3) Foundation Systems
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Foundations and footings
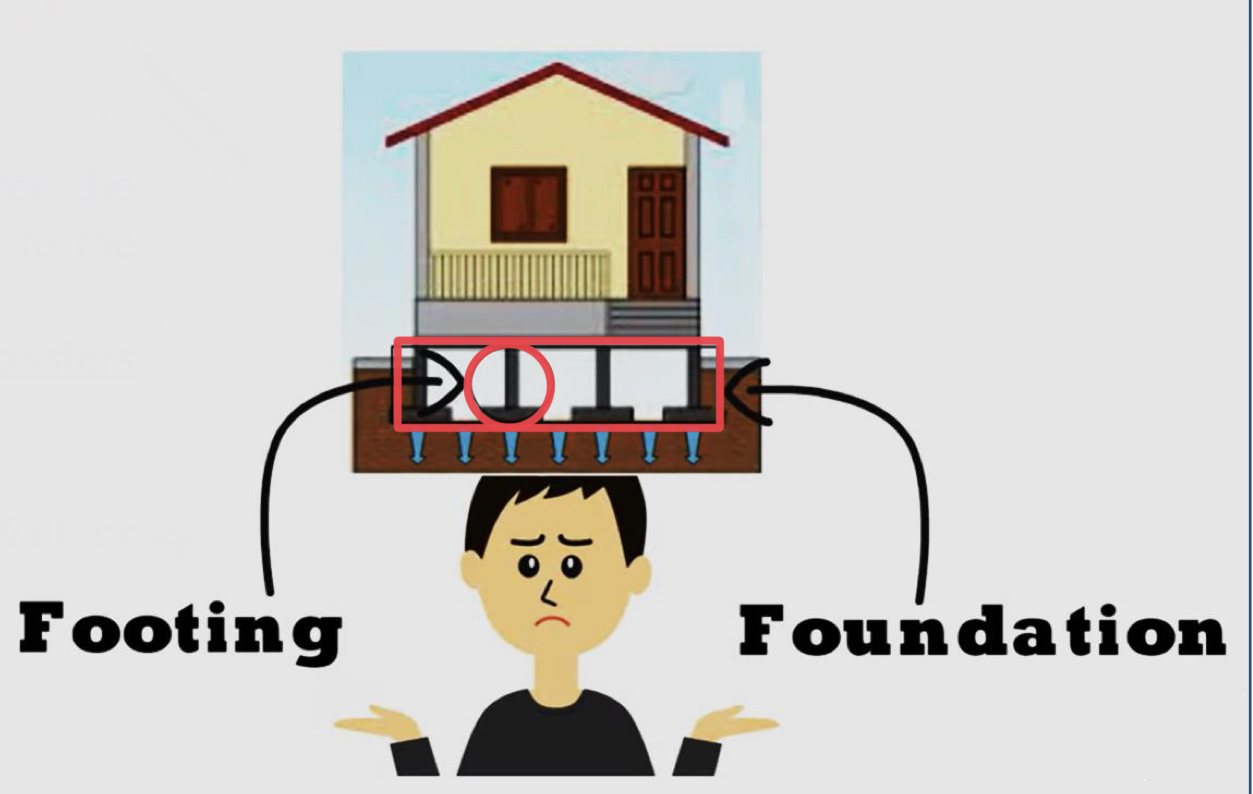
Foundations:
They are the structural elements that transfer the whole loads (dead and live loads) of the building to the ground. The lower portion of a building structure that transfers building loads to the soil below.
Footings:
They are a foundation under the base of a wall or column
Functions of the foundation
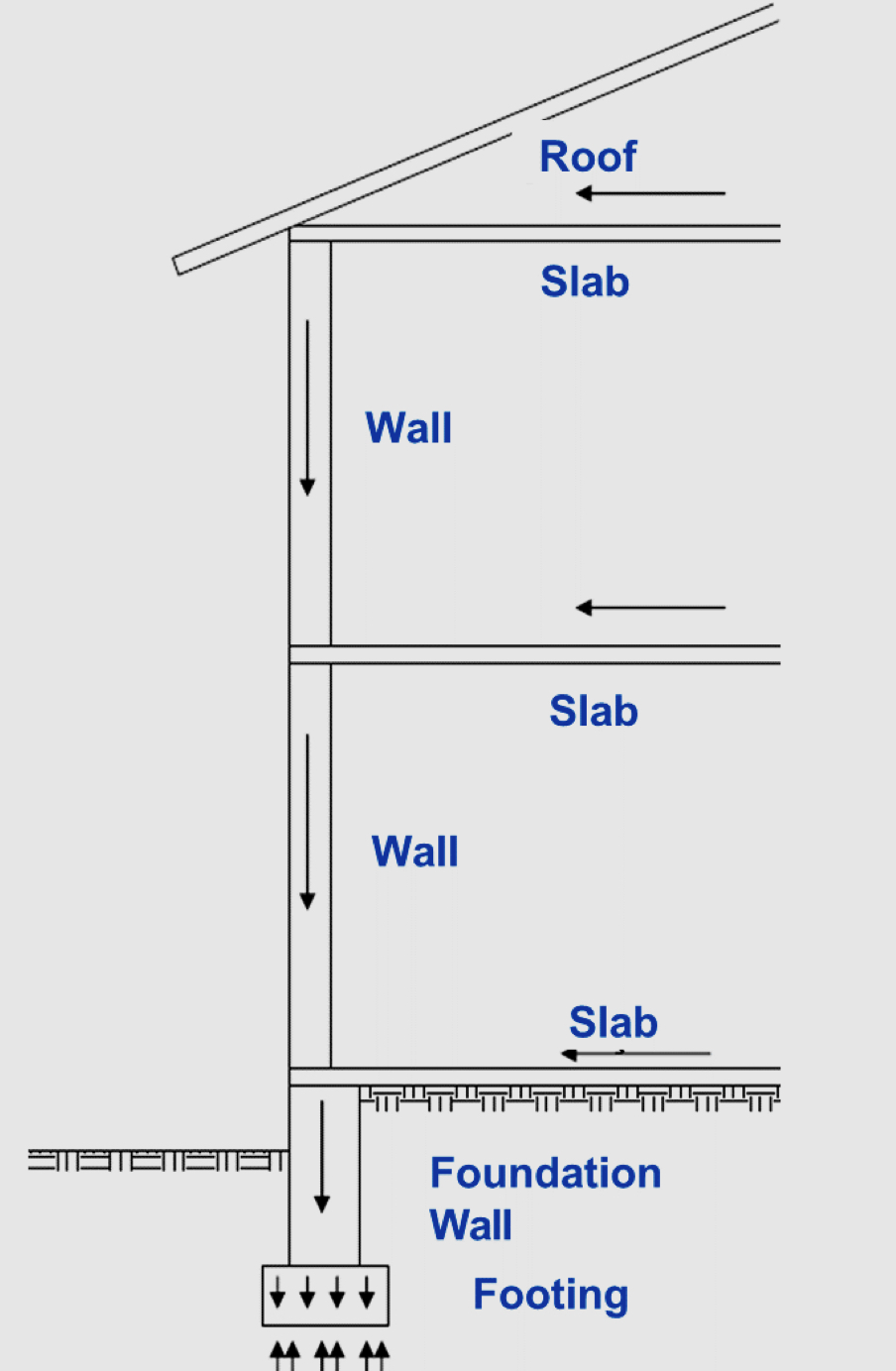
Load bearing : to transfer loads to the ground
Insulation (thermal, water, damp, acoustical) : water and damp insulation are important because of the corrosion problem of the steel elements under the ground. The concrete of the foundation surface should be covered with bituminous insulation materials
Requirements of foundations
Strength and stability
Having this would prevent movement of the structure due to the shrinkage and swelling of subsoil, and it would resist lateral forces due to the soil movement

Factors to consider when selecting a suitable footing
loads from the building
Depth of soil
Type of soil (gravel, sand, silt, clay)
Site topography
Type of superstructure
Type of structure in neighbourhood/its impact on adjacent properties
Subsurface and groundwater conditions
Building code requirements
Construction method and risk

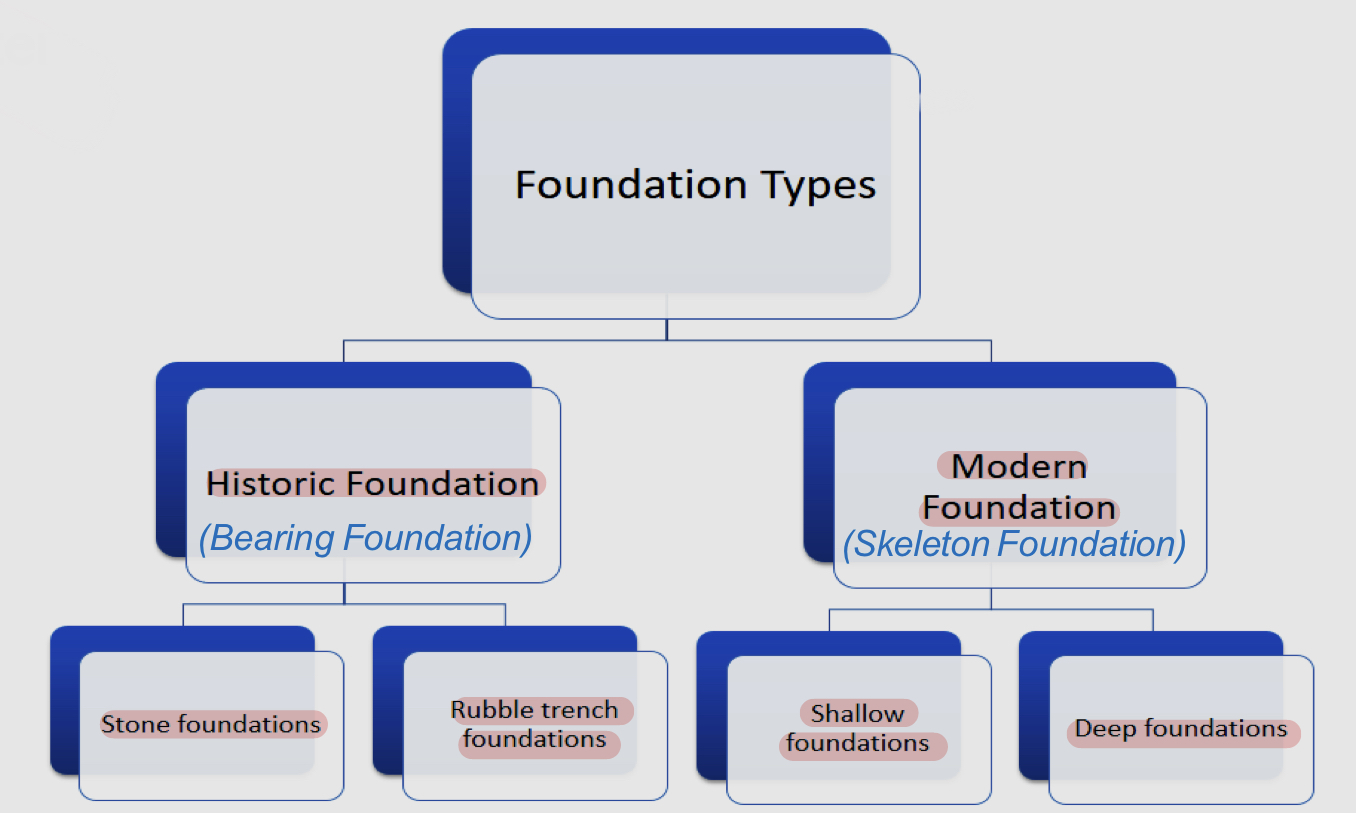
Types of foundation systems
Historic/bearing foundation
Stone foundations
Rubble trench foundations
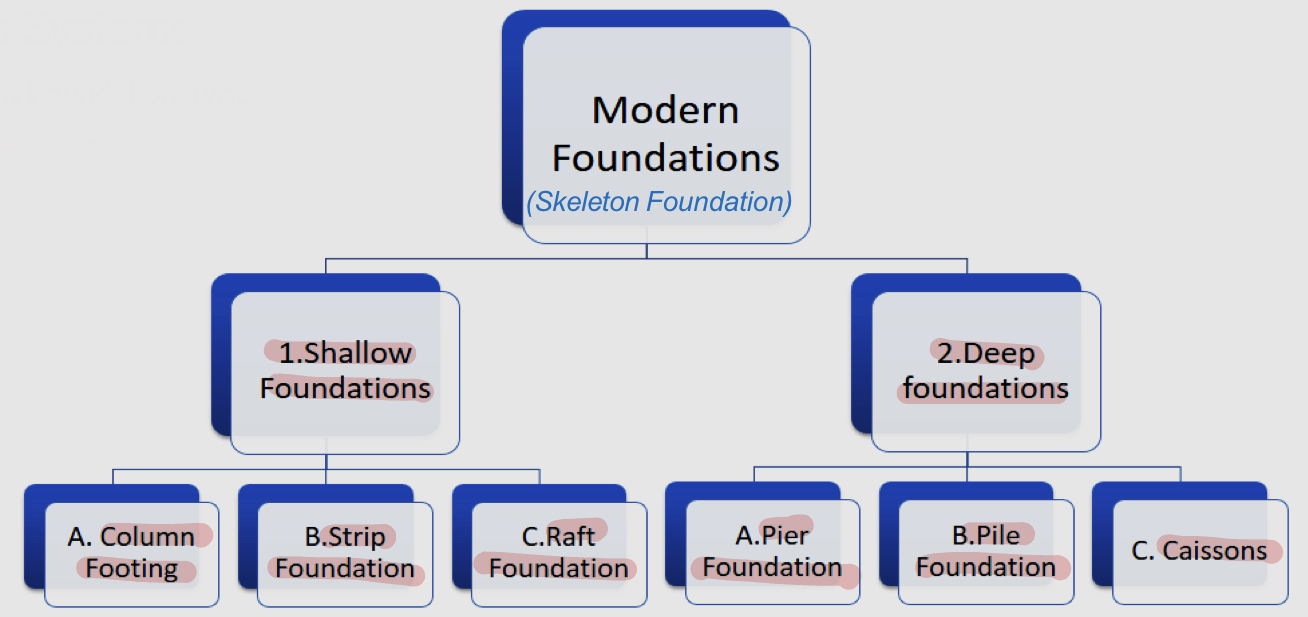
Modern/skeleton foundation
Shallow foundations
Deep foundations
Historic/bearing foundation: stone foundation
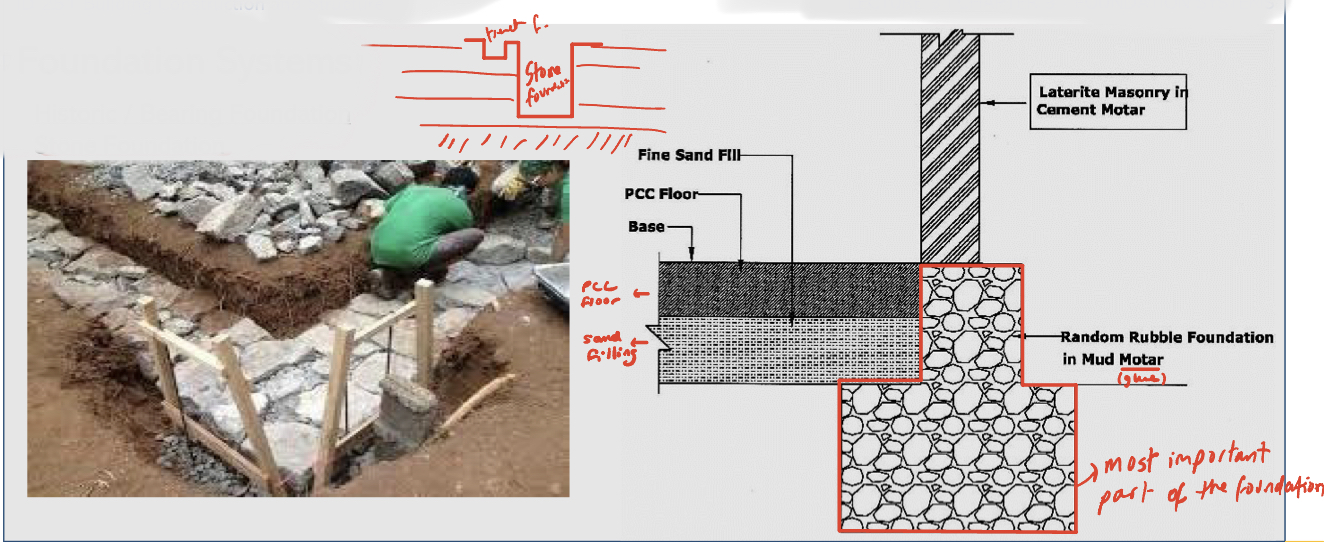
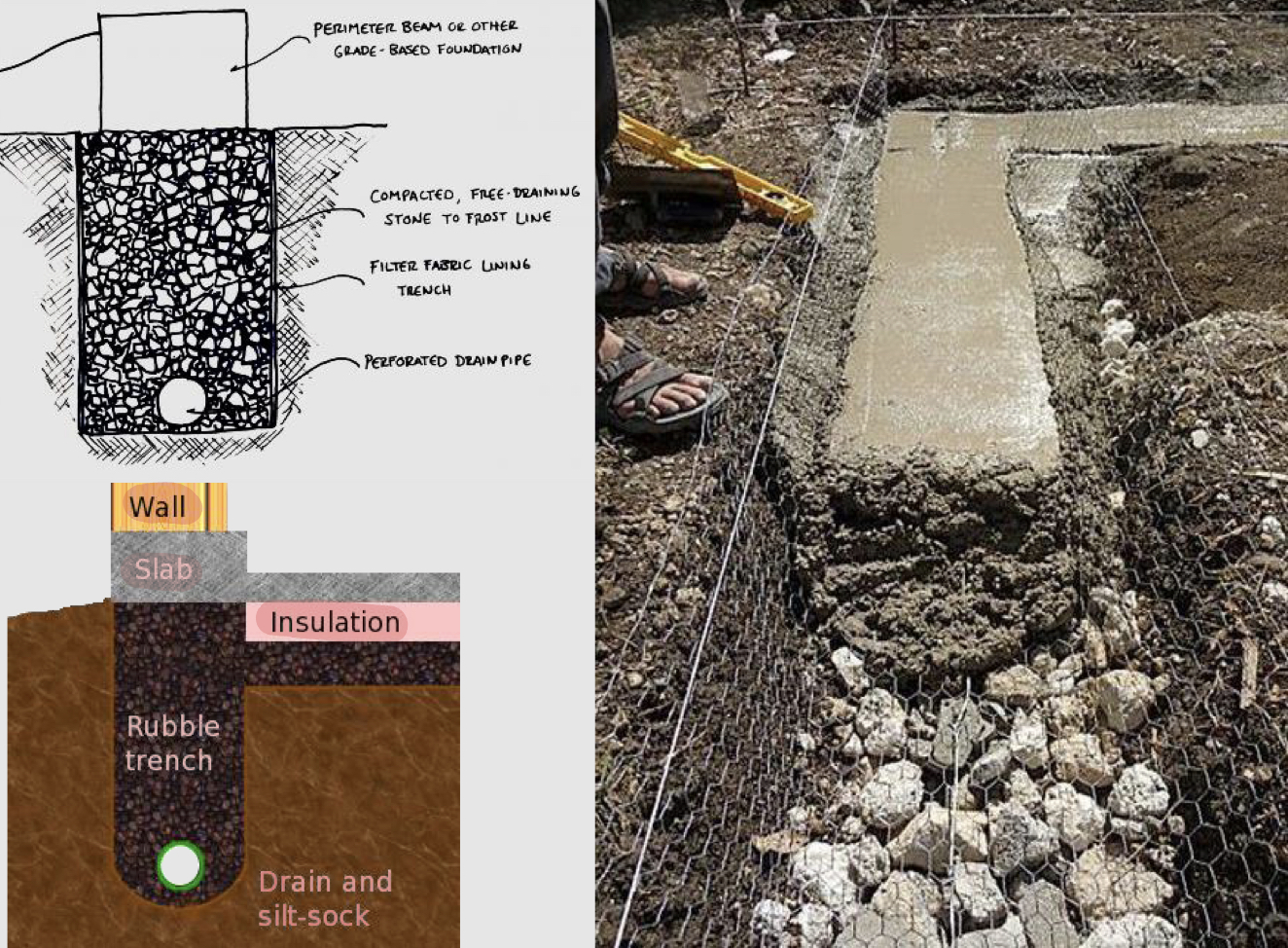
Historic/bearing foundation: rubble trench foundation
A shallow trench is filled with rubble and stones
These foundations may have a drain pipe that helps ground-water drain away
Types of modern/skeleton foundations
Shallow foundations
Column footing
Strip foundation
Raft foundation
Deep foundations
Pier foundation
Pile foundation
Caissons
Modern/skeleton foundations : Shallow foundations
They transmit structural loads to the near-surface soil
Used for most residential buildings (small & light) or buildings with moderate height on soil that has enough bearing capacity (enough strength) at reasonable depth
Used for economical consideration
Place below the lowest part of a substructure
Transfers building loads to the supporting soil by vertical pressure
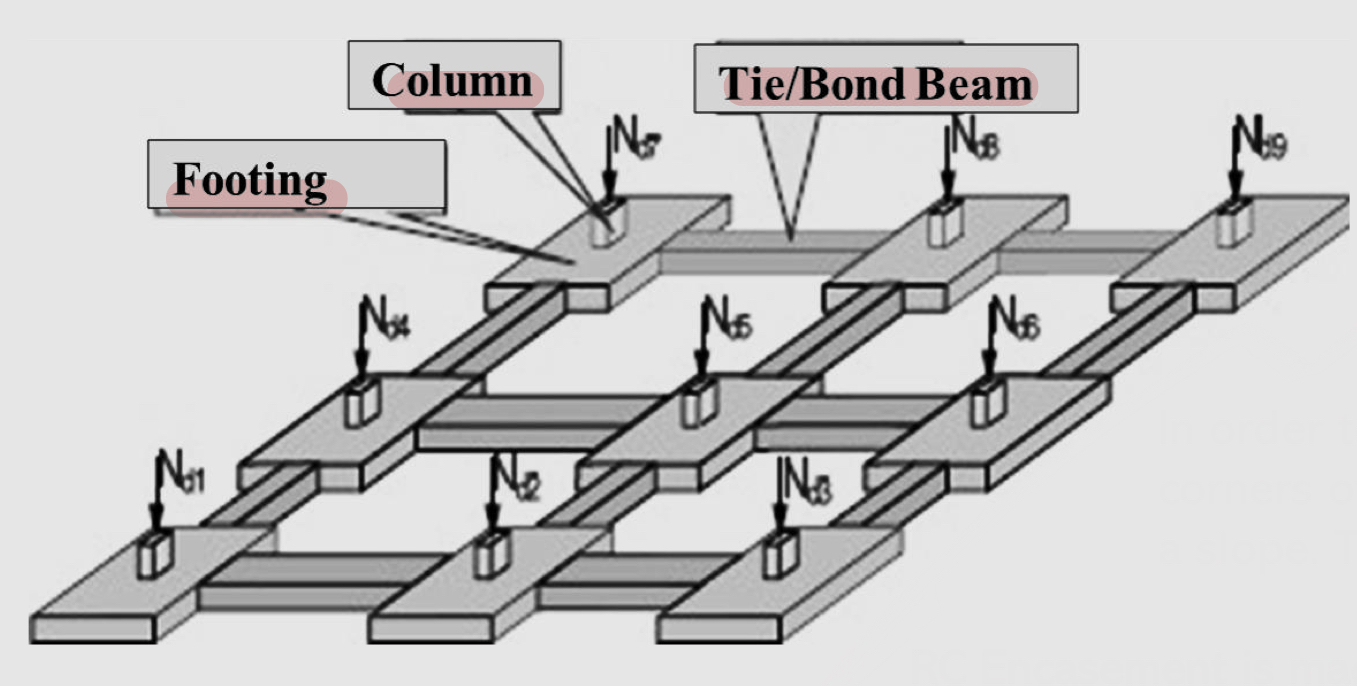
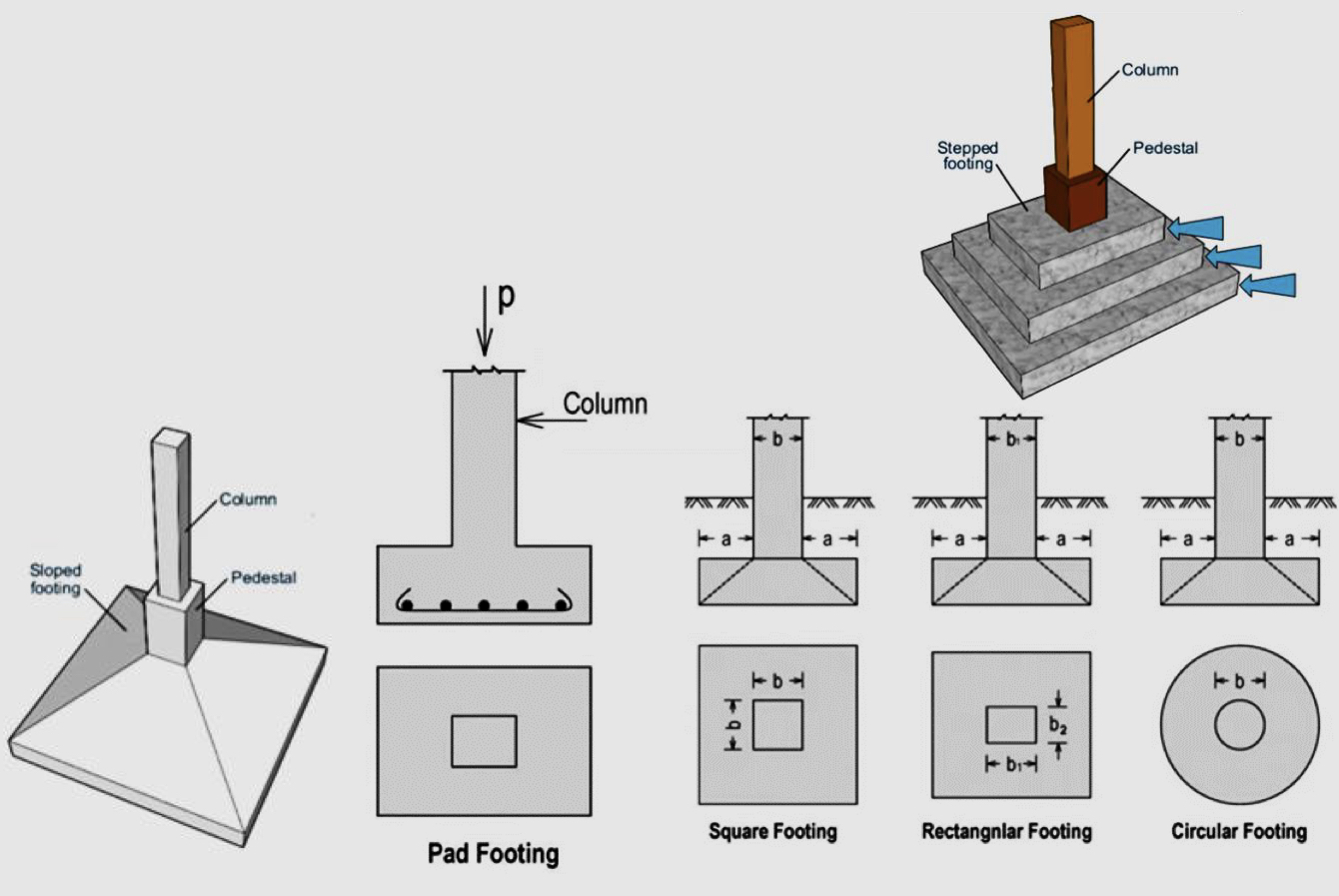
Shallow foundations : Pad foundations
also known as individual/isolated/column footing
Used in high soil bearing capacity
Used at the skeleton systems with less columns and long spans
Pad foundations should sit at the same level
Isolated footings are the individually spread footings that support freestanding columns
Can be square, rectangle , or circle
Is central or symmetrical
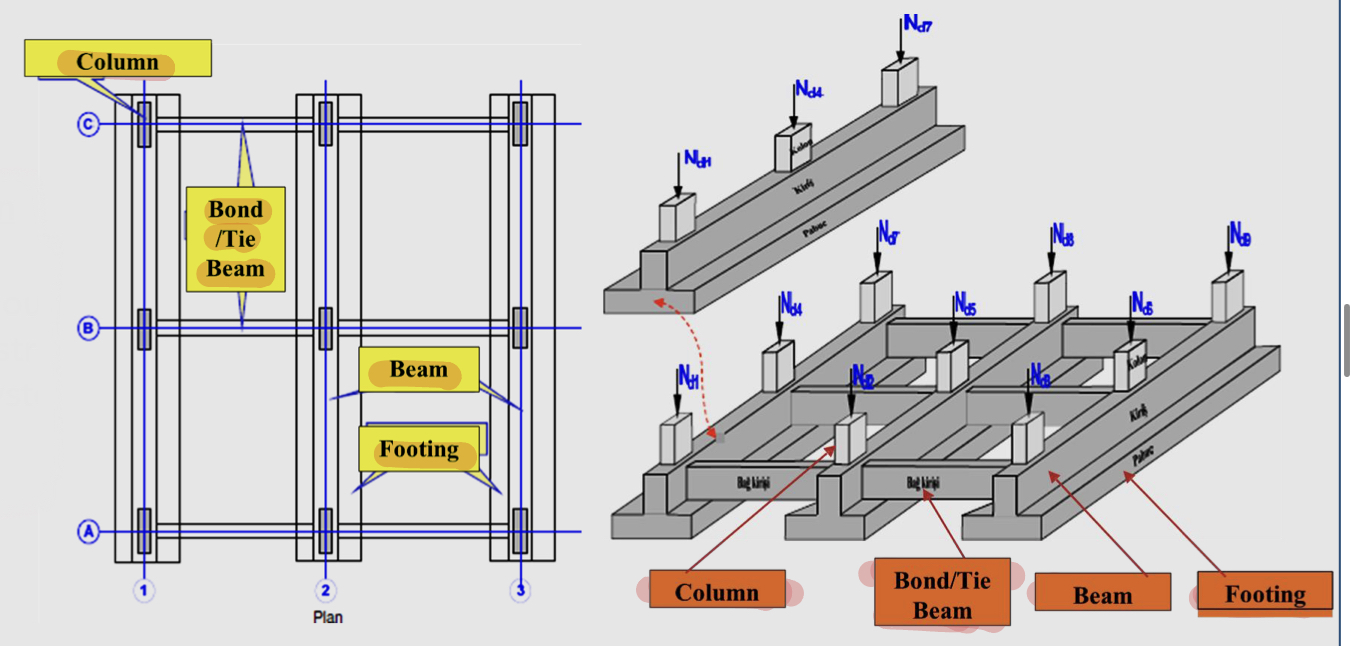
Should be connected with tie/bond beams to provide horizontal loads
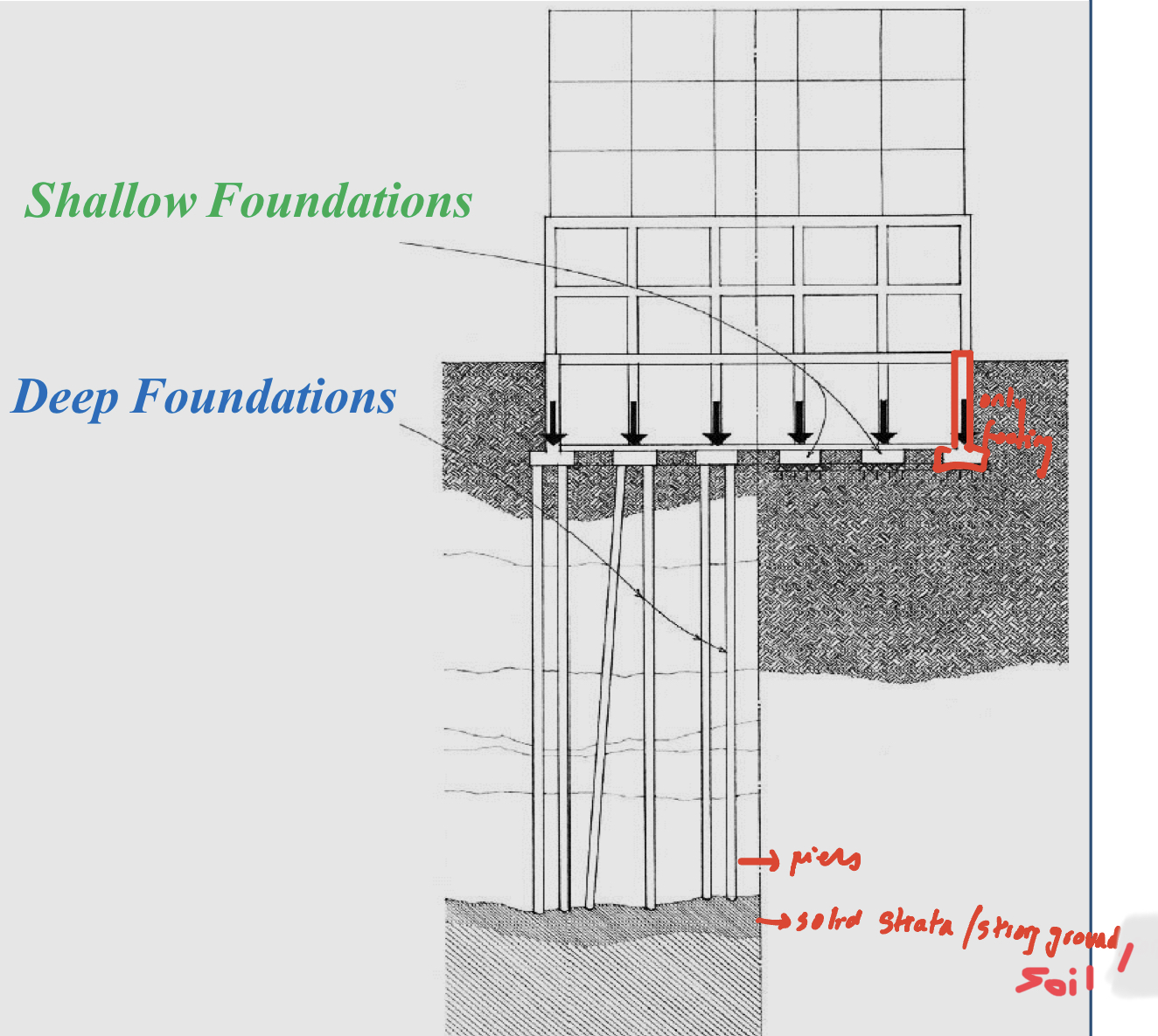
Modern/skeleton foundation: Deep foundation
Used when the soil under a foundation is unstable or has low bearing capacity
used for larger structures
They extend through unsuitable soil to transfer building loads to a more appropriate-bearing stratum of rock of dense sands below the superstructure (they don’t excavate, they drill since it’s deep)
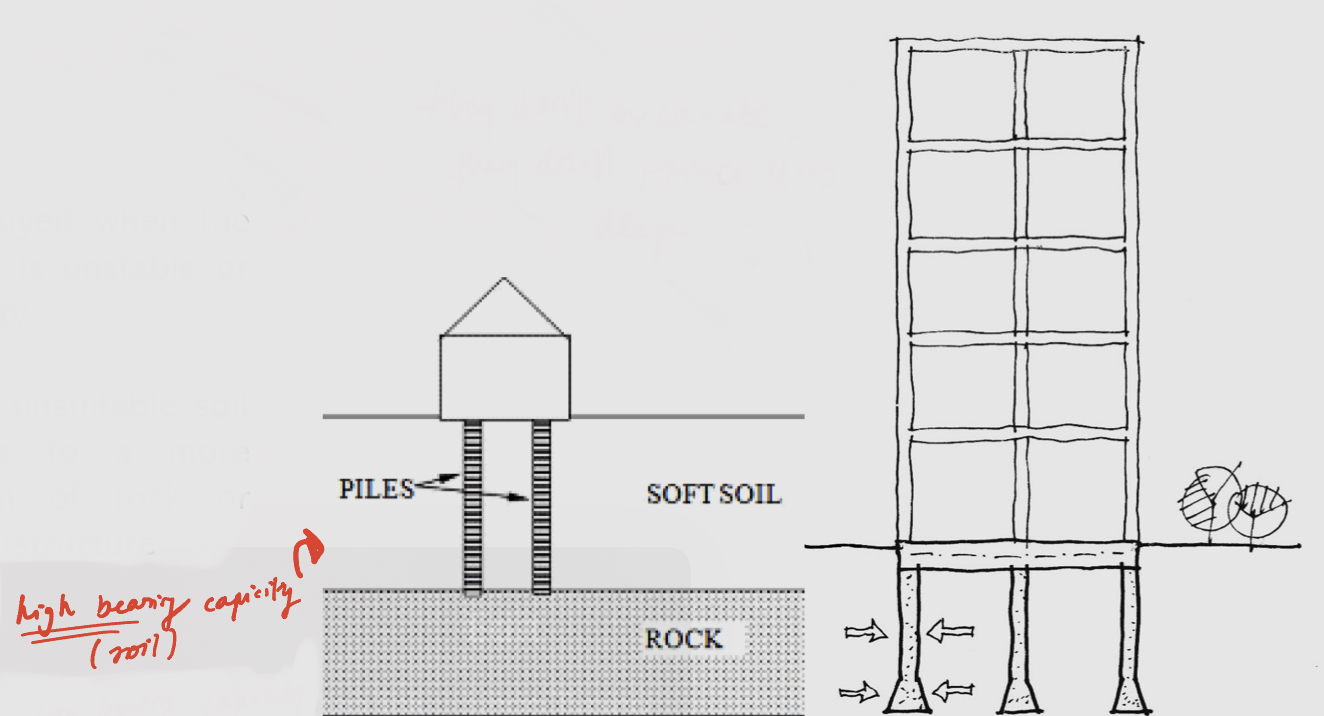
2 types of soil for foundations
High bearing capacity soil
Low bearing capacity soils
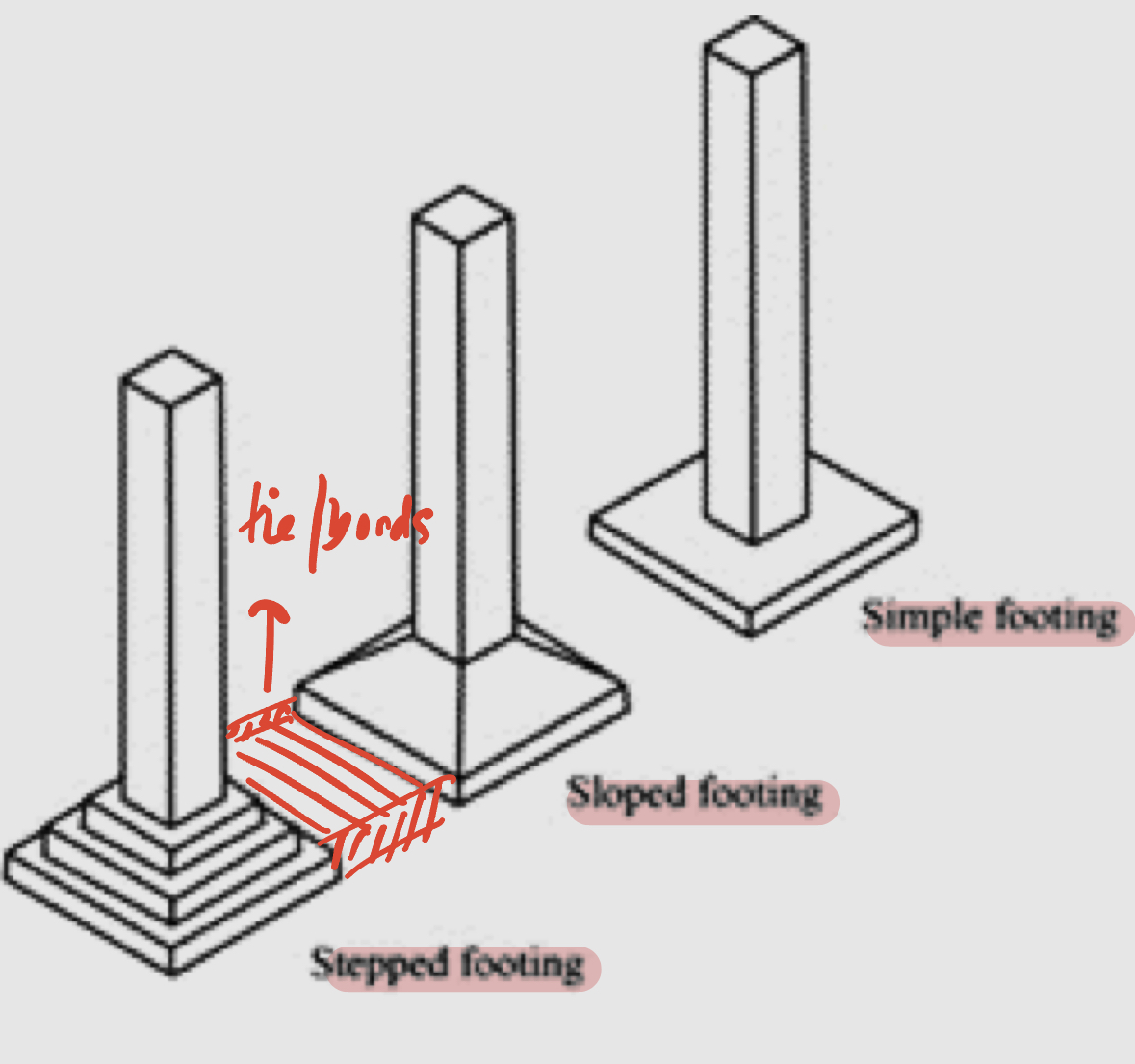
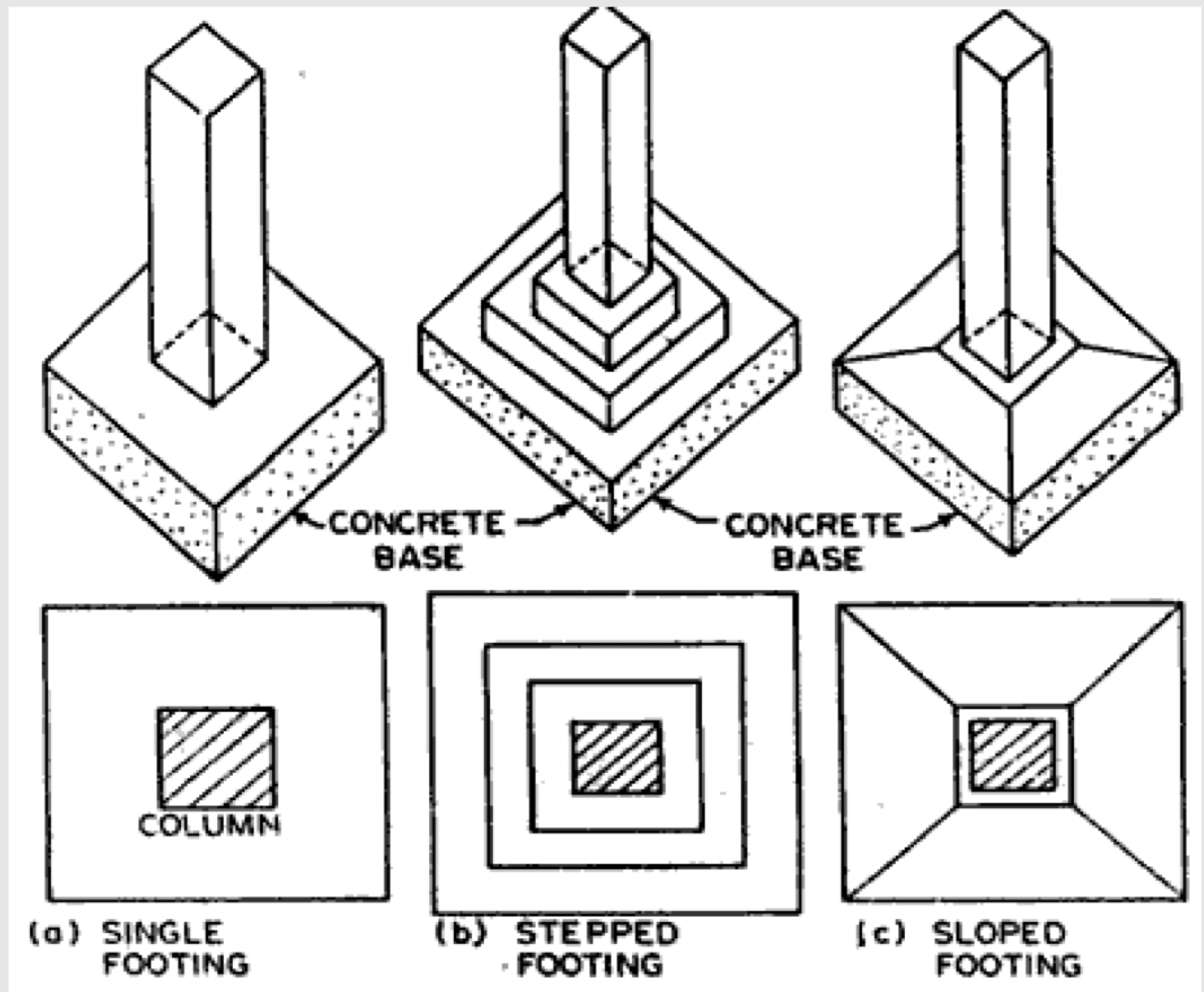
Types of pad foundations
1- stepped footing
2- sloped footing
3- simple footing
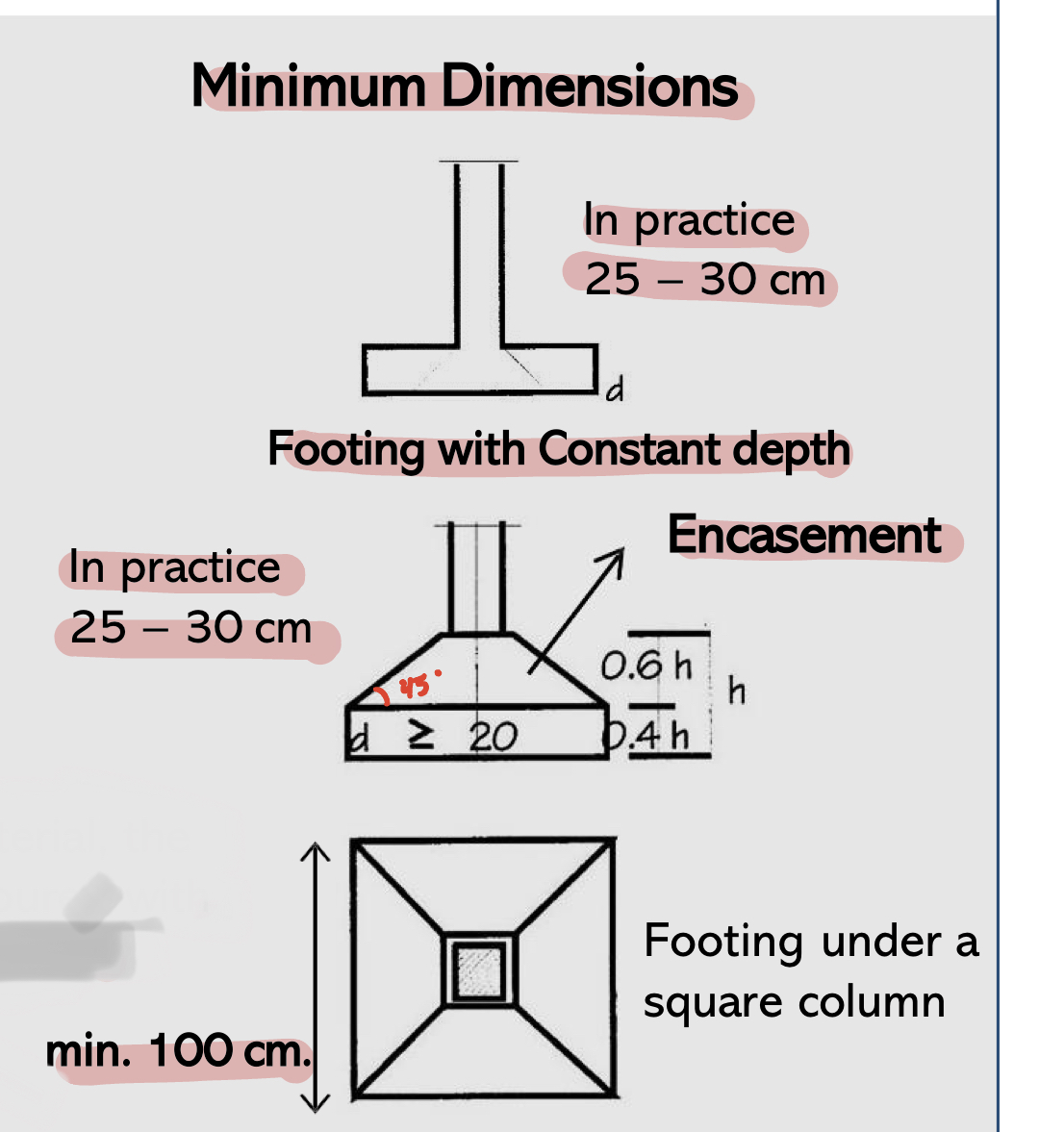
Encasement in footings
In order to prevent waste material, the corners of the footings are poured with a slope (45 deg)
Shallow footing: pad foundation LABELING
1- footing
2- column
30 tie/bond beam
Shallow footing: minimum dimensions
in practice (25-30 cm)
When do we use pad foundations
Used for low-ride but large buildings built on rocky sand
Pad footing labeling
1- vertical bars
2- footing

Difference between Stepped - Sloped - Simple Footings
Stepped footing : in the olden days, they maintained the required depth at all points around a building.
Sloped footing : trapezoid top, slope of 45 deg from all sides, saving the cost of concrete and steel.
Simple footing : pad, flat, and plain
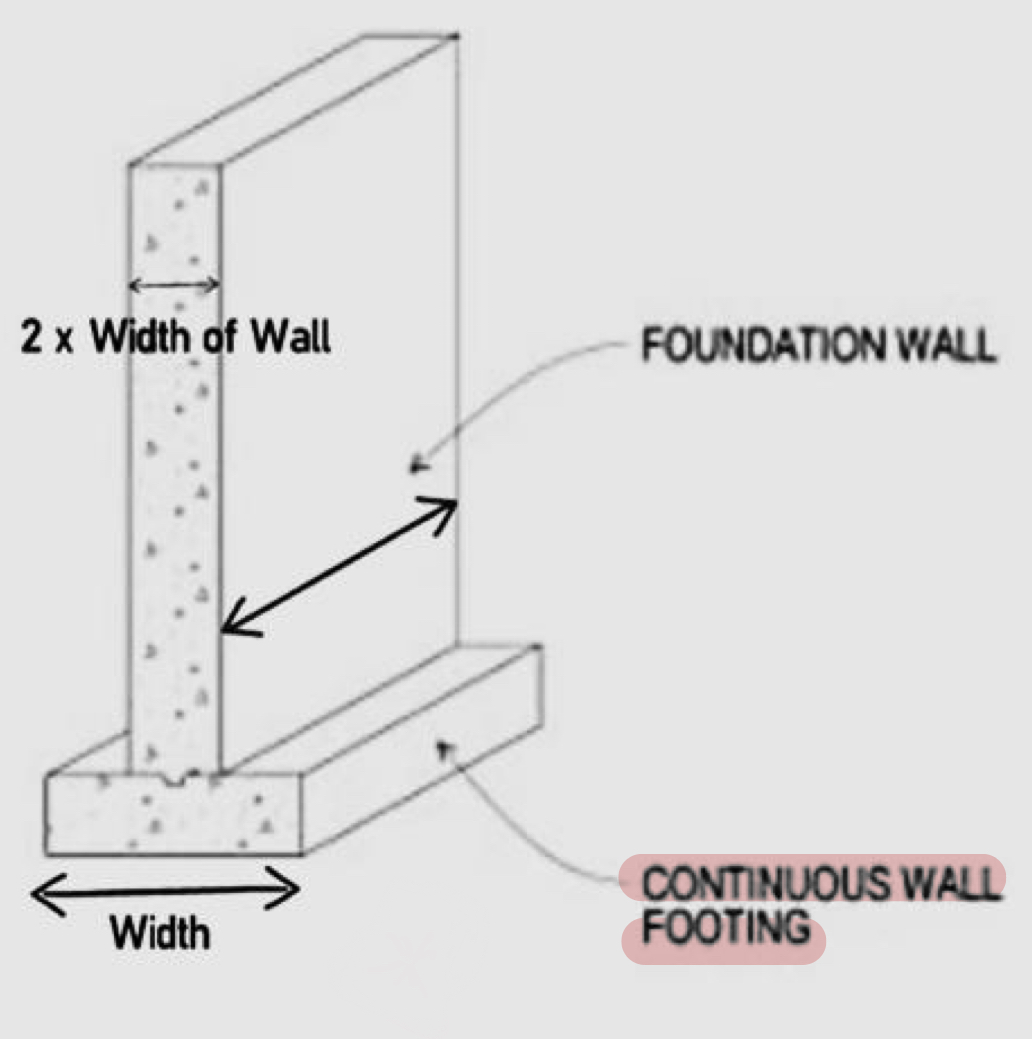
Shallow foundations: Strip foundation / continuous wall footing
it is a continuous concrete footing extended to support a row of columns, bearing walls, and shear walls.
individual footings are replaced by a continuous strip footing that supports more than two columns in a row
it’s objective is to spread the loads to a wider strip.
easy to build and doesn’t require expensive tools.
durability is less.
Strip foundations : when are they used?
Ground and subsoil is weak
Heavier and taller buildings are constructed
Pad/column foundations are dense
When the bearing capacity of the subsoil is low so that large bearing areas become necessary
Shallow foundations : types of strip foundations
one- way strip foundation
two-way strip foundation
Shallow foundations : continuous footing v.s strip footing
Continuous footing:
reinforced concrete footing extended to support a row of columns
Strip footing:
continuous spread footings of foundations walls
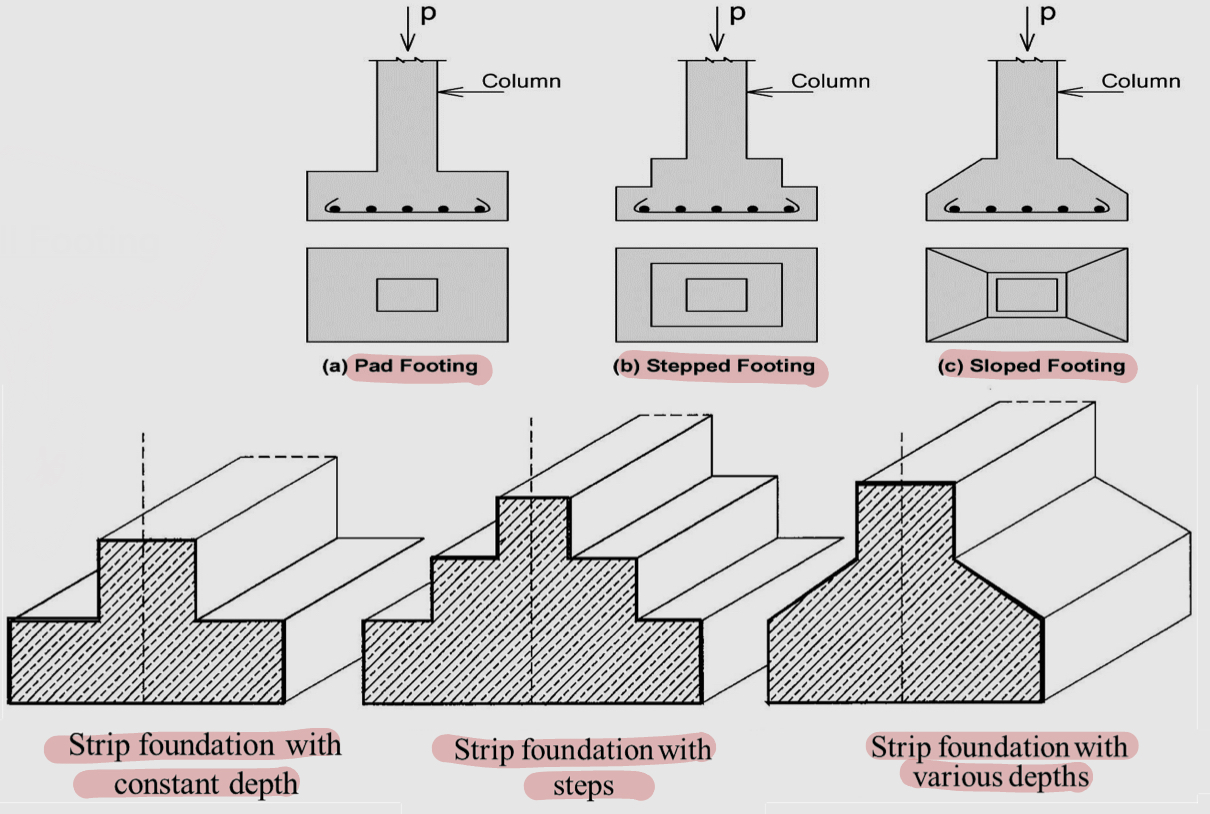
Shallow foundation: Strip foundation forms/types
A. Pad foundation (strip foundation with constant depth)
B. Stepped foundation (Strip foundation with steps)
C. Sloped foundation (strip foundation with various depths
One-way strip foundation
They should be connected to the parallel structure in order to unify the whole system gains earthquake loads
Two-way strip foundation
More suitable for taller buildings
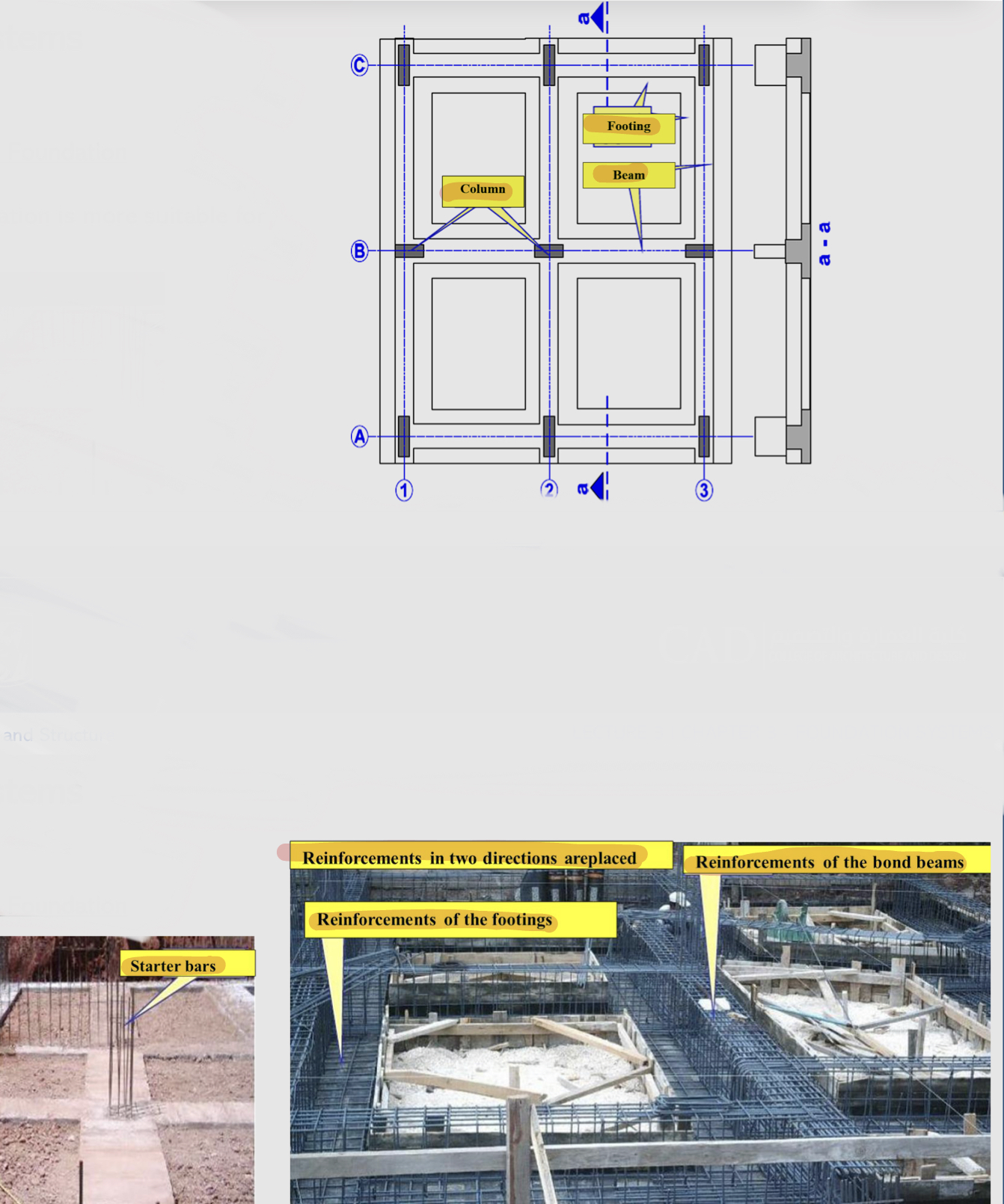
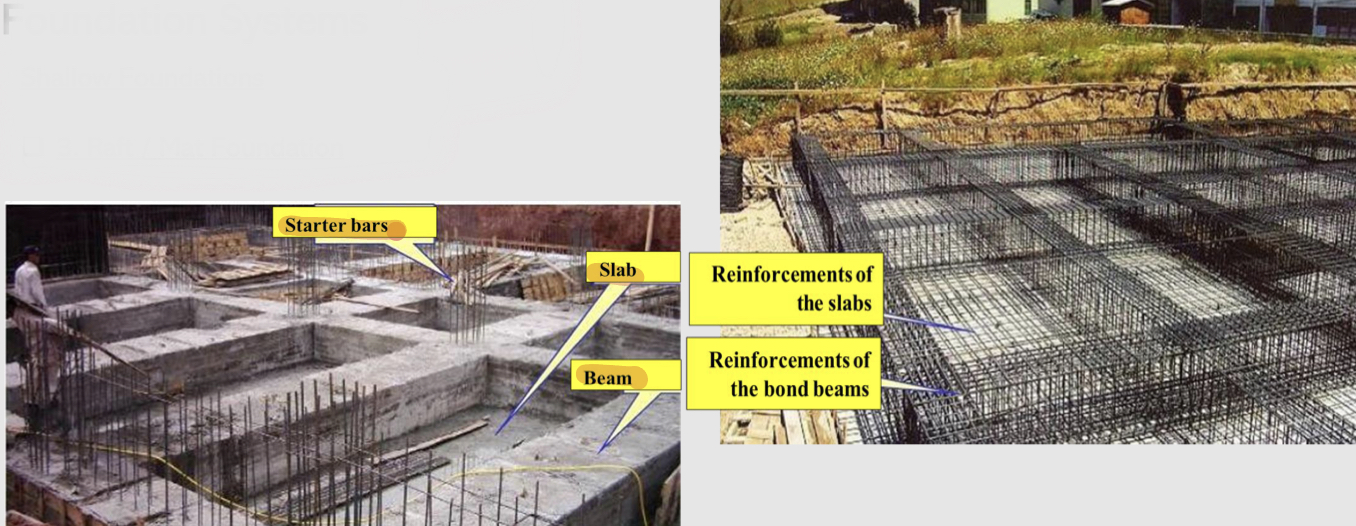
Shallow foundations : raft / mat foundation
it is a large foundation that extends over a great area, frequently an entire building or (a thick, heavily reinforced concrete slab that serves as a single footing for a number of columns or an entire building)
they are used when the allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil is low.
When the total area of the strip foundation is more than half of the whole building area, the mat foundation is more economic.
This foundation spread the dead loads more homogeneously/evenly.
it has no tie bonds and no beams.
may be stiffened by a grid of ribs, beams, or walls.
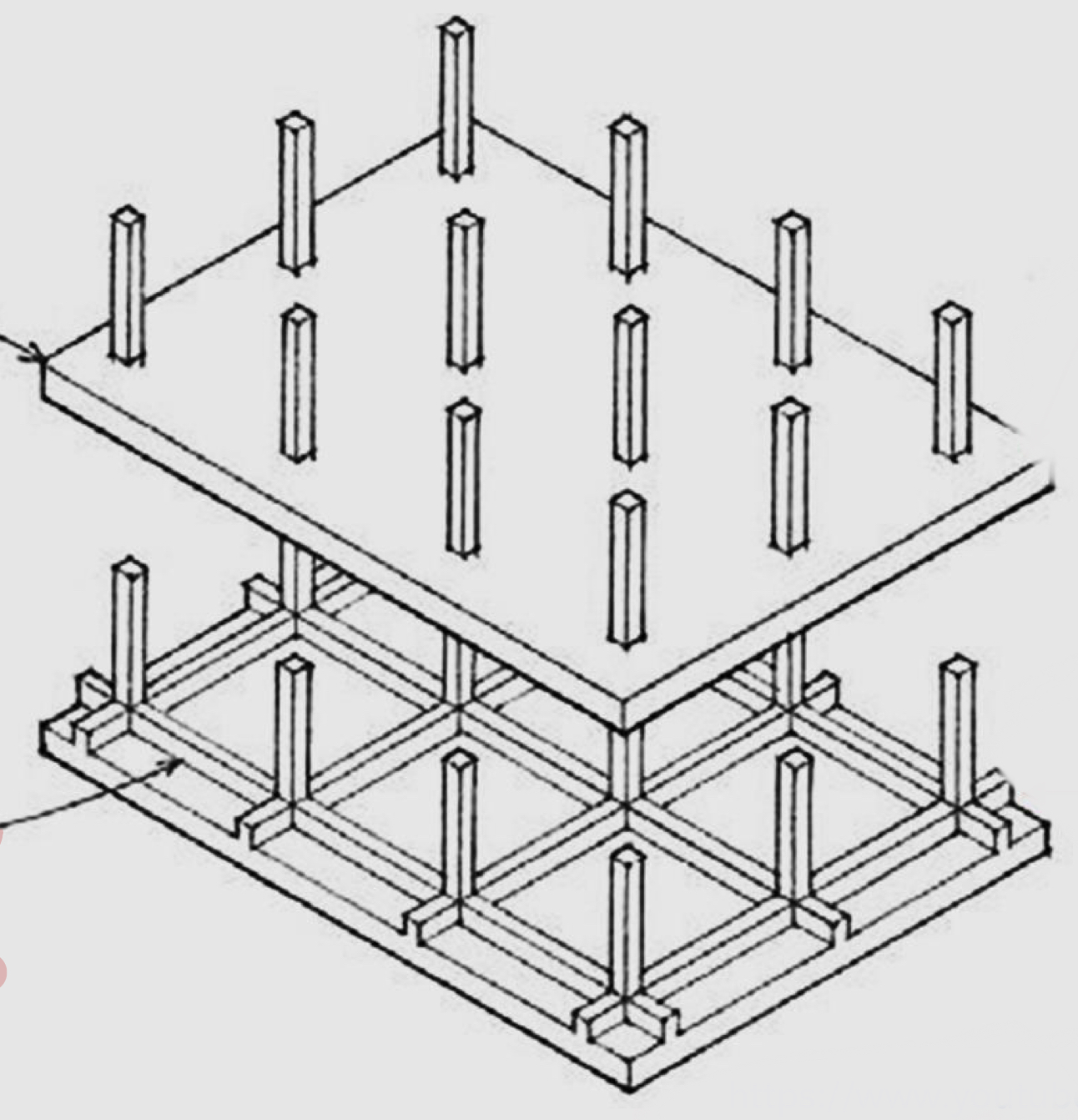
Raft / mat foundation : when do we use it?
when the allowable bearing capacity of foundation soil is low relative to building loads
when interior column footings become so large that it becomes more economical to merge them into a single slab.
Types of Raft Foundations
Raft / mat foundations without bond / tie beams
Raft / mat foundations with bond / tie beams
Mushroom raft / mat foundation
Raft / mat foundation with shear walls
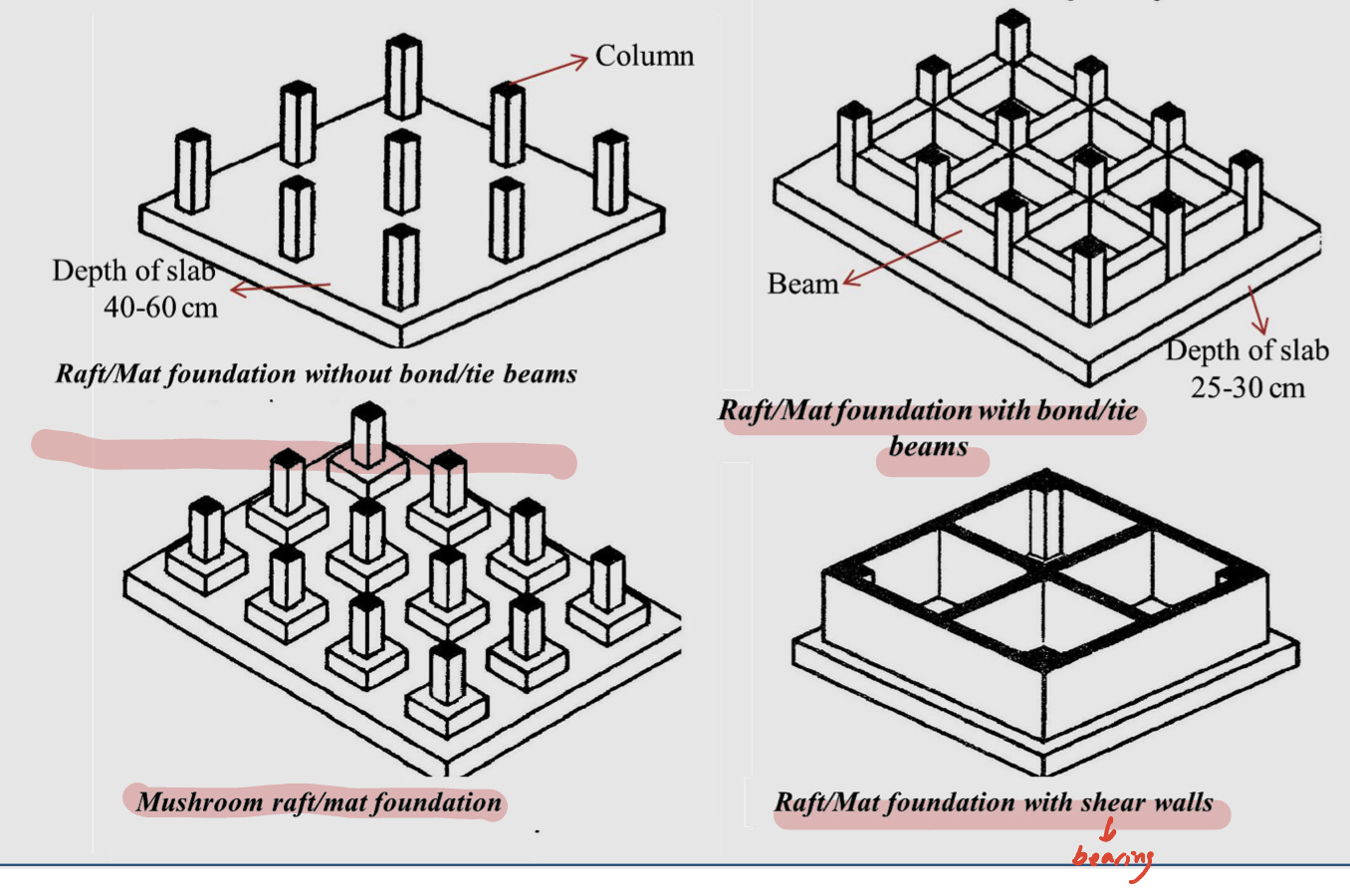
Raft / mat foundation labeling
Type of deep foundations
Pier foundation
Pile Foundation
Caisson
Deep foundations : Pier foundation
support and transfer the large loads to firm strata below
can be placed above the ground
has footing
useful when building on steep slopes and in areas subject to flooding
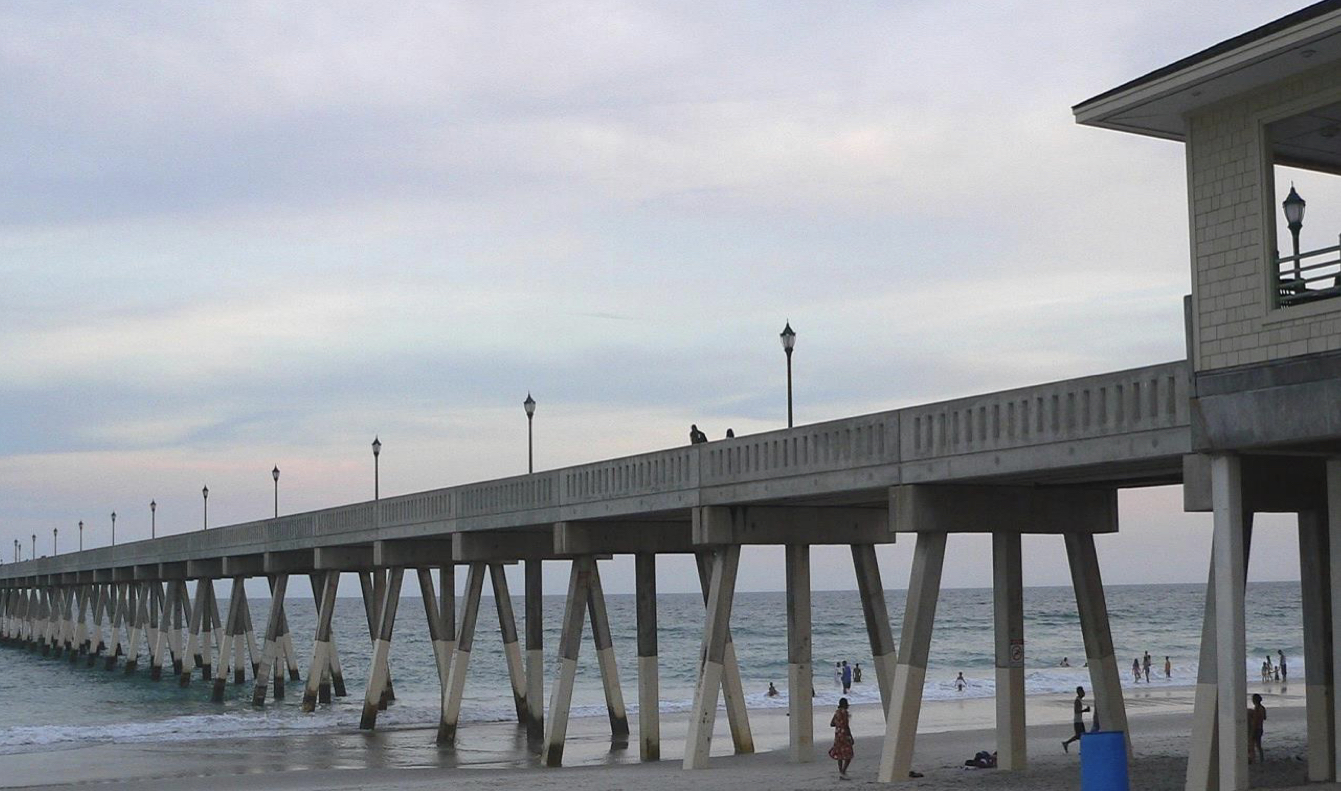

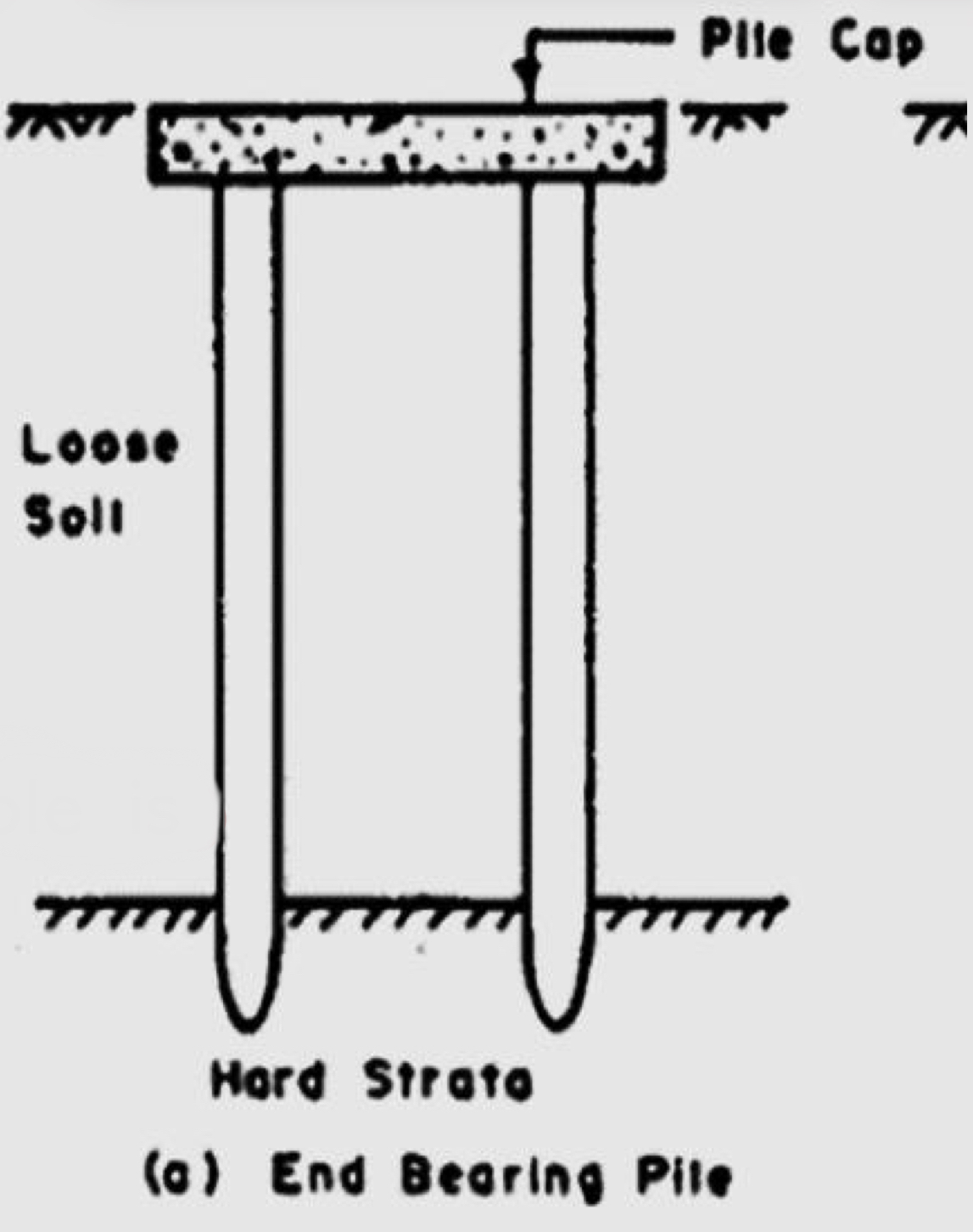
Deep foundations : Pile foundation
used in order to reach a stronger (high-density) ground level
a ground-level platform is built on very weak grounds (pile cap), it distributes the loads equally among the piles.
the columns fit on this platform, and are placed below the ground (piles), usually two or more
doesn’t have footing
pre-fabricated piles are the main types (saves time, effort, cost…)
cost of pile foundations is higher than most foundations
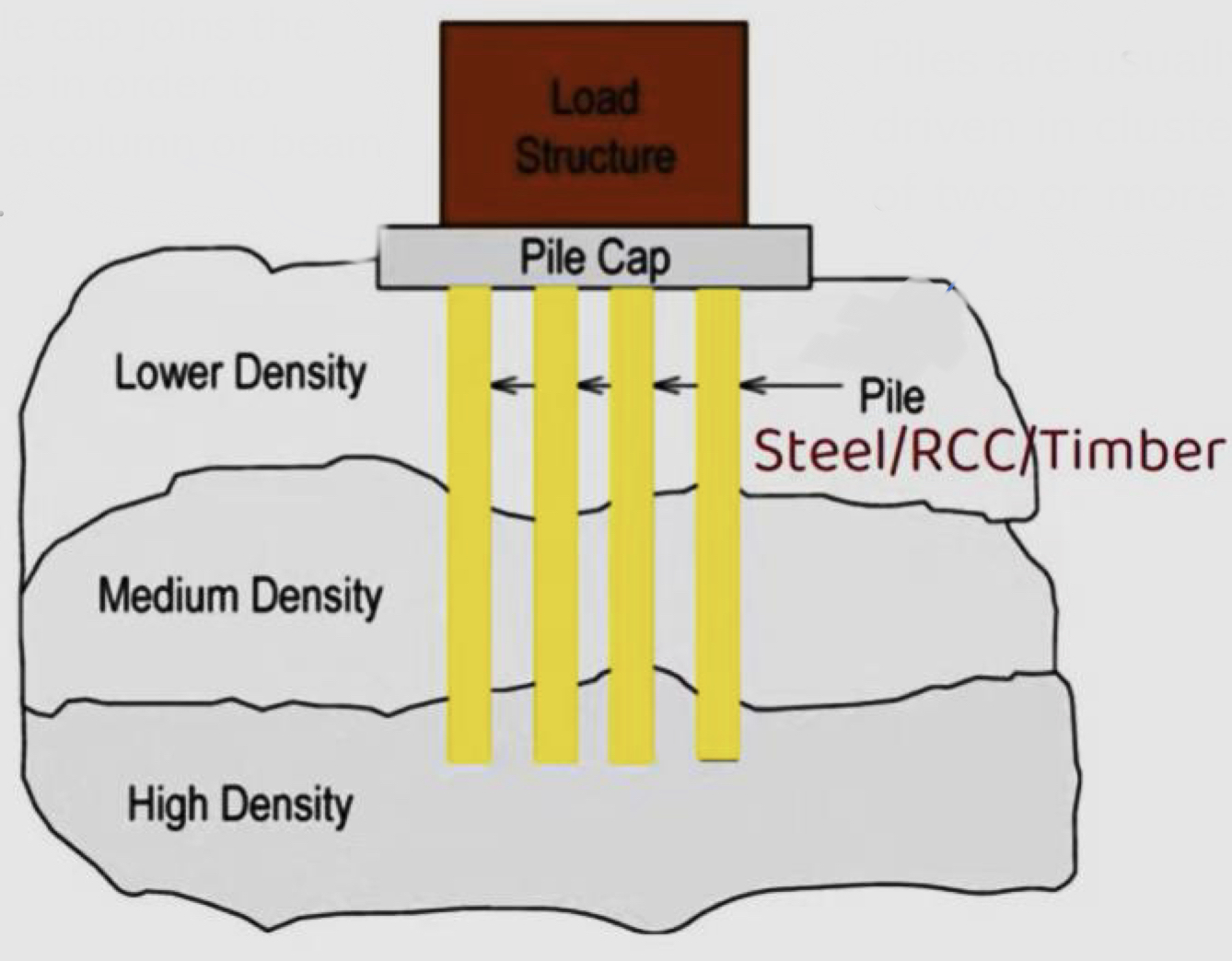
When do we use pile foundations?
When soil is weak
When the groundwater table is high
Soil erosion
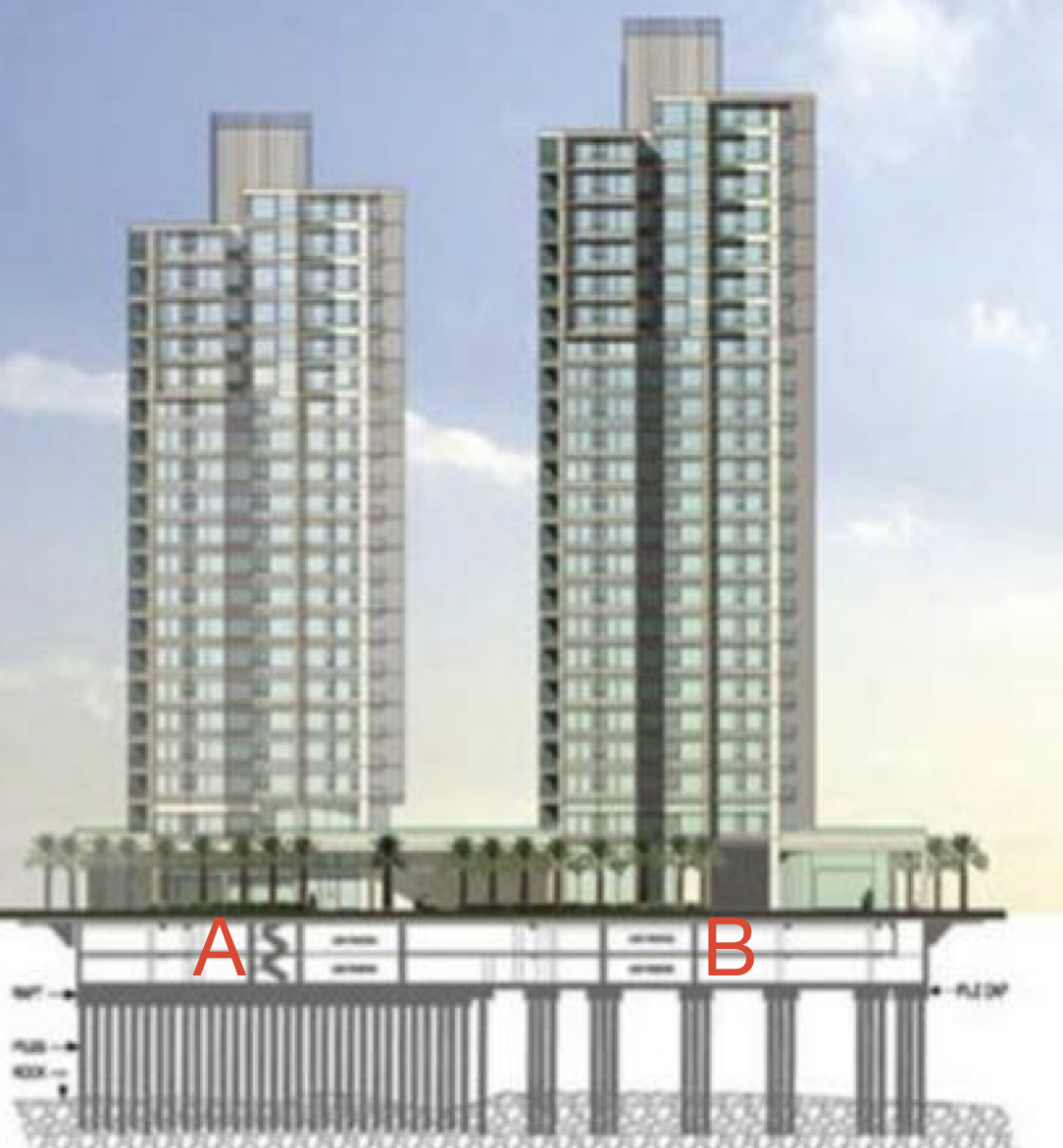

Pile foundation: what is the difference between A and B’s pile foundation?
A) has less density because there is less distance between the piles
B) has more density because there is more distance between the piles
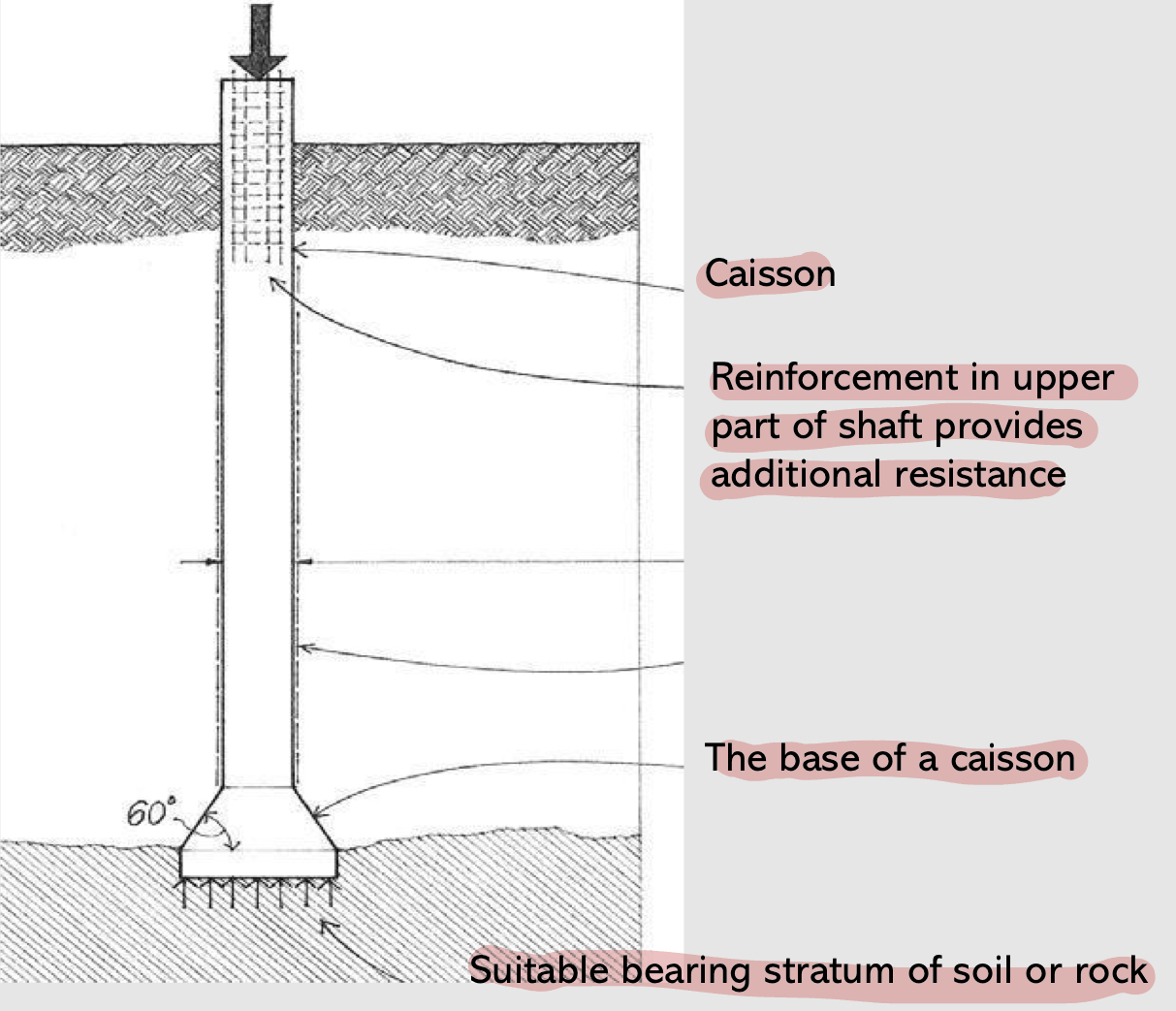
Deep foundations : Caisson / well foundation
well foundations are constructed in rivers, lakes, bridge structures, and Barbour constructions.
used when the high-density ground level is deep and bigger foundations are needed
more suitable four deep foundation underwater
doesn’t have footing
cost is very high

Caisson foundation : in situ v.s pre-fabricated caisson foundation
In Situ Caisson foundation: provided/made on-location
Pre-fabricated caisson foundation: pre-made off site
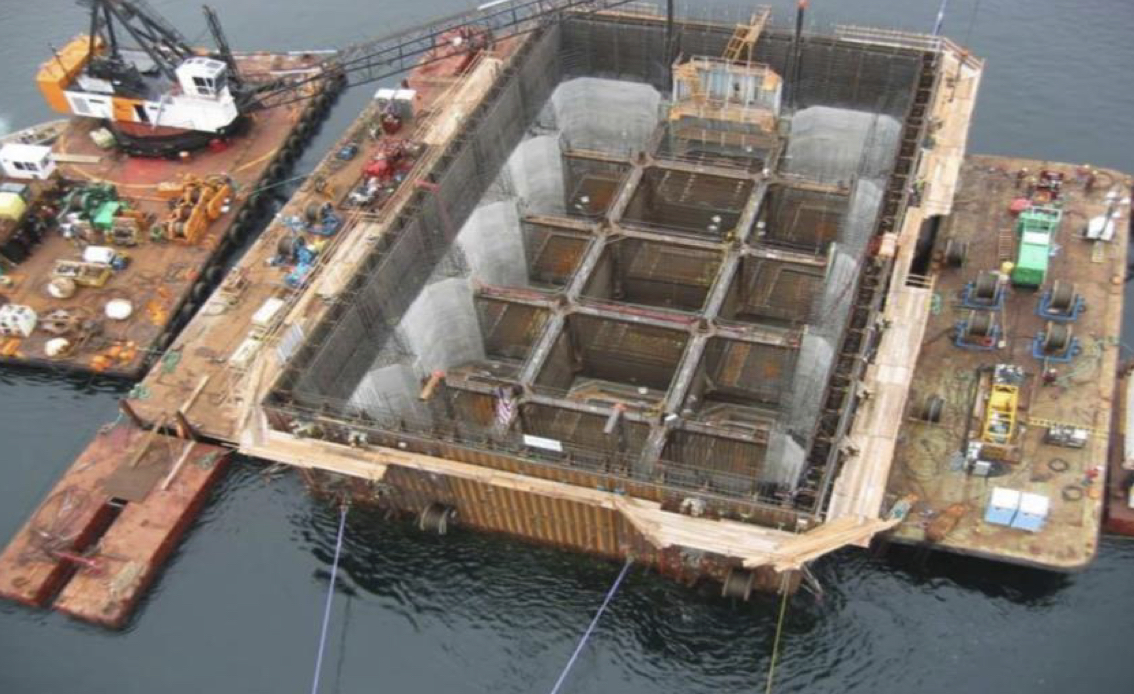


Caisson foundation: labeling
Caisson
Reinforcement and Additional Resistance
Base of Caisson
Bearing Stratum of Soil or Rock
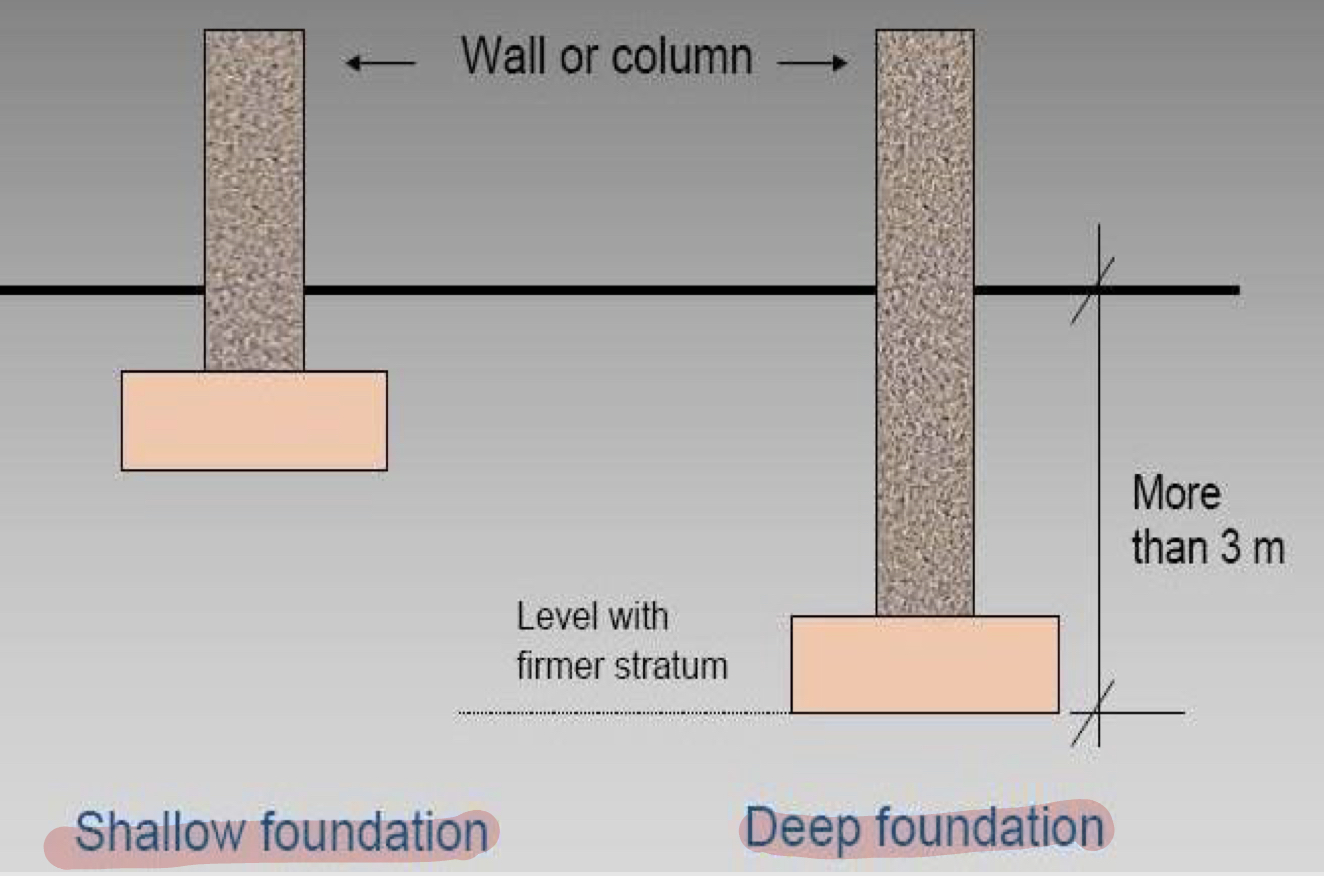
Shallow foundation v.s Deep foundation
Shallow: less than 3m
Deep: more than 3m
Pad foundation v.s Pile foundation
Pad: stops at footing in regular soil
Pile: stops at pile in bed rock
Pad foundation v.s Strip foundation
Pad: uses columns and is isolated (one at a time)
Strip: uses walls and is a whole strip
Why do Pad Foundations sometimes need tie-beams?
Because it helps balance the tilting effect due to different turning moments
Retaining Walls
vertical structured designed to retain material on one side, preventing it from collapsing, slipping, or preventing soil erosion.
they many be independent structures or may be part of a wider construction work, such as a building.
they may include a parapet that extends above the height of the retained material for safety reasons
Main use of retaining walls:
To help prevent soil erosion
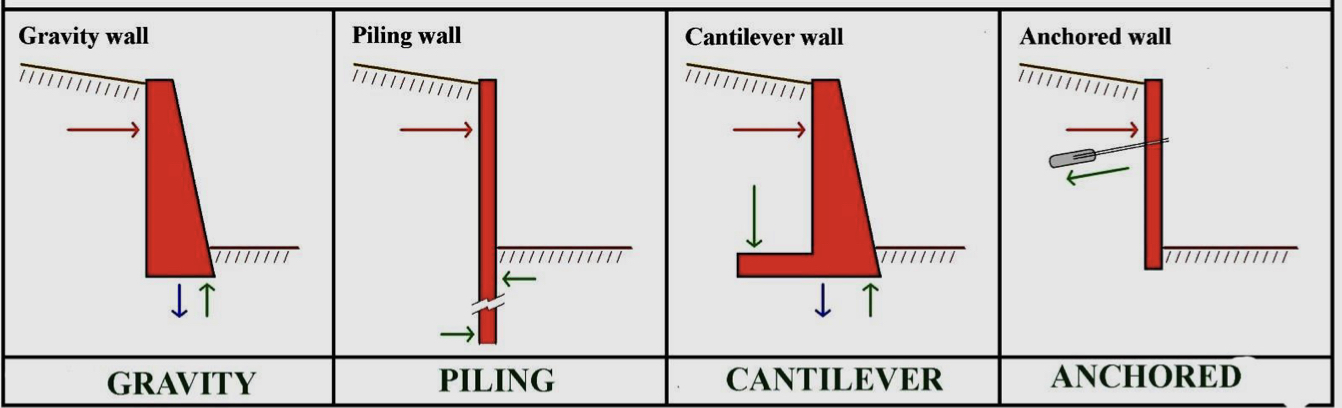
Different types of retaining walls:
Gravity wall
Piling wall
Cantilever wall
Anchored wall
Waterproofing
To prevent water passage
Used where groundwater is plain
Used when the need to protect sub-structure space from moisture is critical
What is the next most important factor in building a construction after structural integrity?
Waterproofing
What is the source of the vast majority foundation problem?
Water
Wet soil beneath a foundation can swell or lose strength
Waterproofing systems protect against water intrusion with the goal of:
Maintaining long-term structural durability
Surface protection
Occupant comfort in buildings
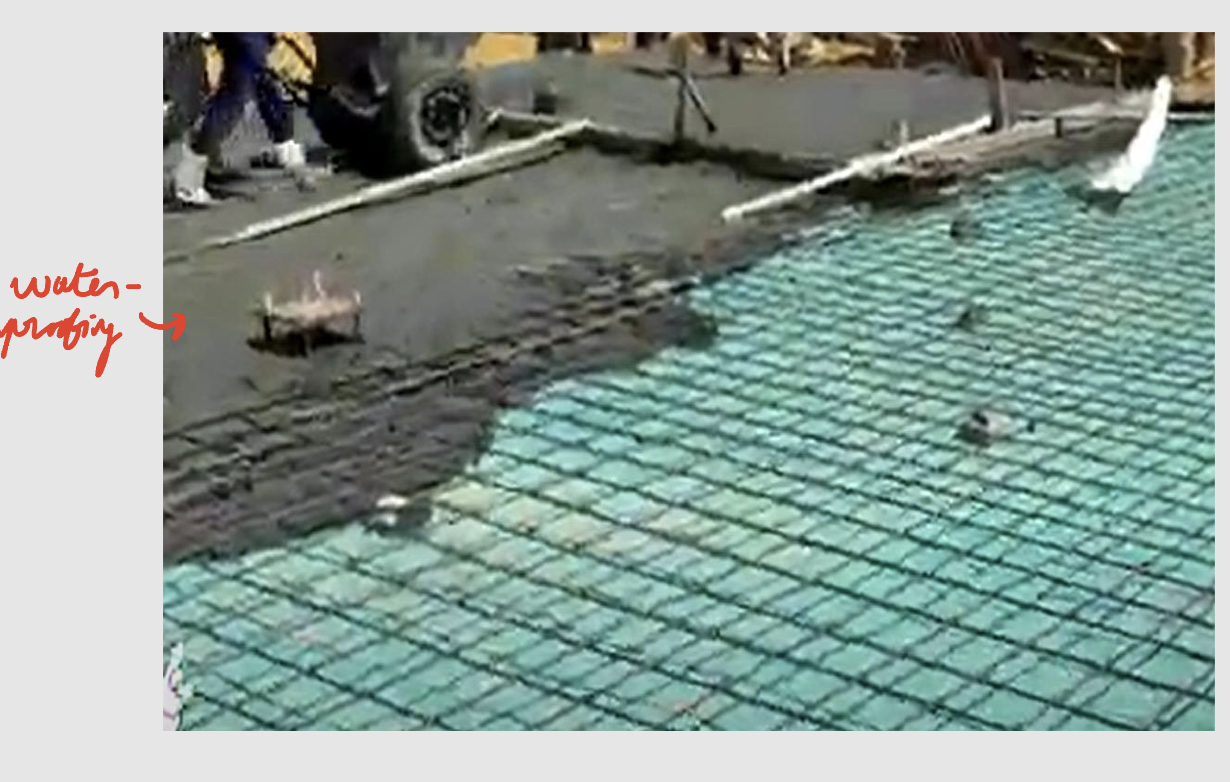

Commonly used materials for waterproofing in buildings:
Cementitious material
Bituminous material
Liquid waterproofing membrane
Liquid membrane
Which part of a building is the most important place to waterproof?
below grade waterproofing
roof waterproofing

Graphic material and symbols
