Circle of Willis
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Anterior cerebral arteries
A?
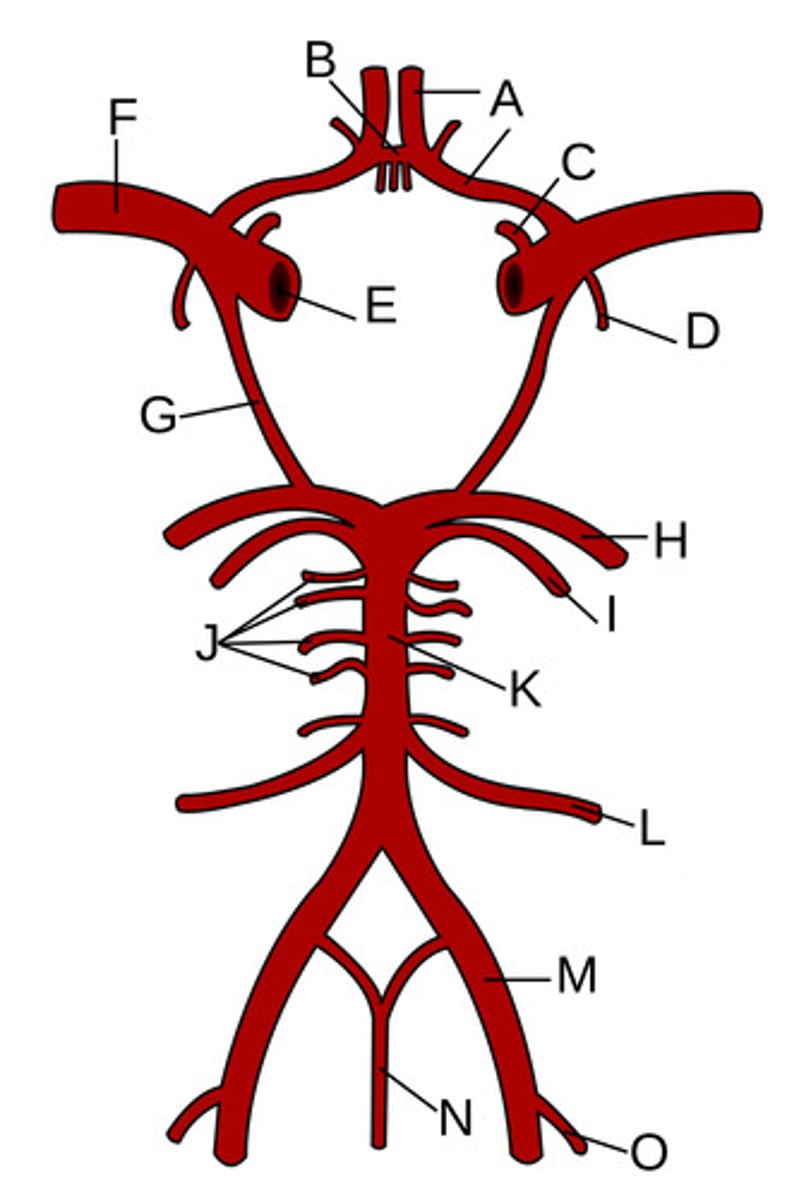
Anterior communicating artery
B?
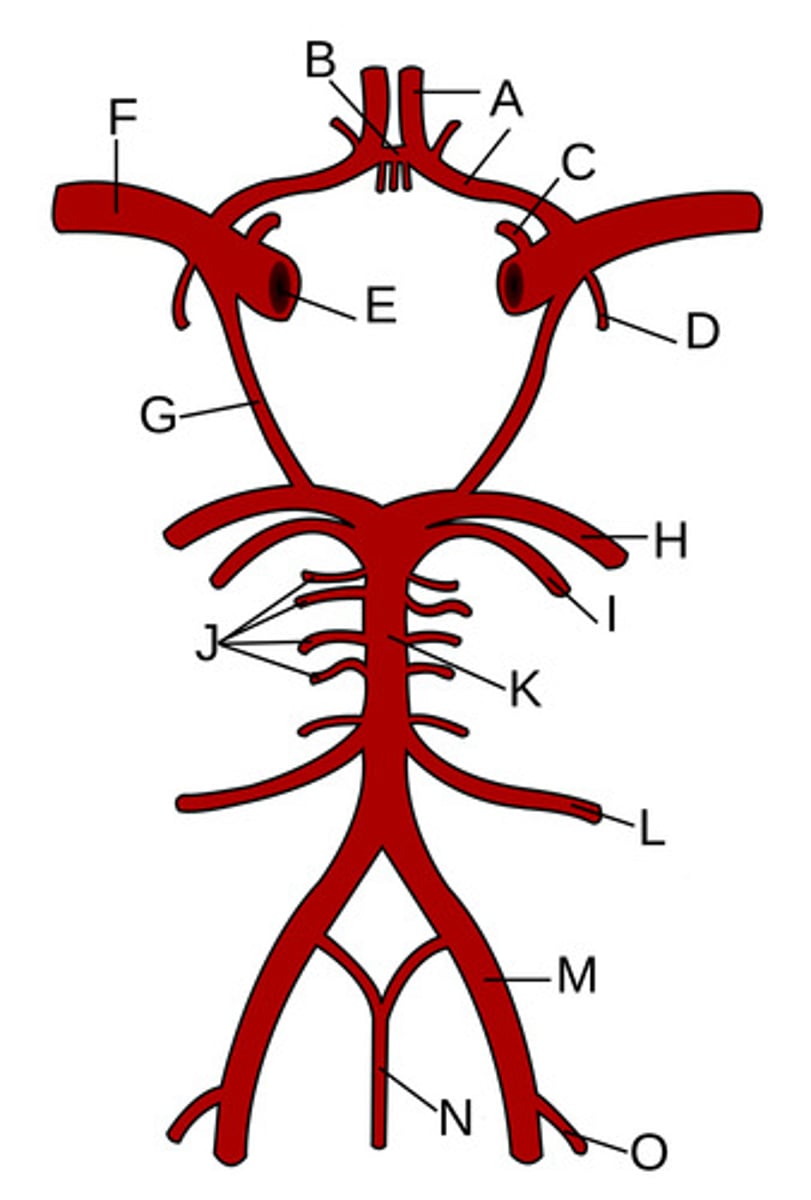
Opthalamic Artery
C?
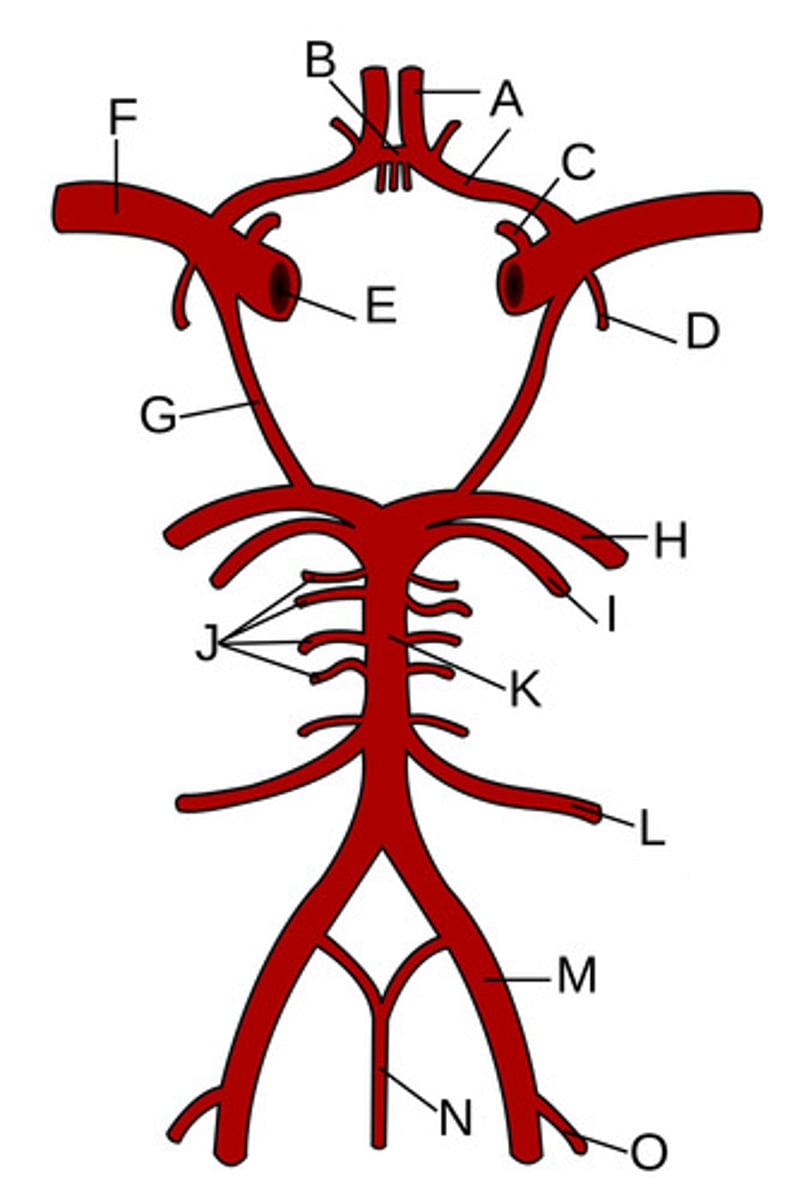
Anterior choroidal artery
D?
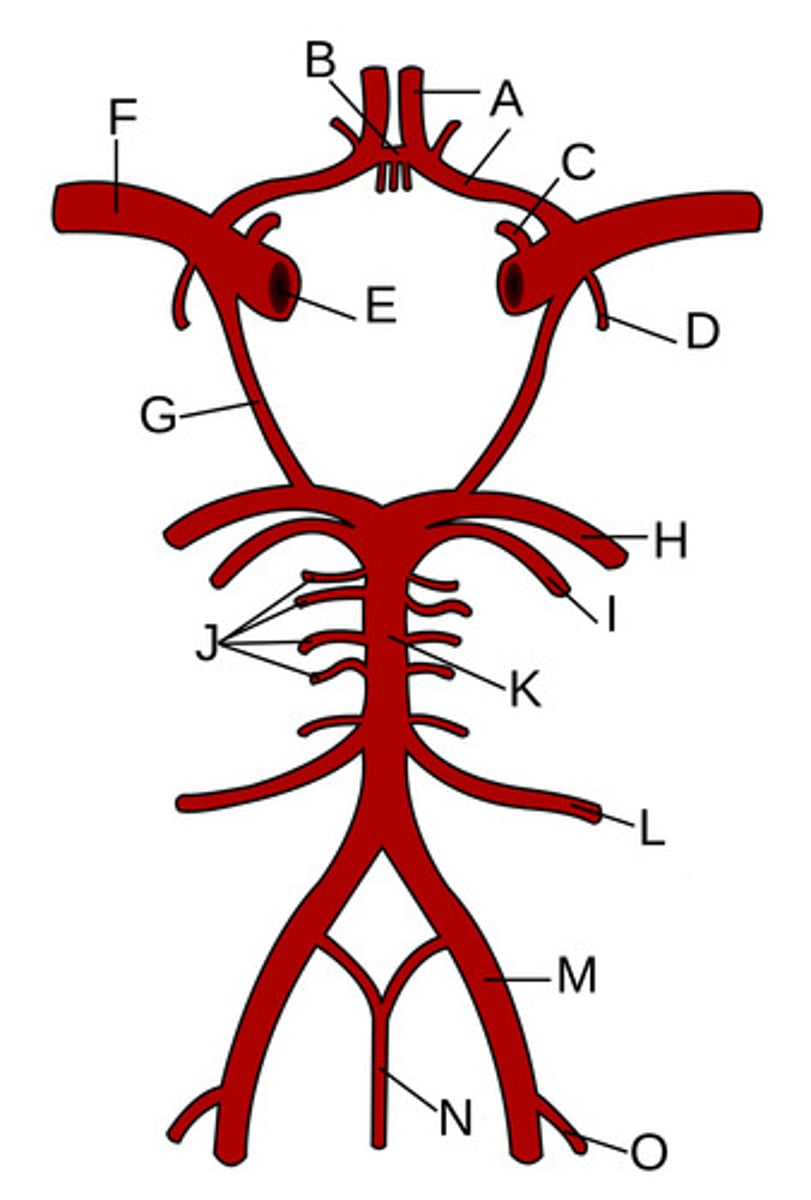
Internal carotid artery
E?
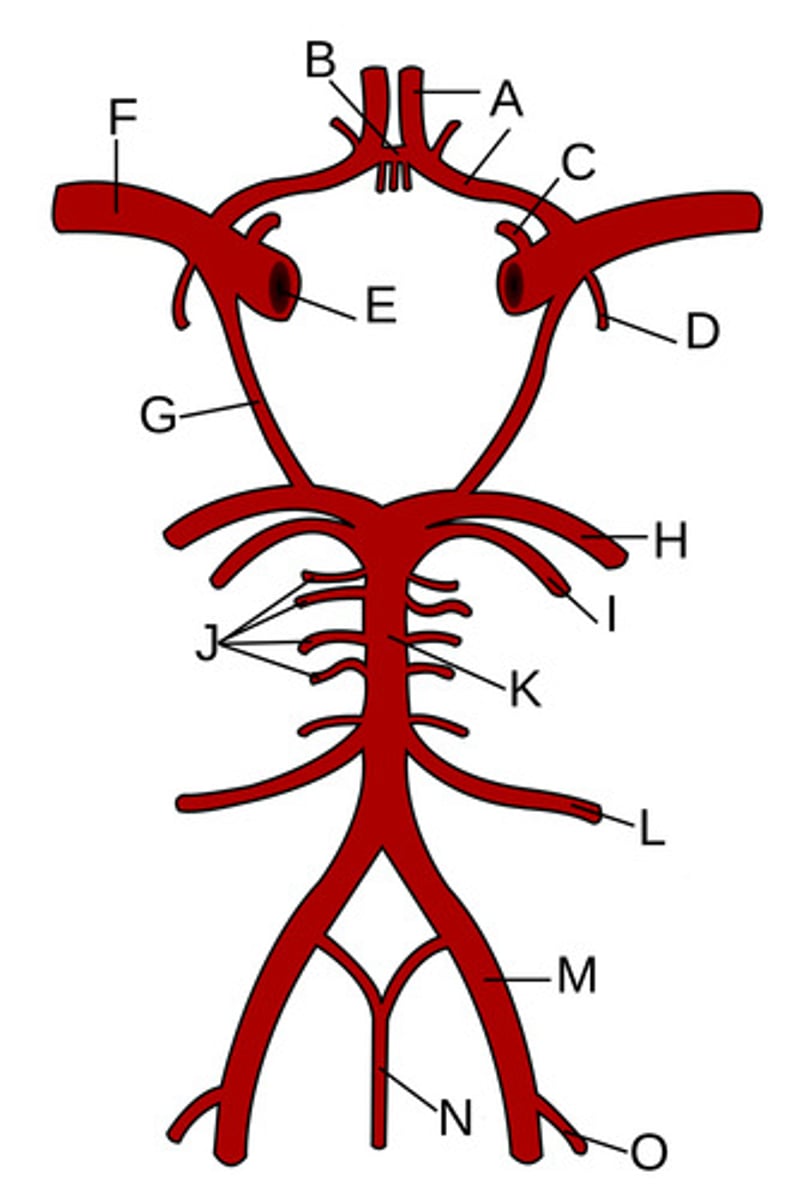
Middle cerebral artery
F?
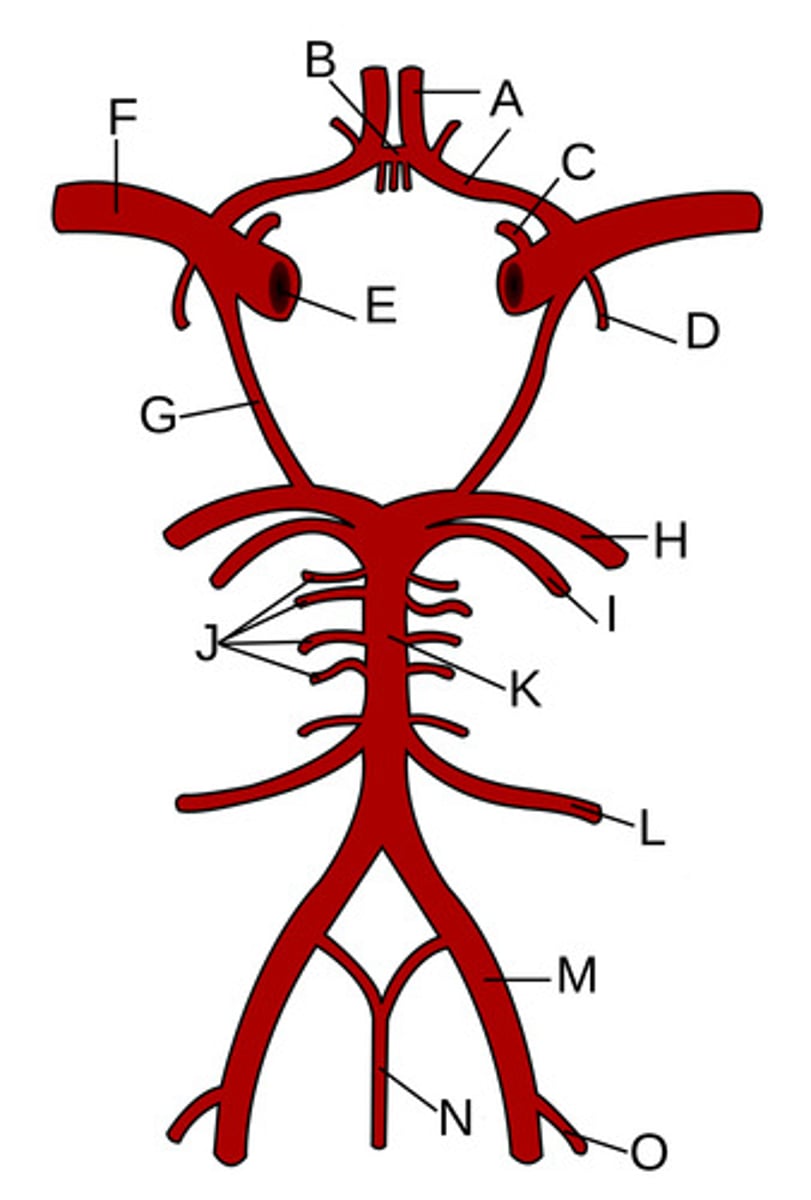
Posterior communicating artery
G?
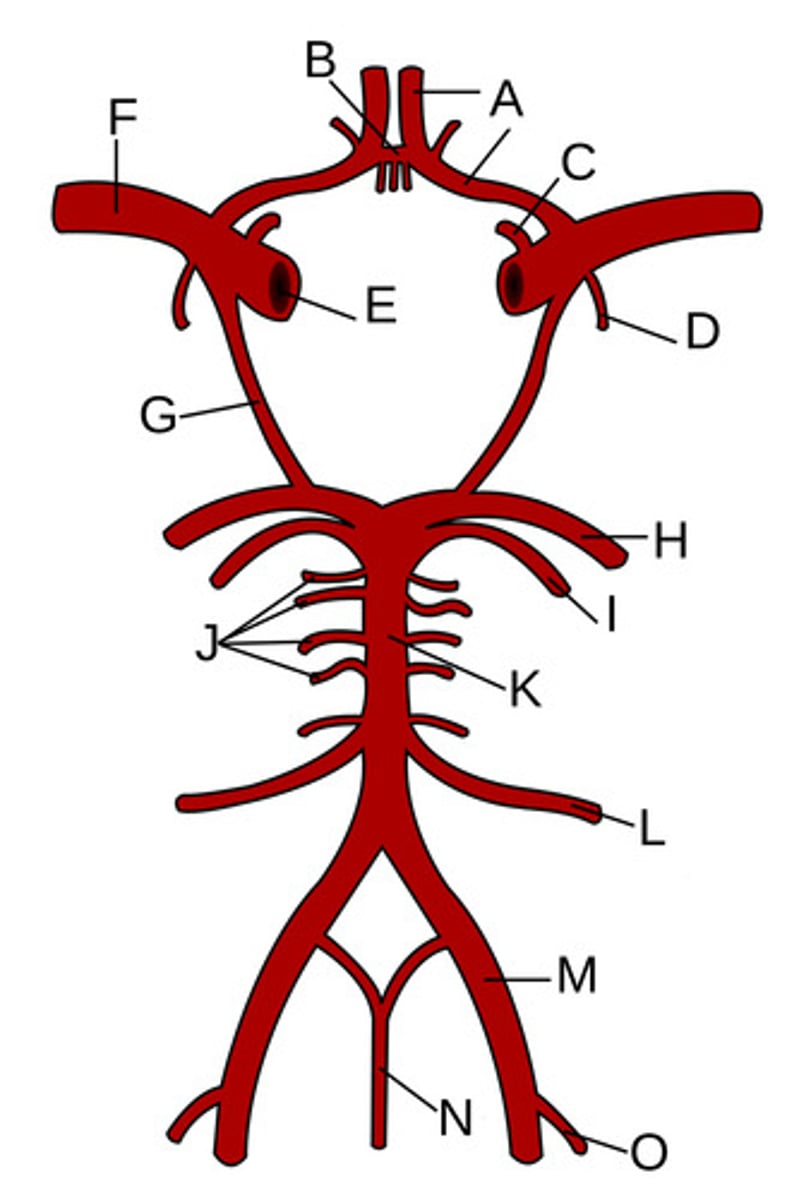
Posterior cerebral artery
H?
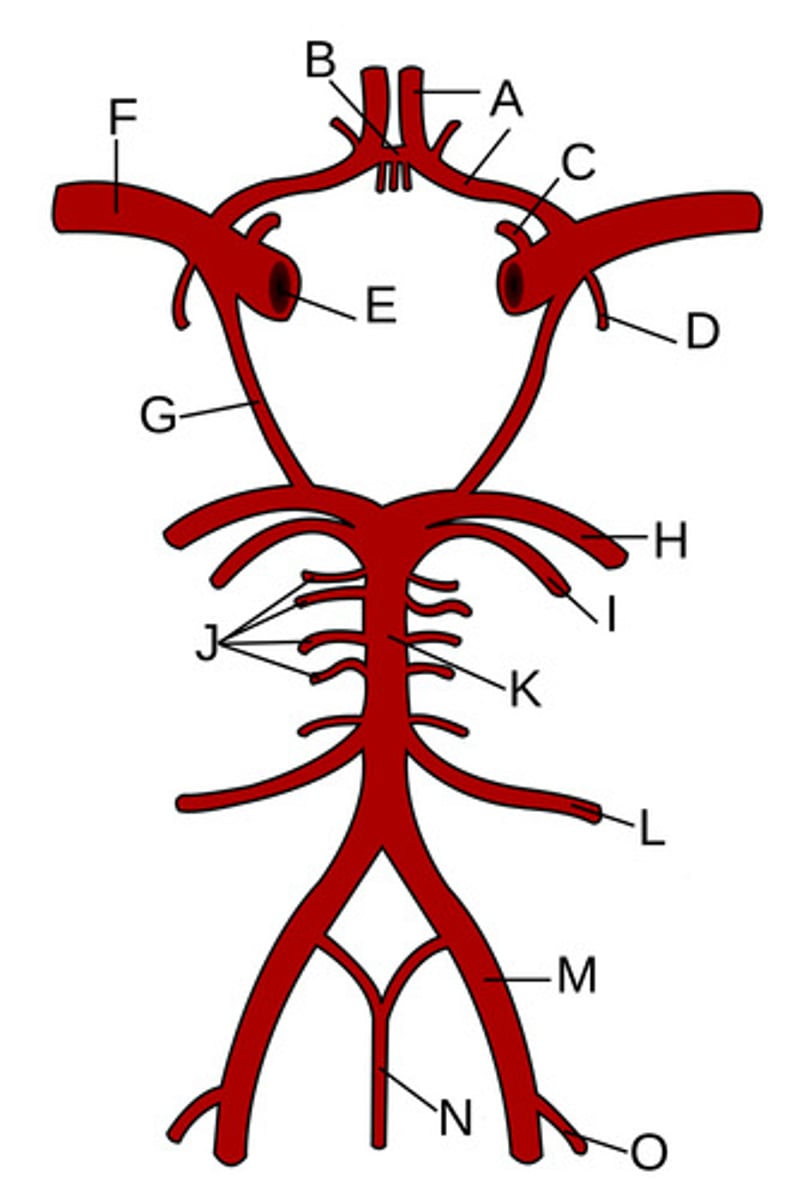
Superior cerebellar artery
I?
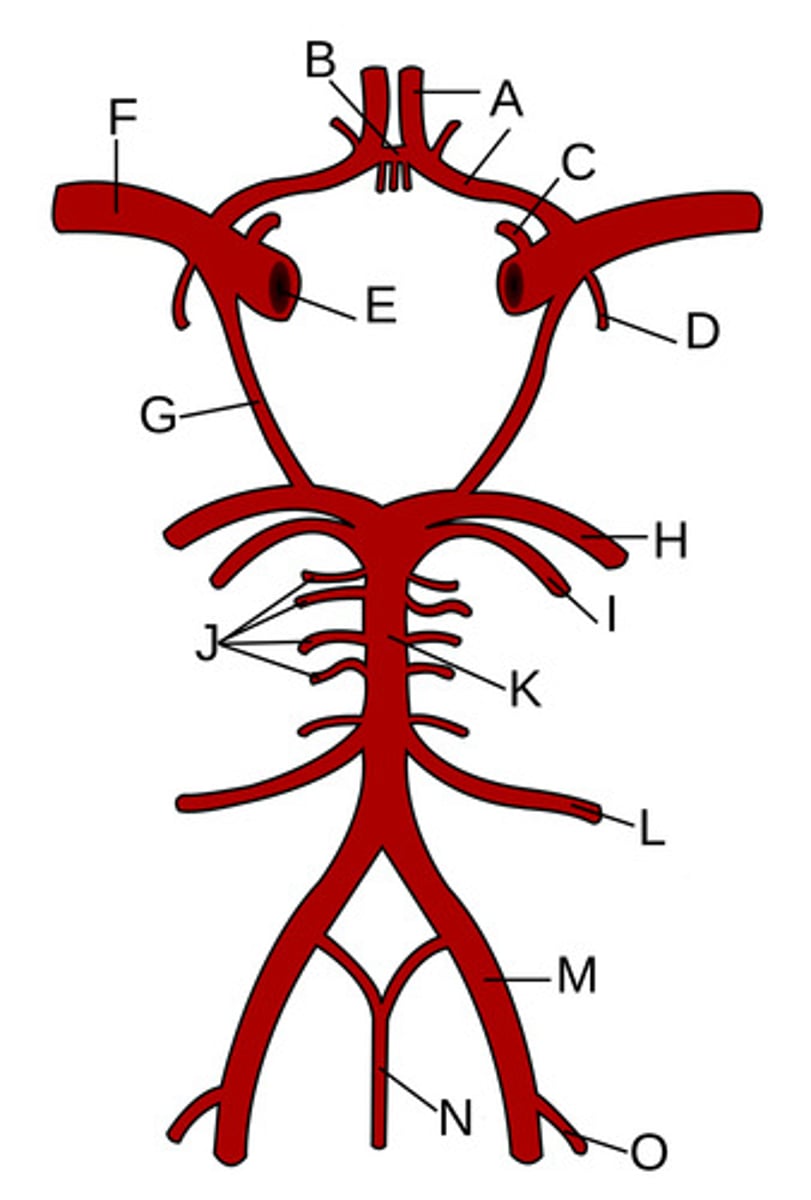
Pontine arteries
J?
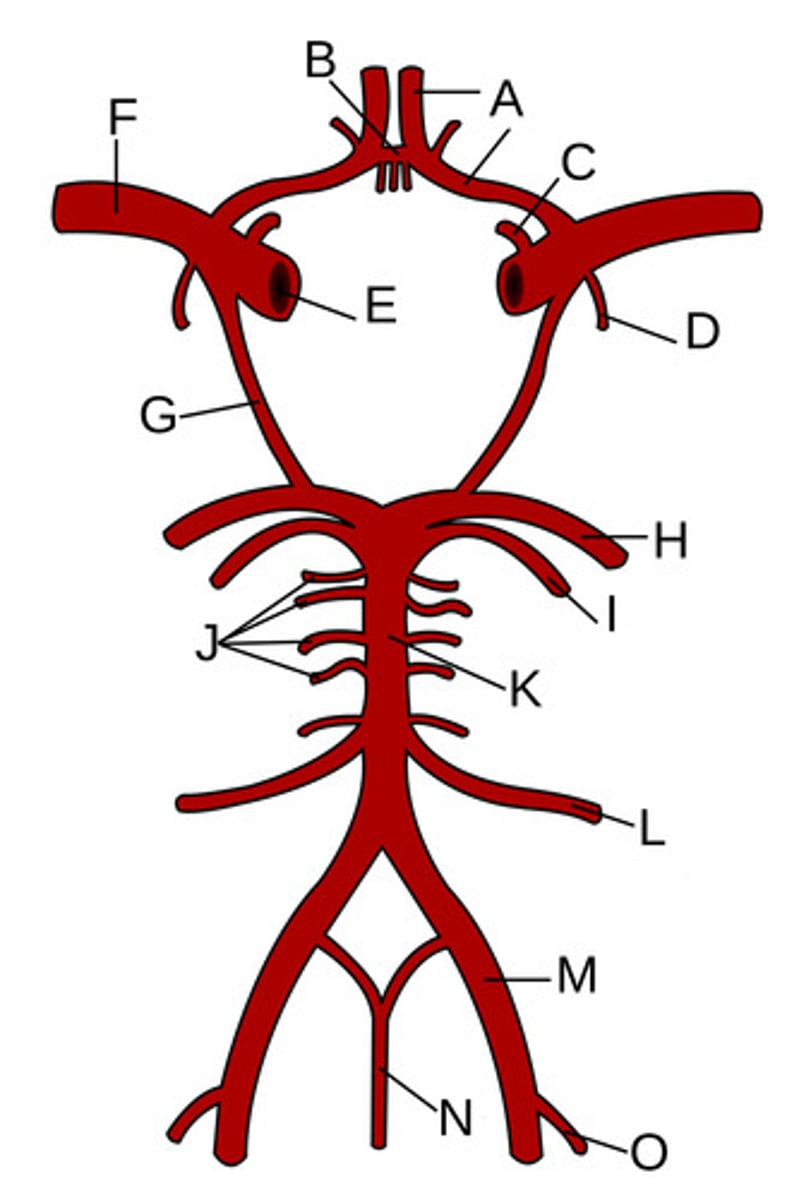
Basilar artery
K?
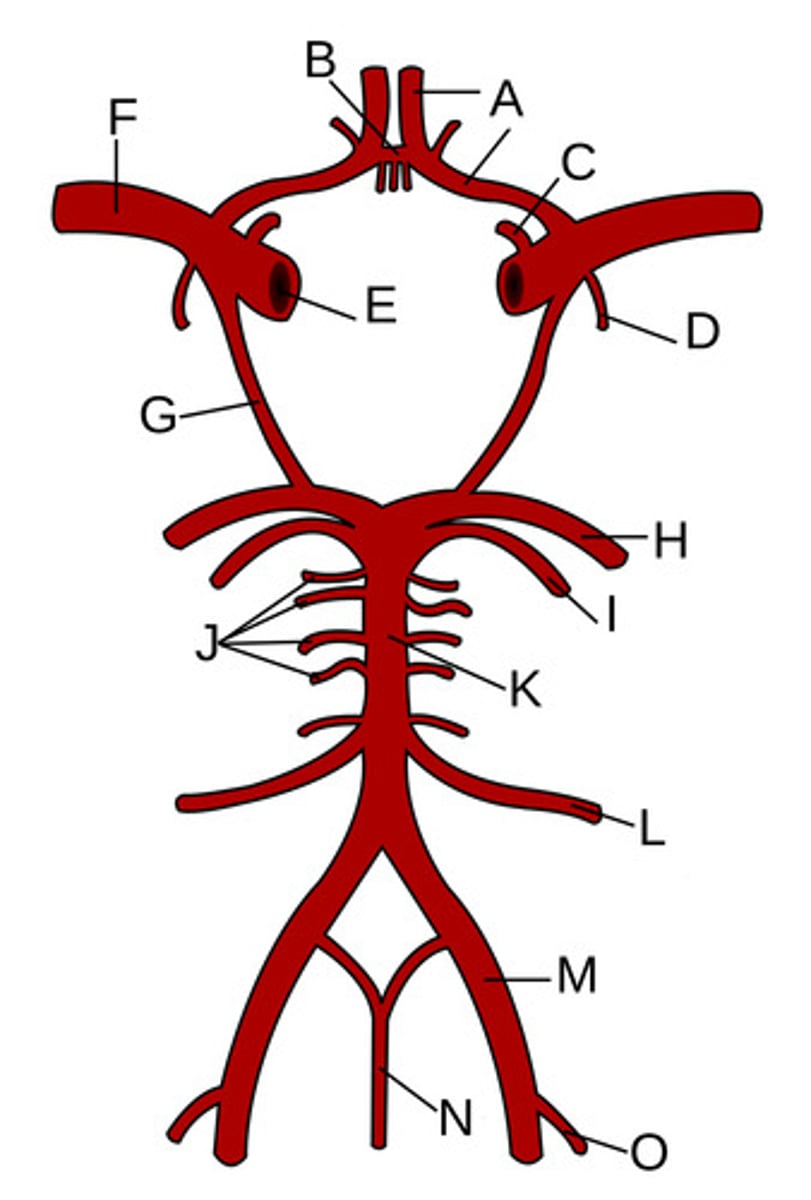
Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
L?
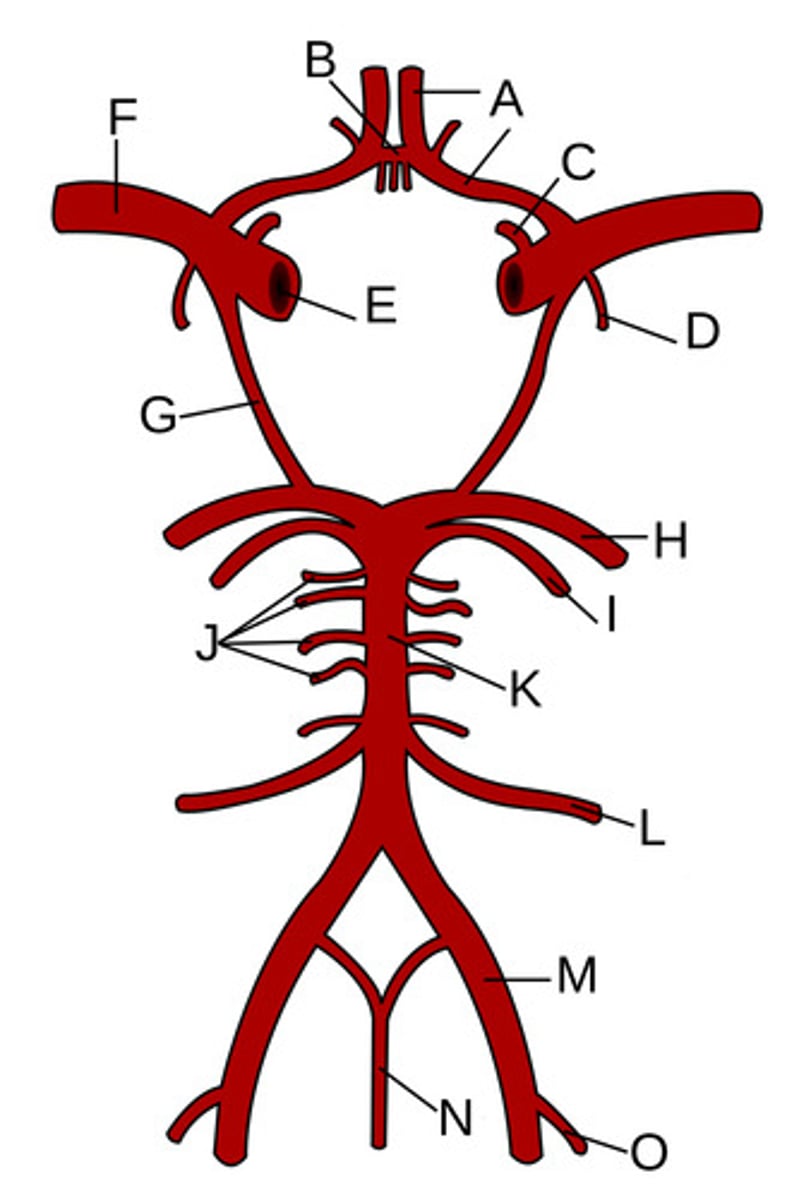
Vertebral artery
M?
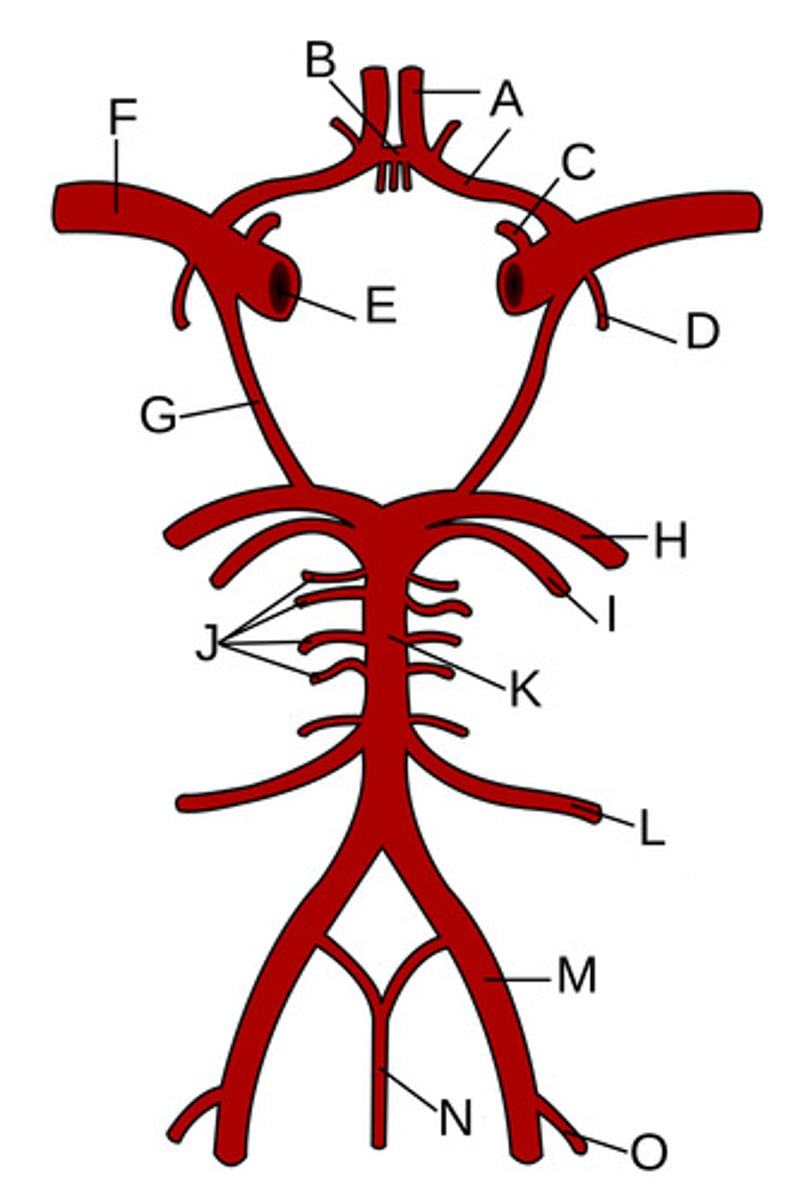
Anterior spinal artery
N?
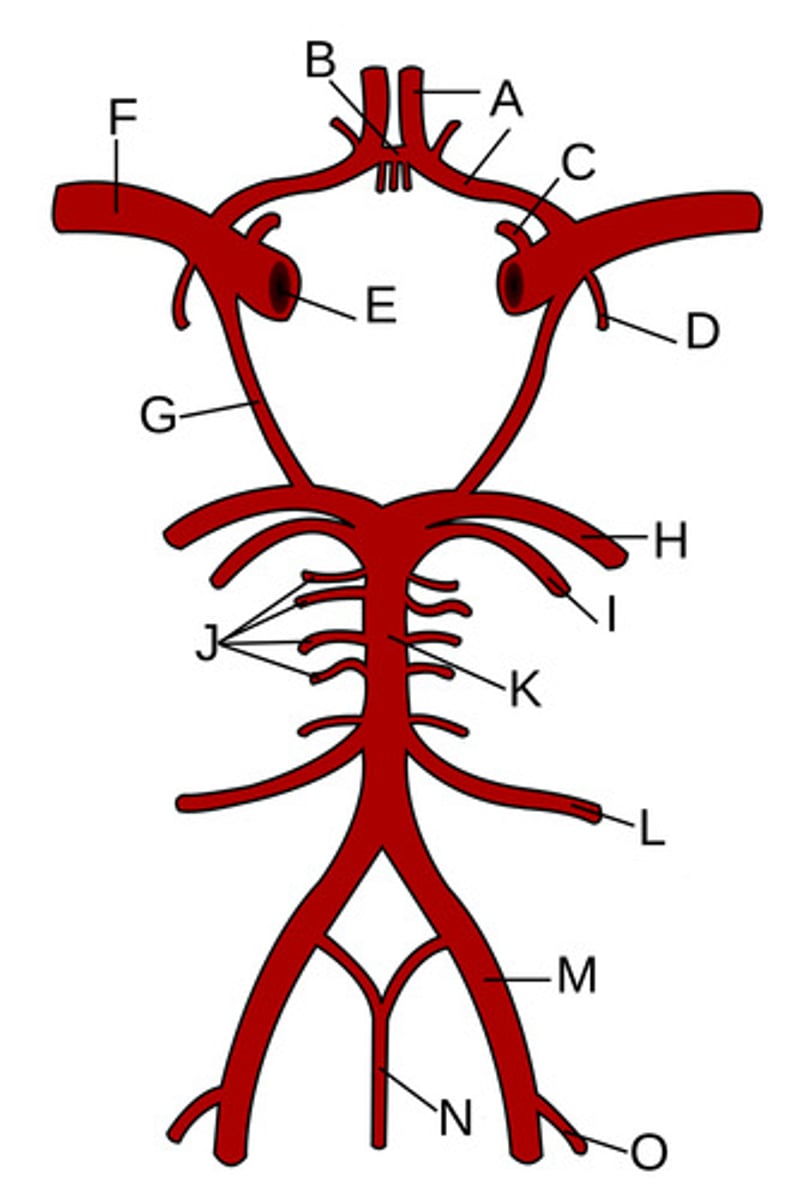
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
O?

80%
Anterior circulation supplies what proportion of the brain?
20%
Vertebral arteries supply what proportion of the brain?
Internal Carotid
The anterior circulation making up the circle of willis is supplied by which artery?
Vertebral arteries
The posterior circulation of the brain is supplied by which artery?
Anterior communicating artery
Berry aneurysms occur most commonly on which artery?
Internal carotid artery
The opthalamic artery is a branch of which artery?
Middle cerebral artery
The anterior choroidal artery is a branch of which artery?
Paralysis of the spinal cord
What will happen if the anterior spinal artery is occluded?
Anterior cerebral artery
Which artery supplies A?
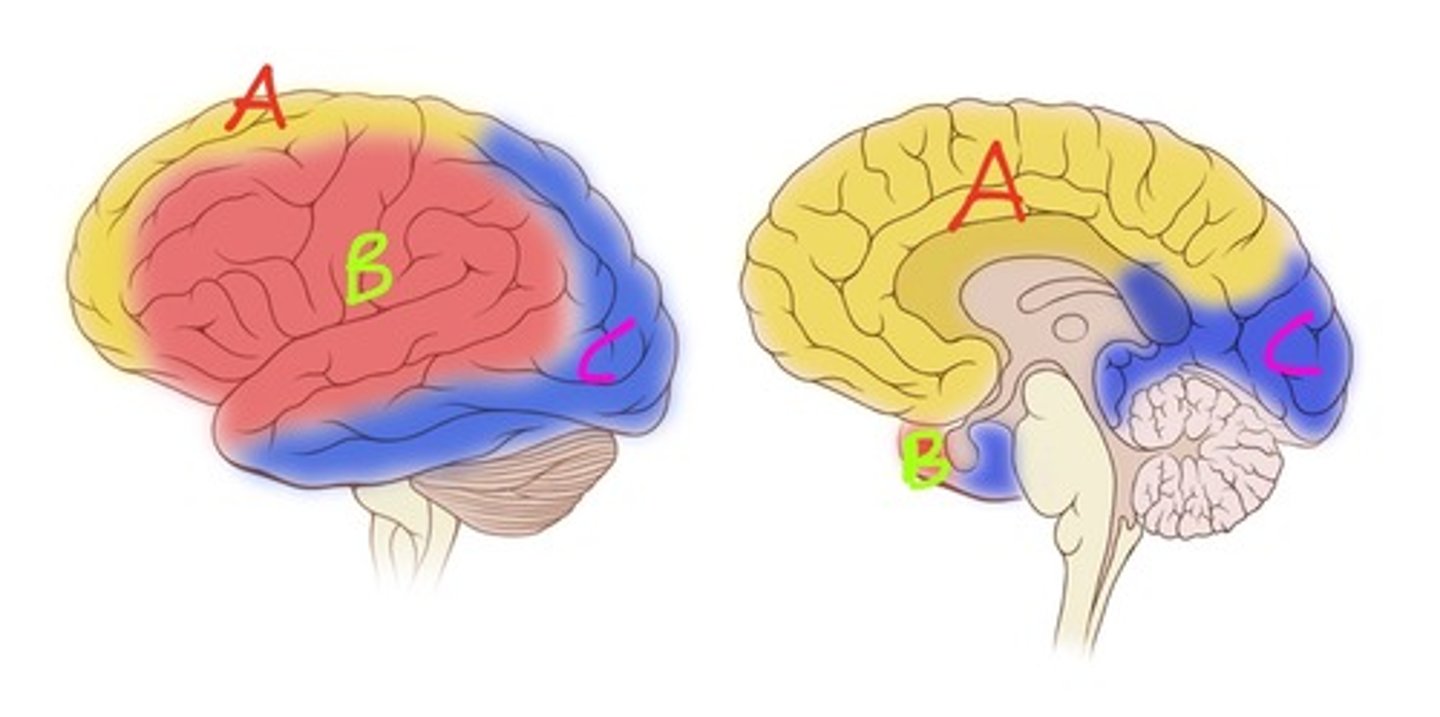
Middle cerebral artery
Which artery supplies B?
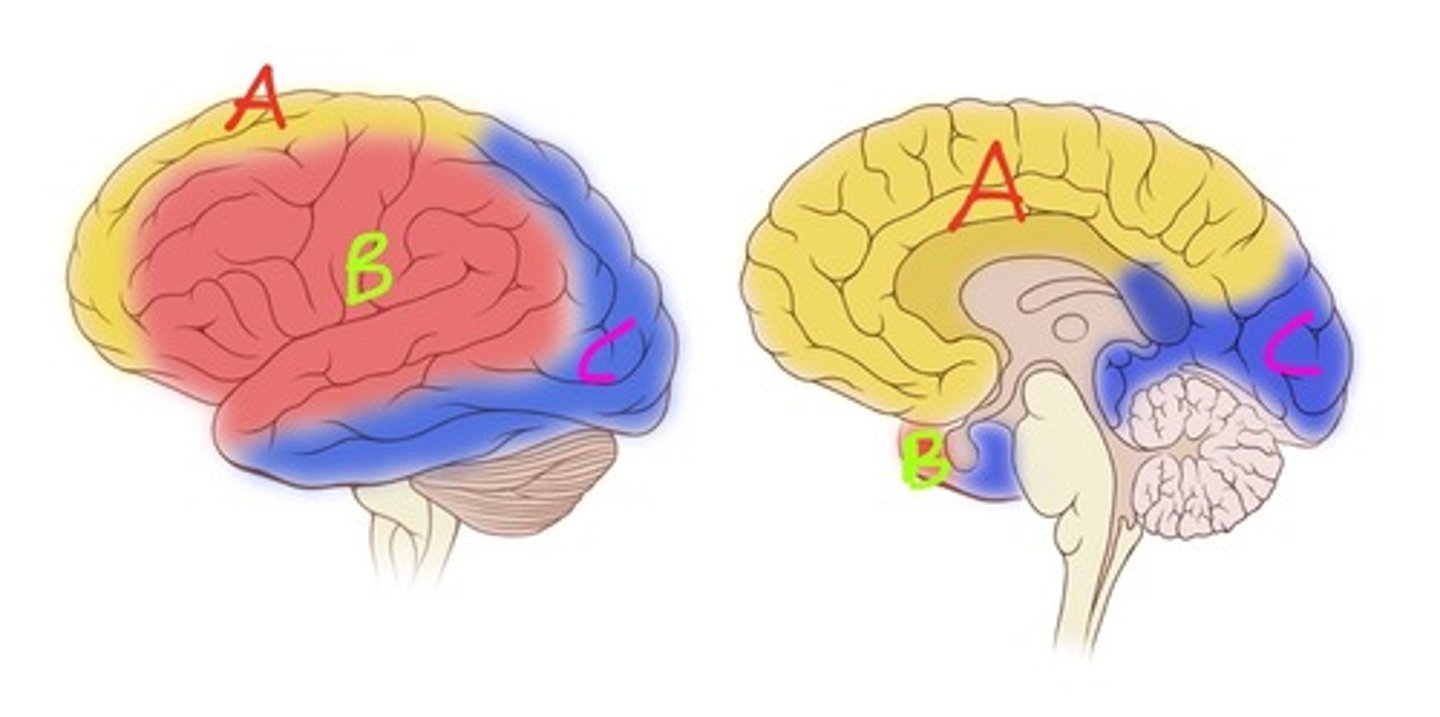
Posterior cerebral
Which artery supplies C?
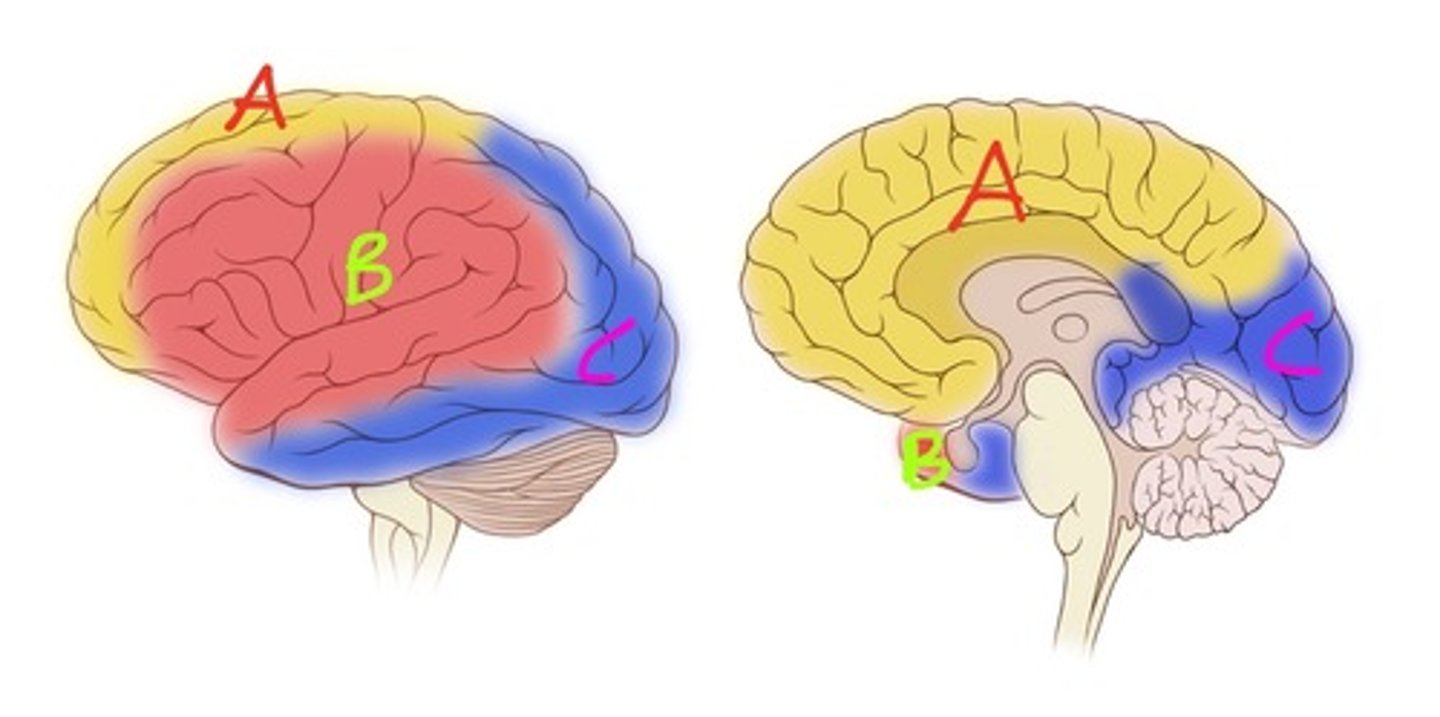
Bulk of lateral surface of hemisphere except superior strip of frontal and parietal and inferior part of temporal lobe
Supplies broca's area and wernicke's areas
Supplies basal ganglia and internal capsule
Which lobes are supplied by the middle cerebral artery?
Latero-inferior frontal lobe
Where does broca's area lie?
Left hemisphere for right-dominant
Mostly left hemisphere for left dominant
Which hemisphere is broca's area in?
Middle cerebral artery
Which artery supplies broca's area?
Superior sagittal sinus
Which vein does Broca's area drain into?
44
What brodmann's area is Broca's area?
Language expression
What is the function of Broca's area?
Expressive aphasia
A lesion in broca's area would give?
Lateral temporal lobe (superior temporal gyrus)
Where does wernicke's area lie?
Left hemisphere in 95% of right handed;
Left hemisphere in 60% of left handed
Which hemisphere does Werncike's area lie in?
Middle cerebral artery
Which artery supplies Wernike's area?
22
Which brodmann's area is Wernicke's area?
Language comprehension
Function of Wenicke's area?
Receptive aphasia
Lesion in Wernicke's area would give?
Weakness of contralateral face and arm;
sensory loss of contralateral face and arm;
Damage to dominant hemisphere, usually left
Receptive and expressive aphasia
Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery would give?
Medial portions of frontal and superior parietal lobes, medial longitudinal fissure, corpus callosum, olfactory bulb and tract
Which lobes are supplied by the anterior cerebral artery?
Paralysis of contralateral foot and leg (motor);
sensory loss in contralateral foot and leg;
Occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery would give?
Occipital lobe (visual cortex), inferomedial part of temporal lobe
Which lobes are supplied by posterior cerebral artery?
Contralateral pain and temperature sensation loss; visual field defects; contralateral deficits of facial nerve (only lower face)
Occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery would give?
brainstem; cerebellum; occipital lobe
Which brain regions are supplied by vertebro-basilar system?
pontine; anterior inferior cerebellar; labyrinthine; superior cerebellar; posterior cerebral
Basilar artery gives off which branches?
Middle ear
What structure does the labyrinthine artery supply?
Anterior cerebral arteries; anterior communicating arteries
Anterior perforating arteries are given off which branch?
Posterior communicating; posterior cerebral arteries
Posterior perforating arteries are given off which branch?
Subclavian artery
Vertebral arteries arise from which artery?
Foramen transversum
Vertebral arteries ascend through which foramen in the cervical vertebral canal?
Common carotid
Internal carotid arises from which artery?
Foramen lacerum
Which cranial fossa does the internal carotid enter through?
orbit; frontal and ethmoid sinuses; frontal scalp; dorsum of nose
The ophthalmic artery supplies which structures?
Optic tract; choroidal plexus of lateral ventricle; deep structures
The anterior choroidal artery supplies which structures?
Single anterior spinal artery;
Paired posterior spinal arteries
Which arteries supply the spinal cord?
Medially, ventral surface
What surface of the spinal cord does the anterior spinal artery descend?
posterolateral surface
What surface of the spinal cord do the posterior spinal arteries descend?
Anterior and posterior spinal arteries alone are insufficient to supply the spinal cord below cervical
Why do radicular arteries form anastomoses with spinal arteries below cervical level?
segmental and intercostal branches; passes into intervertebral foramen
Where do the radicular arteries arise?
Opthalmic artery
Which artery passes through optic canal?
Ethmoidal artery and vein
Which BVs pass through ethmoidal foramen?
Superior opthalmic vein
Which vein passes through the superior orbital fissure?
Middle meningeal artery
What artery passes through the foramen spinosum?
Labyrinthine artery
What artery passes through the internal acoustic meatus? (auditory canal)
Vertebral arteries
What artery passes through the foramen magnum
Internal jugular vein
What vein passes through the jugular foramen?
Vertebral arteries, basilar artery, posterior cerebral arteries
Posterior circulation consists of?
Anterior cerebral artery, middle cerebral artery
Anterior circulation consists of?
Bleeding into subarachnoid space between pia and arachnoid mater
Subarachnoid haemorrhage?