Networks, IoT, and Cybersecurity in Management Information Systems
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Modem
A device that modulates/demodulates signal for transportation.
Modulation and Coding
Techniques used by modem to adapt the signal to the media.
Signal
Binary information we want to send.
Signal Frequency Spectrum
All the frequency components of a signal.
Bandwidth
Maximum bits per second that can be transmitted. This is how network speed/capacity is measured.
Circuit Switching
Older technology that originated with telephone calls; inefficient for digital transmission.
Packet Switching
Transfers data or voice; files are broken into packets, numbered sequentially, routed individually to their destinations, and reassembled at the destination.
Internet Protocol (IP)
The basic technology that makes global communication possible; each device attached to a network has a unique IP address that enables it to send and receive files made up of packets.
Intranet
Used within a company for data access, sharing, and collaboration.
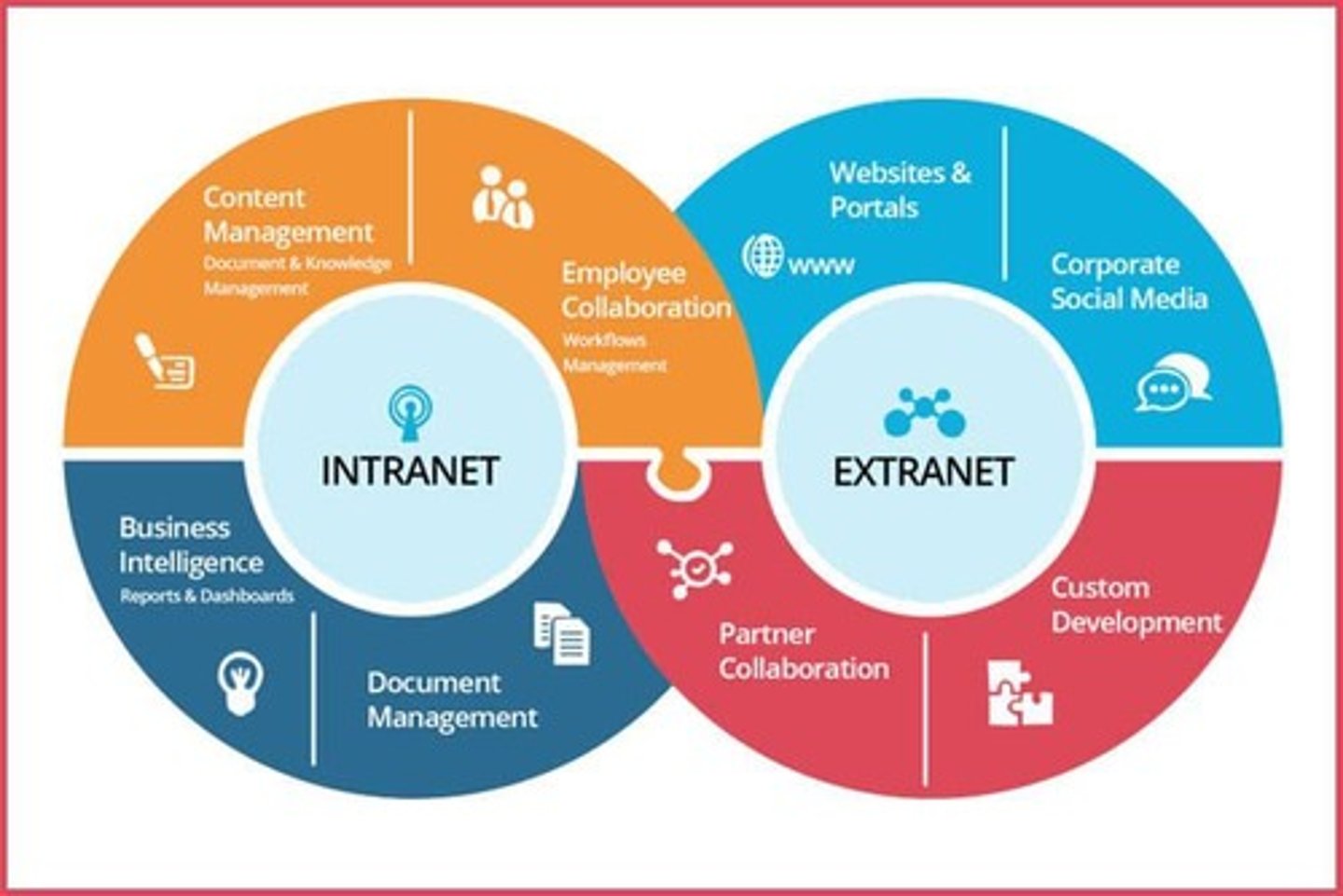
Extranet
Private, company-owned networks that can be logged into remotely via the Internet.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Used where security of transmissions is a concern, because they encrypt the packets before they are transferred over the network.
Quality of Service (QoS)
A measure of the overall performance of a network, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network.

Latency-sensitivity
Data such as real-time voice and high-quality video.
Prioritized Traffic
Data and apps that are time-delay-sensitive or latency-sensitive apps.
Throttle Traffic
Gives latency-sensitive apps priority; other types of traffic need to be held back (throttled).
Traffic Shaping
The ability to prioritize and throttle network traffic.
Bluetooth
Short-range wireless communication technology allowing device pairing.

Wi-Fi
Standard way to wirelessly connect computing devices through routers commonly connected to the Internet.
Cellular Data Networks
The 3G, LTE, 4G, and 5G cellular data networks that we use on mobile devices today.
Near-Field Communication (NFC)
Enables two devices within close proximity to establish a communication channel and transfer data using radio waves; more secure than other wireless technologies.
Examples of NFC
Apple watch, digital tickets providing access to concerts, transmit public transport payment through phones.

Internet of Things (IoT)
The network of physical objects embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity that enables data collection and exchange.
Cyberthreat
A threat posed by means of the Internet and the potential source of malicious attempts to damage or disrupt a computer network, system, or application.

Vulnerability
A gap in IT security defenses of a network, system, or application that can be exploited by a threat.
Incident
An attempted or successful unauthorized access to a network, system, or application; unwanted disruption or denial of service.
Data Breach
The successful retrieval of sensitive information by an individual, group, or software system.
Unintentional Cyberthreats
Cyberthreats caused by human error, poorly designed systems, faulty programming, and environmental hazards.
Intentional Cyberthreats
Cyberthreats that are deliberately caused, including hacking, phishing, and crimeware.

Hacking
Intentionally accessing a computer without authorization or exceeding authorized access.
White Hat
A computer security specialist who breaks into protected systems to test and assess their security.
Black Hat
A person who attempts to find computer security vulnerabilities and exploit them for personal or financial gain.
Gray Hat
A person who may violate ethical standards but without malicious intent.
Hacktivist
is short for hacker-activist, or someone who performs hacking to promote awareness, or otherwise support a social, political, economic, or other cause.
Malware
refers to hostile or intrusive software, including computer viruses, rootkits, worms, Trojan horses, ransomware, and other malicious programs used to disrupt computer or mobile operations, gather sensitive information, gain access to private computer systems.
Spyware
is tracking software that is not designed to intentionally damage or disable a system but to monitor or track activities.
Adware
is software that embeds advertisement in the application.
Ransomware
is a type of malware that is designed to block access to a computer system until a sum of money has been paid.
Botnet
is a group of external attacking entities and is a totally different attack method/vector from malware, which is internal to the system.
Zombies
are a group of infected computers that can be controlled and organized into a network on the command of a remote botmaster (also called a bot herder).
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)
crashes a network or website by bombarding it with traffic (i.e., requests for service) and effectively denies service to all those legitimately using it.
Telephony Denial-of-Service (TDOS)
floods a network with phone calls and keeps the calls up for long durations to overwhelm an agent or circuit and prevent legitimate callers from using network resources.
Permanent Denial-of-Service (PDOS)
prevents the target's system or device from working, aiming to completely prevent the target's device(s) from functioning.
Data tampering
is a common means of internal attack, referring to an attack during which someone enters false or fraudulent data into a computer, or changes/deletes existing data.
Insider and Privilege Misuse
is a form of intentional cyberthreats that involves employees misusing their access privileges.
Physical Theft
is a form of intentional cyberthreat involving the physical stealing of devices or data.
Phishing
is a form of intentional cyberthreat that involves tricking individuals into providing sensitive information.
Crimeware
is a term that encompasses various forms of malware used for criminal activities.
Internal Threats
Threats from employees that can be some of the most challenging to defend against.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
Launched by attackers through phishing to gain access to an enterprise's network, designed for long-term espionage.

Hackers and Hacktivists
Individuals or groups who carry out high-profile attacks to further their personal agendas.
Social Engineering
All techniques aimed at talking a target into revealing specific information or performing a specific action for illegitimate reasons.
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
Employees providing their own (mobile) devices for business purposes to reduce expenses through cut purchase and maintenance costs.
BYOD Usage Rate
Roughly 74% of U.S. organizations are using or planning to use BYOD.
BYOD Cost Benefit
Cuts business costs by not having to purchase and maintain employees' mobile devices.
BYOD Security Risks
Mobile devices rarely have strong authentication, access controls, and encryption even though they connect to mission-critical data and cloud services.
Social Media Vulnerabilities
Social networks and cloud computing increase vulnerabilities by providing a single point of failure and attack for organized criminal networks.
Social Media-related Events
FBI reports that social media-related events have quadrupled over the past five years.
Business continuity
Maintaining business functions or restoring them quickly when there is a major disruption.
Business continuity plan
Covers business processes, assets, human resources, and business partners to keep the business running after a disaster occurs.

Types of disasters covered by business continuity planning
Includes fires, earthquakes, floods, power outages, malicious attacks, and other types of disasters.
Risk (in cyber risk management)
Quantified as the probability of a threat successfully exploiting a vulnerability multiplied by the estimated cost of the loss or damage.

Probable Maximum Loss (PML)
A calculation executed to determine the cost of security, defined as Probability x total cost of harm.
Factors leading to increased risk of cyberattack
Includes interconnected, interdependent, wirelessly networked business environment; smaller, faster, cheaper computers and storage devices; decreasing skills necessary to be a computer hacker; and international organized crime taking over cybercrime.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs)
Scans for unusual or suspicious traffic as a passive defense.

Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPSS)
Designed to take immediate action, such as blocking specific IP addresses, whenever a traffic-flow anomaly is detected as an active defense.

Antivirus Software
Designed to detect malicious codes and prevent users from downloading them.
Blockchain
A system comprised of transactions, immutable ledgers, decentralized peers, encryption processes, consensus mechanisms, and optional smart contracts.
Distributed ledger
Represented by a sequential chain of data blocks that records transactions, establishes identity of the user, and establishes contracts.

Decentralized peers
In a blockchain, each NODE has a copy of the ledger, contrasting with a centralized 'Hub and Spoke' type of network.
Consensus in blockchain
Ensures that the next block in a blockchain is the one and only version of the truth and keeps powerful adversaries from derailing the system.
Proof of Work (POW)
A consensus mechanism where the miner gets block rewards based on the amount of work they have done.
Proof of Stake (POS)
A consensus mechanism where a new block creator is selected based on the number of coins they hold, and miners only take transaction fees.
Mining pools
Groups of miners that work together to increase efficiency.
Cost-effectiveness of POS
POS is decentralized and very cost-effective.