Lab module#2 practice(histology, integ and bones), Axial skeleton(LSC Human Physiology) , Appendicular skeleton(Human intro: LSC), Integumentary lab
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
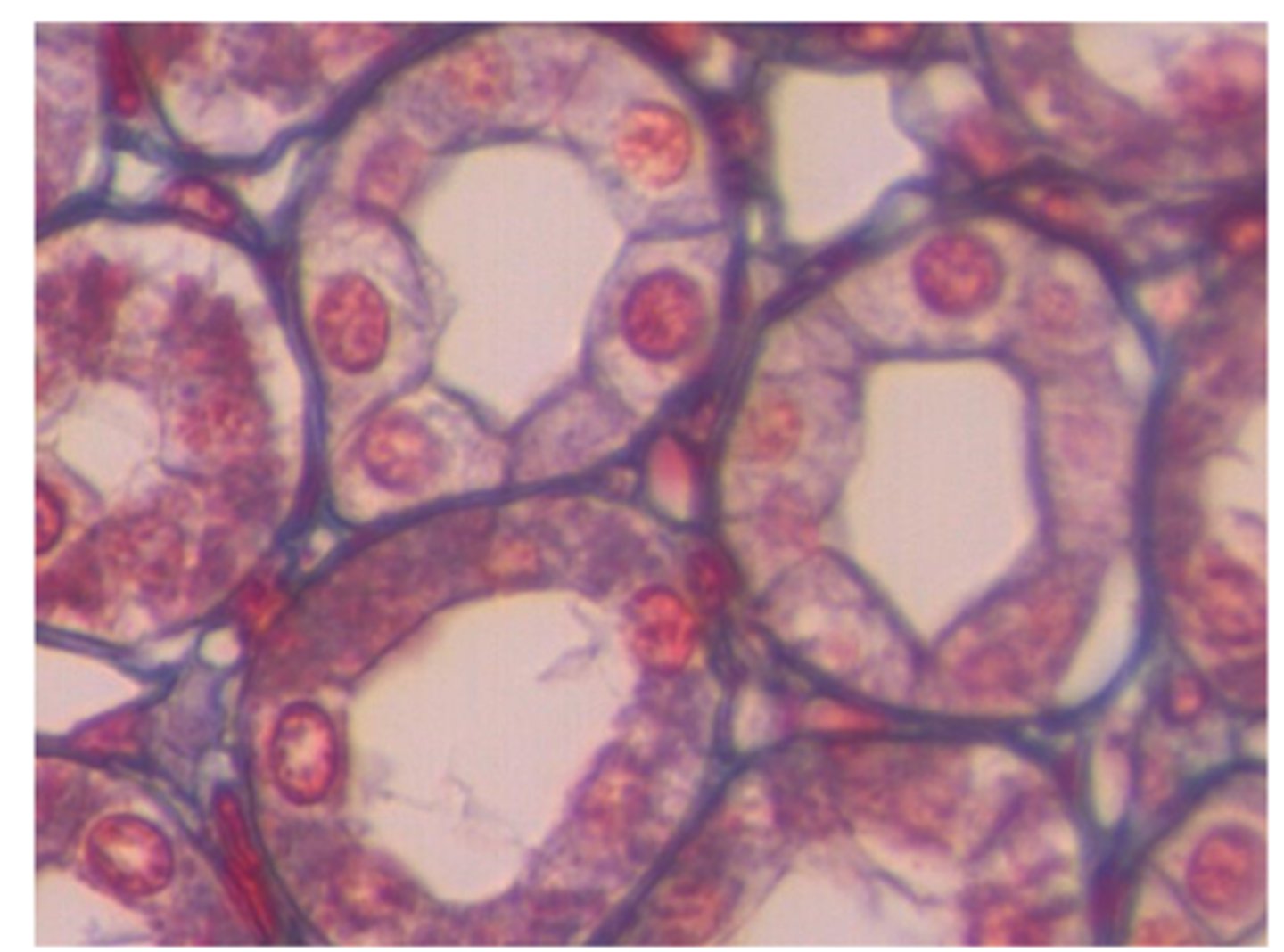
Simple cuboidal epithelial
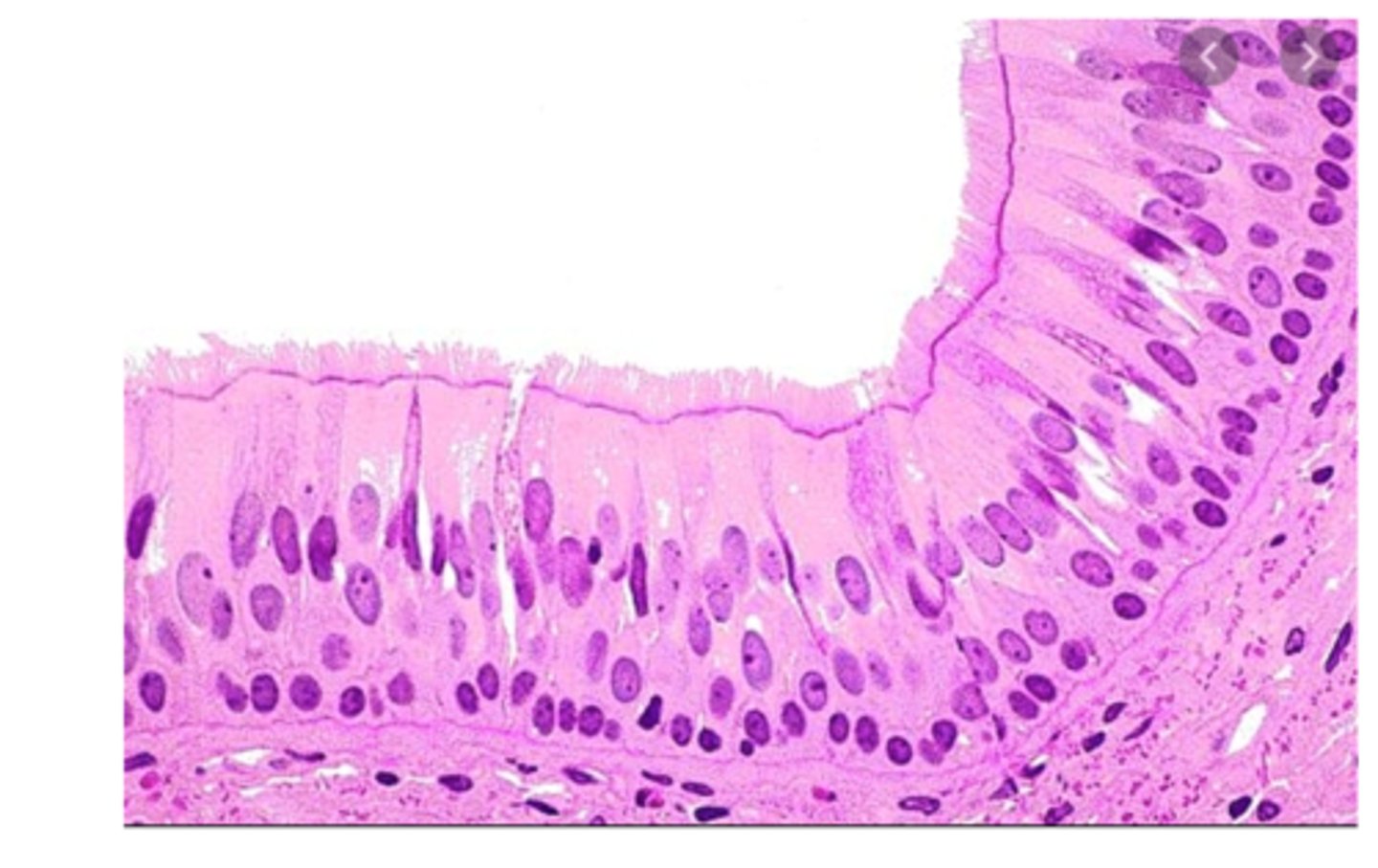
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
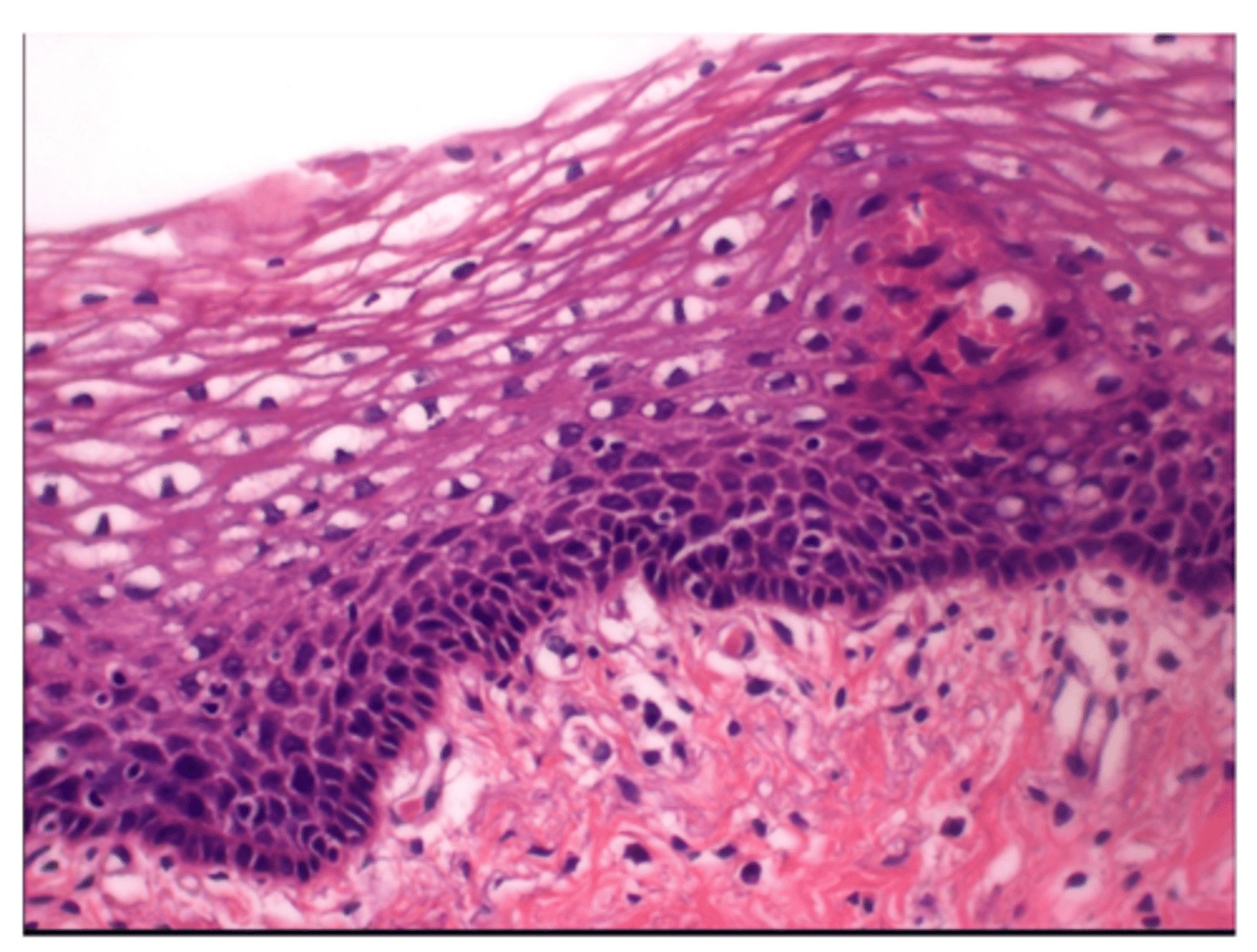
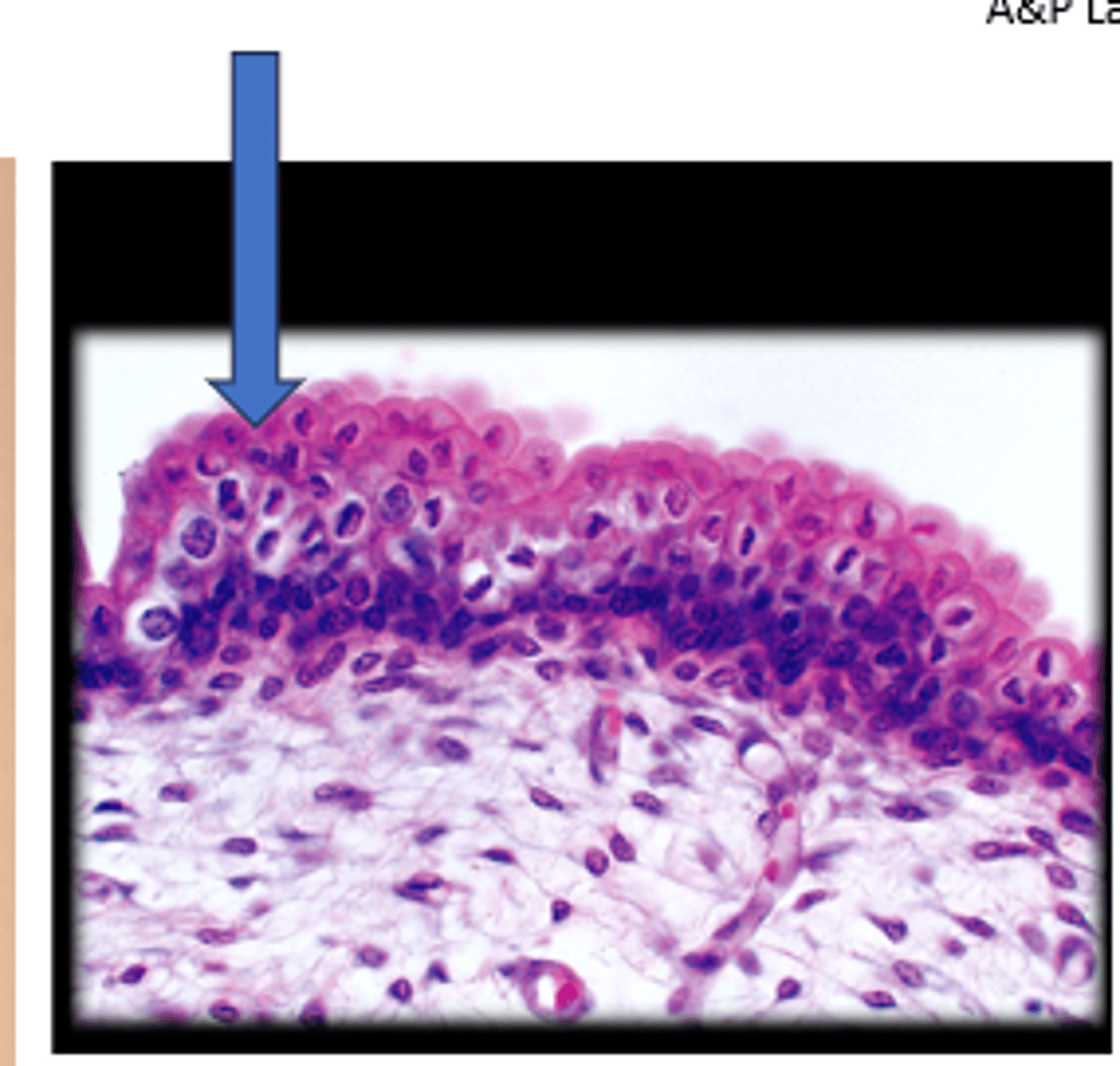
Stratified squamous epithelial
Transitional epithelial
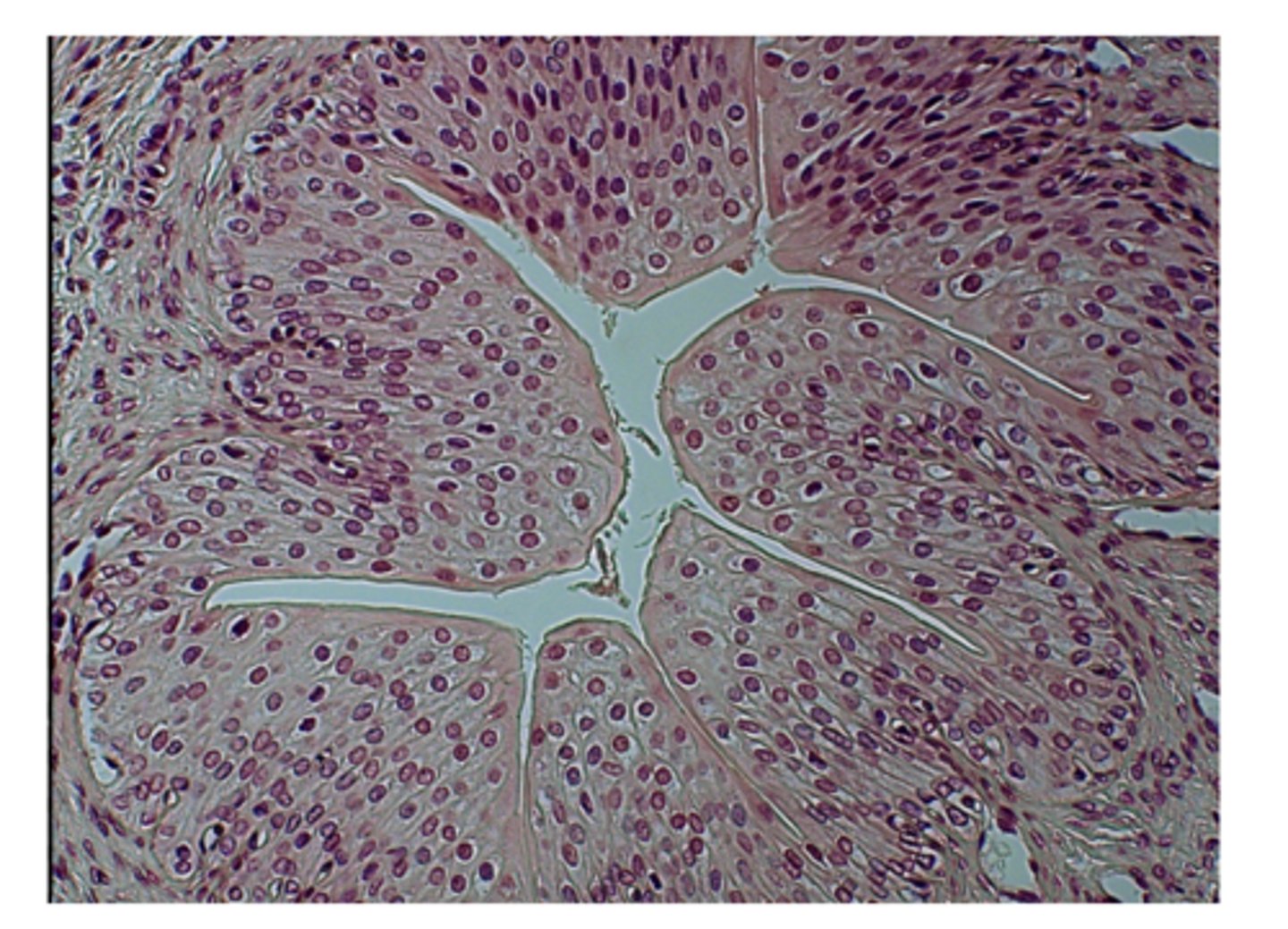
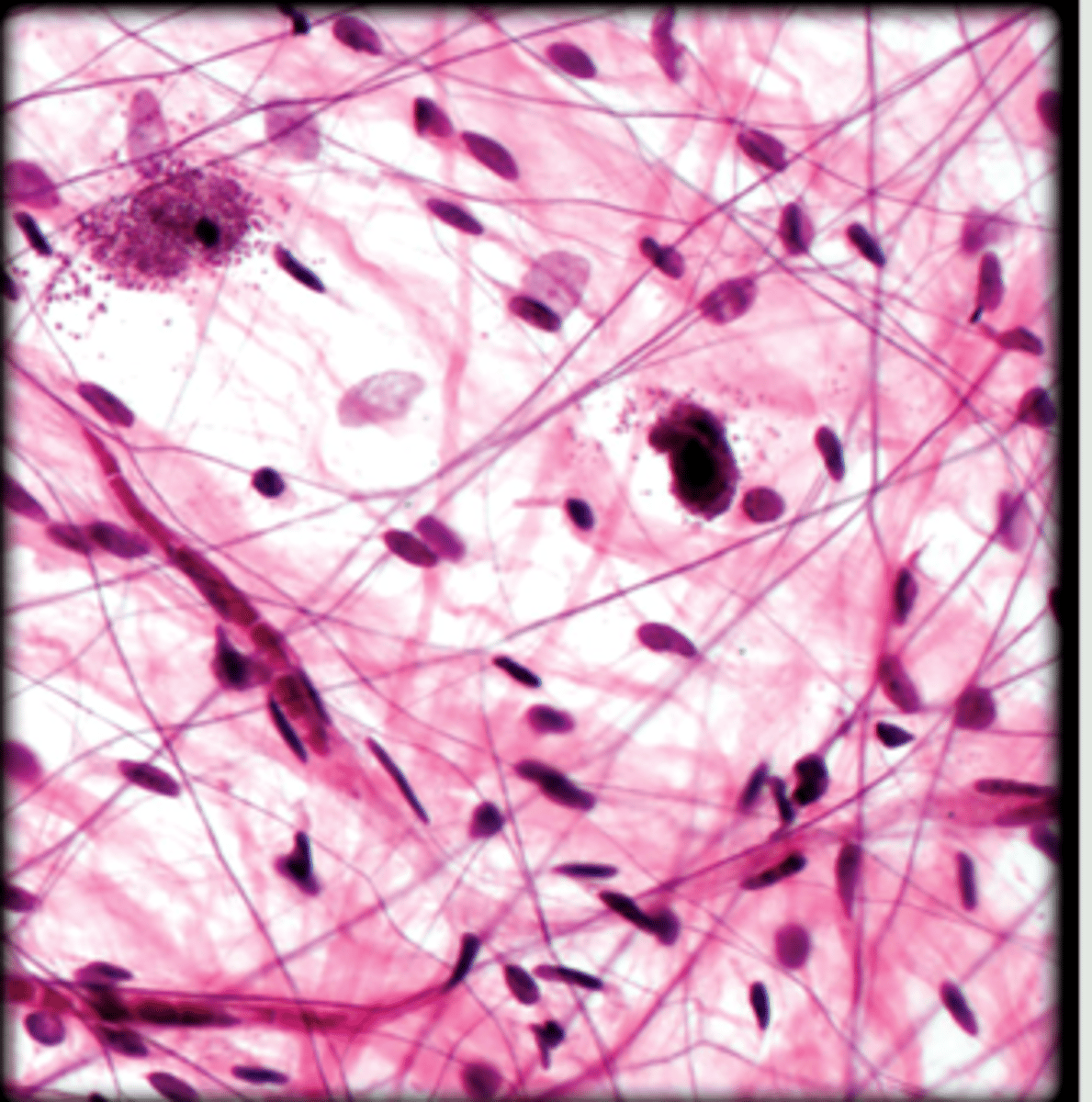
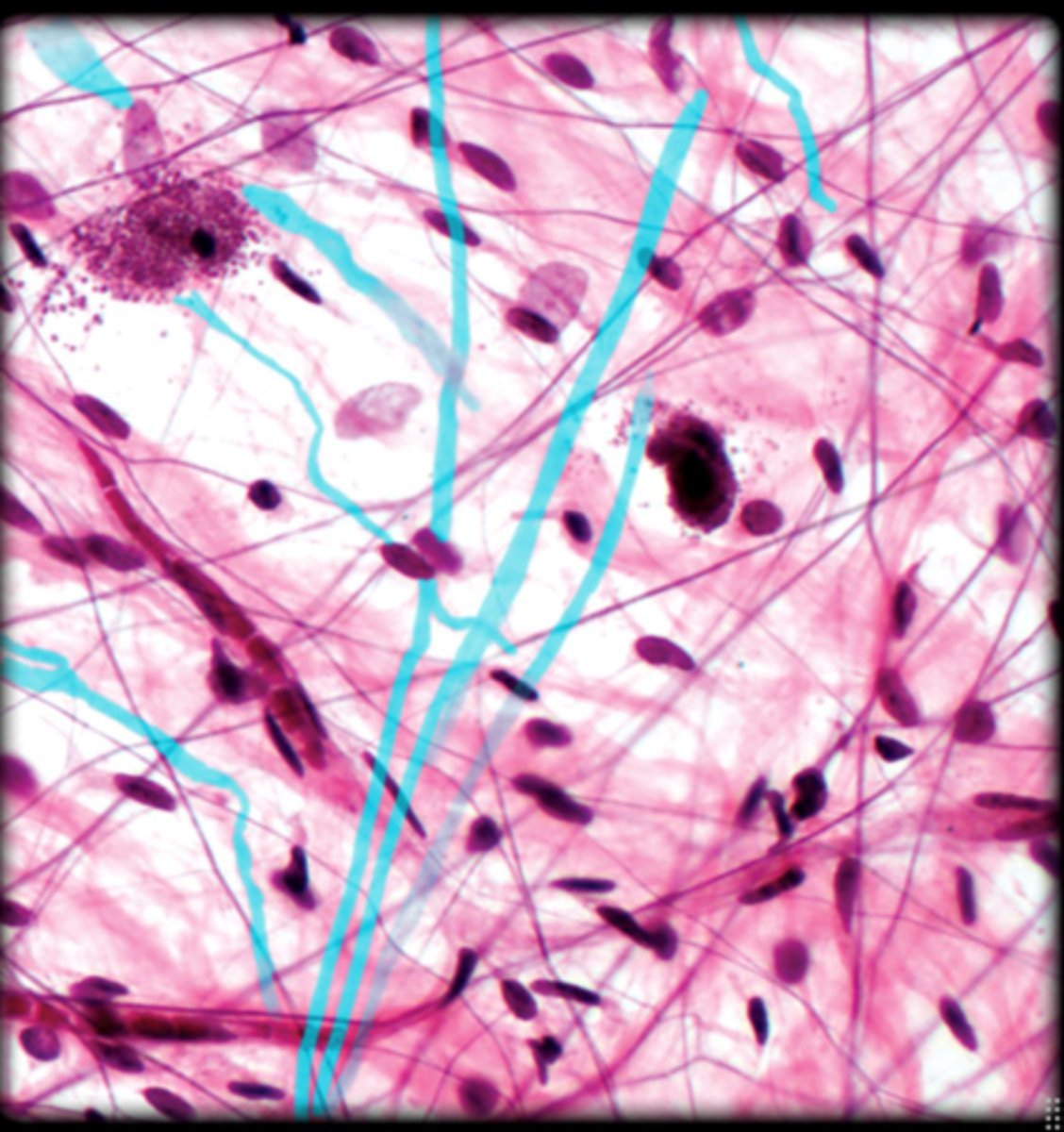
areolar connective tissue
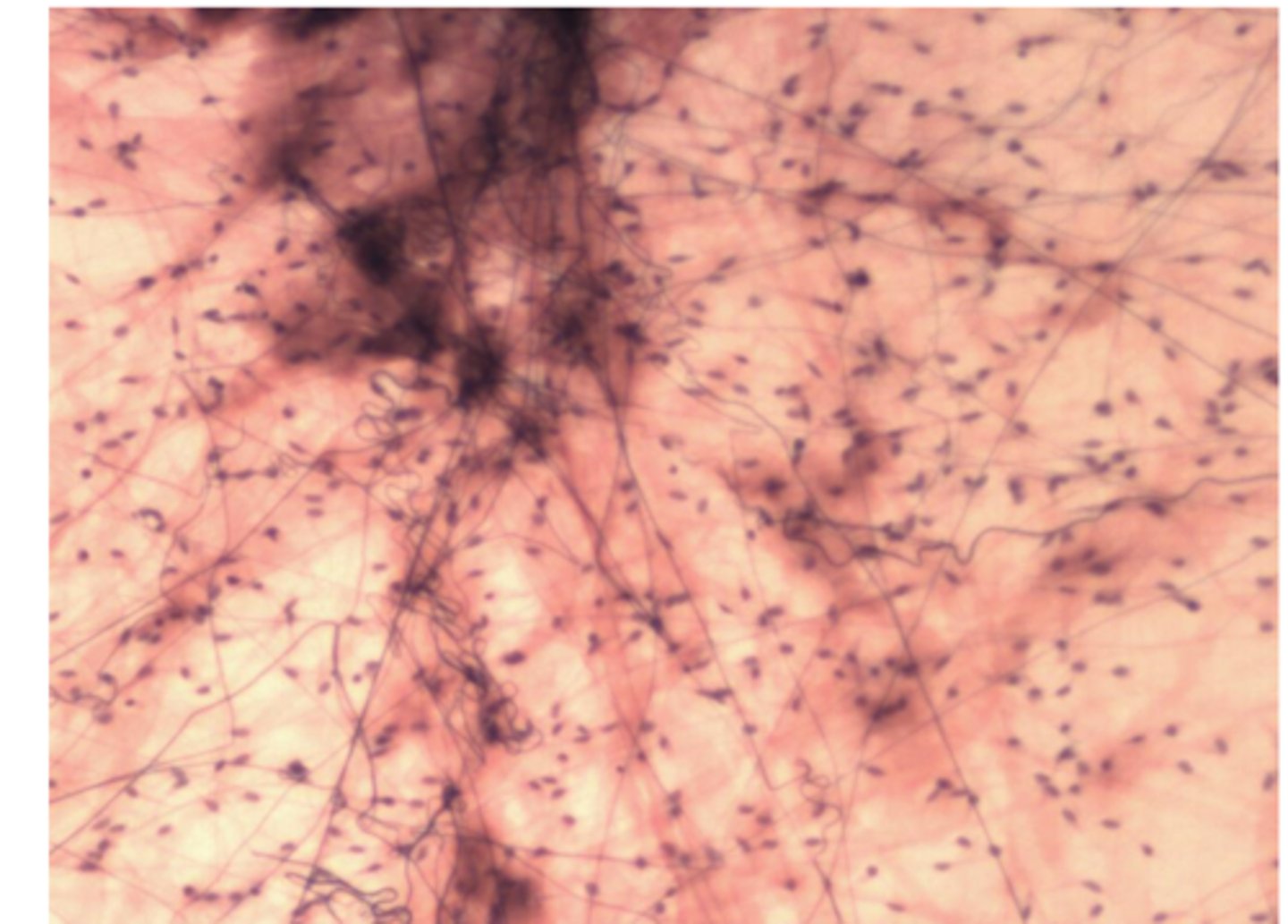
reticular connective tissue
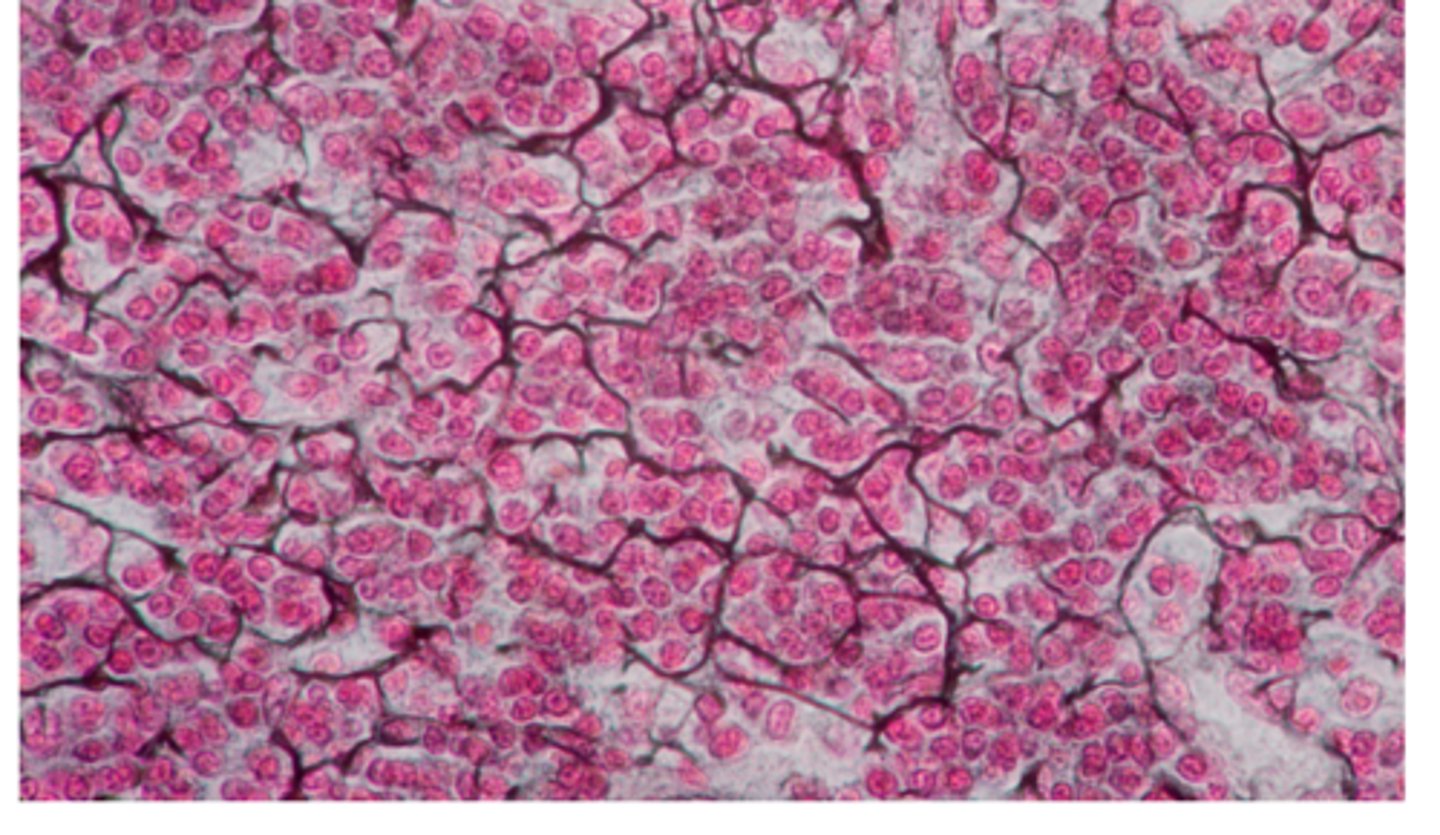
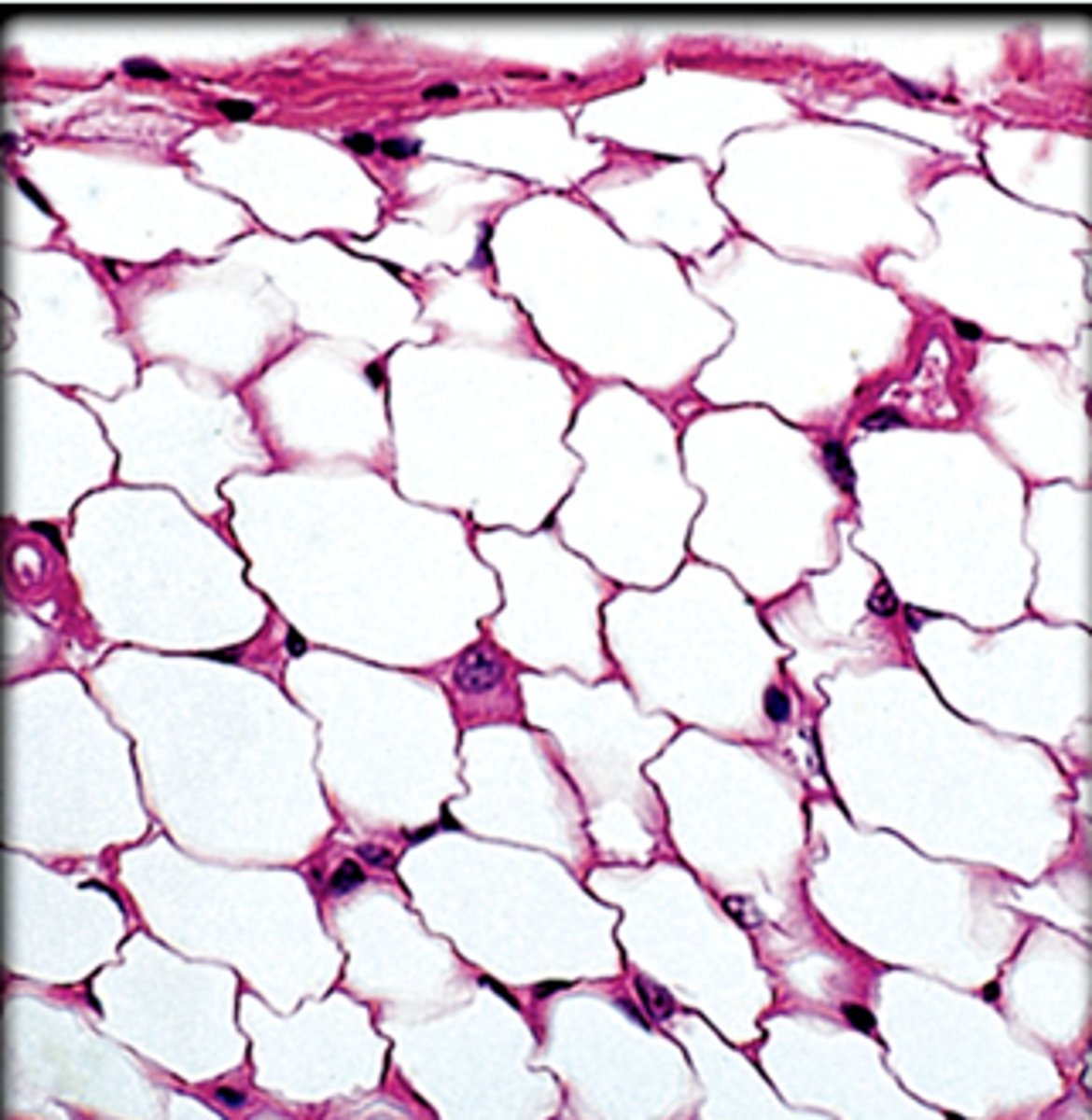
adipose connective tissue
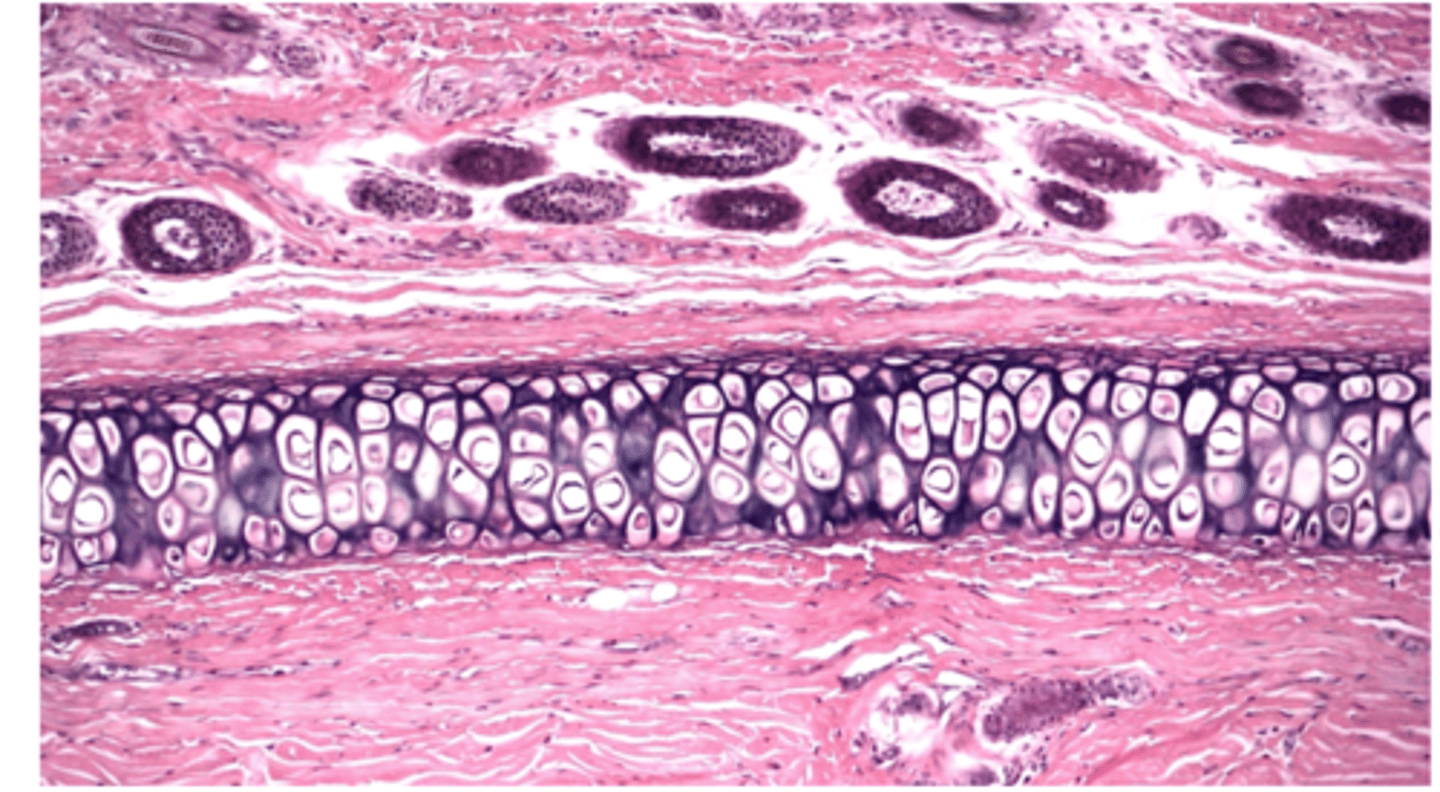
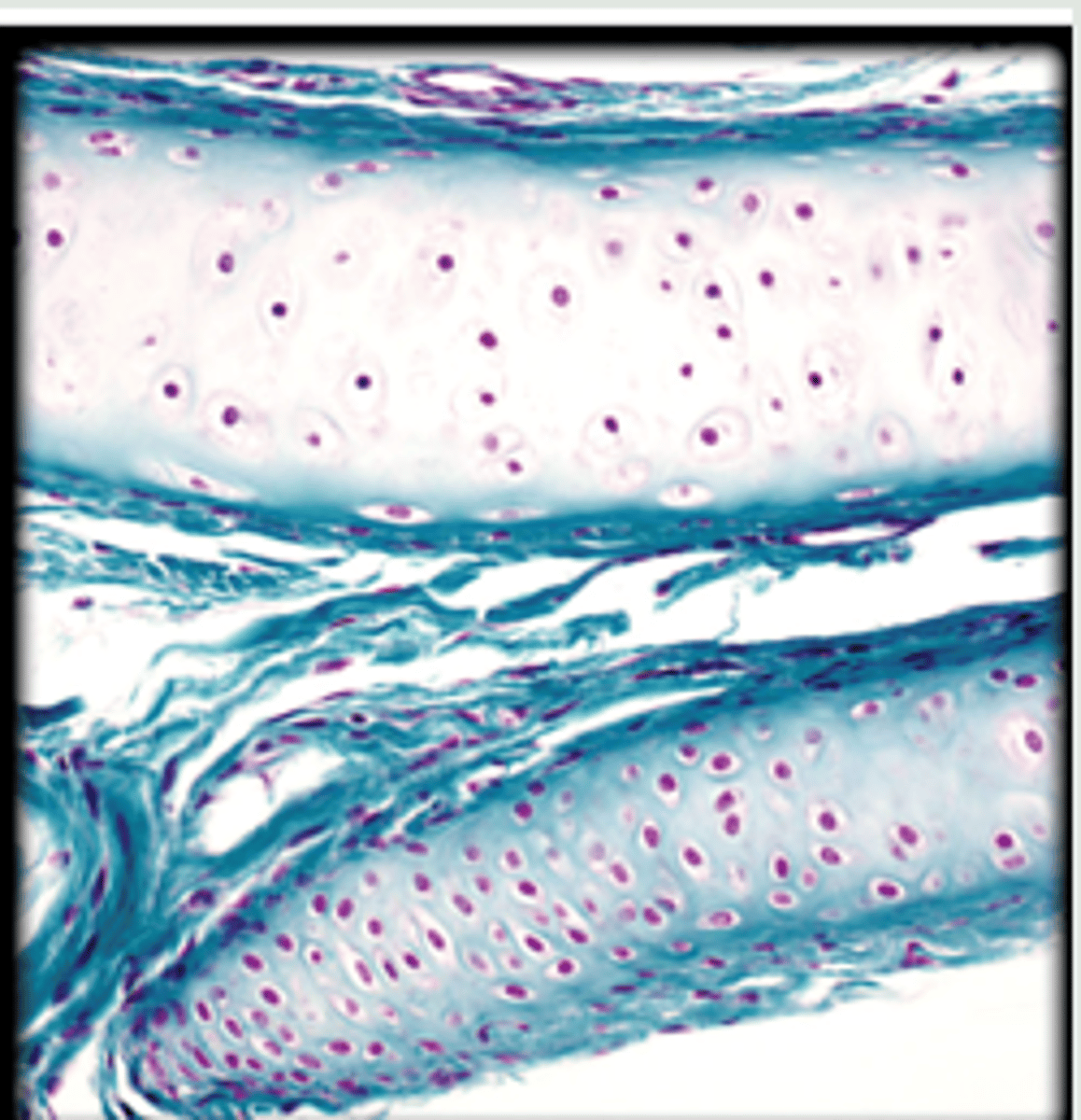
hyaline cartilage
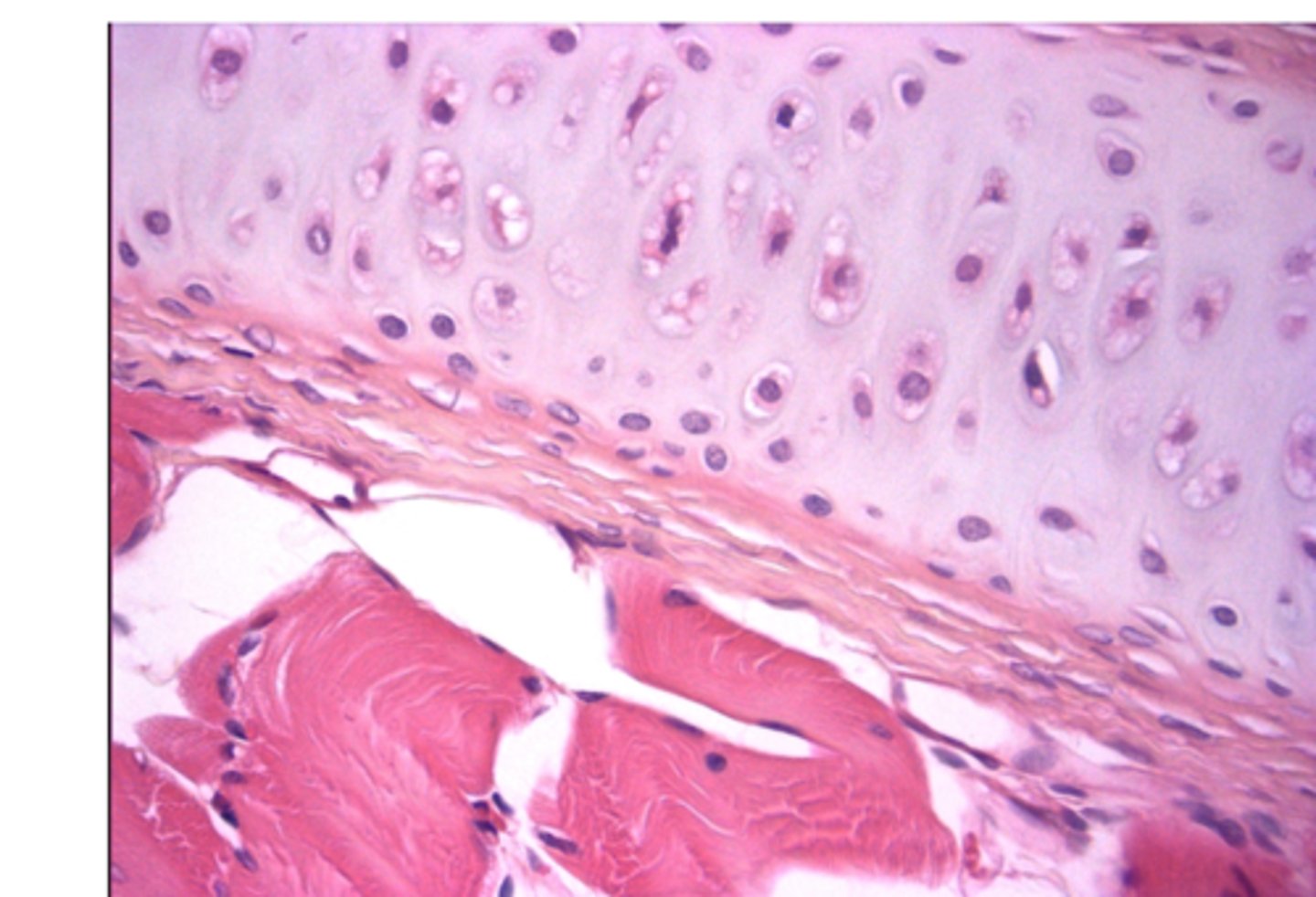
Fibrocartilage
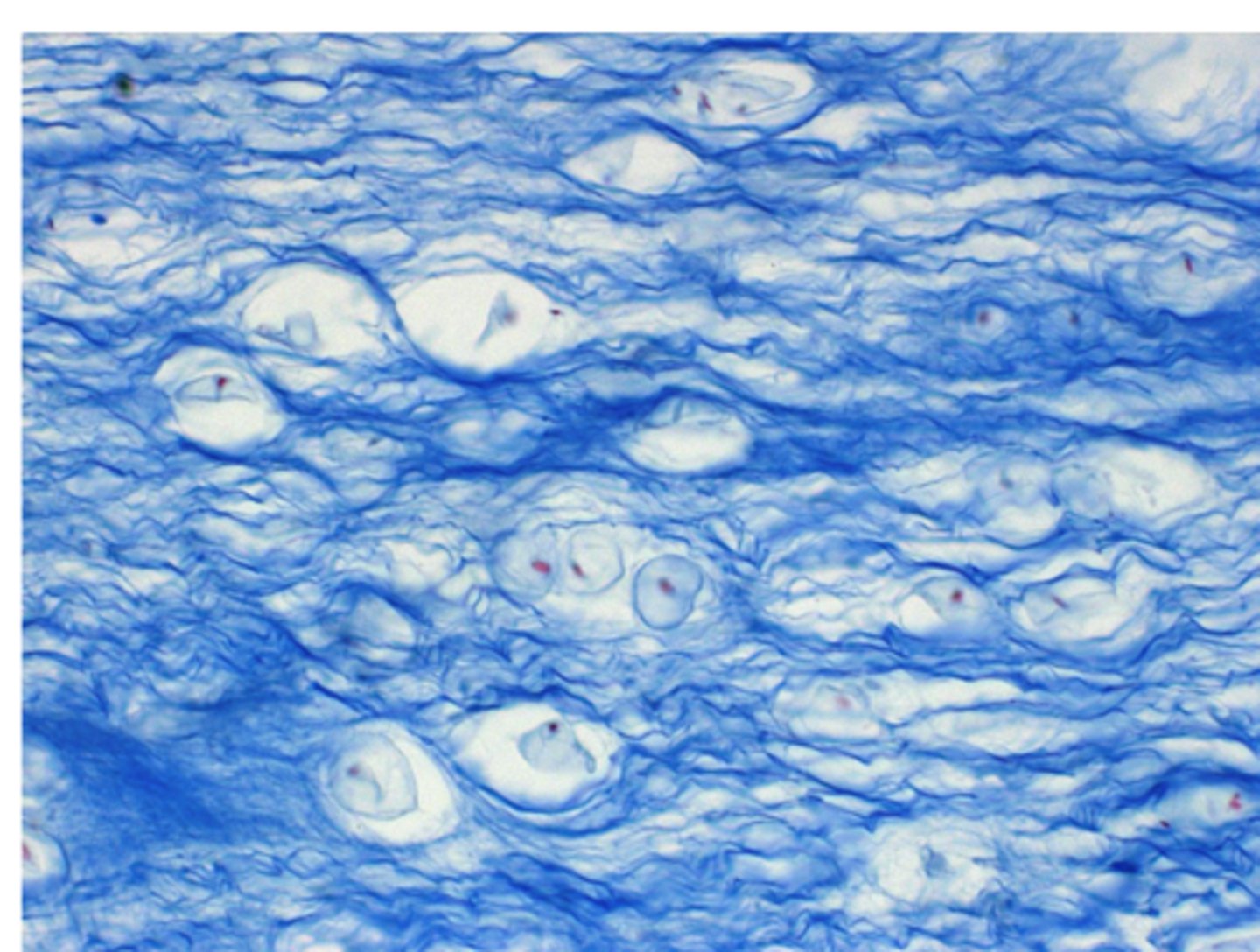
Elastic cartilage
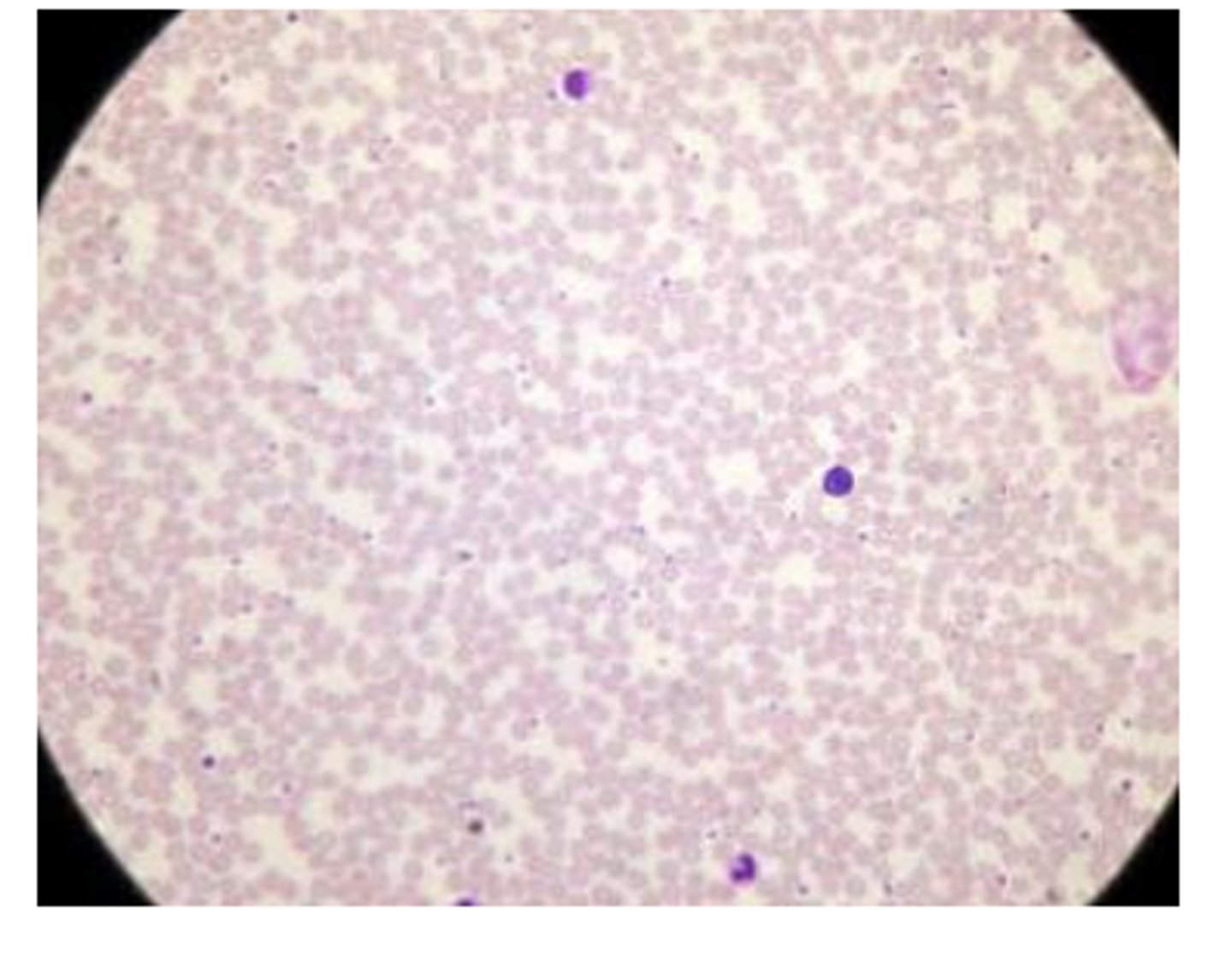
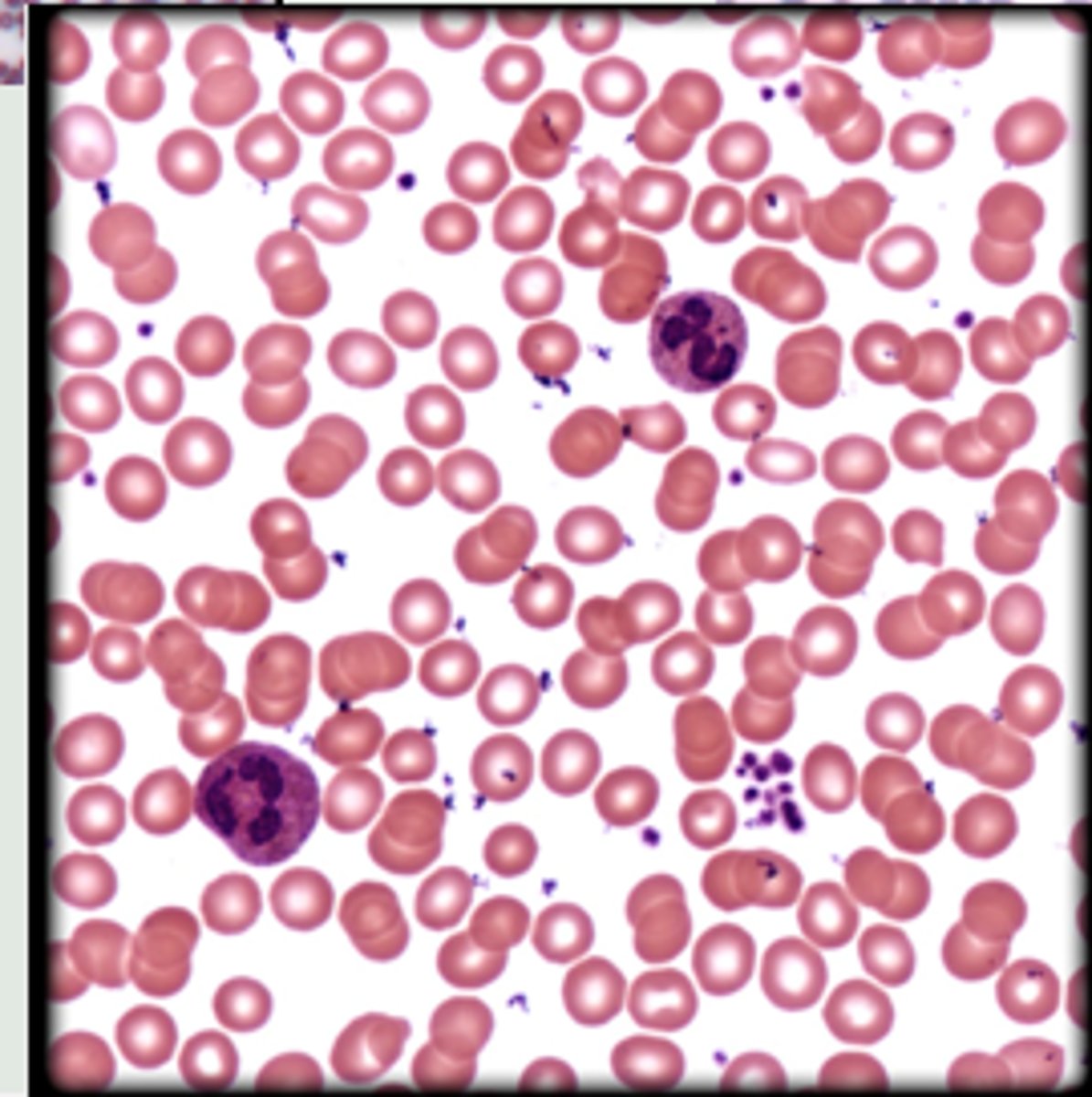
blood connective tissue
compact bone
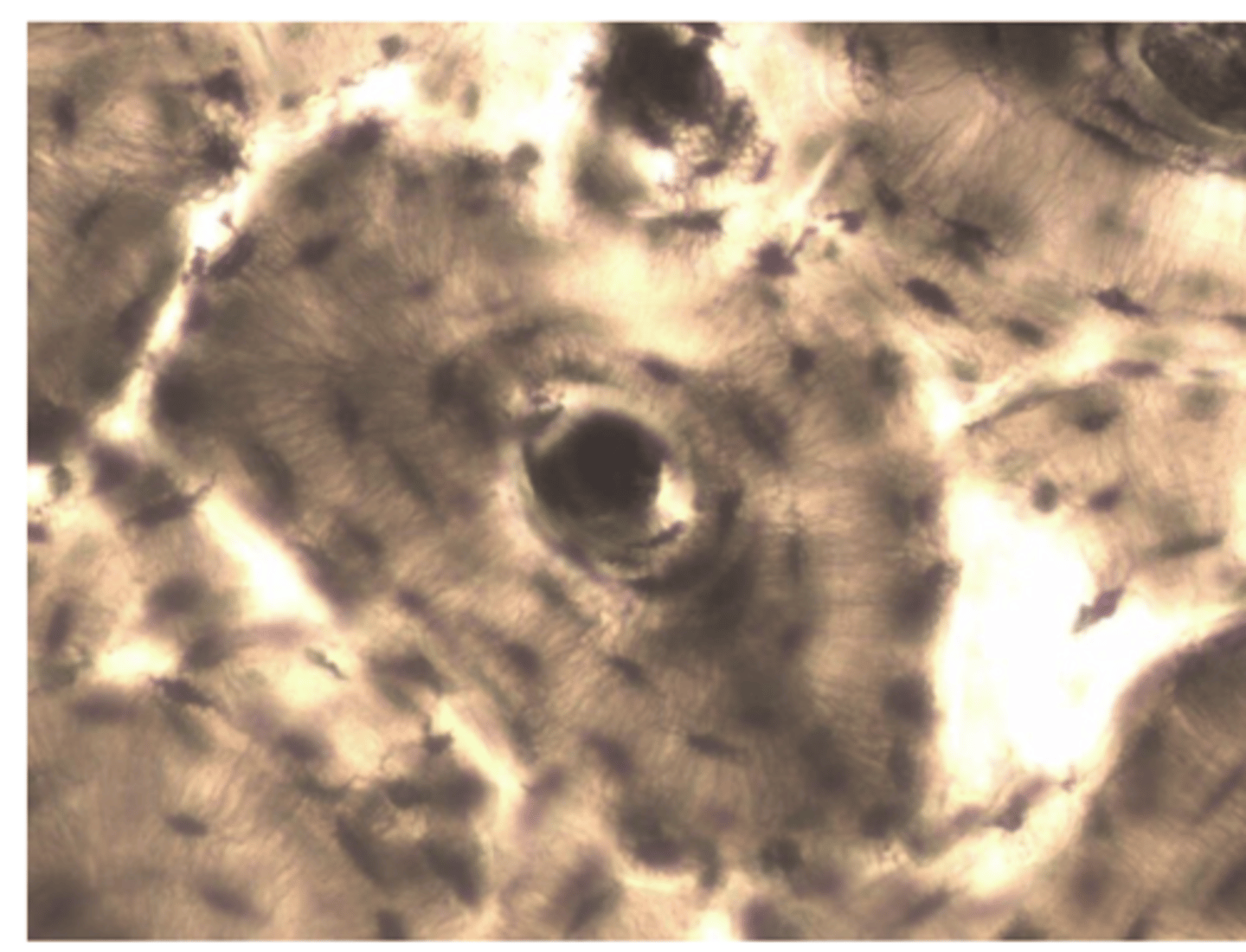
Smooth muscles
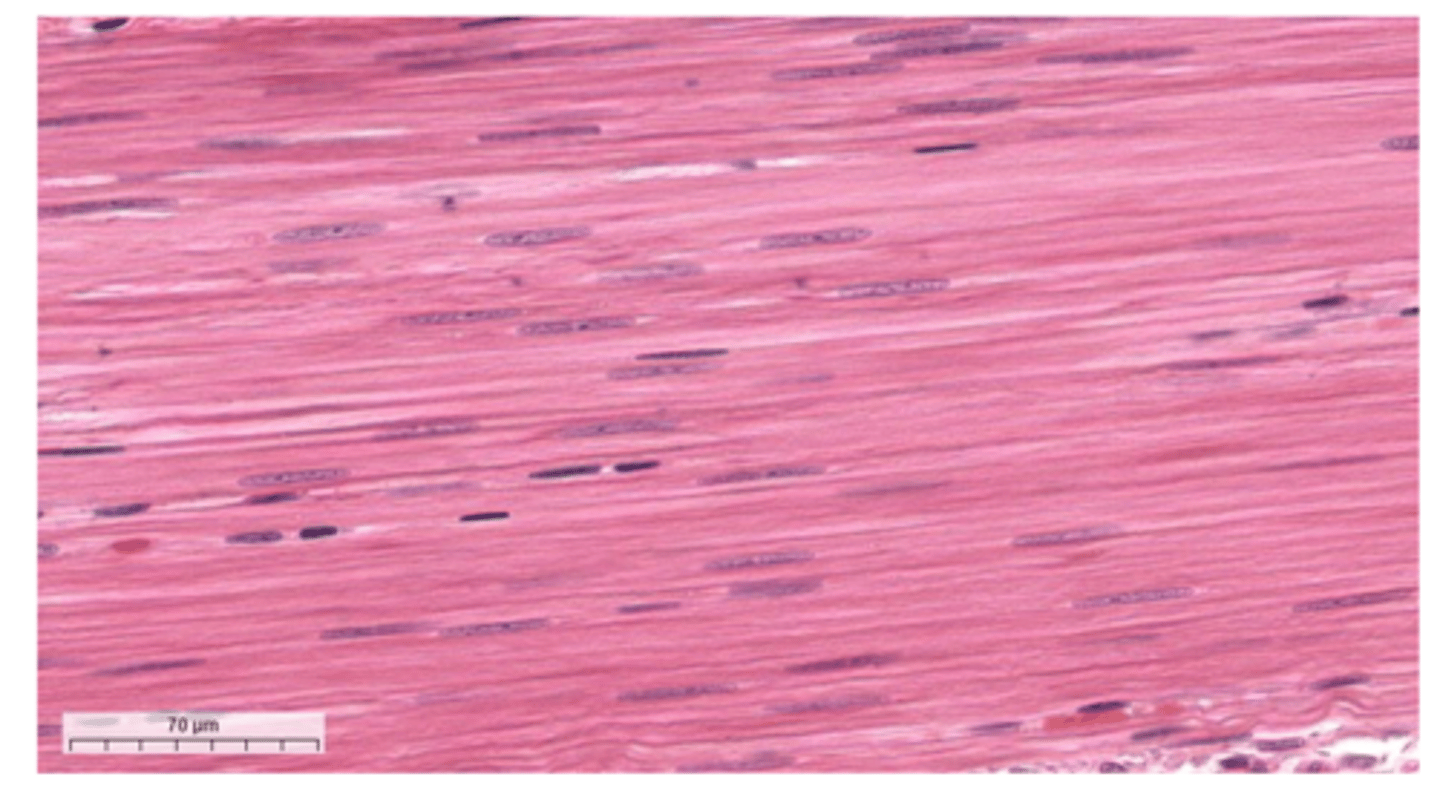
skeletal muscle tissue
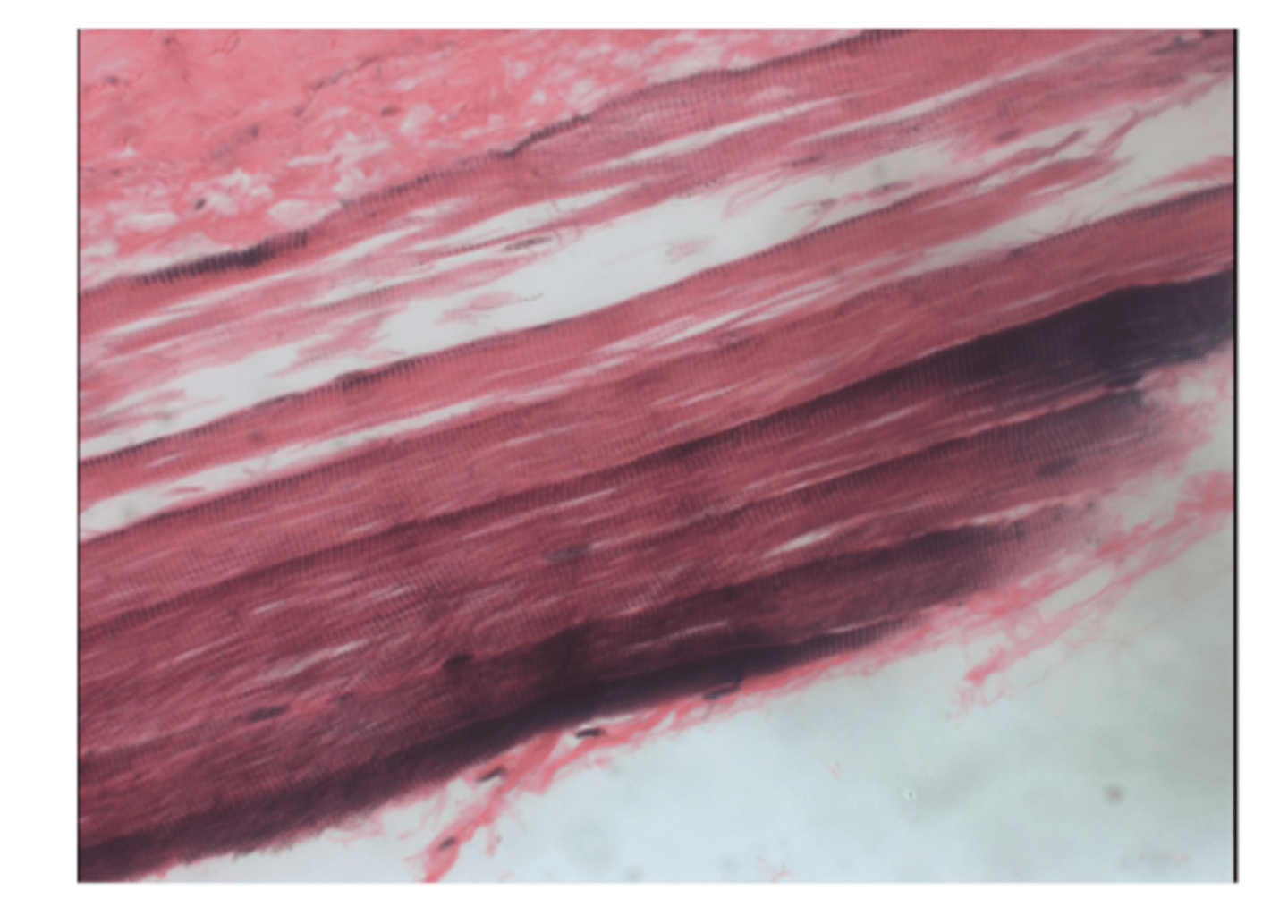
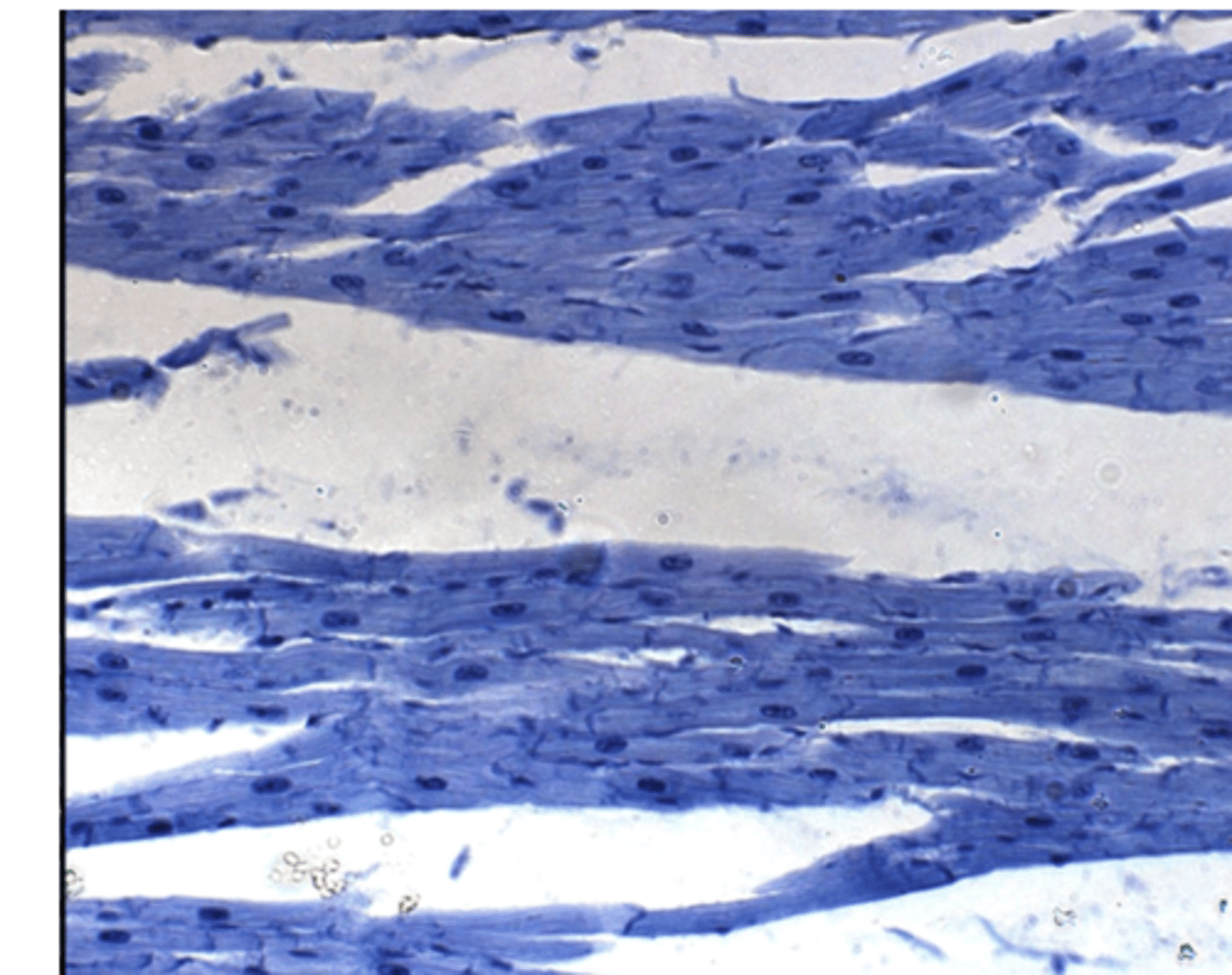
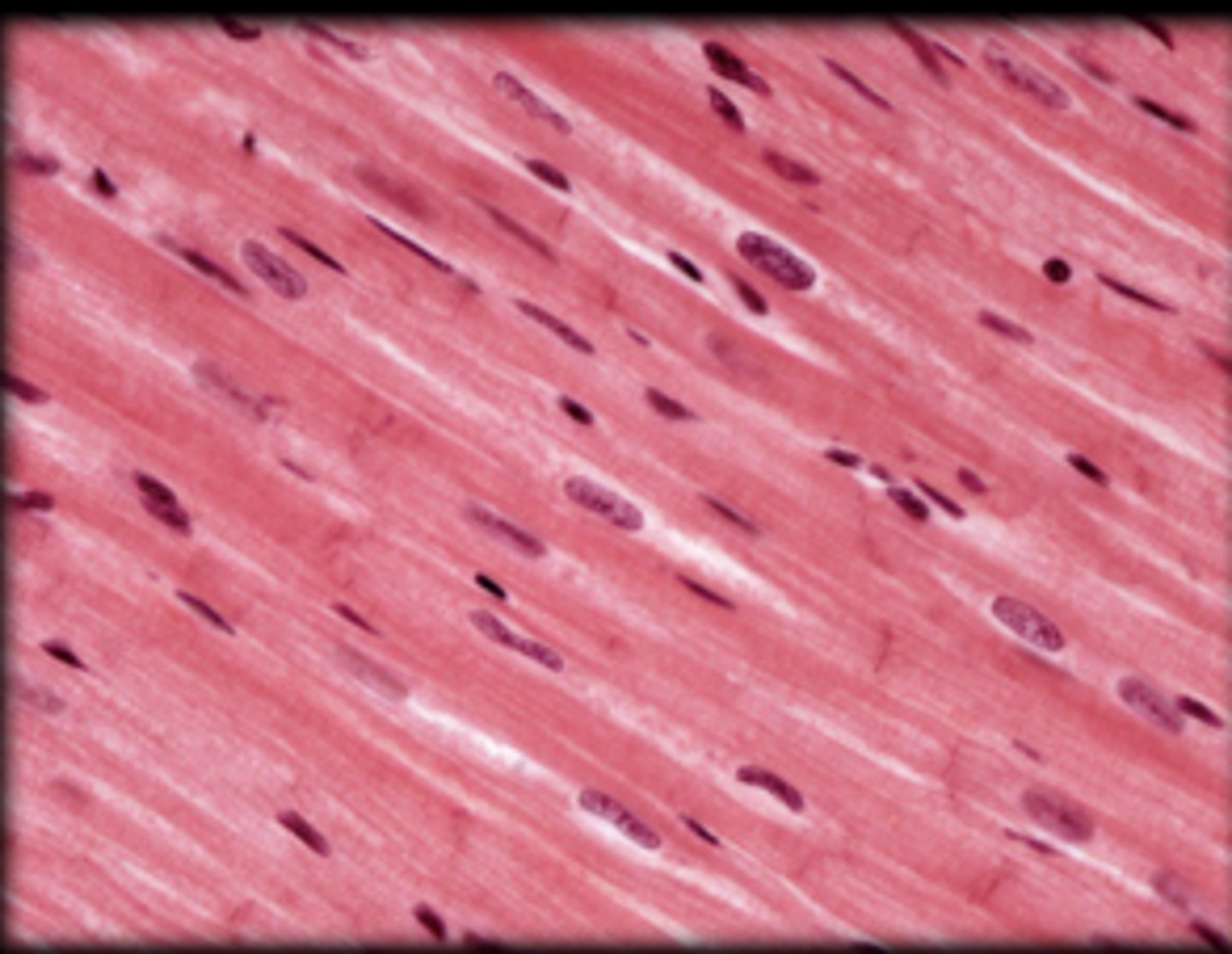
cardiac tissue

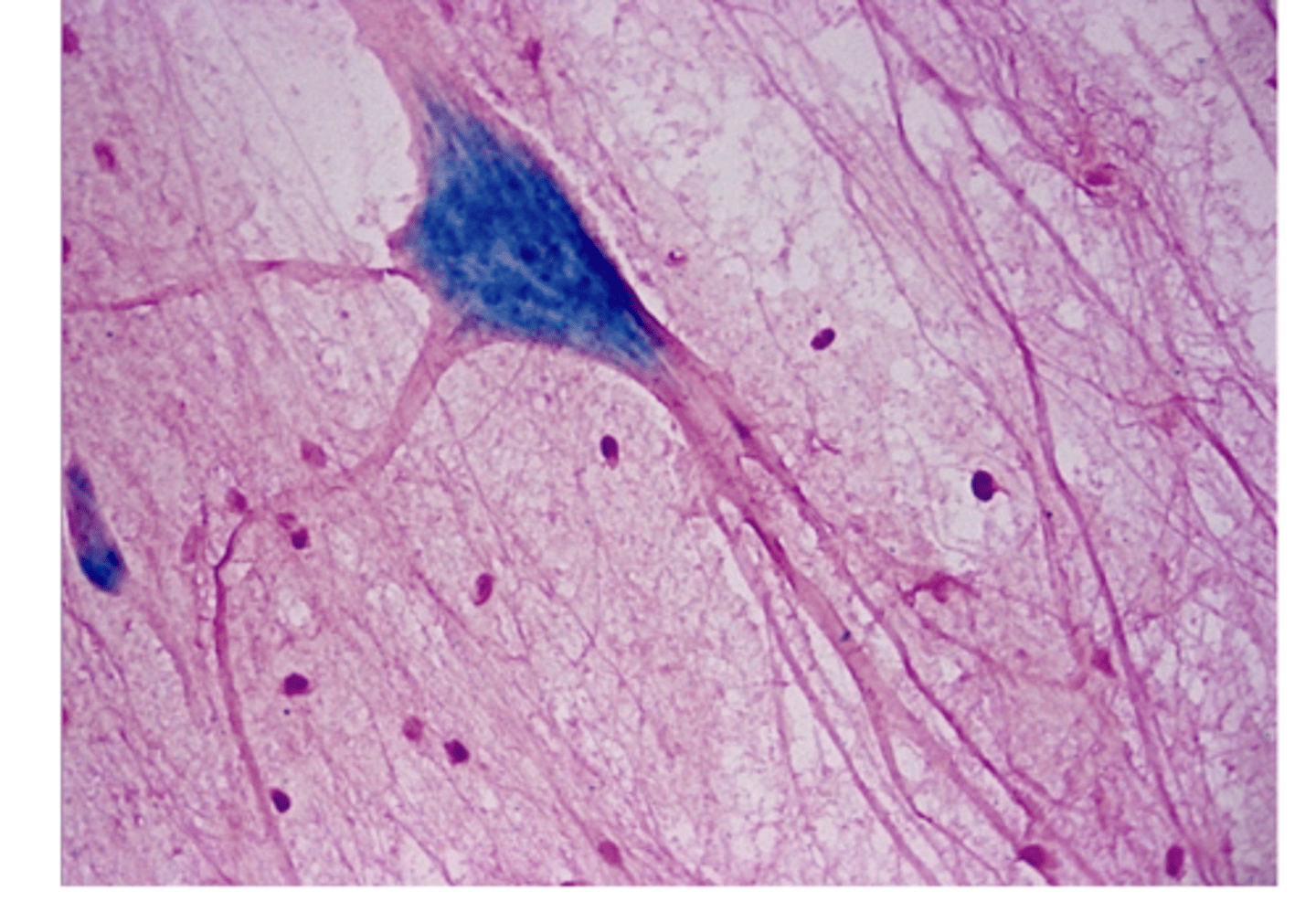
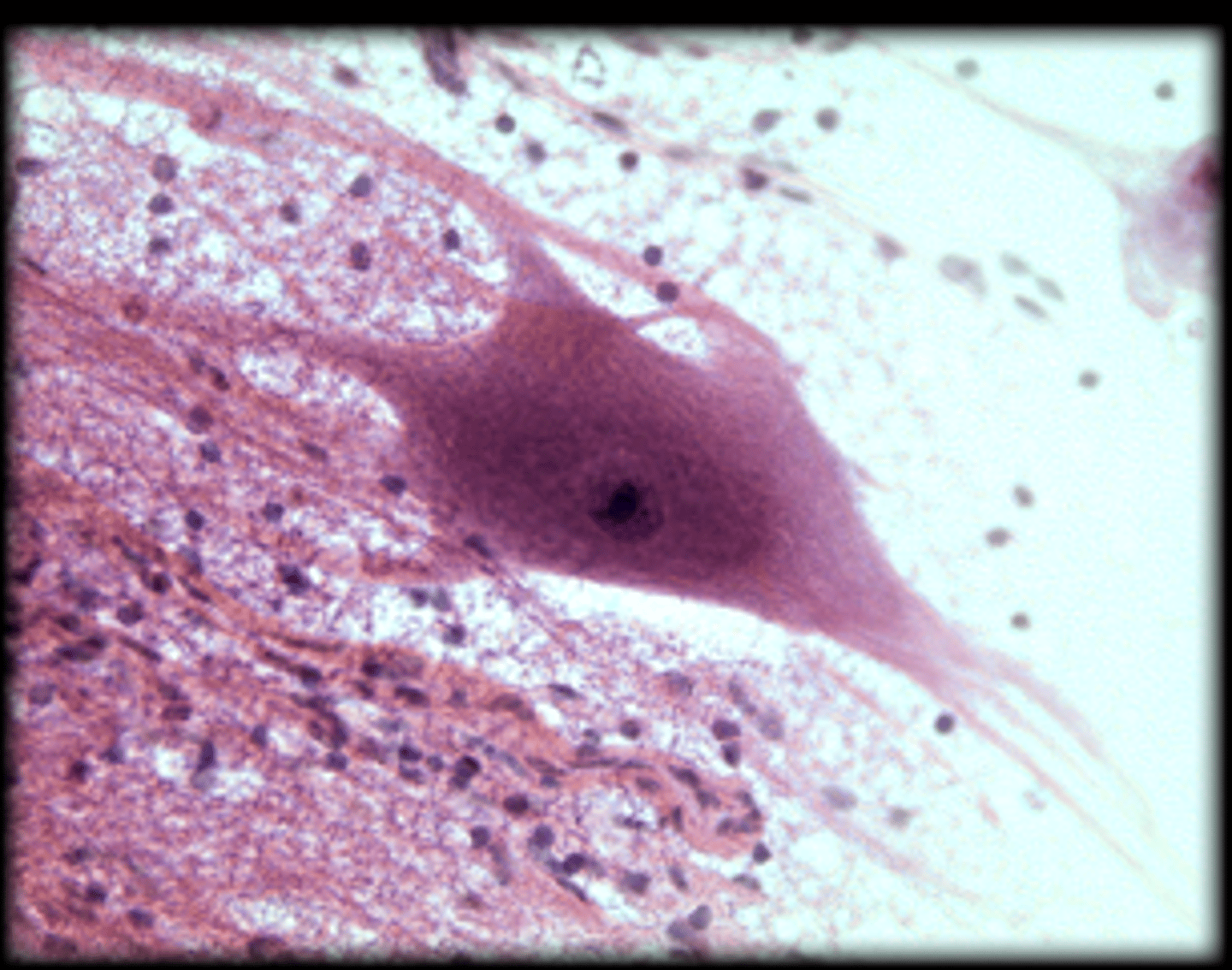
multipolar neuron
The function of intercalated discs found in cardiac muscle is to?
Send out electrical impulses
3 multiple choice options
which of the following is a function for stratified squamous
Protection from abrasion
3 multiple choice options
simple cuboidal epithelium
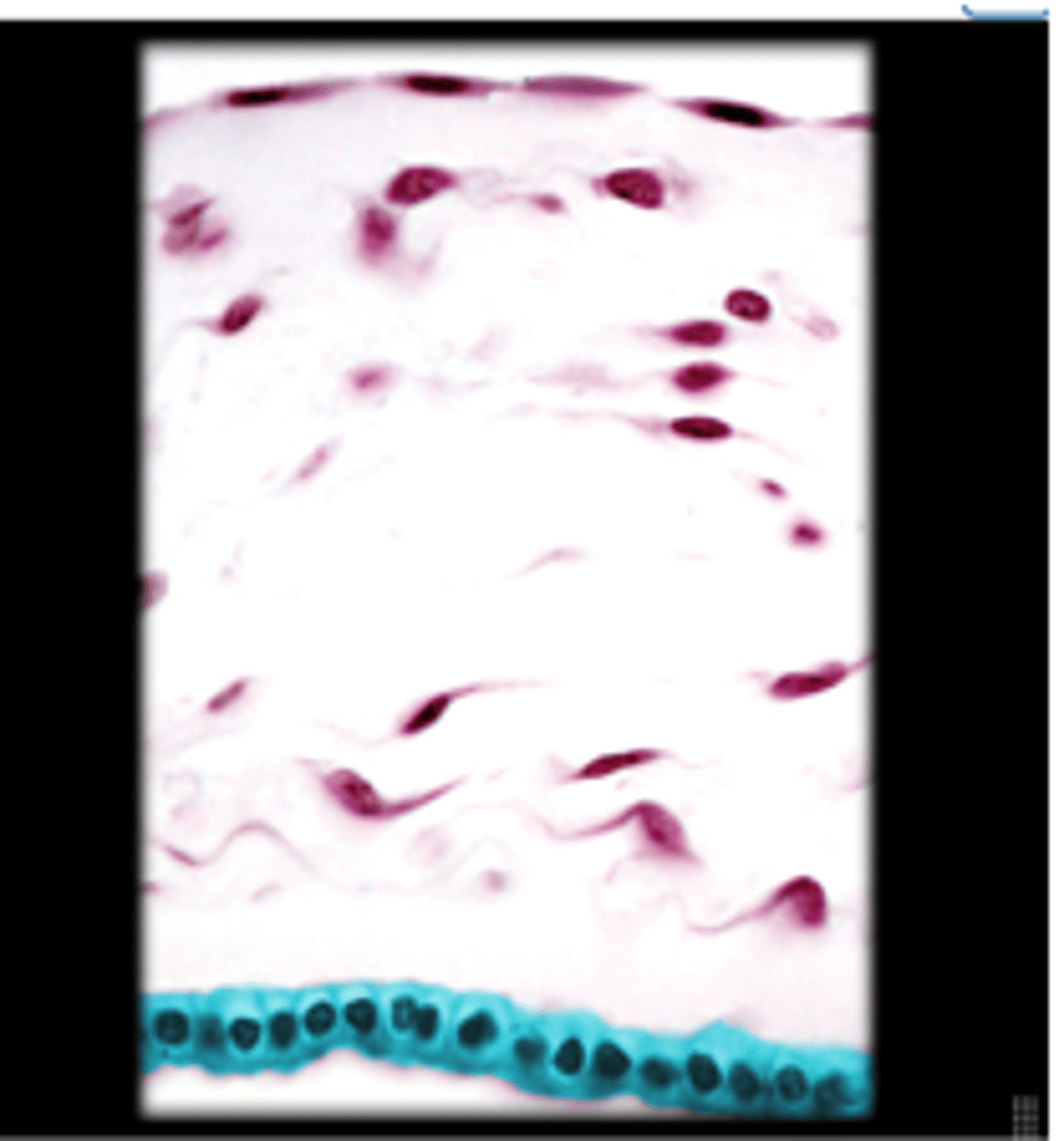
simple columnar epithelium
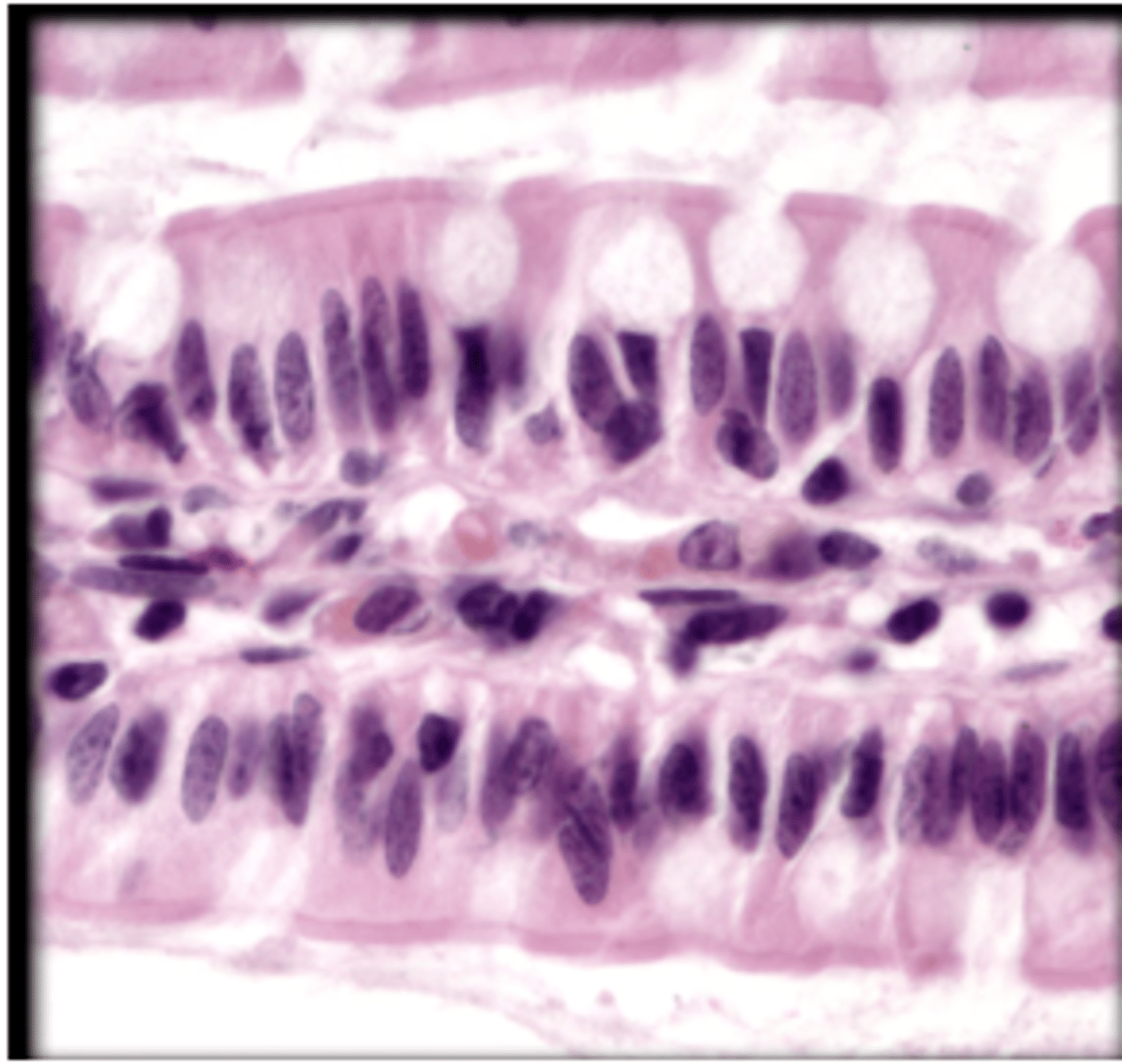
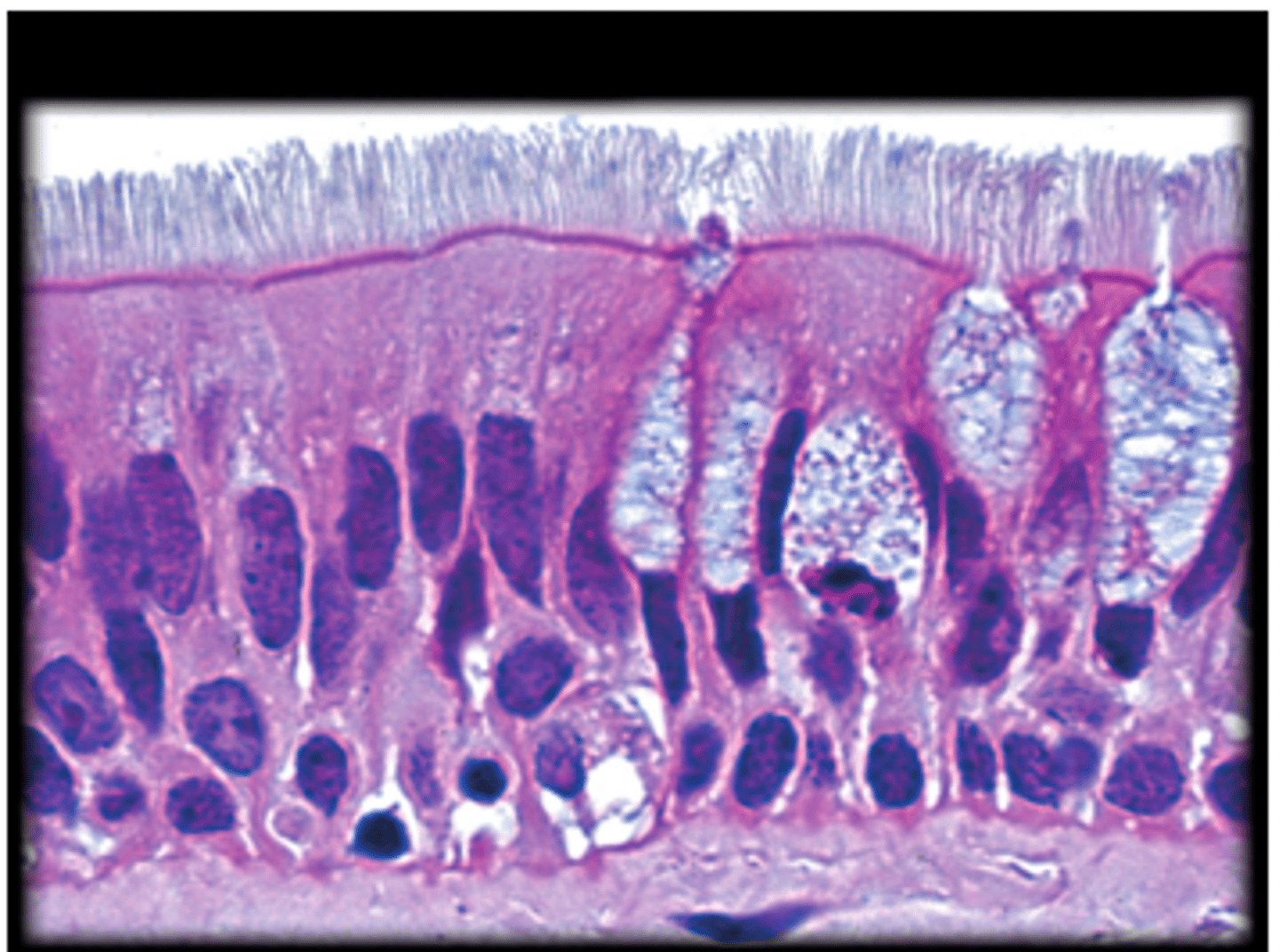
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar
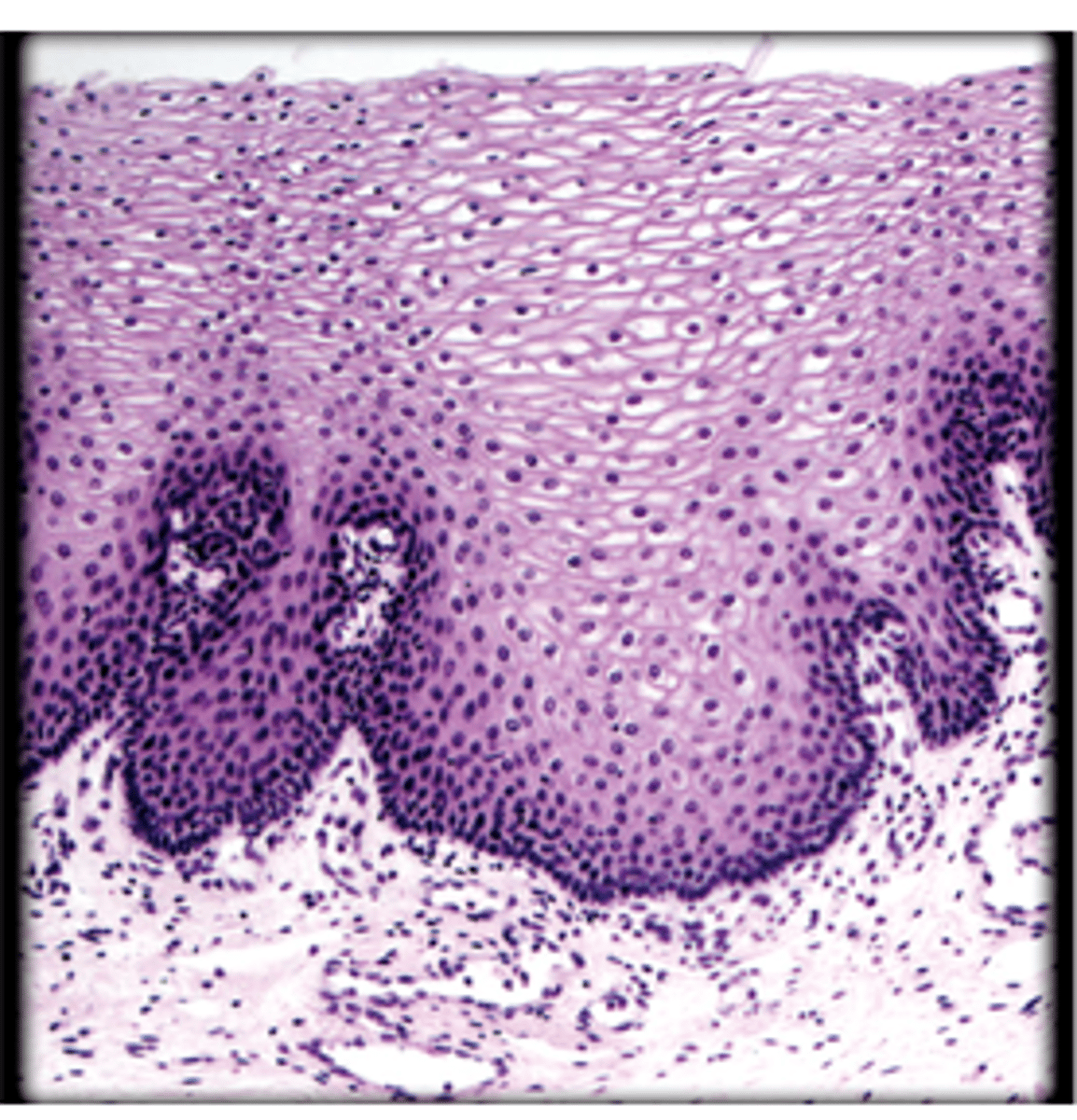
stratified squamous epithelium
transitional epithelium
areolar connective tissue
Areolar tissues in general
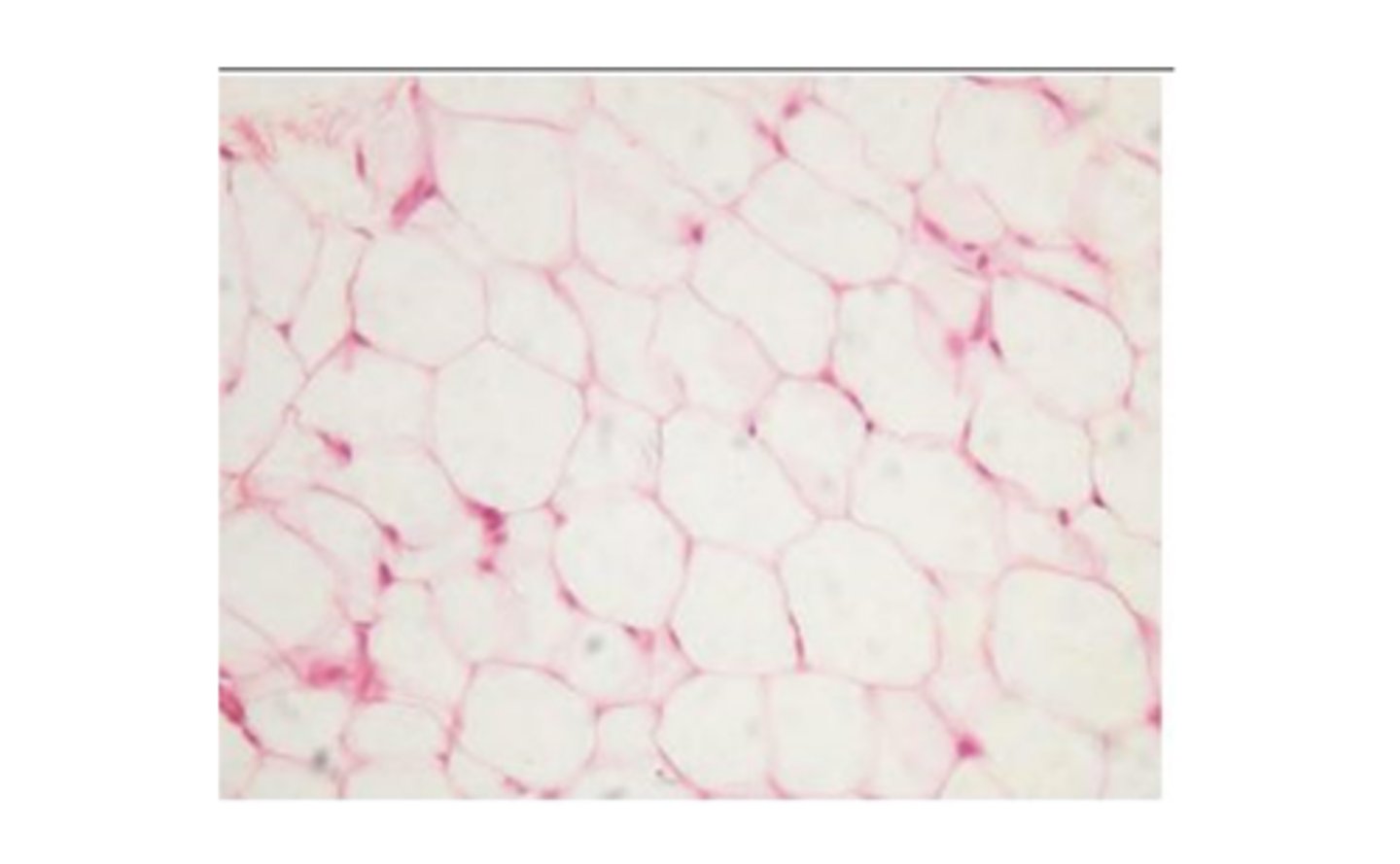
adipose tissue
hyaline cartilage
Blood tissue
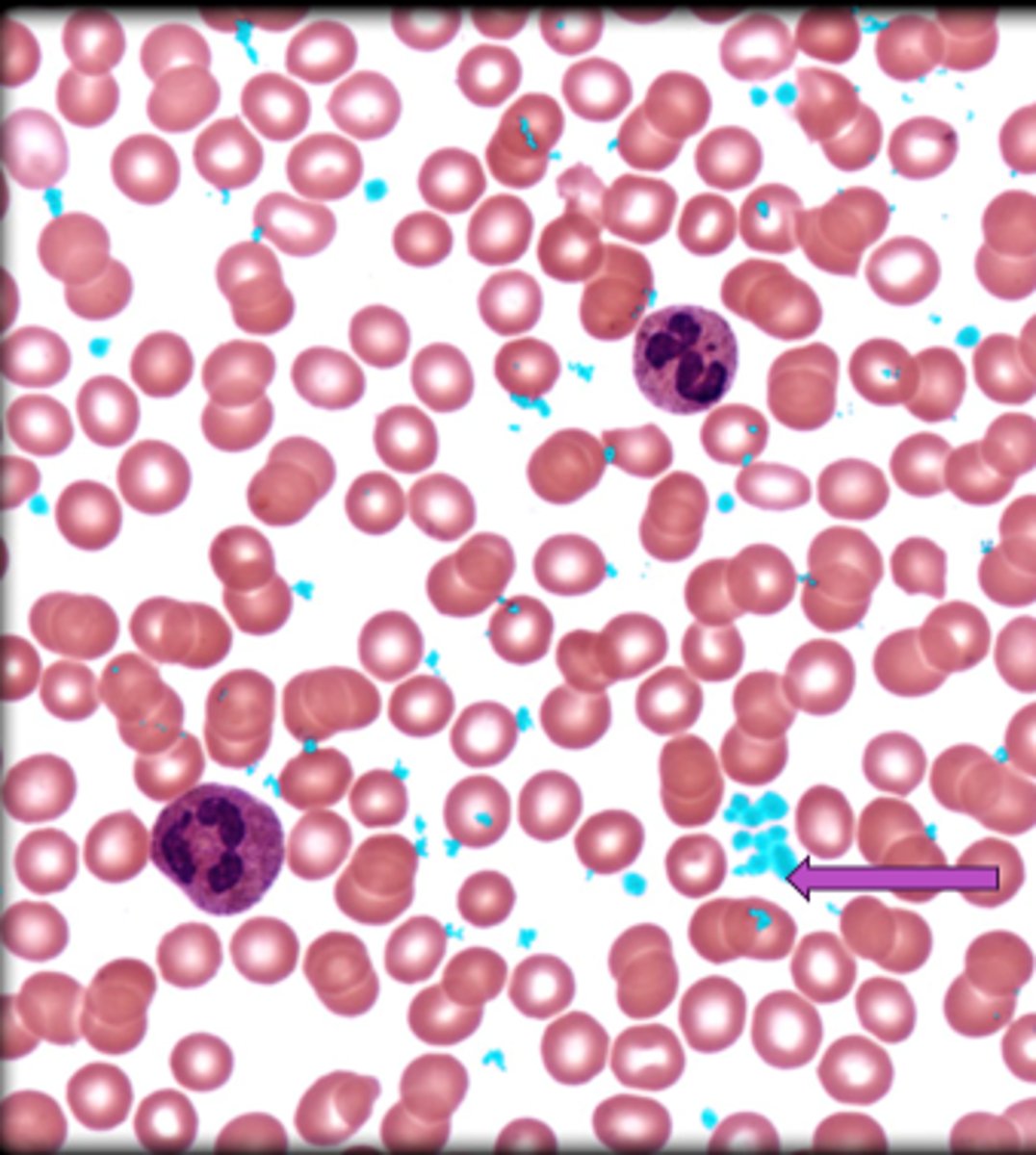
Platelets
Osteons
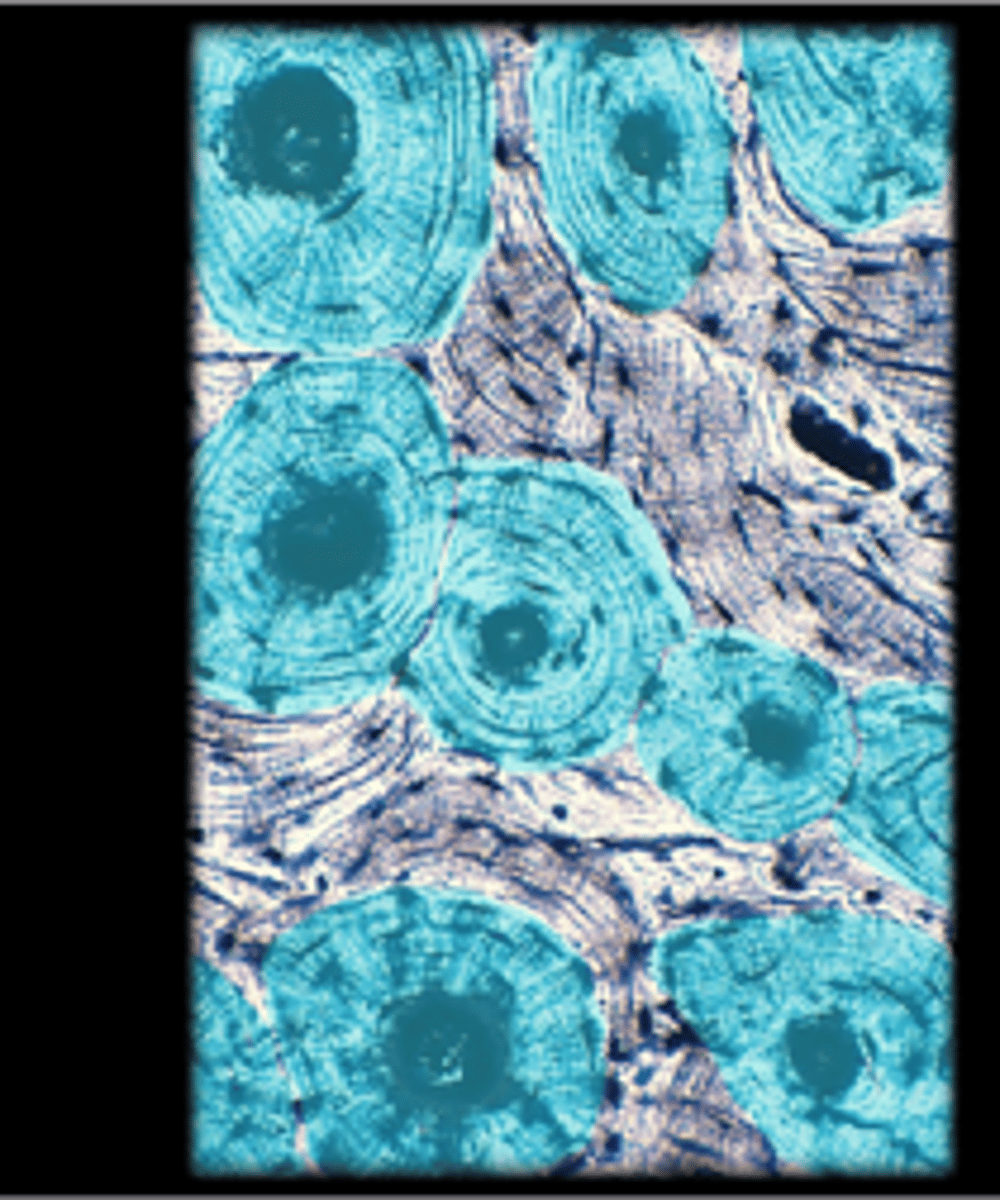
Compact Bone (Bone Tissue)
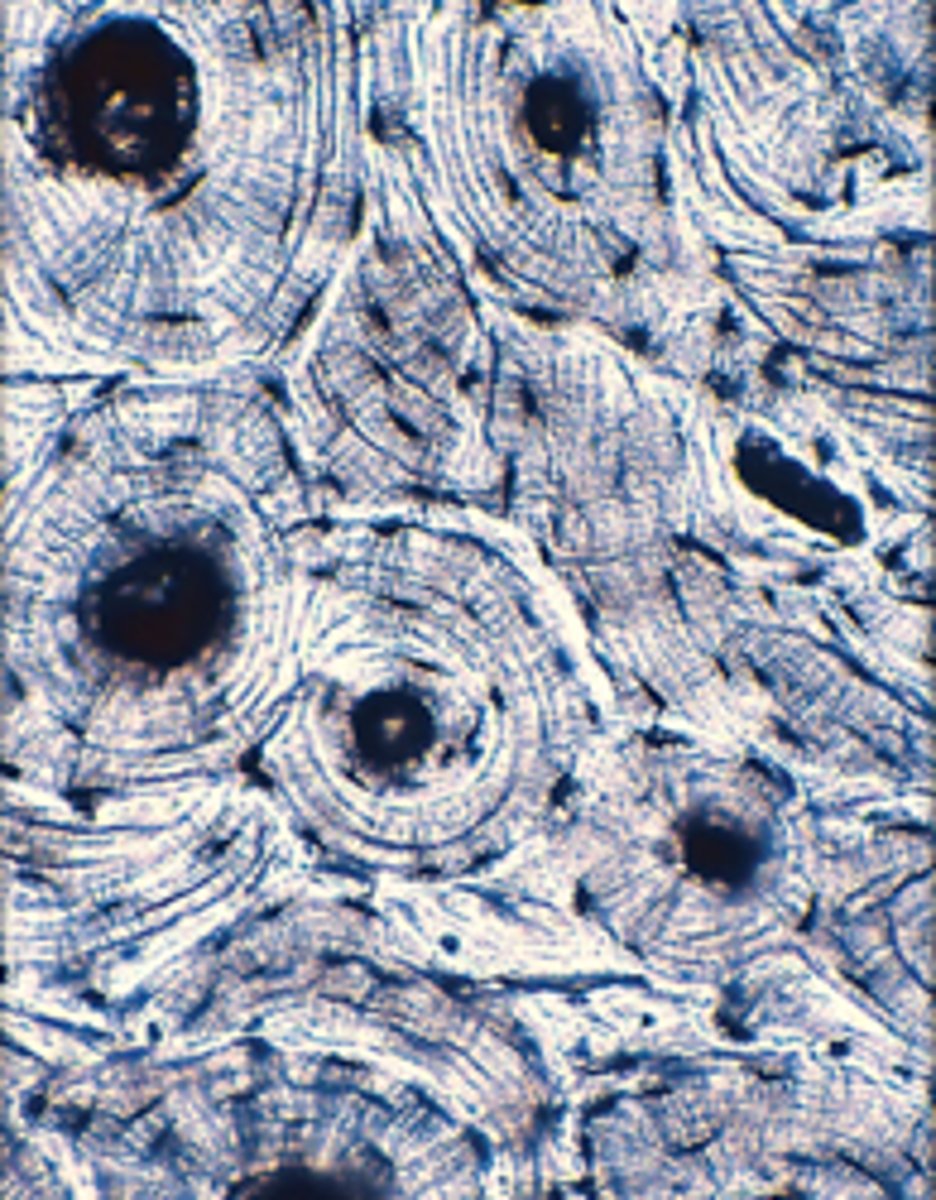
Smooth muscles
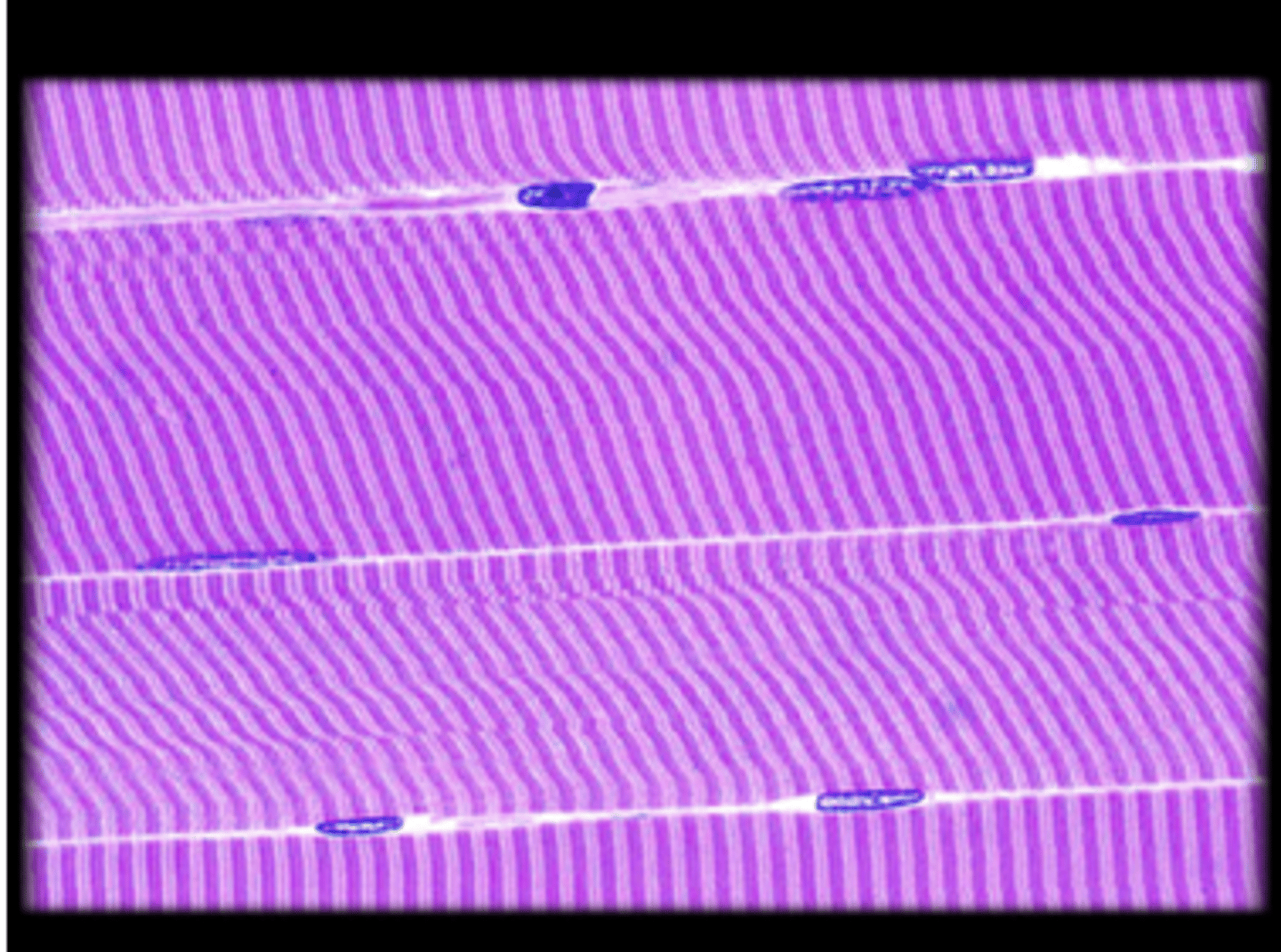
skeletal muscle tissue
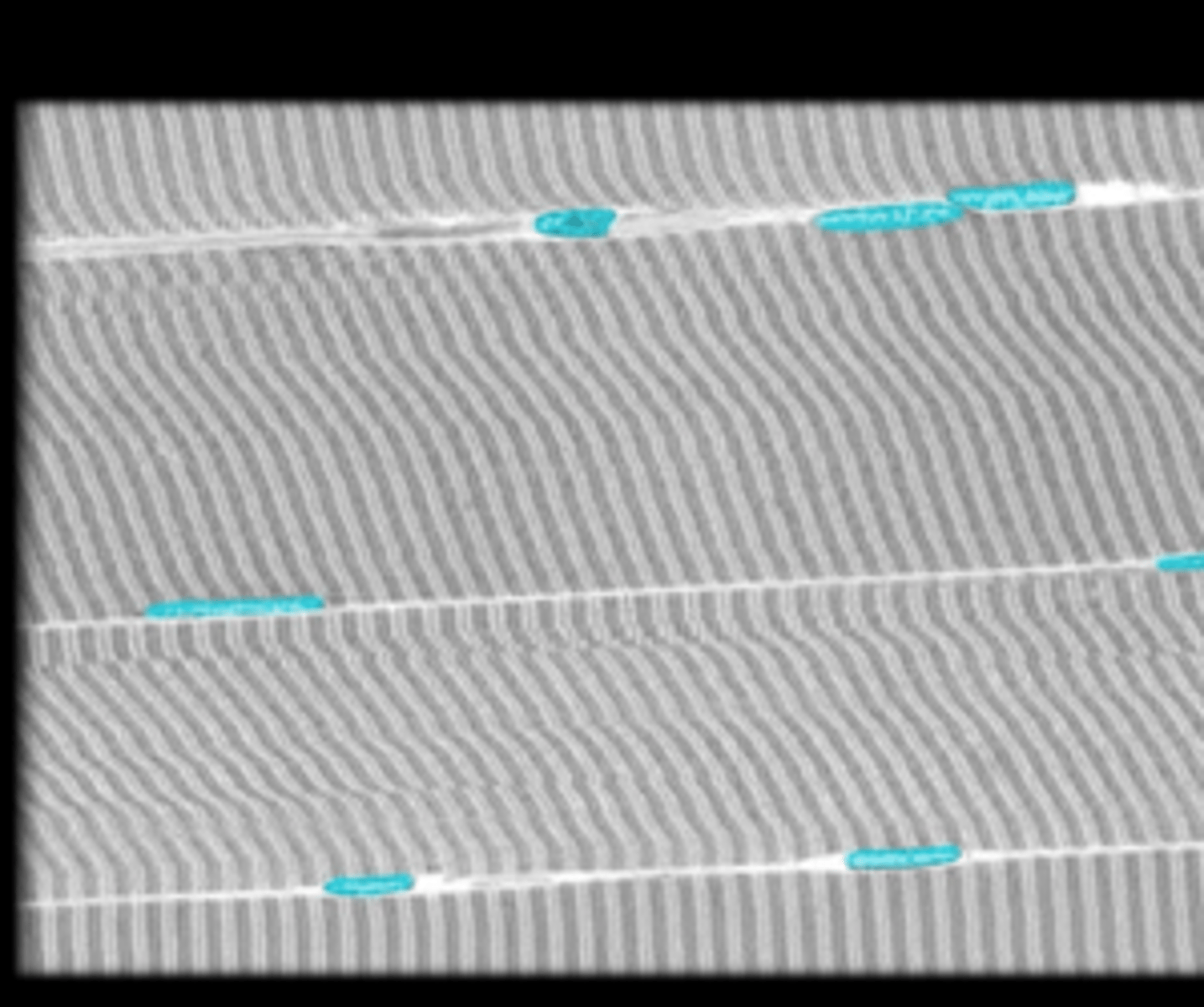
nucleus of skeletal tissue
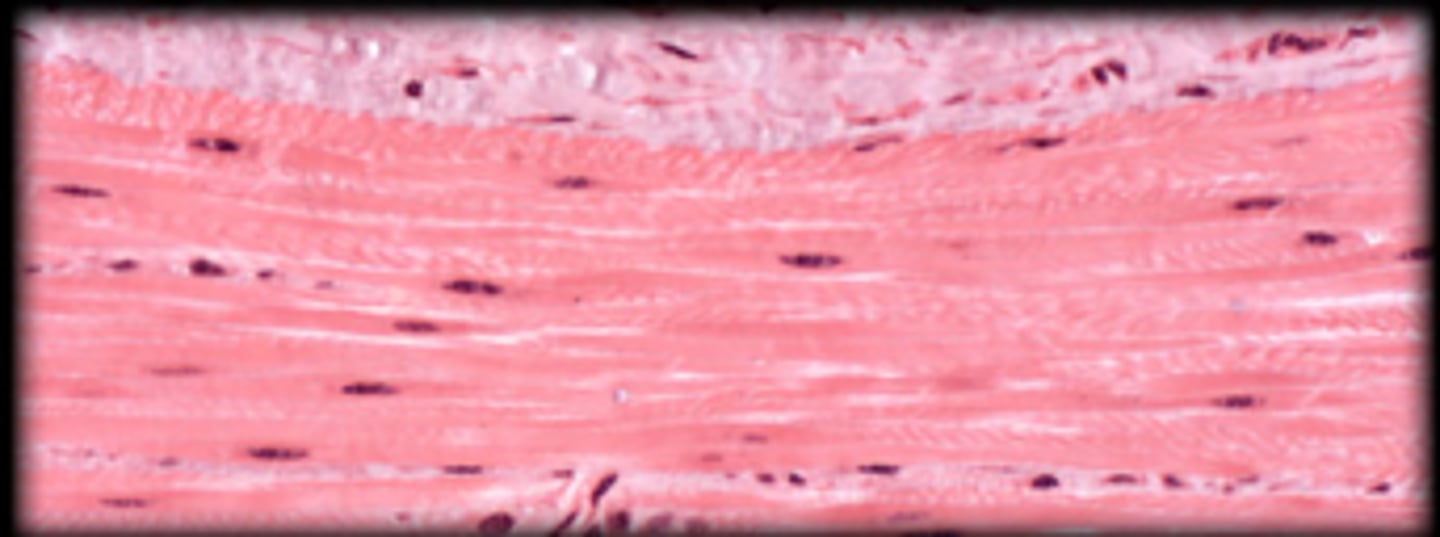
Cardiac muscle tissue
Neuron
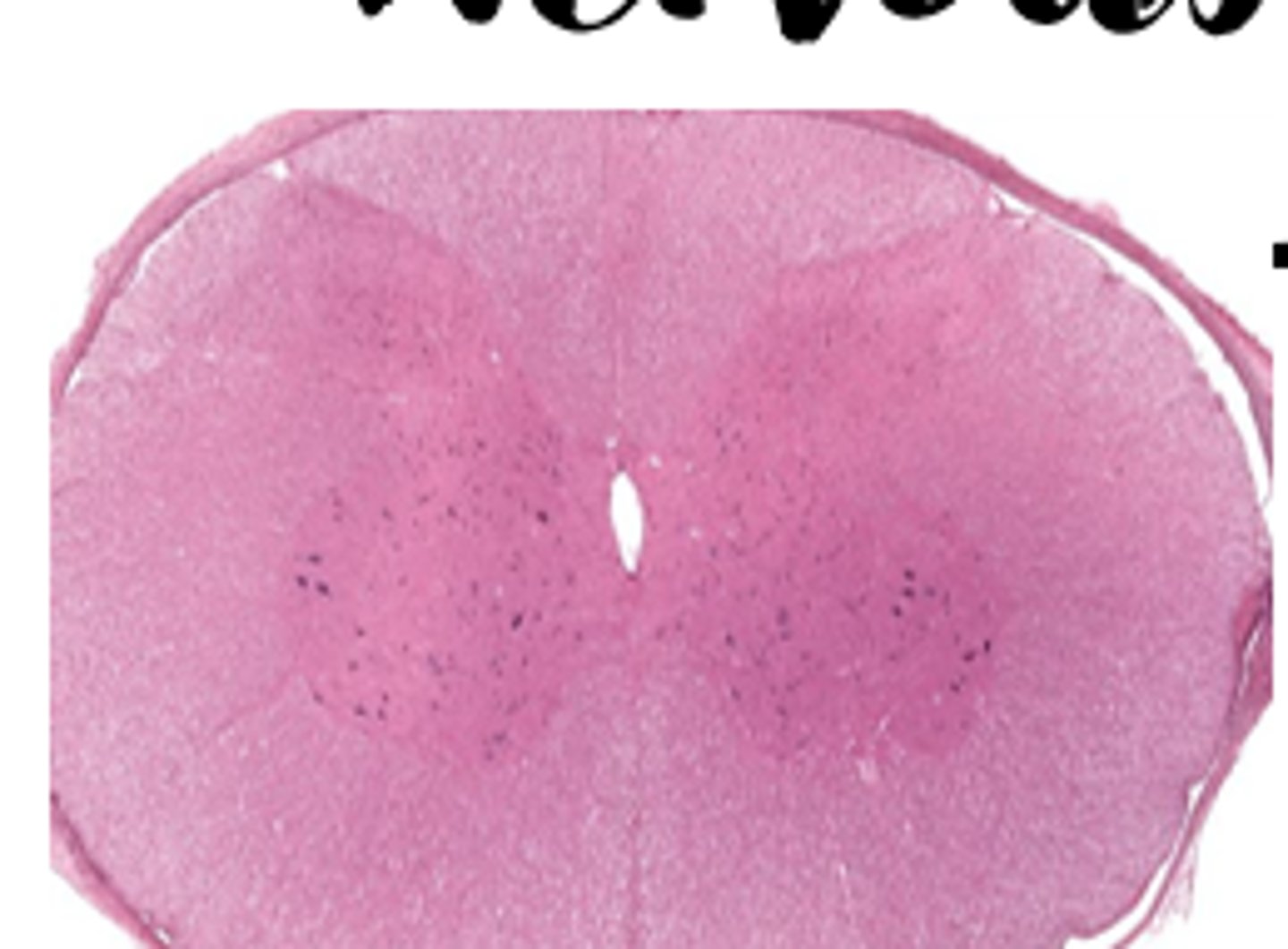
Spinal cord histology
Axon of a neuron
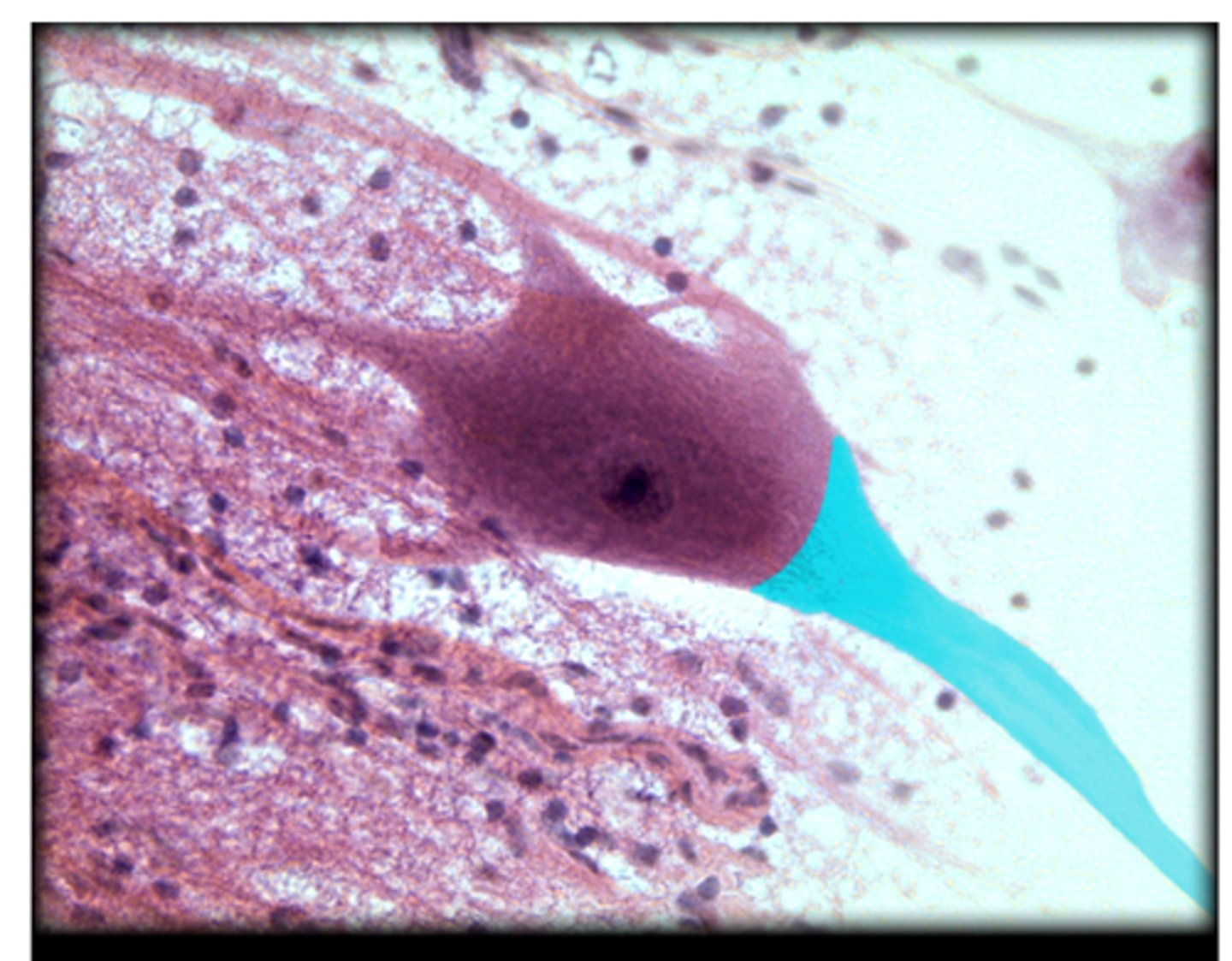
dendrites of a neuron
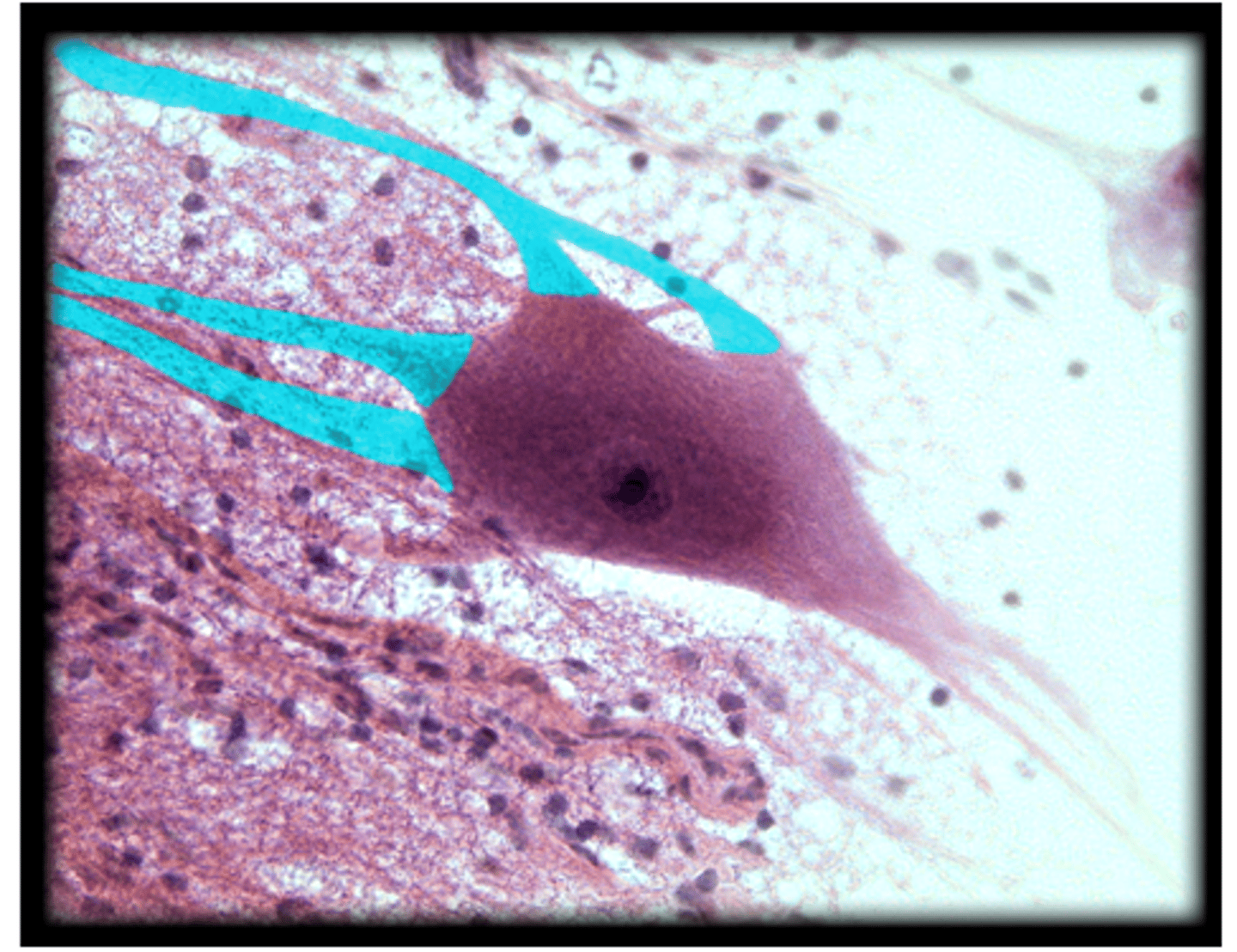
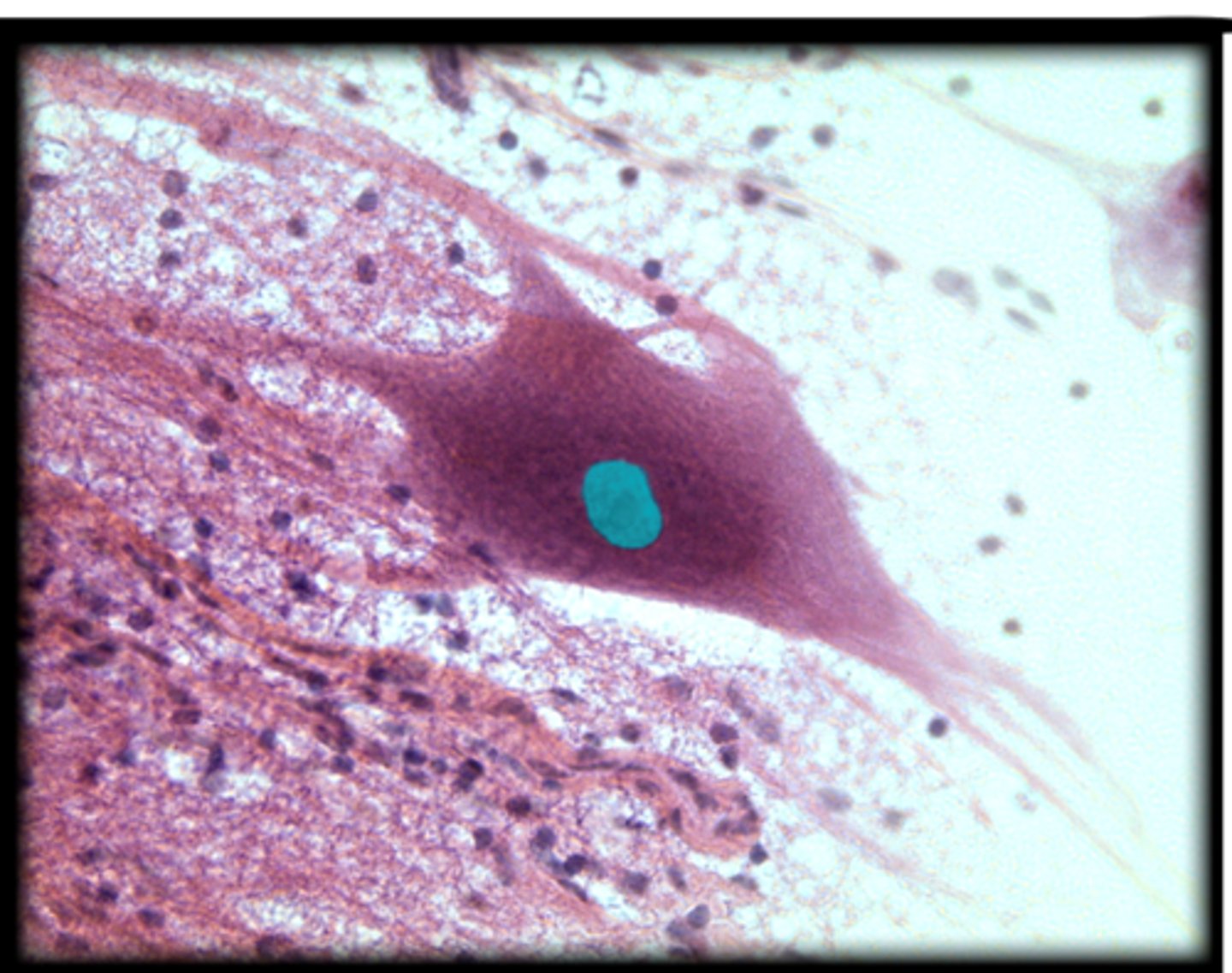
Nucleus of a neuron
Which of the following is a location for transitional epithelium
bladder
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following place can you find cardiac tissue
Heart
3 multiple choice options
Simple squamous epithelium can be found in which of the following location
Lungs
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is a function of blood
All of the above
3 multiple choice options
Frontal bone
Forehead bone forming the anterior cranium.
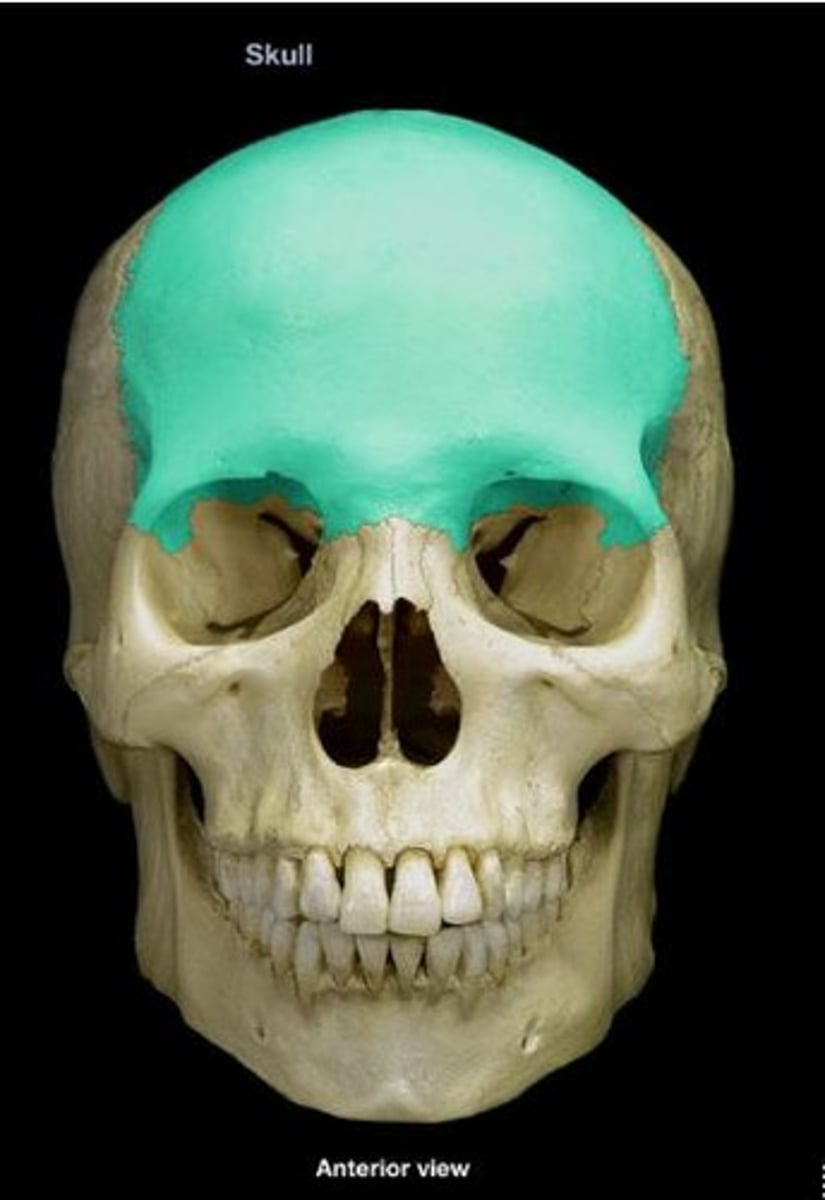
Parietal bone
Two bones forming the top and sides of the skull.
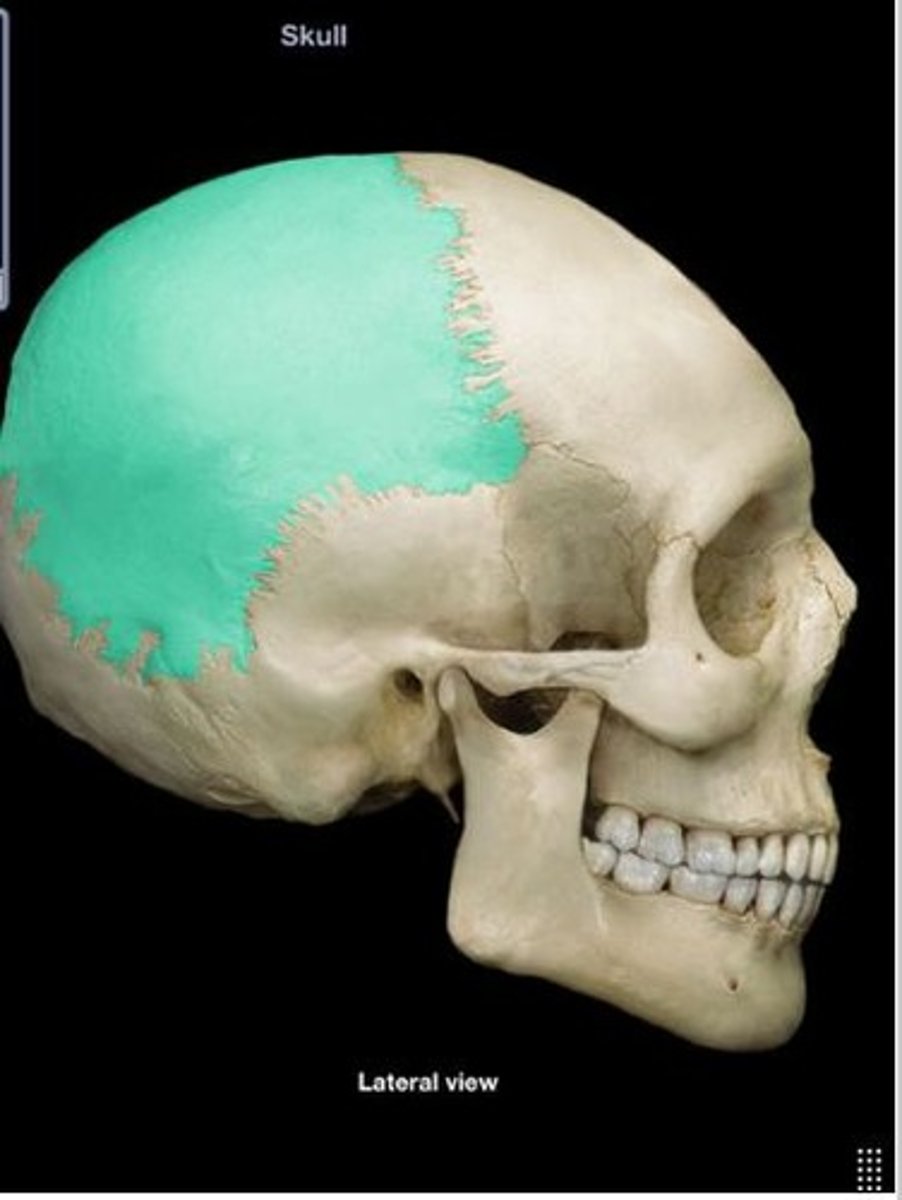
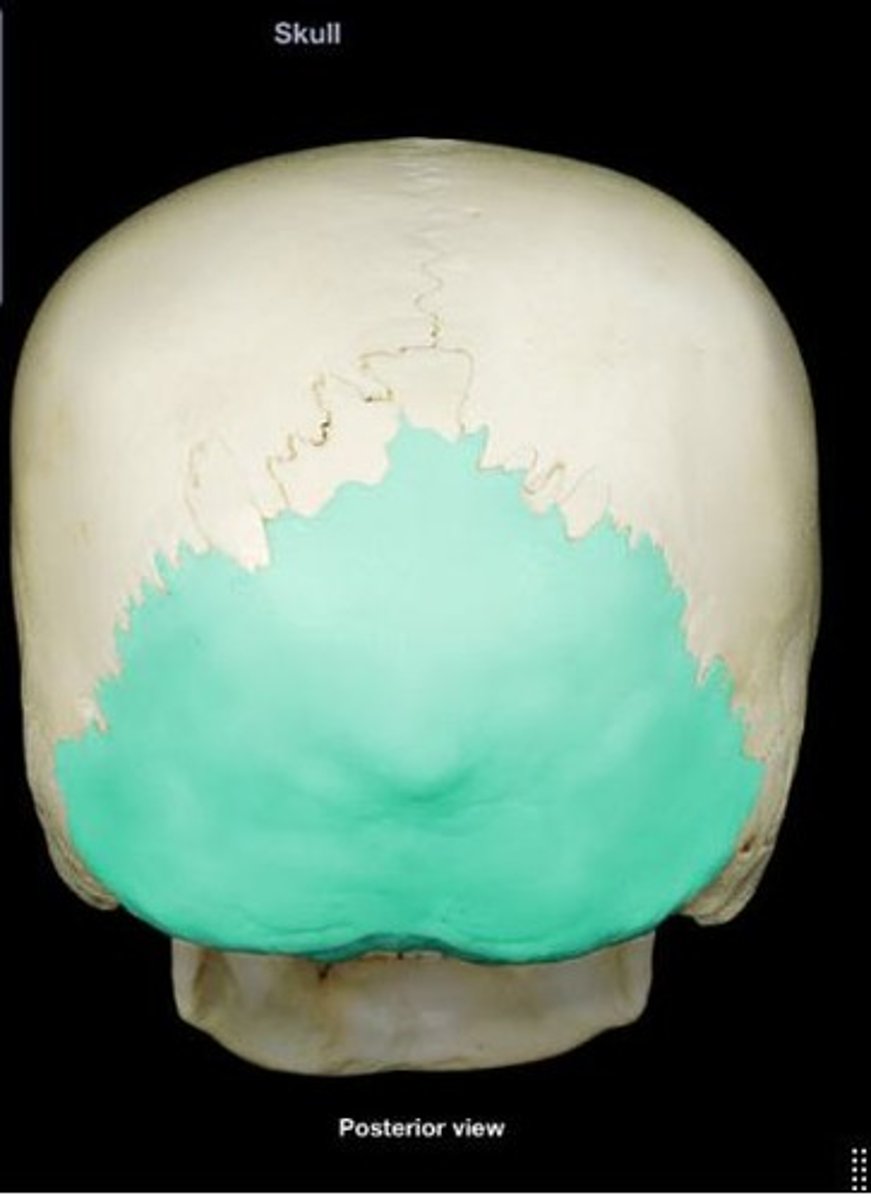
Occipital bone
Bone at the back of the skull.
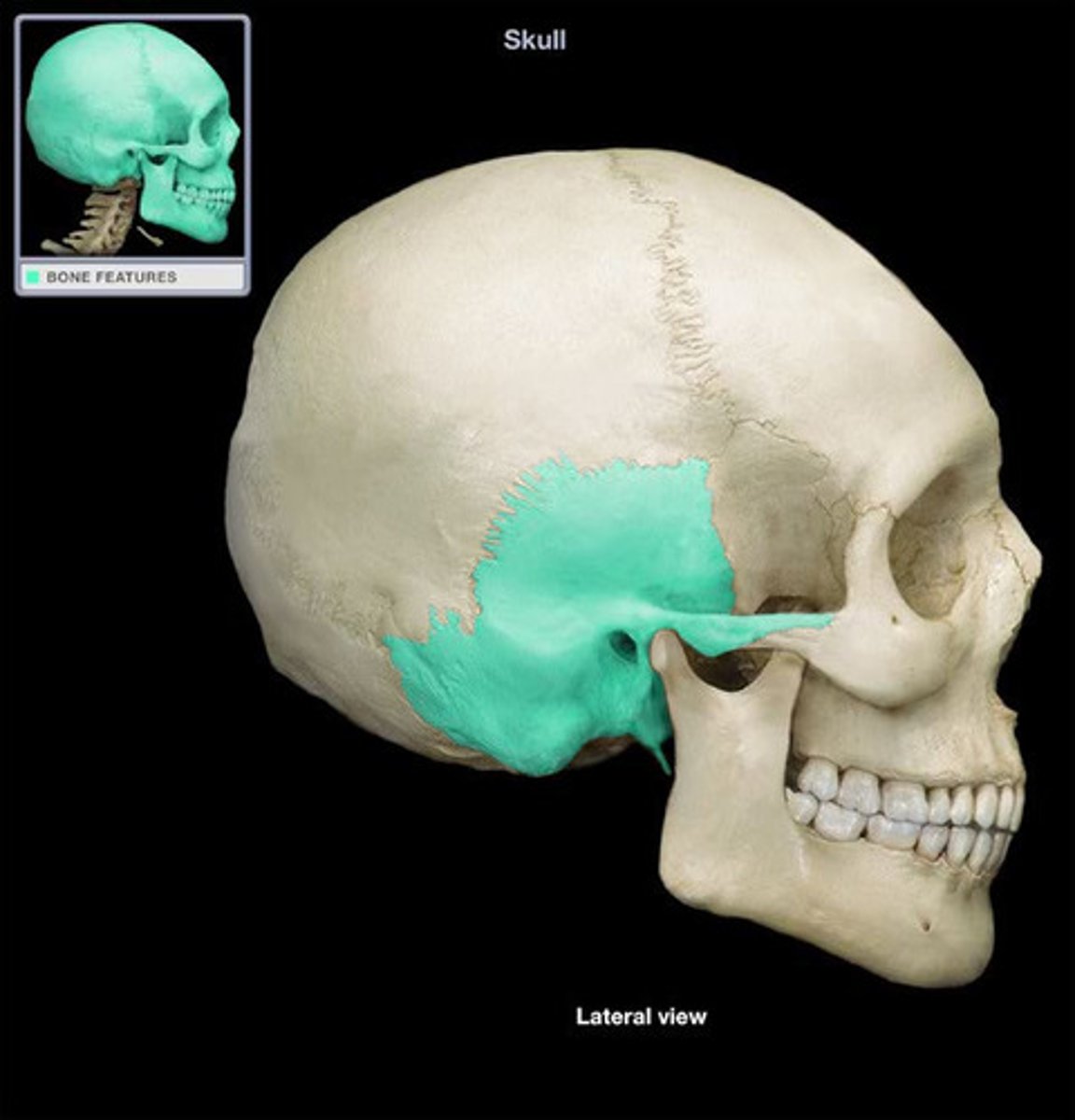
Temporal bone
Bones located at the sides of the skull.
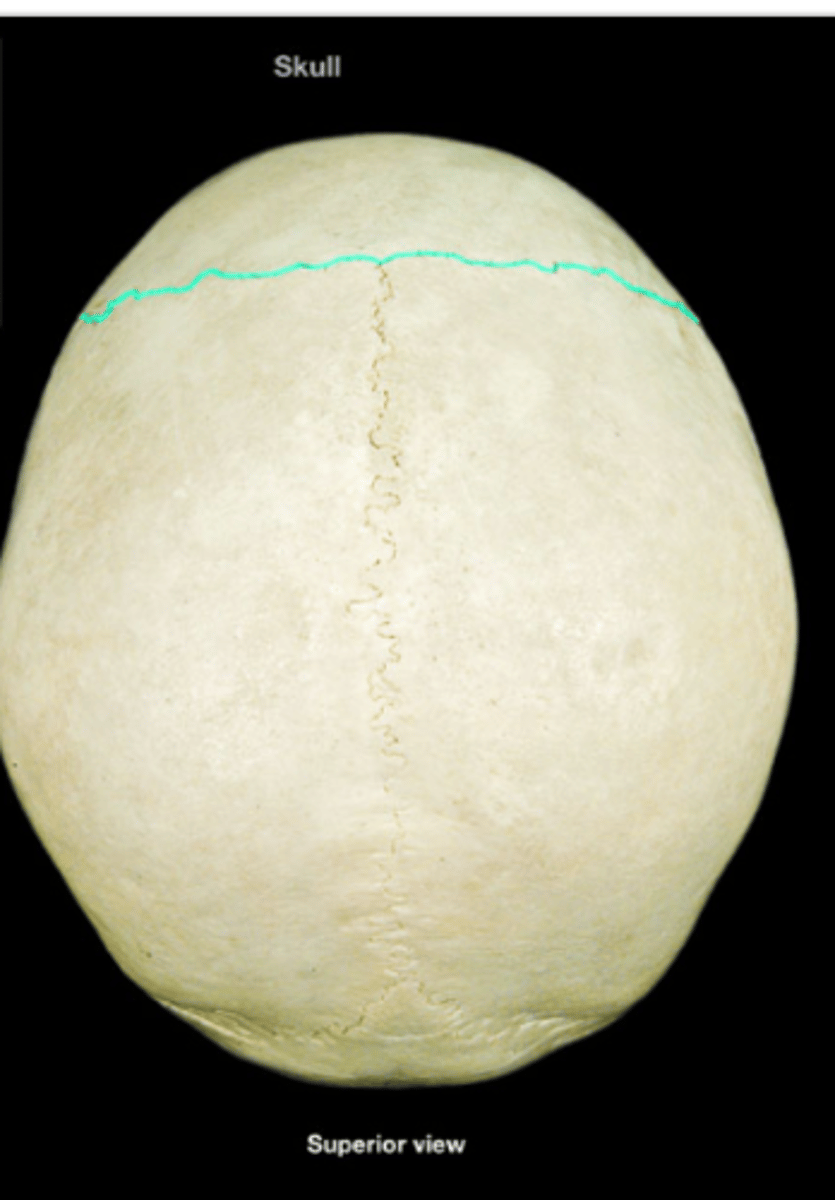
Coronal sutures
Suture between frontal and parietal bones.
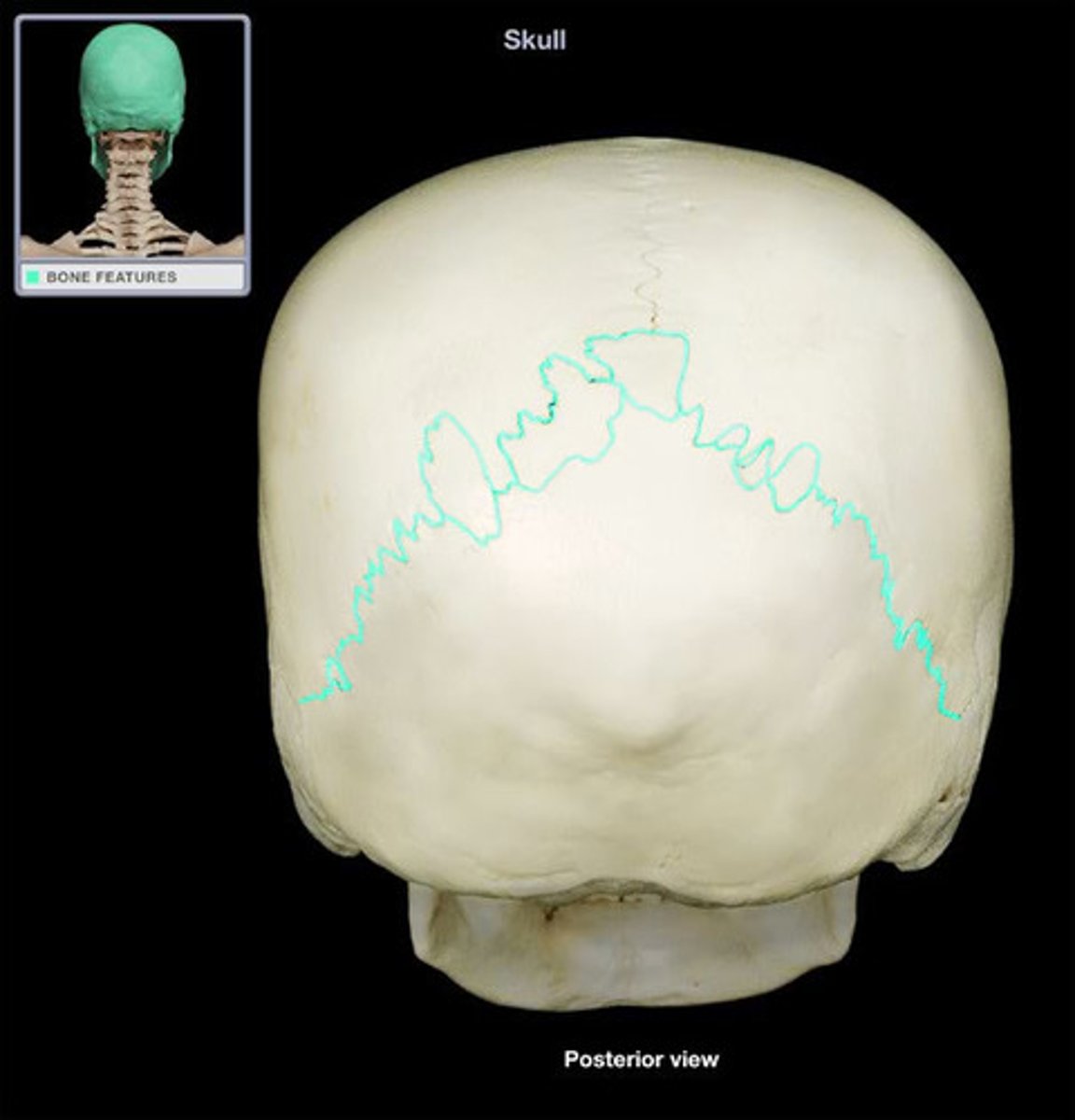
Lambdoid sutures
Suture between parietal and occipital bones.
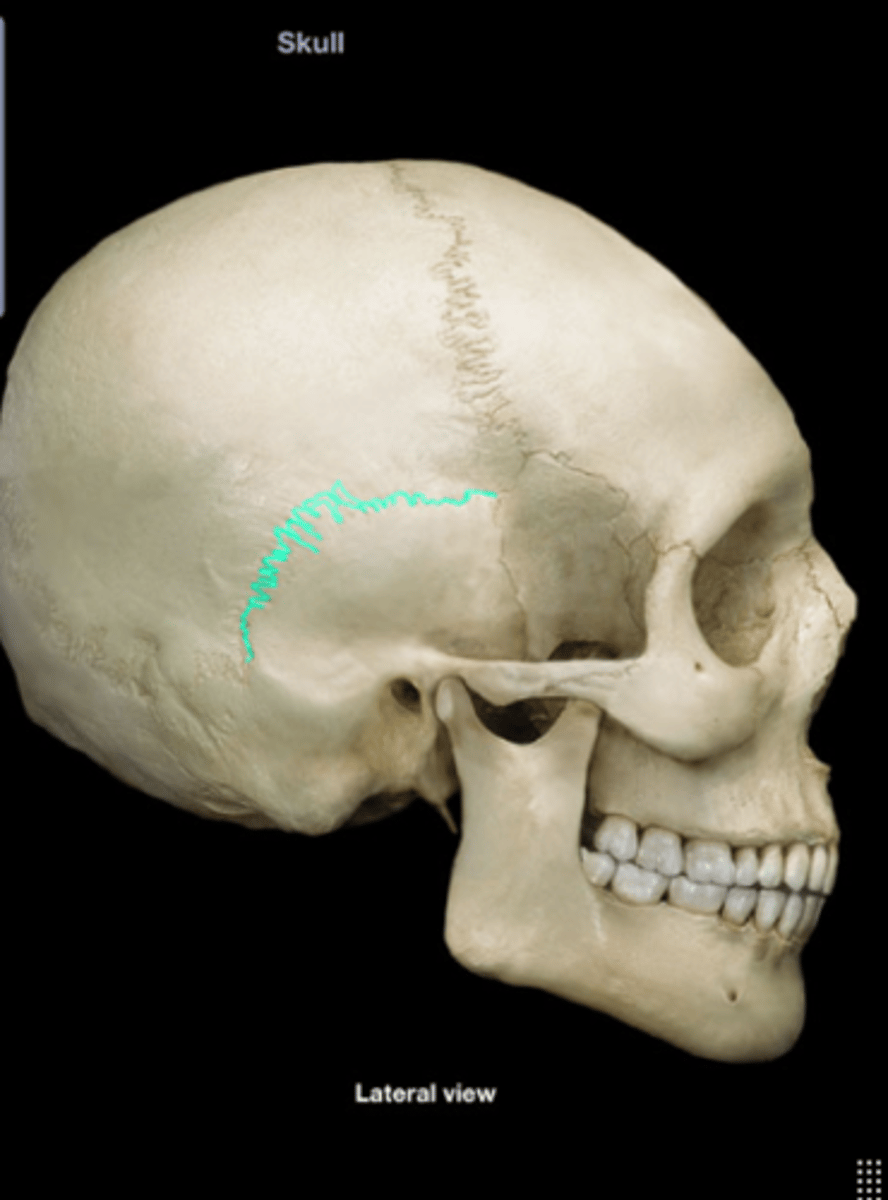
Squamous sutures
Suture between parietal and temporal bones.
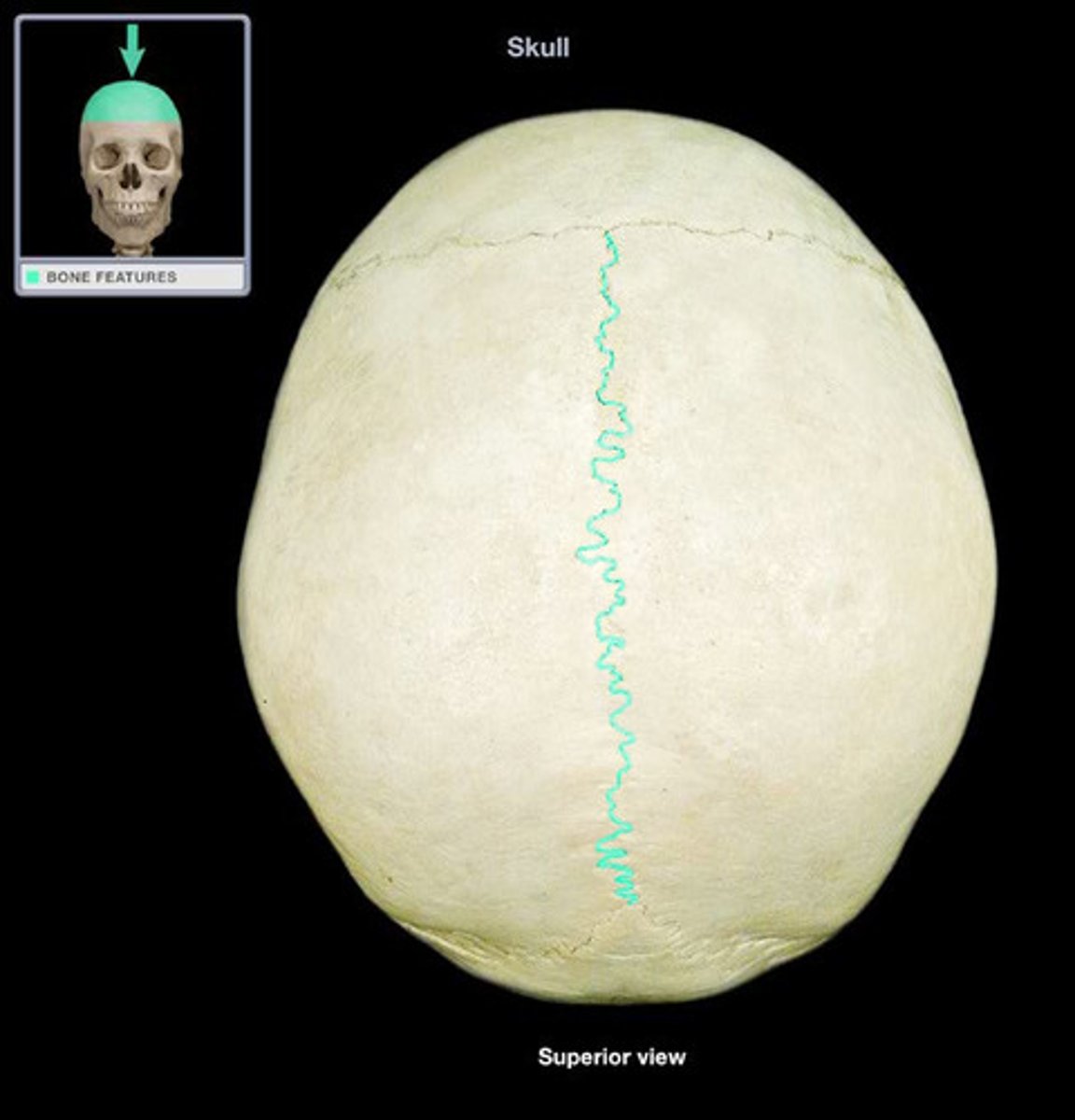
Sagittal sutures
Suture between the two parietal bones.
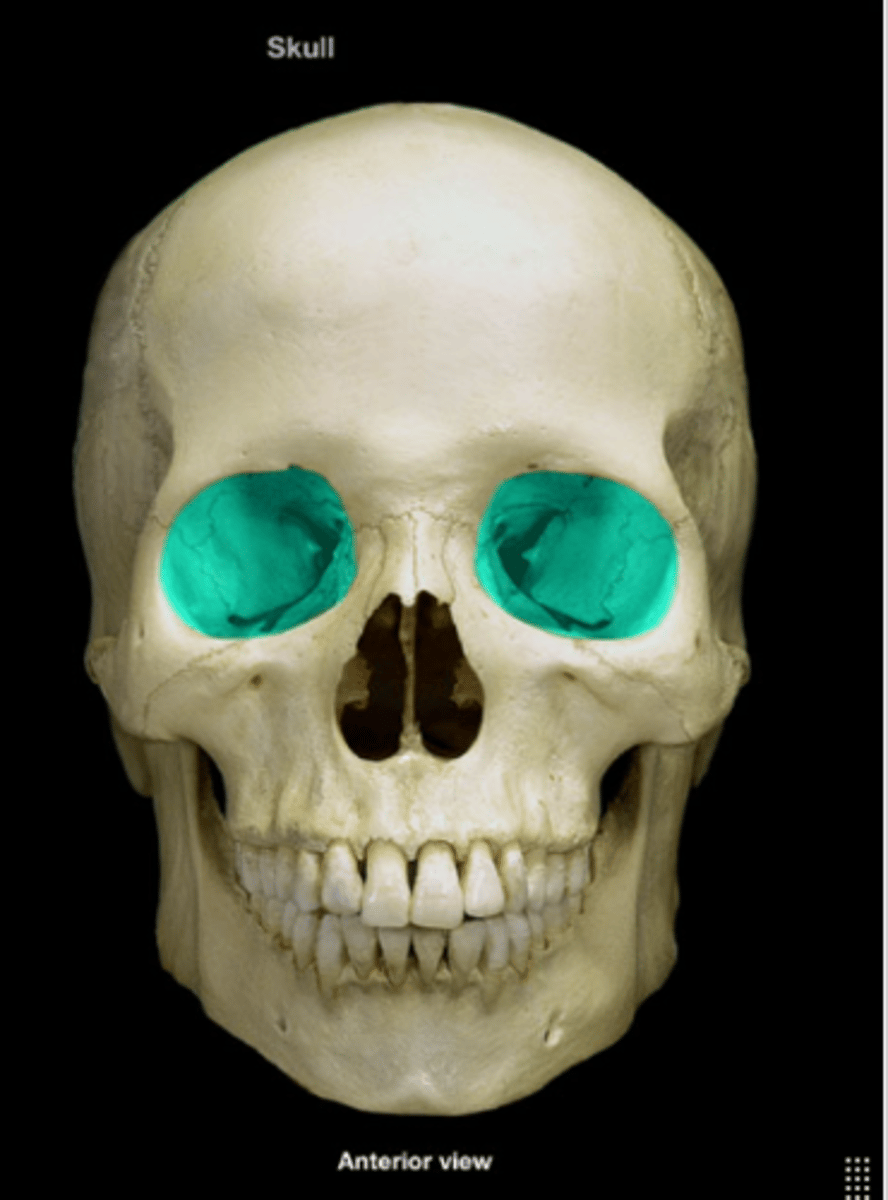
Orbit
Bony cavity containing the eyeball.
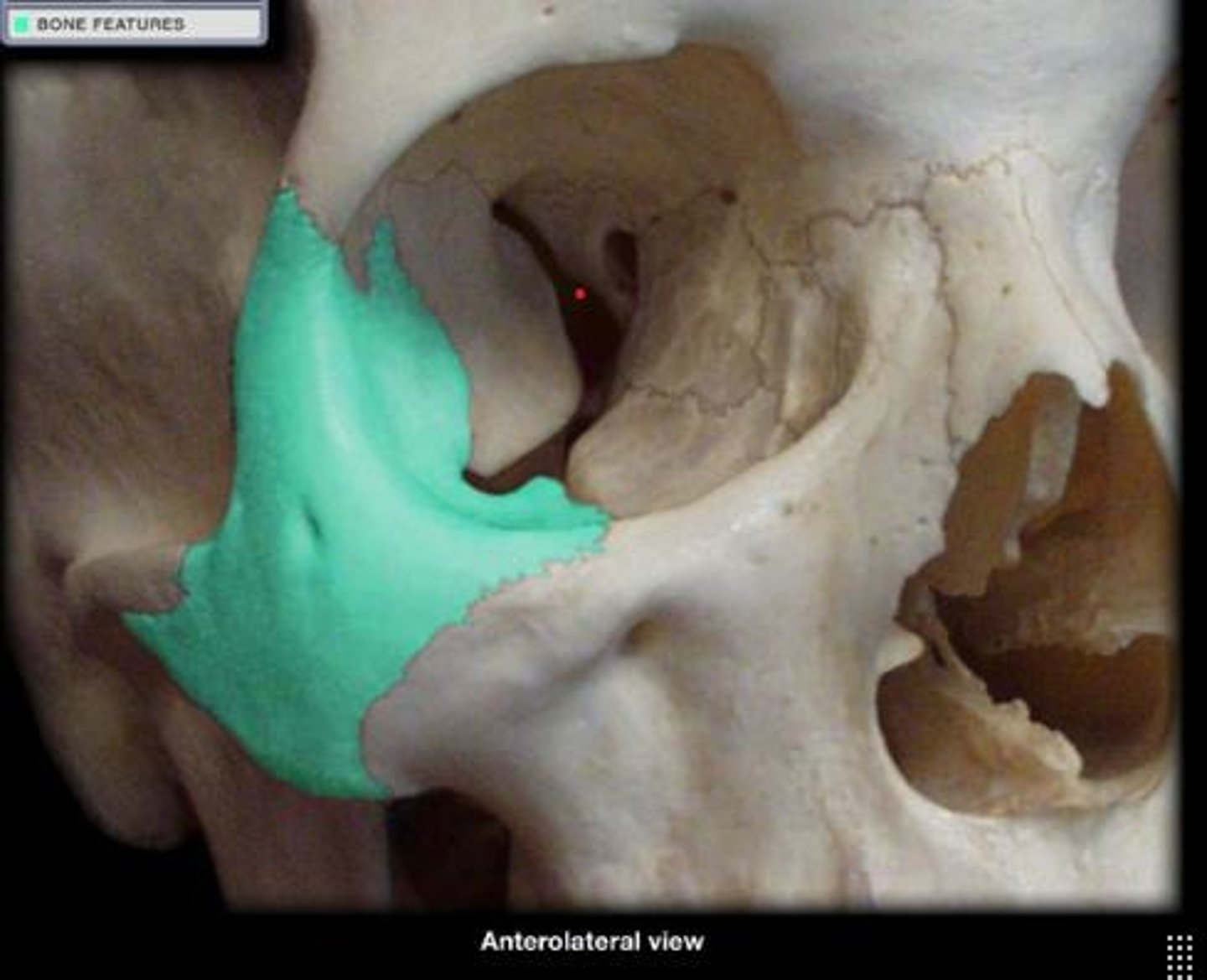
Maxilla
Upper jawbone forming the mouth's structure.
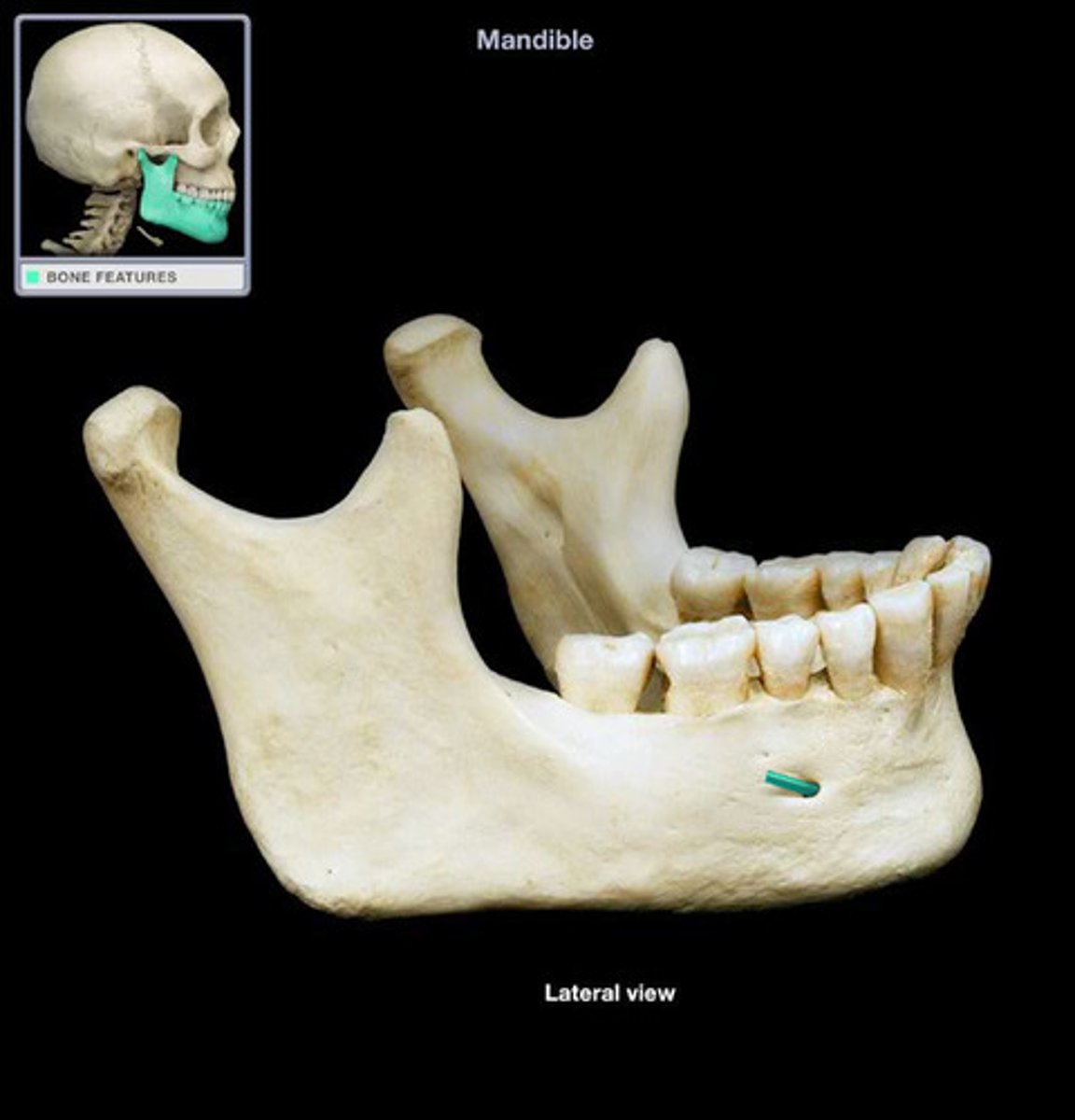
Mandible
Lower jawbone, the only movable skull bone.
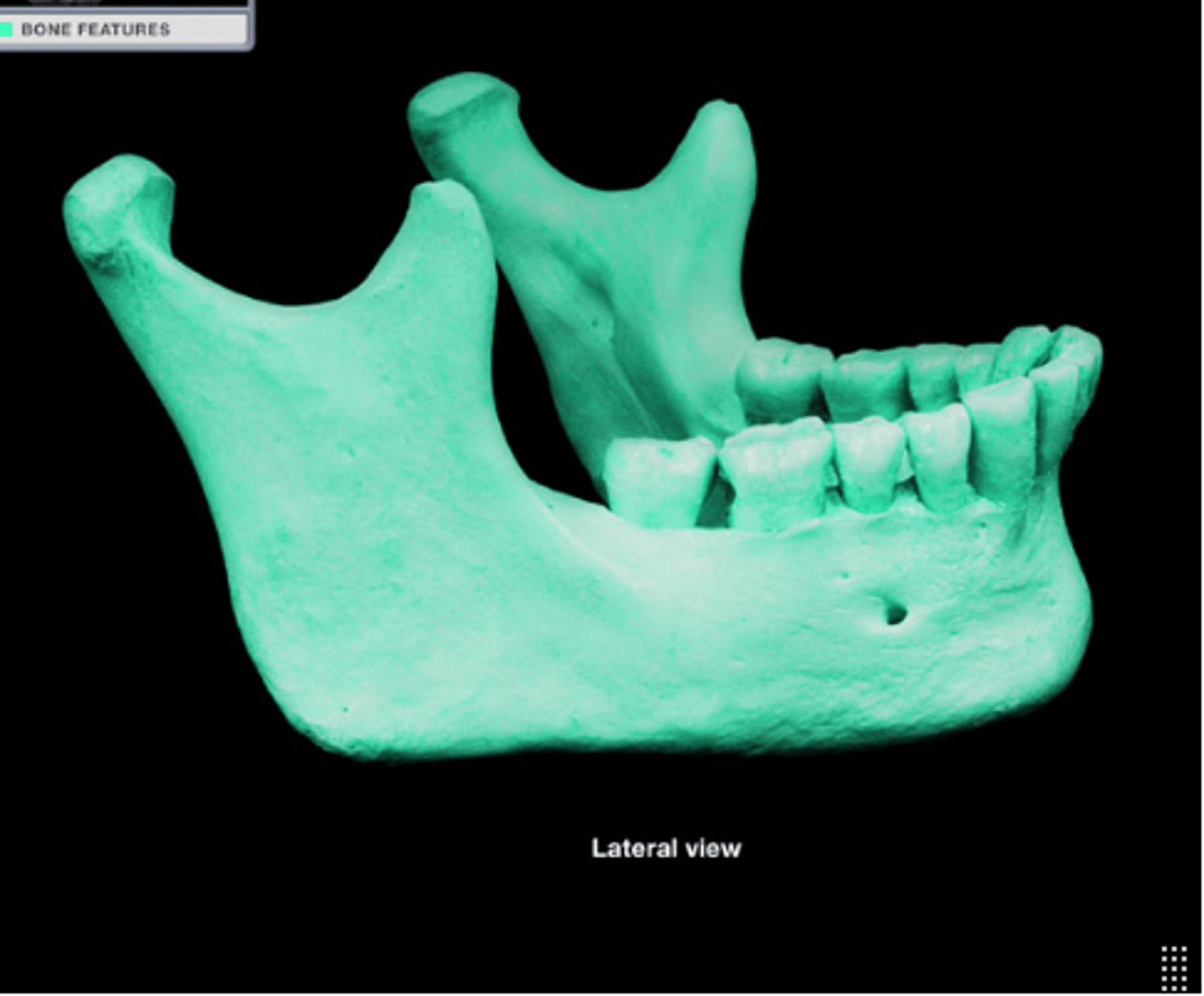
Mental foramen
Opening in the mandible for nerves.
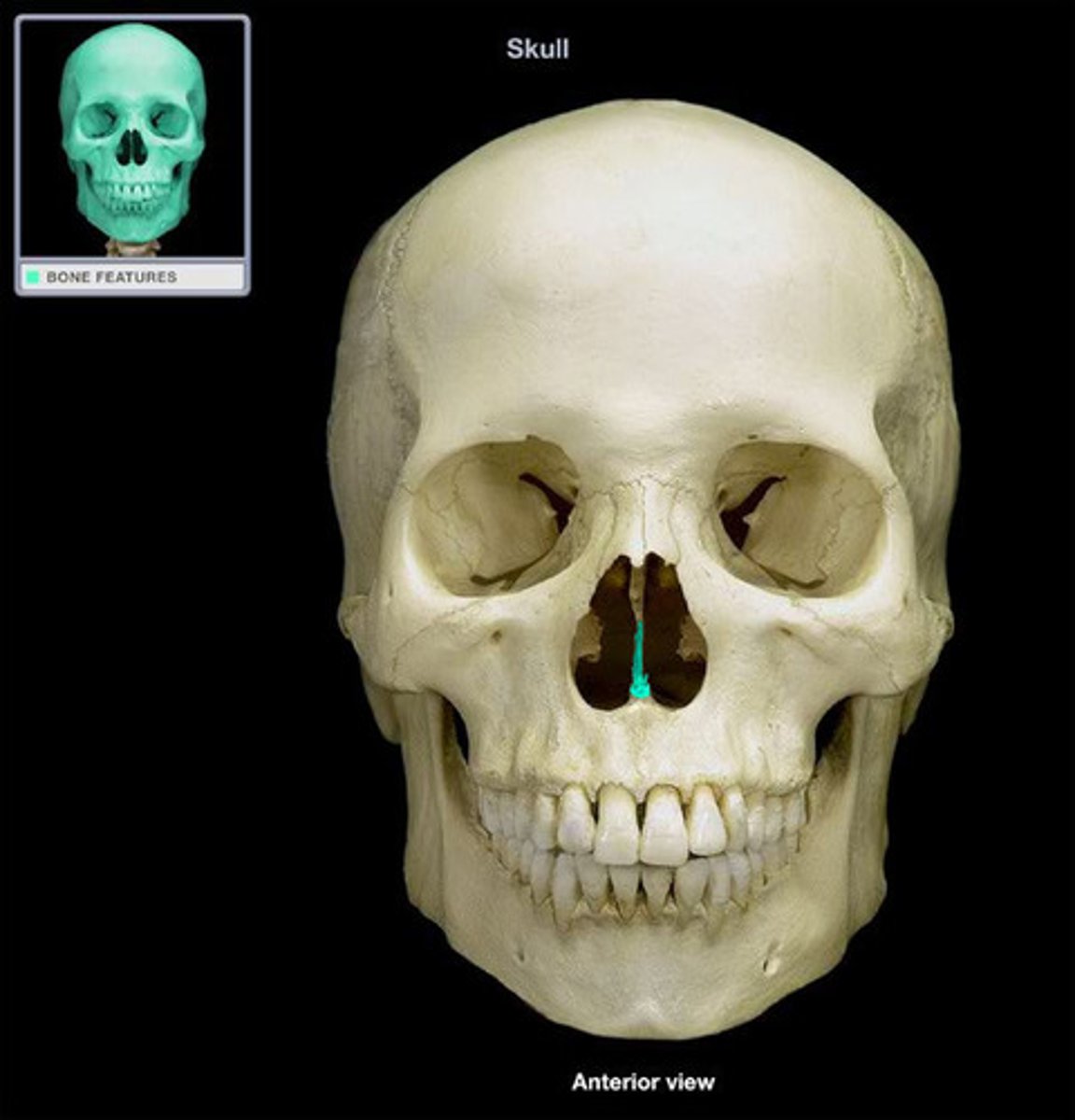
Vomer bone
Bone forming part of the nasal septum.
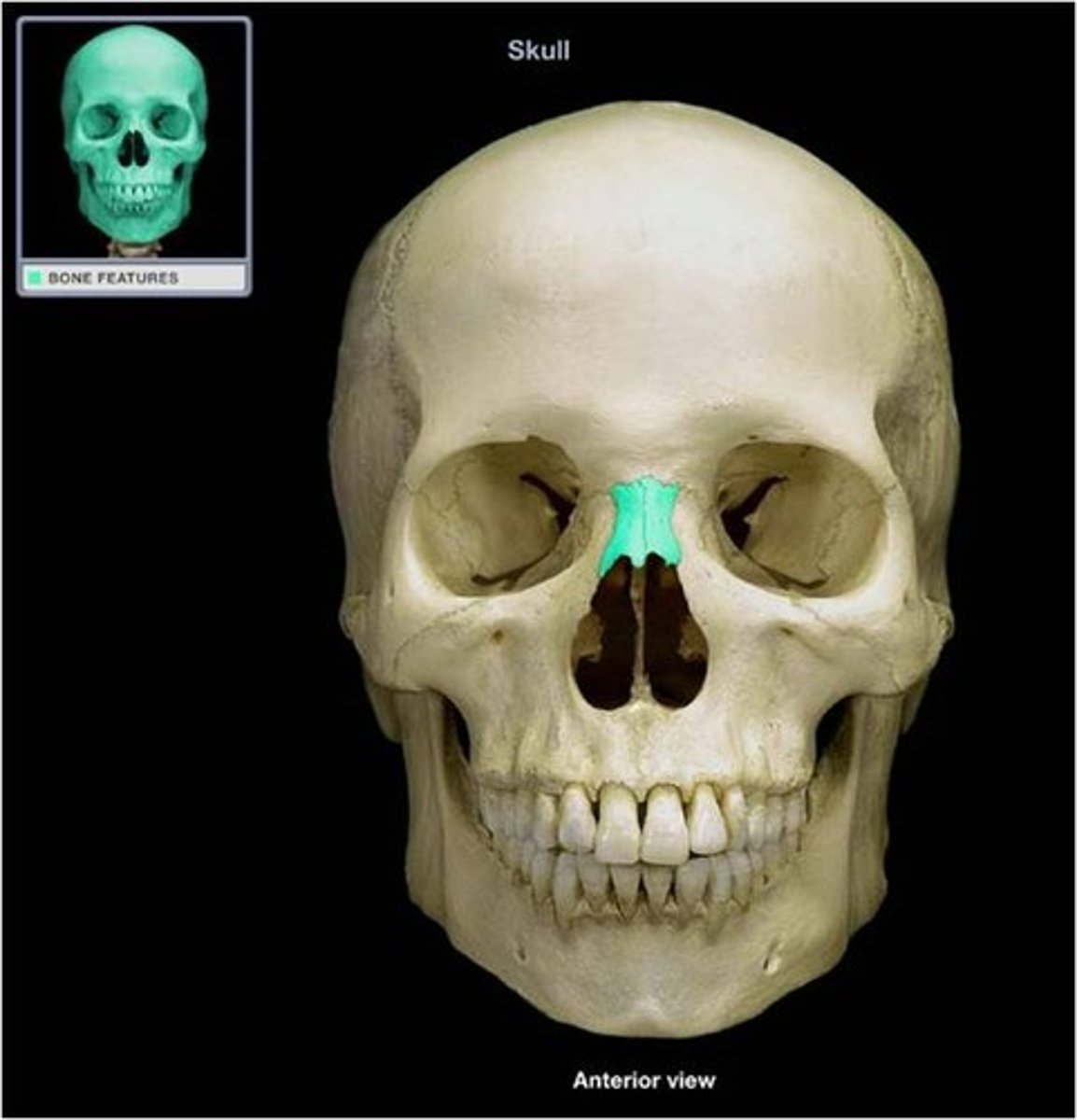
Nasal bone
Two small bones forming the bridge of the nose.
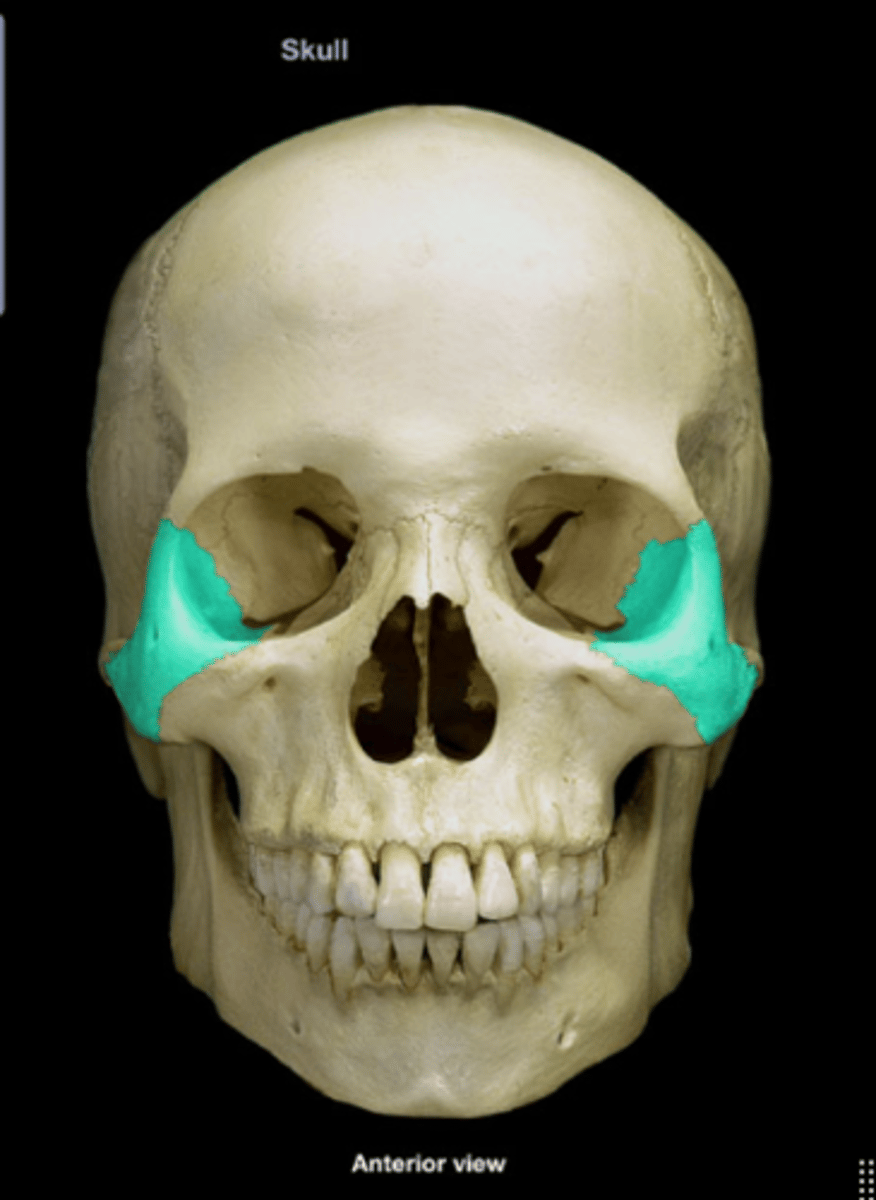
Zygomatic bone
Cheekbone, contributing to the eye socket.
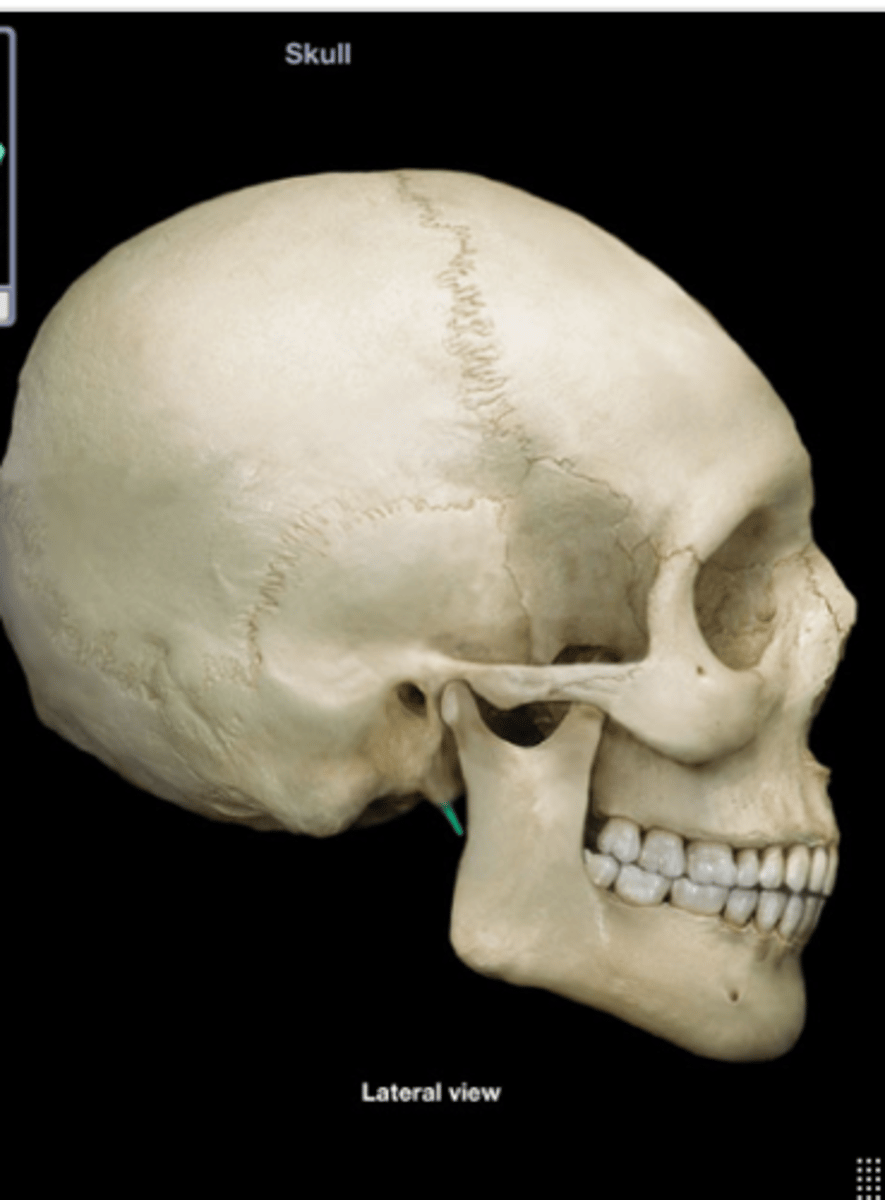
Styloid process
Pointed projection of the temporal bone.
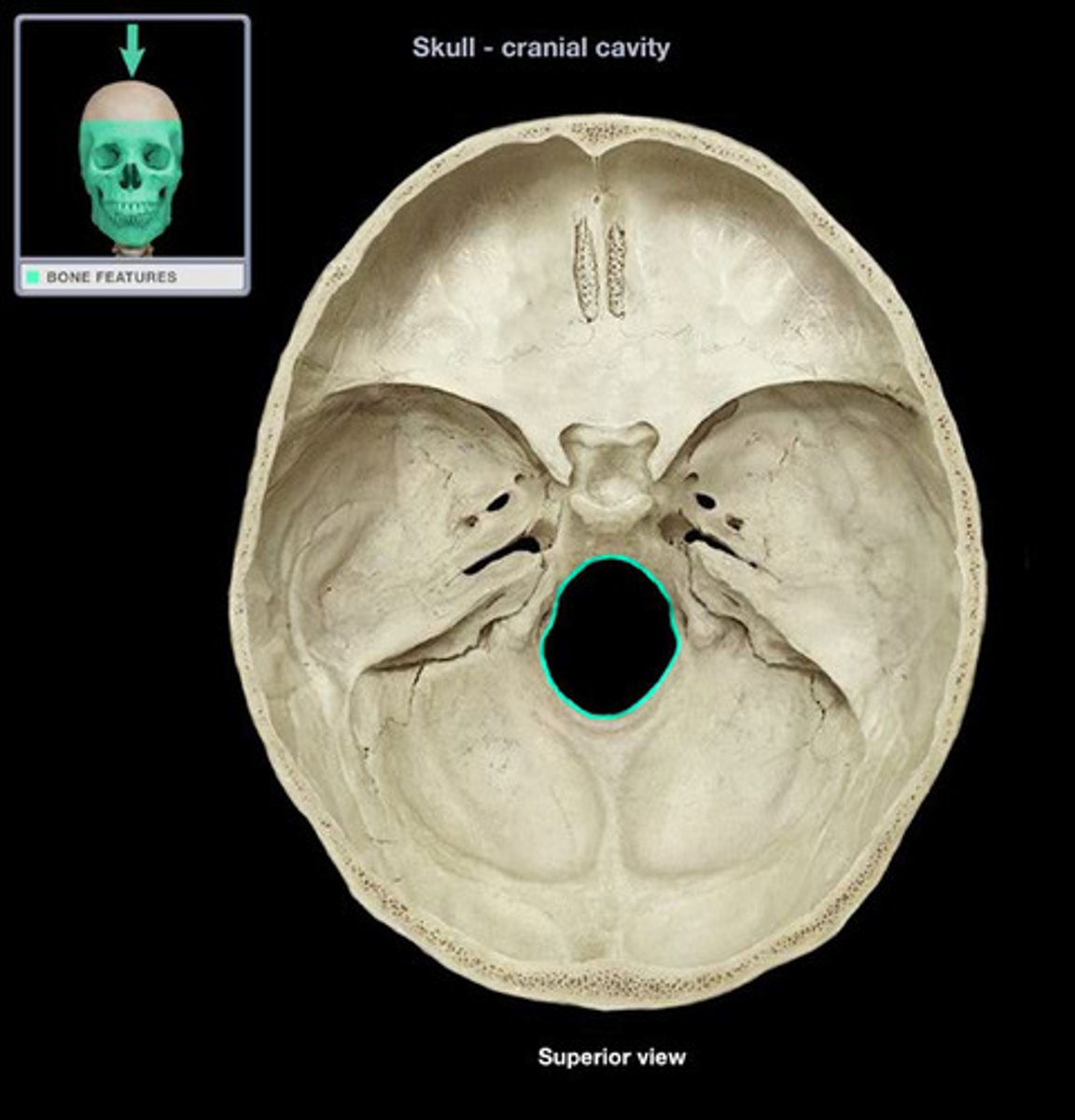
Foramen magnum
Large opening in the skull for spinal cord.
Foramen magnum
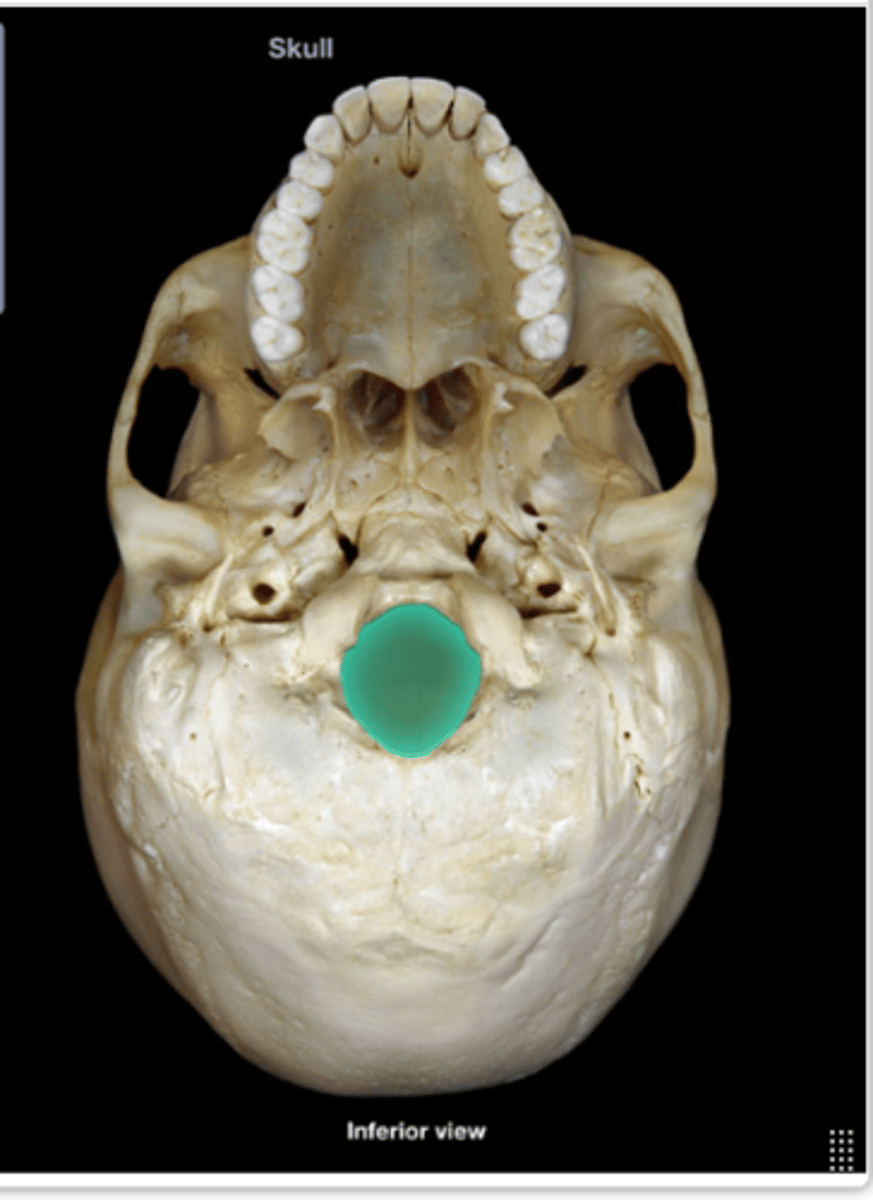
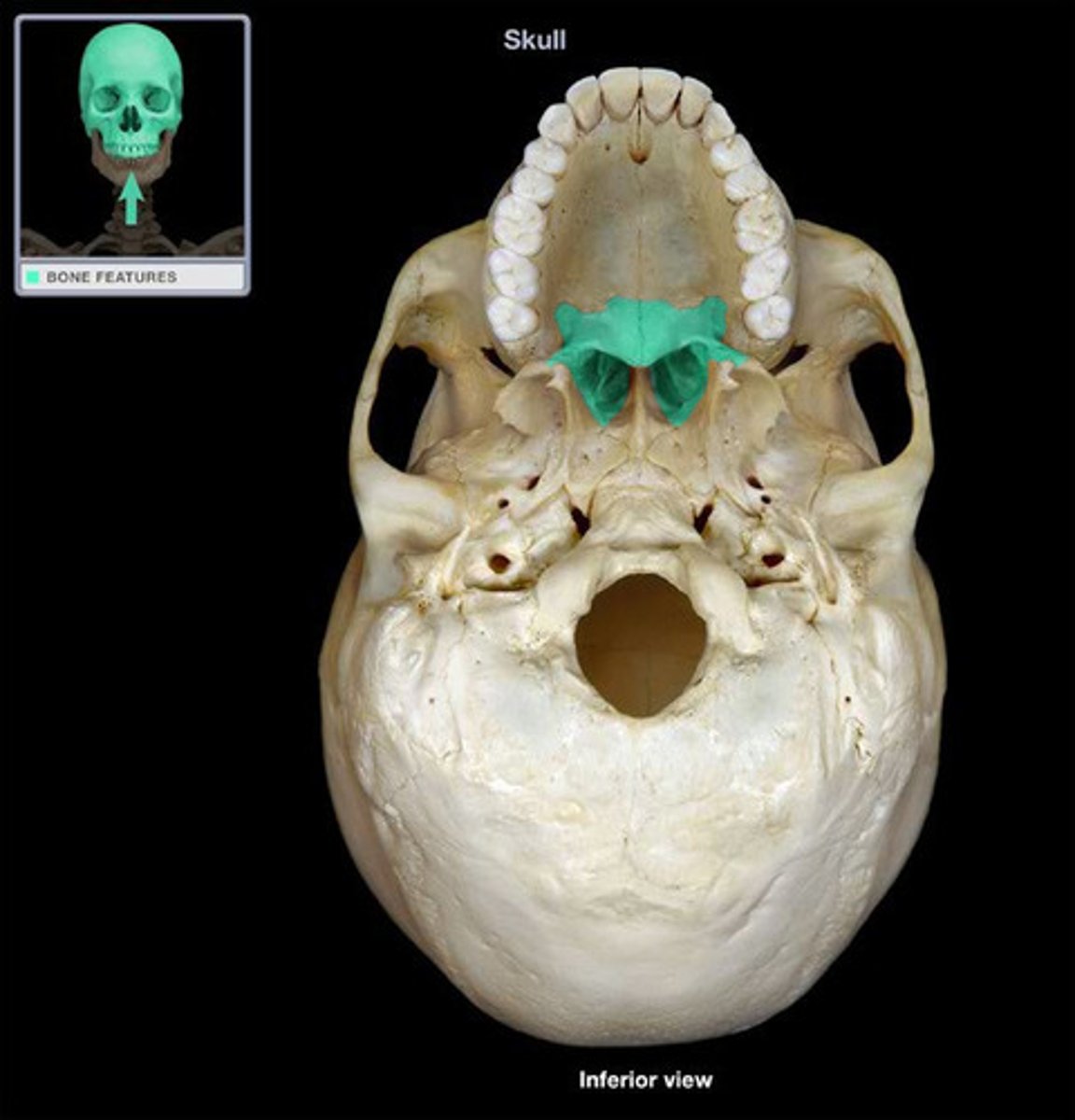
Palatine bone
Bone forming the back part of the hard palate.
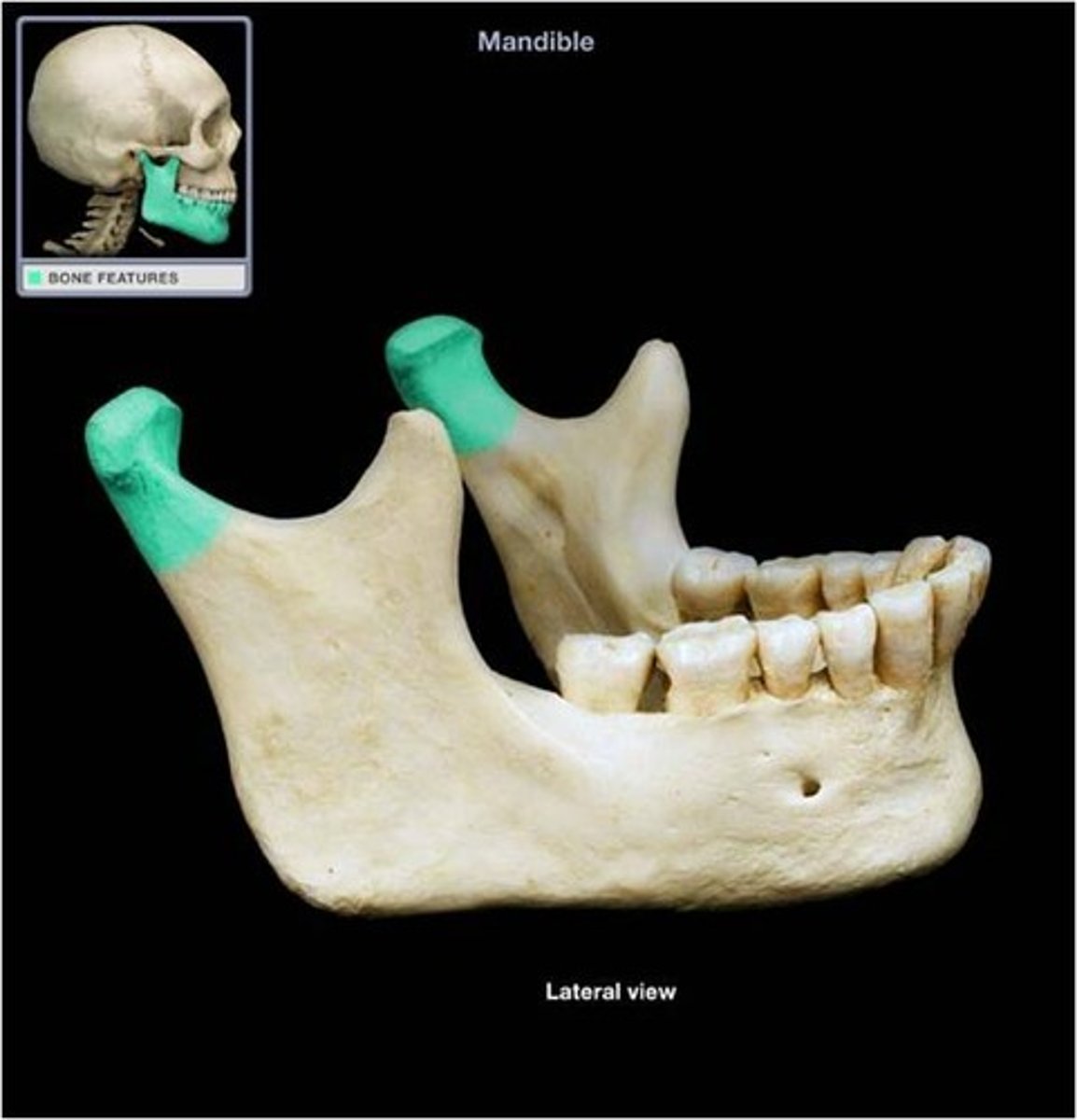
Mandibular condyle
Rounded end of the mandible for jaw articulation.
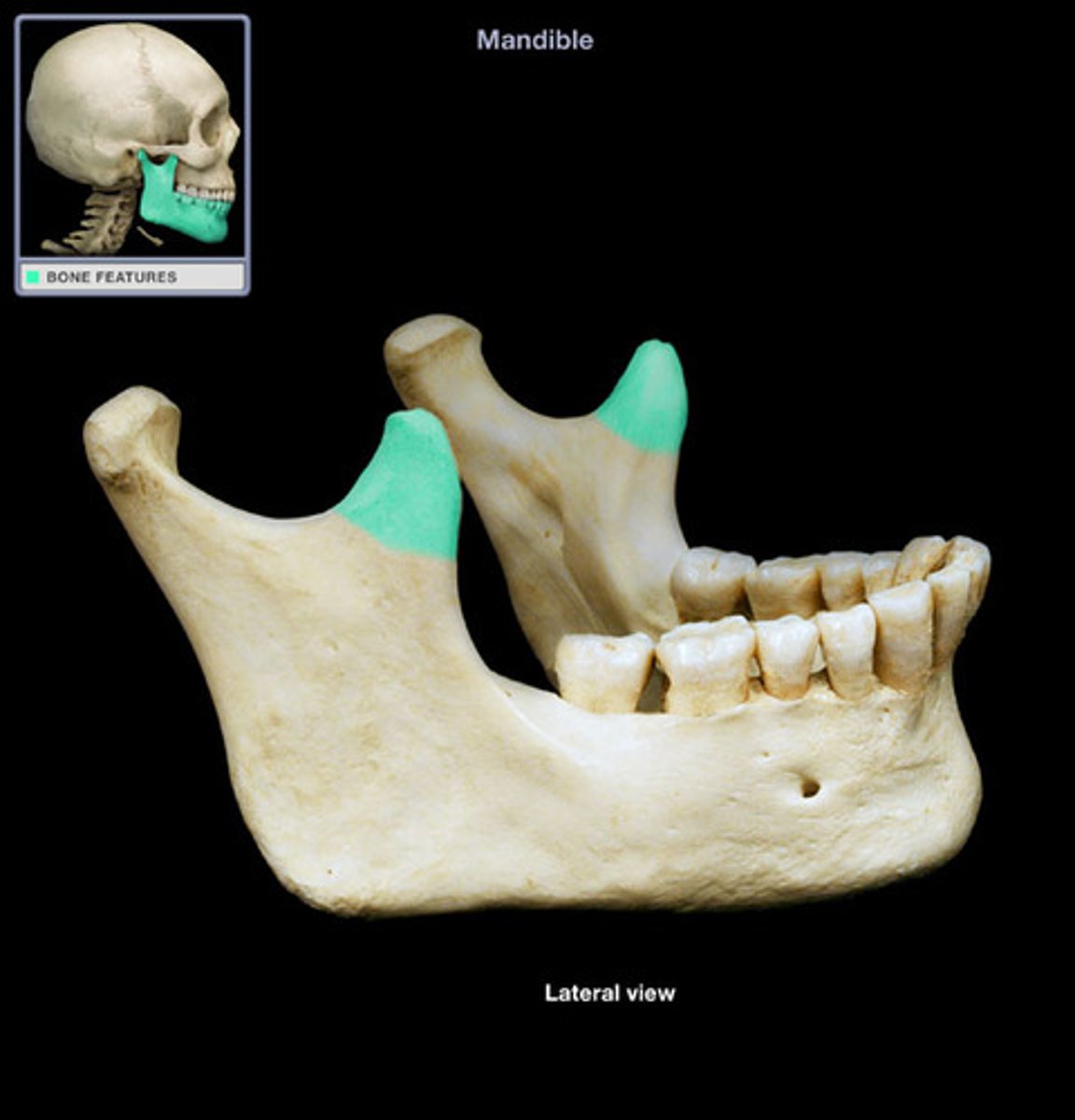
Coronoid process
Triangular projection of the mandible for muscle attachment.
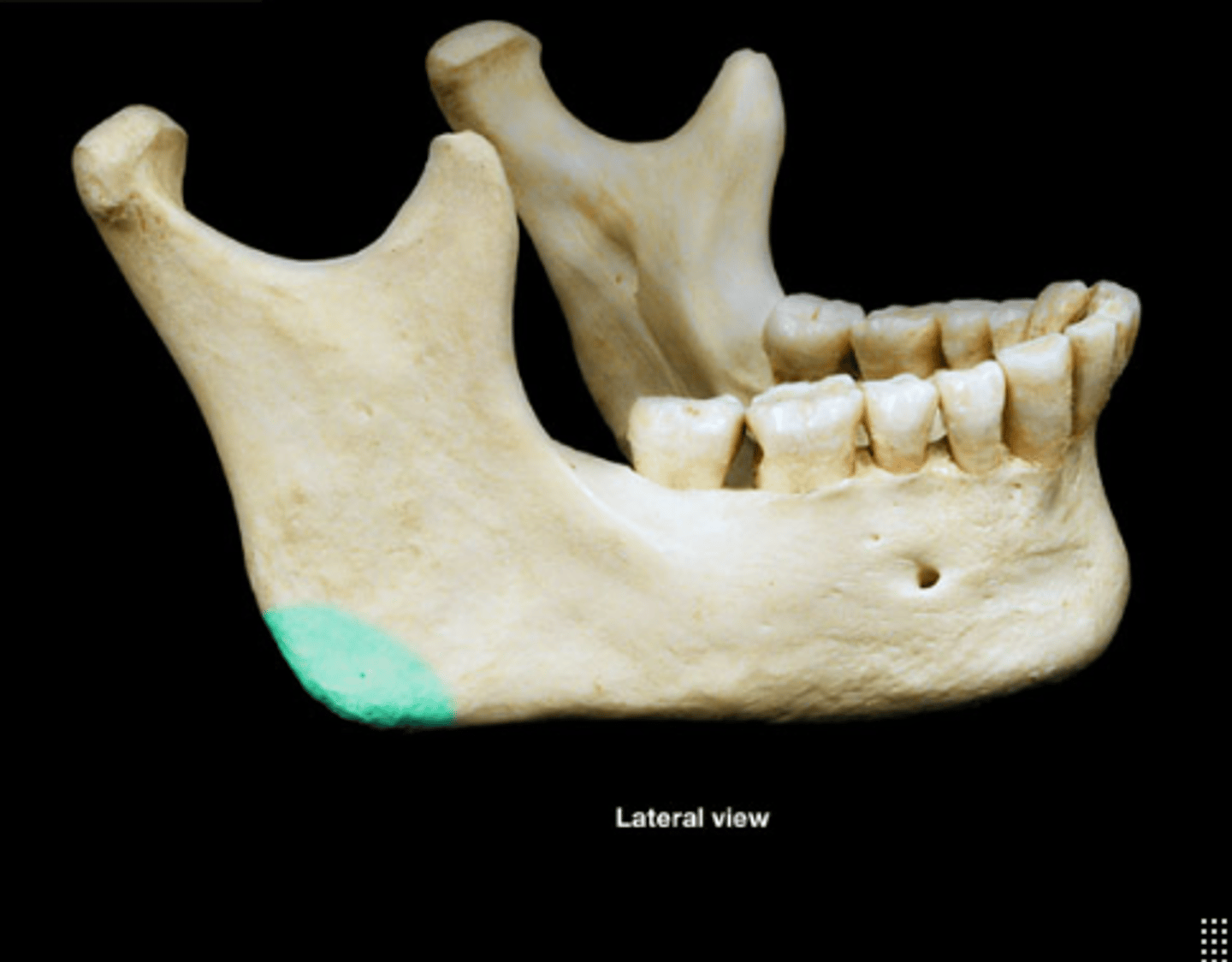
Angle of mandible
Corner where the body and ramus meet.
Body of mandible
Main horizontal portion of the lower jaw.
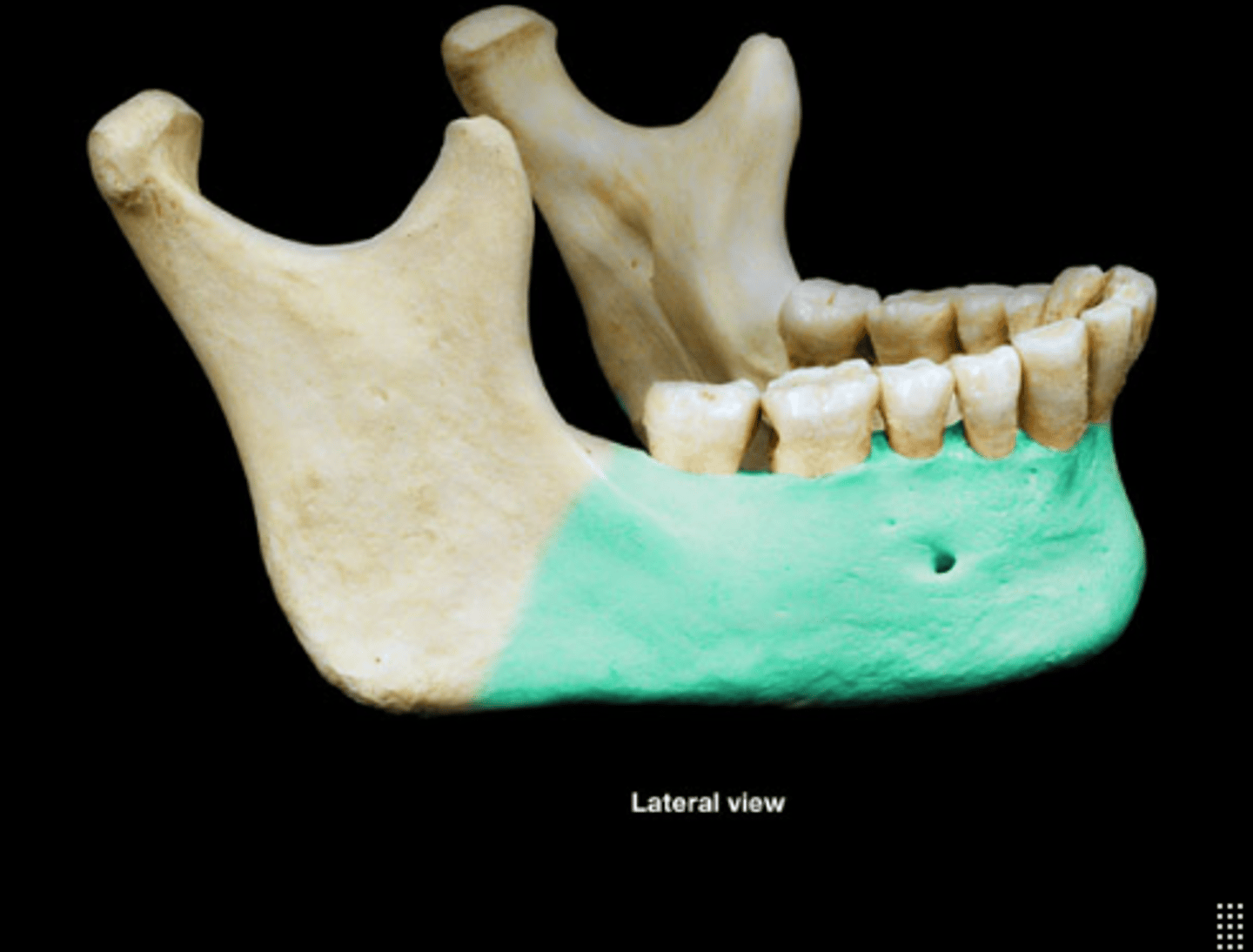
Ramus of mandible
Vertical part of the mandible.
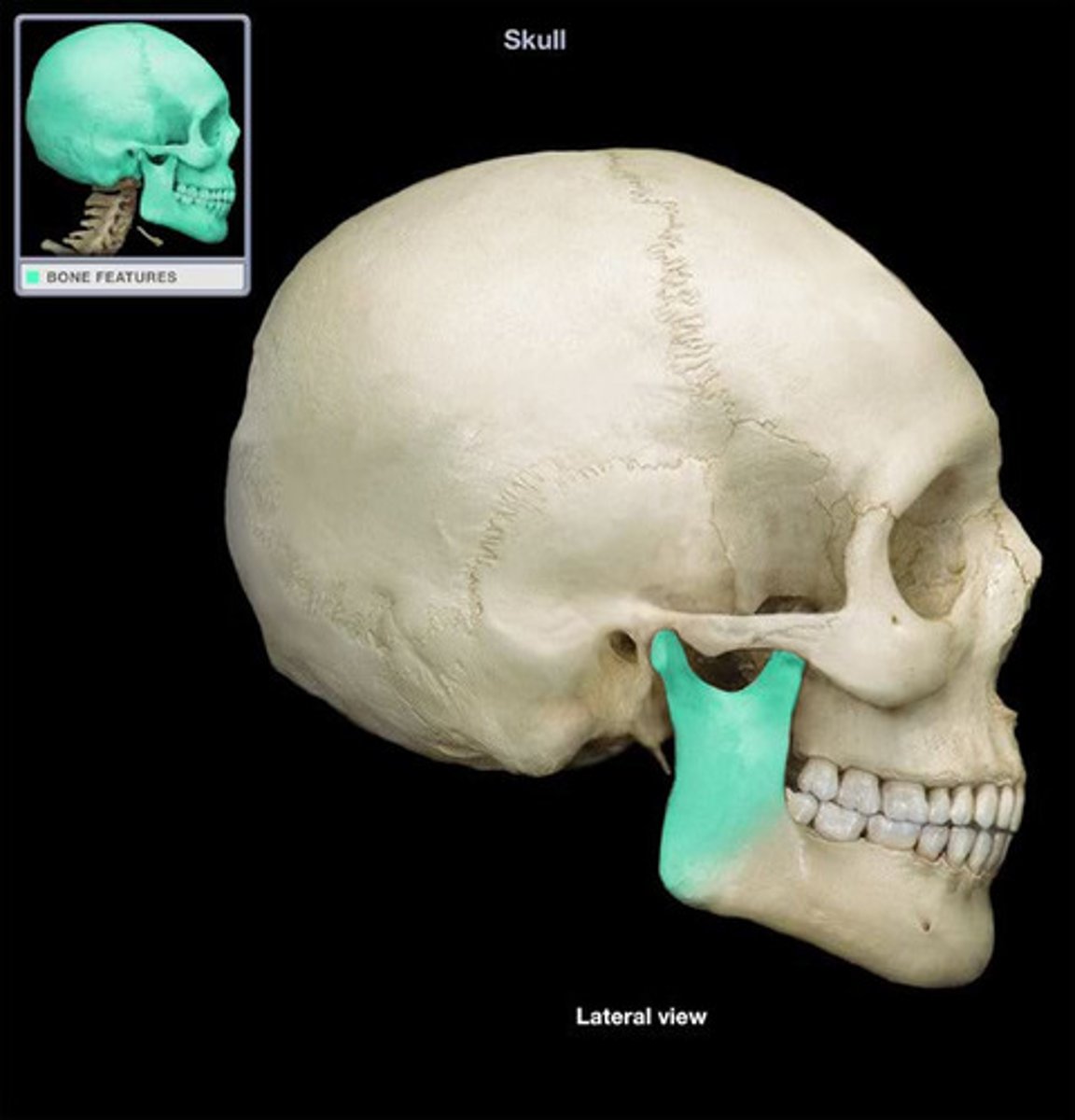
Sphenoid bone
Bone at the base of the skull.
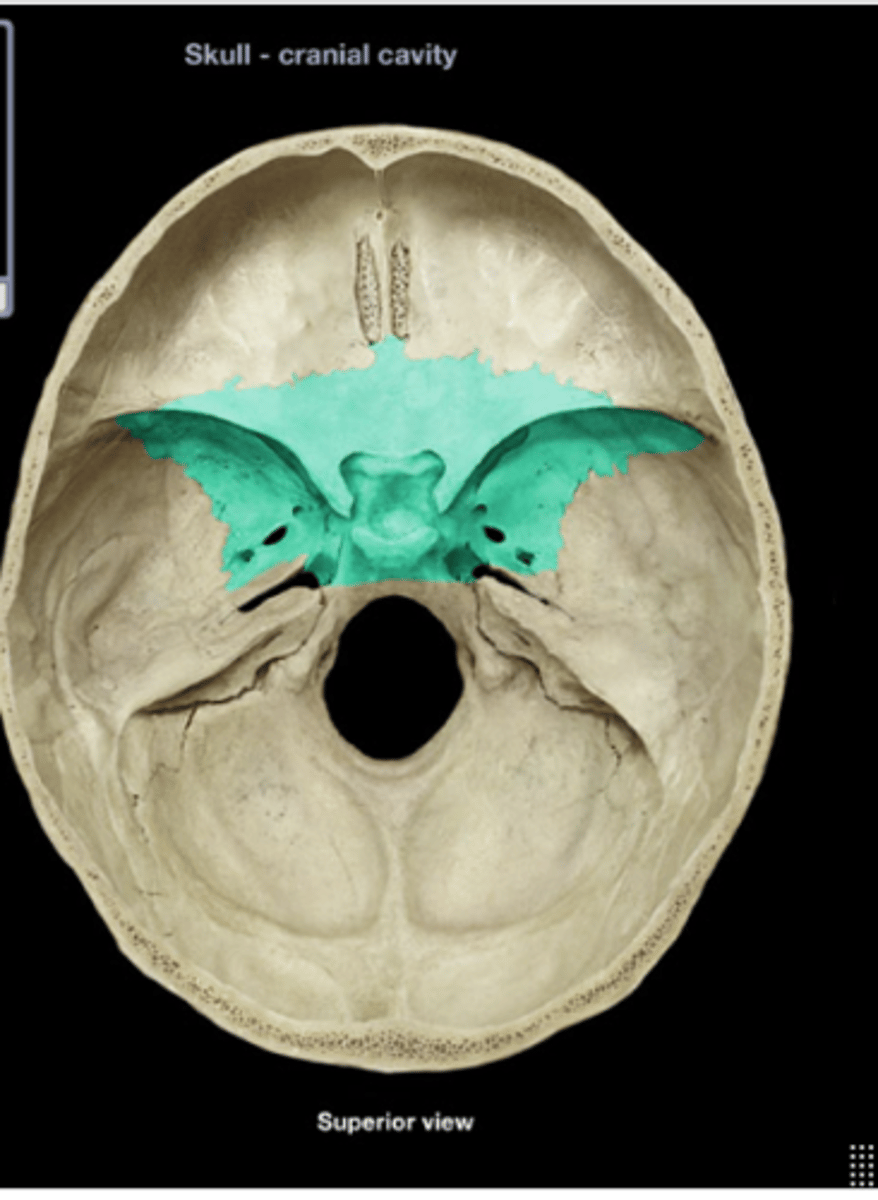
Sphenoid bone
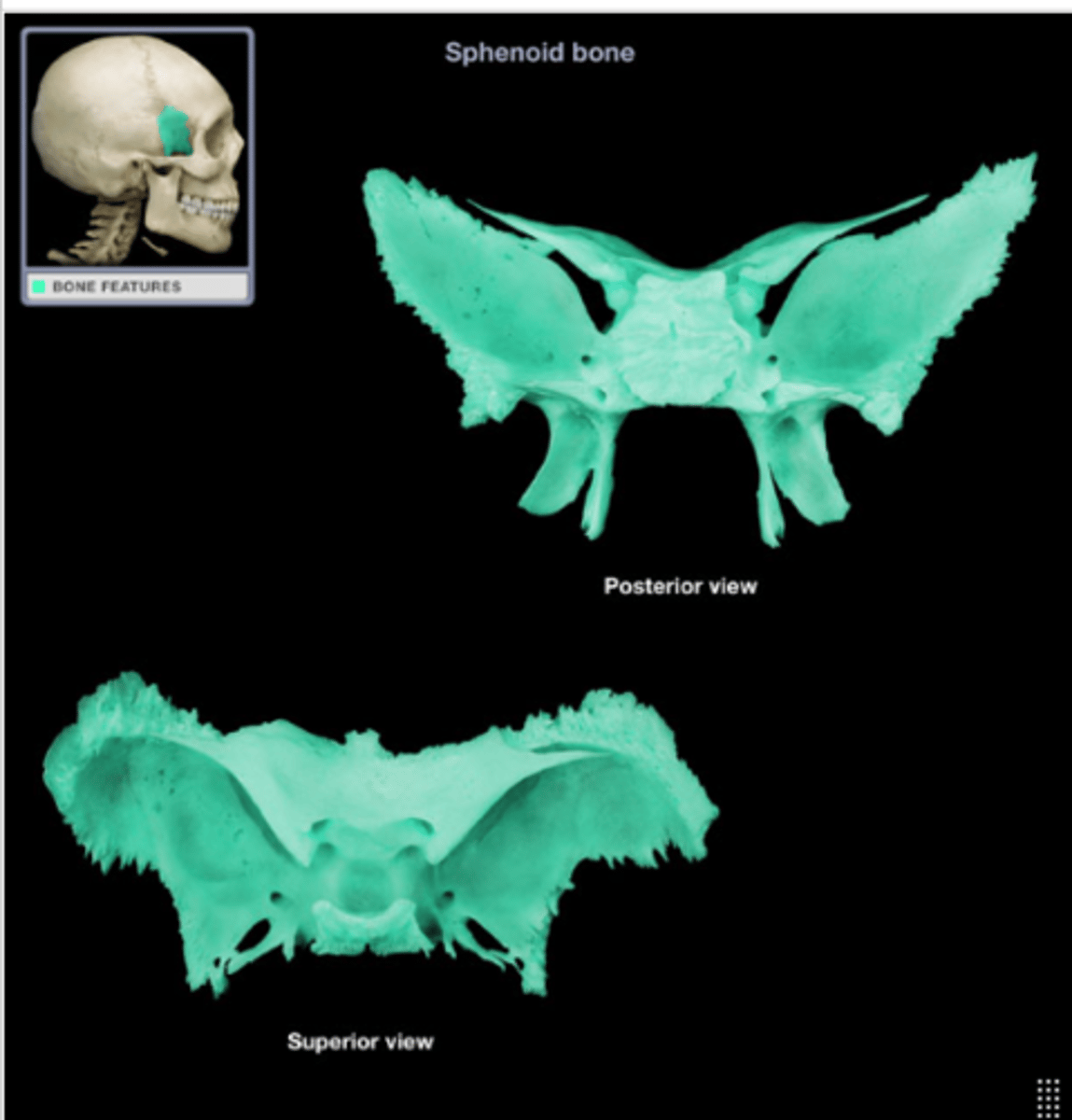
Optic canal
Passage for optic nerve in the sphenoid.
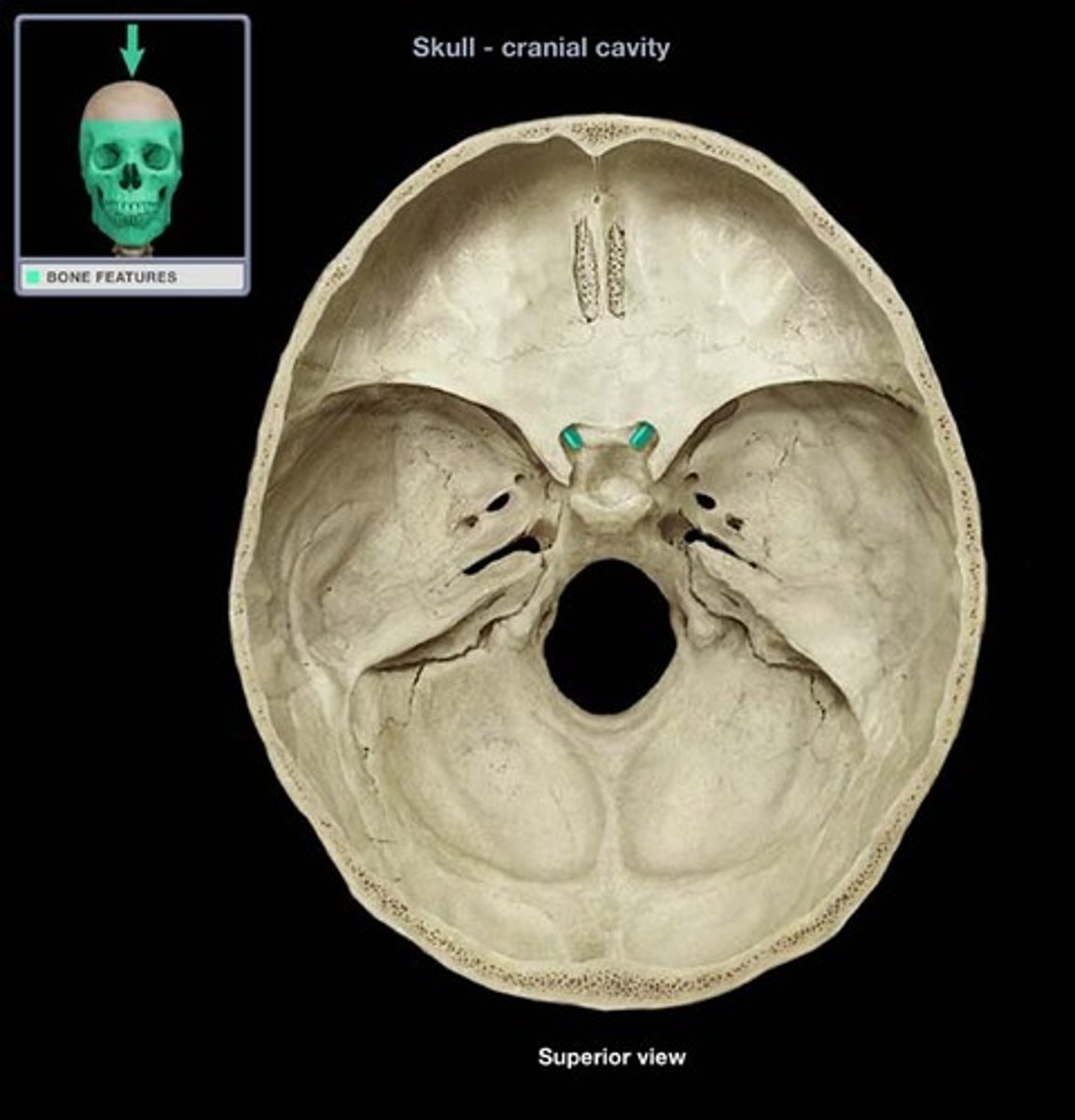
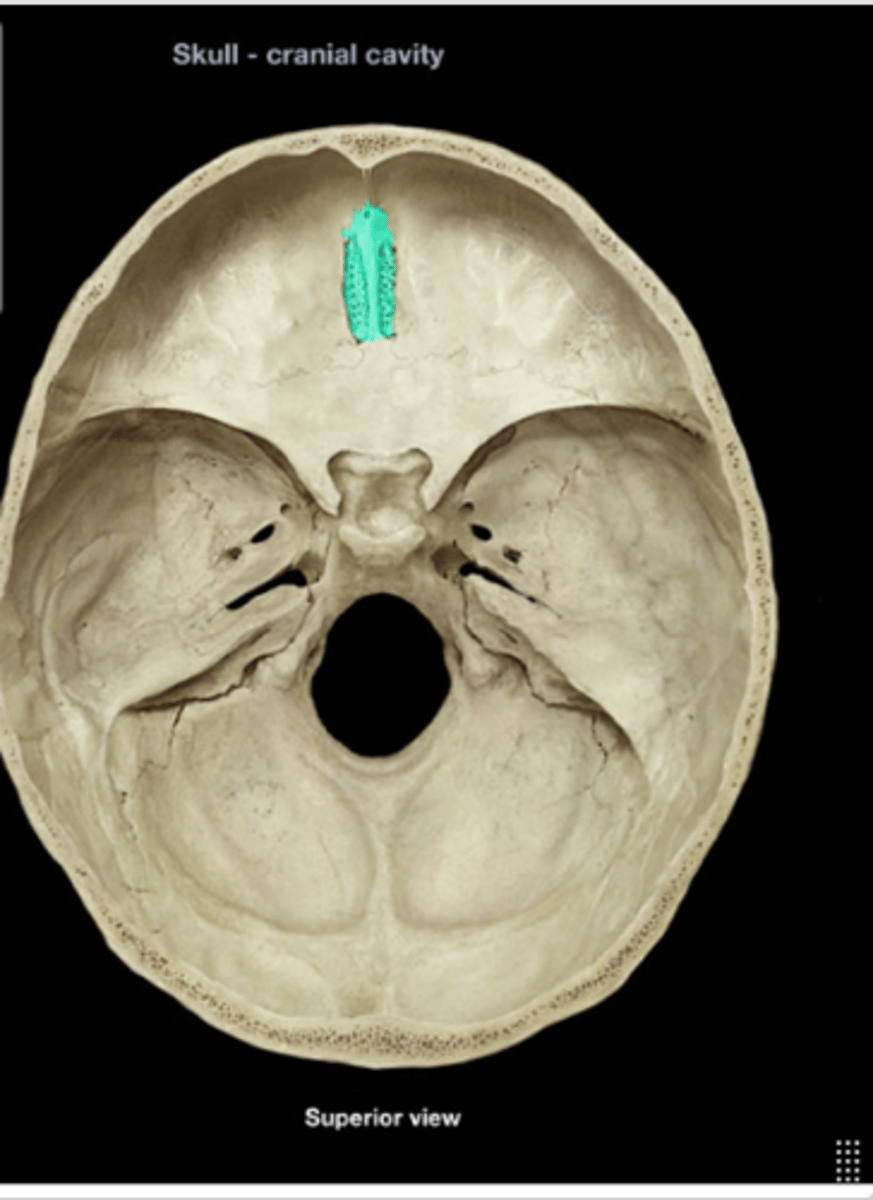
Ethmoid
Bone forming part of the nasal cavity and orbits.
Vertebrae
Individual bones forming the vertebral column.
Cervical vertebrae
Seven vertebrae in the neck region.
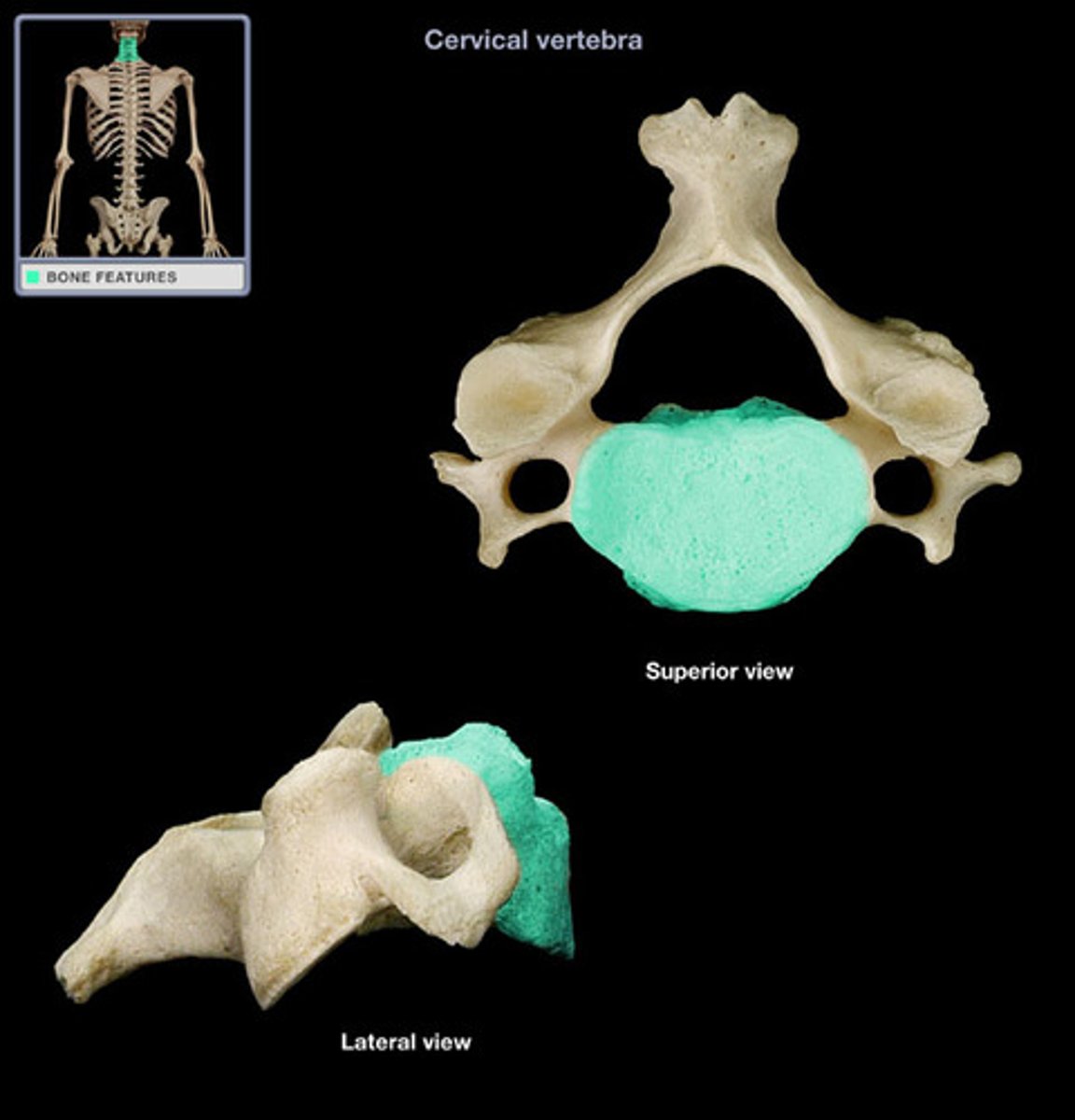
Body of cervical vertebrae
small, wide side to side
Transverse process of cervical
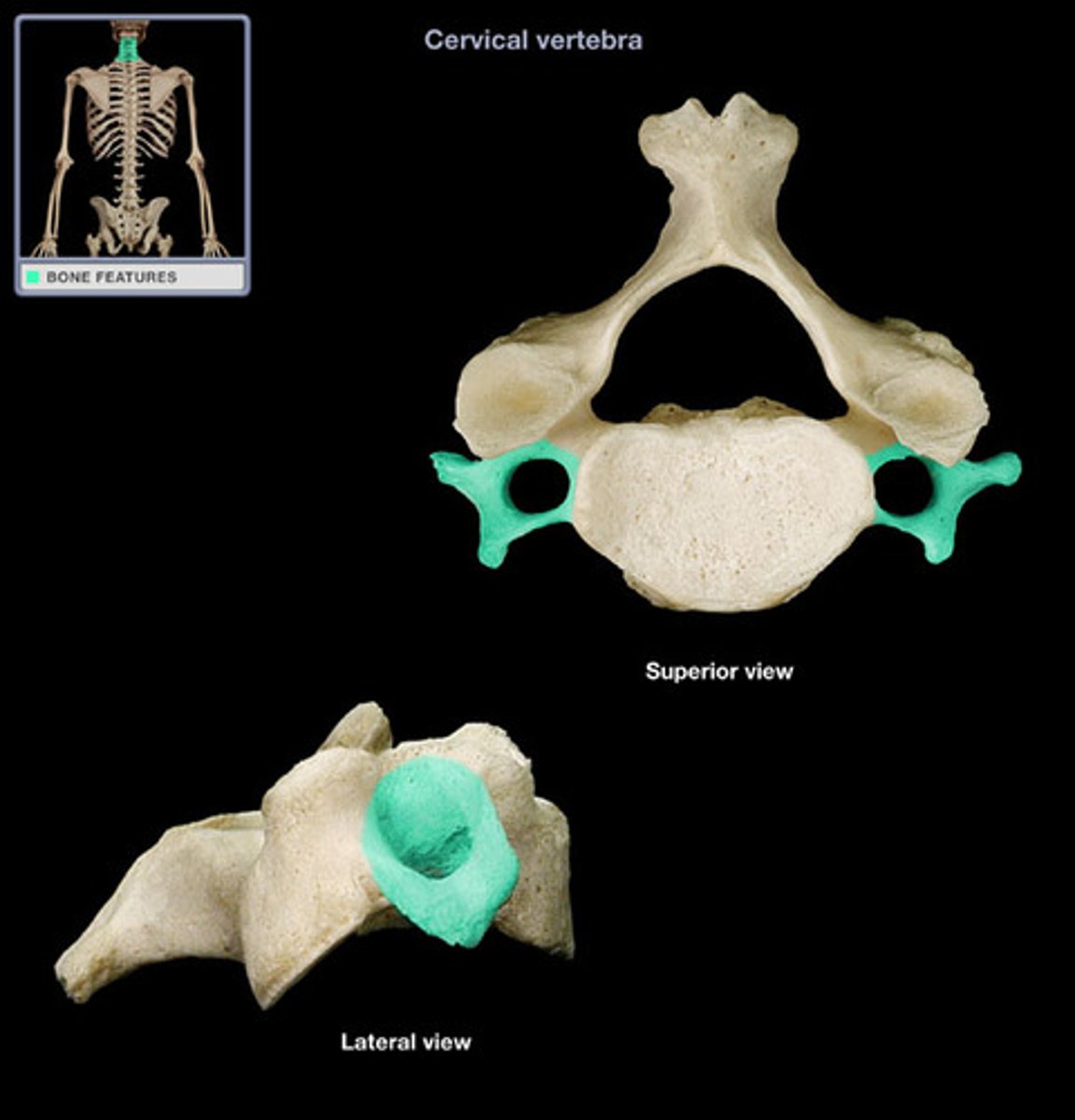
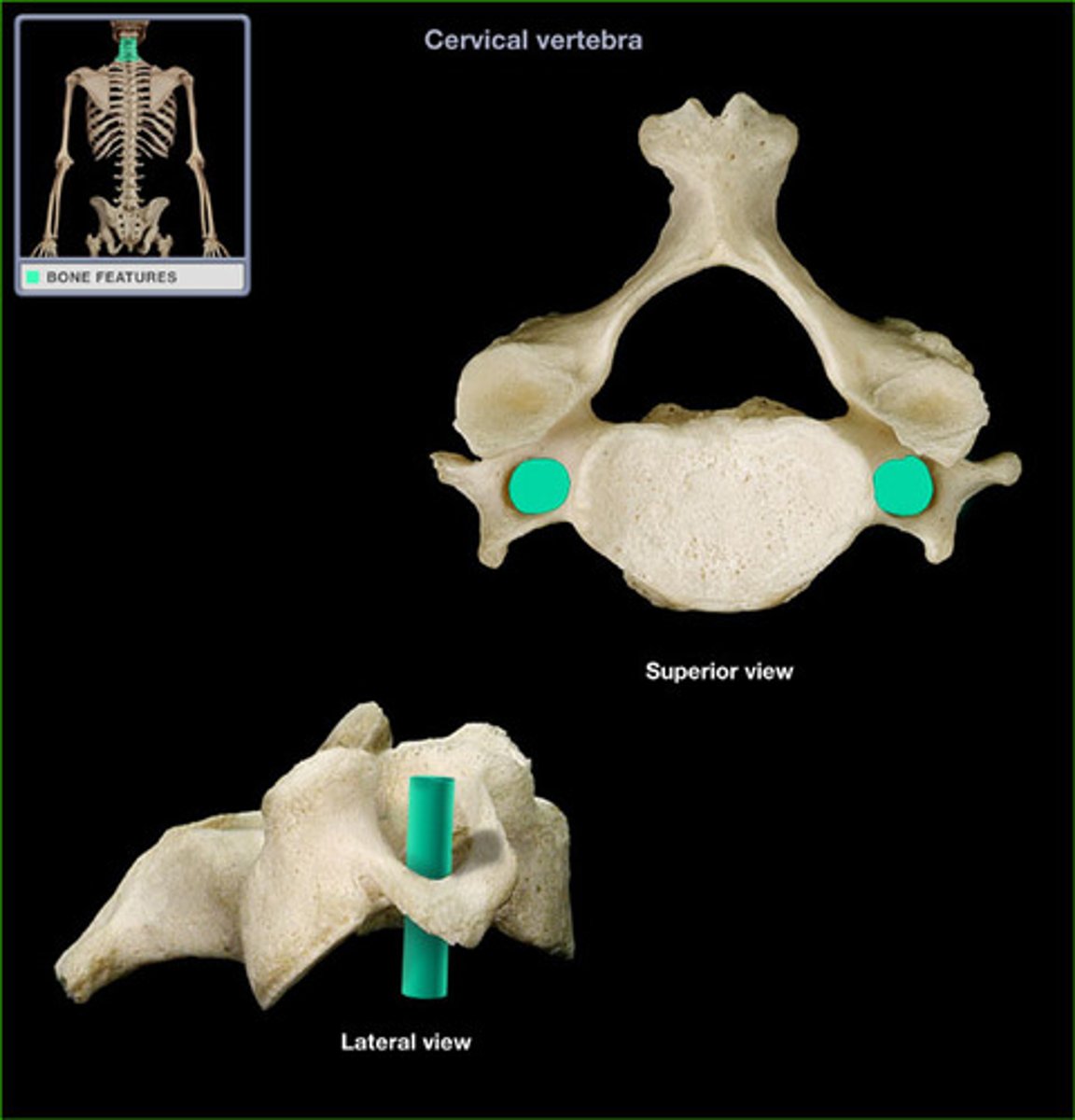
transverse foramen of cervical
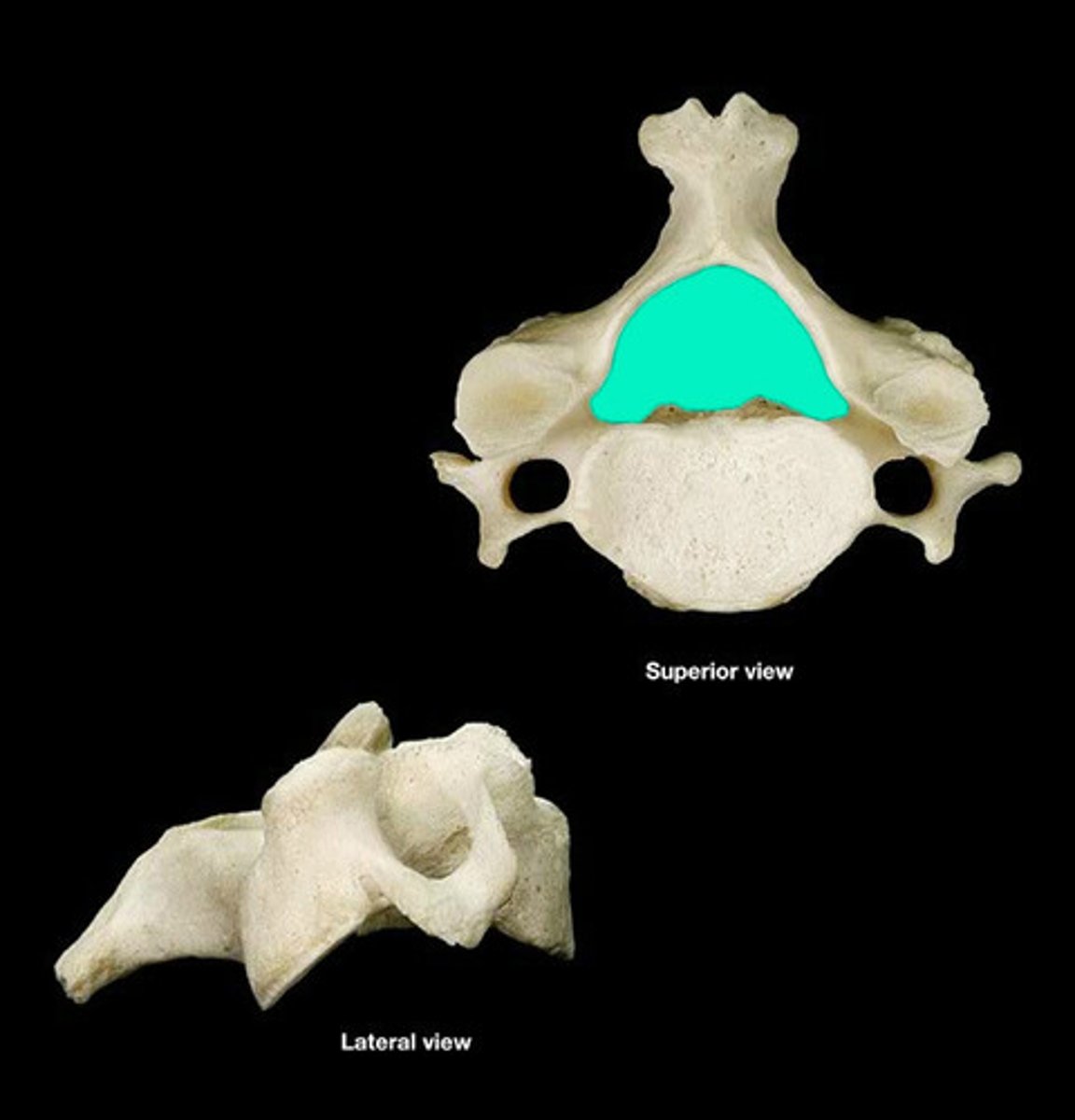
vertebral foramen of cervical
hole in the vertebrae
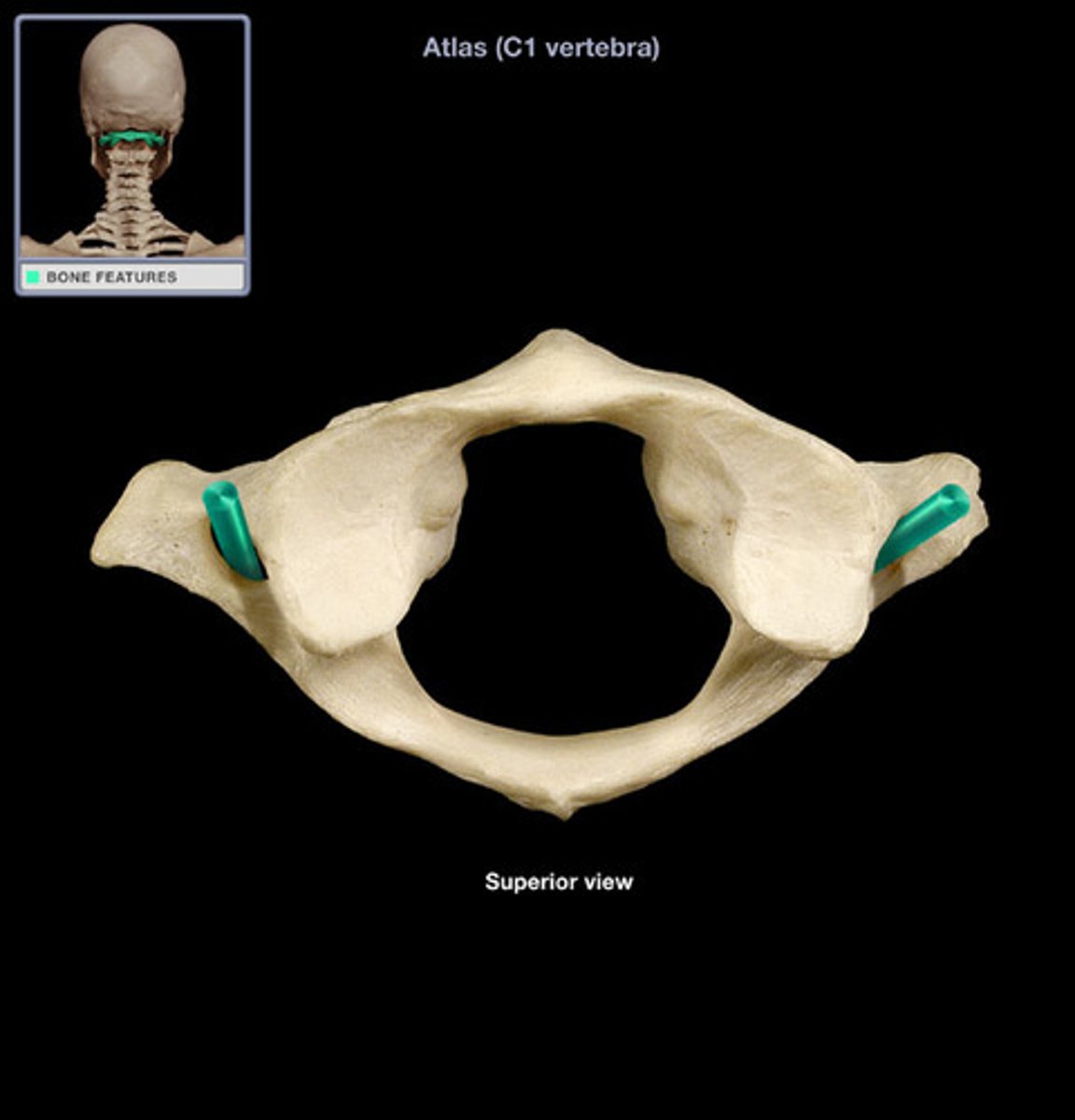
Atlas (C1)
First cervical vertebra supporting the skull.
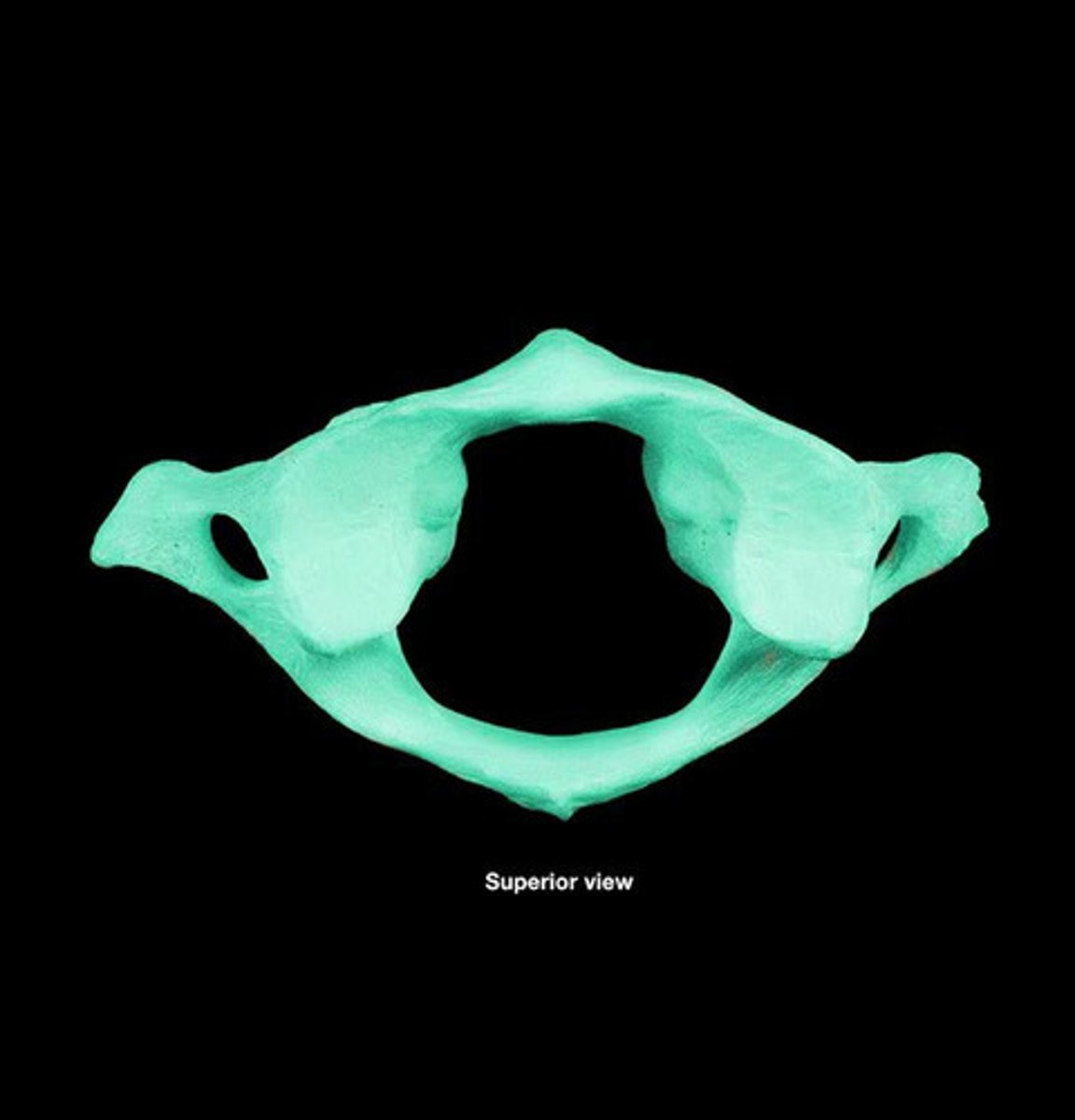
transverse foramen of atlas
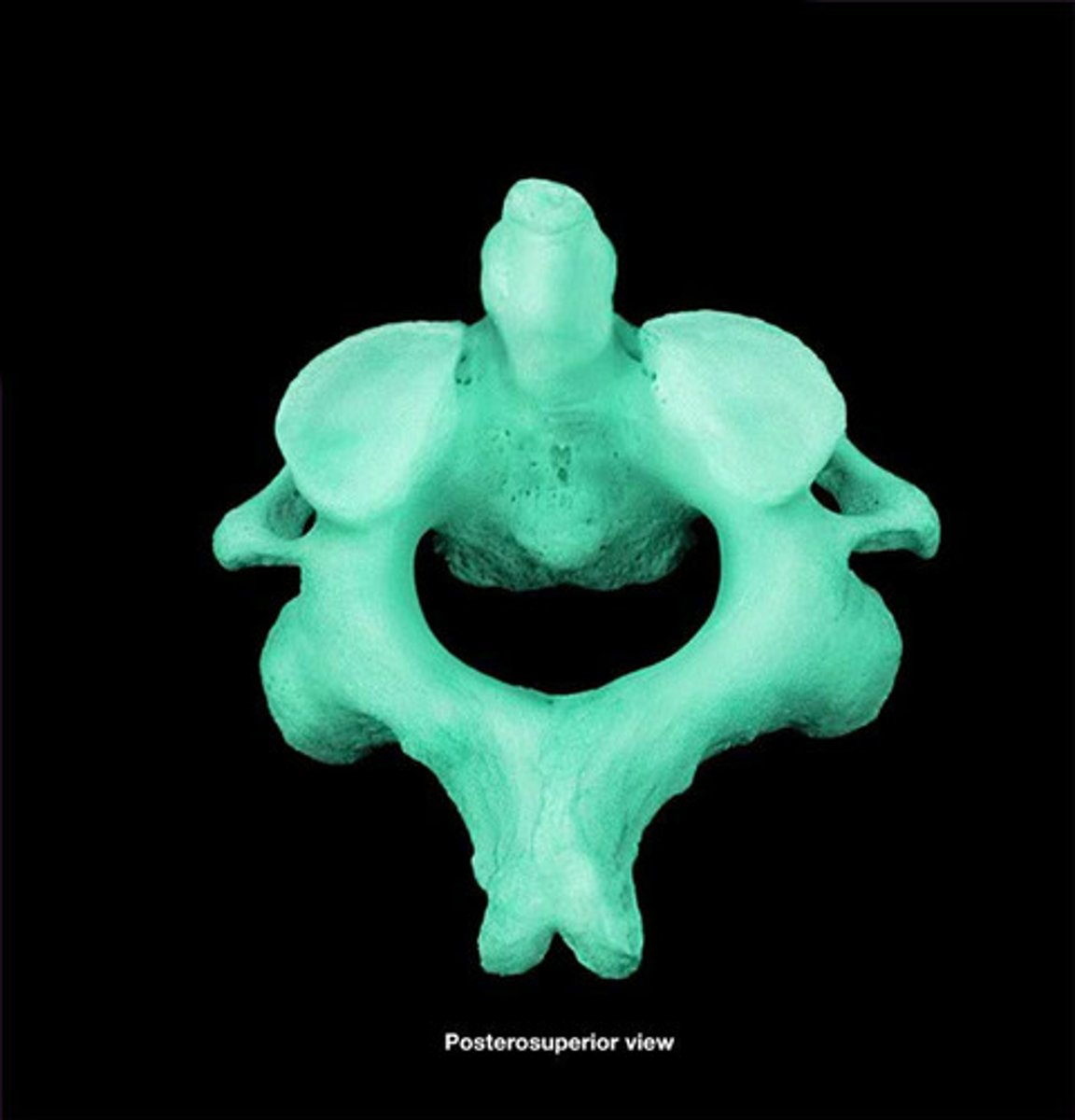
Axis (C2)
Second cervical vertebra allowing head rotation.
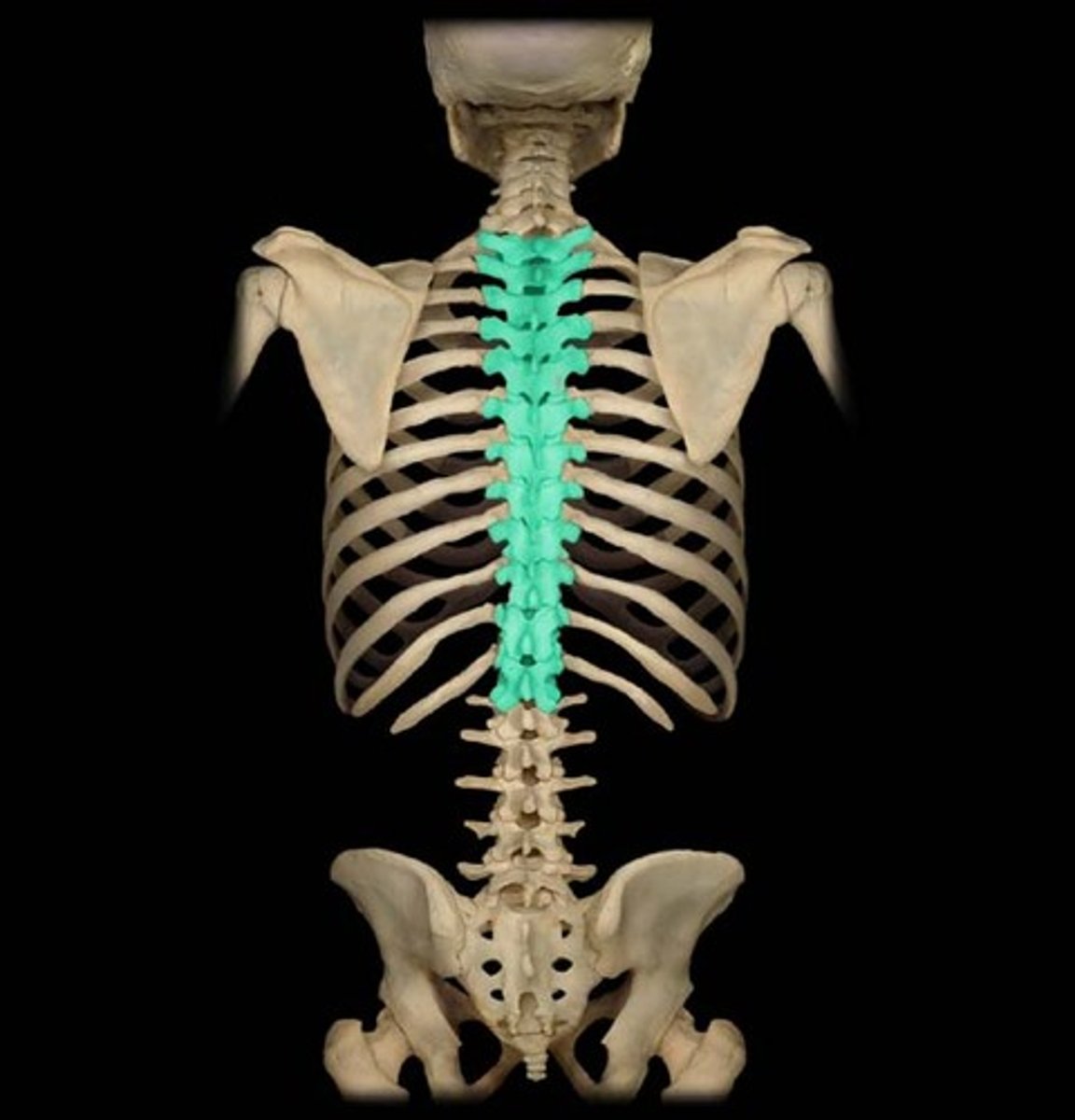
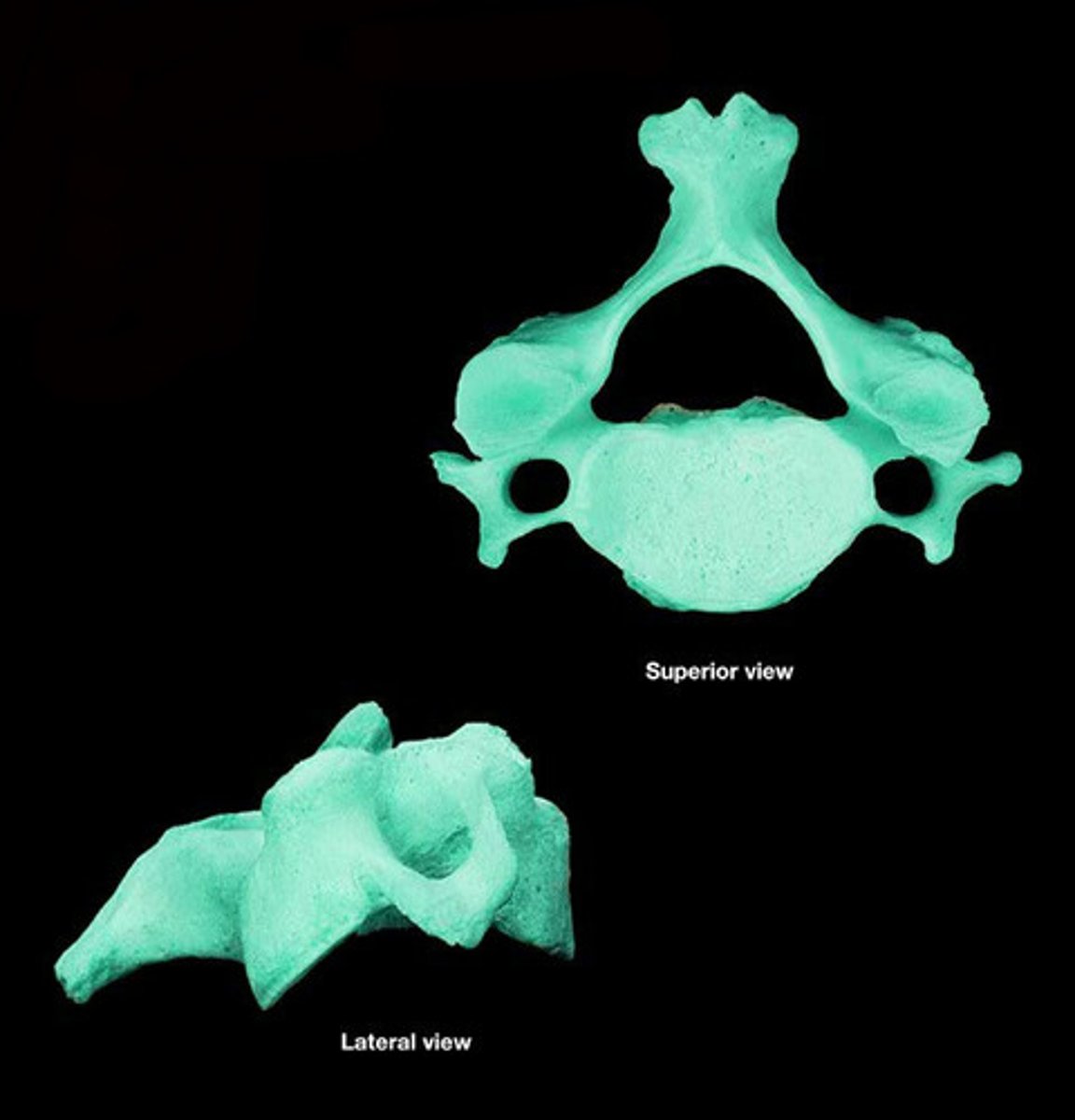
Thoracic vertebrae
Twelve vertebrae in the upper back.
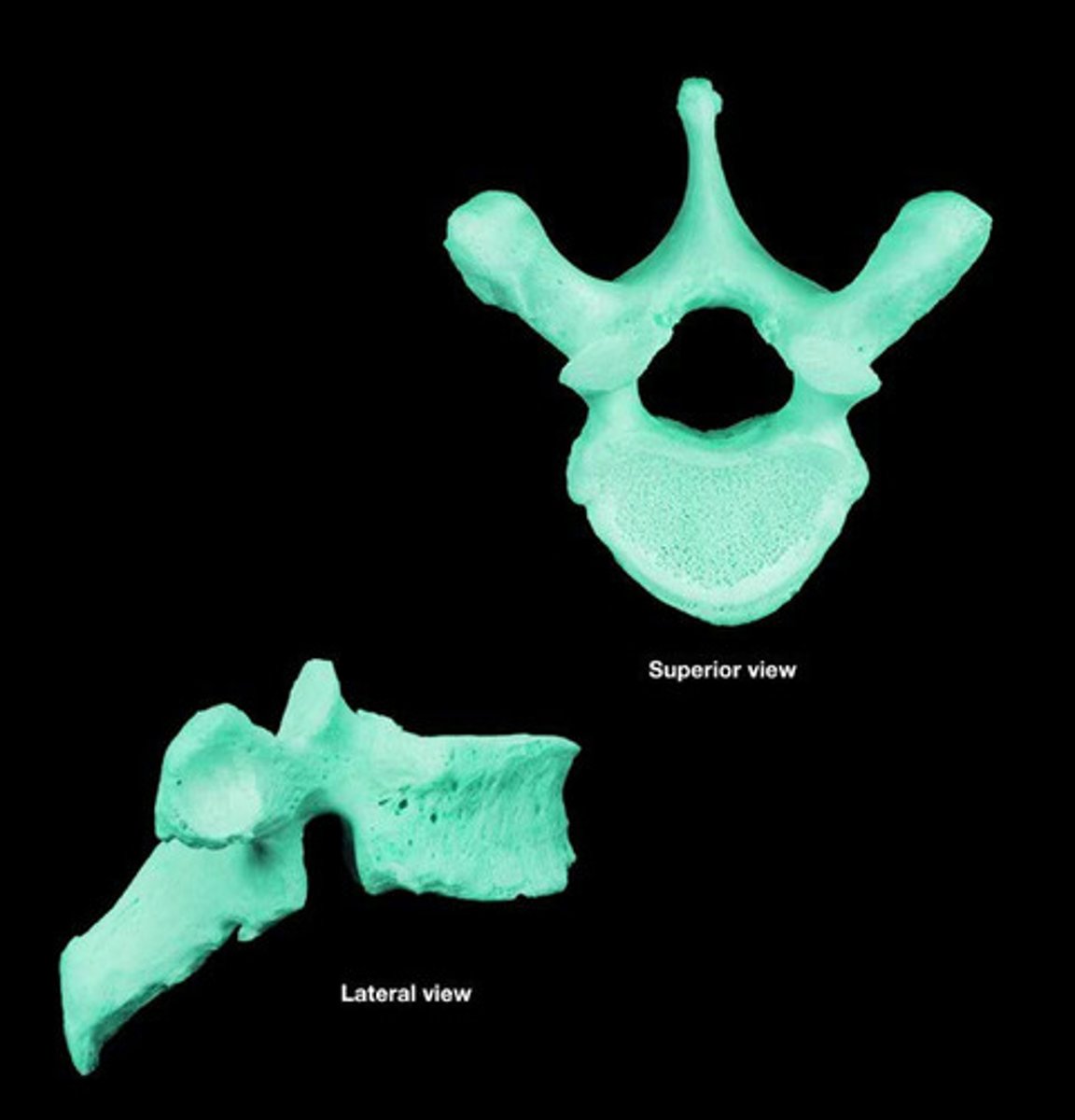
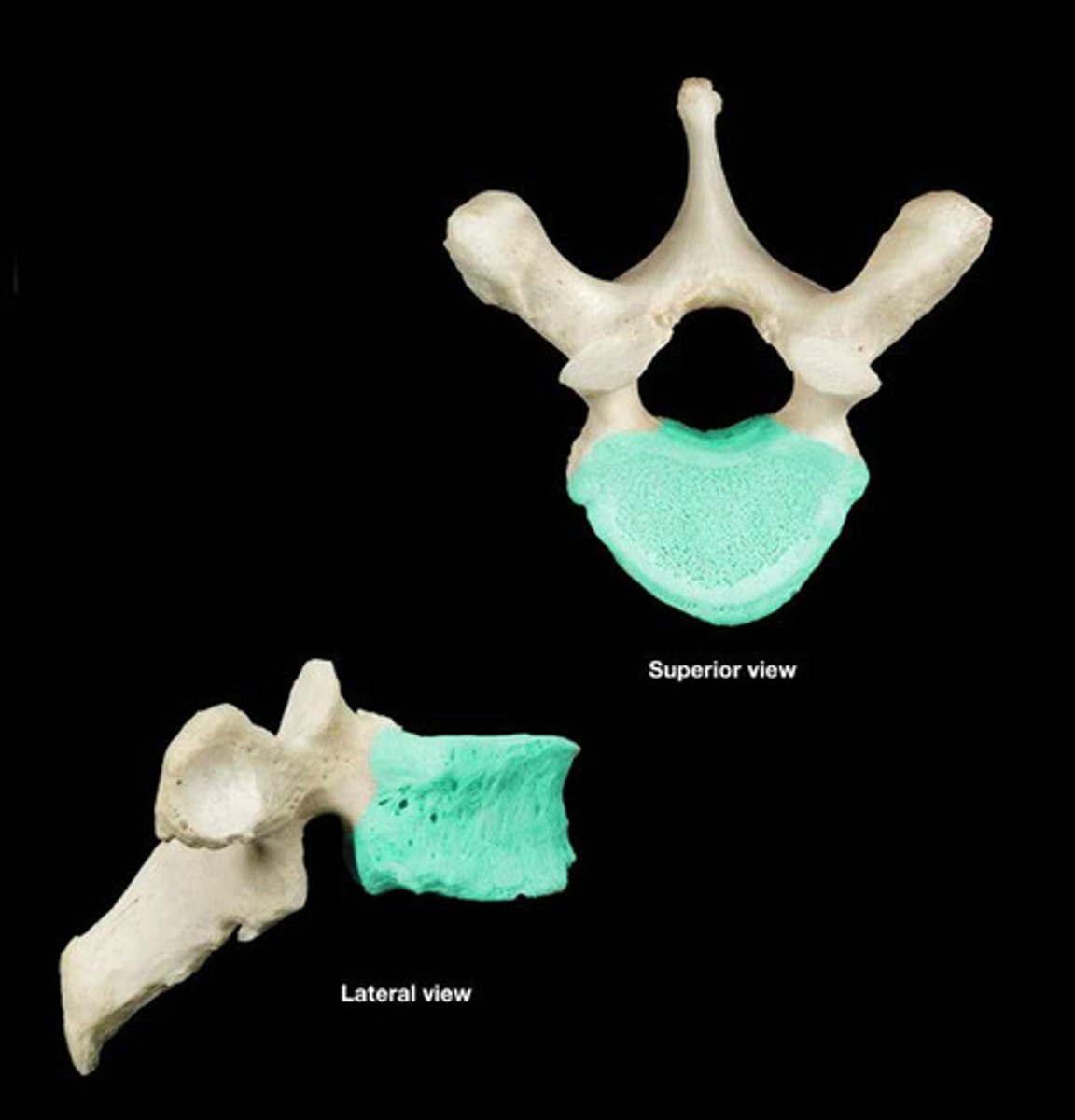
body of thoracic
Larger than cervical; heart shaped; bears costal facets
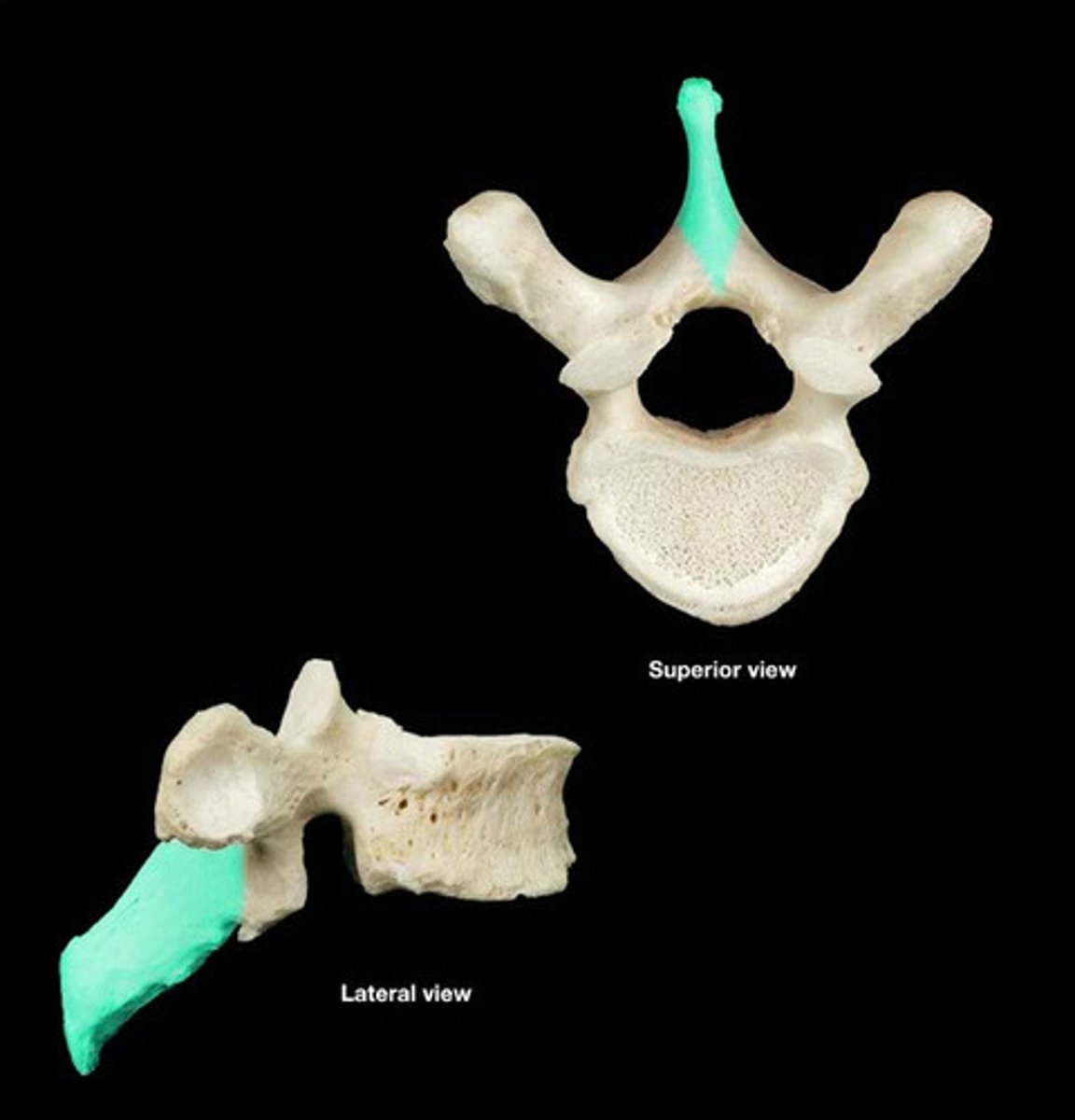
spinous process of thoracic
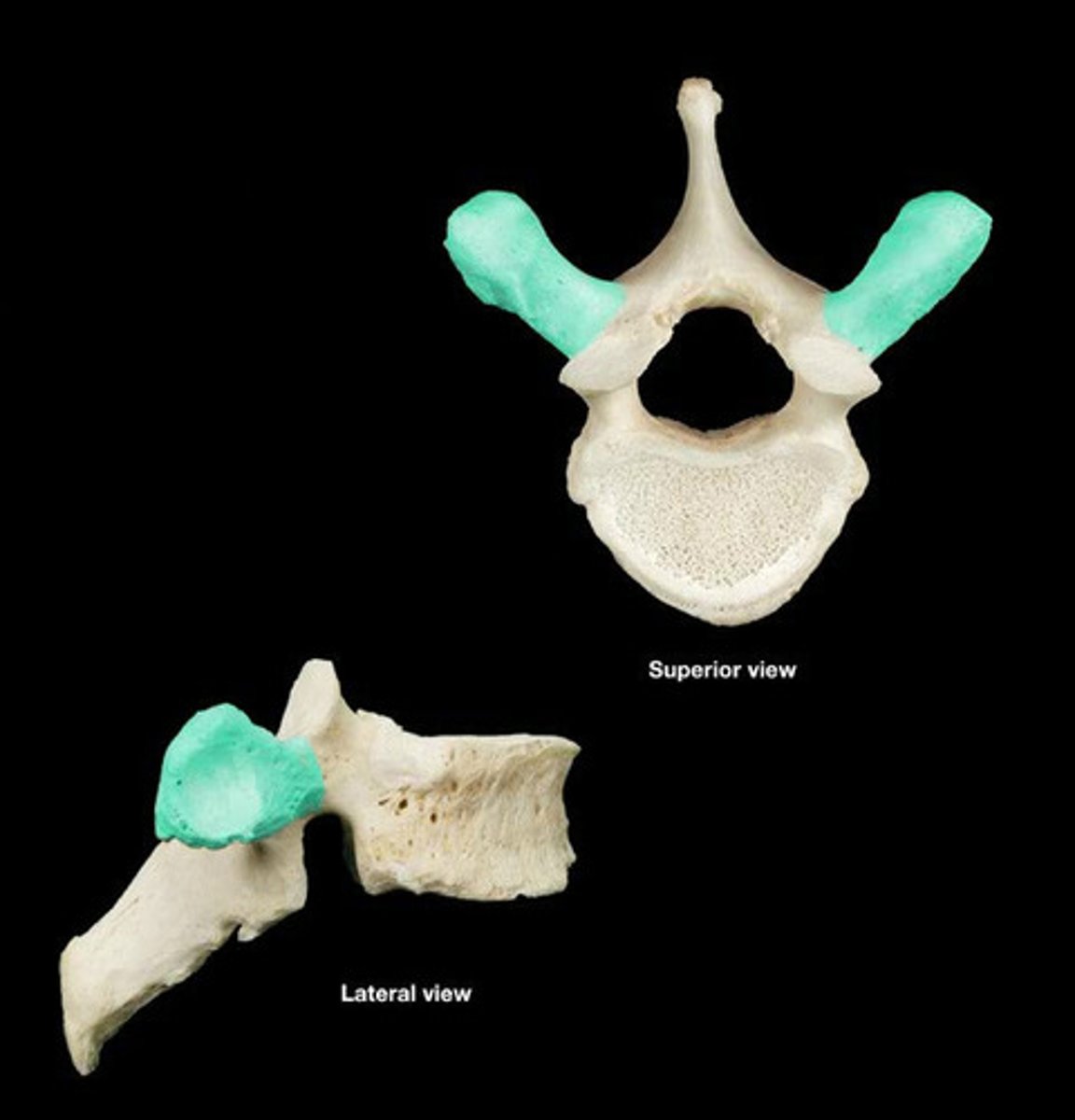
transverse process of thoracic
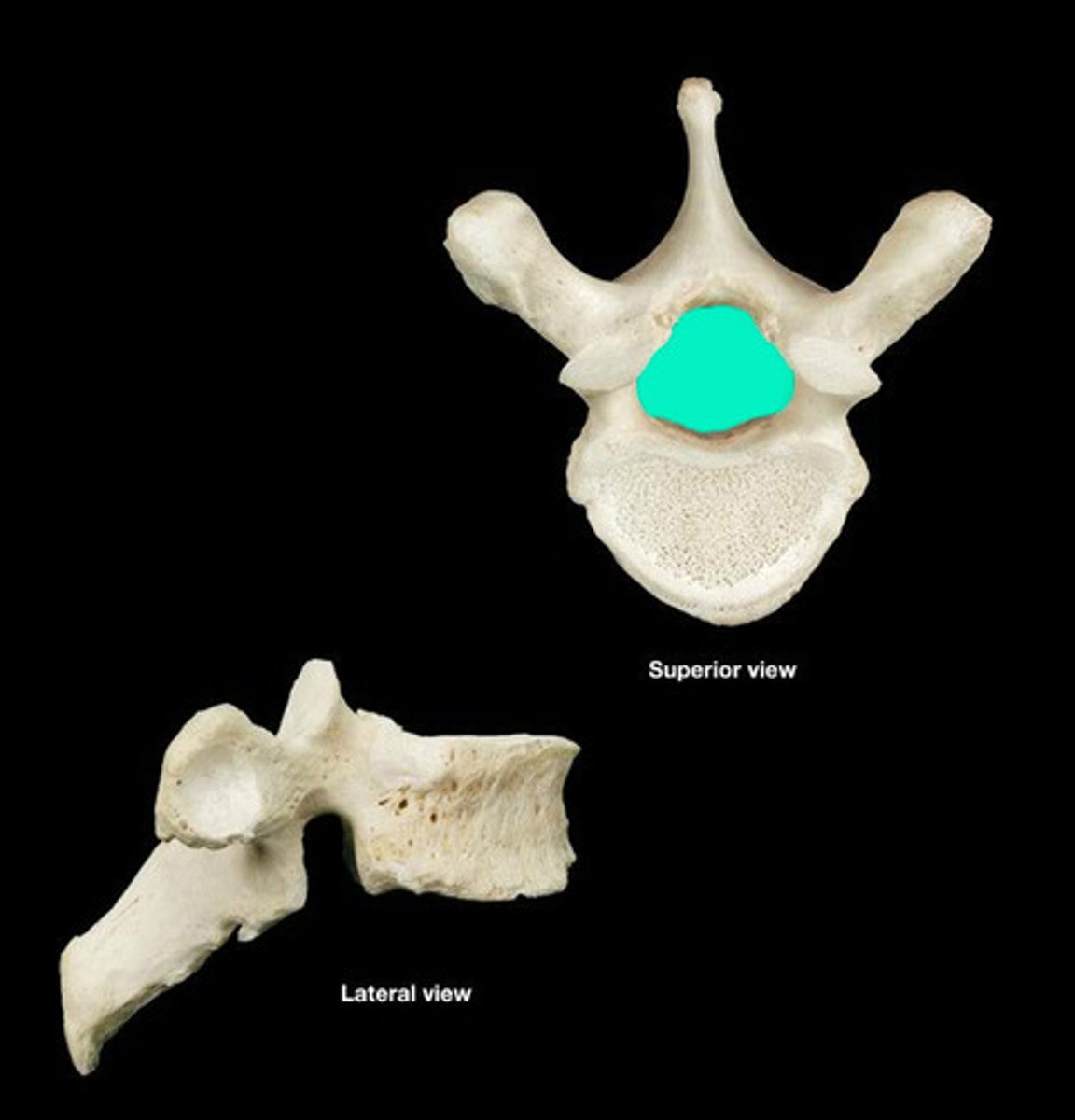
vertebral foramen of thoracic
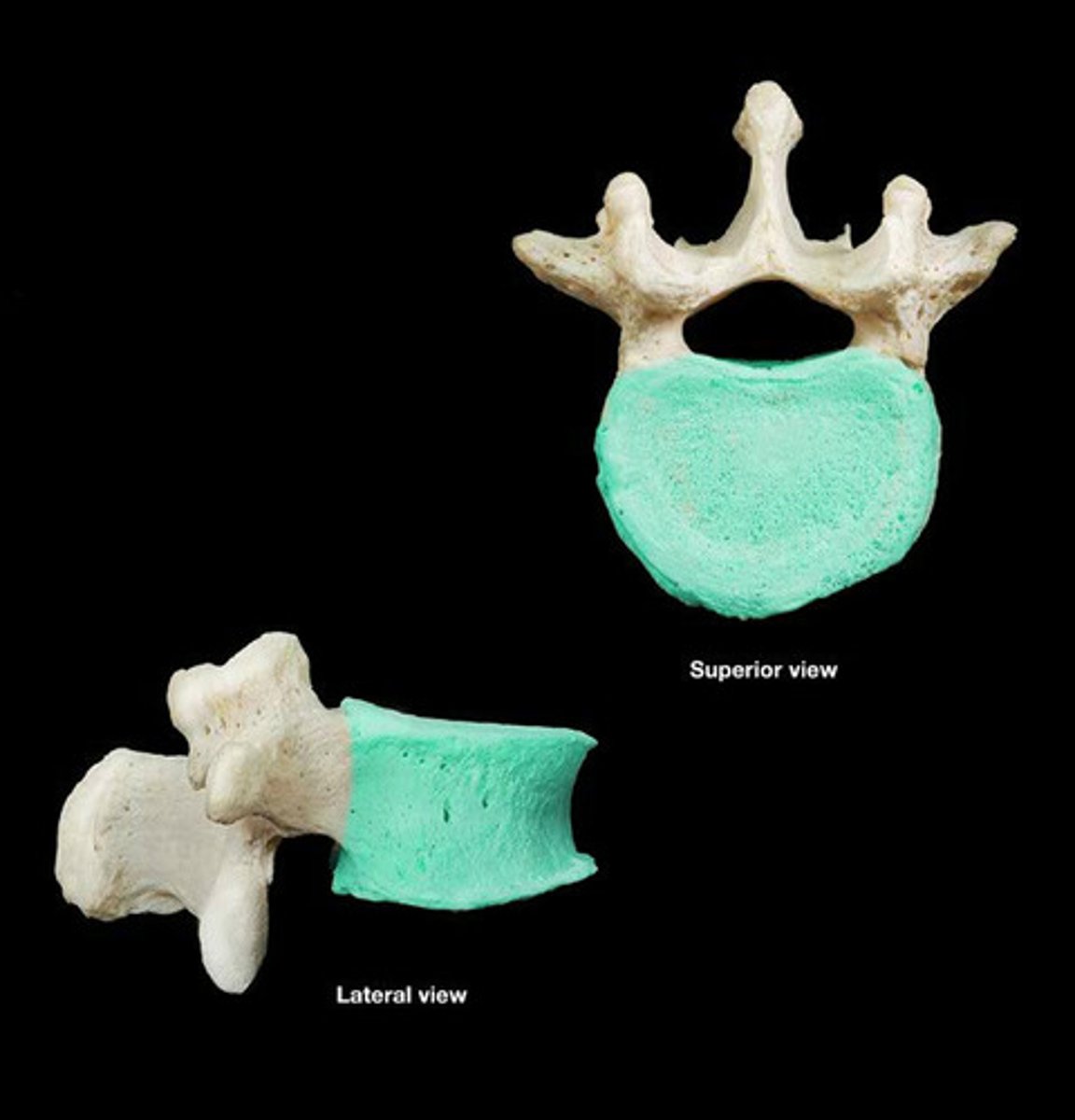
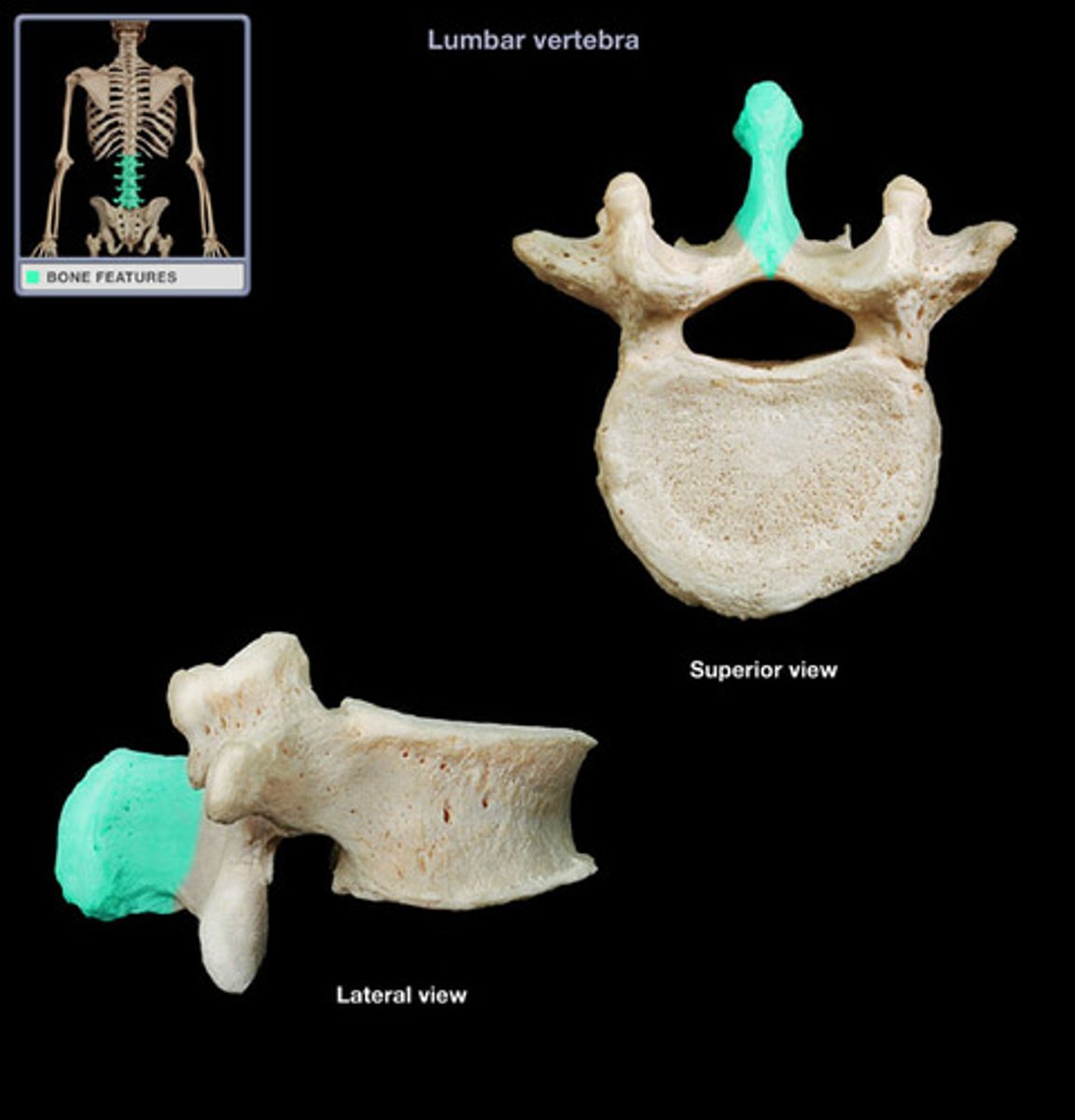
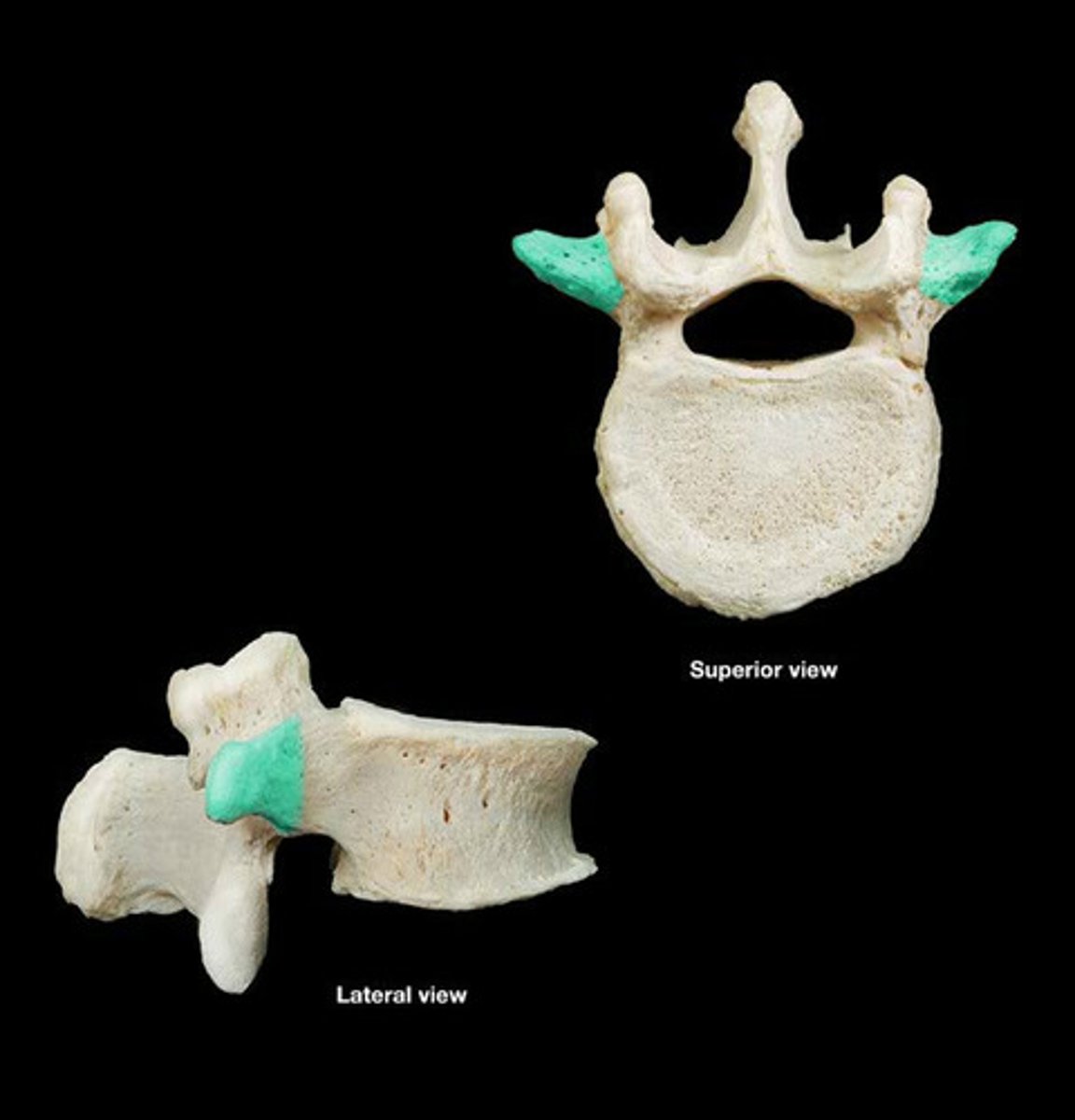
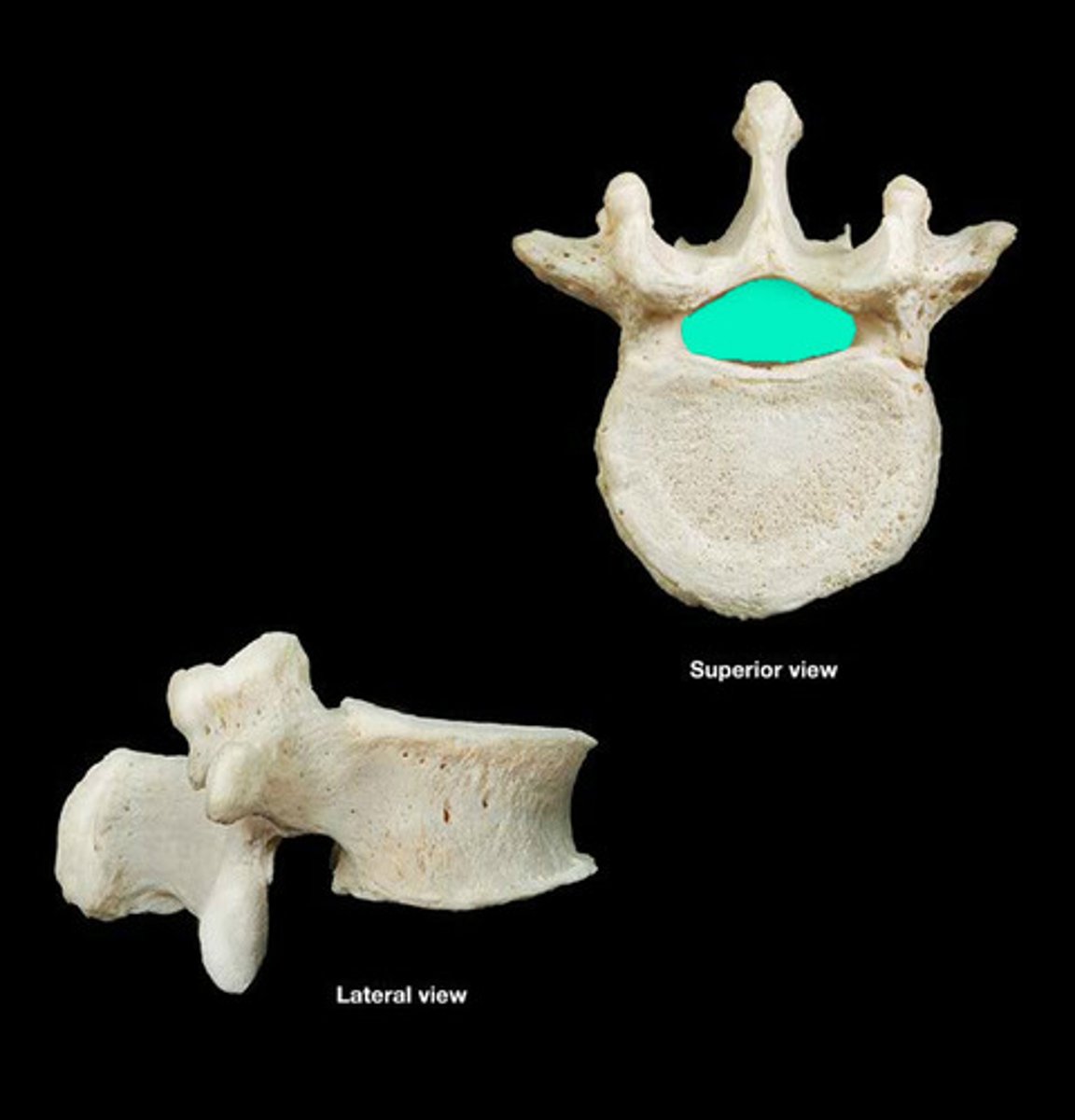
Lumbar vertebrae
Five vertebrae in the lower back.
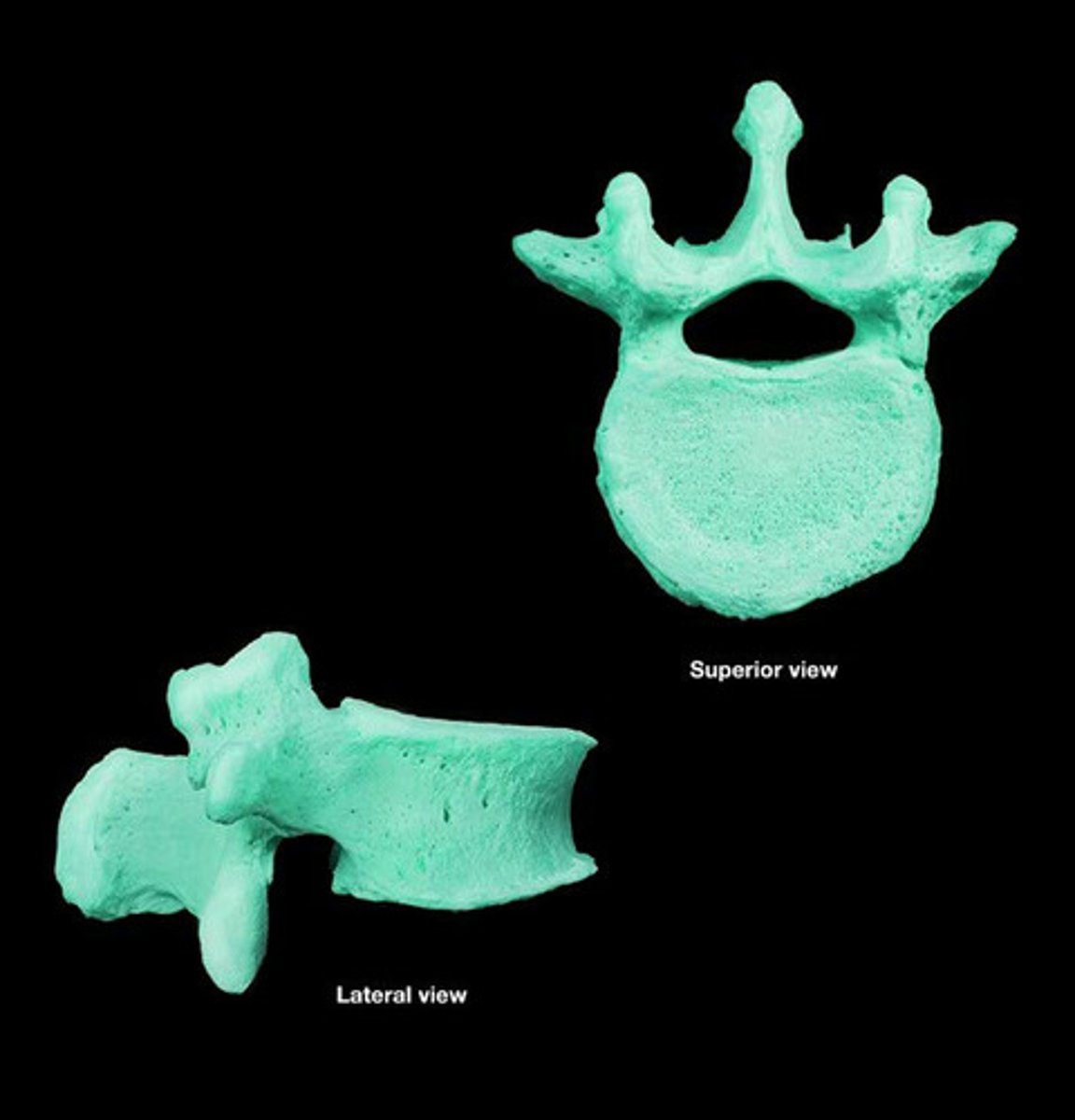
body of lumbar
spinous process of lumbar
transverse process of lumbar
vertebral foramen of lumbar
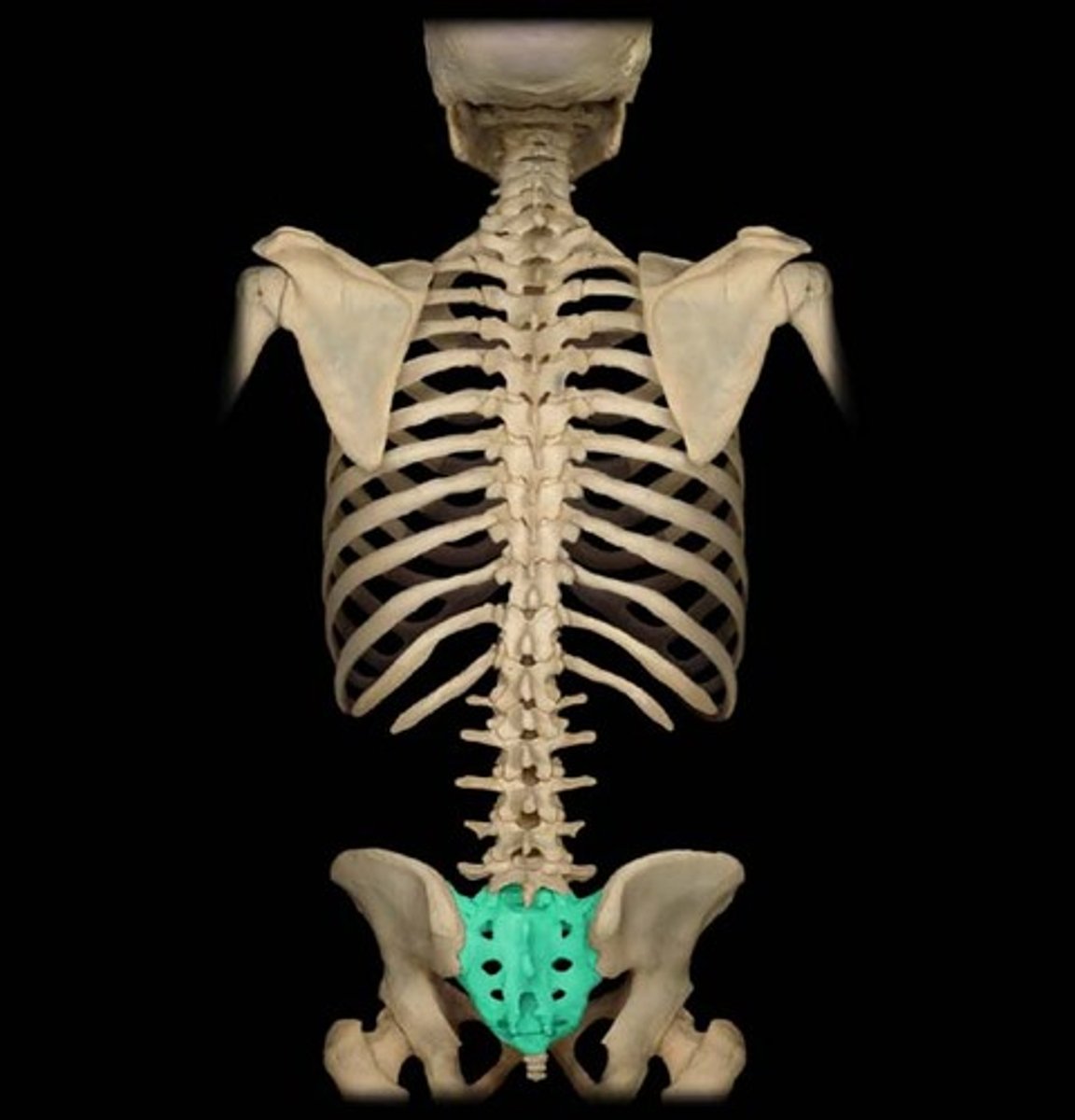
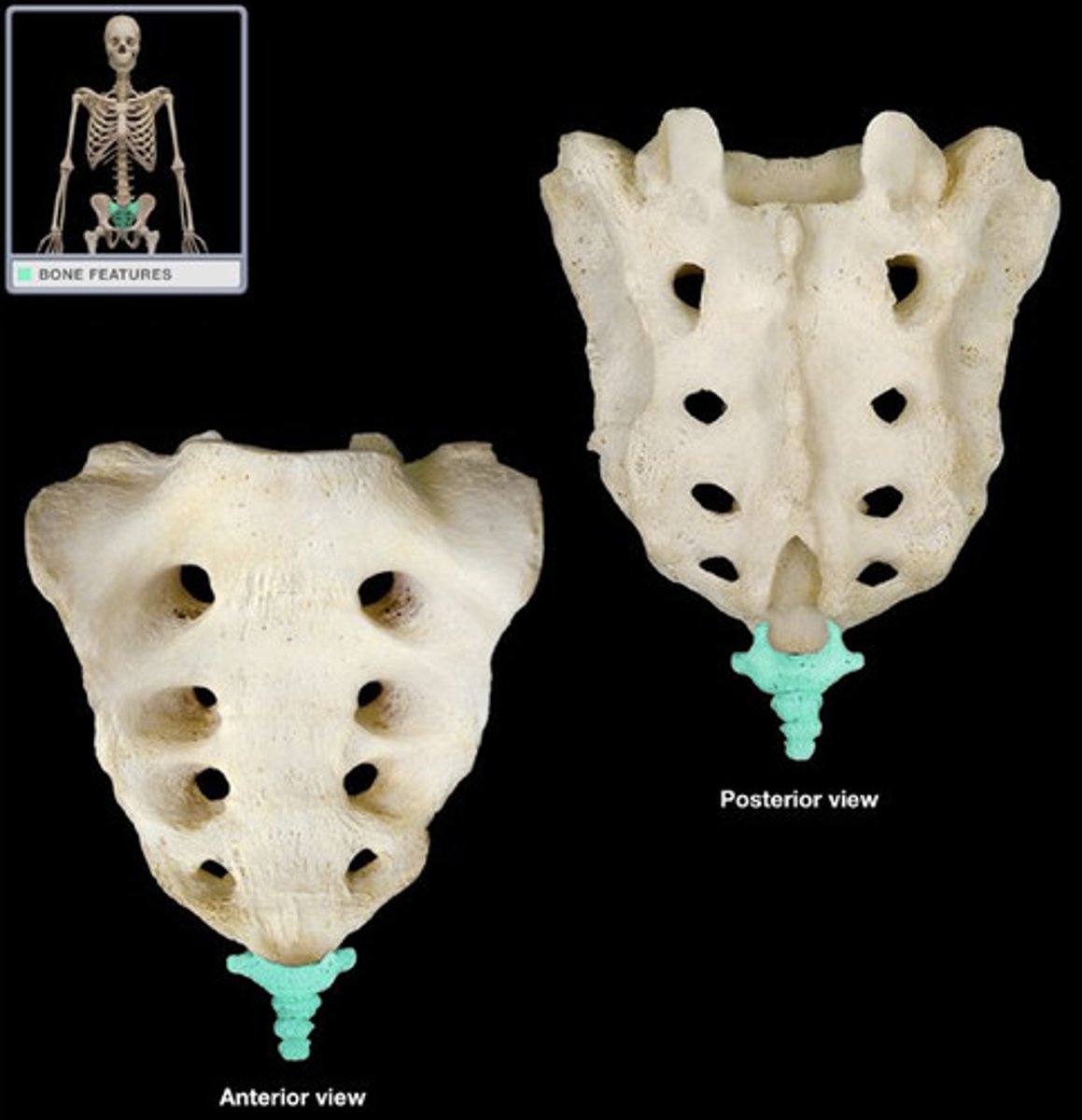
Sacrum
Five fused vertebrae forming the posterior pelvis.
Coccyx
Small bone at the base of the spine.
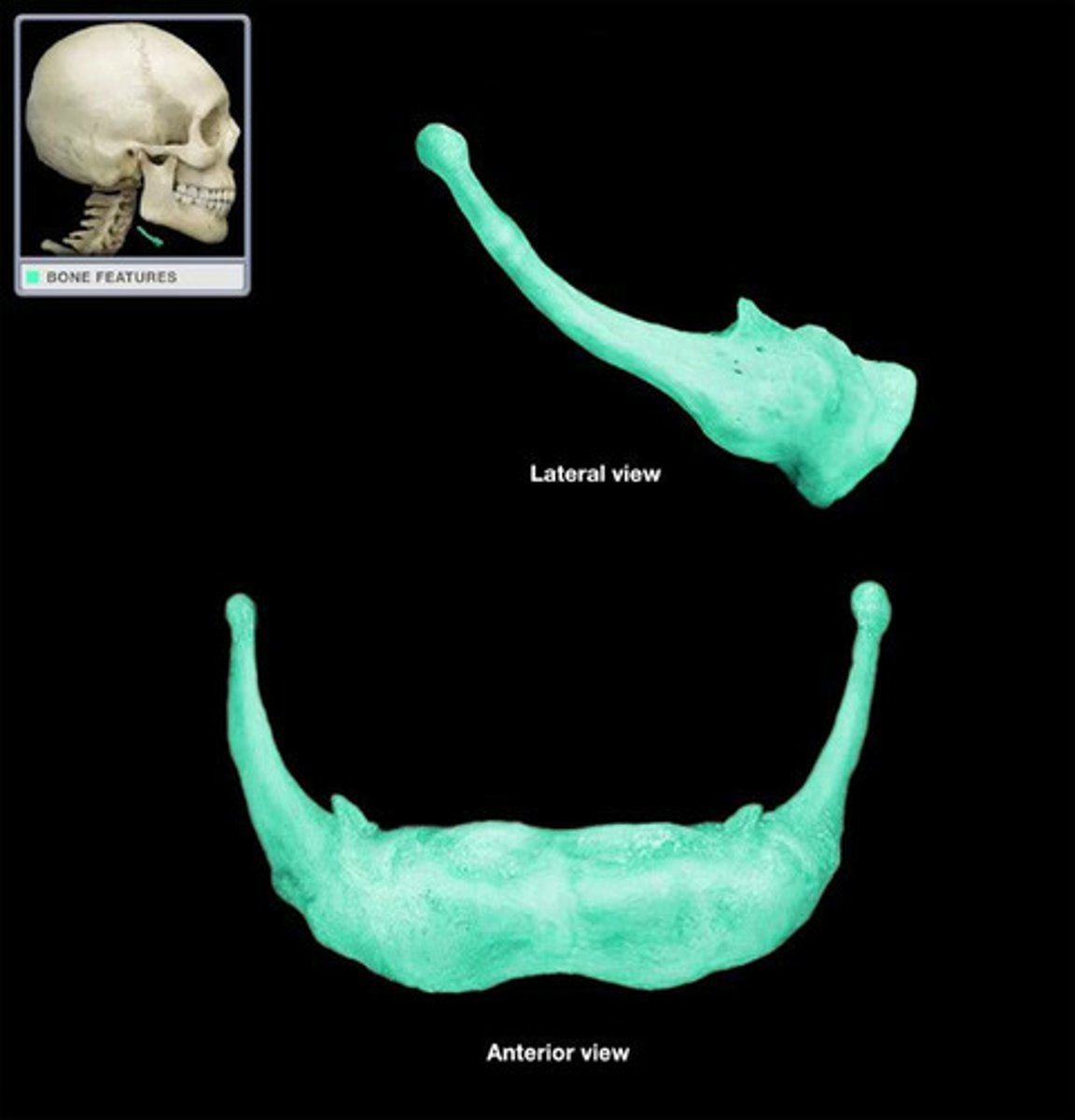
Hyoid
U-shaped bone in the neck supporting the tongue.
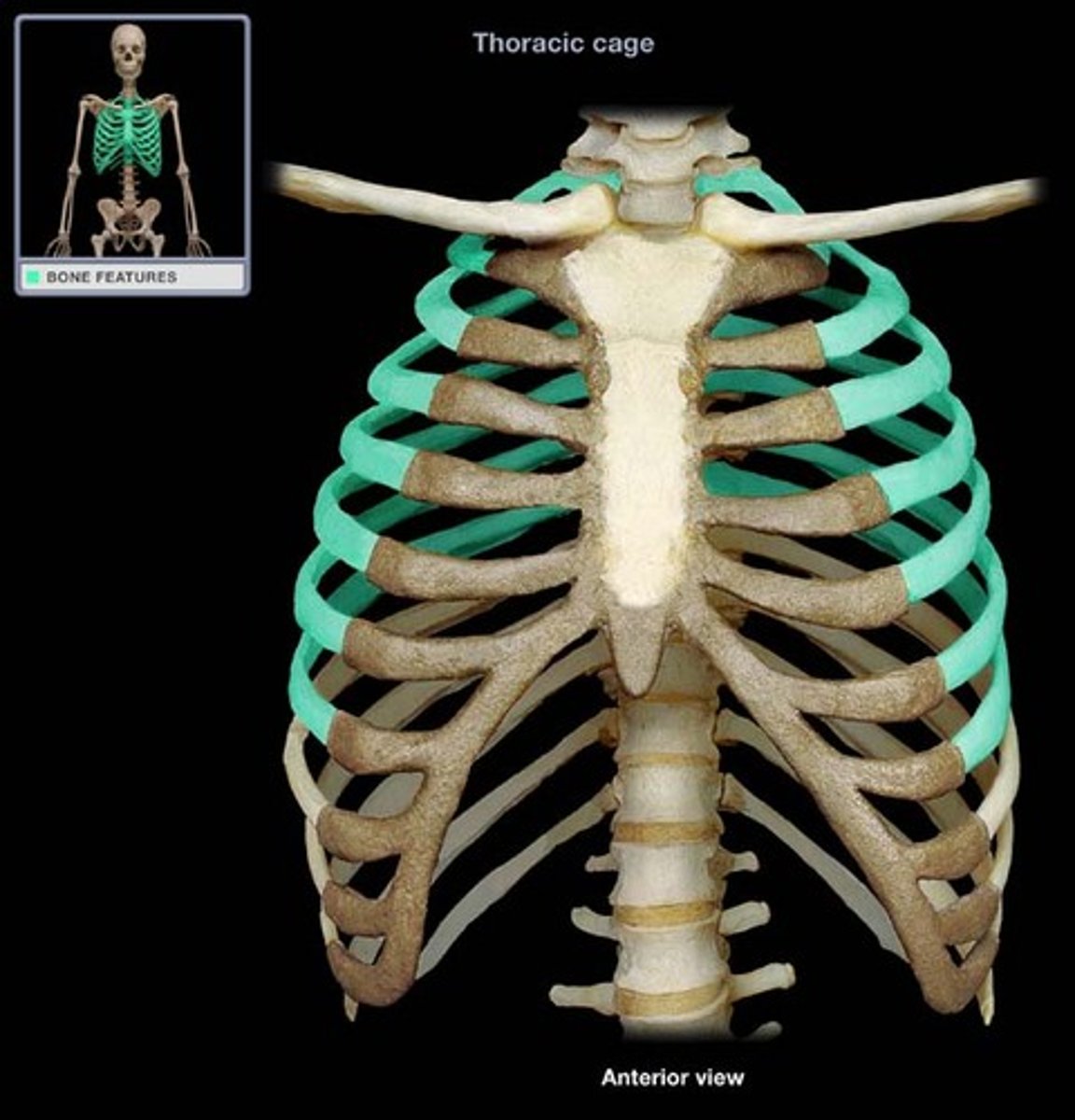
Ribs
Curved bones forming the rib cage.
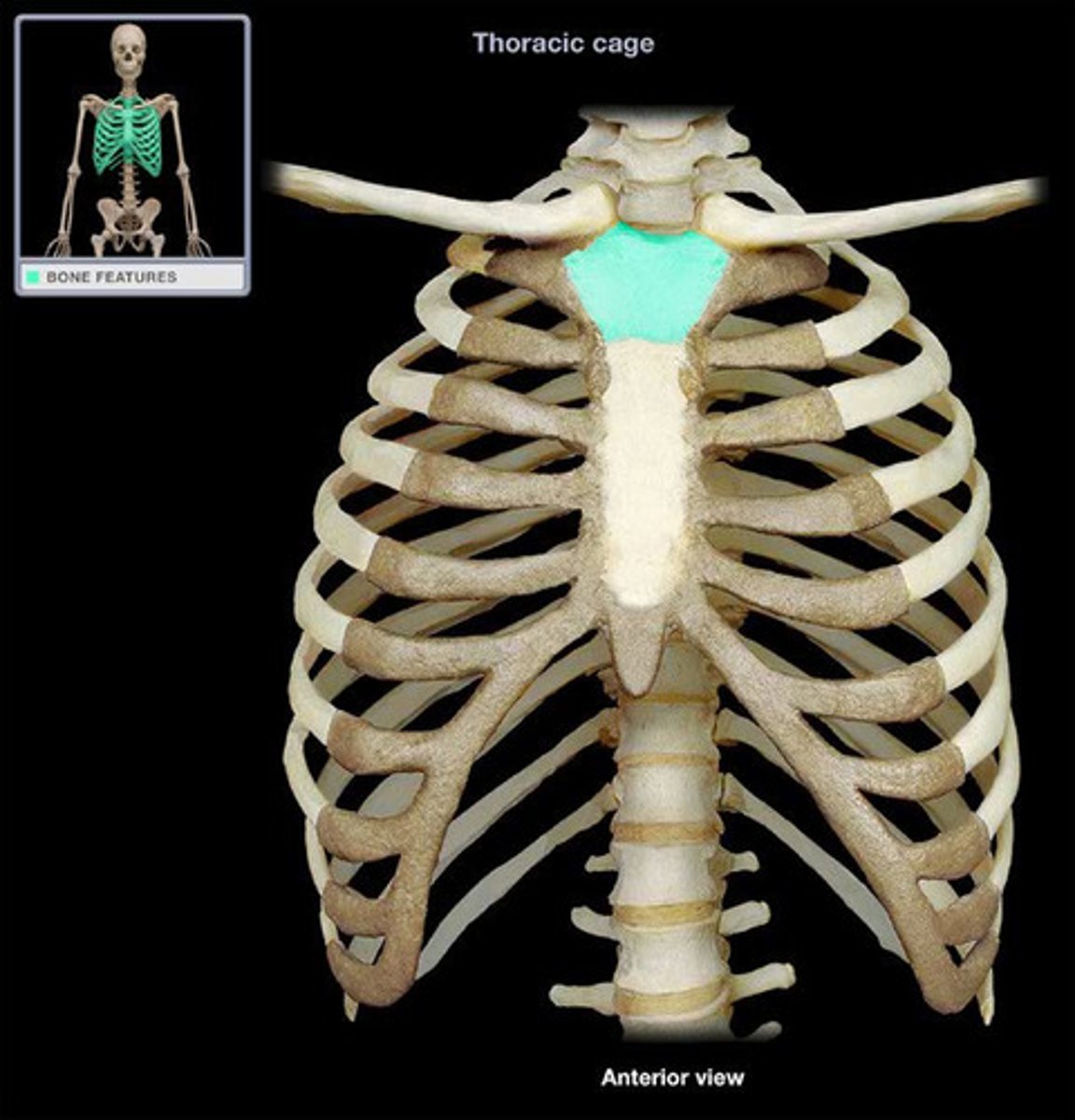
Manubrium
Upper part of the sternum.
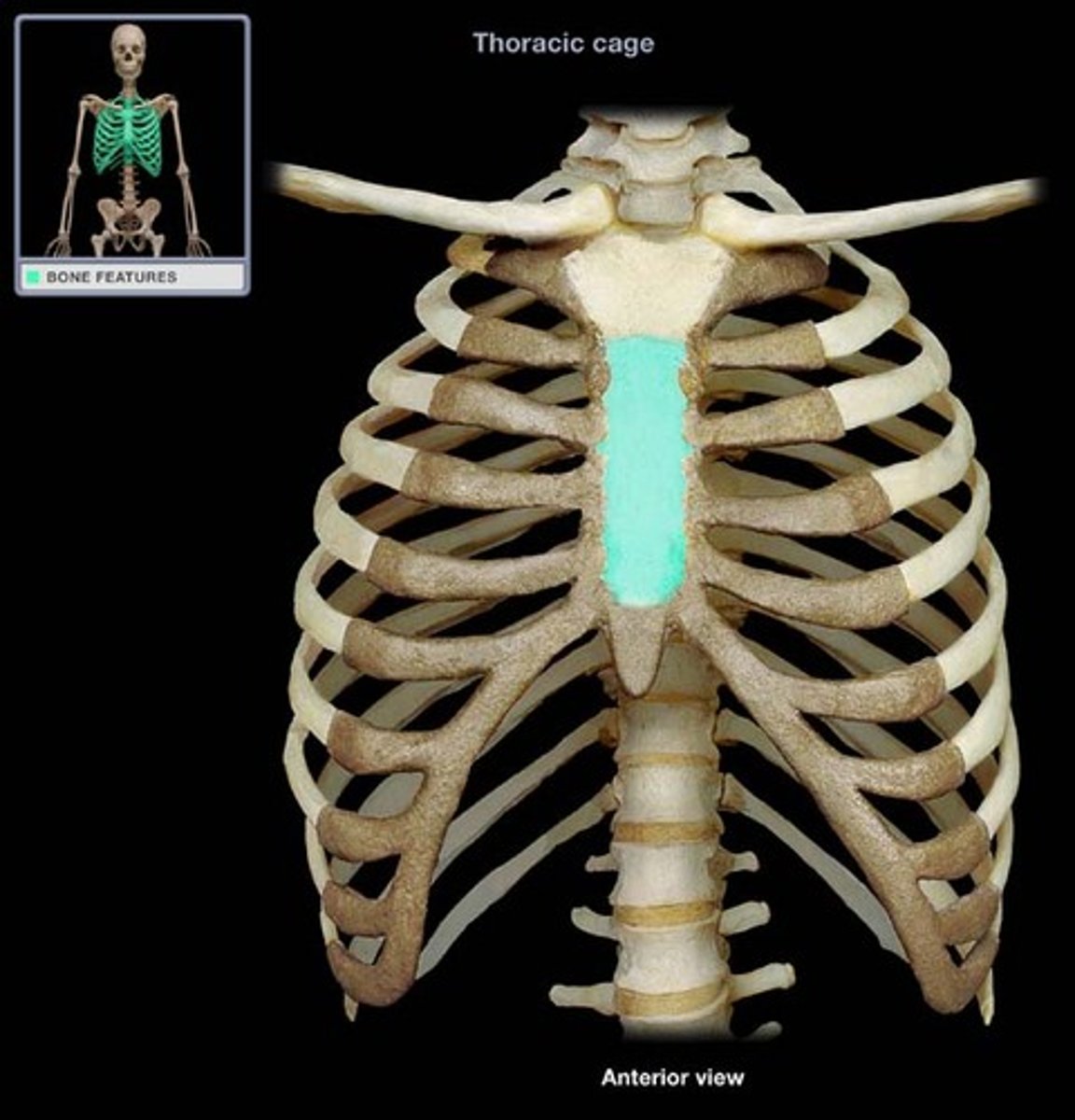
Body of sternum
Middle section of the sternum.
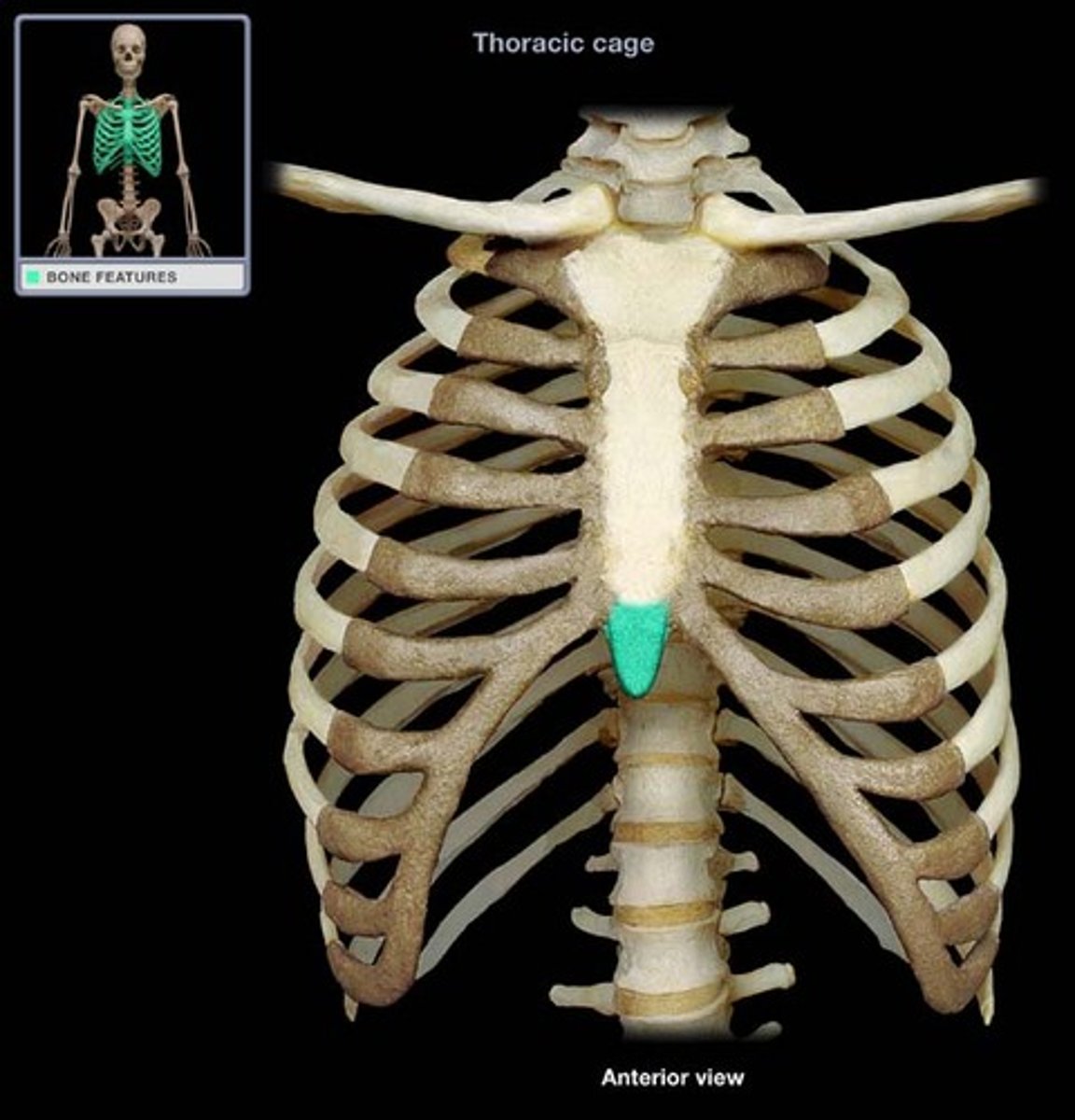
Xiphoid process
Lower tip of the sternum.
Jugular notch
Notch at the top of the sternum.
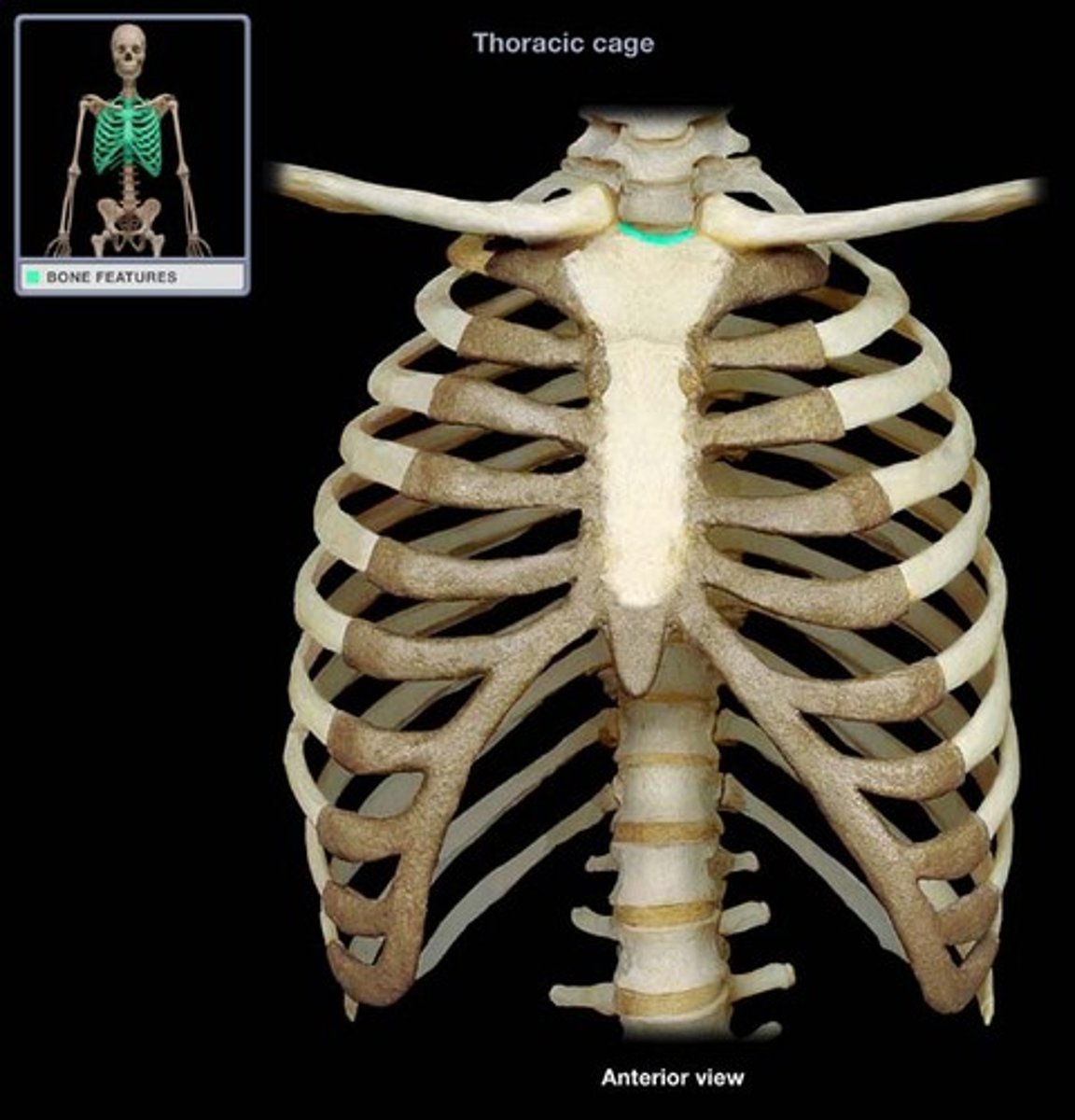
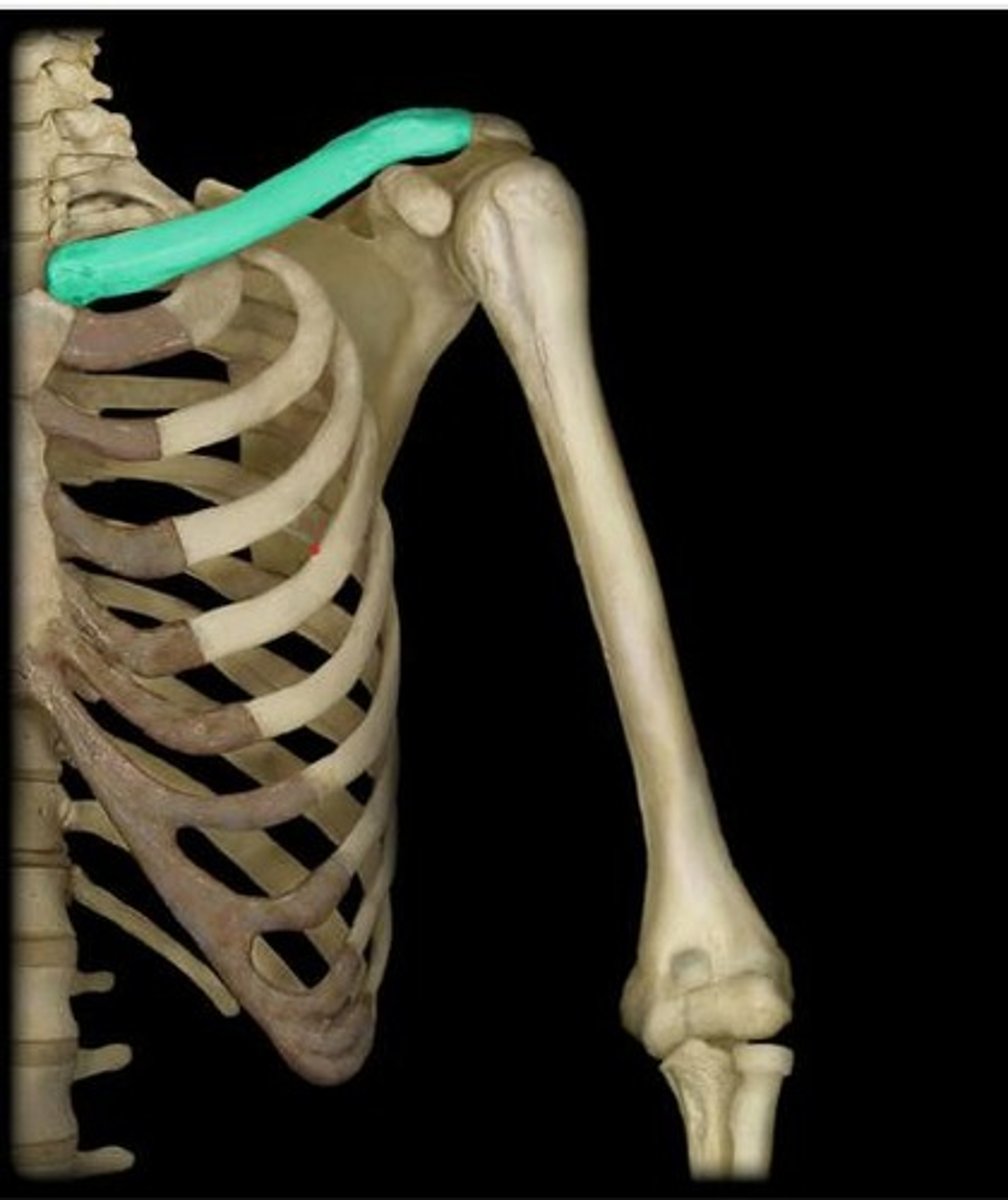
Clavicle
Collarbone connecting sternum to scapula.