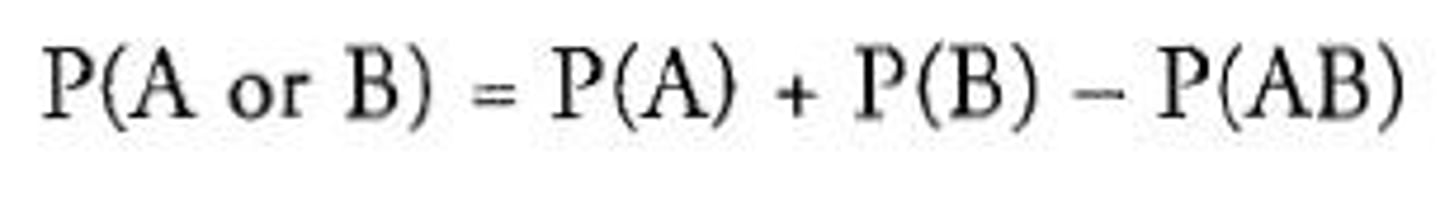Understanding the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
What is an integral part of the Cell Cycle?
Cell Division
What are the functions of Cell division?
1) Reproduction 2) Growth and Development 3) Tissue Renewal
What is a Genome?
A genome is all the DNA in an organism, containing the instructions for its traits and functions.
What are the genomes in Prokaryotic Cells?
singular circular DNA molecule
What are the genomes in Eukaryotic Cells?
several linear DNA molecules
What are Histone Proteins?
Histone proteins are proteins that DNA wraps around to keep it organized and compact in the cell.
What is Chromatin?
Chromatin is DNA wrapped around proteins, helping to organize it in the cell.
What is a chromosome?
A chromosome is a thread-like structure inside a cell's nucleus that carries genetic information, made up of DNA tightly coiled around proteins
What do Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of?
Chromatin
What are the two things that Chromatin does?
a) Condenses during cell division
b) DNA wound around histone proteins into nucleosomes
What are Nucleosomes?
Nucleosomes are DNA wrapped around histone proteins, keeping it organized in the cell
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46
What is ploidy?
number of sets of chromosomes in a cell
What are Haploid Cells (n)?
Haploid cells have only one copy of each chromosome.
What are Diploid Cells (2n)?
Cells that have two sets of chromosomes.
What are Somatic Cells?
cells found in the body
What are Gametes?
sex cells (sperm and egg)
Where are diploid cells found?
somatic cells
Where are haploid cells found?
gametes
What do chromosomes contain?
Genes: These are like small sections of instructions that tell the cell how to make proteins, which are important for the cell’s functions and traits.
Centromere: The narrow, pinched area in the middle of the chromosome that holds it together and helps it split correctly during cell division.
What are the steps of DNA Preperation for Mitosis?
In the S phase, DNA replication occurs, resulting in each chromosome being duplicated to form sister chromatids (two identical copies). These chromatids remain joined, so the chromosome count (ploidy) doesn't change, but the DNA mass is doubled. This prepares the cell for division, ensuring that each new cell will receive a complete set of genetic information.
What are sister chromatids?
2 identical copies of DNA held together by a centromere
What are the phases of the Cell Cycle in order?
G1, S, G2, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
What happens in the G1 phase of interphase?
This is longest phase of the cell cycle. The cell produces more ribosomes and other organelles. And there is a synthesis of proteins and enzymes.
What happens in the S phase?
DNA synthesis (or replication) occurs during this phase. At the beginning of the phase, each chromosome is single. At the end, after DNA replication, each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. The ploidy does NOT change and the DNA is still chromatin
What happens in the G2 Phase?
Regulating the cell growth by increasing the cytoplasm.
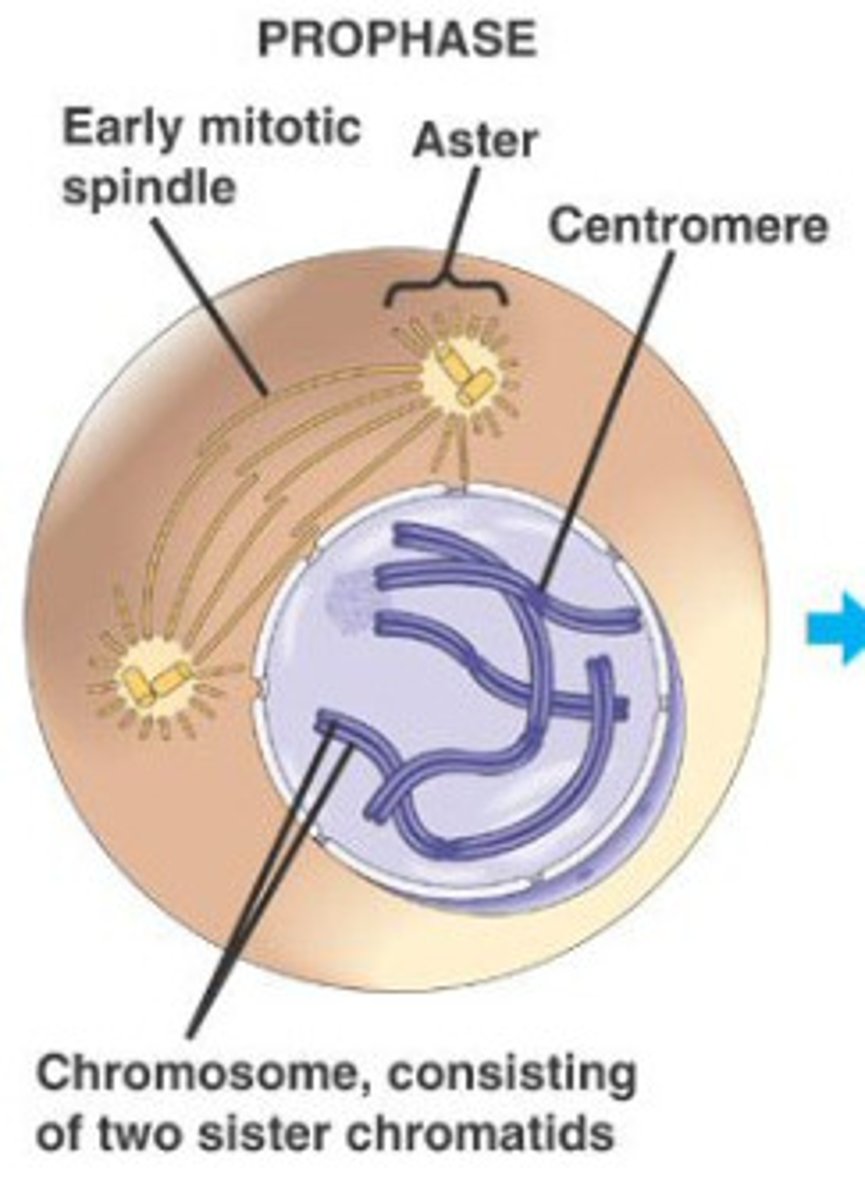
What happens in prophase?
1) Chromosomes Condense 2) Centrosomes to opposite poles 3) Nuclear envelope breaks down 4) Spindle Finer attach to kinetochore handles
what is a miotic spindle?
The mitotic spindle is a fiber structure that separates chromosomes during cell division.
What are centrosomes?
cell structures that help organize fibers to separate chromosomes during cell division.
what is the centromere?
central, pinched parts of chromosomes that hold sister chromatids together and help them separate during cell division.
What are kinetechores?
Kinetochores are protein structures on the centromere where spindle fibers attach to pull sister chromatids apart during cell division.
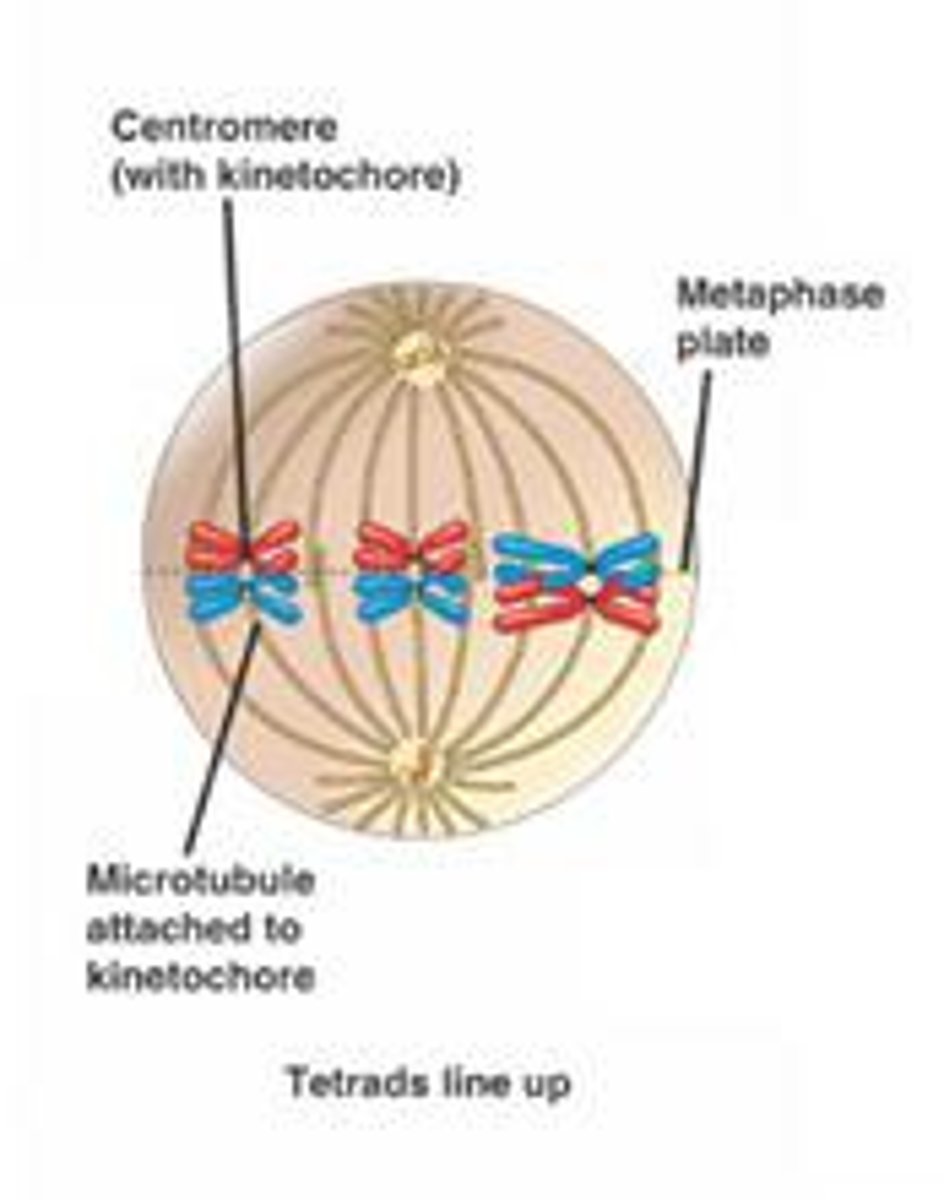
What happens in metaphase?
1) Longest stage of mitosis 2) Chromosomes align on metaphase plate 3) Once they line up, metaphase is over
what is the metaphase plate?
The metaphase plate is an imaginary line in the middle of the cell where chromosomes align during metaphase, preparing for separation in cell division.
What happens in Anaphase?
Shortest stage in Mitosis. Sister chromatids split and move to either pole (Disjunction)
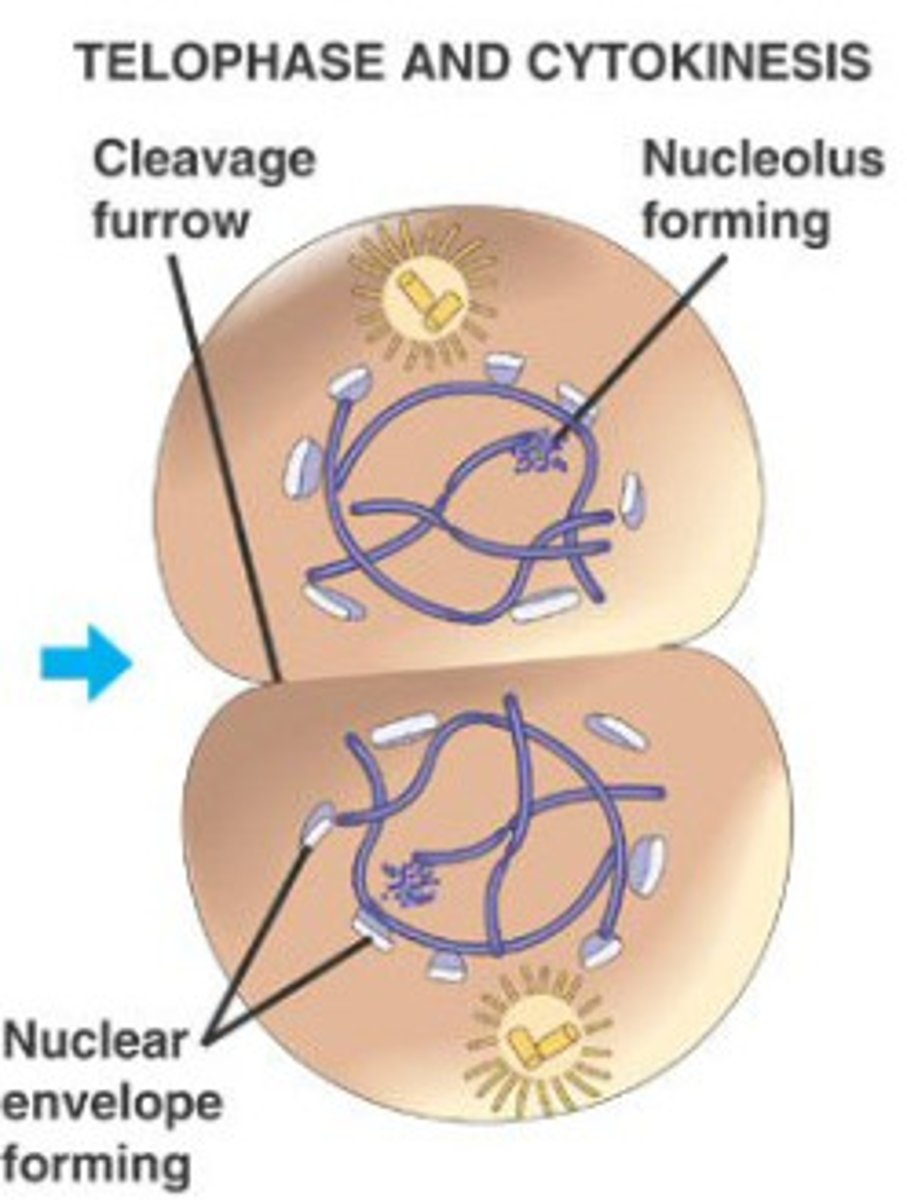
What happens in Telophase?
1) 2 new daughter cells form
2) Nuclear envelope reforms
3) Cytokinesis will divide cytoplasm
What is Cytokenesis?
1) not part of mitosis!
2) Cytoplasm divides
3) Animals: form a cleavage furrow
4) Plants: form a cell plate
5) Each daughter cell gets: full set of chromosomes and organelles
What is cleavage Furrow?
The cleavage furrow is the dent that forms as a cell starts to split into two new cells.
does ploidy change in mitosis?
NO!
What is Asexual Reproduction?
It requires one parent, undergoes mitosis, and clones
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA between individuals in a species.. There is no genetic Variation because its always the same.
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
always the same so don't have way of dealing with changing environment. Mutations passed down due to cloning
What is Sexual Reproduction?
Reproduction involving 2 parent organisms combining genetic material to create diverse offspring using Meiosis.
What are the advantages & disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction?
genetic variation, may evolve genes needed for evolving world but it is hard to find a partner
What kind of chromosomes are in somatic cells?
Diploid Cells (2n). 1) 46 chromosomes = 23 pair of homologs 2) 1 pair of sex chromosomes (XX or XY) 3) 22 pairs autosomes: (body chromosomes)
What kind of chromosomes are in gametes?
haploid cells (n) -> 23 chromosomes
What is a Life Cycle?
from conception to production of own offspring
What is Fertilization?
Fertilization is the process where a sperm and egg combine to form a new cell, starting the development of a new organism.
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is cell division that makes sex cells with half the usual chromosomes.
What are the 2 things that result from Fertilization?
1) Results in a zygote (single celled diploid organism) 2) Grows into a multicellular organism
What are the 4 stages of Meiosis?
1) Interphase (G1, S, G2)
2) Meiosis I (PMAT)
3) Interkinesis
4) Meiosis II (PMAT)
What happens in the S phase of Meiosis?
The chromosomes duplicate.Each chromosome now comprised of 2 sister chromatics
What happens in the G2 phase of meiosis?
Centrioles replicate
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are chromosome pairs, one from each parent, with the same genes in the same order.
What is the main goal of Meiosis I?
separate homologous chromosome pairs
What is the result of Meiosis I?
Results in 22 haploid (n) daughter cells 2n → 2 x n
PLOIDY HALVES IN MEIOSIS I
What happens in Prophase I?
1) Longest stage of Meiosis
2) Chromosomes Condense
3) Homologous chromosomes pairs align by gene.
4) Nuclear envelope disappears
5) Organelles move out of the way
6) Mitotic Spindle Appears
7) Spindle attaches to kinetochores
What is Synapsis?
Synapsis is when homologous chromosomes pair up during meiosis
What happens when synapsis occurs?
A tetrad forms
What is a tetrad?
a group of four chromatids formed when two homologous chromosomes pair up during meiosis.
What is "Crossing over" in Prophase I?
During meiosis, non-sister chromatids in a tetrad swap DNA segments, mixing genes from each parent.
What is Chiasmata?
The X-shaped points where chromatids cross and exchange DNA.
Why is "crossing over" important?
Crossing over creates unique gene combinations (genetic Variability), increasing diversity in offspring.
What happens in Metaphase I?
1) Homologous pairs line up at the metaphase plate (still crossing over) 2) Alignment is random (random assortment) 3) Spindle fibers maneuver homologous tetrads a) Homologous pairs of chromosomes are held together by chiasmata, microtubules attach to the fused kinetochores of the sister chromatids
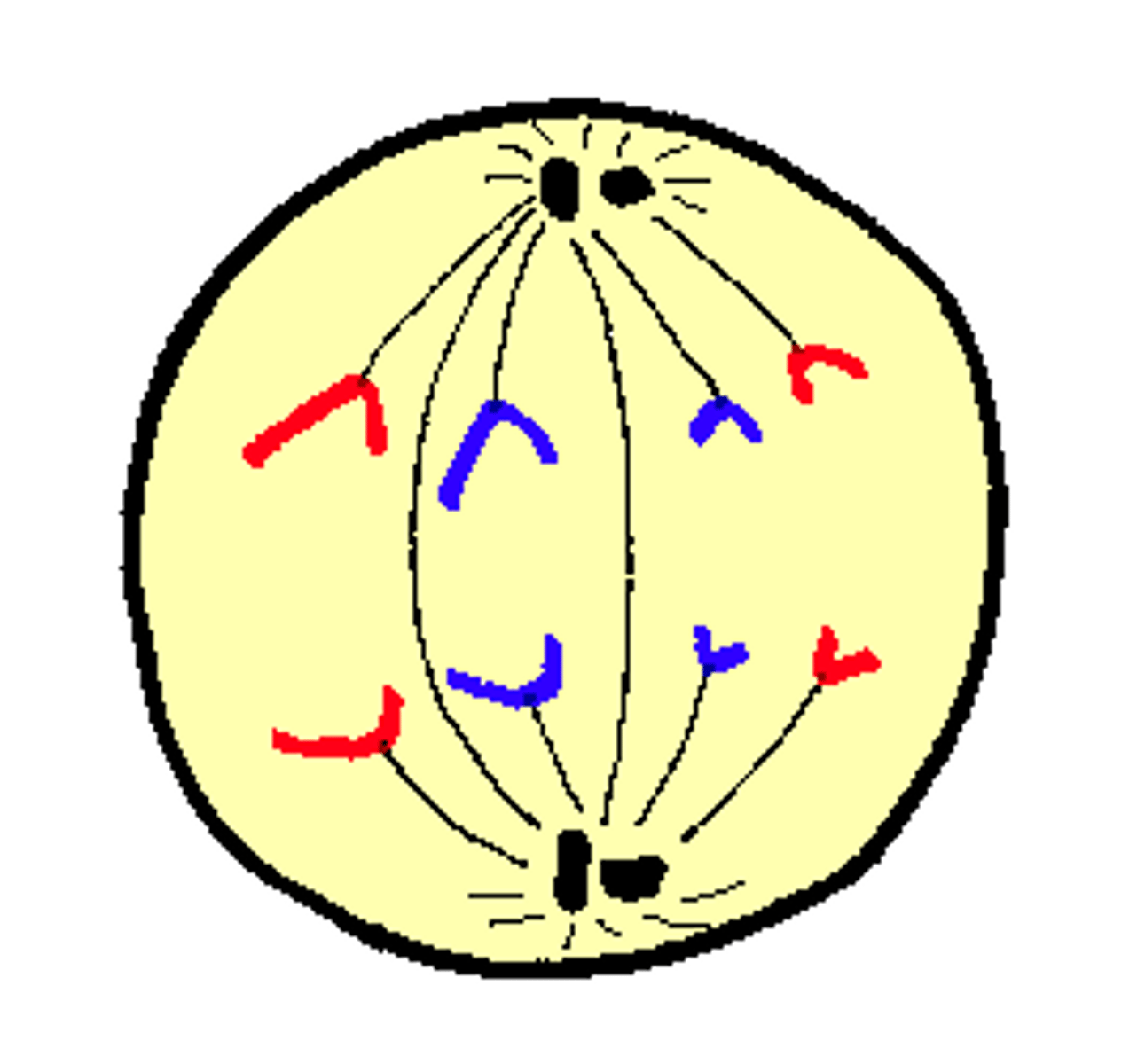
What happens in Anaphase I?
1) Homologous chromosomes separate (disjunction)
2) Sister chromatids stay together - but homologs separate.
3) PLOIDY CHANGES
What happens in Telophase I?
1) Each chromosome has sister chromatids 2) Homologous pairs have been separated 3) Cytokinesis occurs simultaneously
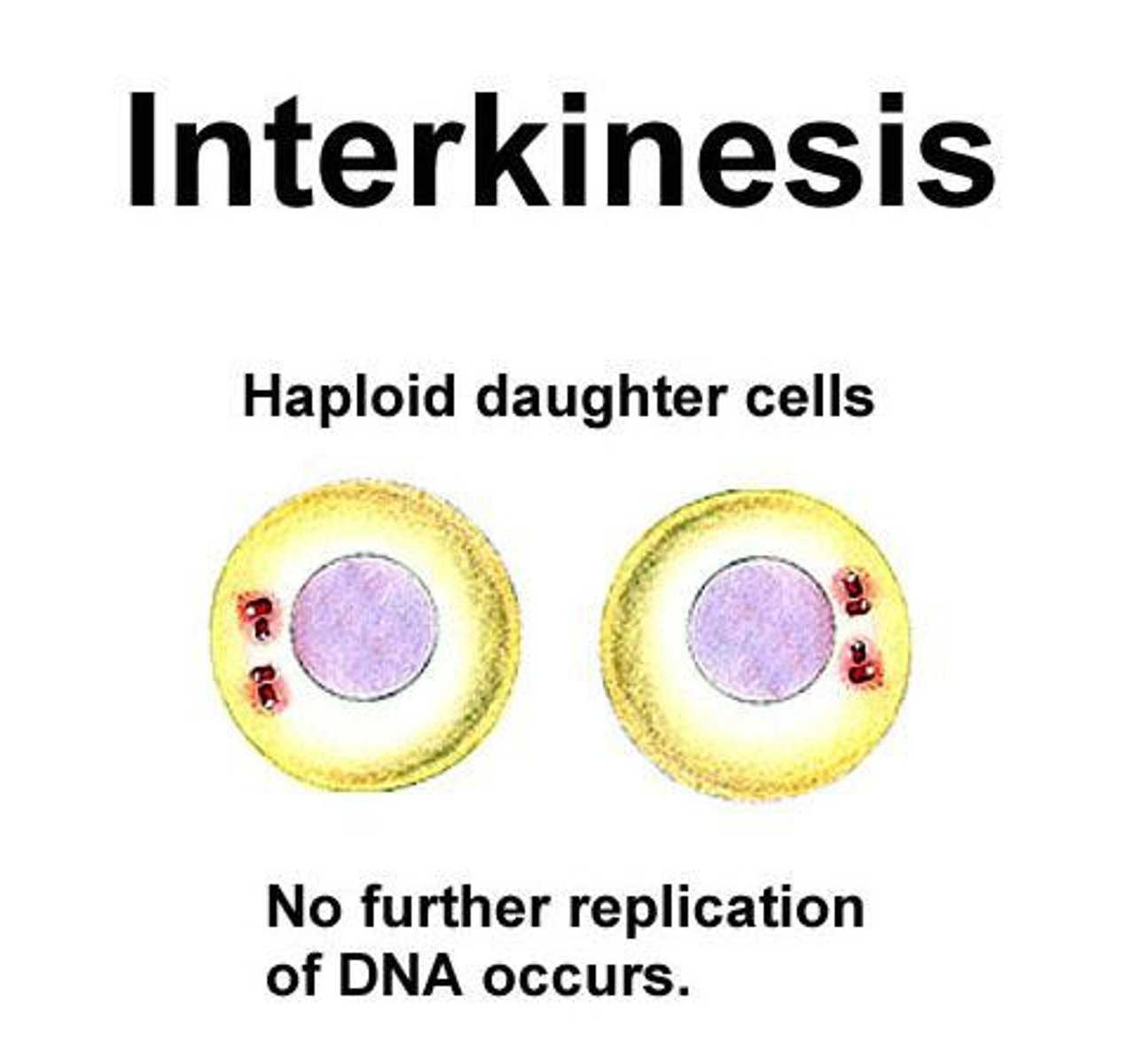
What is after Meiosis I?
Interkinesis
What happens in Interkinesis?
i. NO CHROMOSOME REPLICATION OCCURS, because the chromosomes are already replicated ii. Does not go through S phase again
What is after Interkinesis?
Meiosis II
Does Ploidy change in Meiosis II?
NO!
What happens in Prophase II?
1) Spindle forms, nuclear envelope disappears 2) NO CROSSING OVER 3) Kinetochores attach to microtubules

What happens in Metaphase II?
Sister chromatids line up at metaphase plate
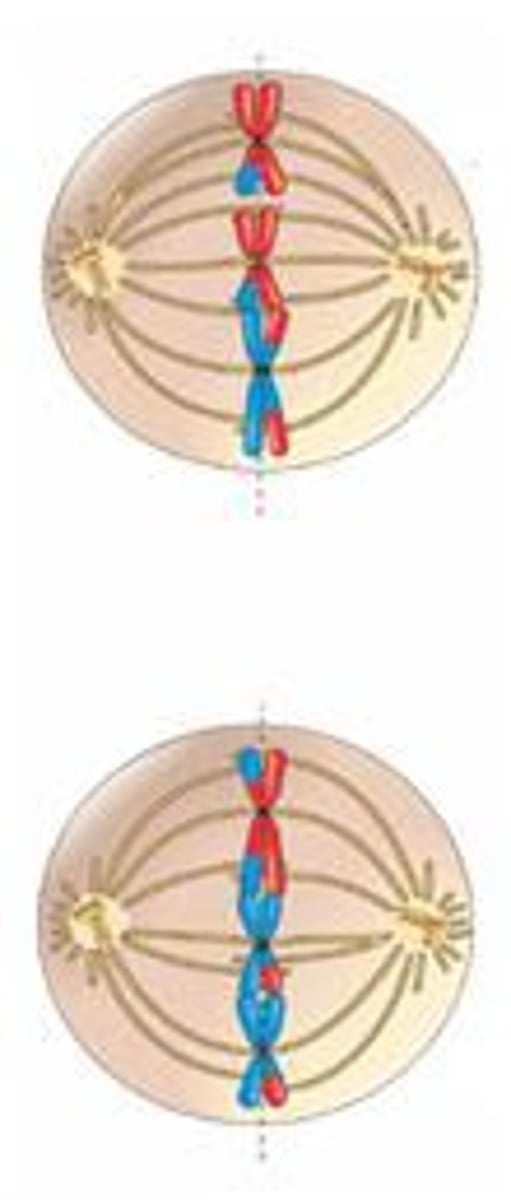
What happens in Anaphase II?
1) Disjunction: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite sides 2) No change in ploidy
What happens in Telophase II?
1) Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles 2) Cytokinesis occurs concurrently
After the process of Meiosis, what are you left with?
End with 4 daughter cells each with haploid set of chromosomes, each daughter cell is genetically distinct
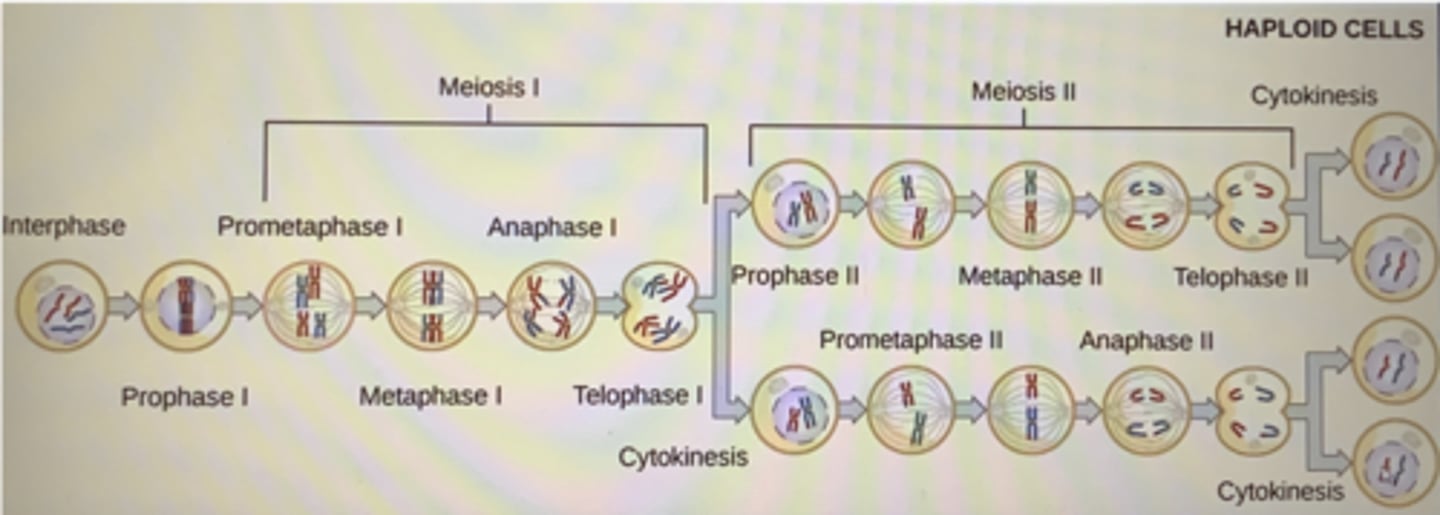
What are the 3 types of Life Cycles?
Haploid-Dominant: Most of the life cycle is in the haploid stage, common in fungi and some algae.
Diploid-Dominant: Most of the life cycle is in the diploid stage, typical in animals.
Alternation of Generations: Life cycle alternates between multicellular haploid and diploid stages, found in plants and some algae.
Whos was Gregor Mendel?
Gregor Mendel was a scientist who discovered the basic laws of inheritance by studying pea plants.
Why did he use pea plants for his experiments?
1) Inexpensive 2) Many varieties 3) Easy to grow, short generation time 4) Lots of offspring 5) Clearly identifiable traits 6) Easy to control pollination
What was the blending theory of inheritance?
The blending theory of inheritance suggested that offspring are a mix, or "blend," of their parents' traits.
Explain how mendel tested the blending theory of inheritance.
Hypothesis: Mendel tested if offspring traits were a mix of parent traits.
Experiment: He crossed two true-breeding plants with opposite traits.
P Generation: The parent plants had clear, separate traits.
Control: Mendel controlled which plants were crossed.
Findings:
F1 Generation: Offspring showed only one parent’s trait, not a blend.
F2 Generation: When F1 plants self-fertilized, a 3:1 trait ratio appeared, with "lost" traits reappearing.
Conclusion: Traits didn’t blend; instead, they were passed as separate units, leading Mendel to reject the blending hypothesis and support his idea of inheritance through distinct genes.
What was Mendel's New hypothesis and explain what it is?
particulate inheritance proposed that traits are passed down as discrete units, or "heritable factors" (now known as genes), rather than blending together.
What are the 4 related concepts of Mendel's Model?
1) Alleles are discrete units of information
2) 2 alleles from each parent (2n)
3) Dominant and recessive alleles
4) The two laws of inheritance
What are alleles?
alternate forms of a gene (2n means 2 of each allele)
What does "locus" mean in Biology?
A specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located.
1. Alleles are discrete units of information
A) Alleles = alternative versions of genes (2n means 2 of each allele)
B) Each allele (gene version) is located at the same spot, or locus, on each homologous chromosome pair from each parent.
2. Two alleles from each parent (2n)
A) The 2 alleles may be identical (like P generation) = homozygous
B) Different (like F1) = heterozygous
3. Dominant and Recessive Alleles
A) If an organism is heterozygous than the dominant allele determines the organism's appearance
B) The recessive allele has no effect on appearance
What are the 2 laws of Inheritance?
Law of Segregation & Law of Independent Assortment
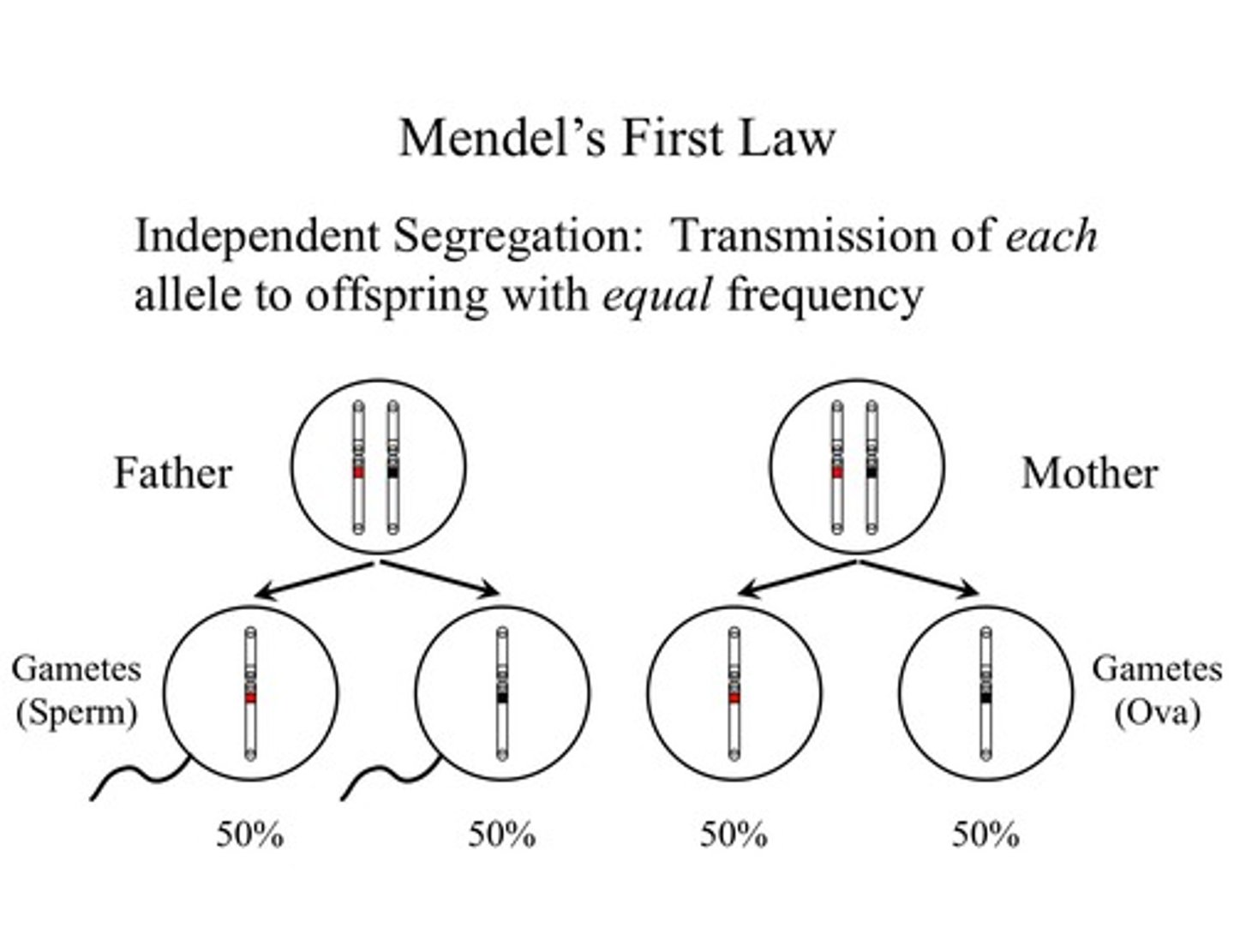
What is the Law of Segregation?
The Law of Segregation states that each parent’s two alleles for a trait separate during meiosis, so each gamete (sperm or egg) gets only one allele.
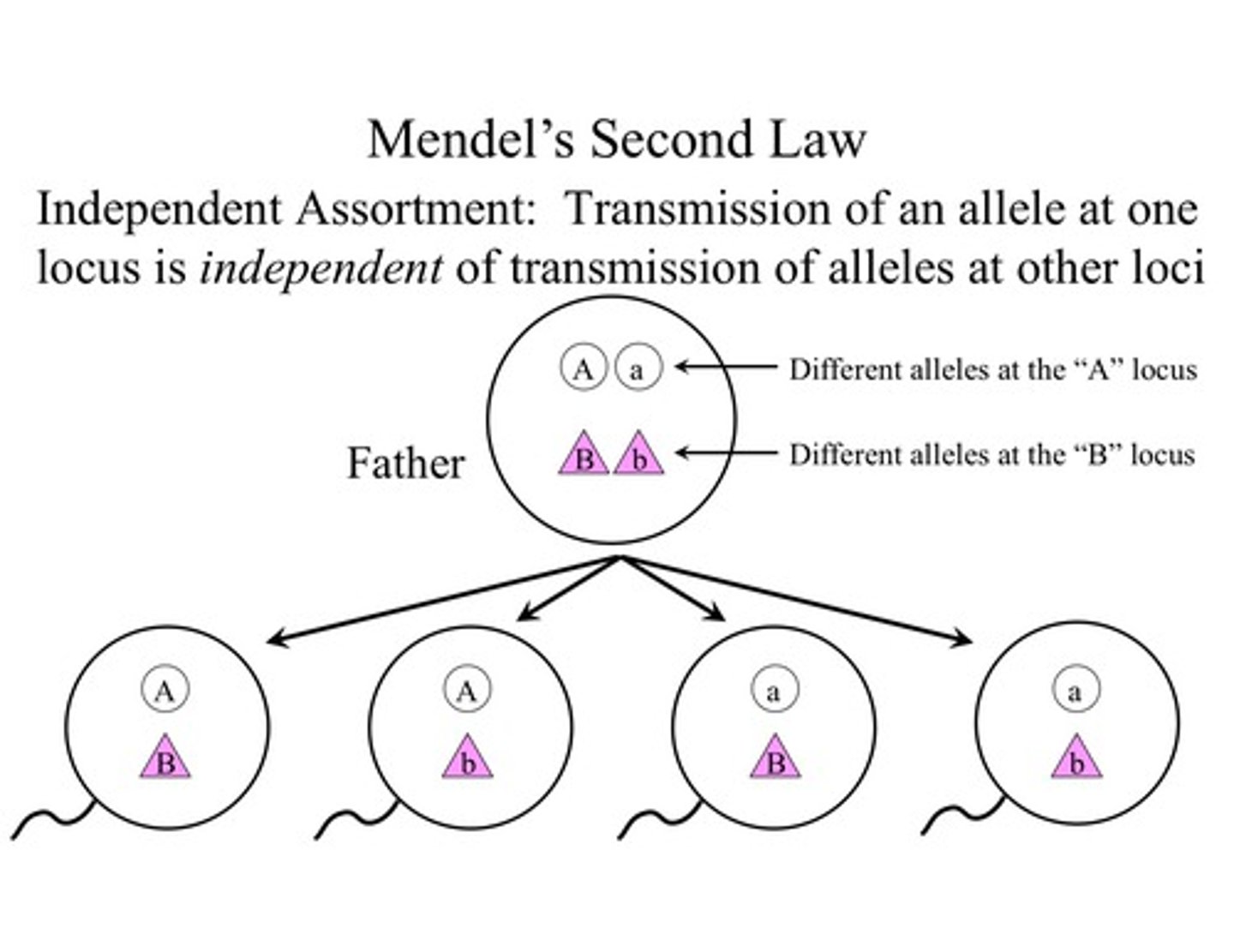
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
The Law of Independent Assortment states that genes for different traits are distributed to gametes independently of each other during meiosis.
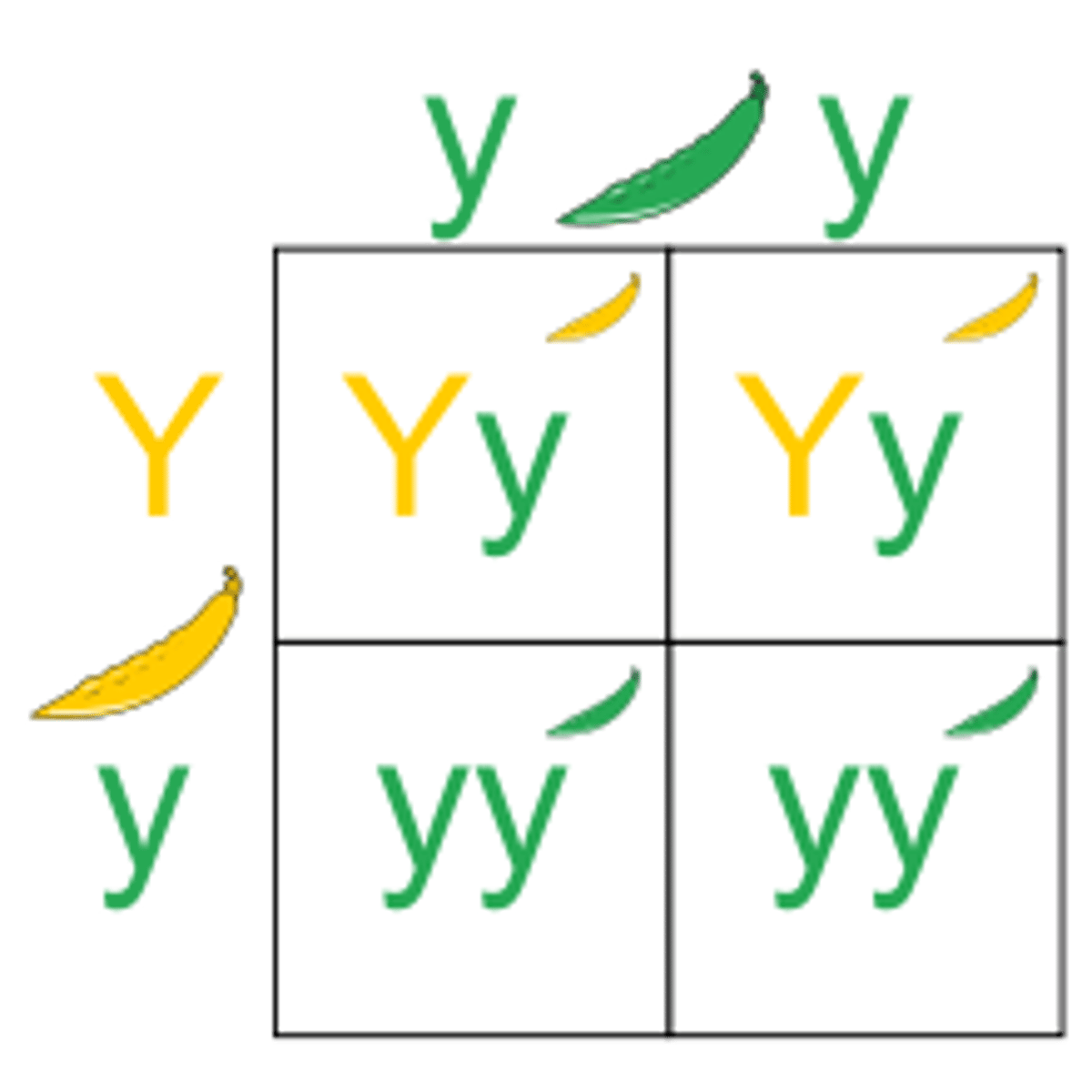
What are Punnet Squares?
Punnett squares are diagrams used to predict the possible genetic combinations and traits of offspring based on the parents' alleles.
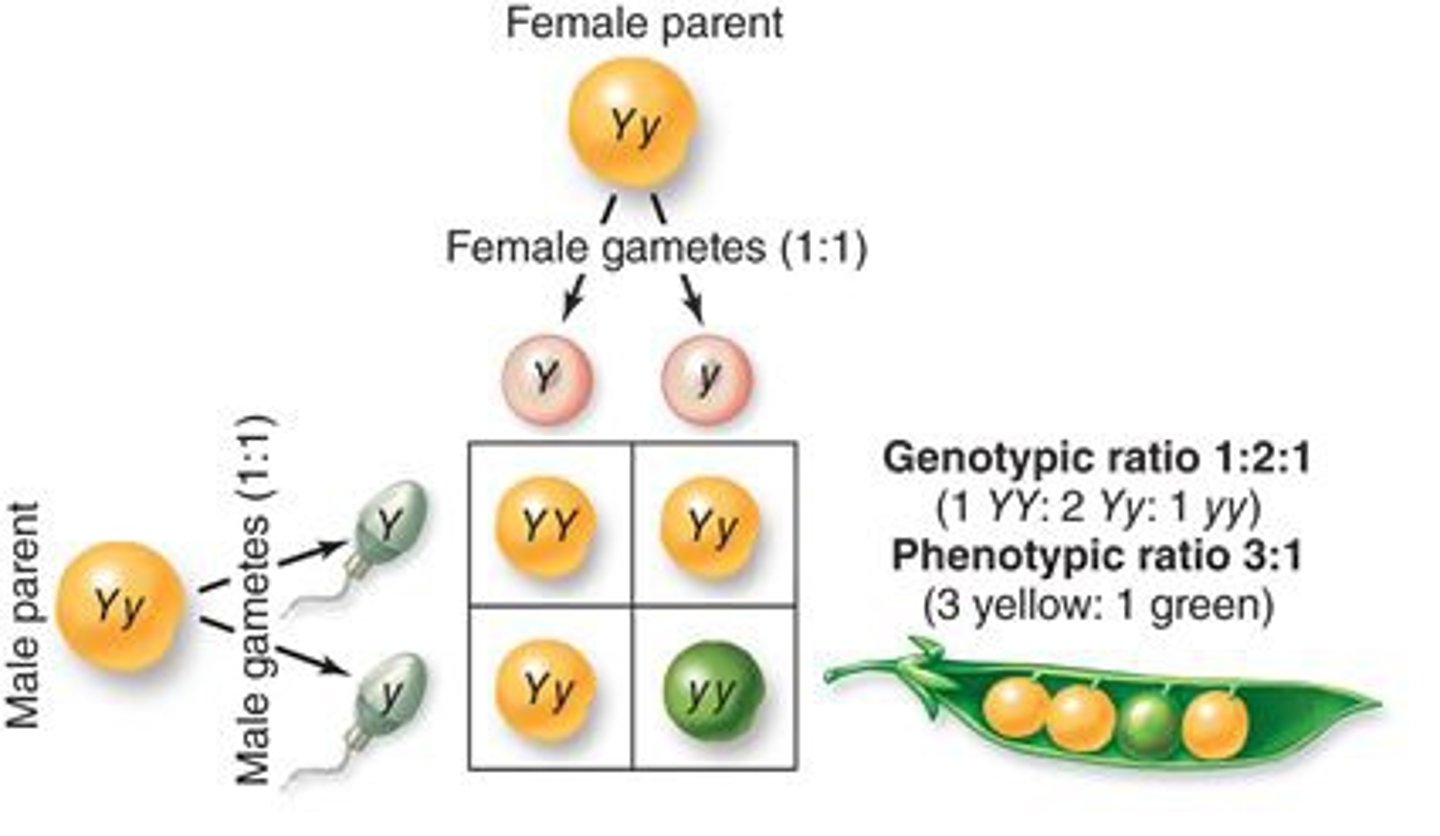
What is a monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross is a genetic cross that examines the inheritance of a single trait with two alleles (e.g., flower color), using parents with different versions of that trait.
What is a phenotype?
A phenotype is an organism's visible traits, like eye color or height.
What is a genotype?
A genotype is an organism's genetic makeup or combination of alleles for a trait.
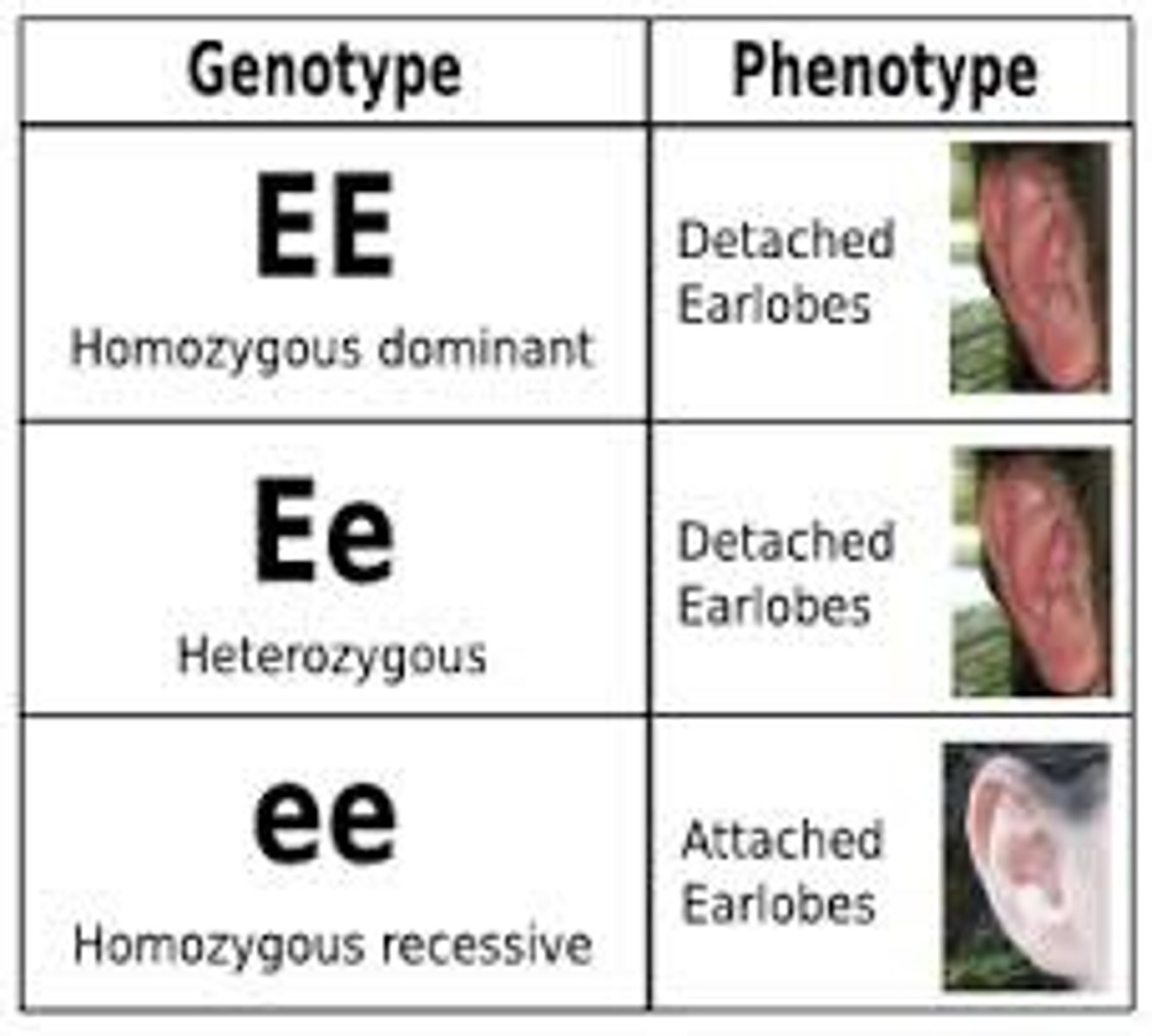
What is probability?
use math to solve squares faster genetic ratios expressed probability
If an event is certain to occur, then the probability is equal to __
1
If an event is certain not to occur, then the probability is equal to __
0
What is the Multiplication Rule?
Predicts combined probabilities of independent events by multiplying their individual probabilities.
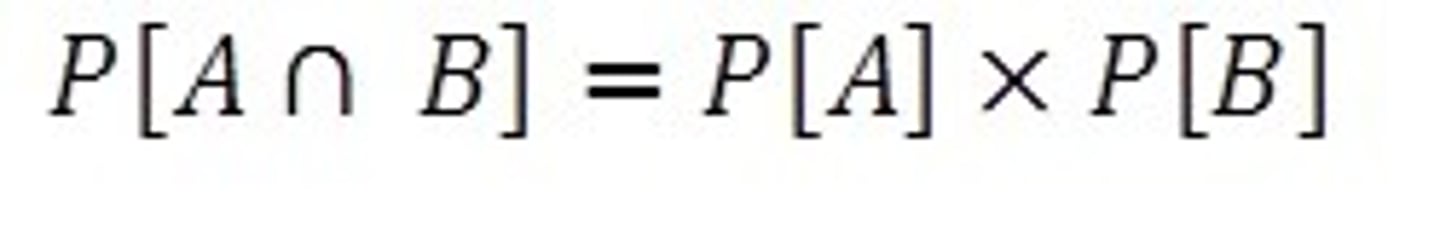
What are independent Events?
one event does not affect probability of each other
What does this mean? P(A) and P(B)
This means that if you want to find the probability of two events both happening (P(A) and P(B)), you multiply the probability of each event. The word "and" indicates that you should multiply the separate probabilities.
What is the Addition Rule?
Predicts combined probabilities of mutually exclusive events by addition