Data collection
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Population
The whole set of items
Census
Measures every member of a population
Sample
A selection of observation taken from subset of population, which is representative of population.
Sampling units
Individual units of population
Sampling frame
sampling units of a population are individually numbered to form a list.
Census Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
gives completely accurate results
Disadvantages
Time consuming and expensive
testing to destruction
hard to process large quantity of data
Sample advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
Less time consuming and expensive than a census
Less data processed
Disadvantages:
Sample may not be large enough to represent small sub-groups of population
What is simple random sampling, advantages and disadvantages:
Simple random sampling is where every sampling unit has an equal chance of being selected.
Advantages
Free of bias
Cheap to implement on small populations and samples
Each sampling unit has equal chance of selection
Disadvantages:
Not suitable when population size is too large
A sampling frame is needed
What is systematic sampling, advantages and disadvantages?
The required elements are chosen at regular intervals from an ordered list.
Advantages:
Simple and quick to use
Suitable for large samples and populations
Disadvantages:
A sampling frame is needed
It can introduce bias if sampling frame is not random
What is stratified sampling, advantages and disadvantages?
The population is divided into mutually exclusive strata, and a random sample is taken from each.
Advantages:
Sample reflects the population
Represents individual groups within the population
Disadvantages:
sometimes population is not clearly classified into distinct strata
A sampling frame required
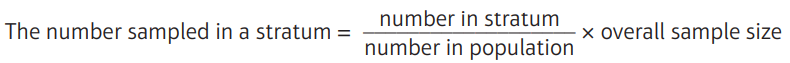
What is Quota sampling, advantages and disadvantages?
An interviewer or researcher selects a sample that reflects the characteristic of the whole population.
Advantages:
Small sample still representative of population
No sampling frame required
Quick, easy and inexpensive
Disadvantages:
Non-random can introduce bias
Population must be divided into groups which can be inaccurate or costly
What is Opportunity sampling, advantages and disadvantages?
Sample is taken from people who are available at the time the study is carried out.
Advantages:
Easy to carry out
Inexpensive
Disadvantages
Unlikely to provide a representative sample
Introduces bias
Different types of variables:
Quantitative: Numerical
Qualitative: non-numerical
Continuous: value given a range
Discrete: only specific values (whole numbers)
Large data set