L14 - Facies/Walther's Law and Mechanisms of Sea Level Change
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Define a facies.
“part of a rock body that has characteristics form which we can infer the depositional environment”
This means that sediments reflect the environment (Physical Conditions) in which they are deposited.
Define Uniformitarianism.
“The present is the key to the past“
Present day process of erosion and deposition can be used to interpret facies in the rock record in terms of their original environment of deposition
How do Sea Facies change laterally over time?
Sand → Silt → Clay → Carbonates
decreasing sediment size
decreasing energy
At what times were the sea levels much higher than today?
Ordovician
Middle to Late Cretaceous
At what times were the sea levels lower than today?
The last ice age
What does Transgression mean?
Sea level is rising
What does regression mean?
Sea level dropping
What does Diachronous mean?
Sediments that are deposited during periods of changing sea level
What does Chronostratigraphic mean?
Sediments that are deposited at the same time. (sand, silts, clays, carbonates)
What is the order of facies in drill cores when sea level is transgressing?
Sands → Silts → Clays → Carbonates
Oldest → Youngest
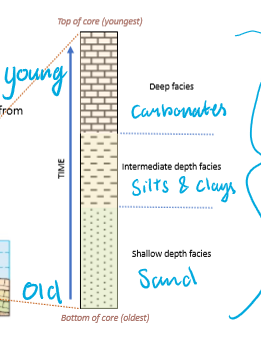
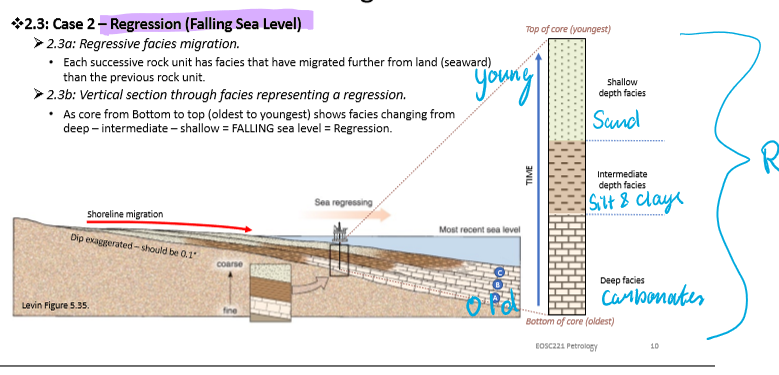
What is the order of facies in drill cores when sea level is regressing?
Carbonates→ Silts → Clays → Sand
Oldest to youngest
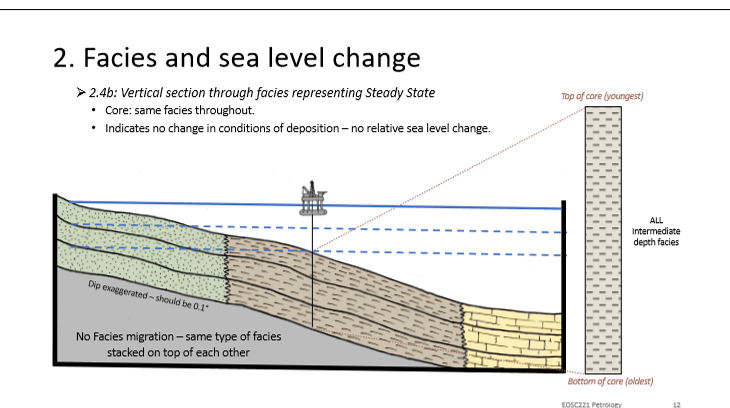
What is the order of facies in drill cores when sea level is at a steady state?
Boundaries don’t migrate and therefore sediment remains the same overtime.
What is Walther’s Law?
Facies represent different environments of deposition.
As conditions change, facies will migrate following the conditions that favor their deposition
Facies will migrate over one another.
Overlapping facies will become stacked on top of each other over time
Vertical successions of facies can be used to track changes in environmental conditions over time.
What is Walther’s Law in Summary?
Facies that occur in a conformable vertical succession of strata were deposited in laterally adjacent depositional environments
What are Eustatic Changes?
Impact sea level on a global scale.
What are Localized changes?
Regional effects - relative to sea level changes
What are some Eustatic Sea level changes?
Glacial periods cause lower sea levels
Emergence of land bridge between Asia and North America (Beringia)
Emergence of land bridge between Britain and Europe (Doggerland)
What are some Mechanisms of Sea level change?
Spreading ridge volume
Crustal deformation
Isostatic Changes
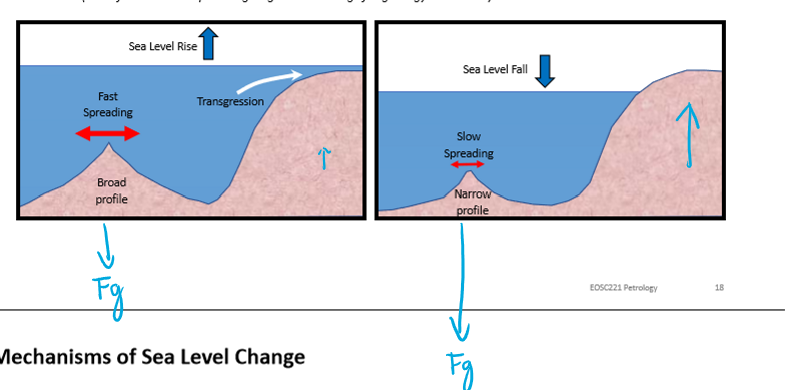
How do Spreading Ridge Rates effect sea level change?
High spreading rates: Broad, Hot, Buoyant ridges - displace large volumes of ocean onto continents
Low spreading rates: Narrow, cool, dense ridges - displace less volumes of ocean onto continents
How does Crustal deformation effect sea level?
Mountain building
Continent is elevated
local (relative) sea level change
What is isostasy?
Describes how the crust “floats” on top of the mantle.
How does isostatic changes effect sea level?
Object with a lot of mass physically depress (“push down“) of the crust into the mantle.
After mass is removed, the mantle flows back (rebounds).
Takes thousands to tens of thousands of years before rebound is complete
Temporary decrease (Glacier present) then increase (during rebound) in sea level