AP Government Political Ideologies and Beliefs
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Exit Poll
a poll taken at randomly selected polling places after the citizens have placed their votes

Political culture
an overall set of values widely shared within a society

political ideology
a more or less consistent set of beliefs about the purpose and scope of government

political socialization
the process by which people gain their political attitudes and opinions

random sample
a polling technique which is based on the principle that everyone has an equal probability of being selected as part of the sample

public opinion
the distribution of the population's beliefs about politics and policy issues
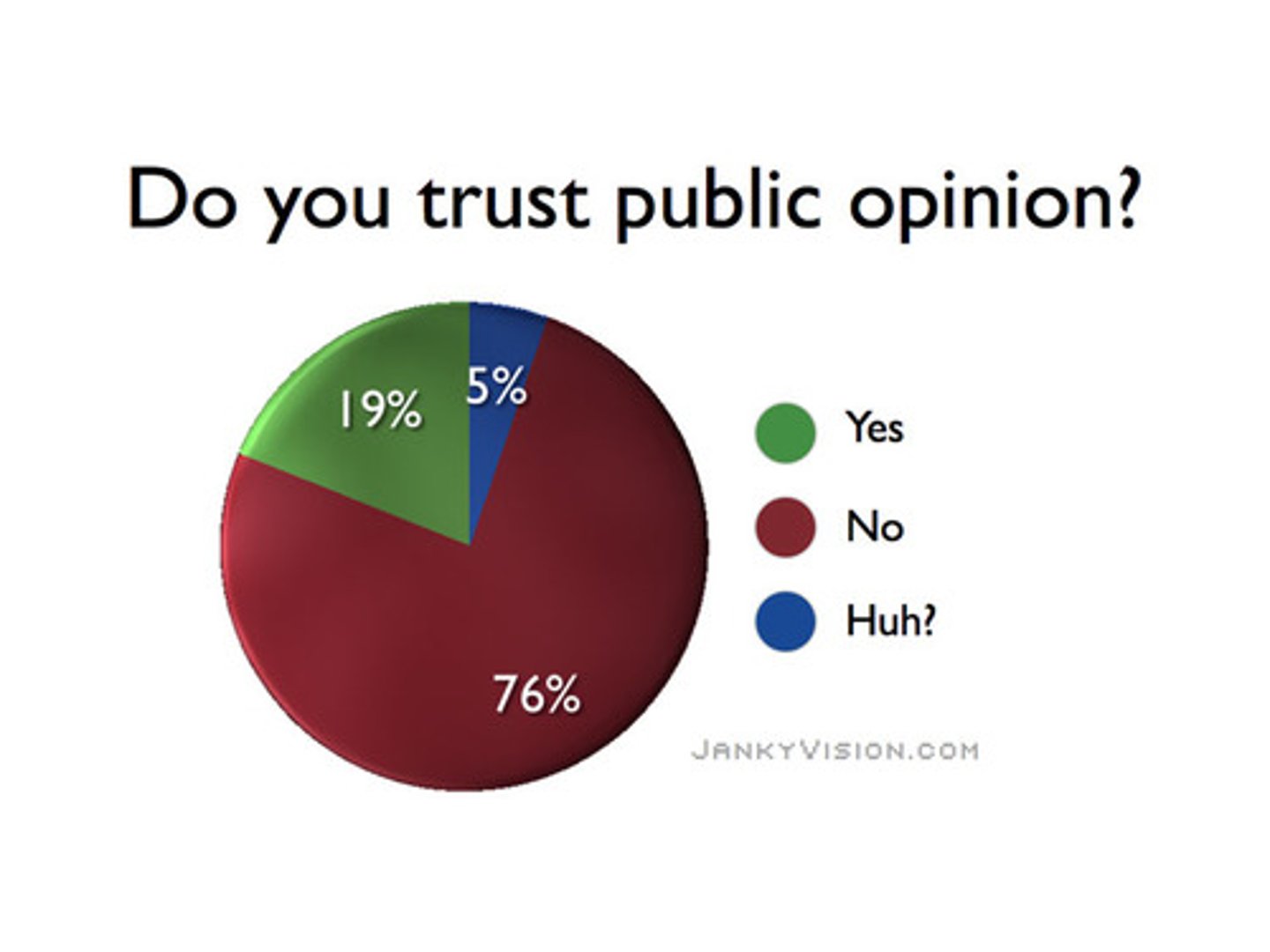
Sampling error
the level of confidence involved in the findings of a public opinion poll; difference between poll results
life-cycle effect
People change as they grow older because of age-specific experiences and thus people are likely to hold age-specific attitudes.

Generational effect
a long-lasting effect of the events of a particular time on the political opinions of those who came of political age at that time
Opinion polls
A method of systematically questioning a small, selected sample of respondents who are deemed representative of the total population.
Benchmark polls
Used in an election to gather information about people's views & concerns

Tracking poll
Tracks the path of public opinion by asking the same or similar questions over time
Focus Groups
Less scientific but allows for deeper insight into a topic

Push Polling
One problem with polls when they are conducted with an ulterior motive rather than neutral questions

Core Values
A principle that guides an organization's internal conduct as well as its relationship with the external world

Individualism
A social theory favoring freedom of action for individuals over collective or state control.

equality of opportunity
the idea that each person is guaranteed the same chance to succeed in life

free enterprise
Economic system in which individuals and businesses are allowed to compete for profit with a minimum of government interference

Rule of Law
principle that the law applies to everyone, even those who govern

Globalization
the process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale.

scientific polling
method of polling that provides a fairly precise reading of public opinion by using random sampling

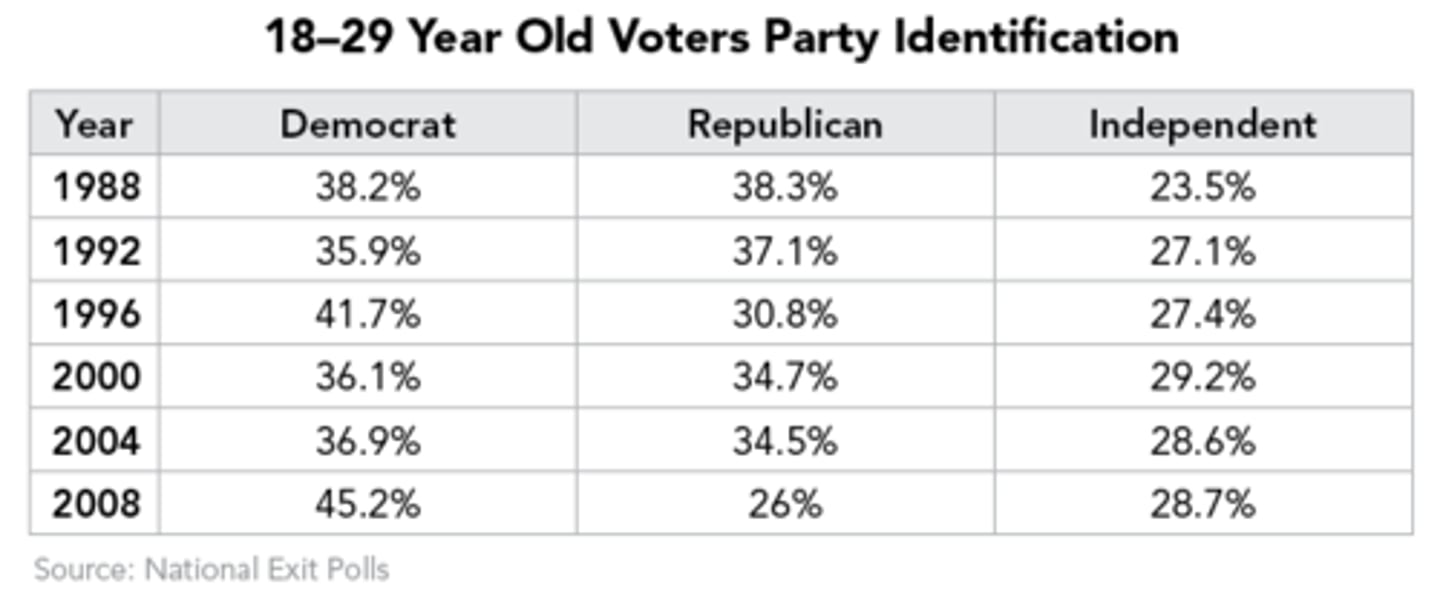
Entrance Poll
A poll that is taken before voters have cast their votes at the polling stations
polling universe
the set of people that a particular poll is meant to represent
representative sample
A sample that reflects the characteristics of the population from which it is drawn
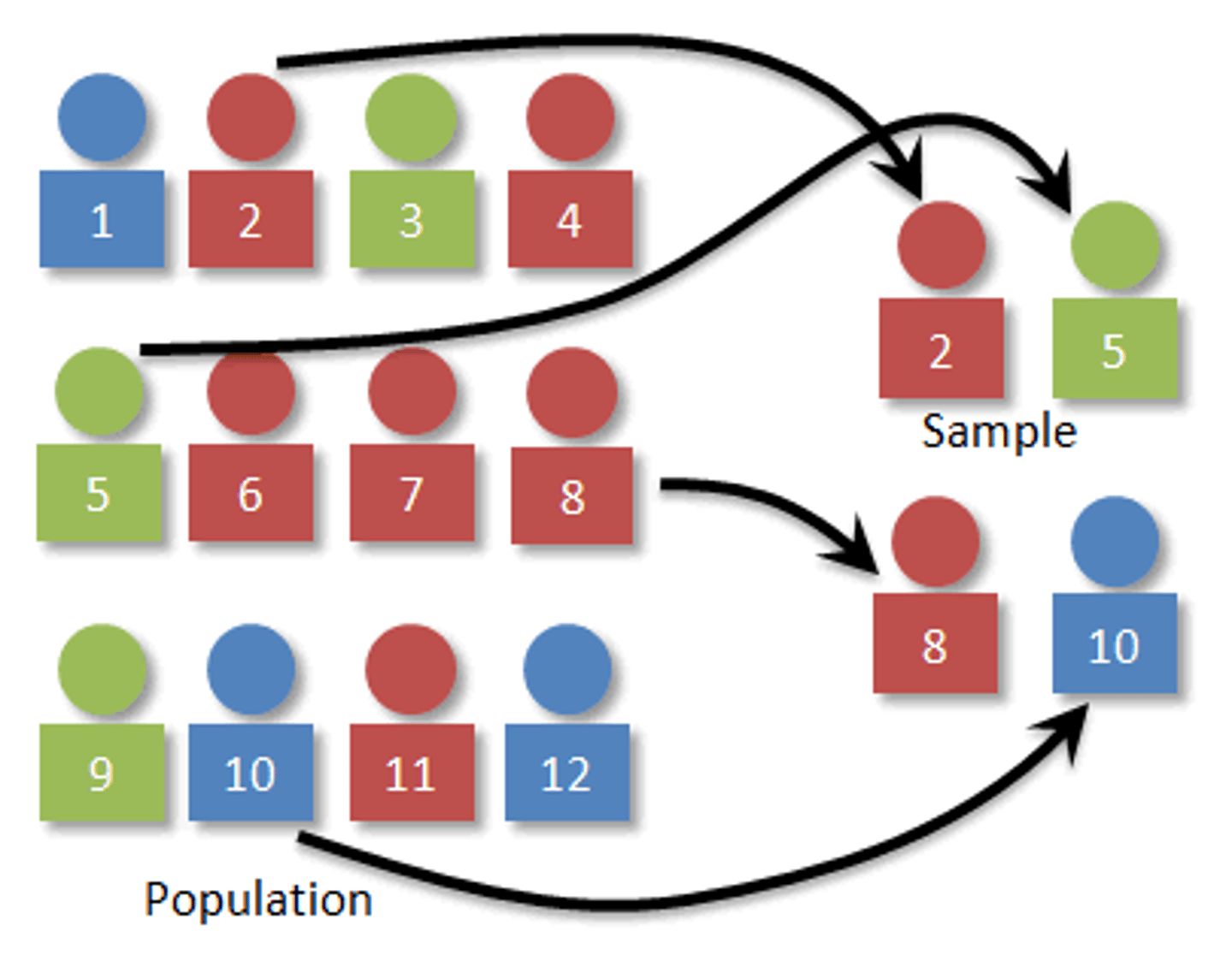
mass survey
a way to measure public opinion by interviewing a large sample of the population
Reliability of data
A state that exists when data is sufficiently complete and error free to be convincing for its purpose and context.

veracity of data
How accurate or truthful a data set might be

Political Spectrum
range of political views
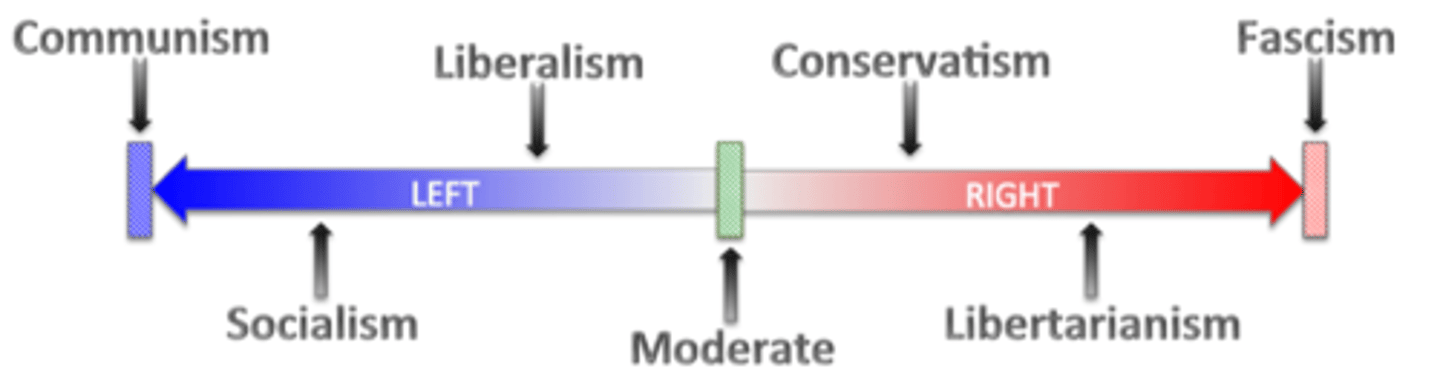
Liberal ideology
An ideology that advocates for more government regulation of the economy and emphasis on redistribution of income, but emphasizes individual freedom/privacy on a range of social issues except in areas of religious and education freedoms

Conservative Ideology
An ideology that advocates minimal regulation of the economy and decreased emphasis on income redistribution, emphasizes religious liberty and free enterprise system

Regulation of the marketplace
Government controls the economy

Libertarian Ideology
An ideology that seeks even more limited government than that promoted by conservatives, little or no regulations beyond property rights and individual property

Keynesian economic theory
The theory that a government policy of increasing spending and cutting taxes could stimulate the economy in a recession.

supply-side economics
An economic philosophy that holds the sharply cutting taxes will increase the incentive people have to work, save, and invest. Greater investments will lead to more jobs, a more productive economy, and more tax revenues for the government.

monetary policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling the money supply and thus interest rates.

fiscal policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling taxing and spending.

social equality
equality in wealth, education, and status

economic equality
idea of fairness in economics, particularly in regard to taxation or welfare economics.

Sampling Techniques
The method used to select people from the population.

political efficacy
The belief that one's political participation really matters - that one's vote can actually make a difference

Polarization
the presence of increasingly conflicting and divided viewpoints between the Democratic and Republican Parties

identity politics
political activity and ideas based on the shared experiences of an ethnic, religious, or social group emphasizing gaining power and benefits for the group rather than pursuing ideological or universal or even statewide goals

random digit dialing
A technique used by pollsters to place telephone calls randomly to both listed and unlisted numbers when conducting a survey.

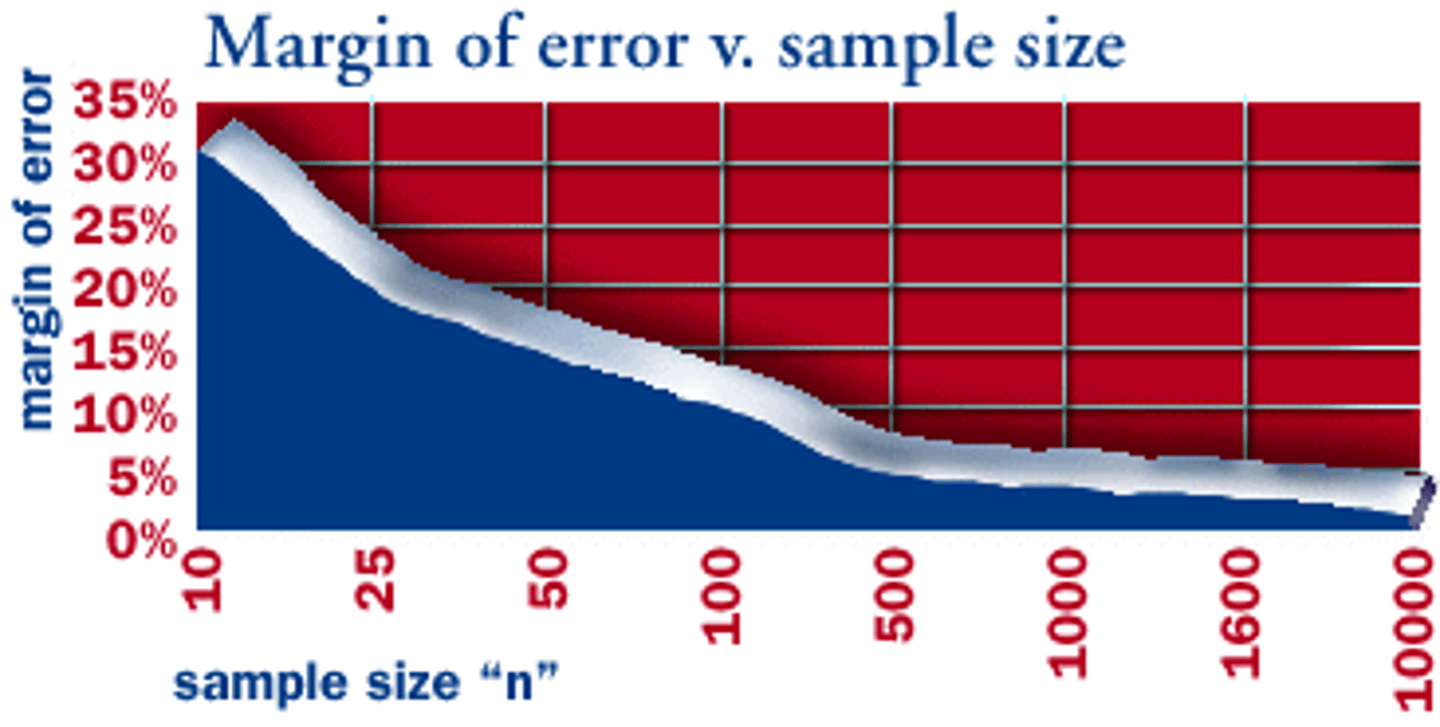
margin of error
a measure of the accuracy of a public opinion poll
wedge issues
a controversial issue that one party uses to split the voters in the other party

nonpartisan
free from party ties or bias
partisan
Devoted to or biased in support of a party, group, or cause

horserace election coverage
Media focuses on who is ahead in the polls than on policies and issues
bandwagon effect
When people join a cause because it seems popular or support a candidate who is leading in the polls

social desirability bias
the tendency for people to say what they believe is appropriate or acceptable

Demographics
statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it.