Communicable Diseases
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Measles (Rubeola)
•Highly contagious, spread through droplet contagion and secretion contact
Fever, URI symptoms, sore throat, Koplik spots
•Complications – Pneumonia, encephalitis
•Prevention: MMR vaccine – 2 doses
•Treatment: symptomatic, antibiotics if pneumonia occurs
•Reportable to departments of health
Rubella
•Viral – Most contagious during the 7 days before rash appears
•Patients should avoid any pregnant women
•Mild rash, fever and swollen lymph nodes
•Headache, URI, Sore throat
•Complications: miscarriage if exposed during pregnancy
•Can cause temporary and extreme joint pain
•Rare: brain infection
Roseola (6th disease)
•Viral - Human herpesvirus 6 or 7 - Most contagious 6 mo. – 2 yr.
•Onset 5-15 days after
•High fever x 3-7 days
•Rash after fever subsides, irritability, anorexia, URI symptoms
•Dx. From symptoms
•Self-limited, symptomatic care
•Complications are rare – febrile seizures
Chickenpox (varicella)
•Highly contagious – Varicella Zoster – Vaccine prevention
Immune following clinical case of chickenpox
•URI symptoms – Contagious from 2 days before rash through scabbing
•Fever, fatigue, headache, anorexia, itchy rash
•Rash – eraser size/color rash - smooth
•Complications – Bacterial pneumonia, encephalitis, Reye’s syndrome risk
•Treatment – Antivirals, Calamine/Benadryl for itch, OTC pain relief
Oatmeal bath, Short nails (cover hands of babies), Symptomatic care
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
•Highly contagious – Vaccine prevention (DTaP)
•Bacterial infection (Bordetella pertussis) – Most contagious under 5 yoa
•Multi-week illness
•Early stage 1-2 weeks, mild URI symptoms
•Paroxysmal stage 2-5 weeks, Severe, unrelenting cough. High-pitched sound of cough. “Whoops” with no break in the cough. Can fracture ribs.
•Convalescent stage (Many weeks) will ultimately fade and resolve
•Complications – Pneumonia, Pregnancy complications, Brain damage, Death.
•Treatment – Azythromycin, fluids and oxygen
Mumps - parotitis
•Viral
•Starts with fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue & anorexia
•Puffy cheeks and swollen jaw
•Onset 2-4 weeks following exposure
•2 week recovery
•Symptomatic Care
•“Locker Room” contagion
•Severe complications rare (can be fatal)
– inflammation of testes, ovaries, brain and pancreas, Loss of hearing
Strep Throat
•Bacterial – Group A Strep
•Settles in the tonsils and throat
•Treatment – Antibiotics – Complete entire regimen and retest
•Complications – Cardiac damage if not cleared – Rheumatic Heart Disease (damages heart valves – Common between ages 5 & 15)
•Symptoms
Severe sore throat, Fever, Swollen lymph nodes of neck/jaw, White or yellow patches in the throat – foul odor, Headache, Nausea and vomiting, Rash – Feels like sandpaper
Otitis
•Primary cause – obstruction of eustachian tube/s (infection, swelling, fluid build-up
•Young immune systems predispose children to this
•Enlarged adenoids
•Antibiotics, pain medications, positional support, surgery
Otitis Media
Middle Ear (Reddened inflamed membrane)
Otitis Externa
Outer Ear (Swimmers Ear)
Otitis Externa (swimmers ear)
•Prescription antibiotic and steroid drops x 10-14 days
•Pain relievers
•Prevent from exposure to water
•Cool hair dryer to dehydrate ear
•Don’t insert anything into the ear
•Lasts 7-10 days with careful treatment
•Hydrogen peroxide to manage ear wax build up and prevent
Gastroenteritis (rotavirus)
•Drug of choice
Amoxicillin, Augmentin, Rocephin
HIV - AIDS management
•Maternal - Prevention – exposure can be from sexual activity or assault, STI’s
•Prenatal testing on all mothers during prenatal period
•Treatment of mother – antiretrovirals during pregnancy and after (suppresses the virus)
•No breast feeding – primary route of transmission to child.
•Treatment of infants and children – antiretrovirals
•Counseling, on-going support and group support
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)
•Known or unknown maternal substance use/exposure
•Symptoms: Continual/excessive high-pitched cry
•Tremors or shaking
•Lack of interest in being held
•Uncoordinated suck/feed
•High pitched cry – not soothed by touch
•Trouble sleeping
•Rapid breathing, sneezing, stuffy nose
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS) Interventions
•Treat with small amounts of drug similar to exposure drug
•Titrate downward
•Co-room with mother if possible
•Quiet darkened room
•Swaddle
•Gentle rocking – minimal touch
•Frequent small feedings with high calorie formula
•Post-discharge support of family
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
•Inability to breakdown amino acid phenylalanine
•Low PHE diet
•Inherited disorder – 1 in every 10,000-15,000 births
•Commonly found in foods
•If not identified/treated children will show no interest in their surroundings, developmental delays occur, pale skin tone, weak.
•Identified via newborn screening
Phenylketonuria (PKU) foods to avoid
Animal protein, Dairy, Legumes, Wheat, oats, barley and Aspartame (artificial sweetener).
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Foods to eat
Fruits, vegetables, butter, margarine, olive oil herbs for flavor and low-protein foods
Hyperbilirubinemia definition
•Presents as newborn jaundice, hemolytic anemia, liver disease
•The immature liver cannot process bilirubin effectively
•More common in preemie babies and breastfed babies
Hyperbilirubinemia nursing
•Treatment: Phototherapy, Exchange transfusion and medications
•Goal – Eat and stool to clear the bilirubin
•TCBM used to screen – Blood draws to validate
•Continual evaluation until WNL
Plagiocephaly
•Flat head on one side, Occurs due to uneven rotation of head, and Pressure on the developing skull causes the misshaping
•Can be positional or congenital
•Treatment Positional:
Increase position on opposite side of head and use pillows or wedges to position
Avoid prolonged sitting in car seat/swing
Congenital:
Surgery to re-form skull or helmet fitting
Meningocele, myelomeningocele
•Neural tube defect that occurs at week 3-4 of development
•Incomplete closure/containment of spinal canal
•Presents at birth - Causes sensory/neuromuscular dysfunction
•Causative factors – Illicit drug exposure, malnutrition of pregnancy lack of Folic Acid during pregnancy
•Radiation/chemical exposure during birth
•Pre-pregnancy obesity, DM, hyperthermia exposure, low B12
Meningocele, myelomeningocele definition
•Neural tube defect that occurs at week 3-4 of development
Trisomy
•3 copies of a usual chromosome rather than 2
•Down Syndrome
•Trisomy 13
•Trisomy 18
Monosomy
•Missing 1 chromosome from a pair (Monosomy X/Turner Syndrome
Trisomy and Monosomy manifestations
•Developmental delays or learning problems
•Heart, kidney or organic defects
•Facial differences, Cleft lip and palate
•Neurologic differences - Seizures
Trisomy and monosomy management
prenatal care
screening before and during pregnancy
early intervention - school districts
home care - G&D surveillance, OT, PT, group supports
Neonatal Sepsis
•Life-threatening blood infection in babies within the first 90 days of life (can be bacterial, viral or fungal – Early onset w/I 7 days of birth
Neonatal Sepsis risk factors
•Premature birth, low birth weight, poor prenatal care, prolonged ROM
Neonatal Sepsis symptoms
• fever or low body temperature, lethargy or irritability, difficulty breathing, poor feeding, vomiting and diarrhea, seizures, rashes.
Neonatal Sepsis diagnostics
•blood culture, urine culture, CSF culture (LP) and physical examinations
Neonatal Sepsis treatment
•IV antibiotics, antivirals and/or antifungals
Failure to thrive definition
•Insufficient growth and development in babies and children (can occur in adults)
Failure to thrive symptoms
•Faltering growth, insufficient weight
•Irritability
•Easily fatigued
•Excessive sleep
•Does not vocalize
•Lack of interest in life/family
Failure to thrive cause
•insufficient nutrition, medical conditions, Environment
Failure to thrive Intervention
•Often easily reversed with aggressive attention to quality diet, stimulation and therapeutic movement/stimulation
•Evaluate underlying causes and treat them:
•Illness, Neglect, Abuse, Malnutrition, Malabsorption, Lack of resources, Lack of knowledge
Measles (Rubeola) hallmark signs
•Fever, URI symptoms, sore throat, Koplik spots
Congenital rubella syndrome
transmitted to mother, born with birth defects; hearing loss, blindness, heart defects and developmental delays.
Rubella hallmark signs
•Mild rash, fever and swollen lymph nodes
•Headache, URI, Sore throat
Roseola (6th disease)
High fever x 3-7 days
•Rash after fever subsides, irritability, anorexia, URI symptoms
Chickenpox (varicella) hallmark signs
•URI symptoms – Contagious from 2 days before rash through scabbing
•Fever, fatigue, headache, anorexia, itchy rash
•Rash – eraser size/color rash - smooth
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) early stage
1-2 weeks, mild URI symptoms
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) paroxysmal stage
2-5 weeks, Severe, unrelenting cough. High-pitched sound of cough. “Whoops” with no break in the cough. Can fracture ribs.
Pertussis (whooping cough) convalescent stage
Many weeks - will ultimately fade and resolve
Mumps - Parotitis hallmark signs
•Starts with fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue & anorexia
•Puffy cheeks and swollen jaw
•Onset 2-4 weeks following exposure
Strep Throat hallmark signs
•Severe sore throat, Fever, Swollen lymph nodes of neck/jaw, White or yellow patches in the throat – foul odor, Headache, Nausea and vomiting, Rash – Feels like sandpaper
MMR vaccine
measles prevention
Varicella Zoster vaccine
chickenpox prevention
DTaP vaccine
Pertussis (whooping cough) prevention
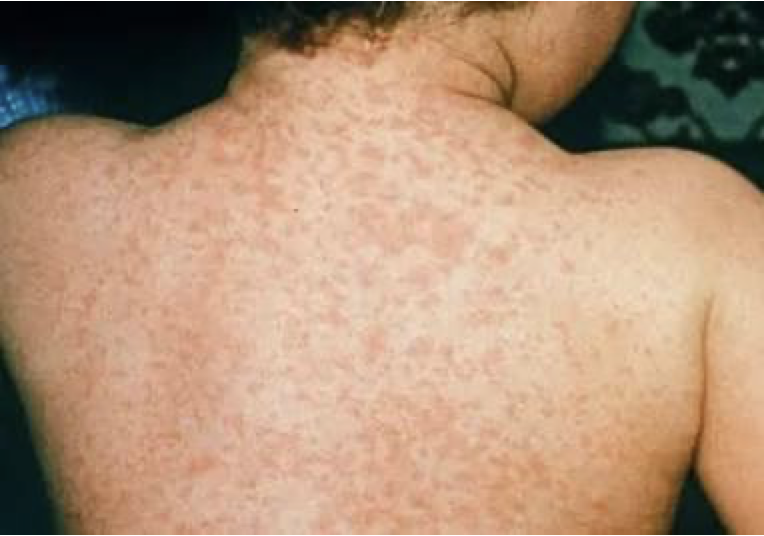
Rubeola rash
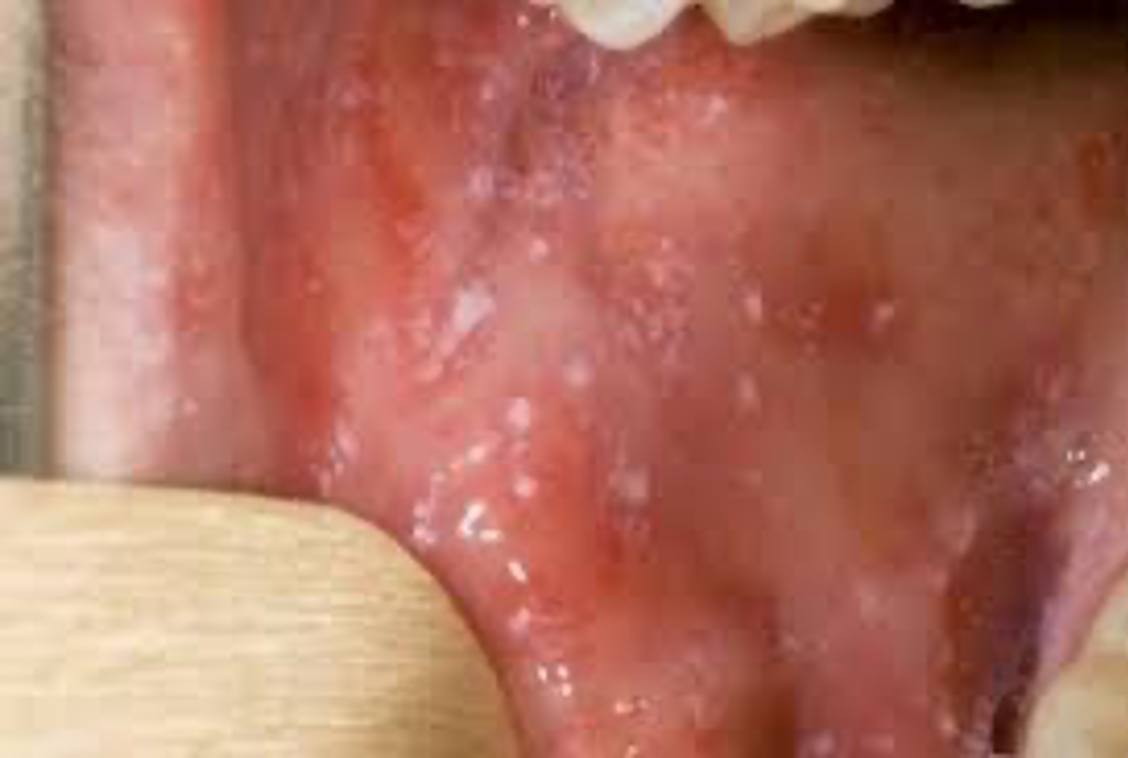
Kopliks Spots
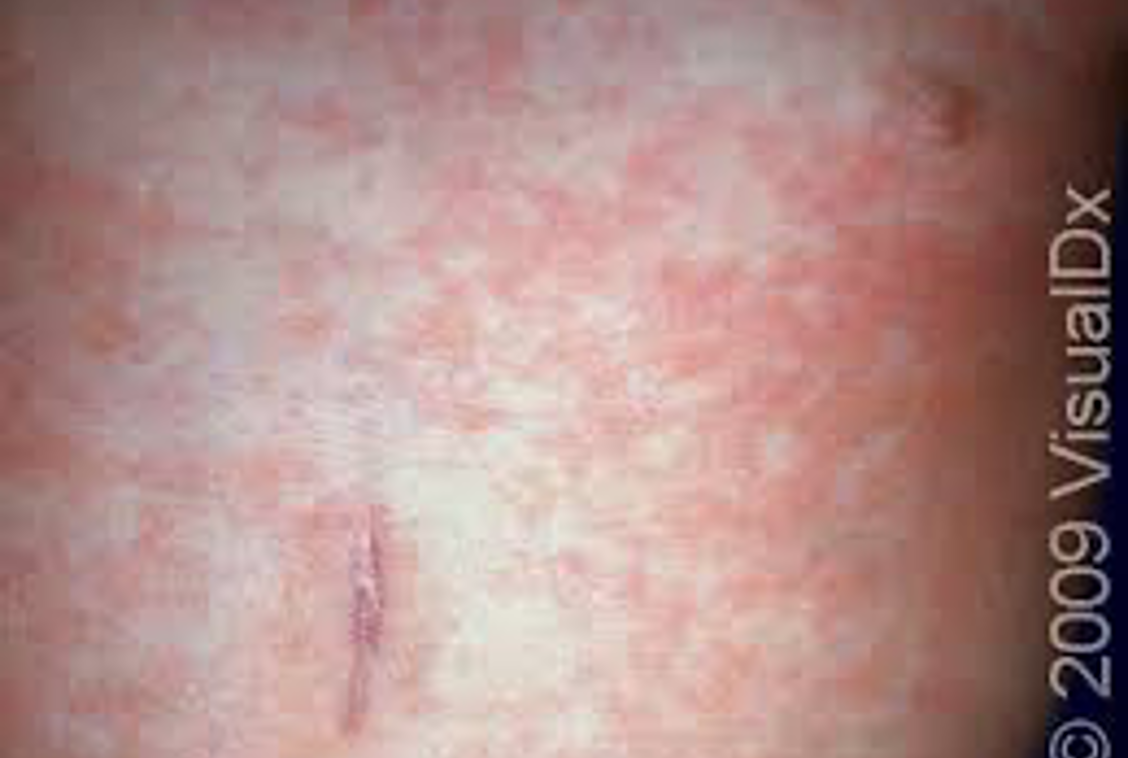
Roseola rash
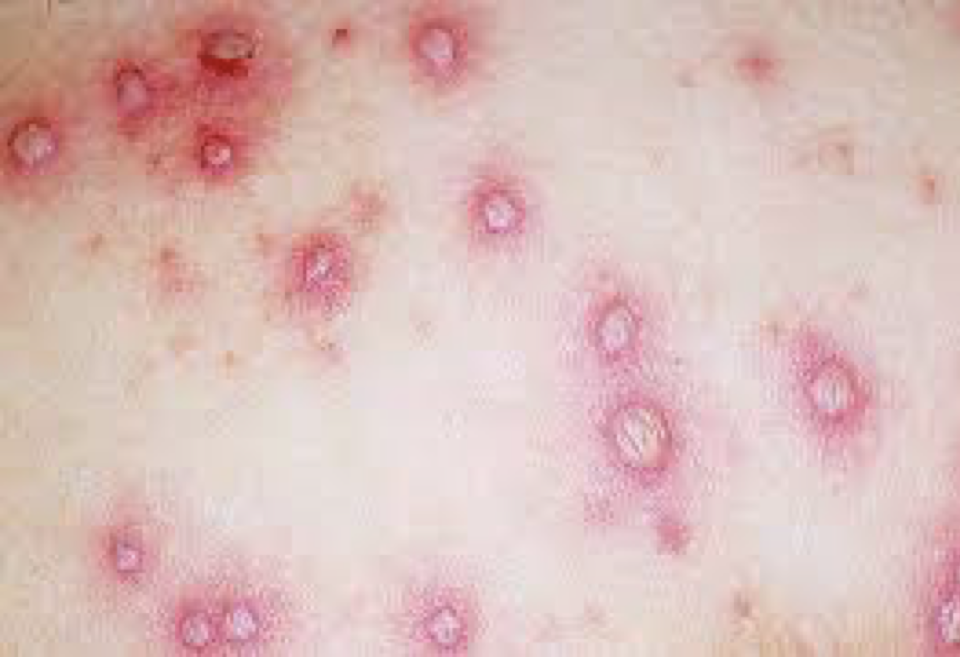
Varicella rash
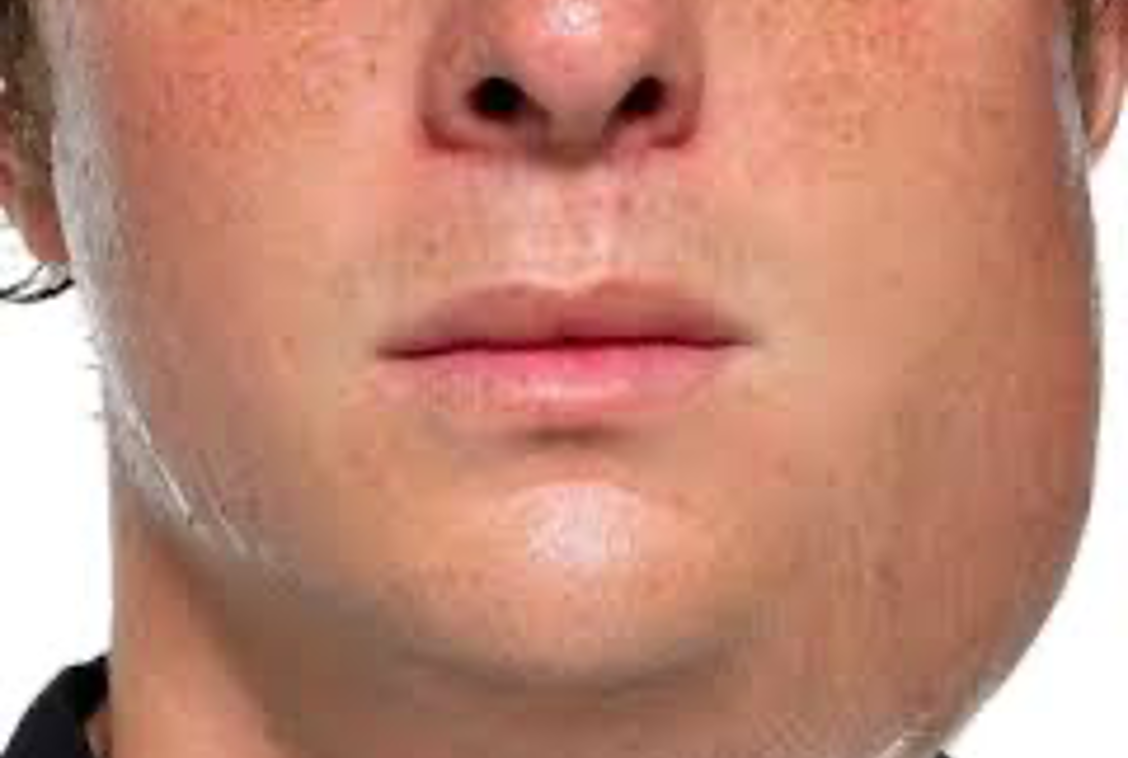
Mumps
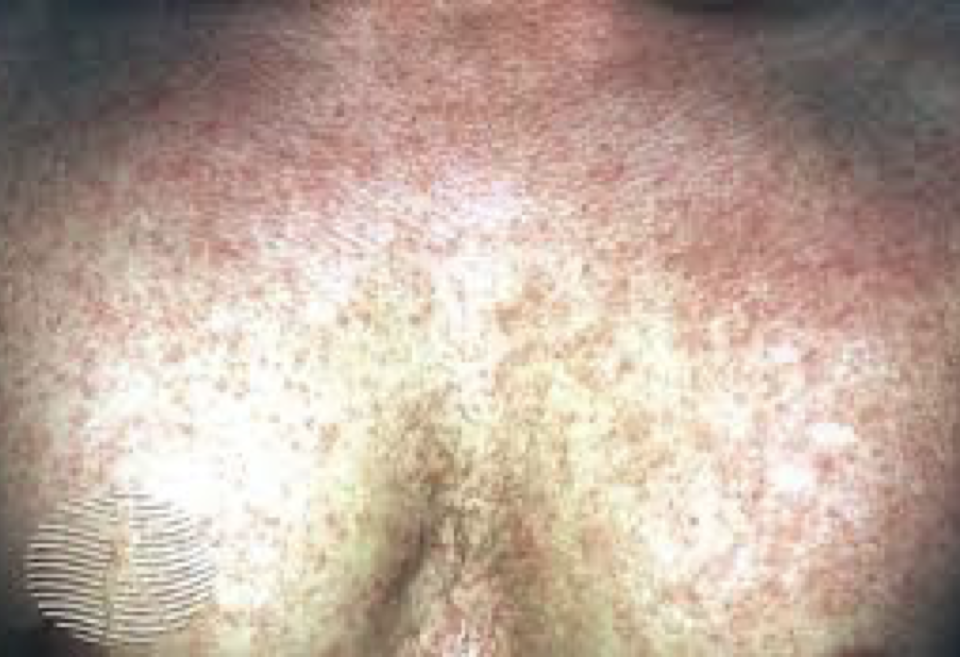
strep
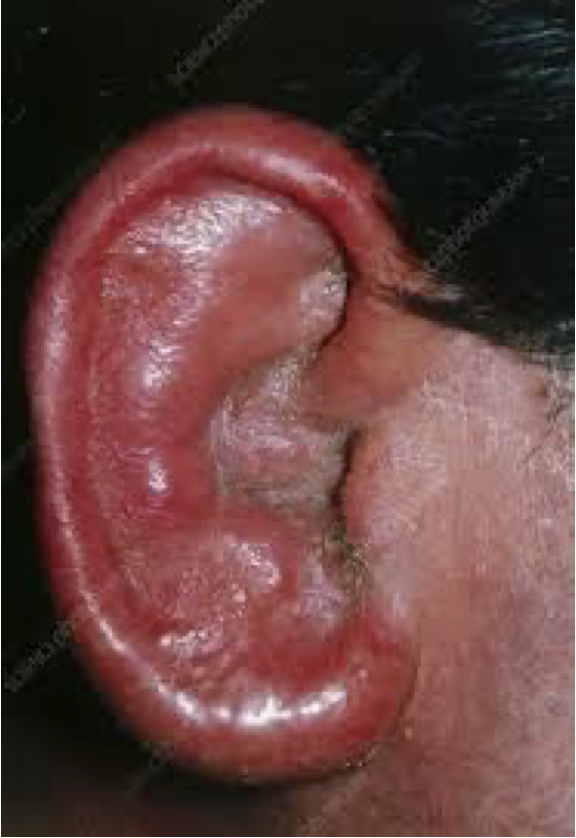
Otitis Externa