W7 Hearing and Vestibular Senses
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is Reinforced Learning (RL)?
It is the process by which an agent (human, animal or machine) learns from experience to make good behavioral decisions
What is the goal of Reinforcement Learning (RL)?
to learn the best possible strategy for mapping states onto actions
What is Policy?
Strategy or set of rules for mapping states onto actions
How is Reinforced learning and Policy related to each other?
goal of RL is to optimize policy
What is Optimal Policy?
[in biology] maximizes reward and minimizes punishment over entire lifespan of organism
What is Return?
sum total of all the pleasure and pain that you will experience for the rest of your life
What is the mathematical expression of Return?
the temporally discounted sum of future reward
r > 0 = positive → reward
r < 0 = negative → punishment
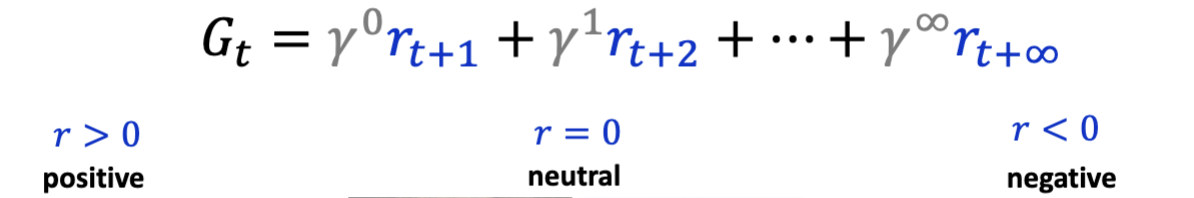
What is Temporal Discount Factor?
y is a value between 0 - 1 that gets progressively smaller over time.
in return equation, variable describes the fact that all else being equal, an earlier reward is preferred over a later reward
Amygdala is attaches ____ to ___ and ____
values to cues and states
What are the two roles of amygdala function?
Appetitive (reward driven) learning
Aversive (punishment driven) learning
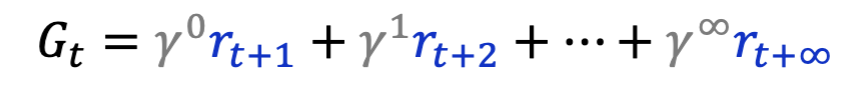
What is G_t in the temporally discounted sum of future reward?
stands for the actual sum of all our future pleasure and pain
prediction as accurately as possible. Cannot actually know with certainty
What is state value (V)?
expected G_t in the current state
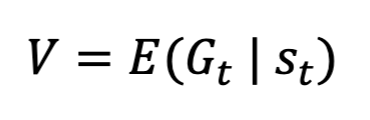
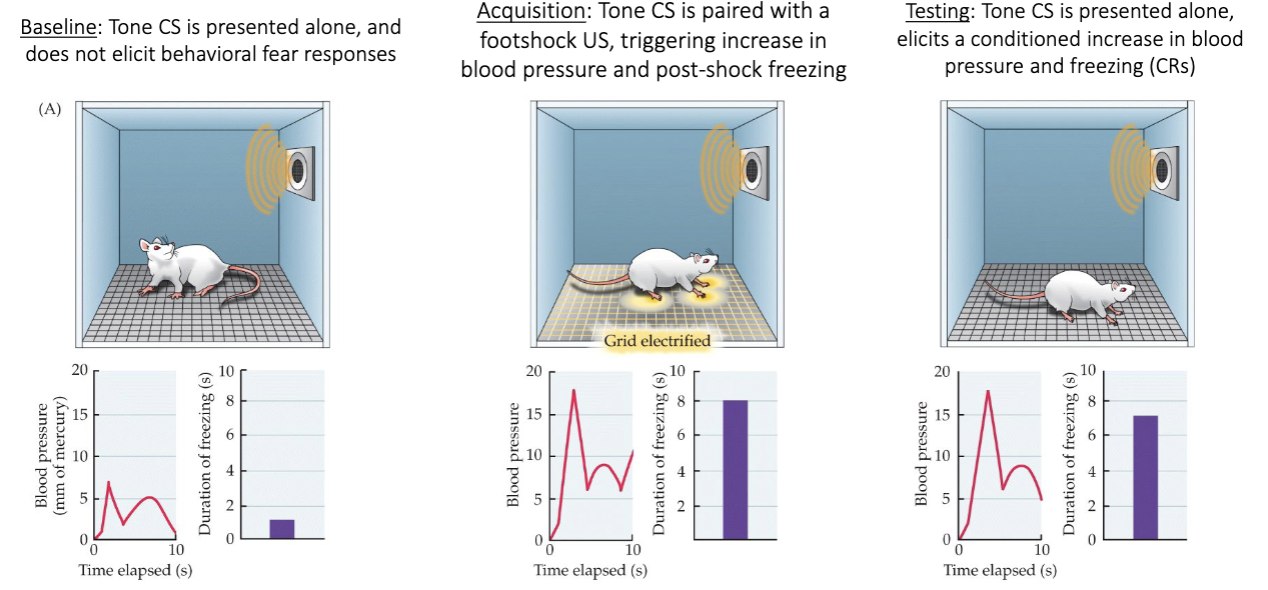
What is Pavlovian Fear Conditioning?
Process where people and animals can be trained to be afraid of cues that predict danger
What pathway does auditory information reach the vPAG so that a fear conditioned CS can trigger a freezing response after it has been paired with an aversive US?
bruin cast
ear → cochlear nucleus → vPAG
What part of the ear gathers sound waves from the environment?
Outer ear (Pinna and canal)
What do air molecules do when there is wind?
Air molecules are moving through space to new locations
What do air molecules do when there is sound?
Air molecules are perturbed, and then return to their original position
How do we perceive sound sensation?
Our tympanic membrane (eardrum) is stimulated by vibrating air molecules
What are pressure waves?
alternate cycles of compressed and rarified air
How do pressure waves propagate?
Air molecules provide as medium so pressure waves can propagate over long distances
What is amplitude?
Loudness
What kind of propagation of displacement of air molecules when there is a quiet sound?
small displacement
What kind of propagation of displacement of air molecules when there is a loud sound?
large displacement