Non-ruminant stomach and oesophagus
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
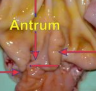
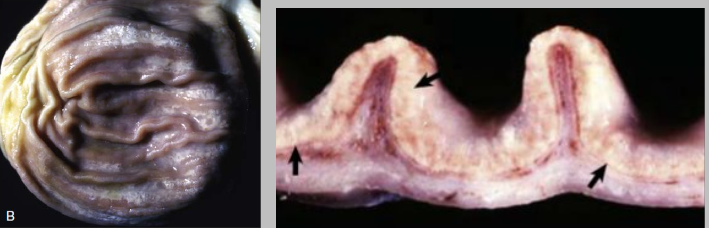
Name the normal structure in the pig stomach pointed by the arrow on the right
Torus
What is the pathophysiology of oesophagitis
Oesophageal mucosa inflammation
Usually due to acid reflux (weak sphincter, herniation, oesophageal mucosal metaplasia)
Iatrogenic (doxycycline in cats, regurgitation during general anaesthetic)
Can result in stricture
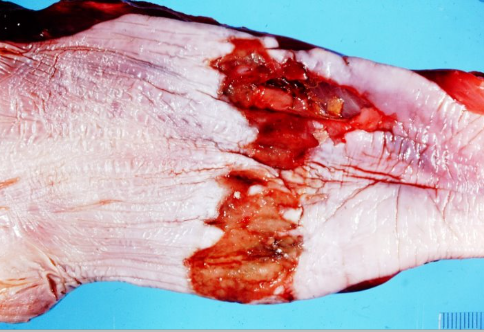
What is this oesophageal disease and its nature
Choke - caused by trauma
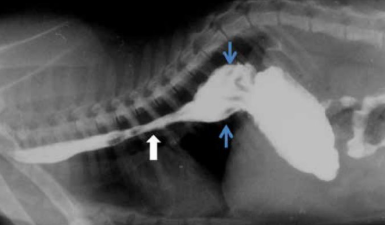
What is this condition in a dog, clinical signs and breed predisposition?
Persistent right aortic arch - German shepherds
Causes oesophageal dilation cranial to stricture
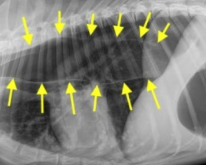
What condition causes diffuse megaoesophagus and its pathophysiology and sequalae
Myasthenia gravis
Congenital
Idiopathic - antibodies produced against acetylcholine receptor (secondary to thymus tumours)
= aspiration pneumonia so needs to be fed upright

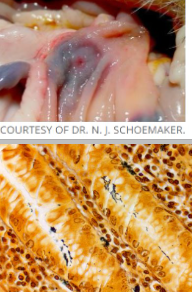
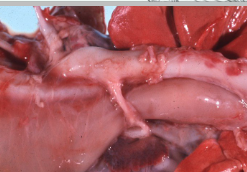
What is this condition in a ferret and its causative agent?
Gastritis - gastric ulcers
Helicobacter mustelae (low numbers normal in cats and dogs)
Shows up on silver stain (Warthin-Starry)
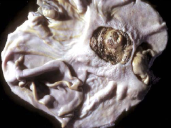
What does this pig have? 3 possible differential causes.
stomach ulcer (affects non-glandular oesophageal portion)
incorrect feed
stress
NSAIDs
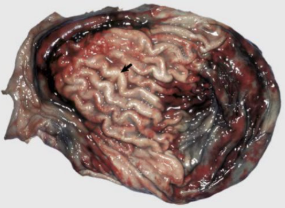
What is this condition linked to azotaemia and explain its pathogenesis.
uraemic gastropathy.
metabolic condition due to build up of urea and creatinine. These toxins are leached into saliva and gastric secretions, metabolised into ammonia and cause ulceration of the mucousa.
Endothelial damage from toxins in the blood vessels too.
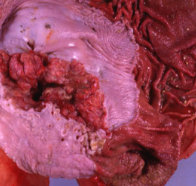
What is this condition caused by? Describe the pathogenesis.
Renal failure
high phosphate and acidosis leads to calcium being deposited in soft tissues, especially the stomach.
What condition does this horse have?
Squamous cell carcinoma
List 5 other neoplastic conditions the stomach can get
Adenocarcinoma
Leiomyoma/sarcoma
Gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Lymphoma
Carcinoids
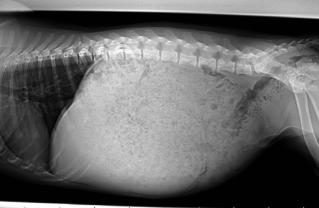
What has happened to this dog?
Gorged on kibble = gastric dilation and distention
Another cause of bloat in a dog. Pathogenesis, sequalae
Gastric dilation and volvulus
Incomplete understanding of pathogenesis. Maybe volvulus occurs first
Compression of caudal vena cava = stomach and splenic necrosis
Fluid lost into stomach = metabolic acidosis, hypovolaemic shock
Clinical emergency
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Most common cause of gastric dilation in horse. Explain the pathogenesis.
Grass sickness - Clostridium botulinum
Causes loss of autonomic neurons, therefore no peristalsis.
Motility disorders tend to result in gastric dilation.
Obstructive colic results in lumen filling with fluid.
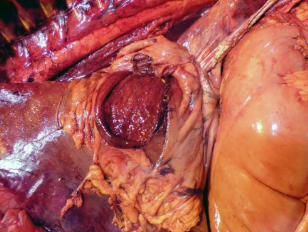
How can you tell this gastric perforation occurred before or after death?
Before death - there is sign of haemorrhage, inflammation and necrosis