Chapter 1: Chemistry and Measurements
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 1 (9/12 & 9/16) lecture covering topics of measurement, conversion, significant figures, density, and more
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Units of measurement
volume
metric - liter (L)
SI - cubic meter (m³)
length
metric & SI - meter (m)
mass
metric - gram (g)
SI - kilogram (kg)
temperature
metric - degree Celsius (ºC)
SI - Kelvin (K)
time
metric & SI - second (s)
SI (international system of units) is a modification of the metric system.
There are other units, but these are the more commonly used in the world of chemistry.
Conversion factors
Conversion factors show equivalent factors — the relationship between the units
The unit of the given value must match the unit of the value in the denominator to cancel out
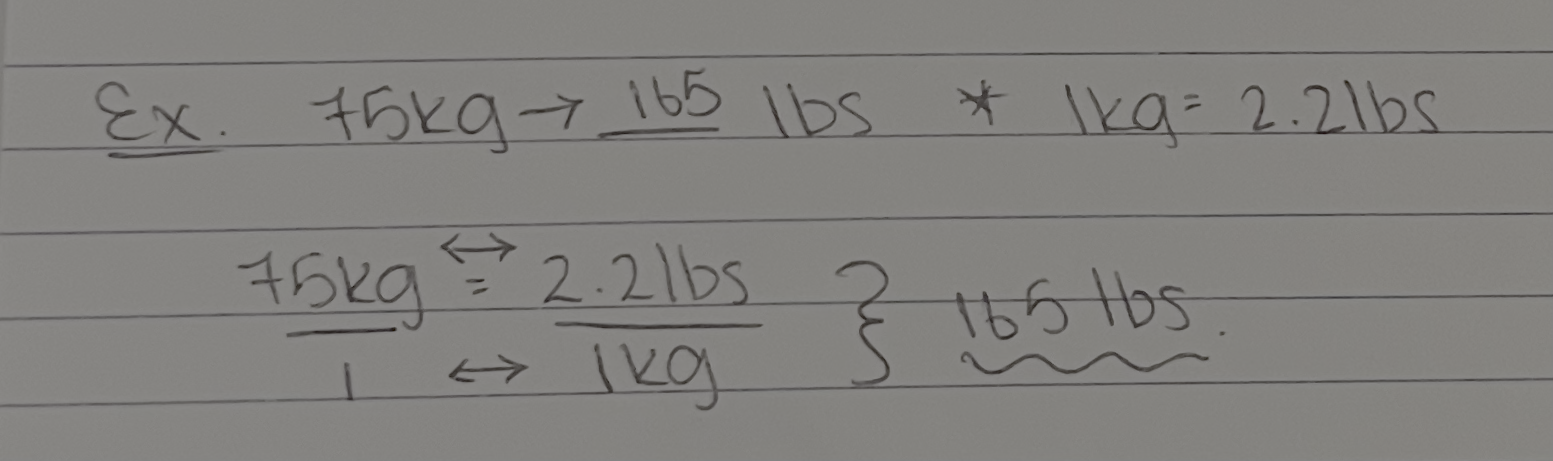
Significant figures
1) Numbers 1 to 9 are all significant figures
2) Zeros
If the value is less than 1, all zeroes BEFORE the first non-zero digit are NOT significant figures; between and the end of the decimal ARE significant figures
If the value is greater than 1 and does NOT have a decimal point, all trailing zeros to the right end of the number are NOT significant figures. If it’s greater than 1 with a decimal point, all digits ARE significant figures.
Examples: 1) .000000218 = 3 SF
2) .000218010 = 6 SF
3) 21000 = 2 SF
4) 21000.1 = 6 SF
Rules for significant figures (math operations)
Multiplication & Division: answer should have the lowest number of significant figures
Ex: 39.521 (5 SF) * 10.1 (3 SF) / 2.12 (3 SF) = 188.284 — final answer: 188
Addition & Subtraction: answer should have the lowest digit after decimal place (only one digit)
Ex: 31.9125 + 2.100 - 15.1 = 18.9125 — final answer: 18.9
Decimal notation → scientific notation
The decimal point must be after the first non-zero digit
Given # smaller than final # → 10-x
Given # larger than final # → 10+x (no need to put the plus sign, just indicating that it would be a positive integer instead of negative)
Ex: 267.52 → 2.6752 × 102
→ When asked for the correct number of significant figures in a problem, focus only on the value with no exponent (highlighted).
Major exponential values to remember
kilo = 10³ (1 km)
mega = 10⁶ (1Mm)
giga = 10⁹ (1 Gm)
deci = 10-1 (1 dm)
centi = 10-2 (1 cm)
milli = 10-3 (1 mm)
micro = 10-6 (1 μm)
nano = 10-9 (1 nm)
Density
Density = mass/volume → D = m/v
Defined as the mass of a given volume; physical property of matter
Mass - typically displayed in grams (g)
Volume - typically displayed in cm³ (cubic centimeter) or mL (milliliter) depending on whether the substance is a solid or liquid
1 mL = 1 cm³, so they can be used as interconvertible units.
If a substance is less dense than its conditions, then the substance will float.
Specific gravity
The specific gravity of a liquid sample is compared to the density of water.
The density of water is 1 g/mL.
Specific gravity = Density of sample liquid (g/mL) / Density of water (g/mL)
The units cancel out, so there is no unit for specific gravity.
Specific gravity can also be measured with a hydrometer.