Chapter 13 Peripheral Nervous system
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
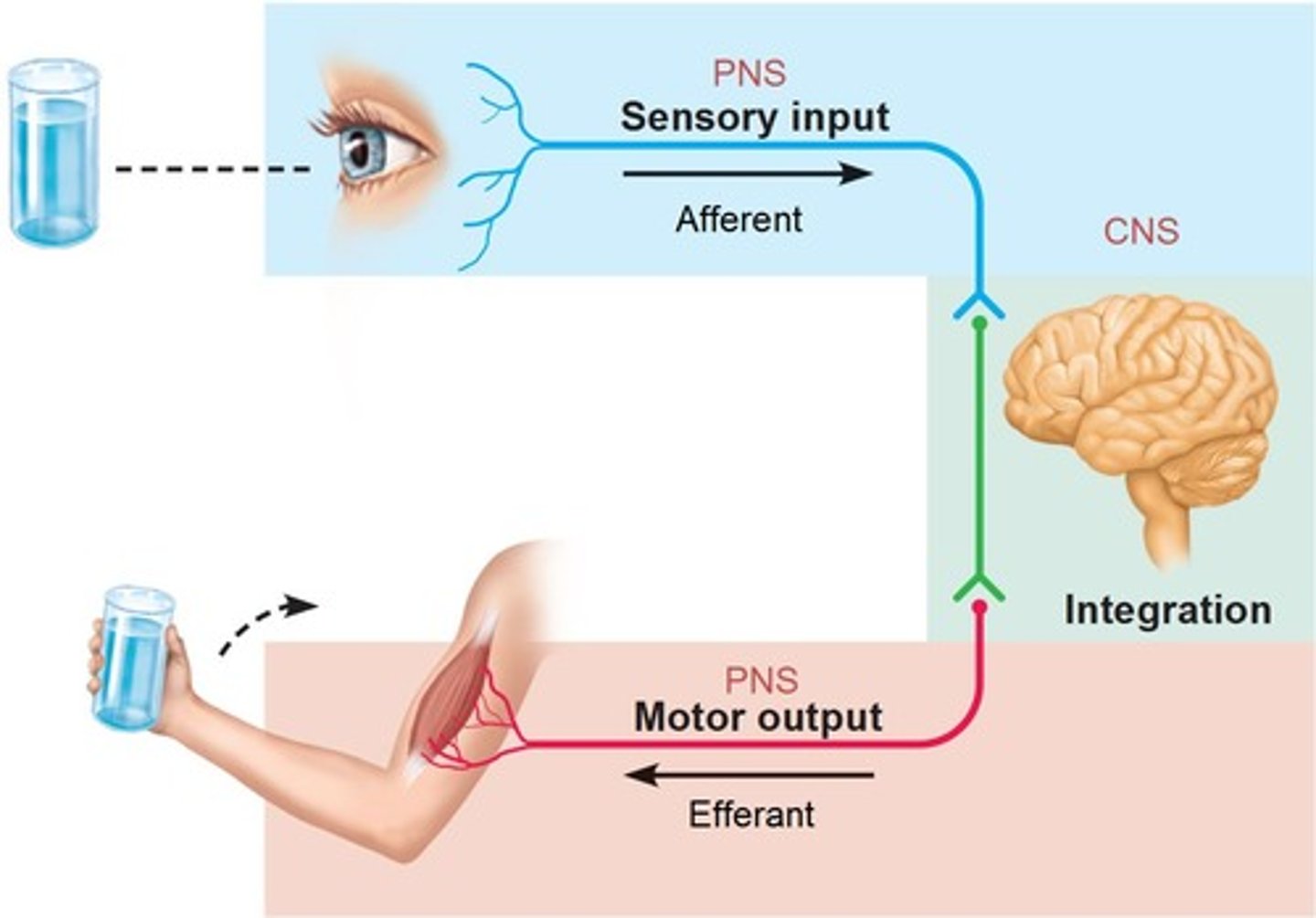
Sensory nervous system
- contains receptors,
- transmits information from receptors to the CNS
Somatic sensory
receives sensory information from skin, fascia, joints, skeletal muscles, special sense
Visceral sensory
recives sensroy information from viscera
Motor nervous system
- transmit information from NS to the rest of the body
- sends motor information to effectors
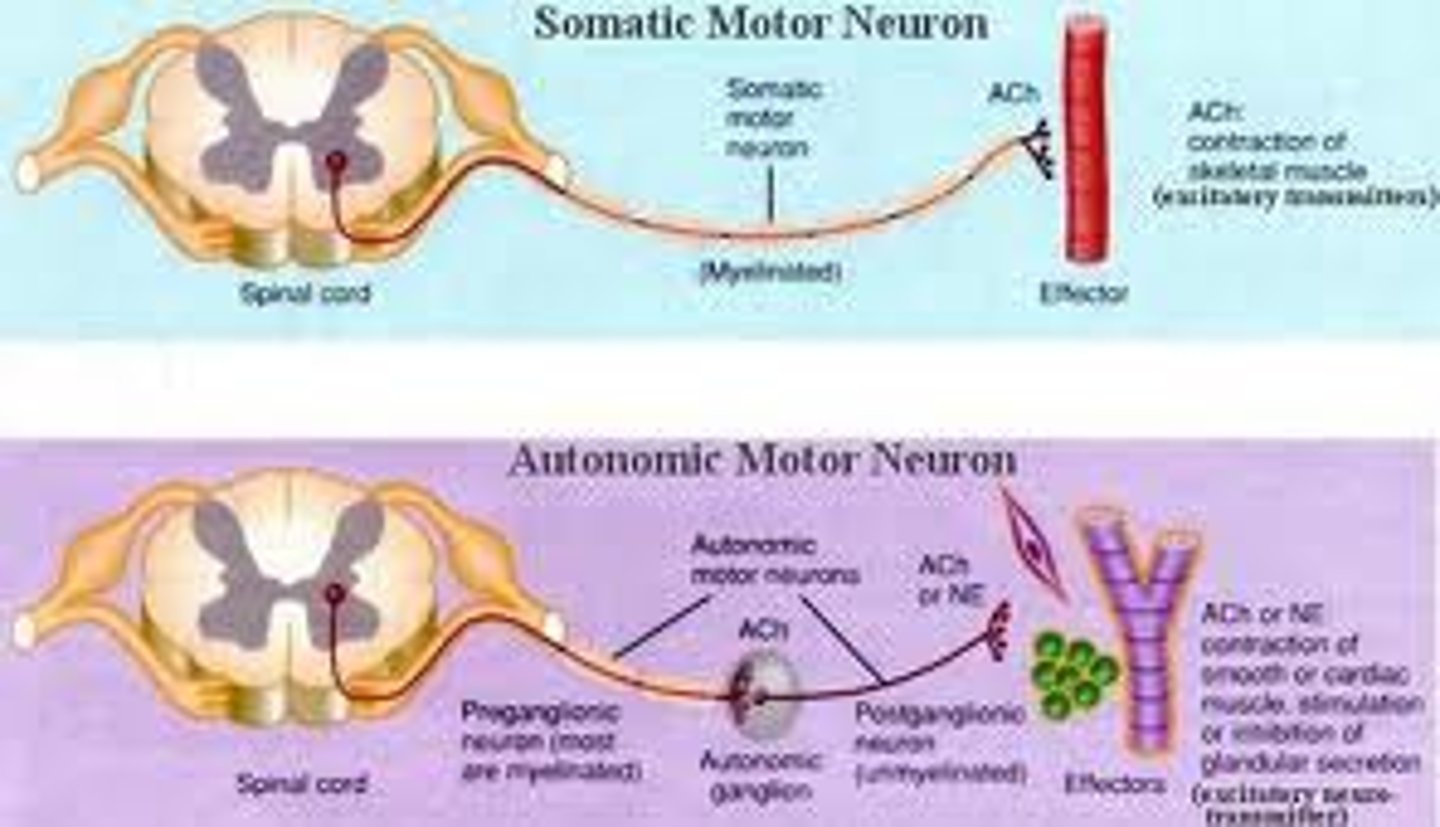
somatic motor
"voluntary" nervous system: innervates skeletal muscle
Autonomic motor
"involuntary" nervous system: innervates cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
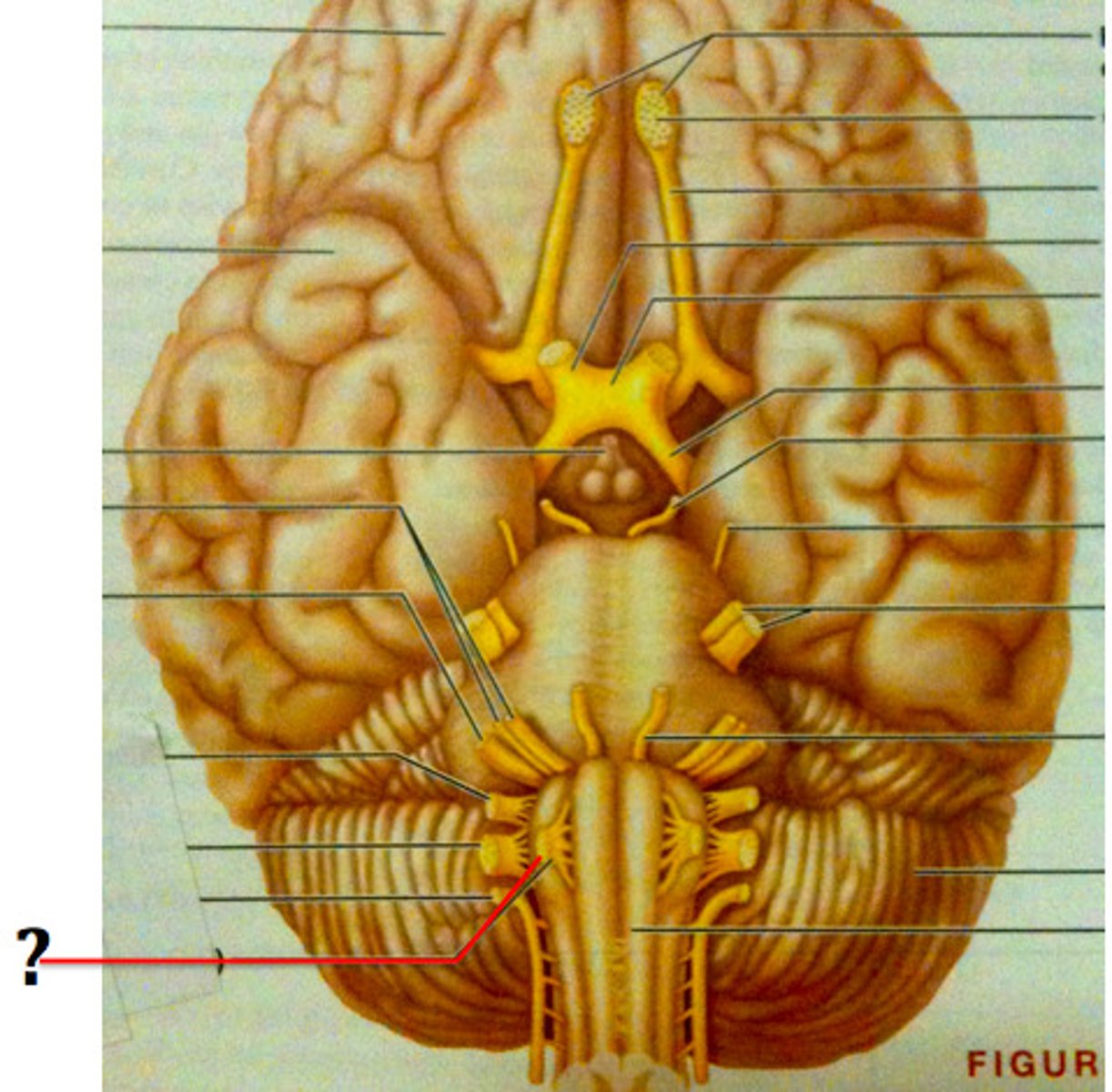
Olfactory nerve
sensory: smell
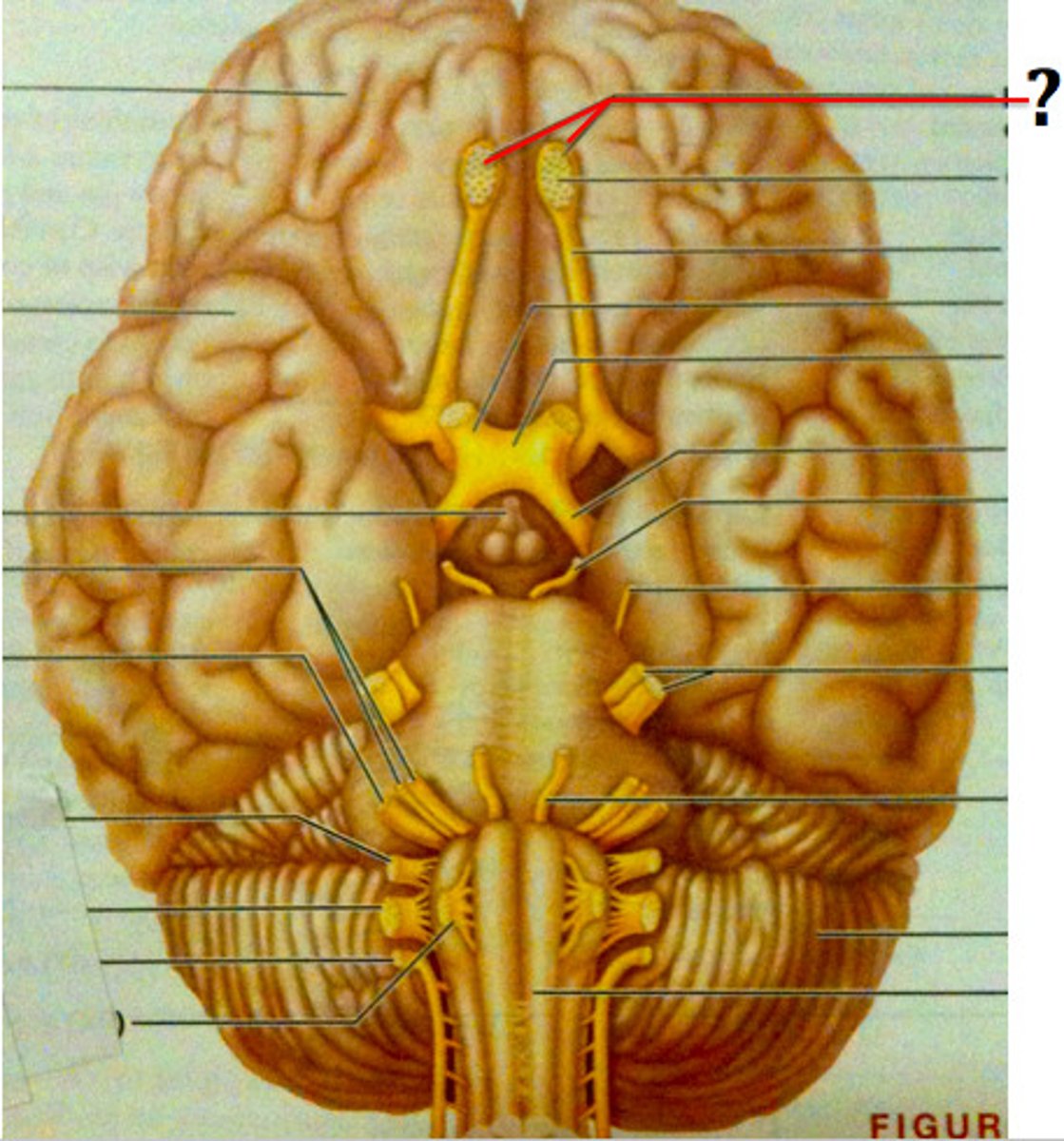
Optic nerve
Sensory: vision
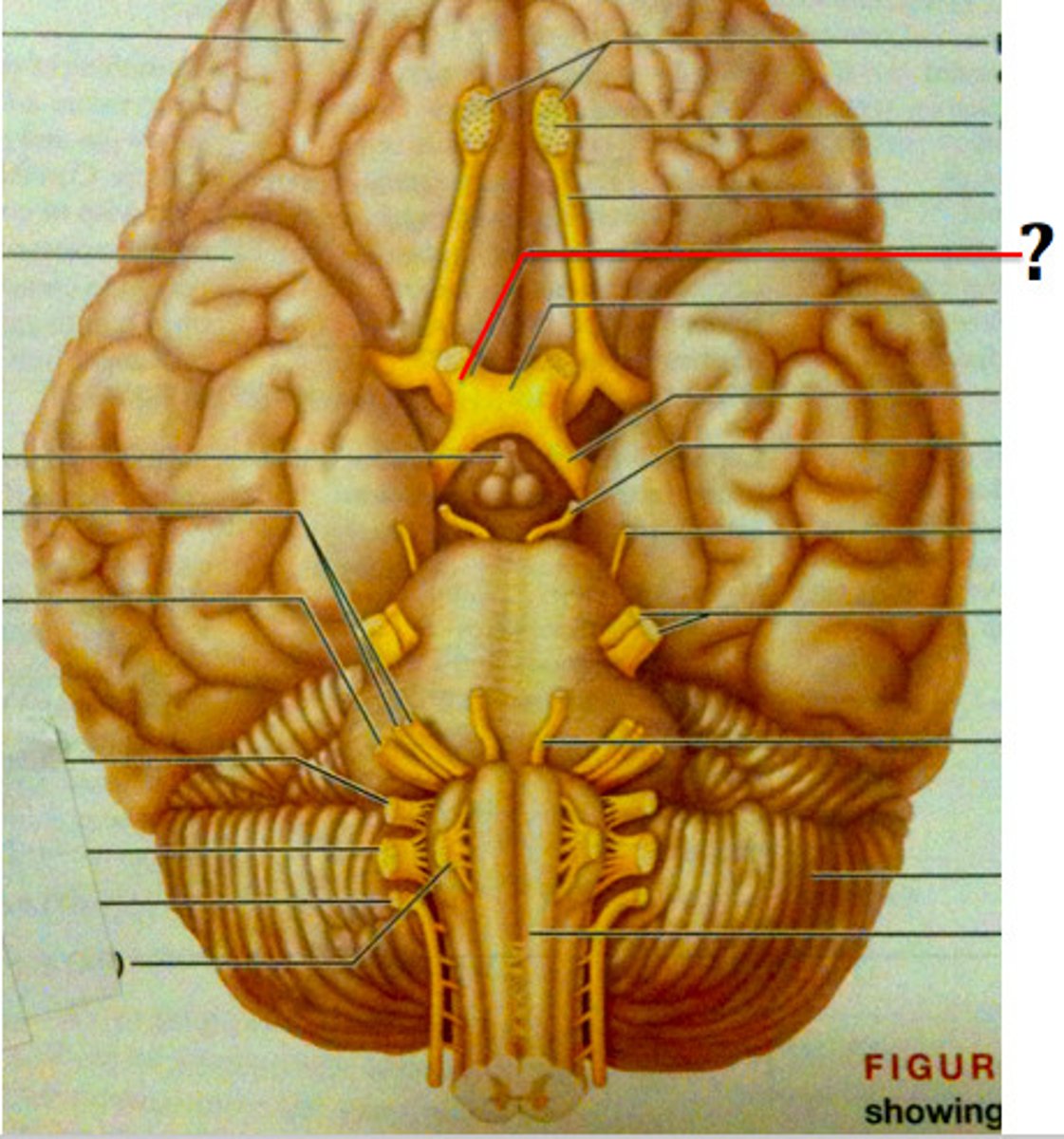
Oculomotor nerve
Motor: eye muscles
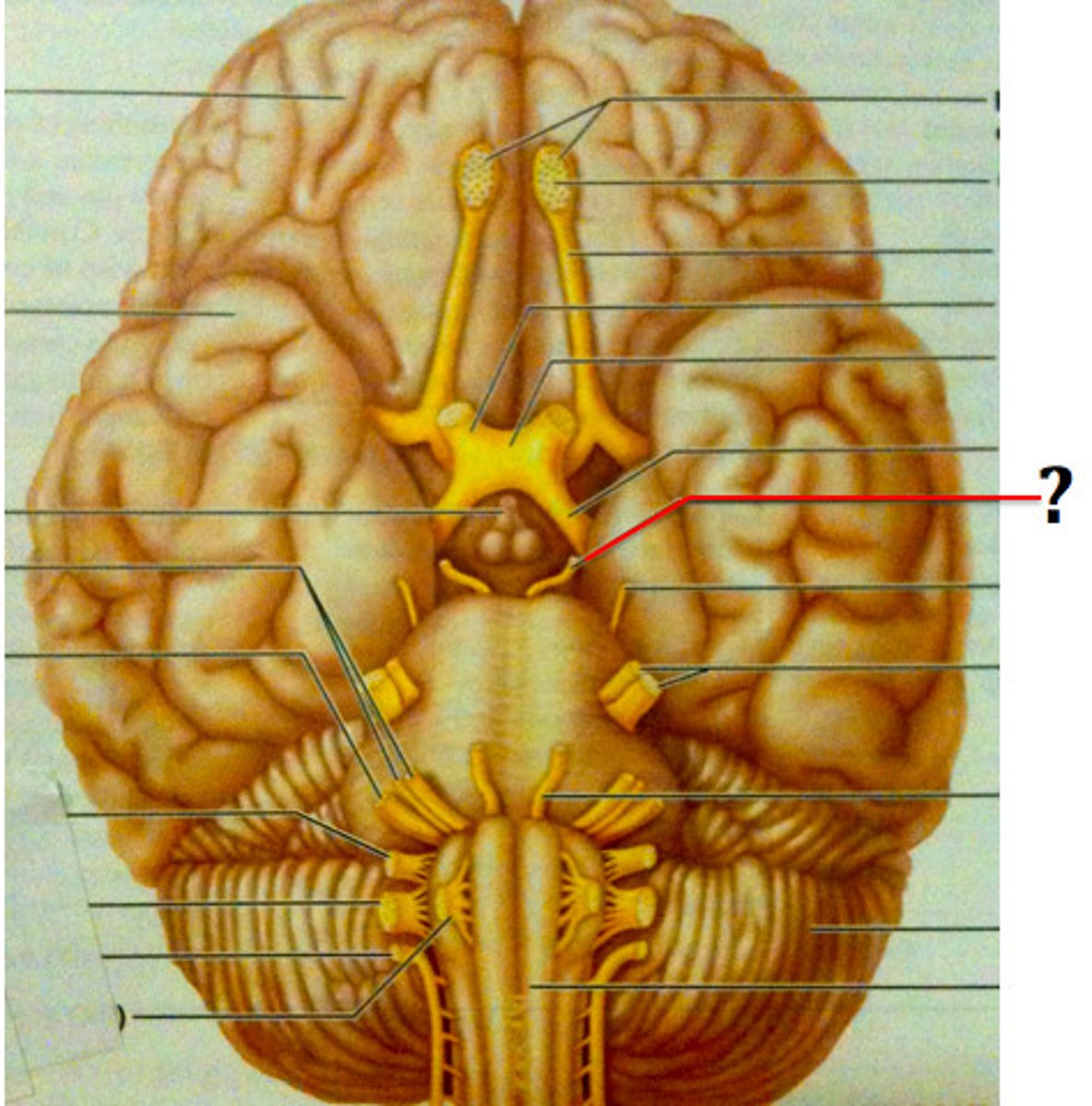
Trochlear nerve
Motor: eye muscles
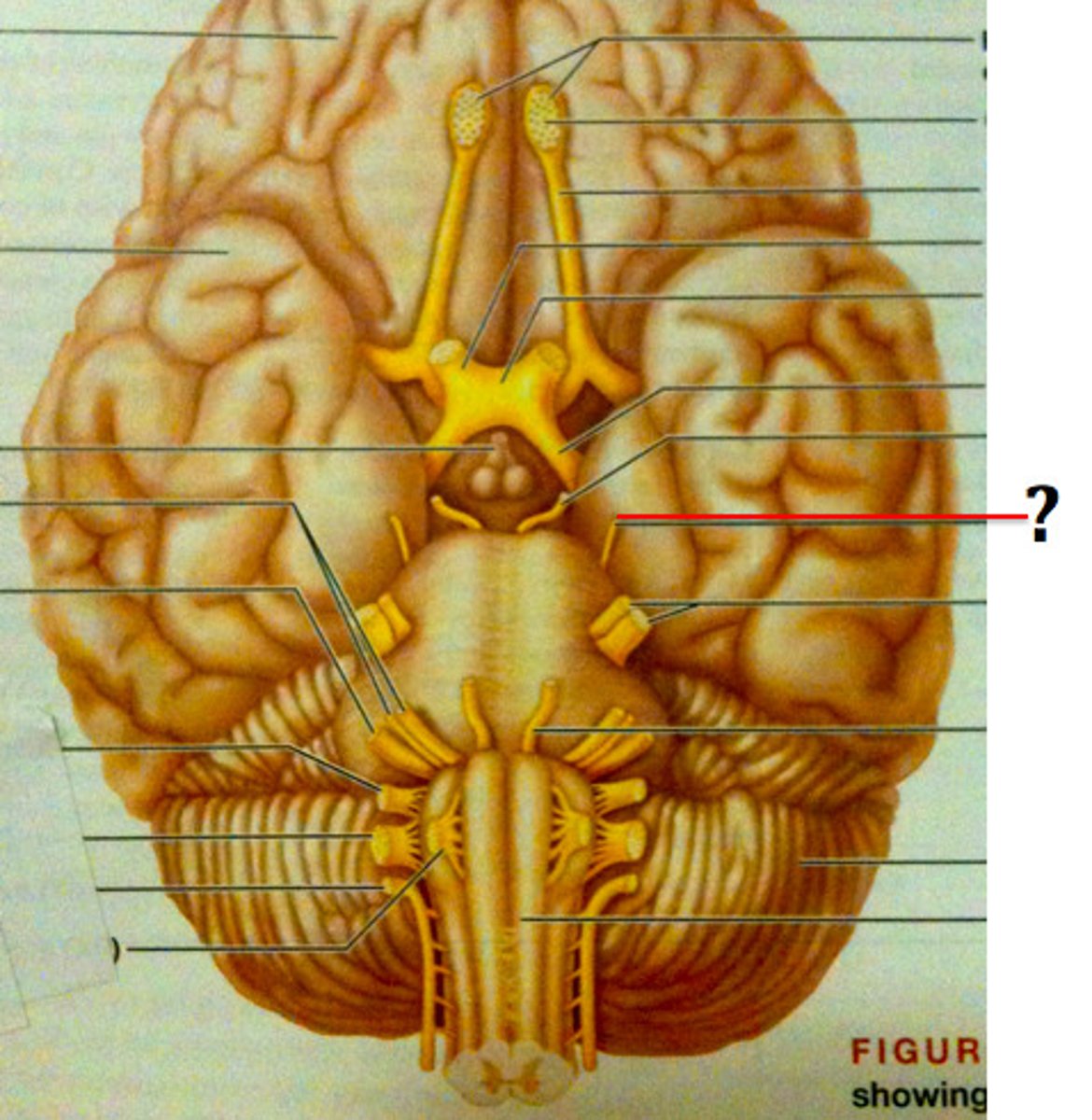
Trigeminal nerve
Sensory: facial skin
Motor: eyeball, chewing
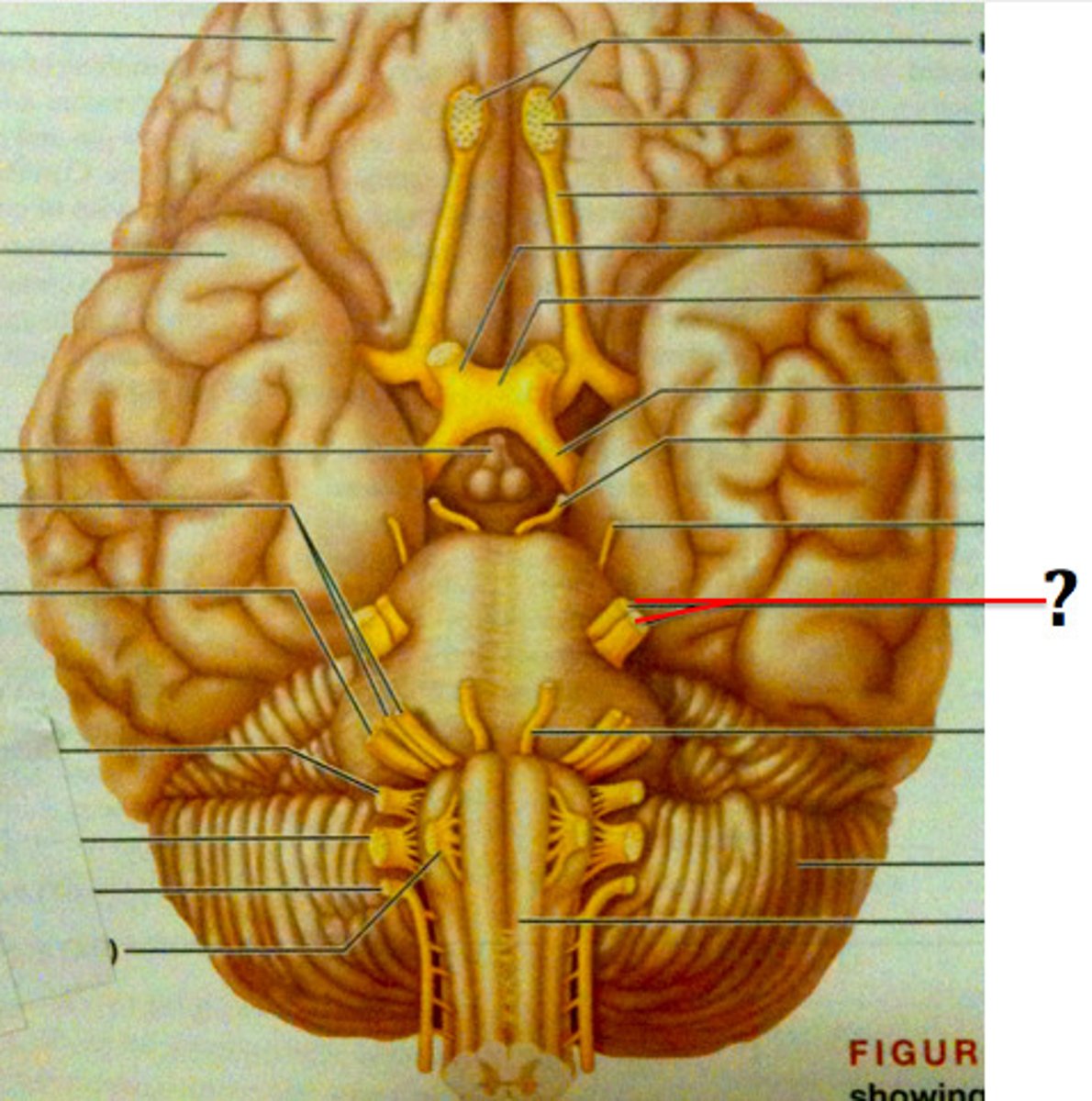
Abducens nerve
Motor: eye muscles
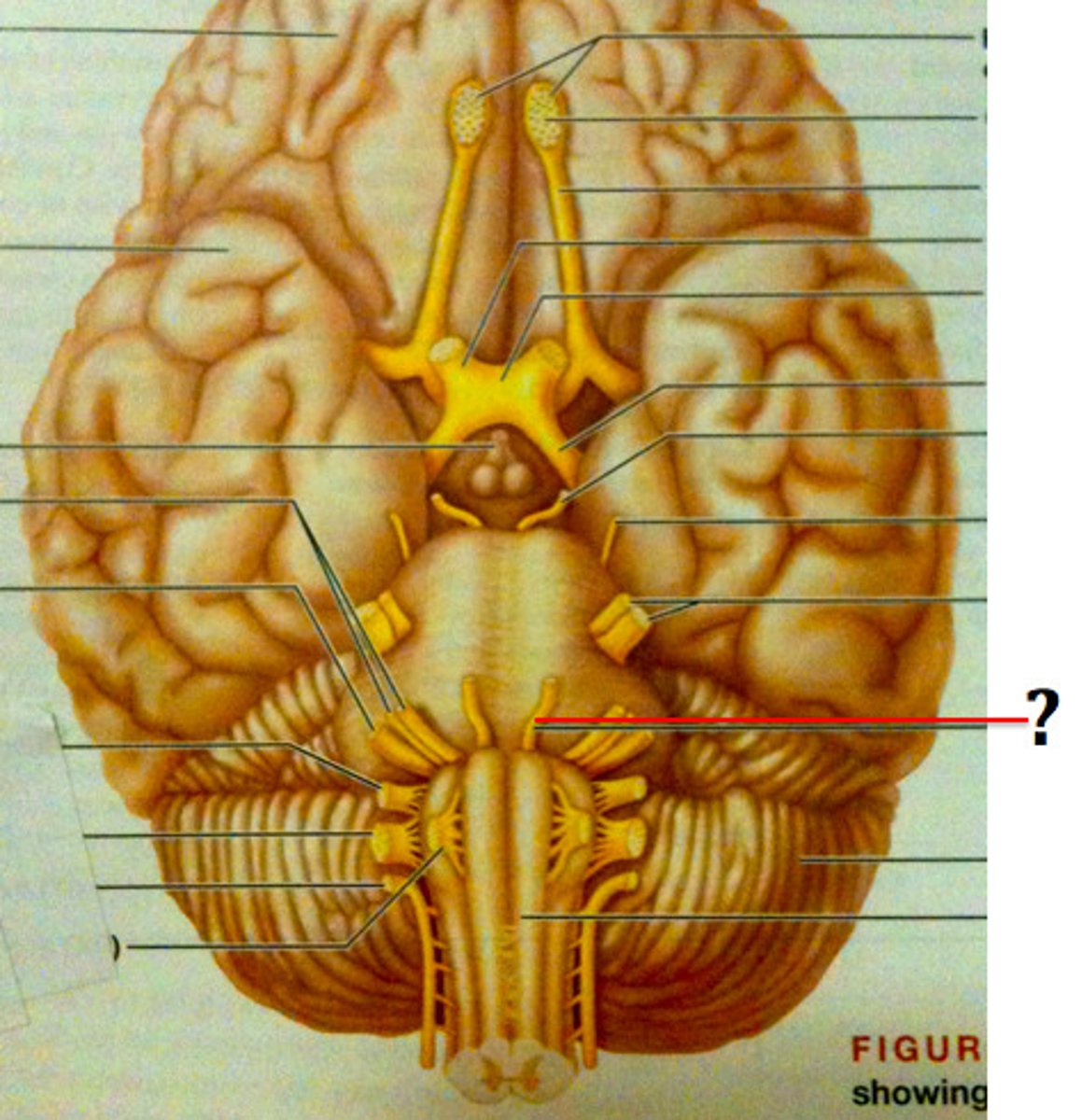
Facial nerve
Sensory: facial expression
motor: taste, tear and salvia production
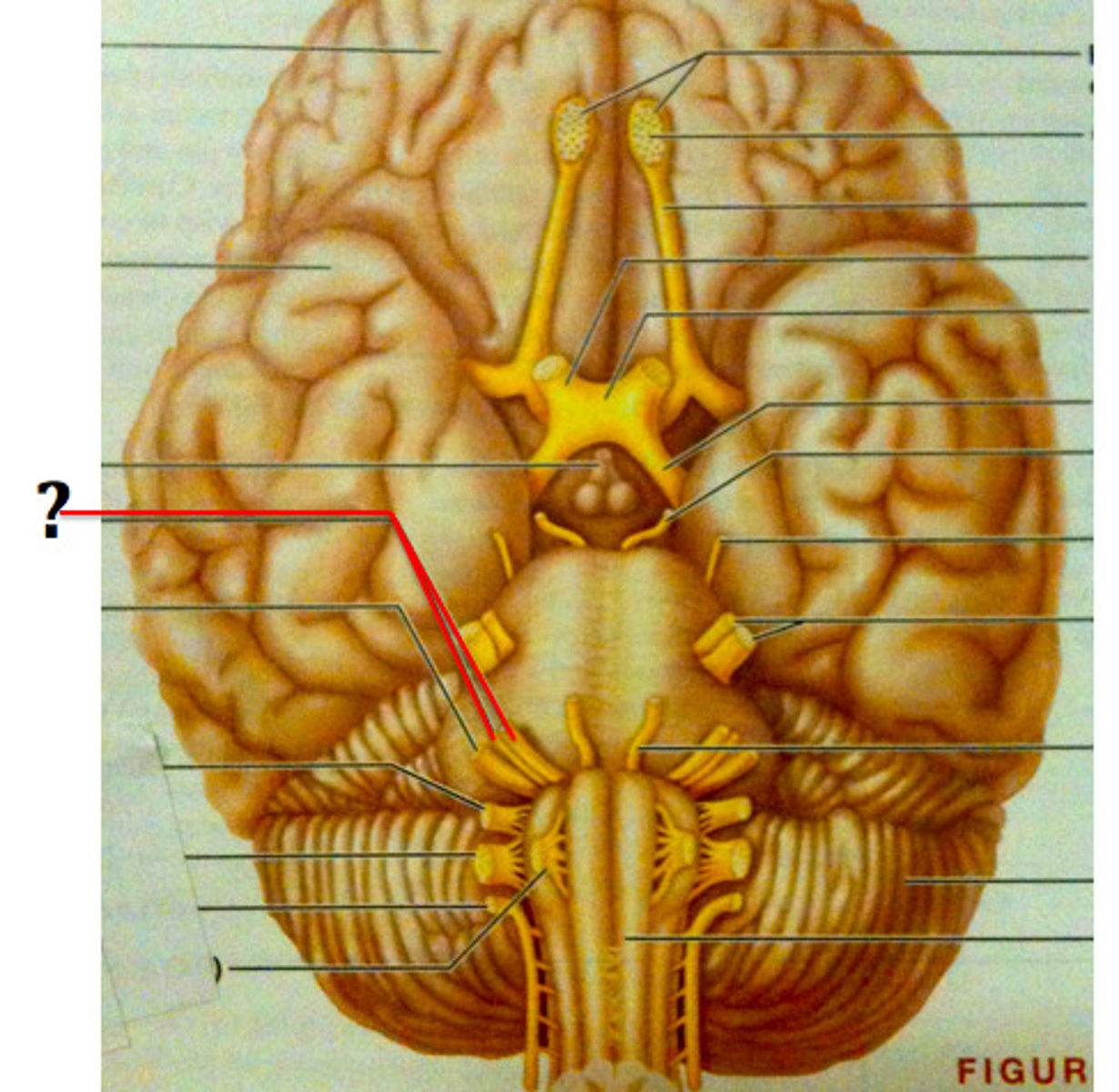
vesitbulocochlear nerve
sensory: equilibrium and hearing
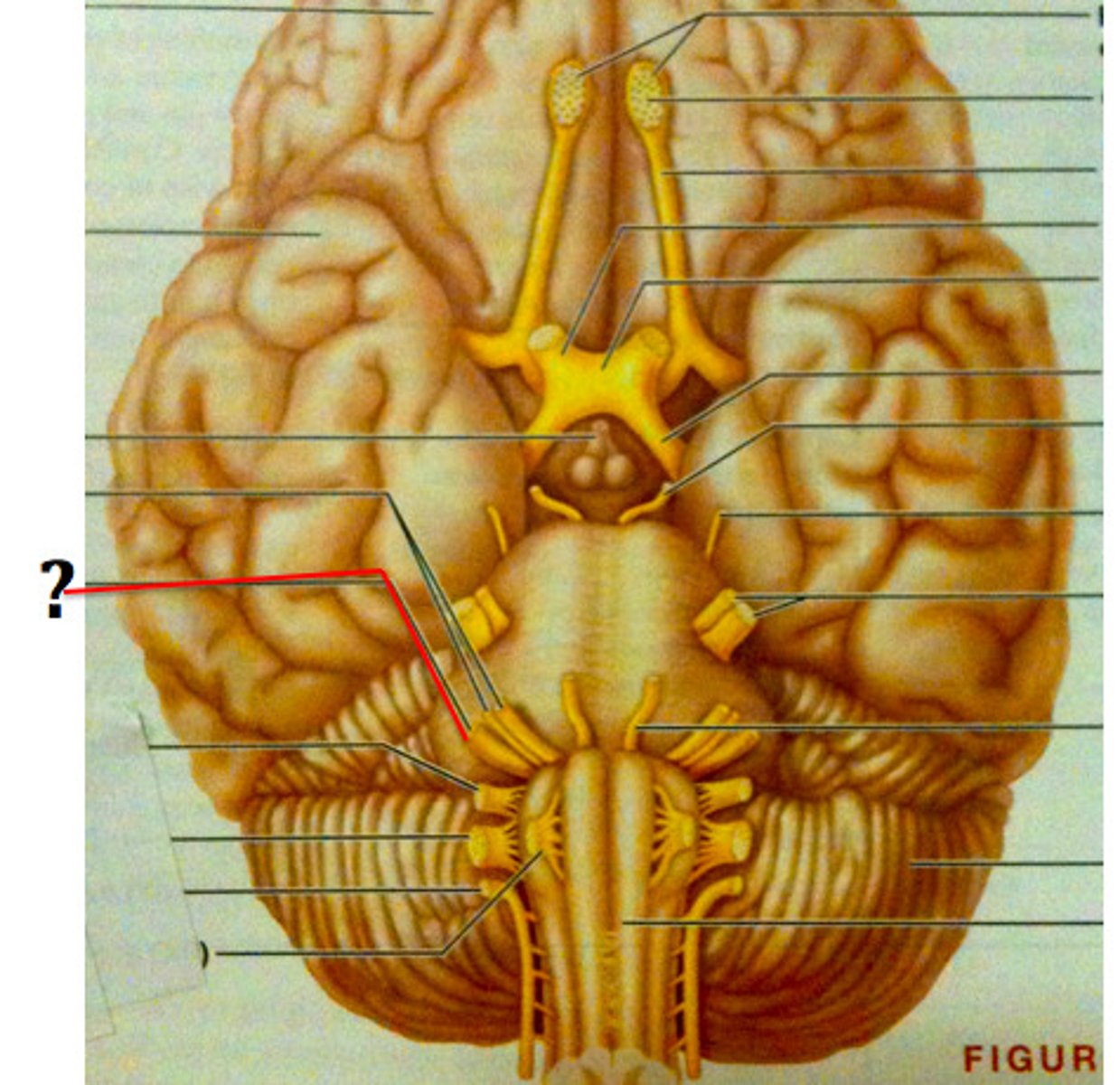
glossopharyngeal nerve
Sensory: taste
Motor: swallowing, speech, salvia
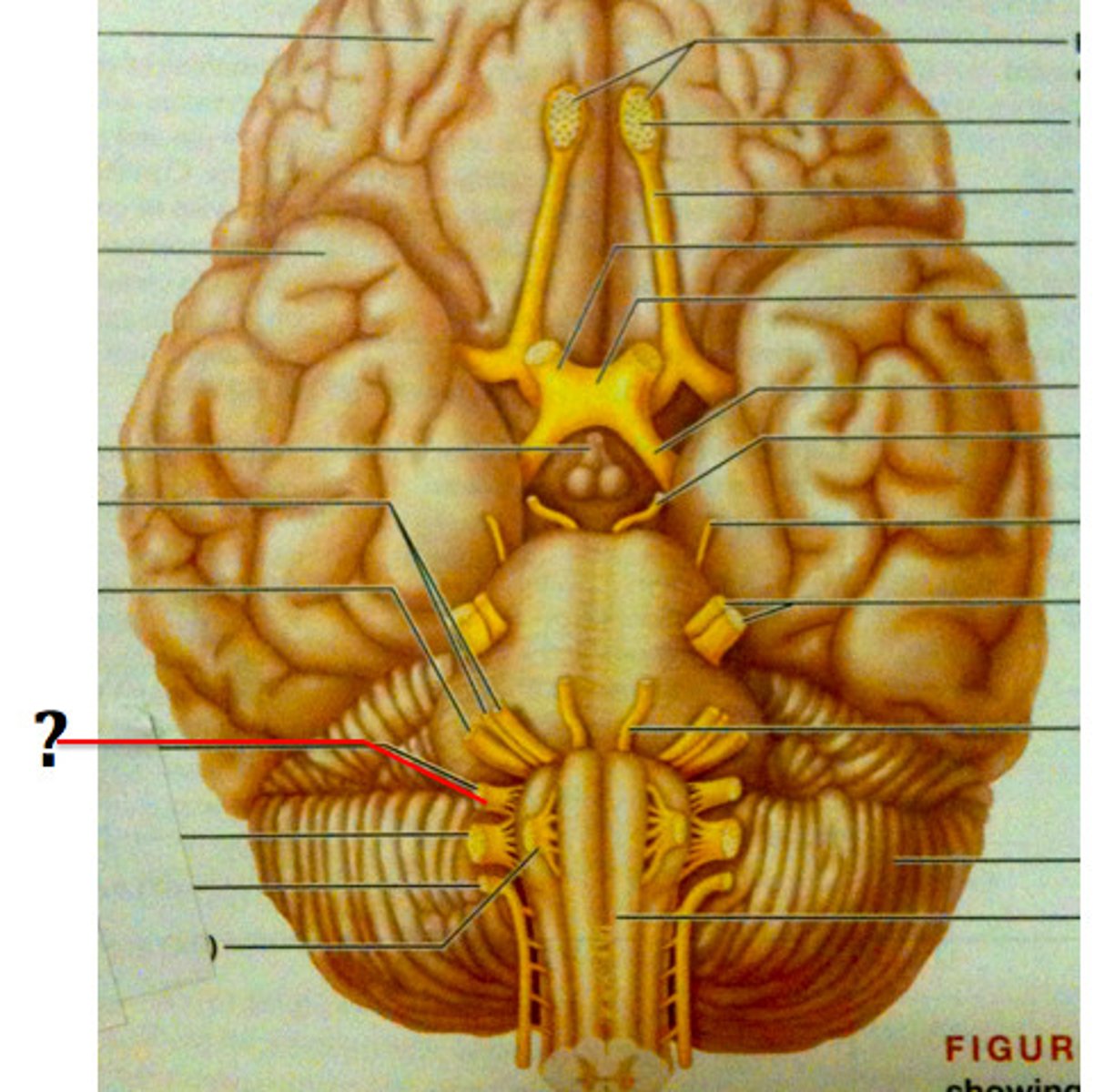
Vagus nerve
Sensory: viscera
motor: including heart and lungs
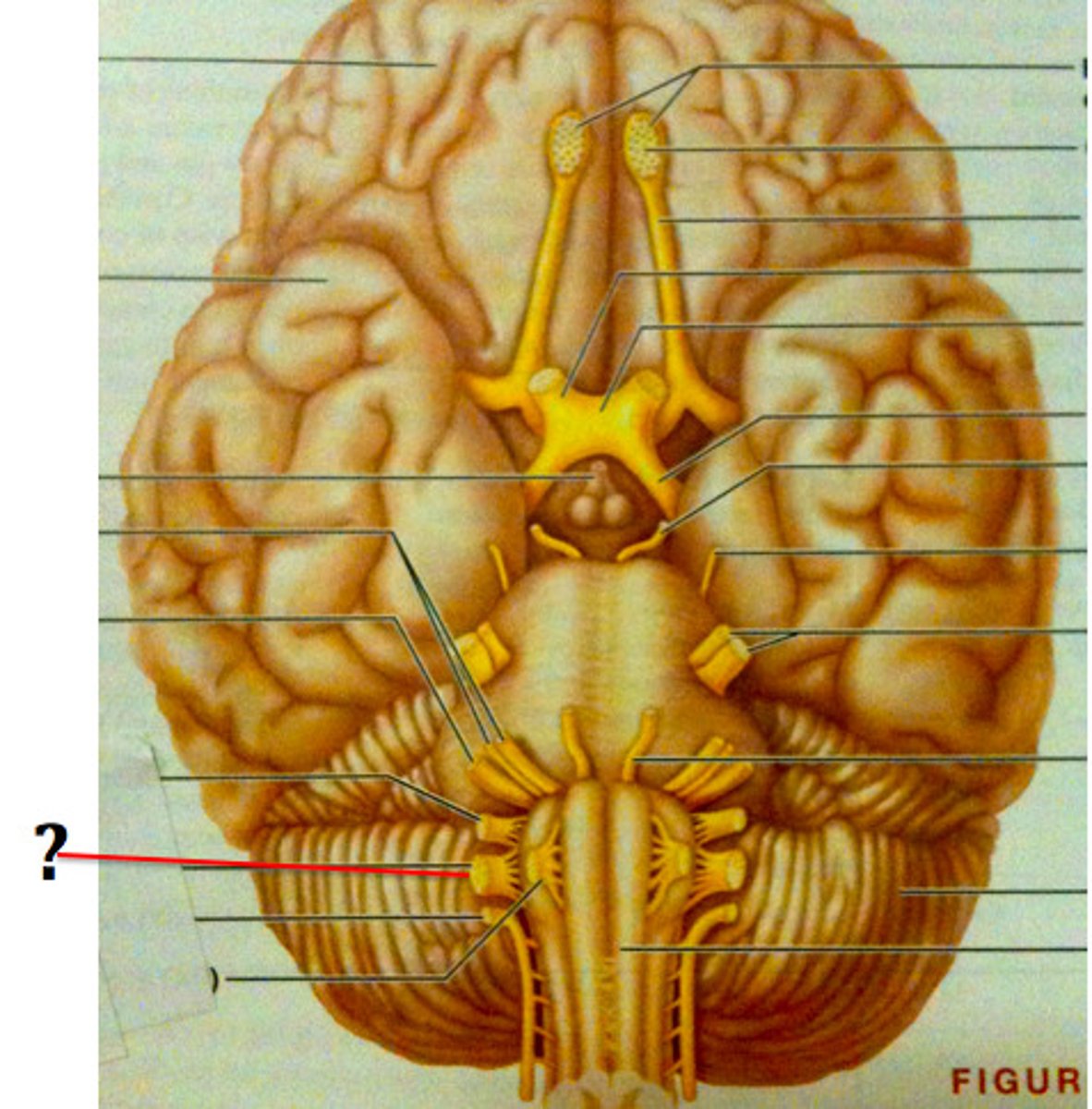
Accessory nerve
Motor: speech, movement of head and shoulders
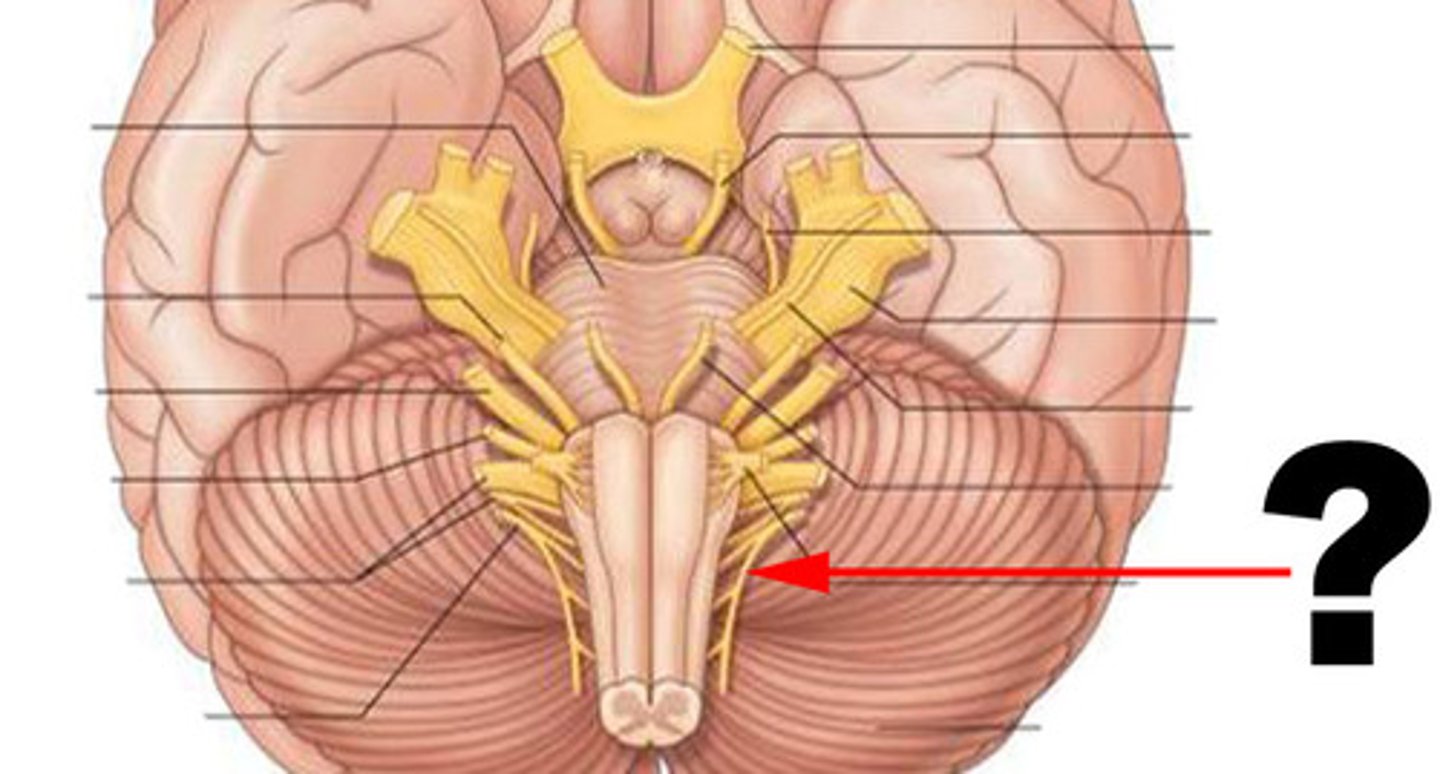
Hypoglossal nerve
motor: swallowing, speech
Anterior root
carries somatic and visceral motor signals from CNS to skeletal muscles and gland cells
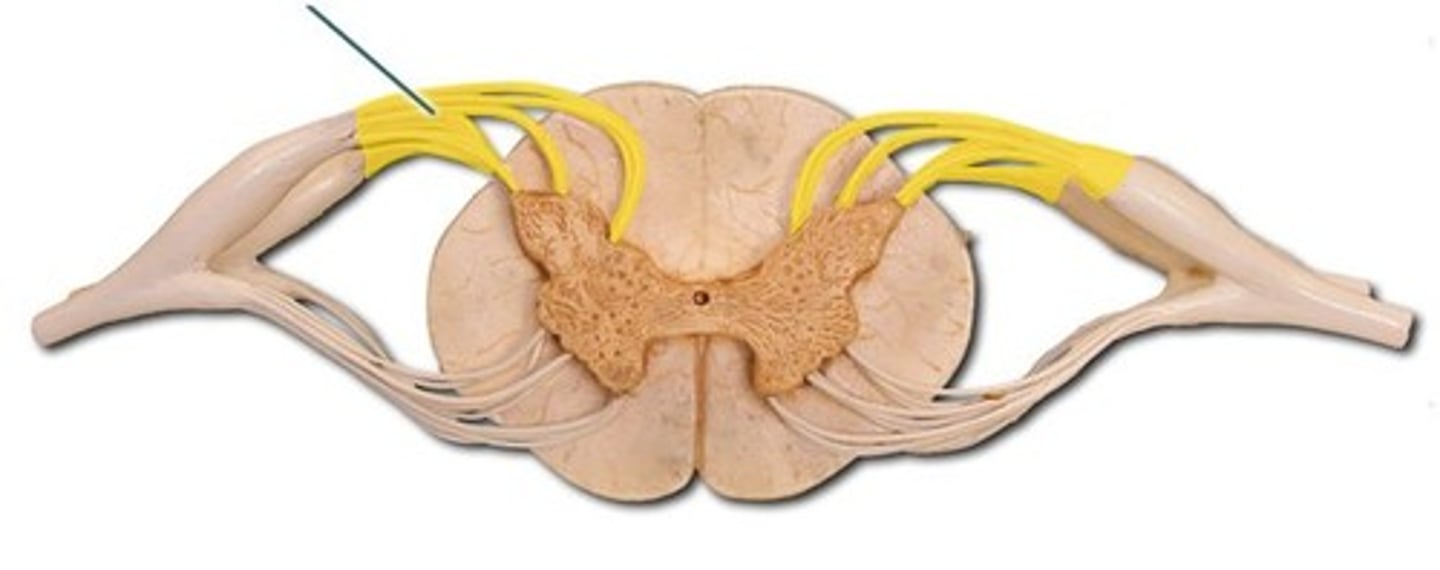
Posterior root
carries sensory signals from PNS to the spinal cord
Posterior ramus
carry sensory signals from sensory receptors in the PNS to the spinal cord
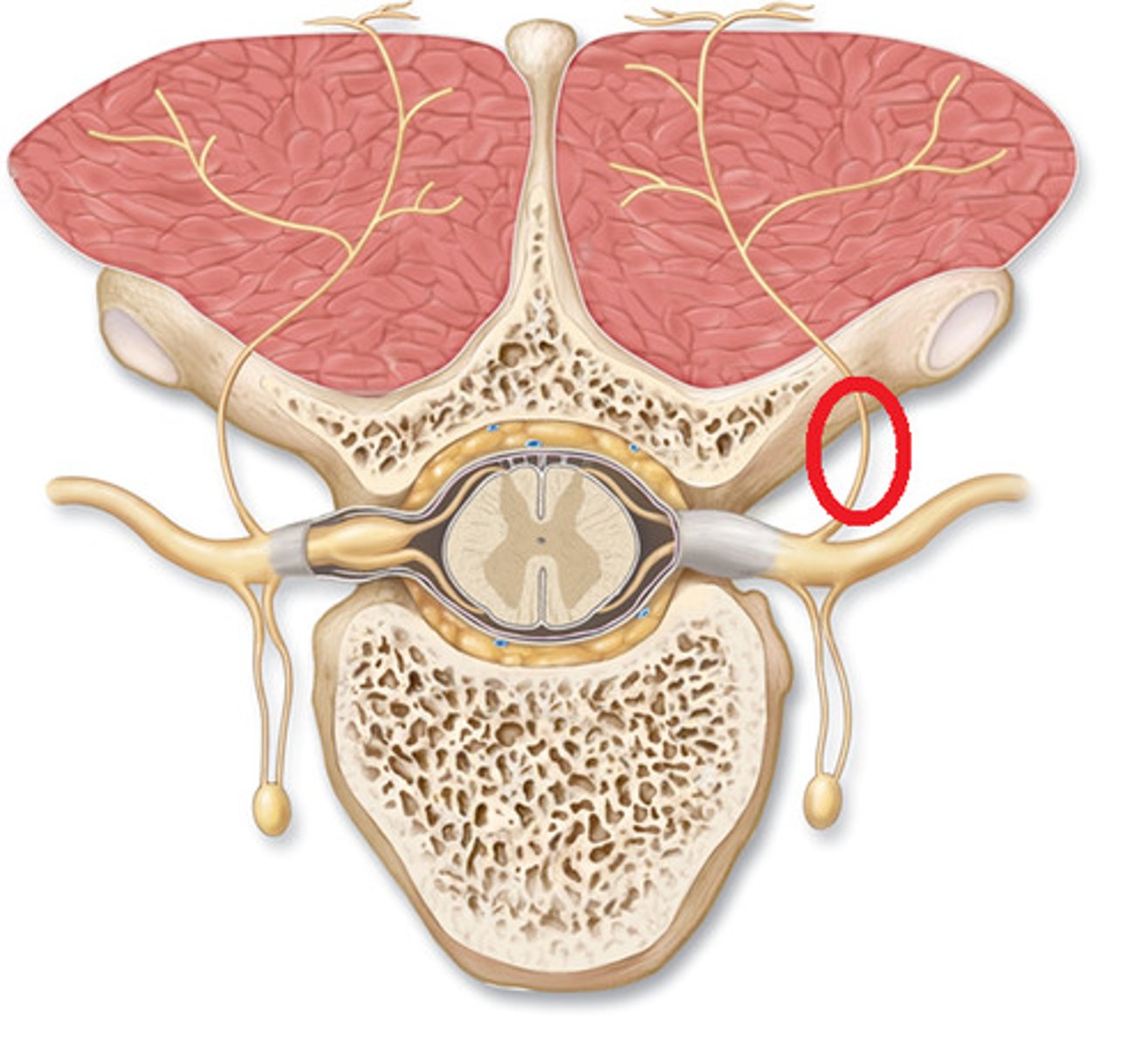
Anterior ramus
Carry somatic motor signals from the CNS to skeletal muscles
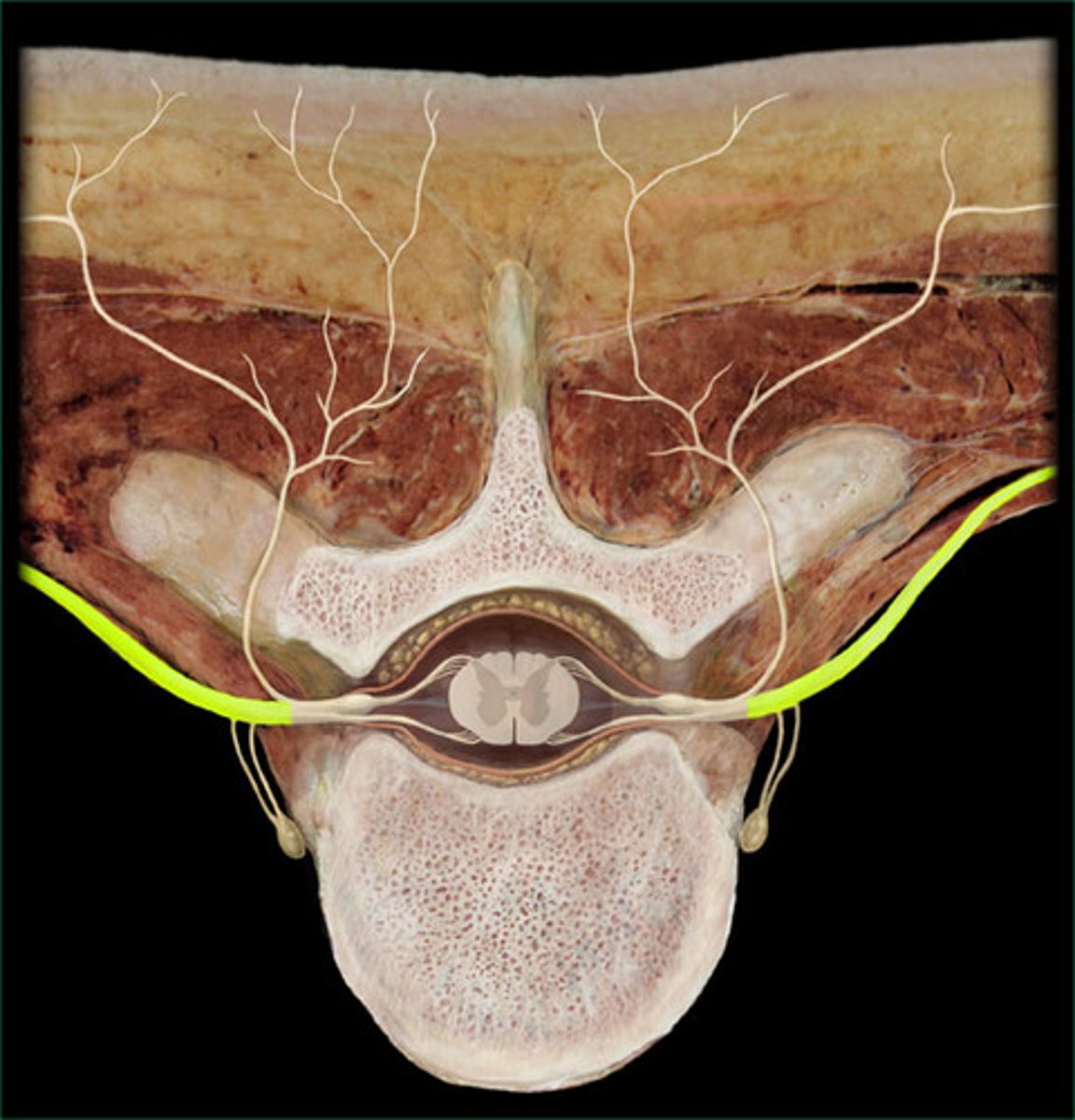
ramus communicans
carries visceral motor signals from the ANS to organs of the ventral body cavity
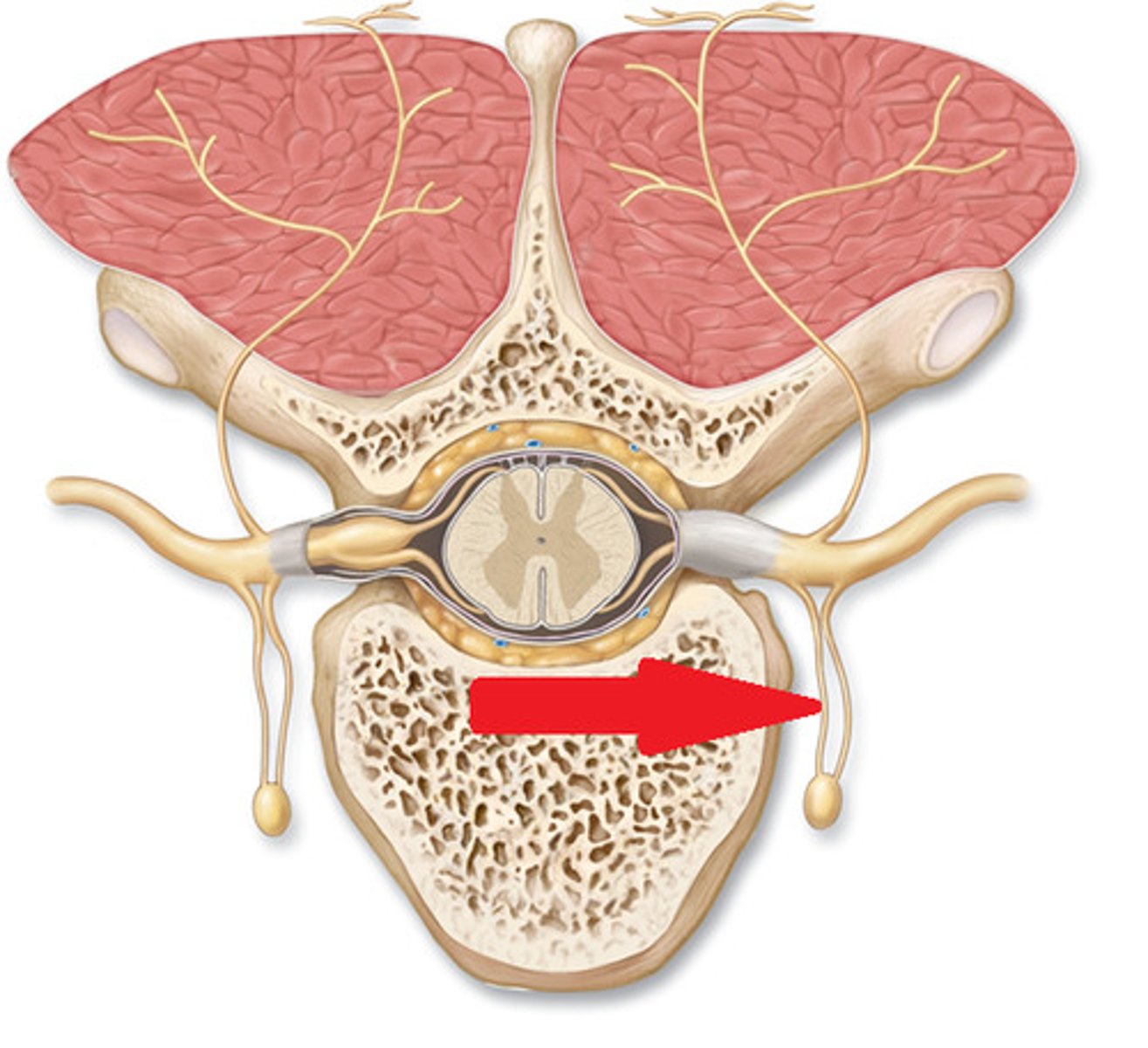
Spinal nerve
carries visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory signals to and from the spinal cord
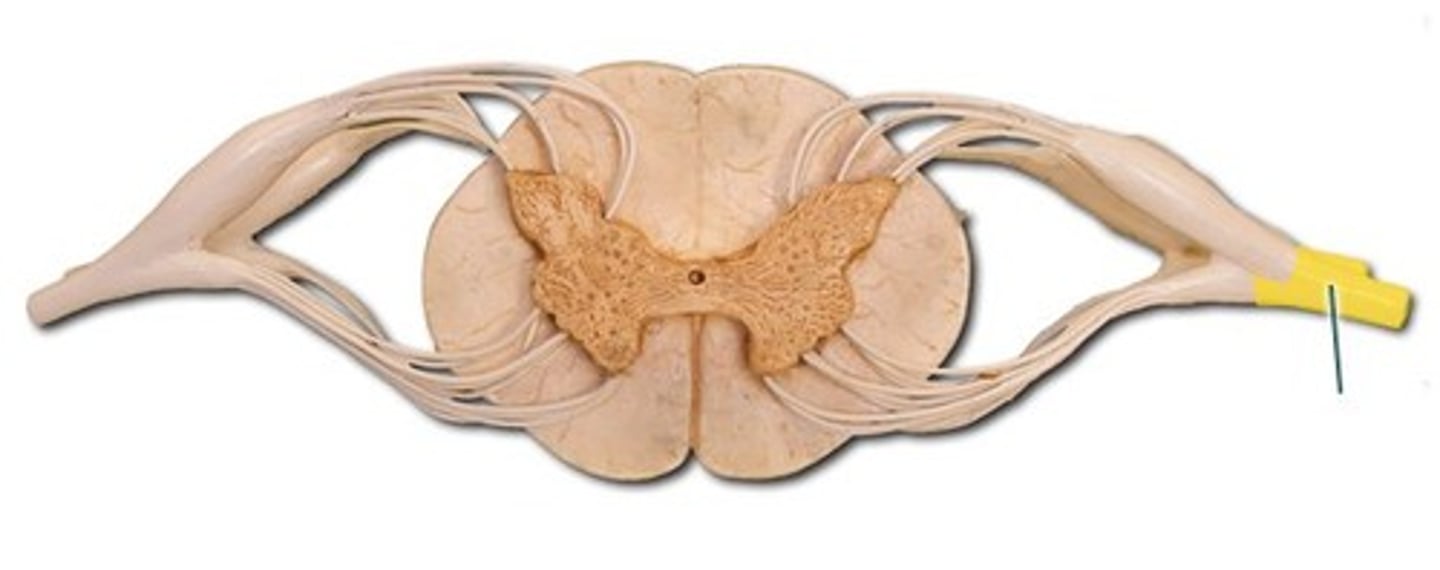
Spinal Nerve Plexuses
- cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral plexus
- merged networks or anterior rami
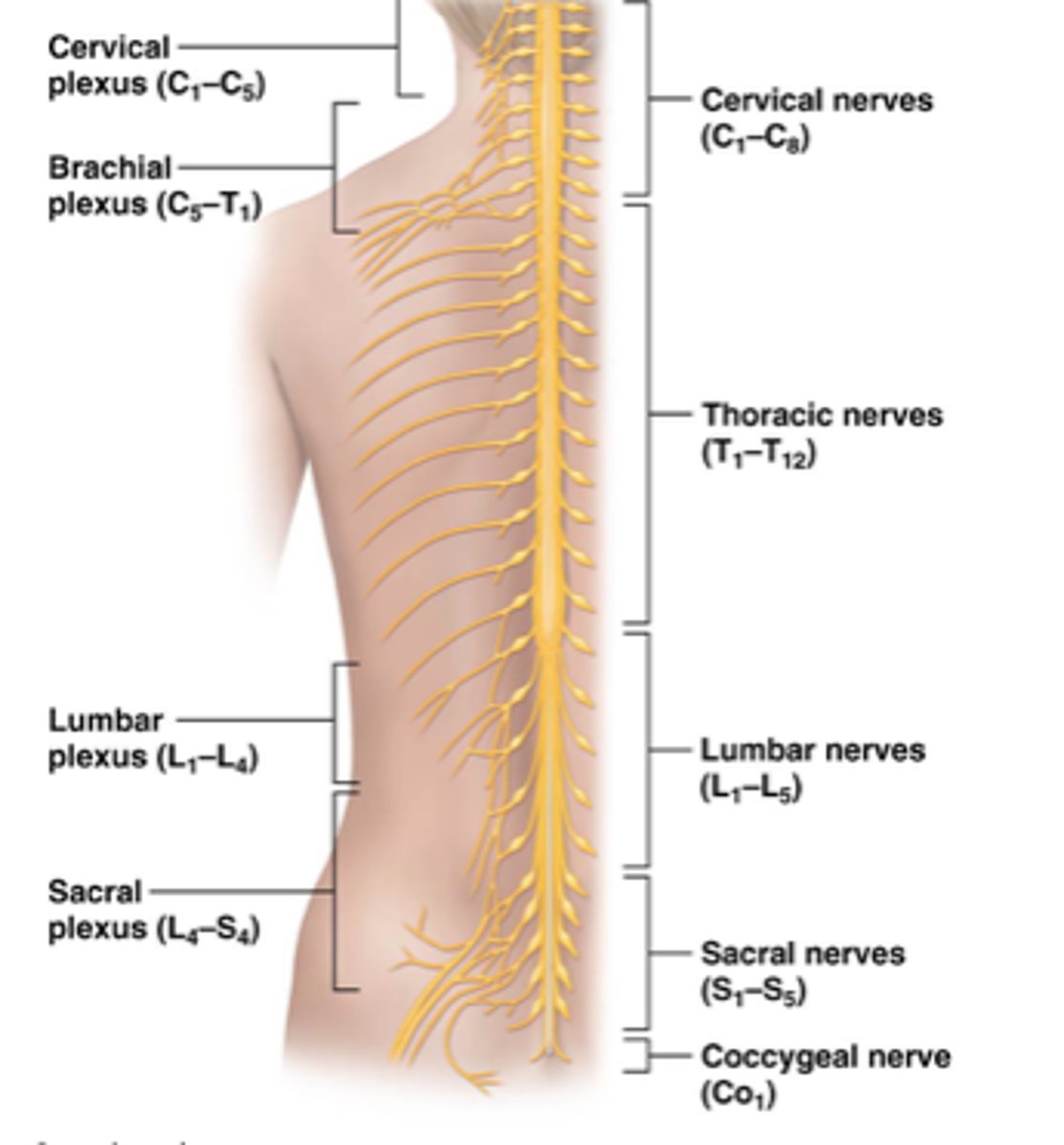
peripheral nerves
branch from plexuses
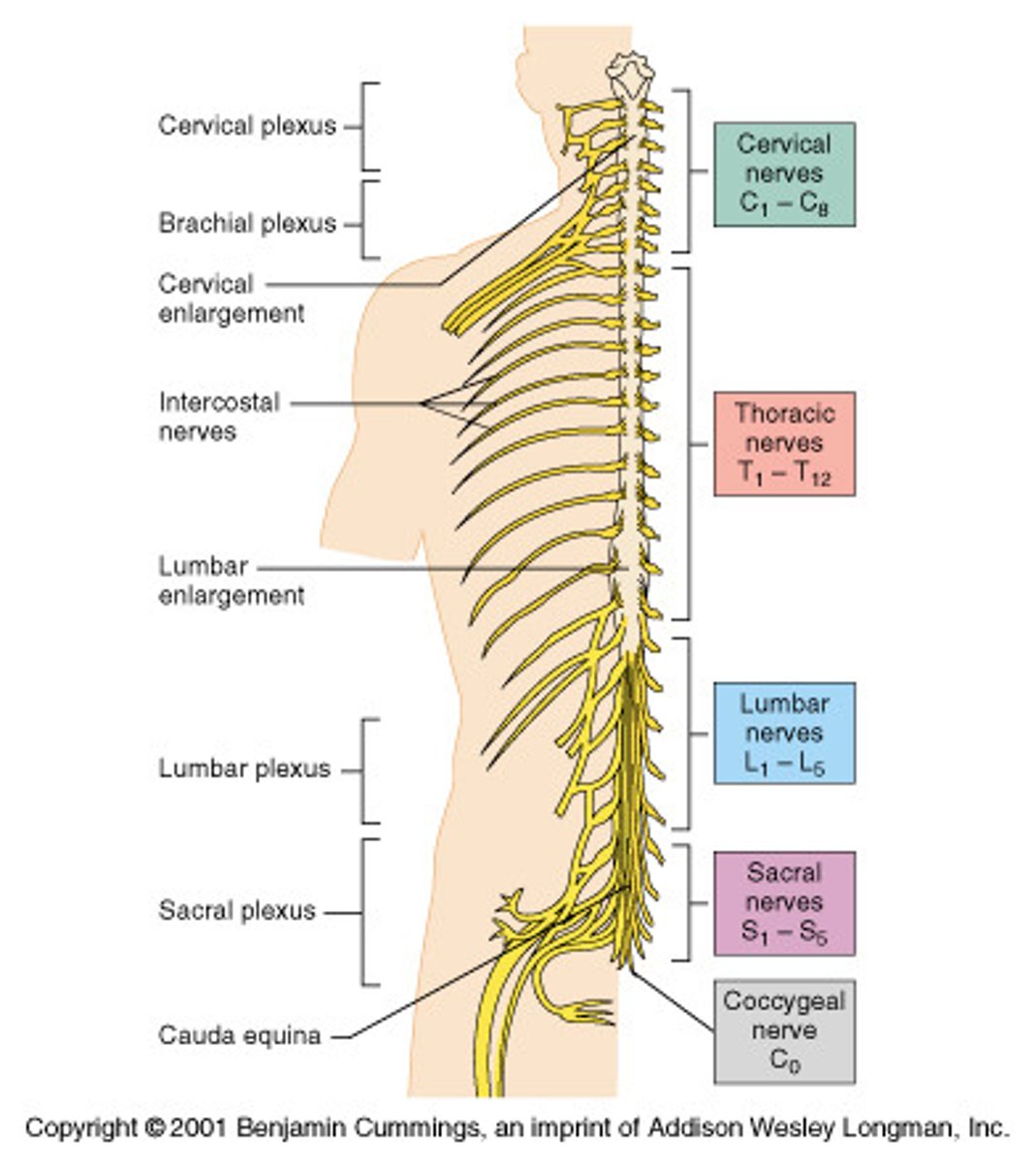
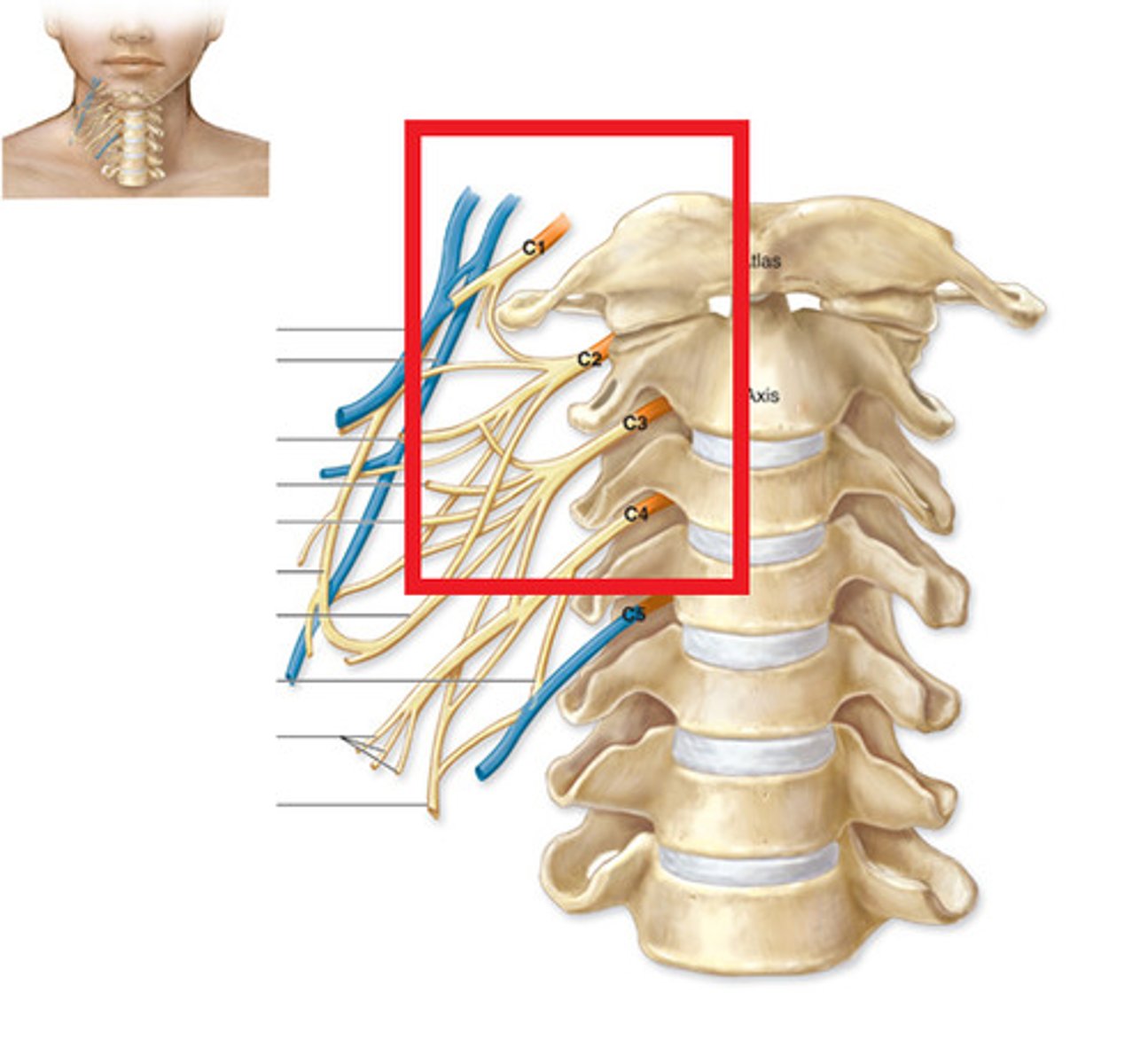
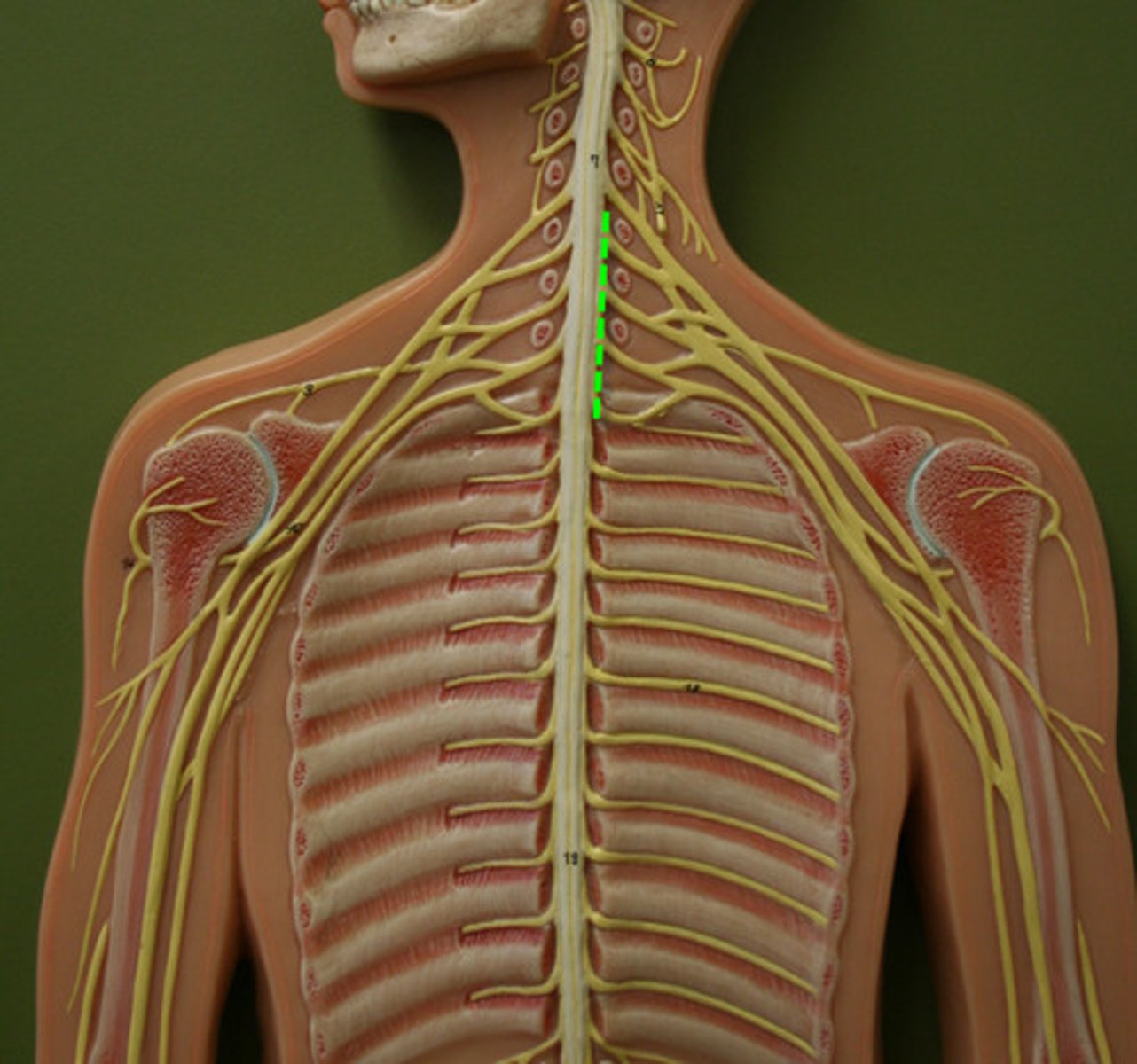
cervical plexus
C1-C5
Brachial plexus
C5-T1
Lumbar plexus
L1-L4
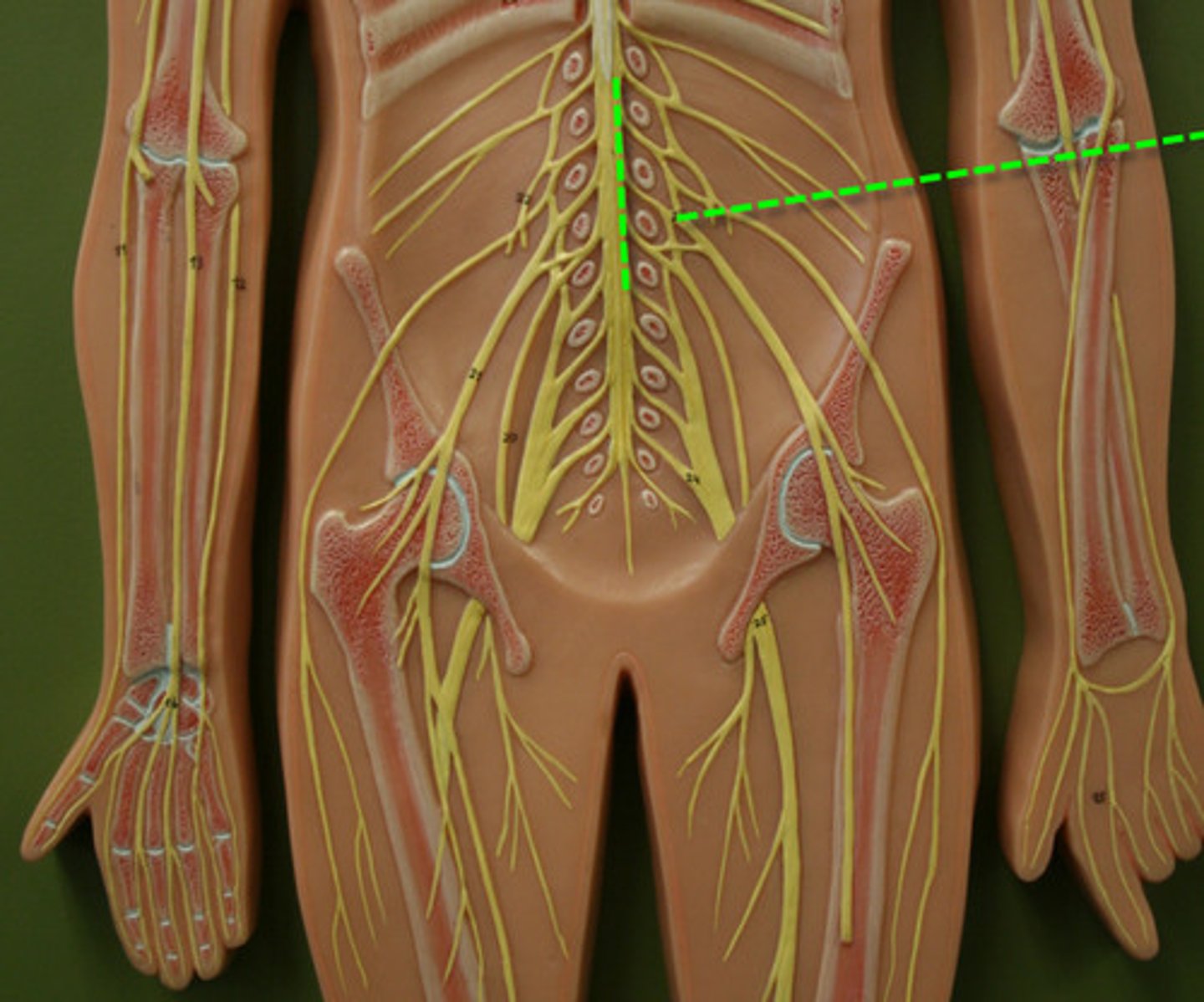
sccral plexus
L4-S4
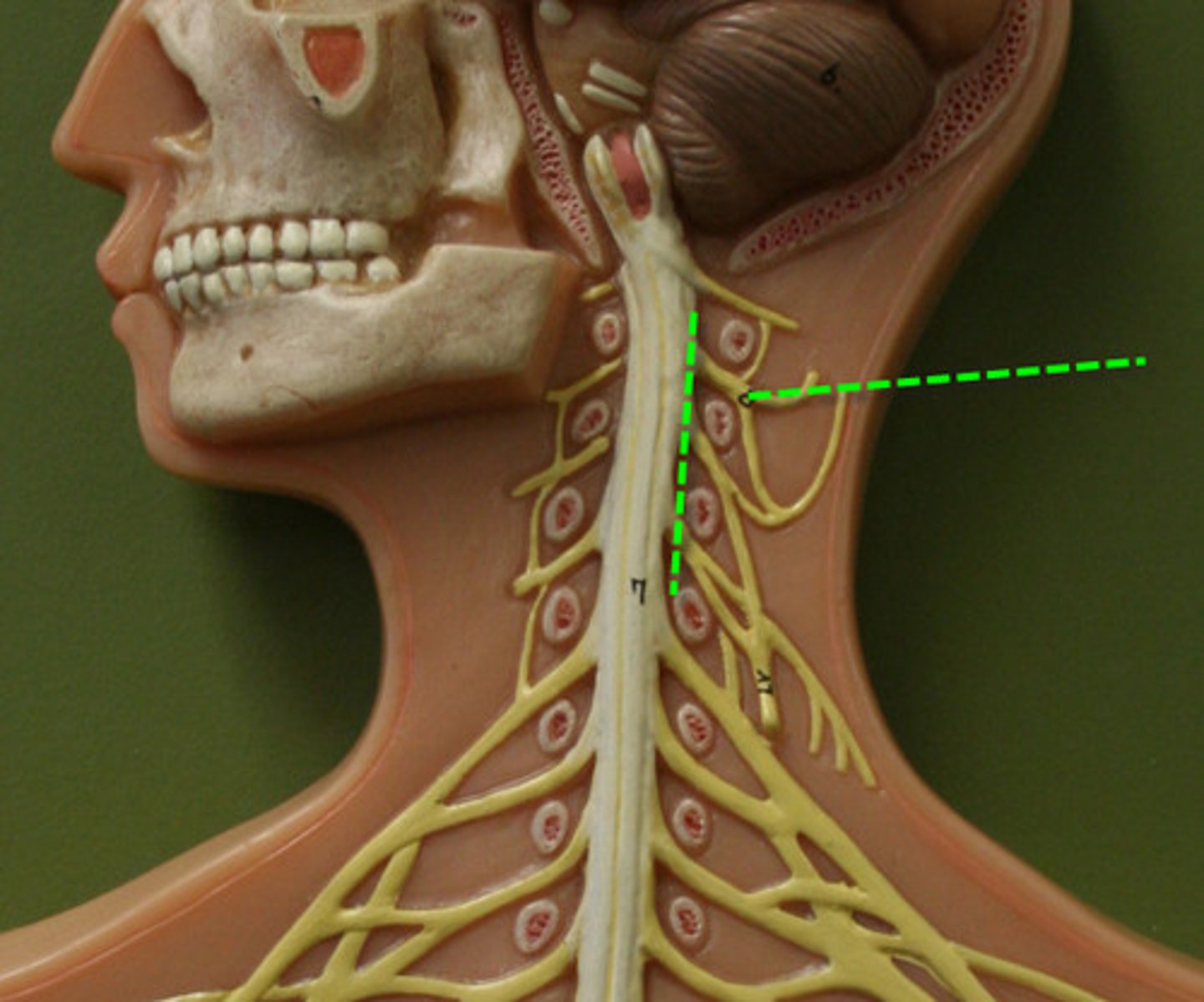
Cervical nerves
C1-C8
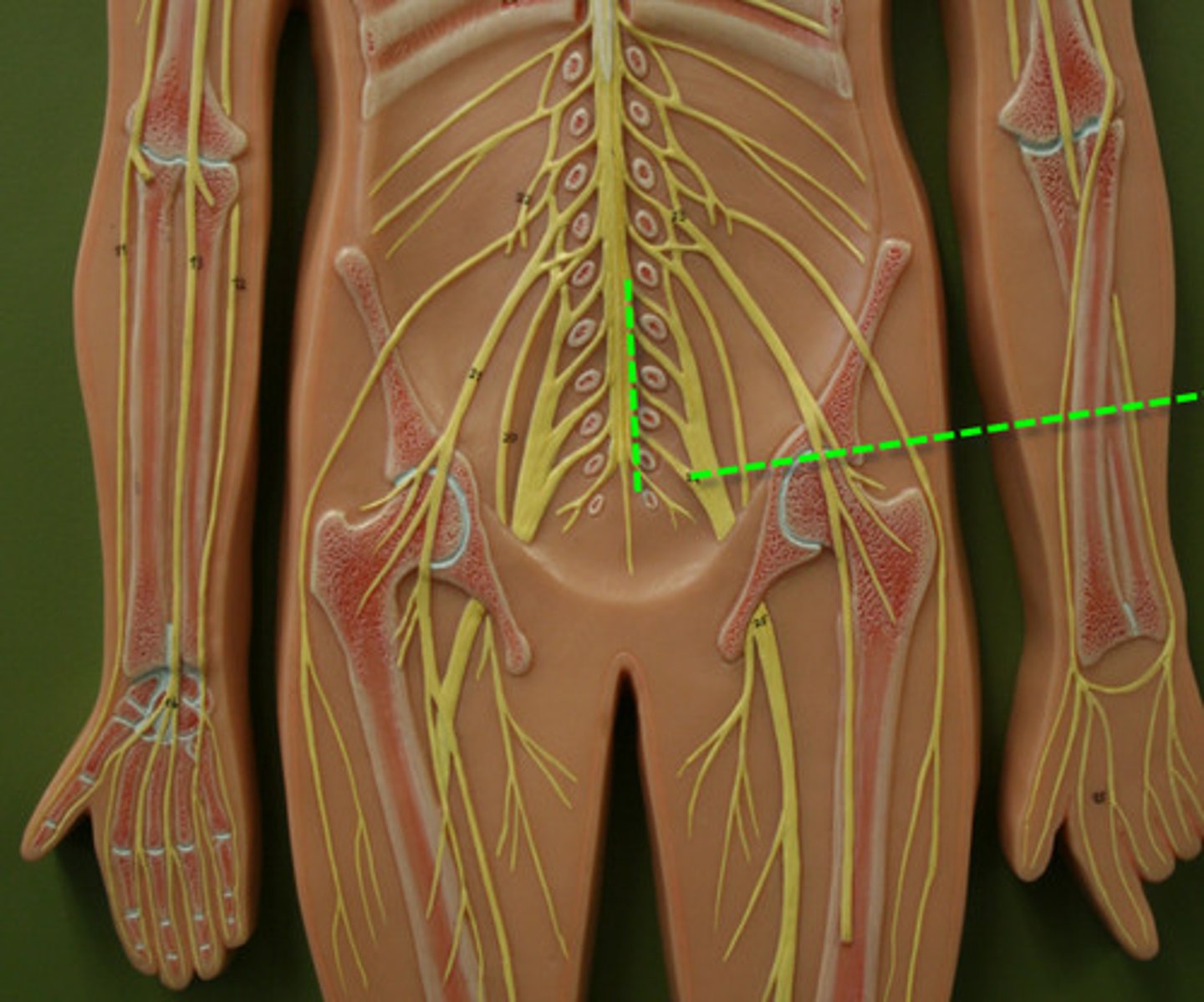
thoracic nerves
T1-T12
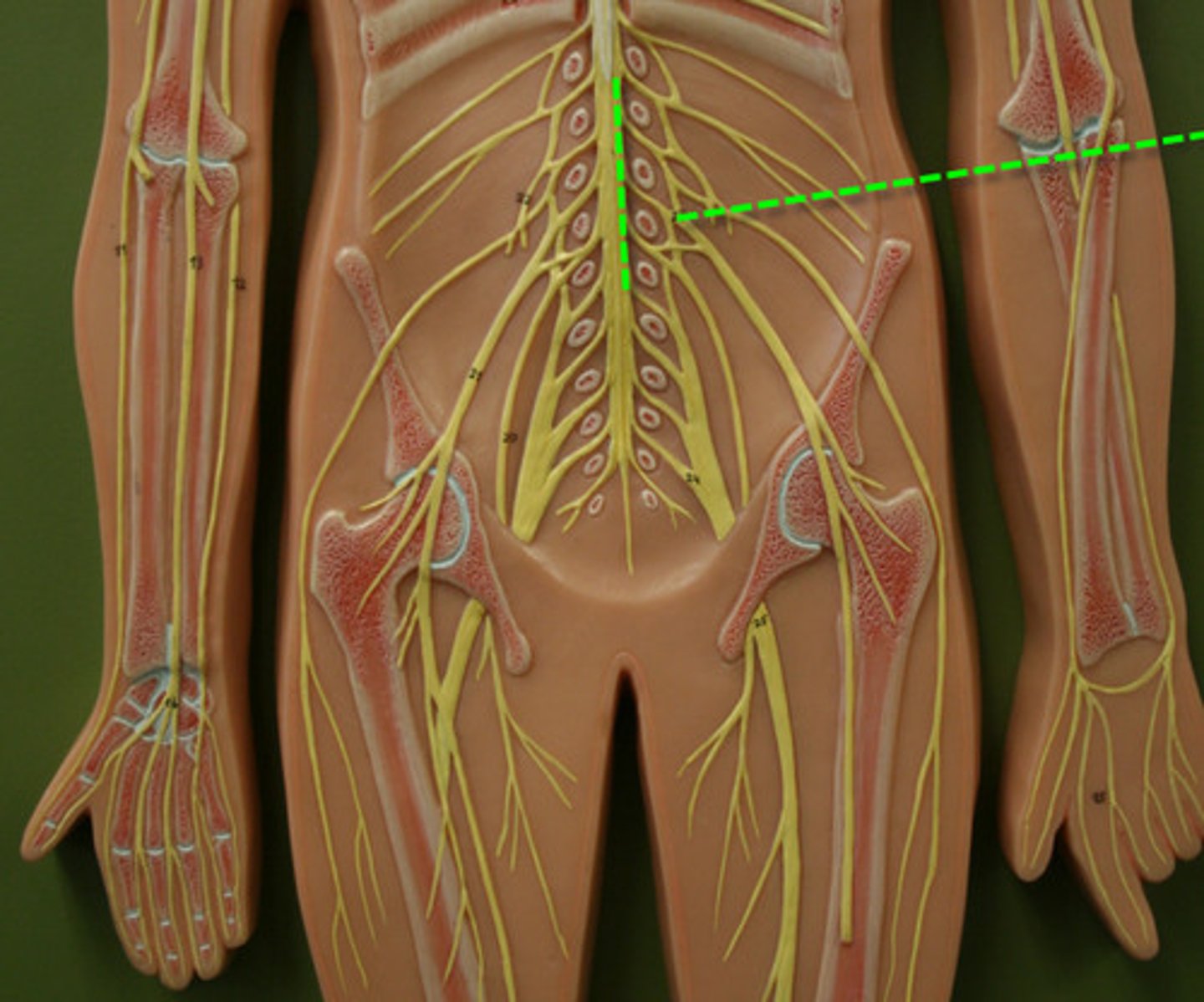
lumbar nerves
L1-L5
Sacaral nerves
S1-S5
Coccygeal nerve
Co1
Visceral( autonomic) reflex
- usually connected with ANS
F: regulates body functions such as respiration, digestion
Example: pupilary light reflex( pupils dilate)
Somatic reflex
- somatic sensory and somatic motor neurons involved ( skeletal muscles)
F: prevents muscle/ tissue damage and maintains posture, balance, locomotion
Simple stretch reflex
- returns muscle to its optimal length after stretching
example: patellar (knee-jerk)
flexion reflex & crossed extenstion reflex
- withdraws affected limb from painful stimulus; simultaneous with crossed-extension reflex- contraction of extensor muscles of opposite limb
example: lift the heel of broken glass while balancing on the other leg
Golgi tendon reflex
-causes muscles to lengthen in response to increased muscle tension( relaxes to prevent damage)
example: drop a heavy weight
crainal nerve reflex
gag and corneal blink
sensor receptor
muscle spindle = stretch receptor in muscle detect stimulus and trigger action potential
Afferent (sensory ) neuron
conducts action potential to CNS/ integration center
integration center
action potential passes between neurons in brainstem or in spinal cord
efferent ( motor) neuron
conducts action potential to effector; 2 nerves
1. stimulates muscle
2. shuts of opposing muscle
effector ( muscle or gland)
Receives action potential and performs work