How Does the Brain Function? - (Key Terms & Practice)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
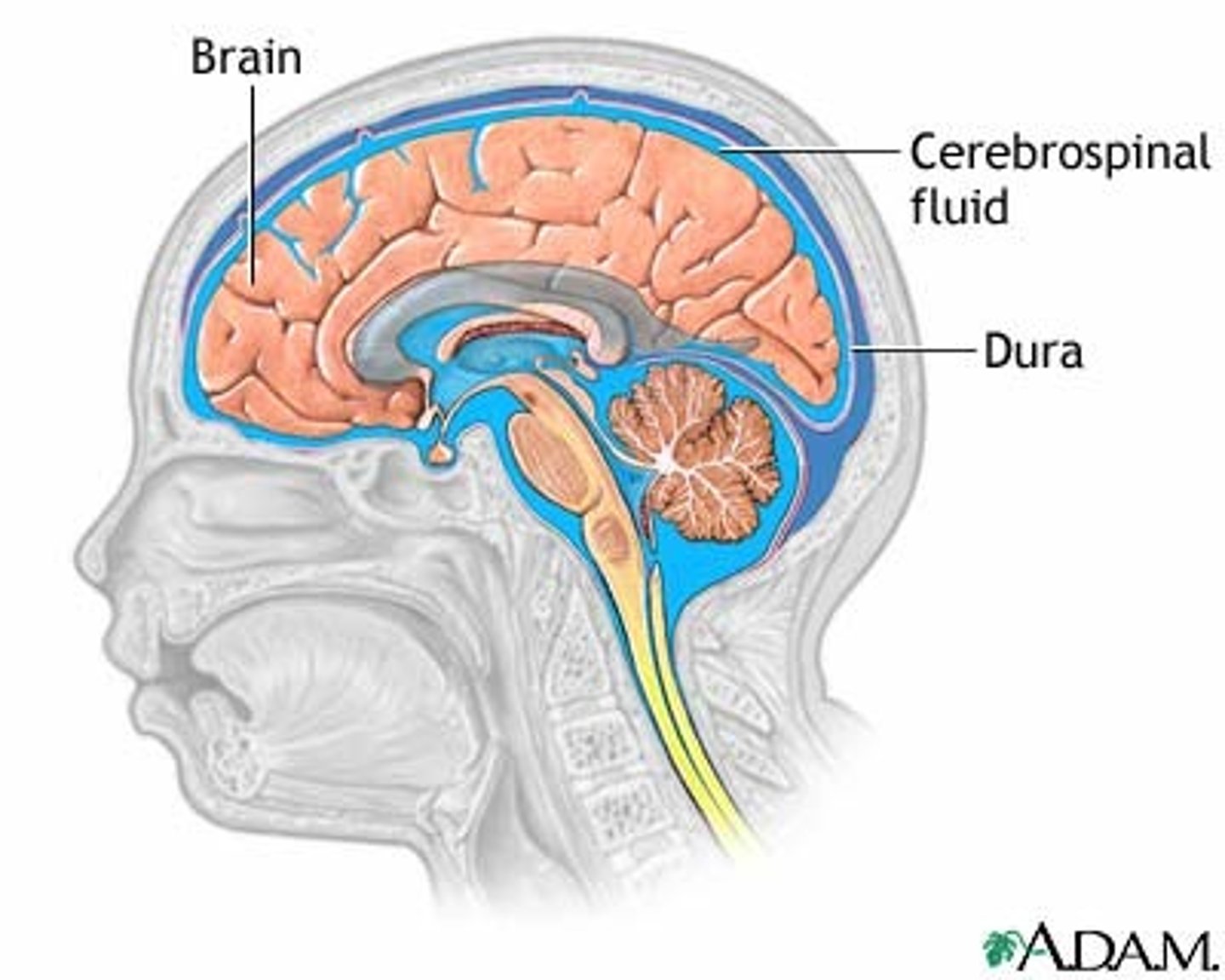
meninges
three membrane layers that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord
cerebrospinal fluid
watery-like liquid that circulates between the membranes and provides a cushion against knocks to the head
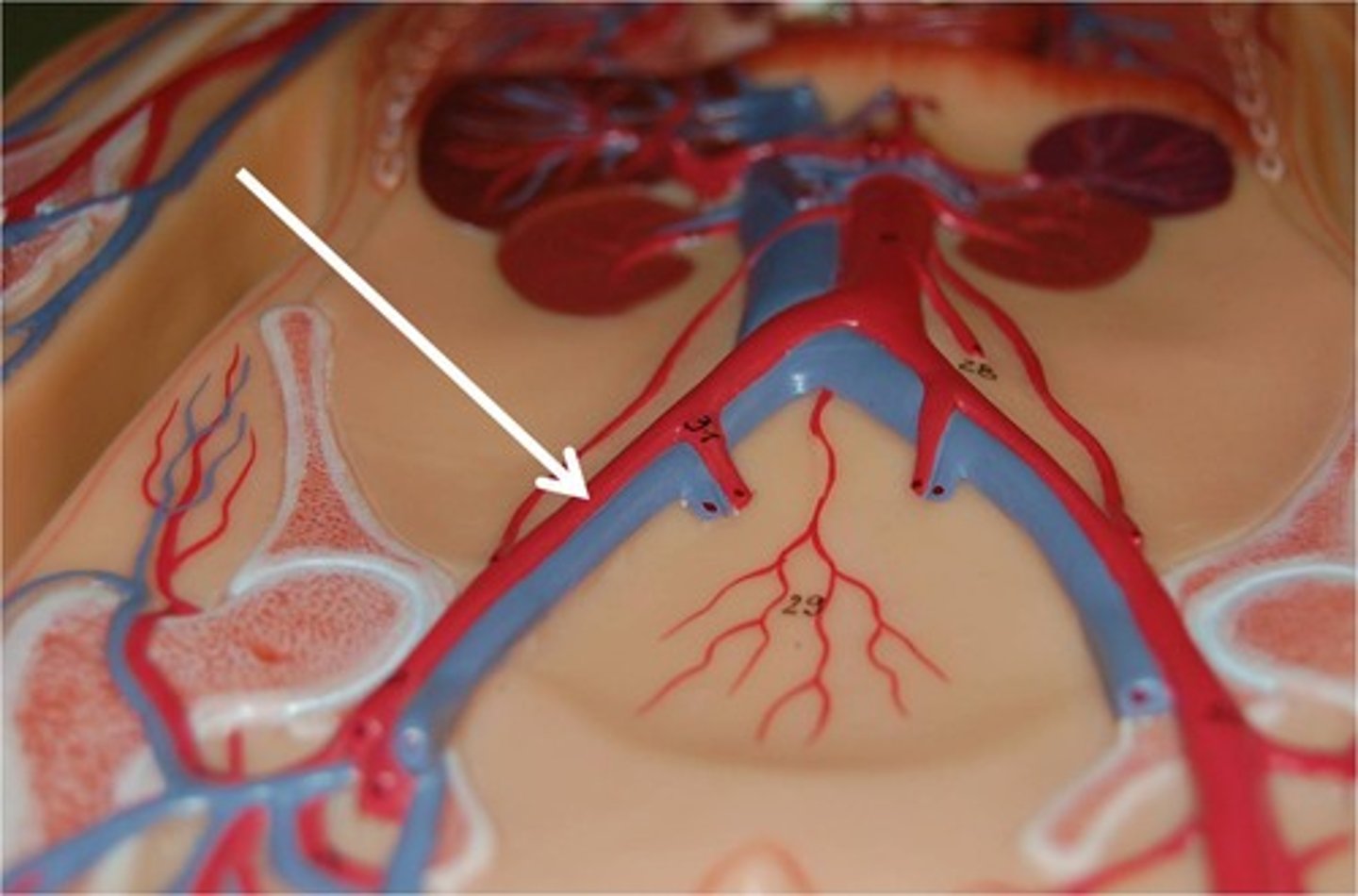
arteries
carry nutrients and oxygenated blood throughout the brain
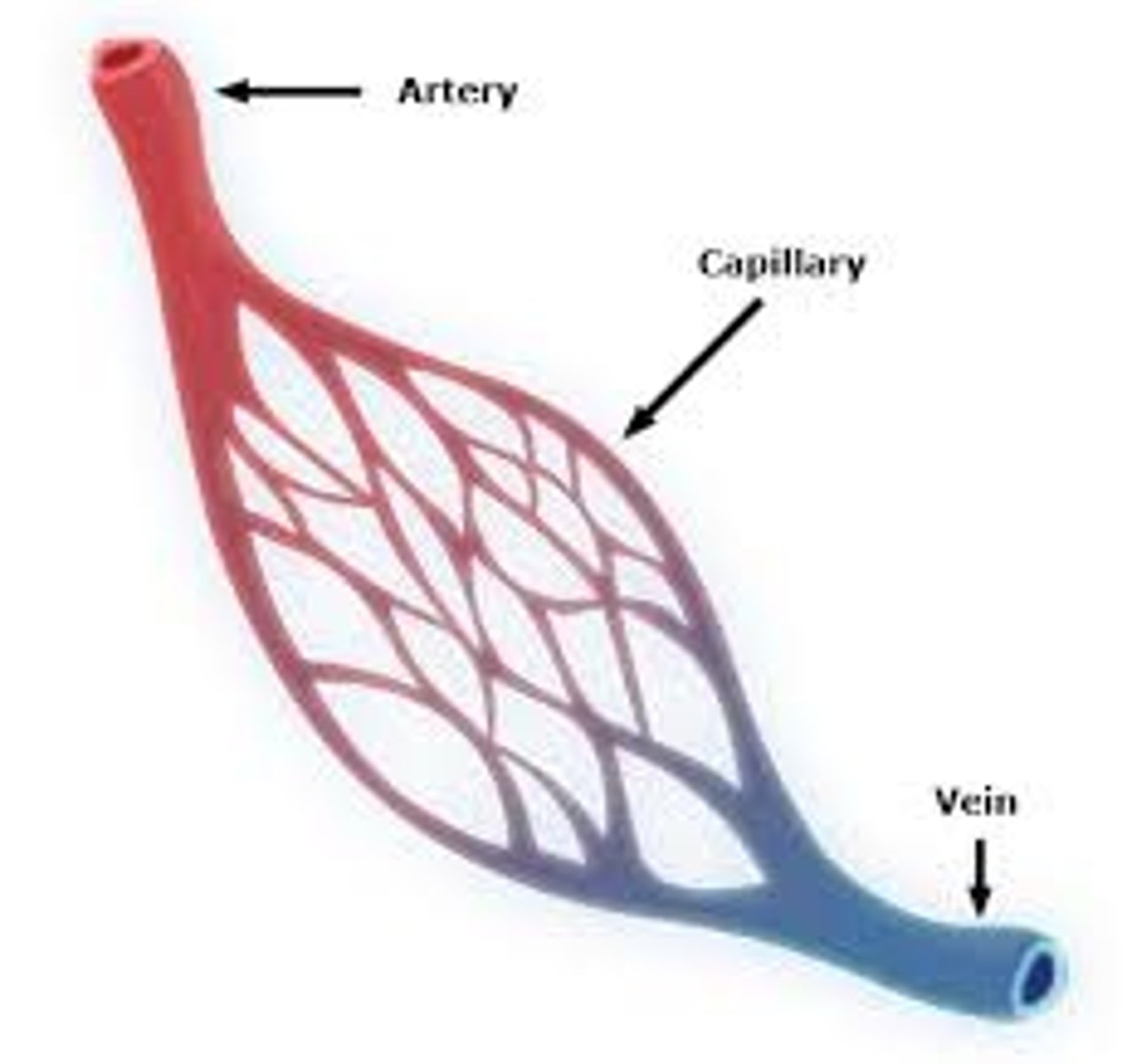
capillaries
very thin blood vessels that form a blood-brain barrier which limits the entry of potentially harmful substances in our blood
grey matter
the dark area largely composed of nerve cell bodies and their local connections to each other
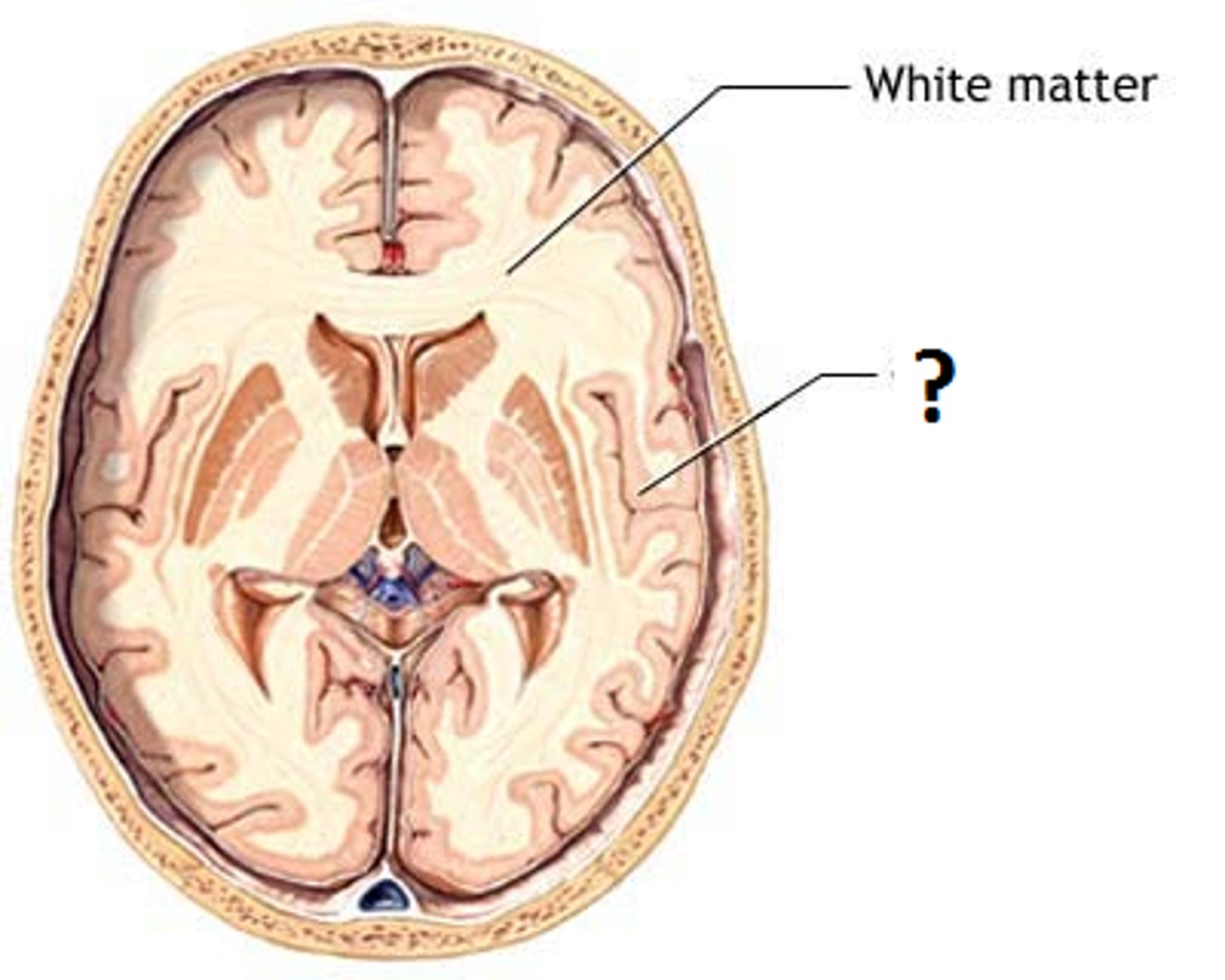
white matter
the light area largely composed of nerve fibres that connect distant brain areas to one another
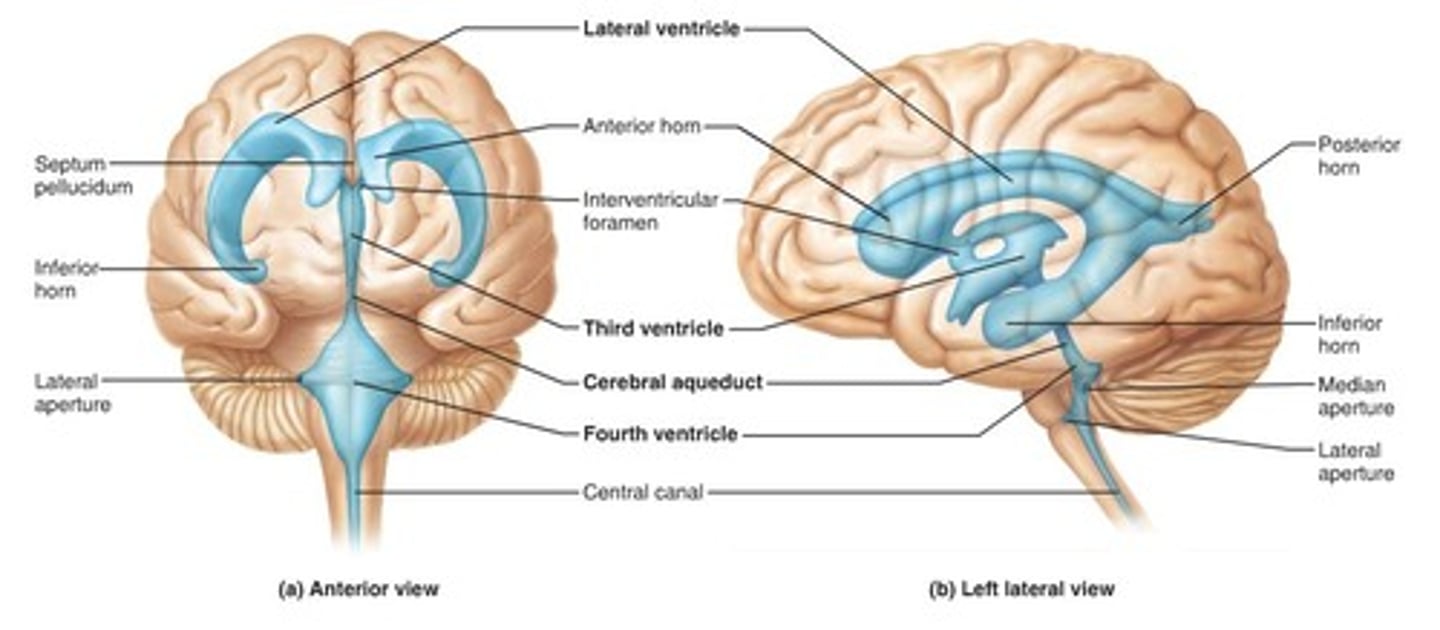
ventricles
two wing-shaped cavities in the cerebrum that form an inner communication network, filled with cerebrospinal fluid that flows between them
brain-heart debate
the question of whether our thoughts, feelings and behaviours originate from our brain or our heart
brain hypothesis
the belief that mental processes are located in the brain
heart-hypothesis
the belief that mental processes are located in the heart
mind-body problem
the question of whether our mind and body are distinct, separate entities or whether they are the same thing
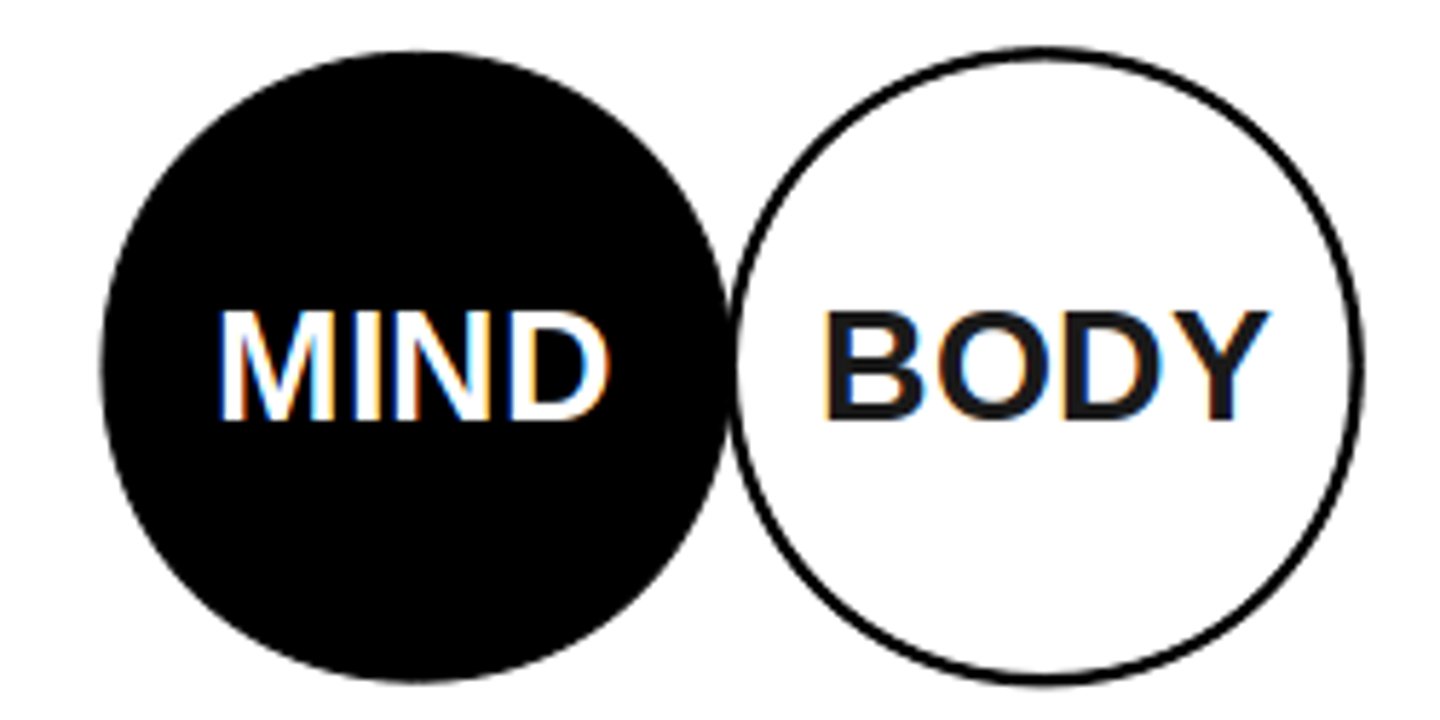
mind
a non-physical, spiritual entity
body
a physical entity that carries out biological processes
cerebral hemisphere
one of two brain areas running from the front to the back of the brain

corpus callosum
a bundle of nerve fibres connecting the two hemispheres, allowing them to communicate
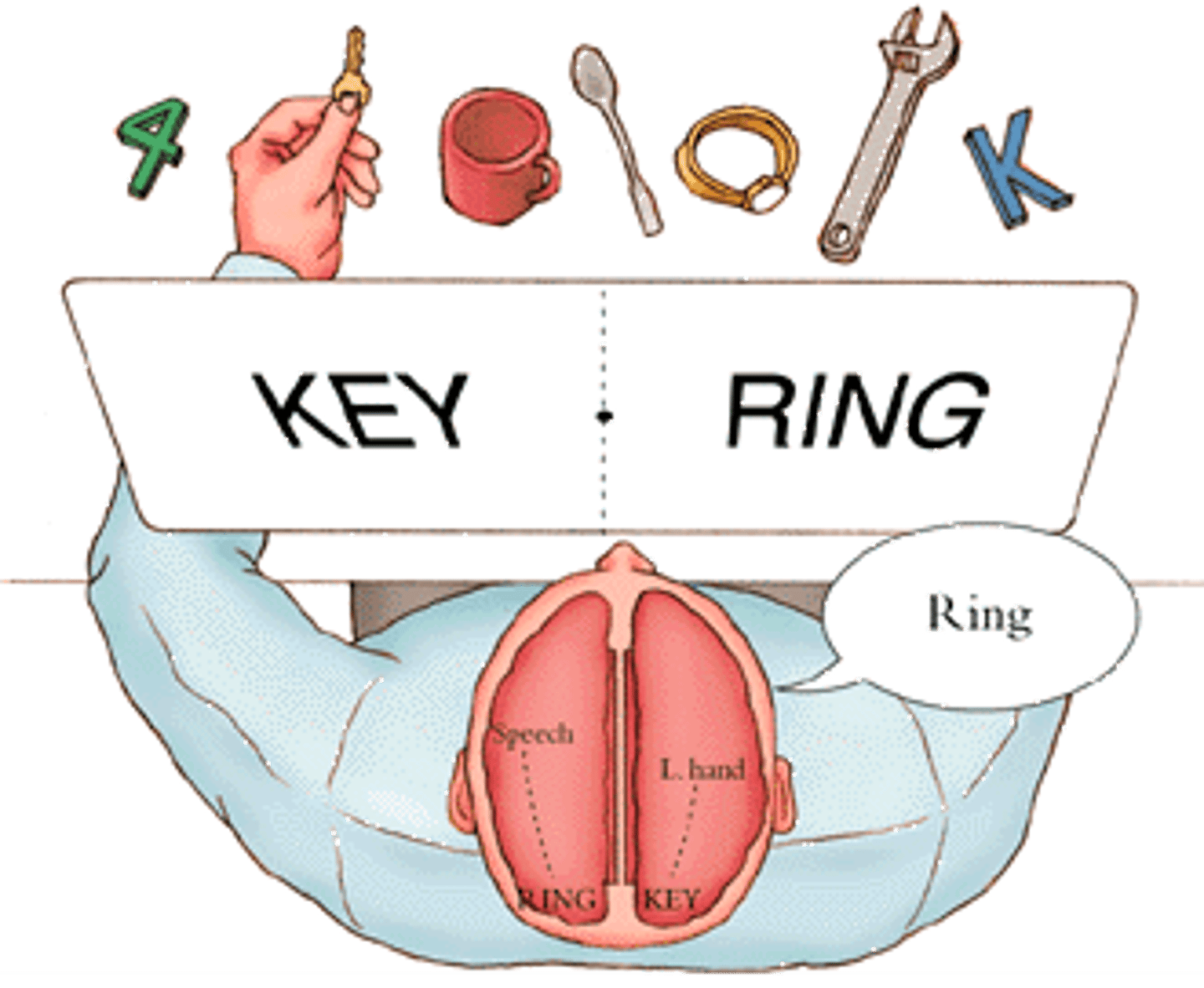
split-brain surgery
a procedure that involves cutting the main band of nerve tissue (corpus callosum) connecting the two hemispheres
brain ablation
a procedure that involves the irreversible removal of part of the brain
brain lesioning
a procedure that involves disrupting the normal structure/function of part of the brain
electrical stimulation of the brain (ESB)
using an electrode to stimulate a specific area of the brain to assess what function that area controls
electrodes
small wires used to electrically stimulate brain tissue or measure electrical activity in these tissues
neuroimaging
a technique that captures a picture of the brain
structural neuroimaging
a neuroimaging technique like CT and MRI scans that provides highly detailed images of anatomical features in the brain
functional neuroimaging
a neuroimaging technique like PET and fMRI that provides an indication of brain activity but not high anatomical detail
brain
a complex organ contained within the skull that coordinates mental processes and behaviour, and regulates bodily activity
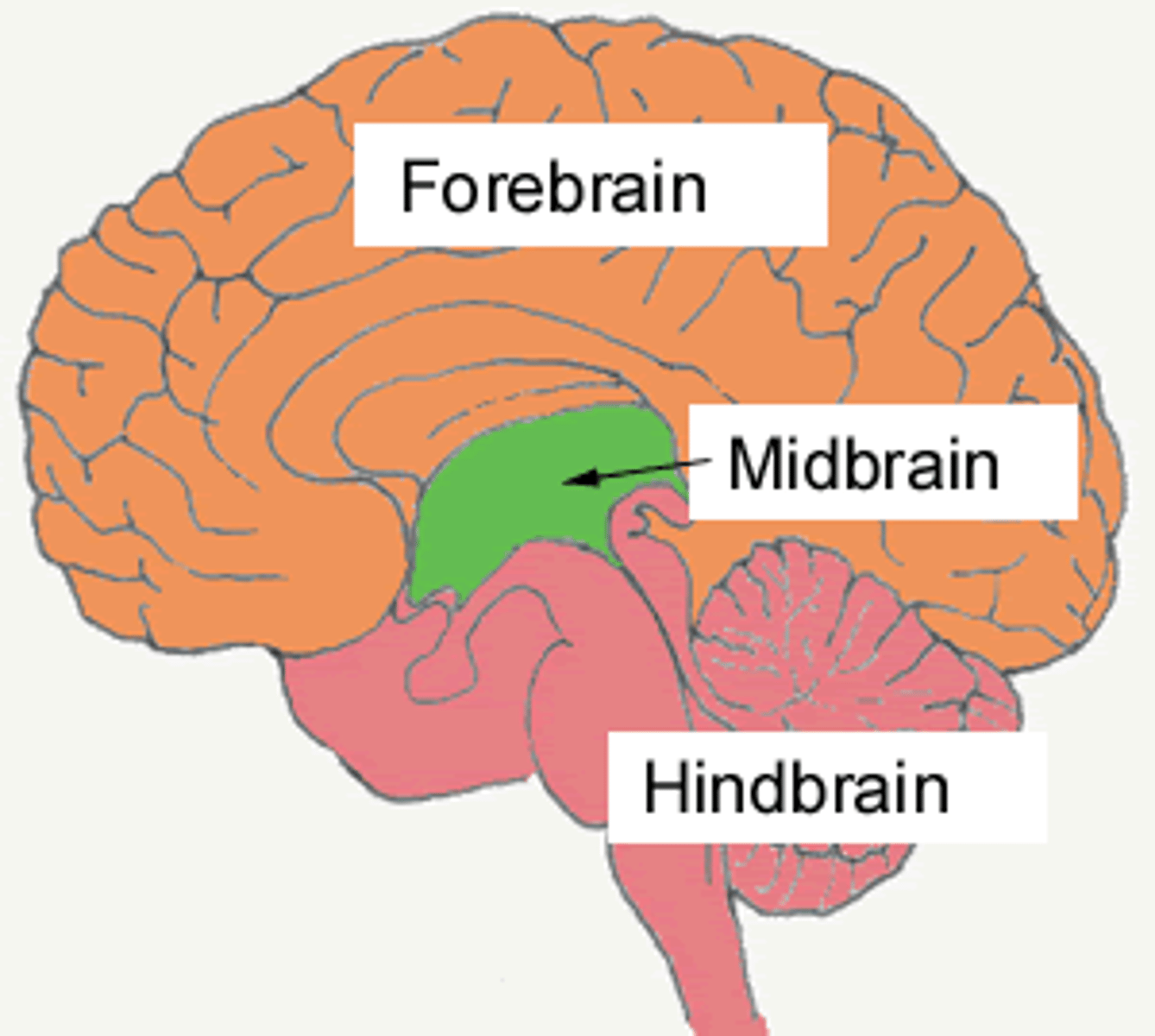
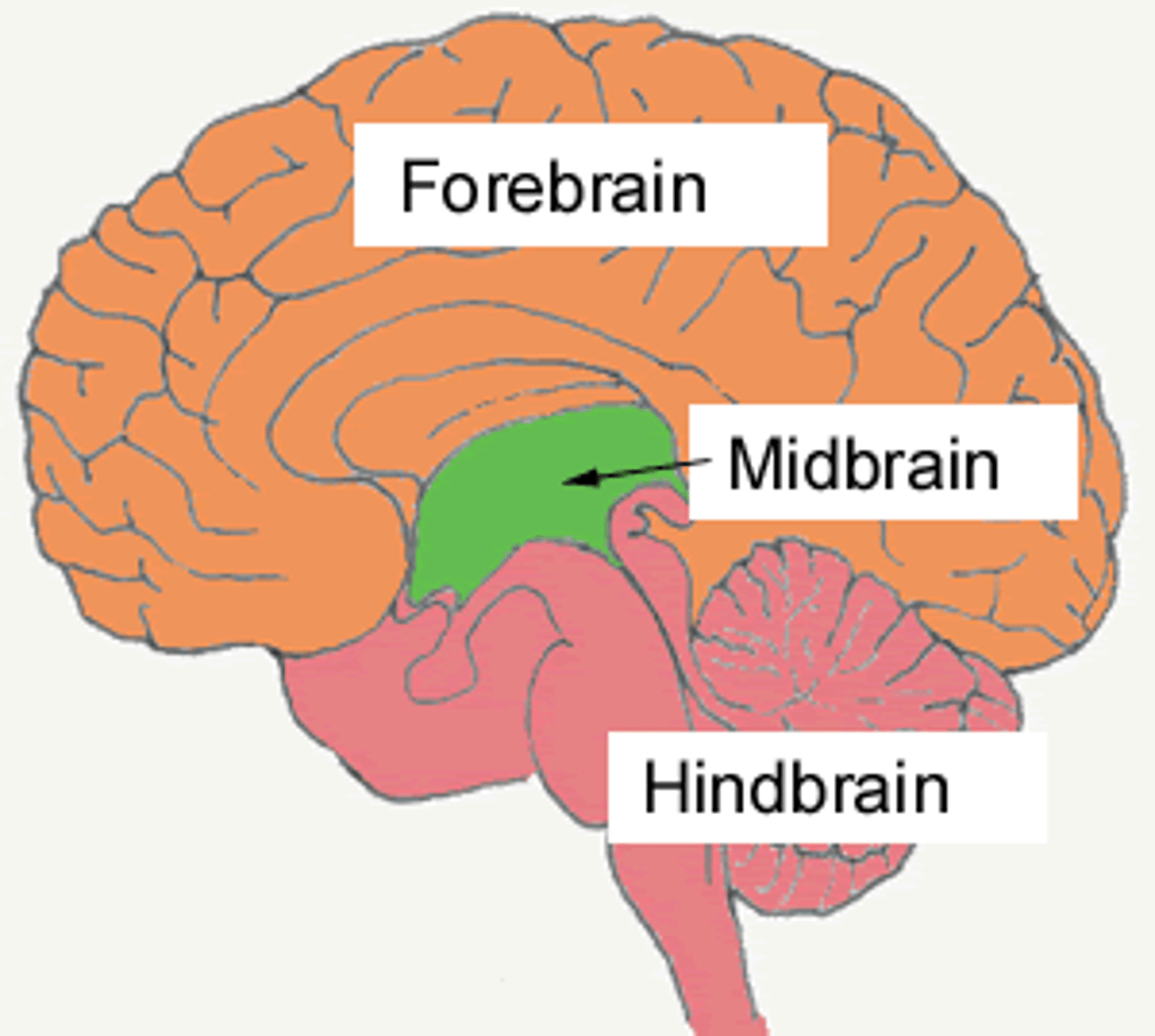
hindbrain
an area of the brain containing the medulla, pons, and cerebellum; involved in regulating vital functions
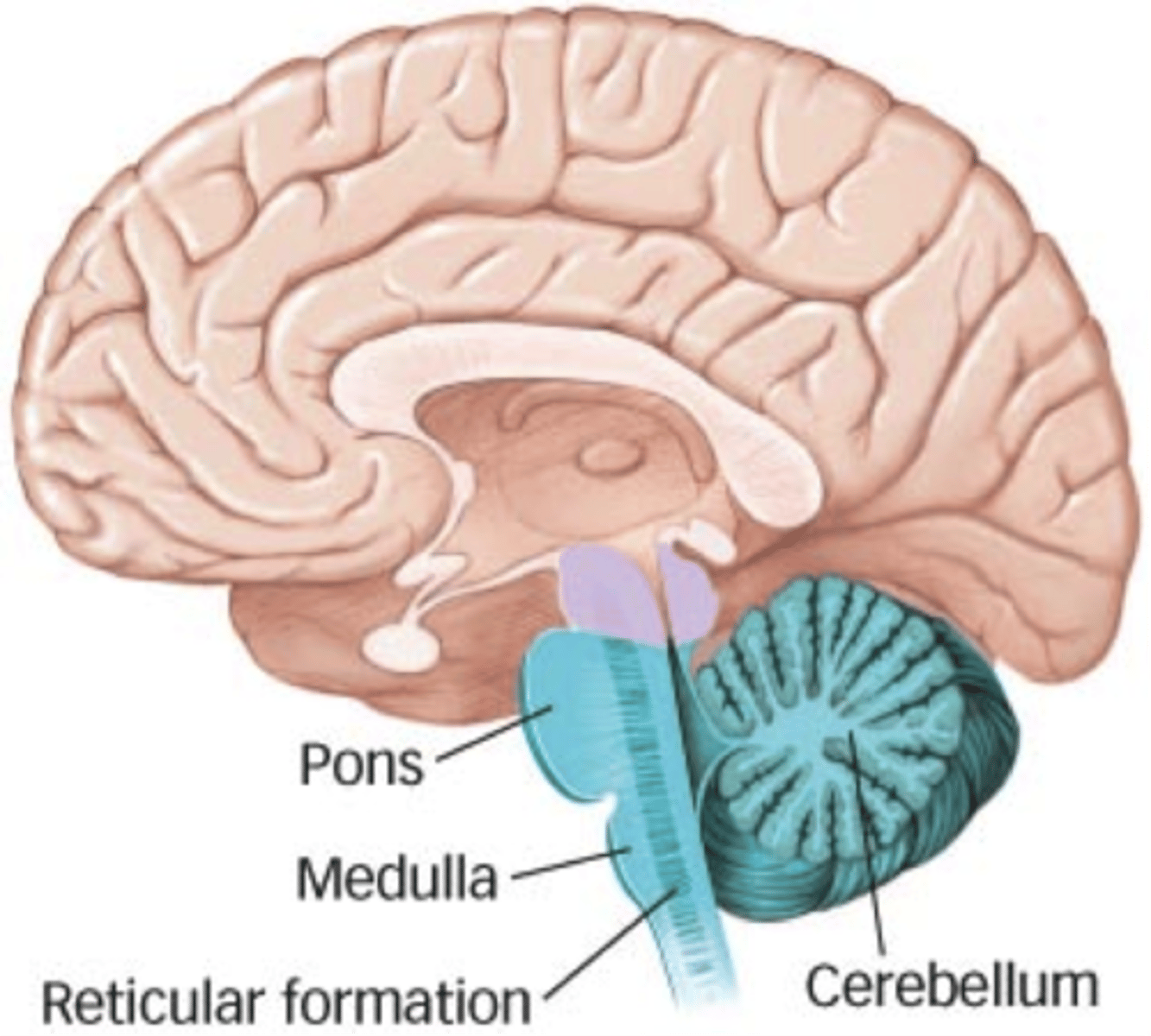
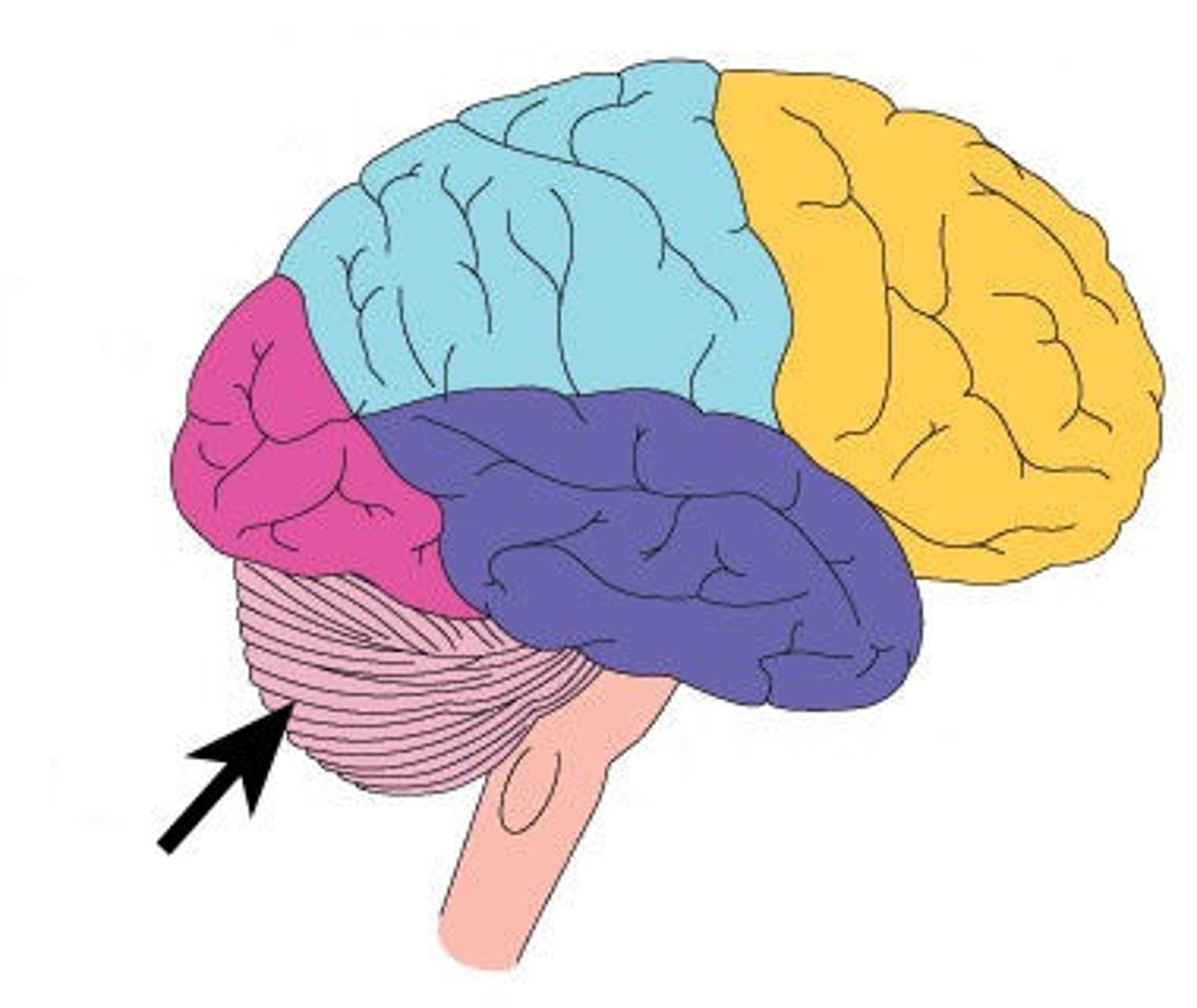
cerebellum
the 'little brain' at the rear of the brainstem, involved in processing sensory input and coordinating movement and balance
pons
a brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
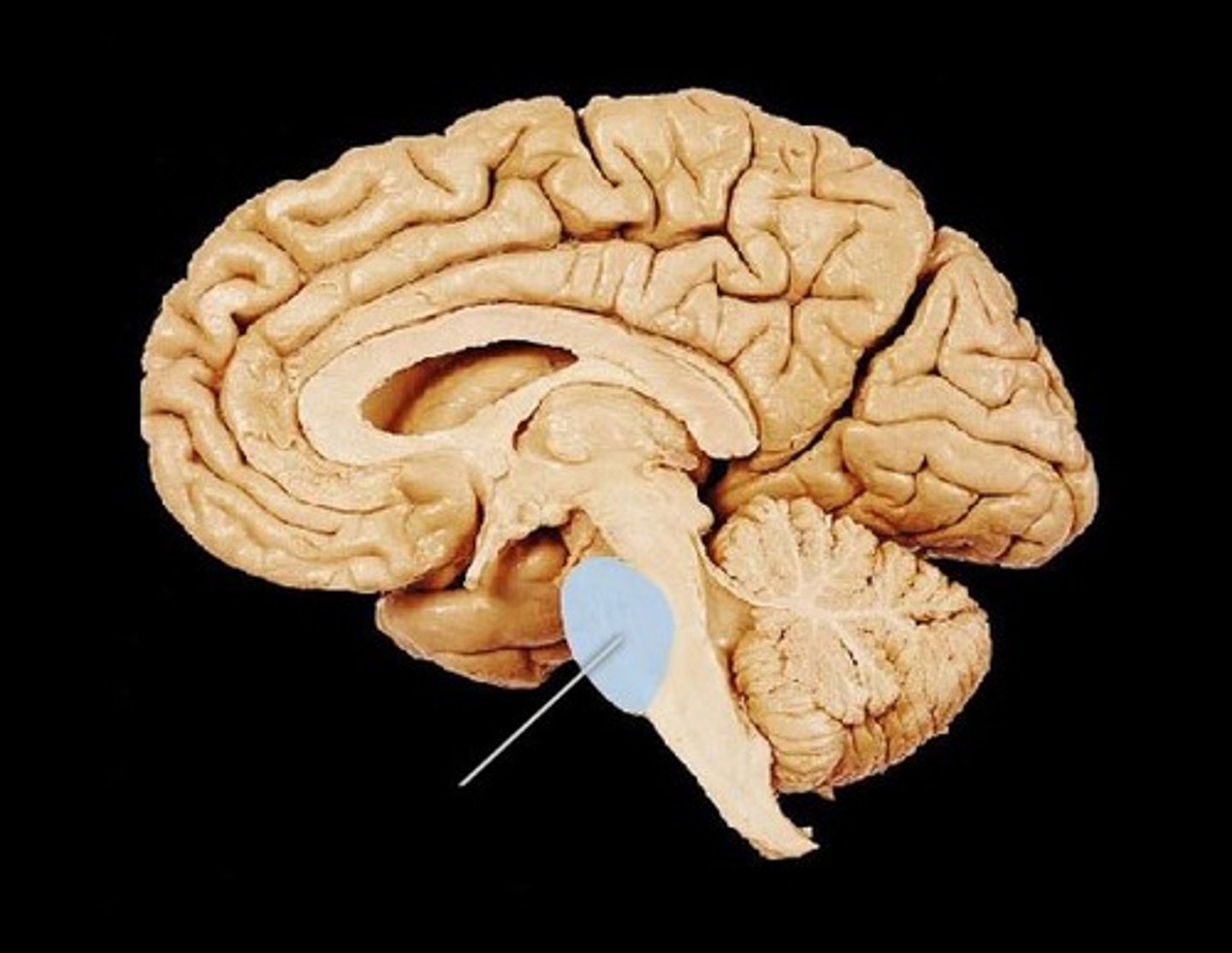
medulla
the base of the brainstem, involved in controlling heartbeat and breathing
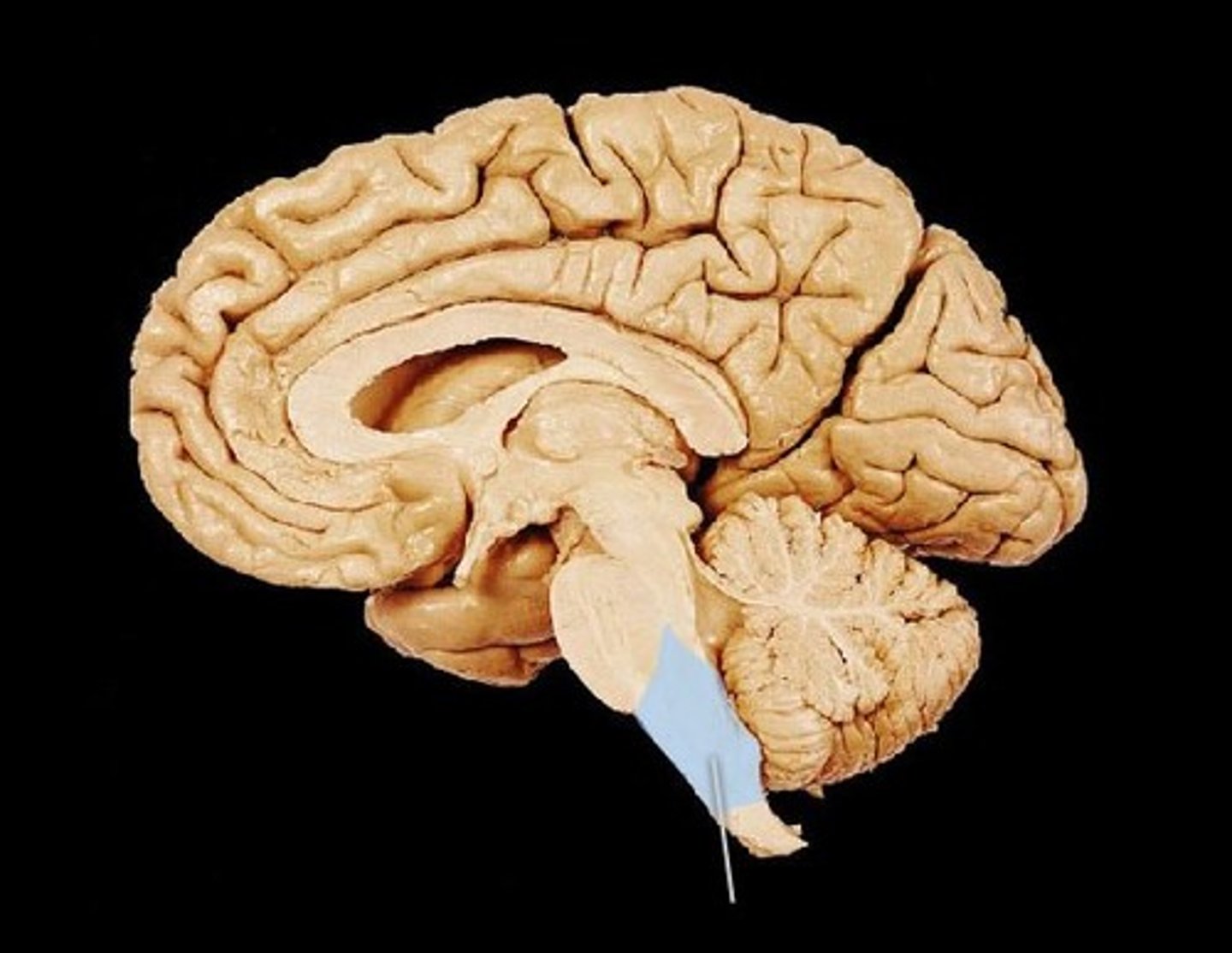
midbrain
an area between the hindbrain and the forebrain, involved in hearing and sight
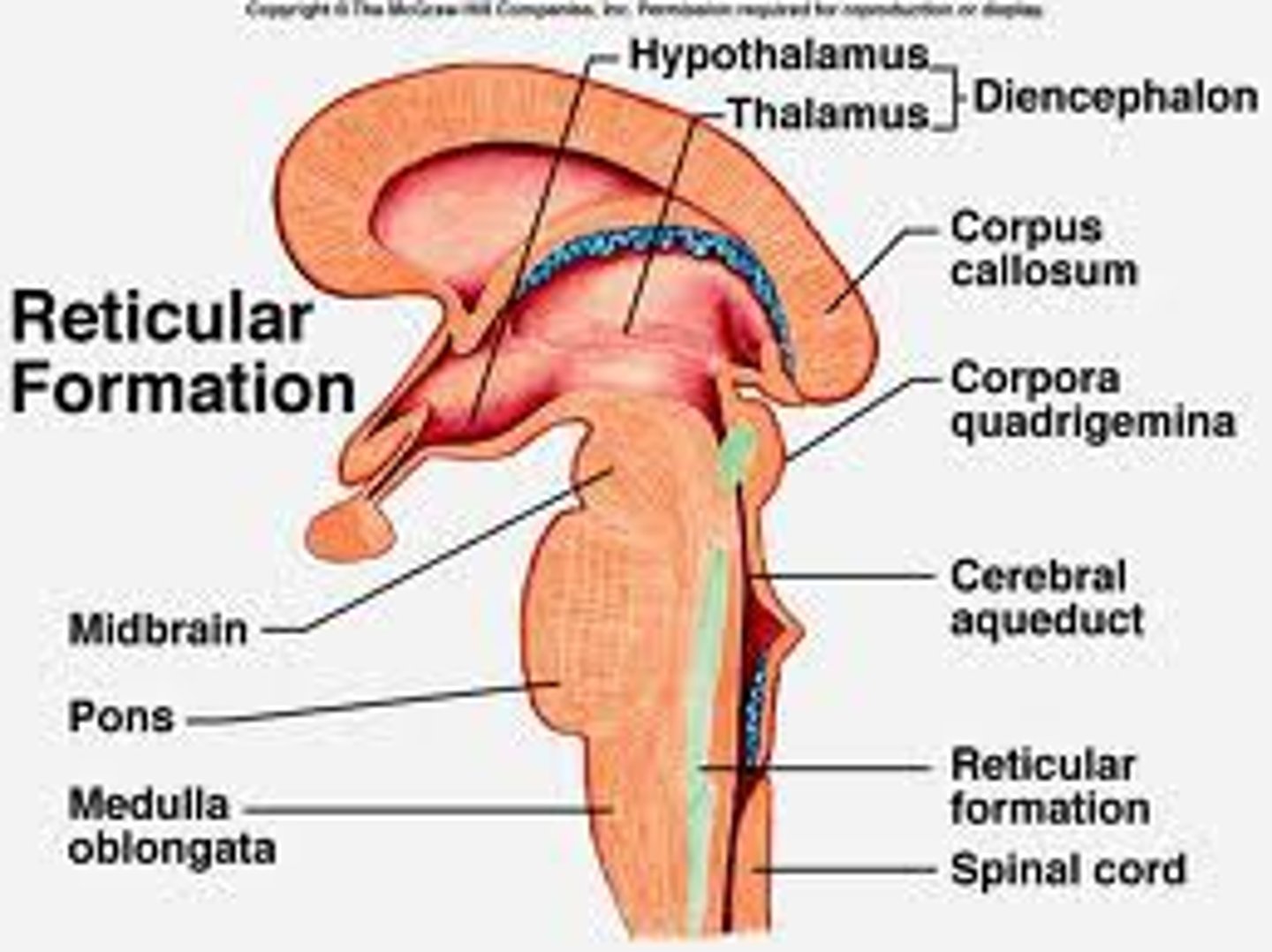
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem, involved in controlling arousal
reticular activating system
the part of the brain involved in attention, sleep, and arousal
forebrain
largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, and the limbic system, among other parts; involved in regulating cognitive processes and motor functions
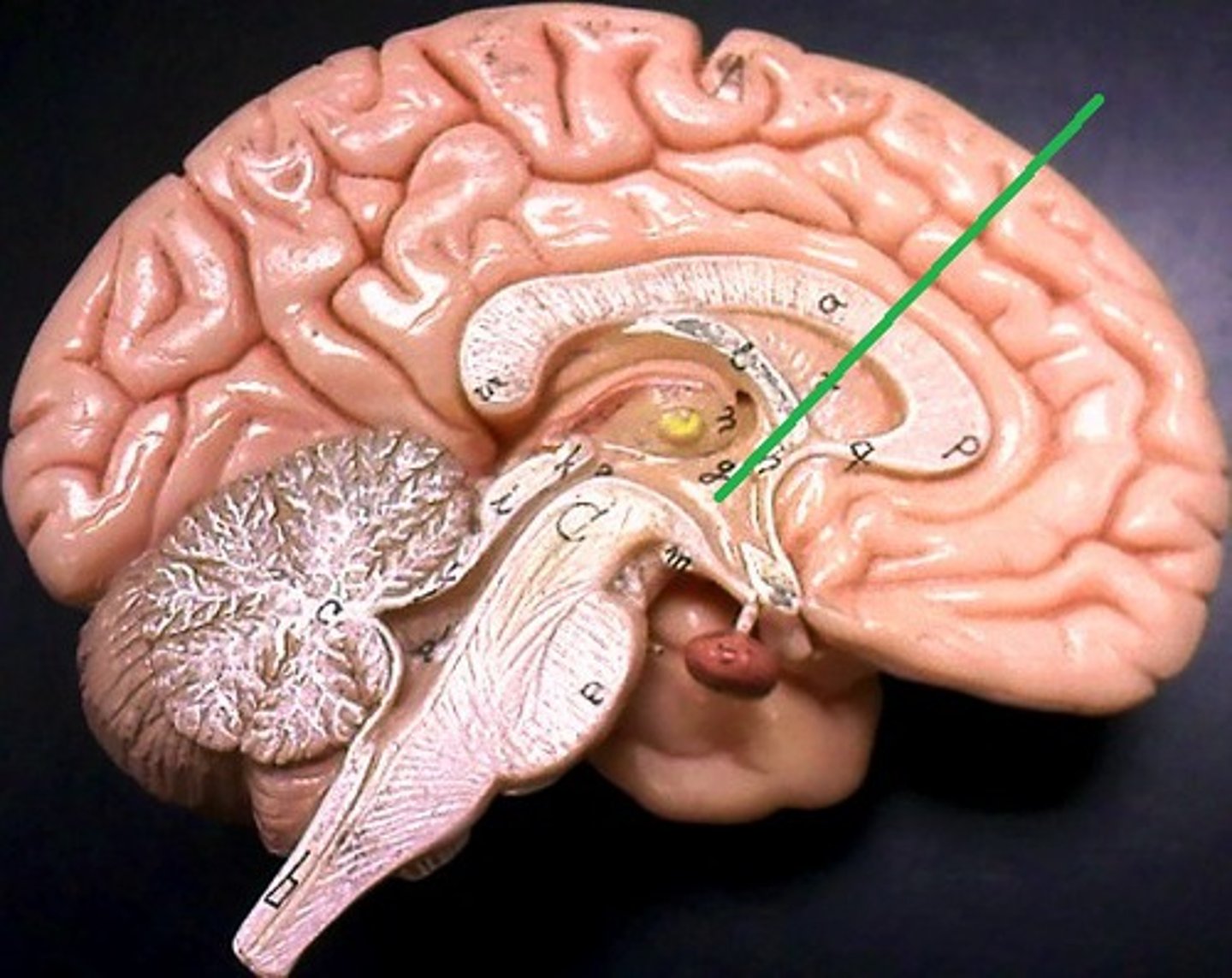
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus, involved in maintaining homeostasis
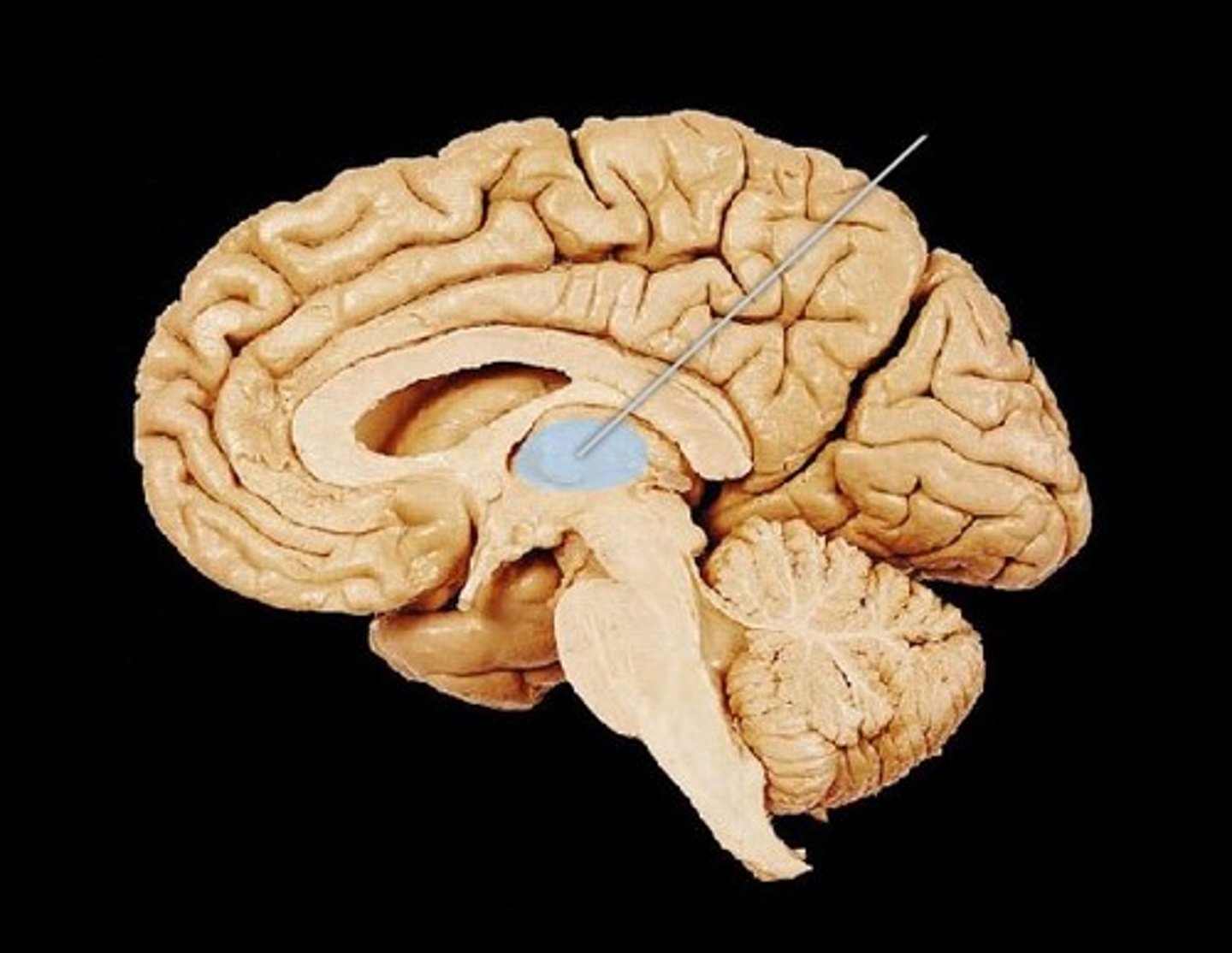
thalamus
a relay station relaying information between different subcortical areas and the cerebral cortex
cerebrum
an area of the brain responsible for conscious thought, memory, and voluntary movement
cerebral cortex
the outer layer of the brain involved in complex functions like perception, memory, and language
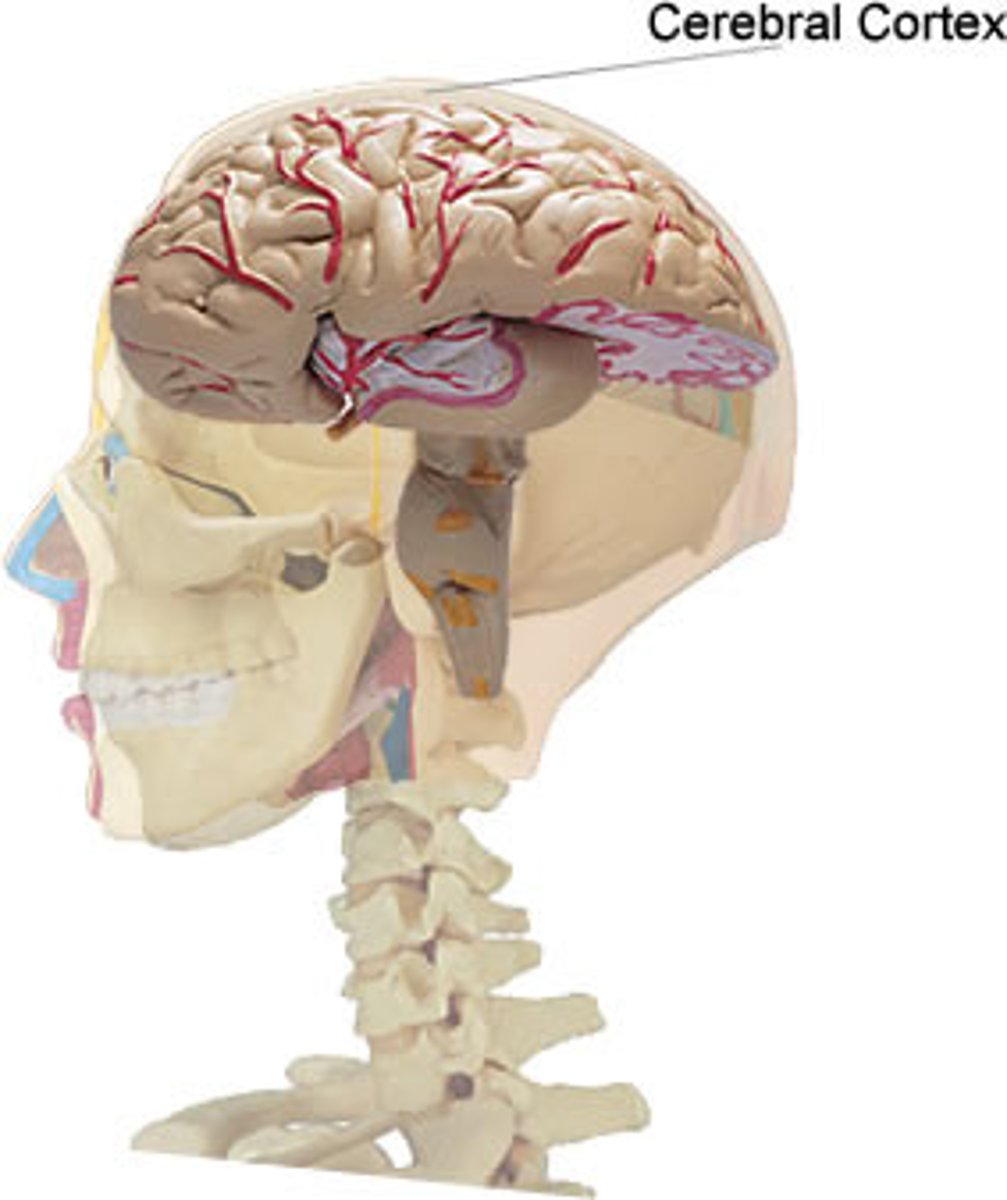
sensory areas
receive and process sensory information
motor areas
control voluntary movement
association areas
surround both sensory and motor areas, dealing with more complex functions requiring integration of inputs of information from different areas
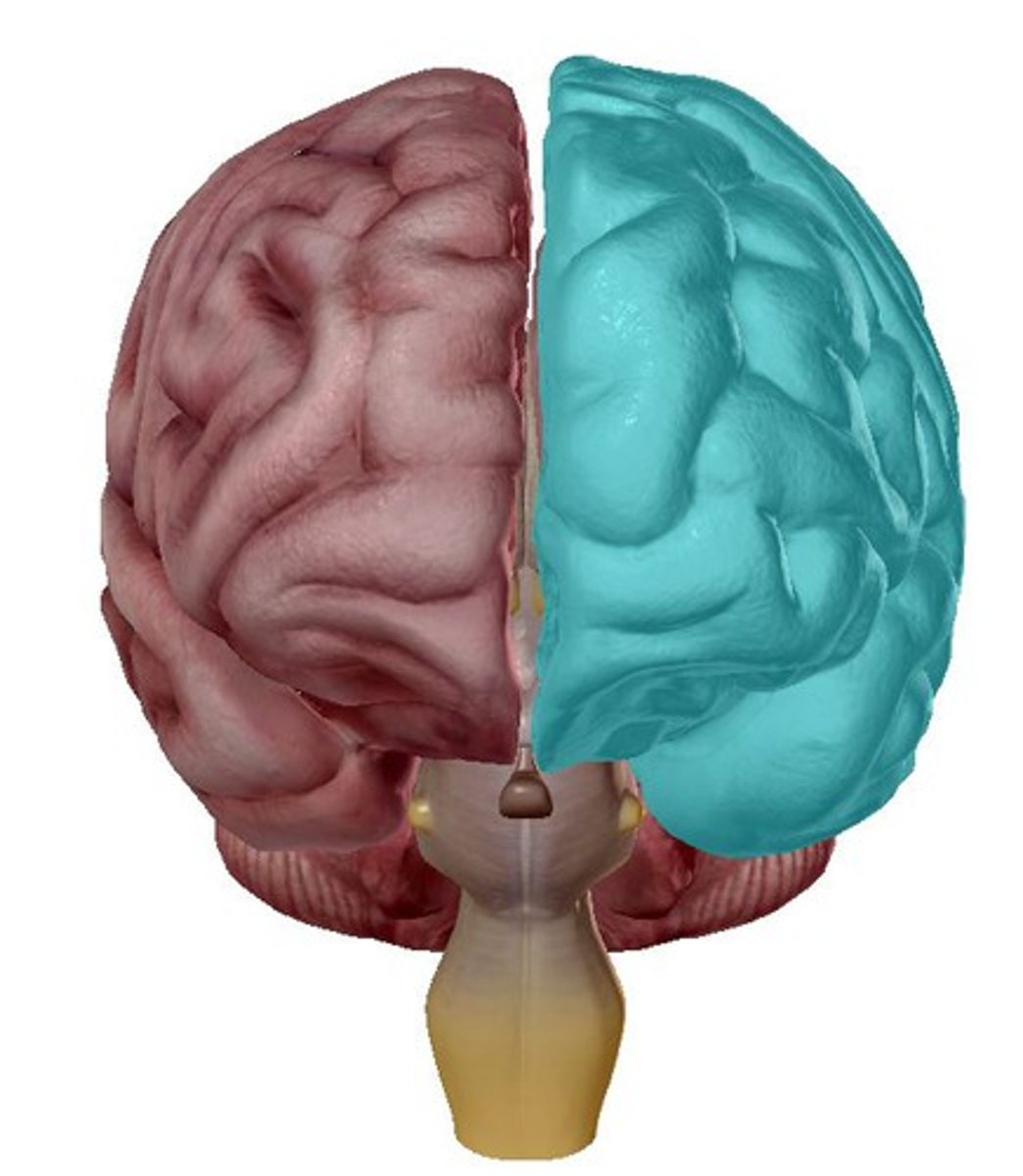
cerebral hemispheres
the right and left halves of the cerebrum
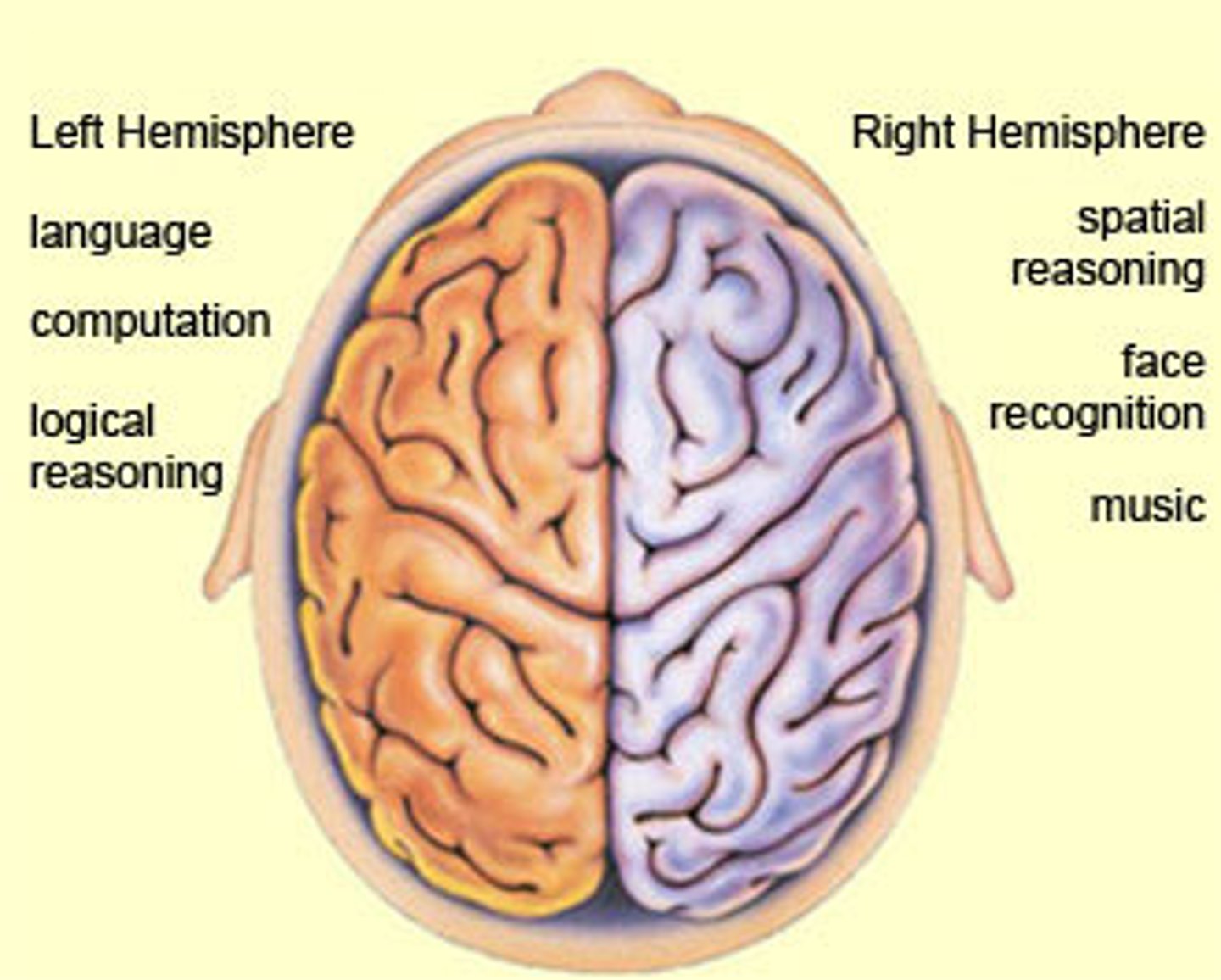
What is the left hemisphere responsible for?
verbal and analytical functions
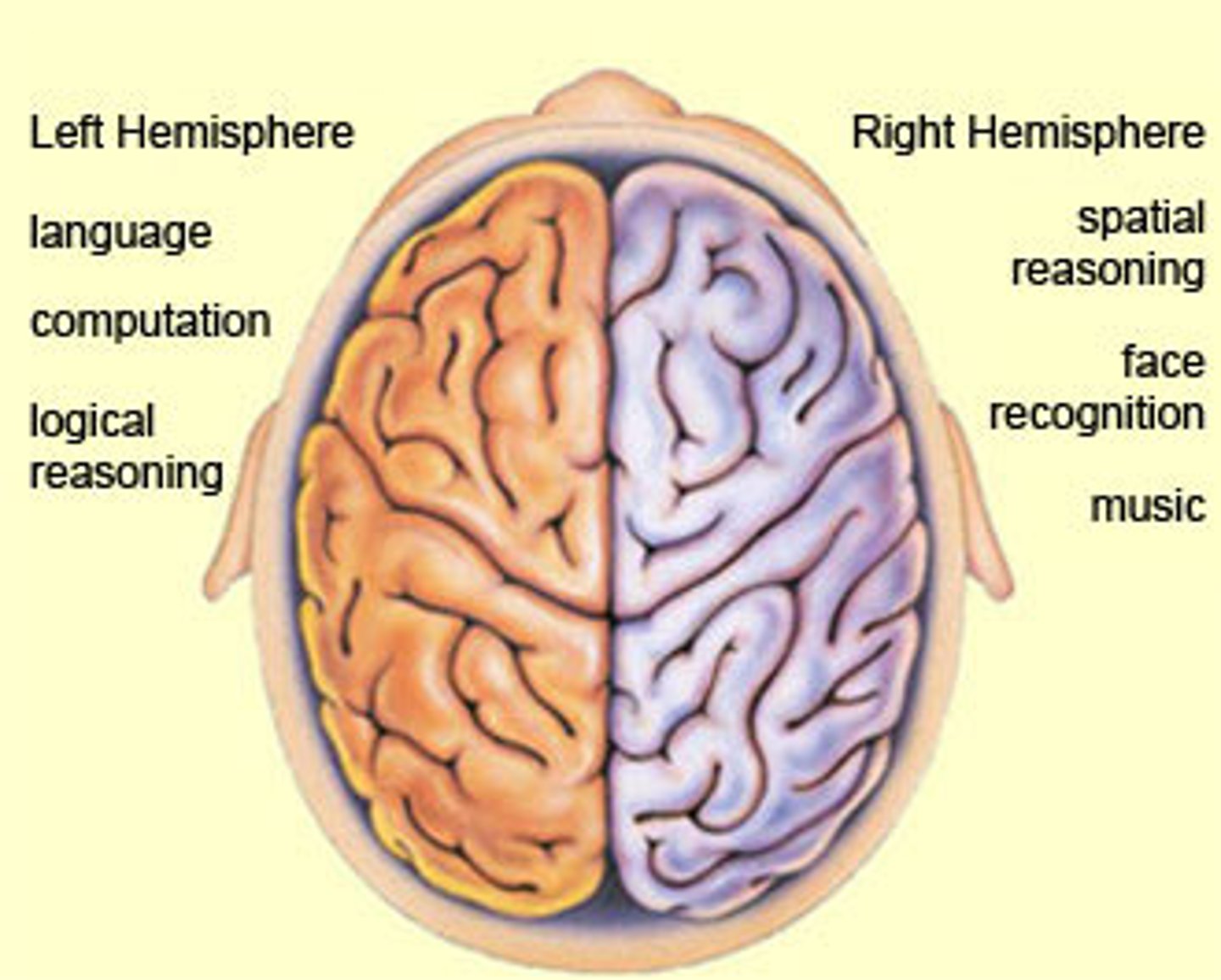
What is the right hemisphere responsible for?
non-verbal functions and spatial/visual thinking
contralateral function
each hemisphere controls the opposite body side
hemispheric specialisation
the idea that one hemisphere has specialised functions or exerts greater control over a specific function
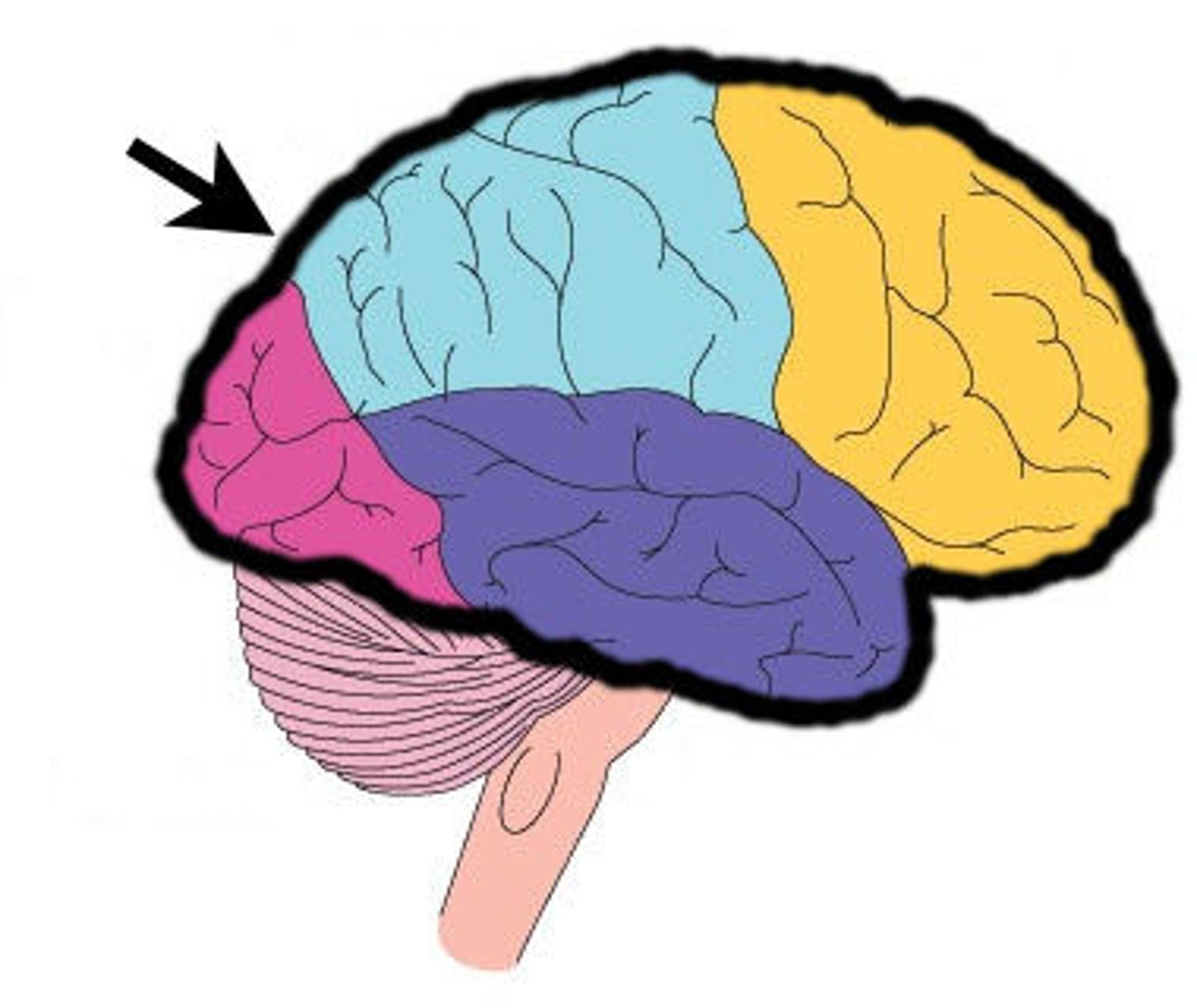
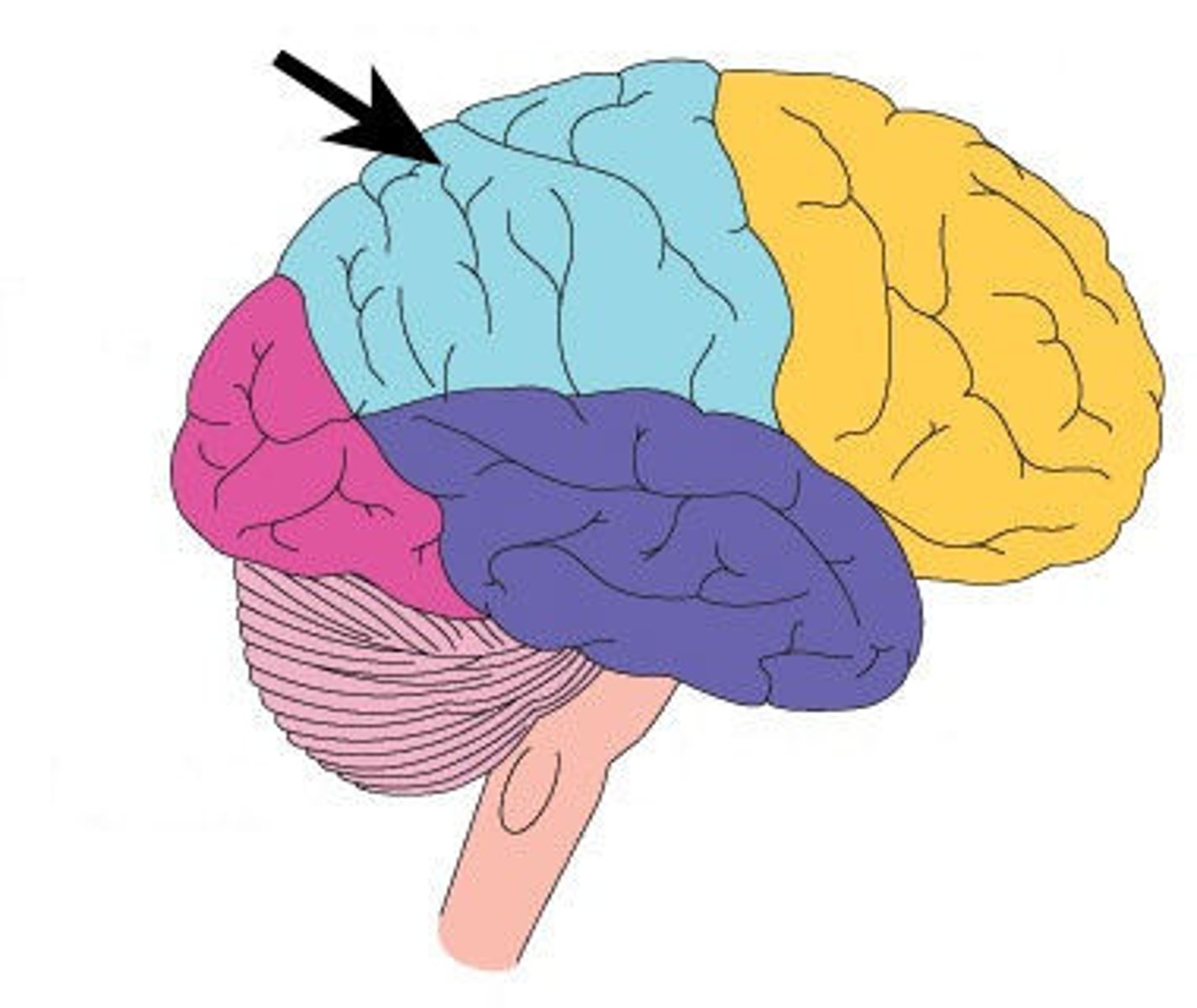
cortical lobes
divisions of the cerebral cortex associated with different functions
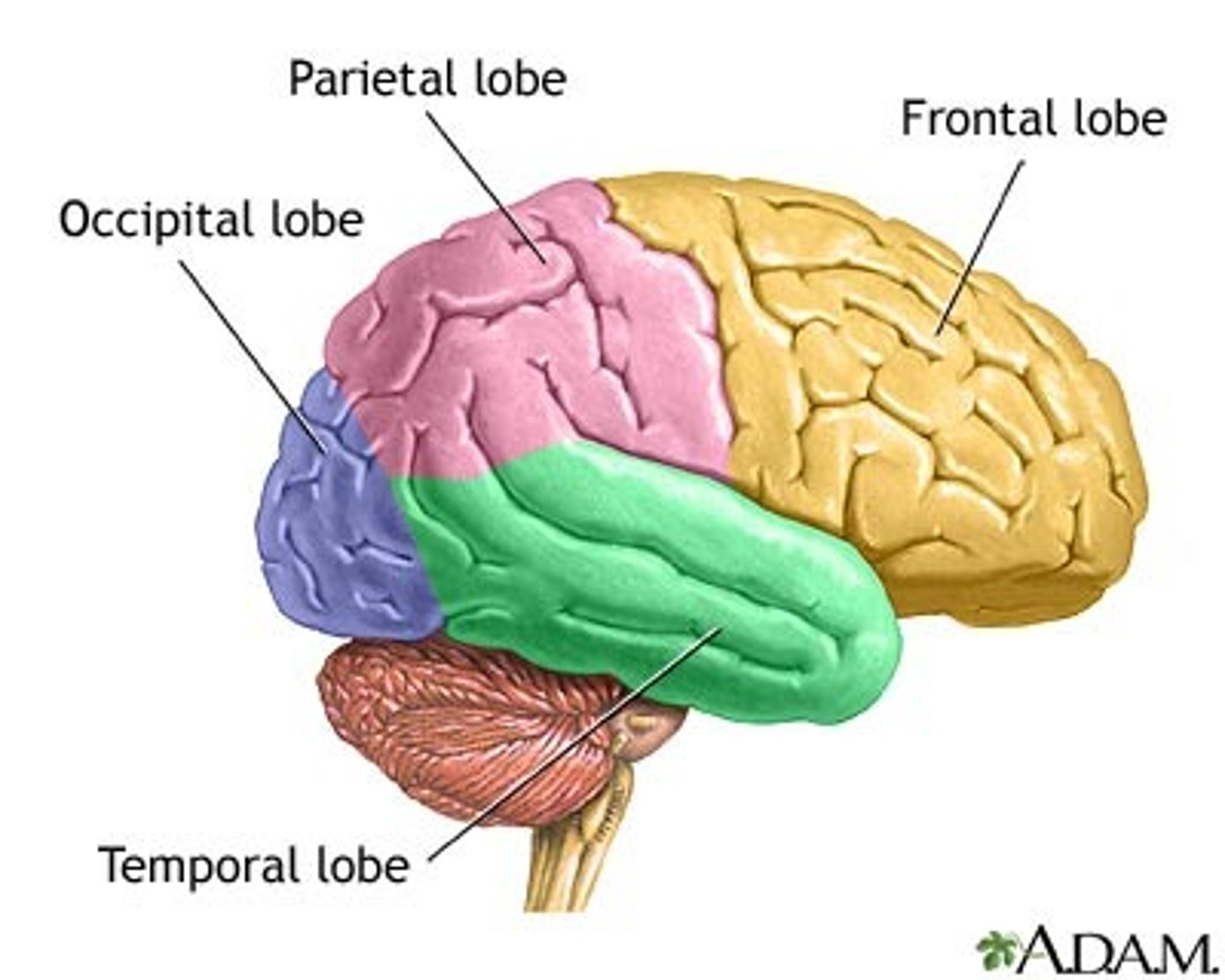
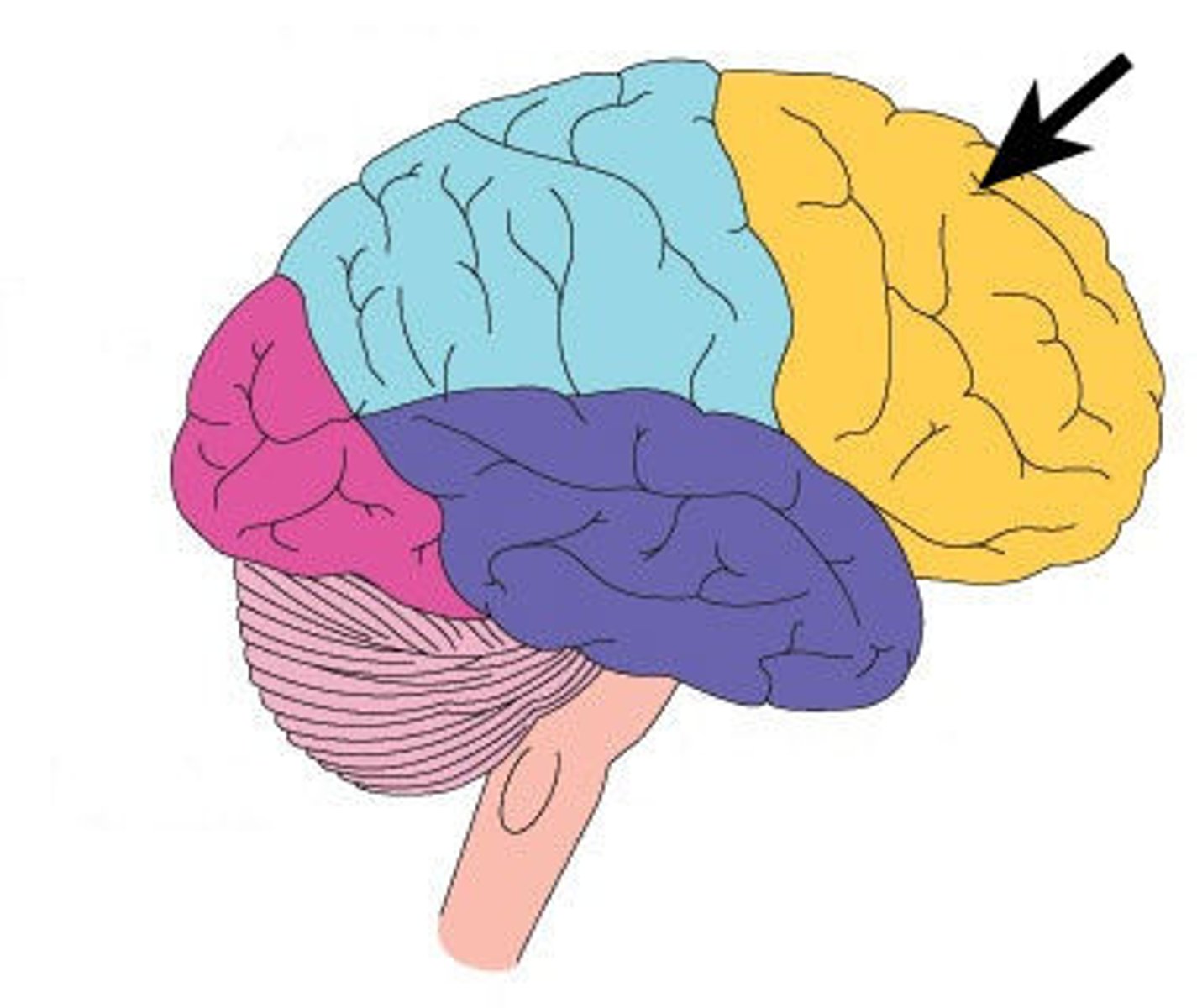
frontal lobe
the frontmost lobe of the cerebral cortex responsible for voluntary movement, language, and managing executive functions
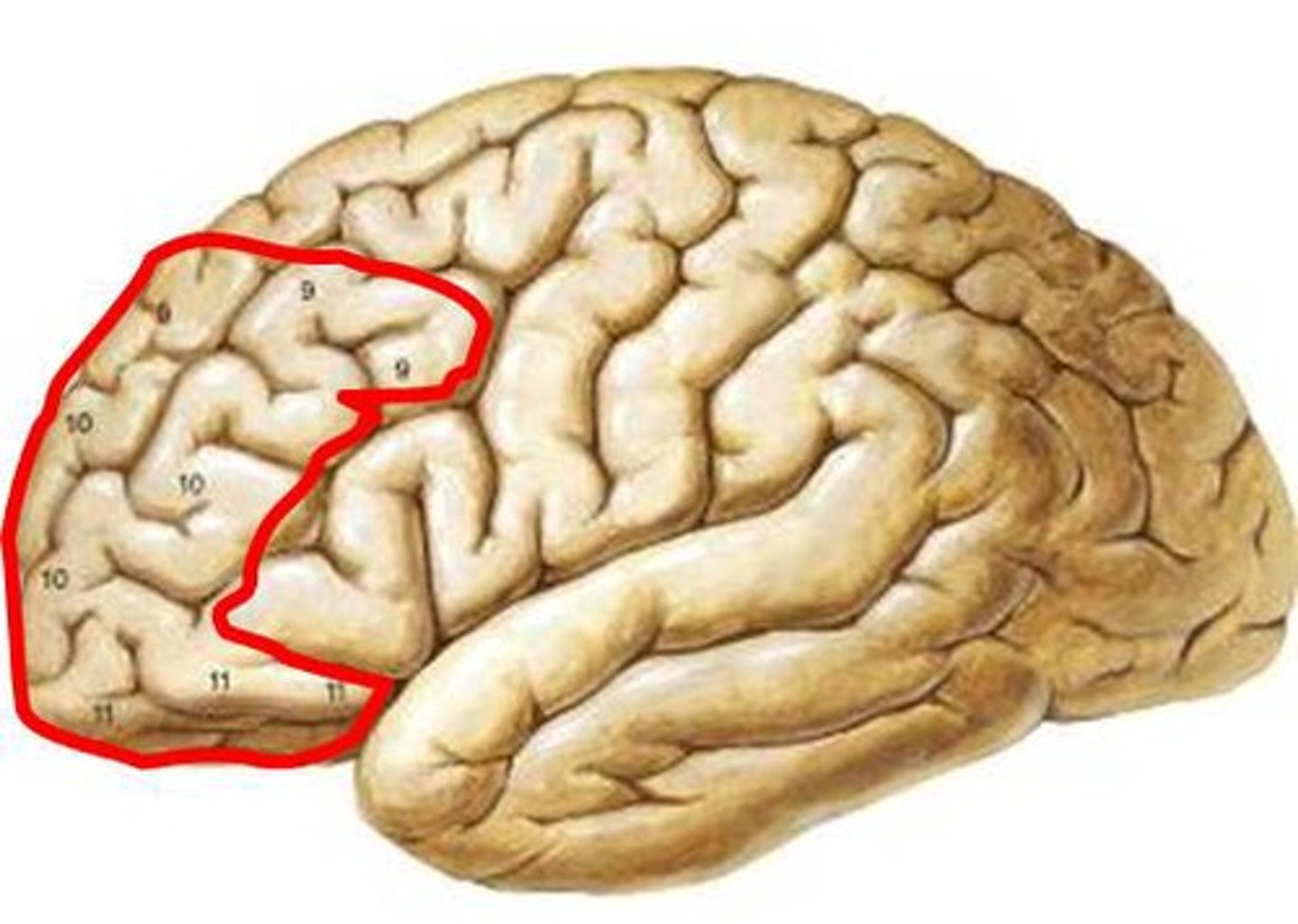
prefrontal cortex
an area in the frontal lobe responsible for higher-level cognitive processes
premotor cortex
an area in the frontal lobe responsible for planning and organising movements
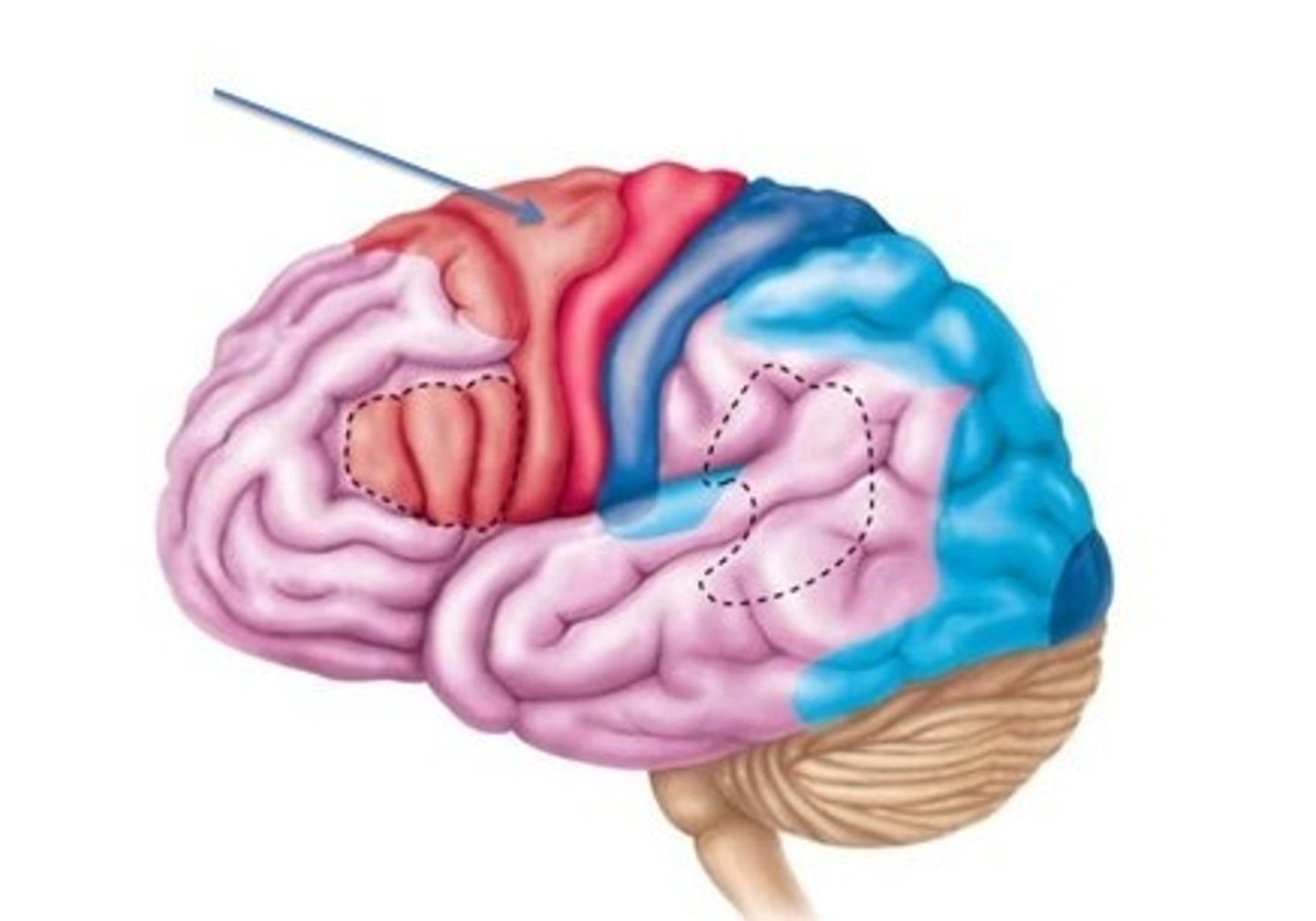
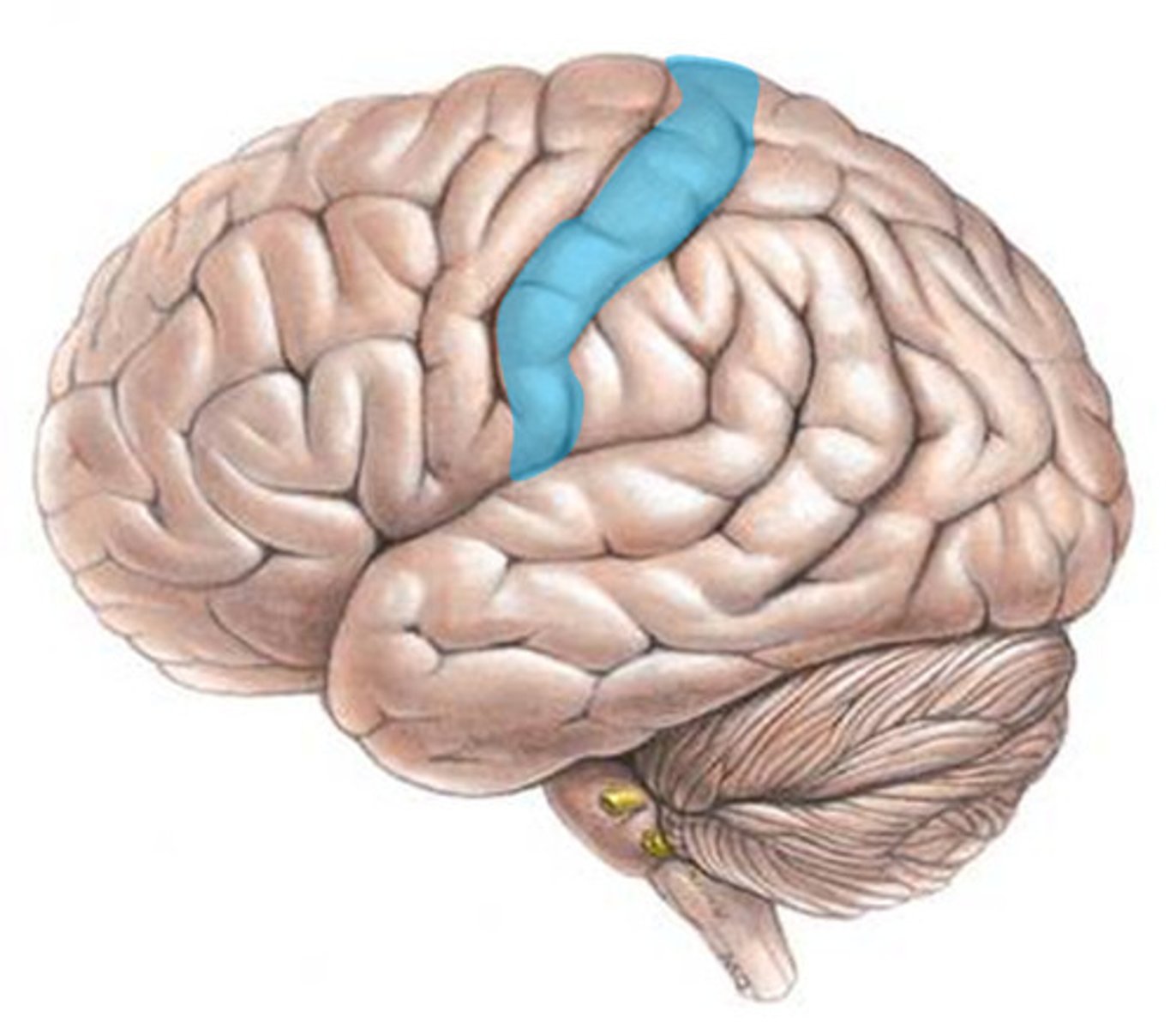
primary motor cortex
an area of the frontal lobe responsible for executing voluntary movement
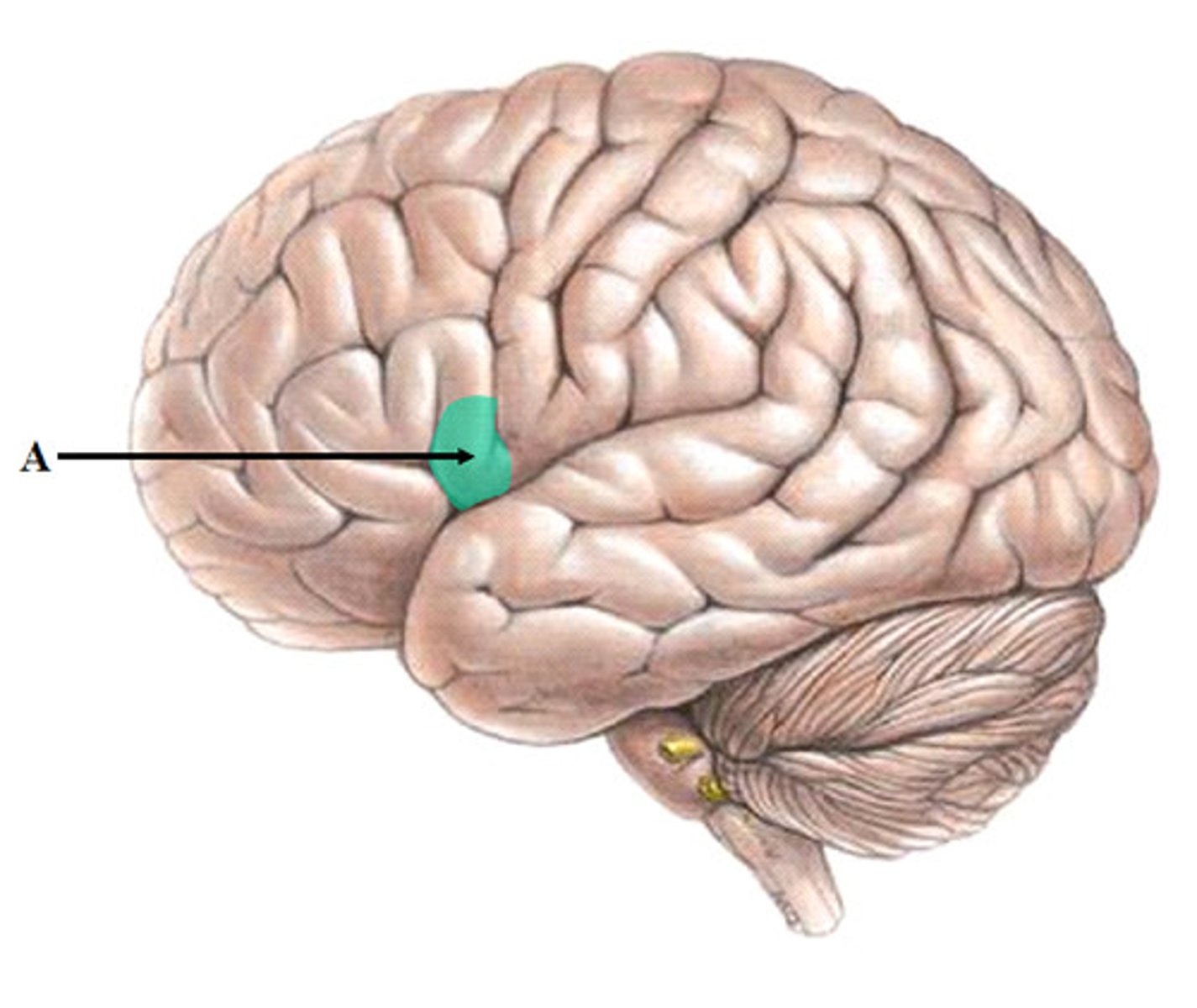
Broca's area
an area of the frontal lobe responsible for directing muscle movements needed for speech
Broca's aphasia
damage to the Broca's area, characterised by an impaired ability to produce speech
parietal lobe
the lobe behind the frontal lobe in the cerebral cortex responsible for integrating and processing sensory information
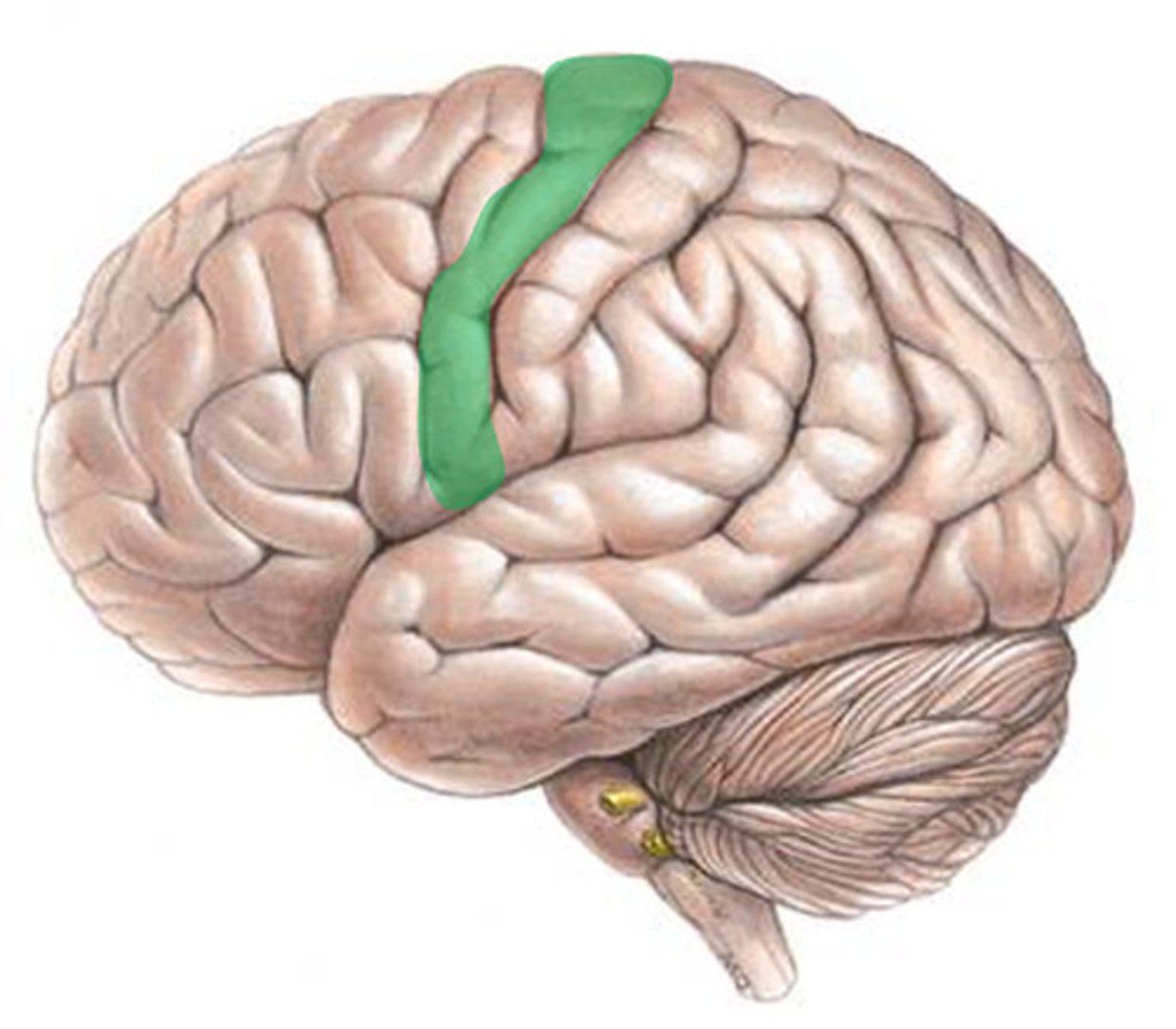
primary somatosensory cortex
an area of the parietal lobe responsible for receiving and processing sensory information from the body parts
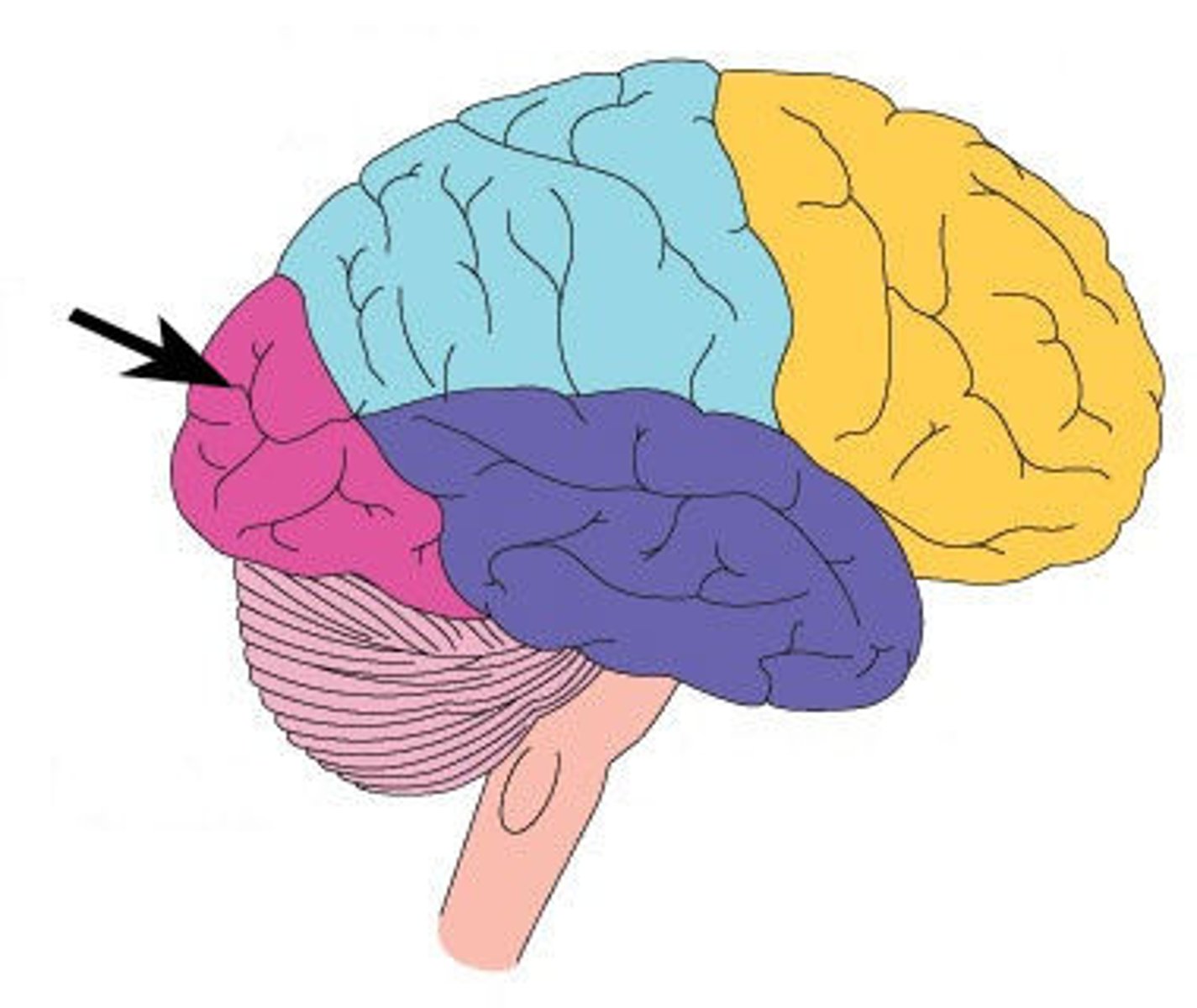
occipital lobe
the rearmost lobe of the cerebral cortex responsible for visual perception
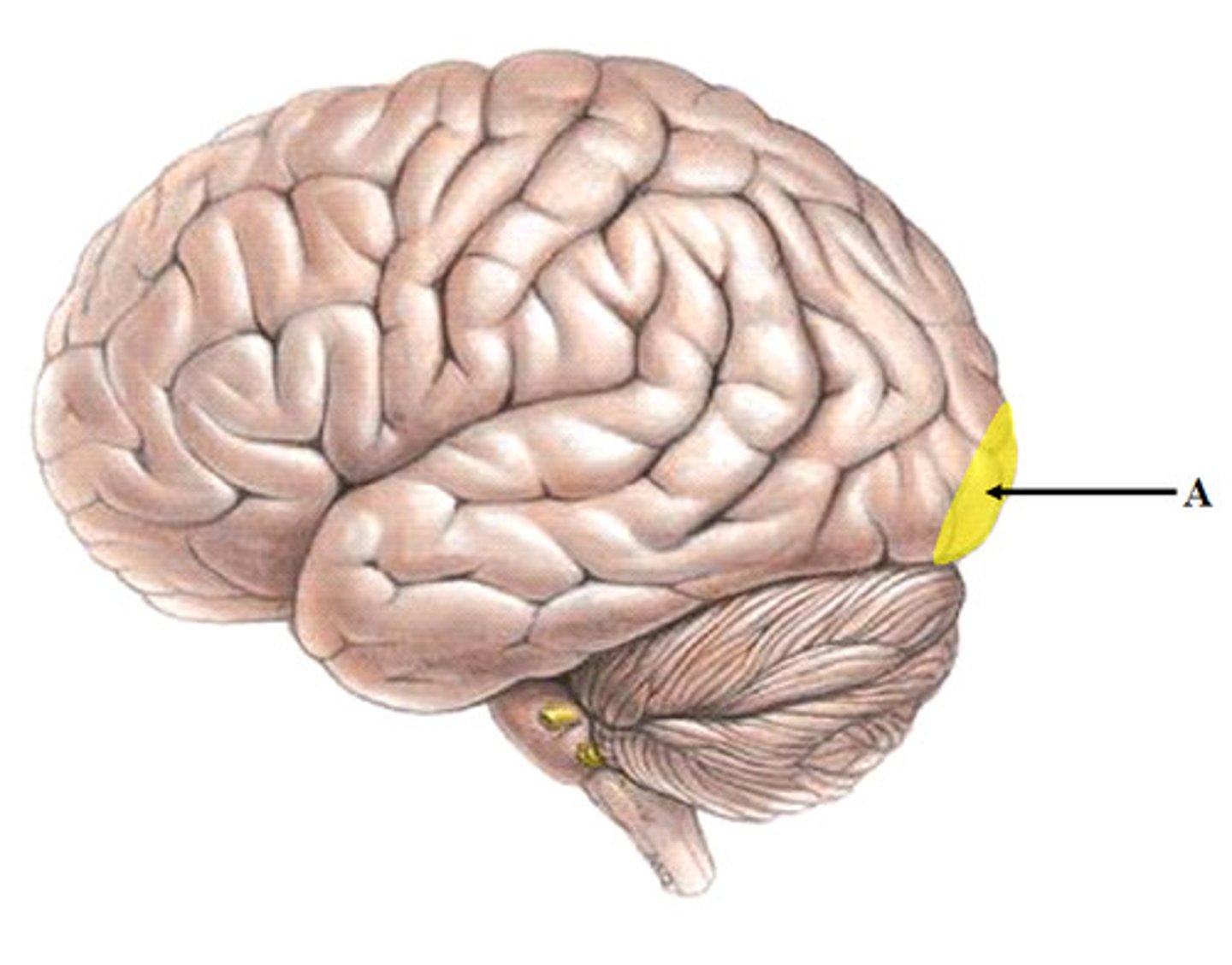
primary visual cortex
an area of the occipital lobe responsible for receiving information directly from the visual system
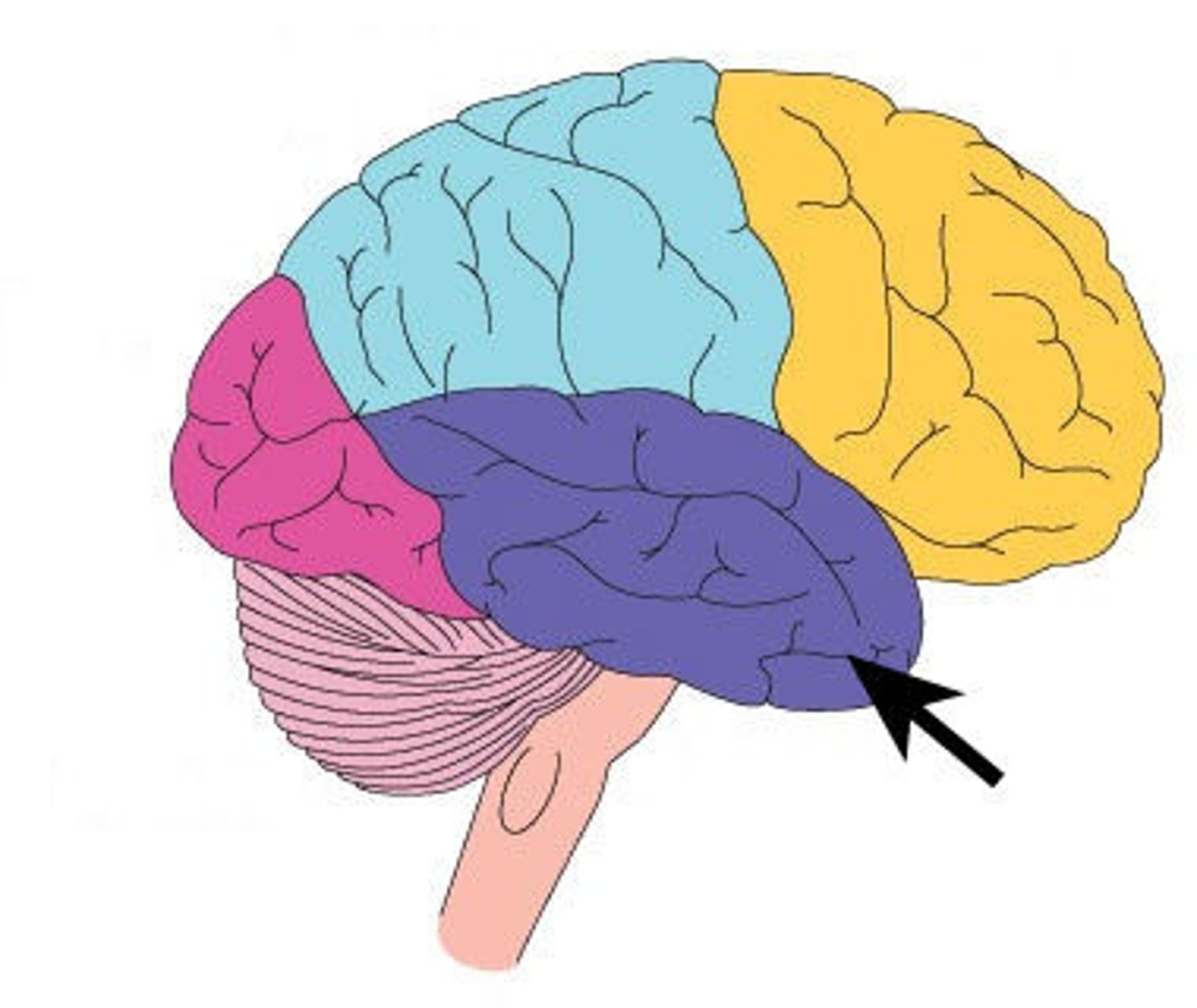
temporal lobe
the lowest lobe of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing auditory information and memory formation
primary auditory cortex
an area of the temporal lobe responsible for processing auditory information
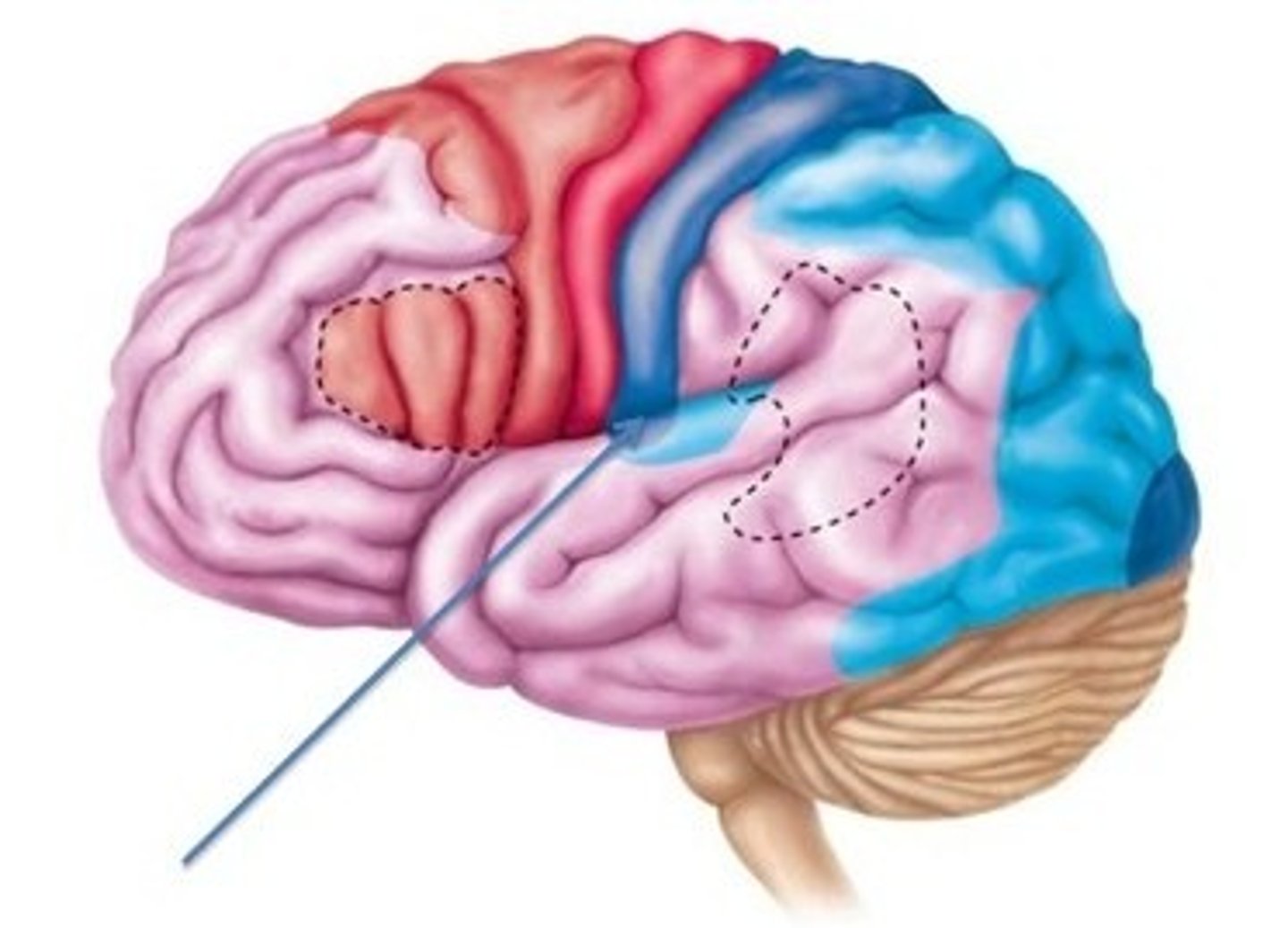
Wernicke's area
an area of the temporal lobe responsible for understanding both spoken and written language
What are the different parts of a neuron?
phrenology
the study of the shape and size of the human skull as an indication of personality and mental abilities
neuroplasticity
the brain's ability to change in response to experience or injury
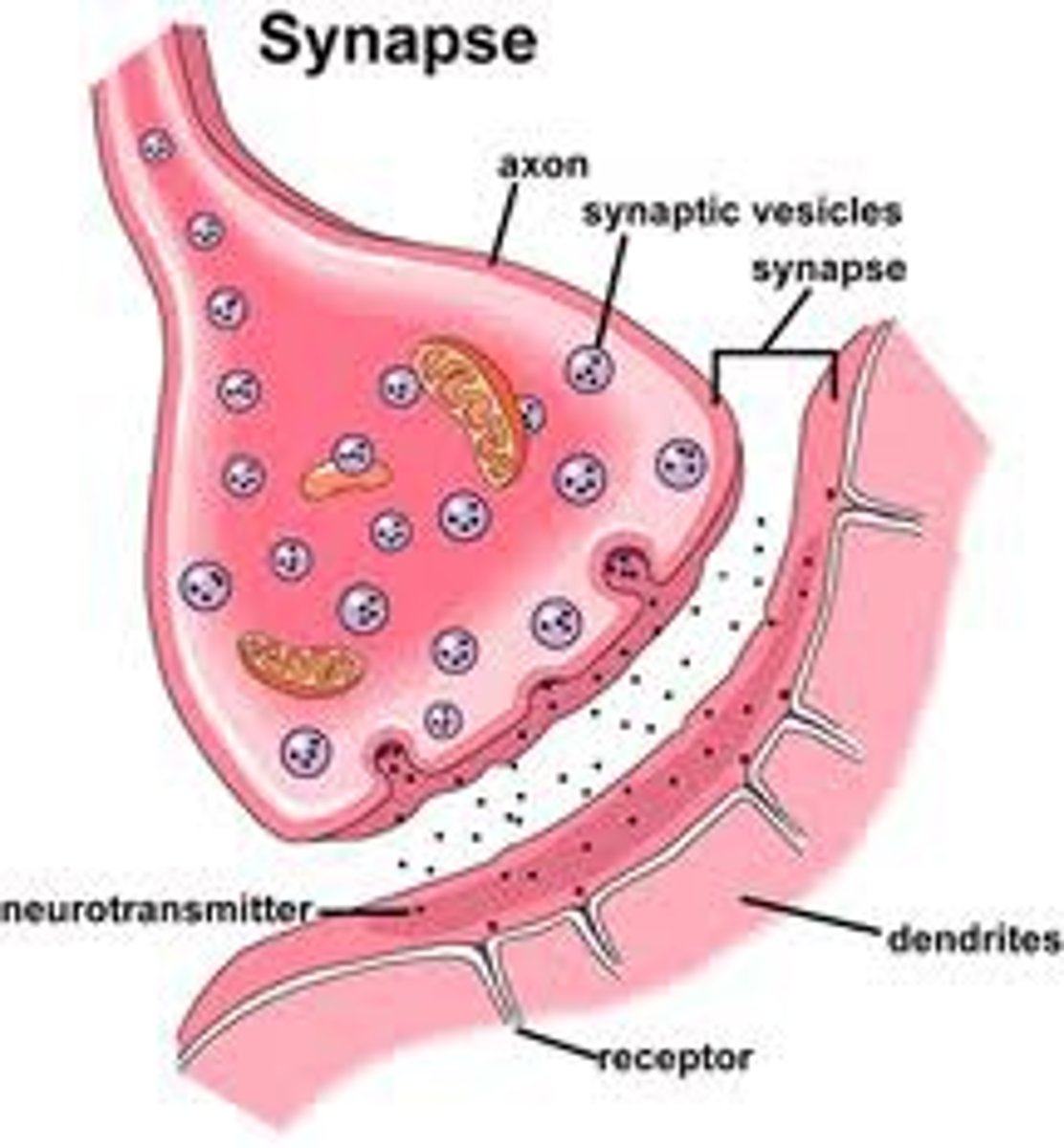
synapse
the site where adjacent neurons communicate by transmitting neural signals to one another
sprouting
new neural pathways form and link up with existing ones
re-routing
existing pathways interconnect with other ones
experience-expectant plasticity
brain change in response to environmental experience that is ordinarily expected
experience-dependent plasticity
brain change that modifies some part of its neuronal structure that is already present
acquired brain injury
a type of brain injury after birth
traumatic ABI
damage to the brain caused by an external force
non-traumatic ABI
damage to the brain caused by internal factors
traumatic brain injury
a type of acquired brain injury caused by an external force that damages the brain
aphasia
a language disorder affecting an area responsible for language production or processing
What is the difference between damage to Broca's area vs damage to Wernicke's area?
Broca: can comprehend, can't talk fluently
Wernicke's: can't comprehend, can talk fluently
Wernicke's aphasia
damage to the Wernicke's area, characterised by a difficulty in understanding language
stroke
damage to the brain due to its blood supply being interrupted
- memory loss
- confusion
- impaired judgement
- impulse control
- depression
- aggression
- dementia