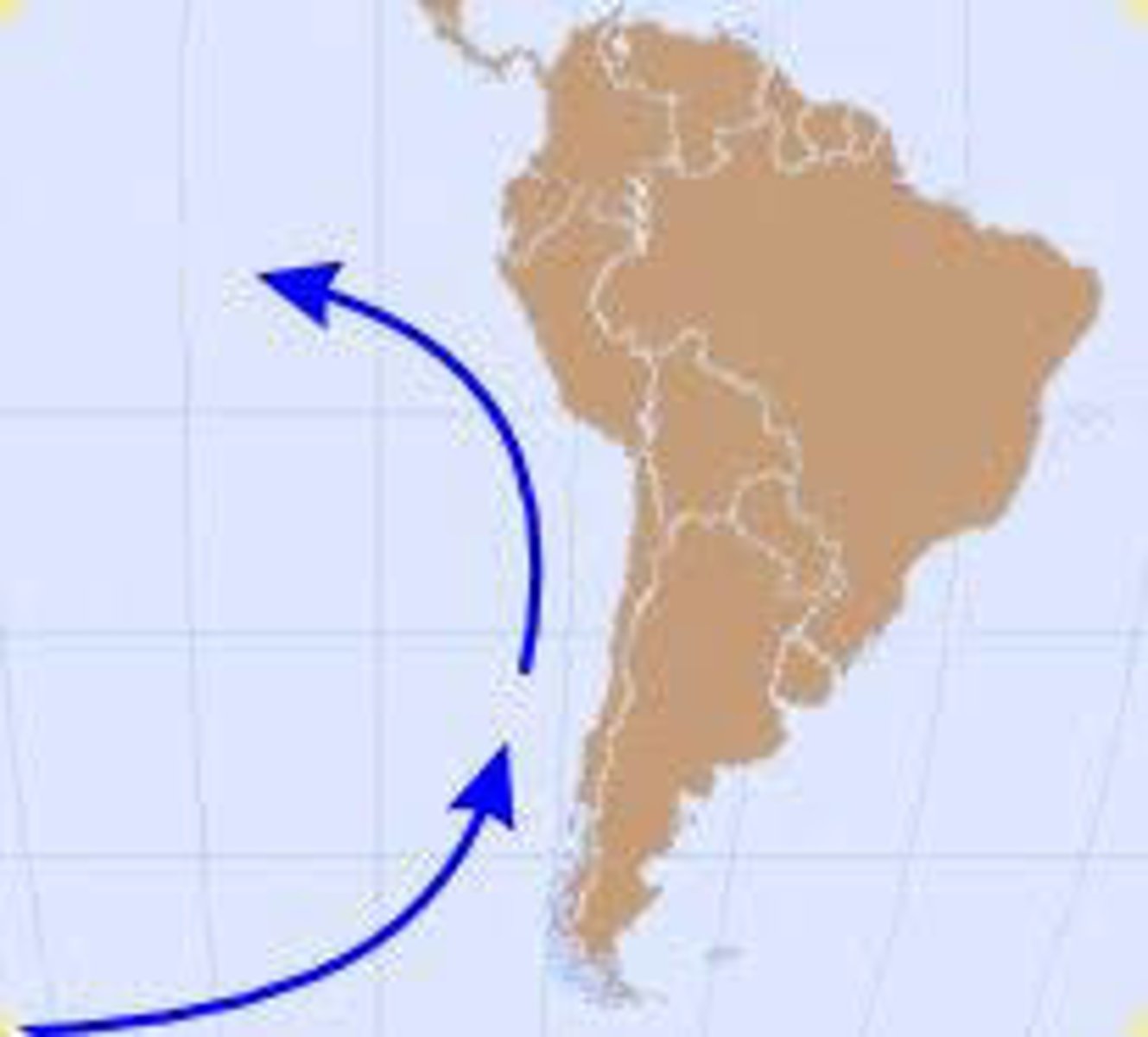
Humboldt Current
A current that brings cool waters from the south up along the Andean coast, accounting for the remarkable wealth of marine resources in the area
Abyssal plain
Flat deep ocean found by continental rise
continental margin
transition zone between continental and ocean crust