uoft bch210 midterm
1/275
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
276 Terms
bio chemical molecules of life
- proteins
- lipids
- sugars
- nucleic acids
- small molecules
- ions
- water
why is structure so important in biochemistry
structure is important for function
examples of proteins in the cell
- enzymes
- transporters
- lipoproteins
- hormones
- signaling molecules
- receptors
- recognition molecules
- glycoproteins
- structural proteins
- motility proteins
what kinds of bonds hold together amino acids
covalent bonds
what are covalent bonds
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
what are non covalent bonds/interactions
- ionic/electrostatic
- h bonds
- van der waals
what kinds of bonds helps chains fold into structures
- non covalent bonds
what are cofactors
- non protein/metal ion that helps a protein with structure and/or function
how do transporters bind to molecules
non covalently
how are cofactors bound
- covalently or non covalently
what are prosthetic groups
- subset of cofactors
- tightly bound by covalent or non covalent forces
how may metal ion cofactors interact with proteins
- involvement in enzyme catalysis
- charges of ions may be important
What are coenzymes?
organic compounds that help enzymes
chain bow convention of protein colouring
blue to red
backwards through the rainbow
which elements participate in h bonding
O, Br, F, N Cl
these electronegative atoms are h bond acceptors
why can carboxylic acids act as h bond donors and acceptors
- hydroxyl group can be a donor
- double bonded oxygen can be acceptor
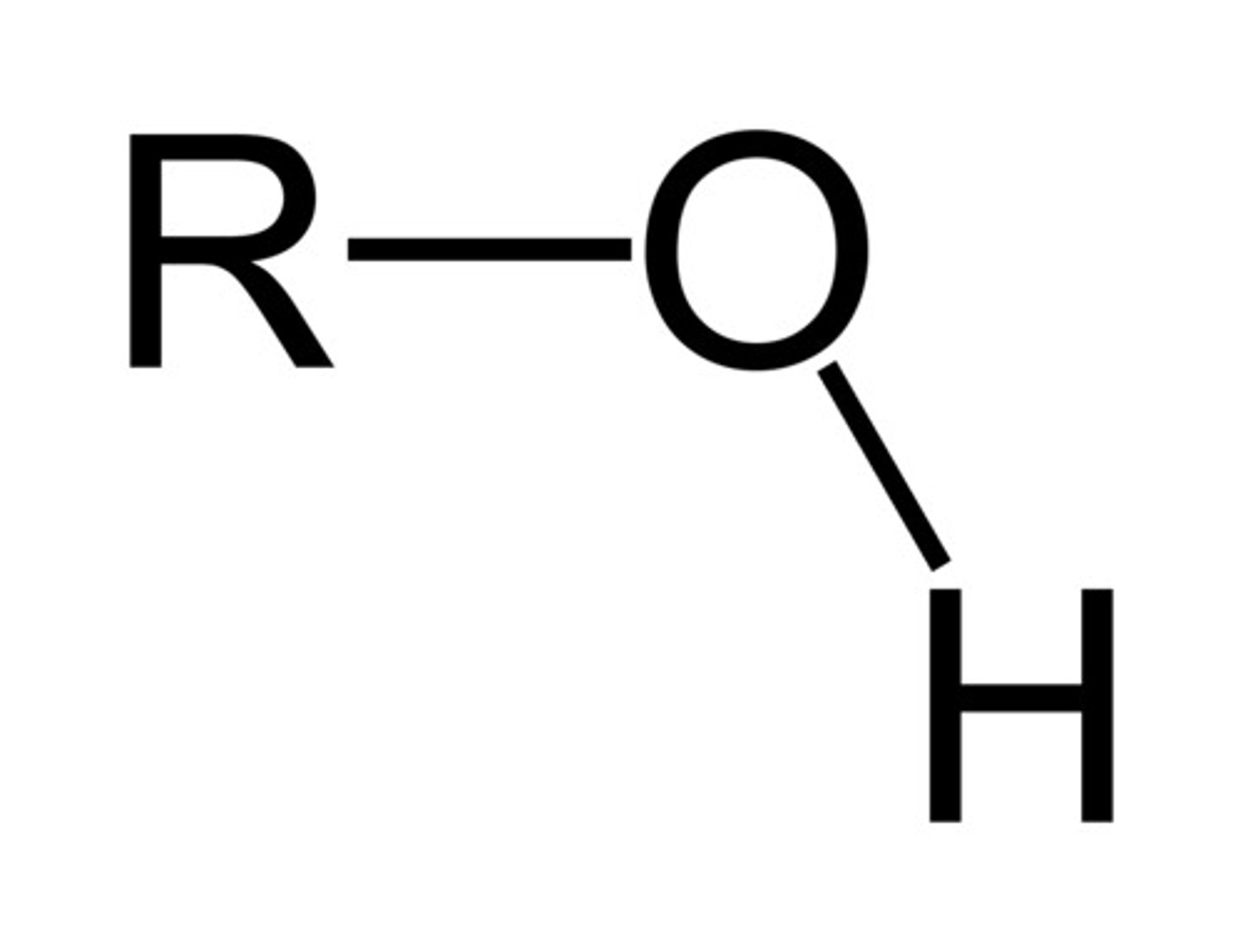
alcohol/hydroxyl
R-OH
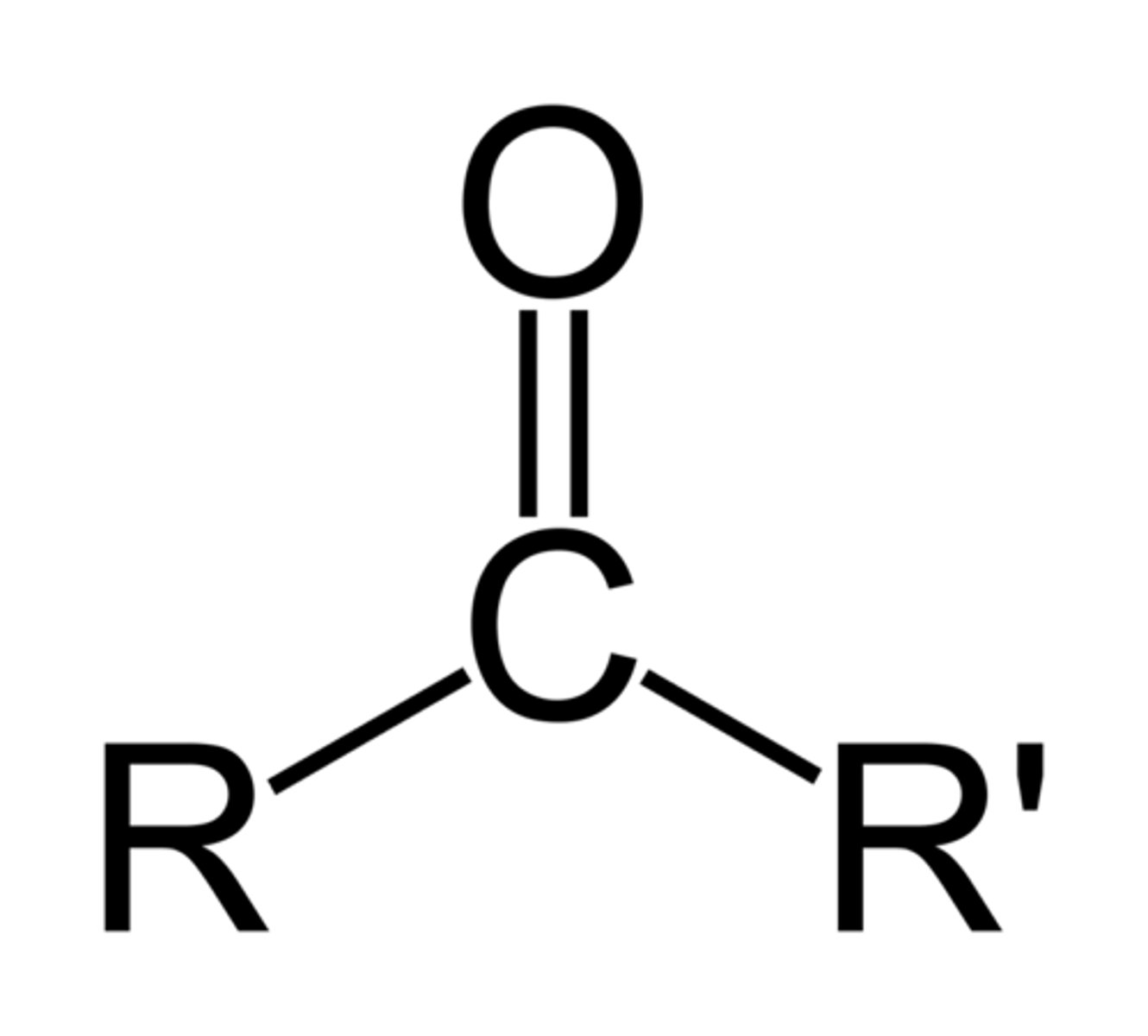
carbonyl/ketone
C=O in the middle
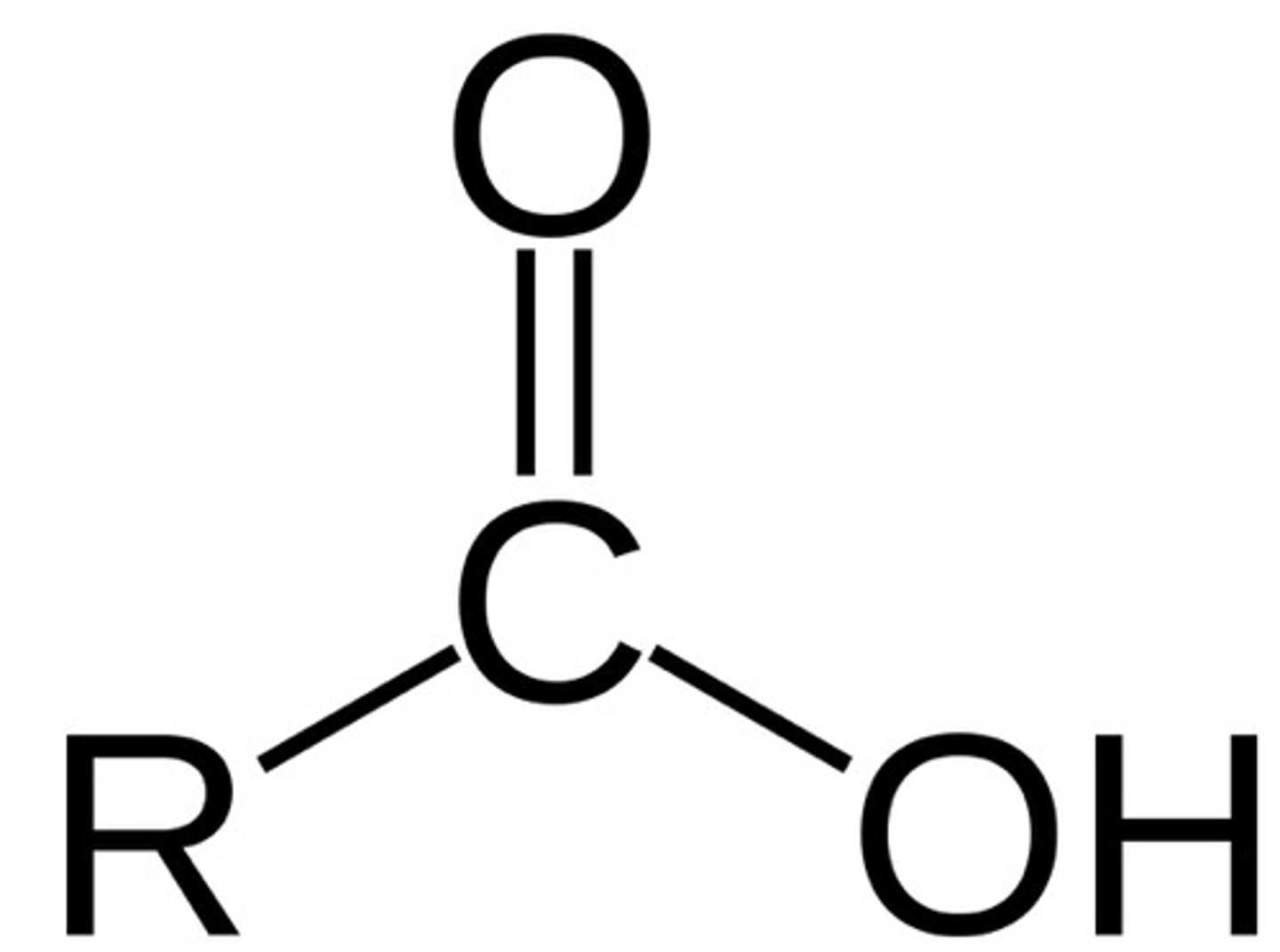
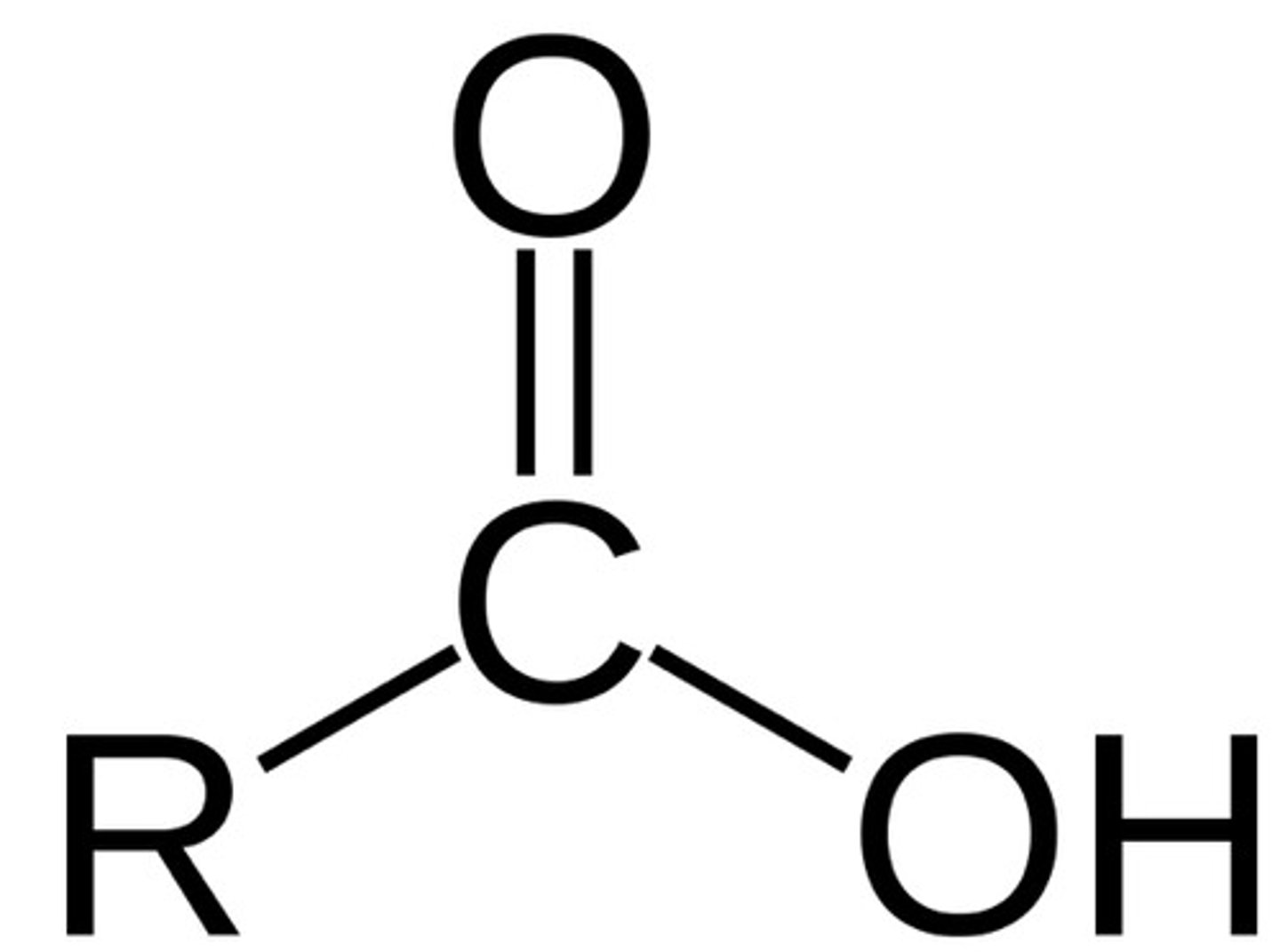
carboxyl
COOH
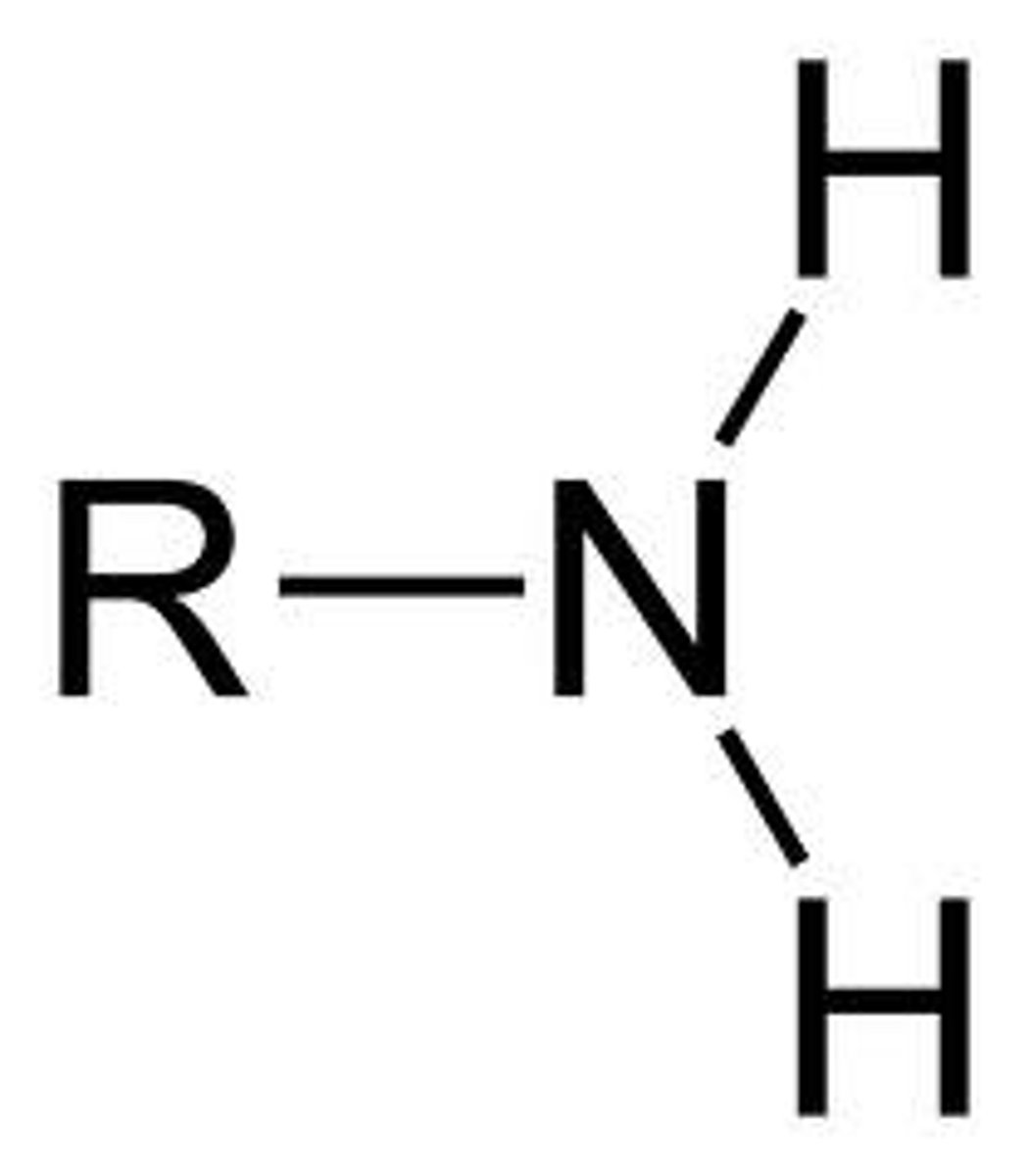
amine
R-NH2
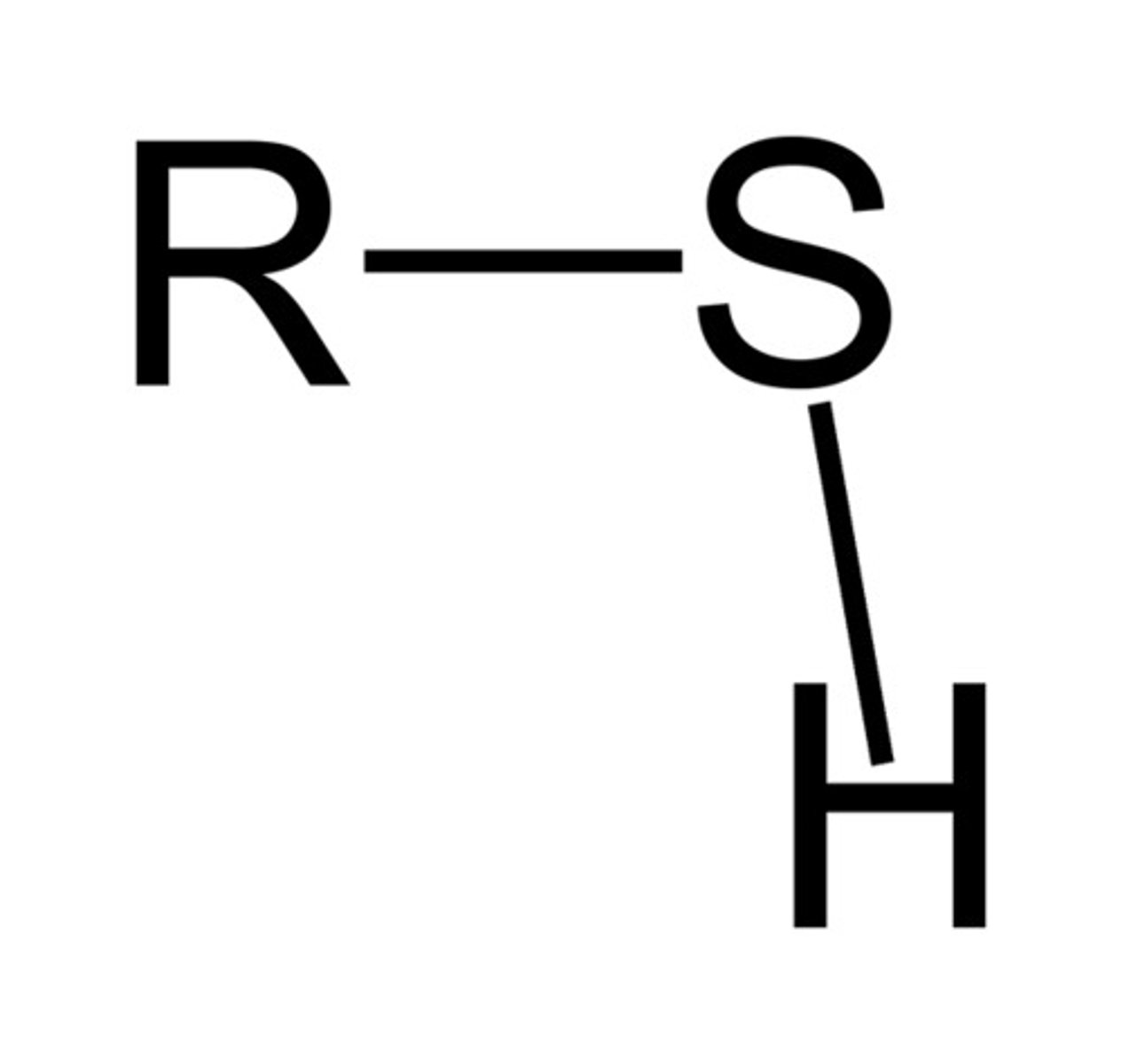
sulfhydryl/thiol
R-SH
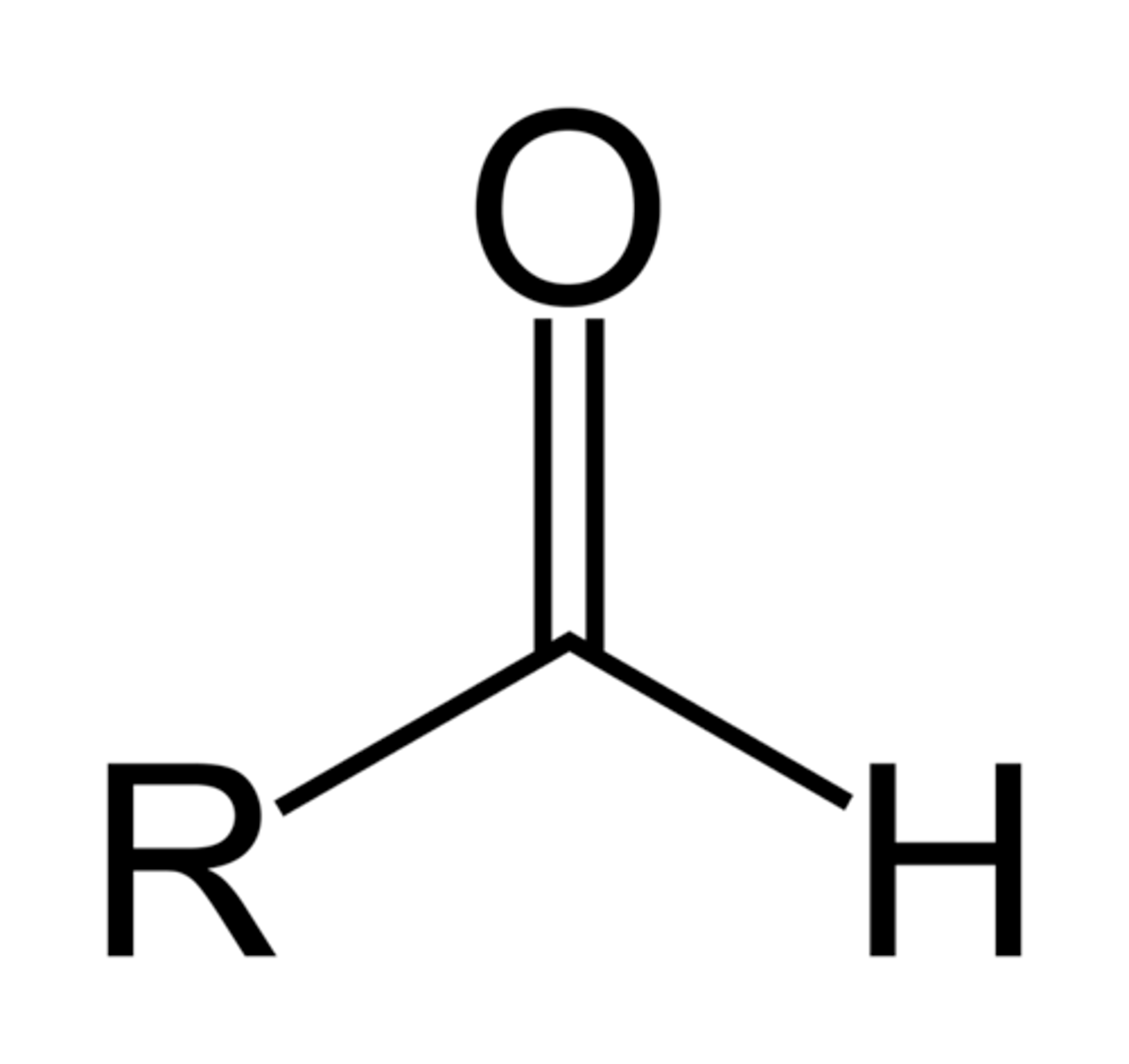
aldehyde
CHO
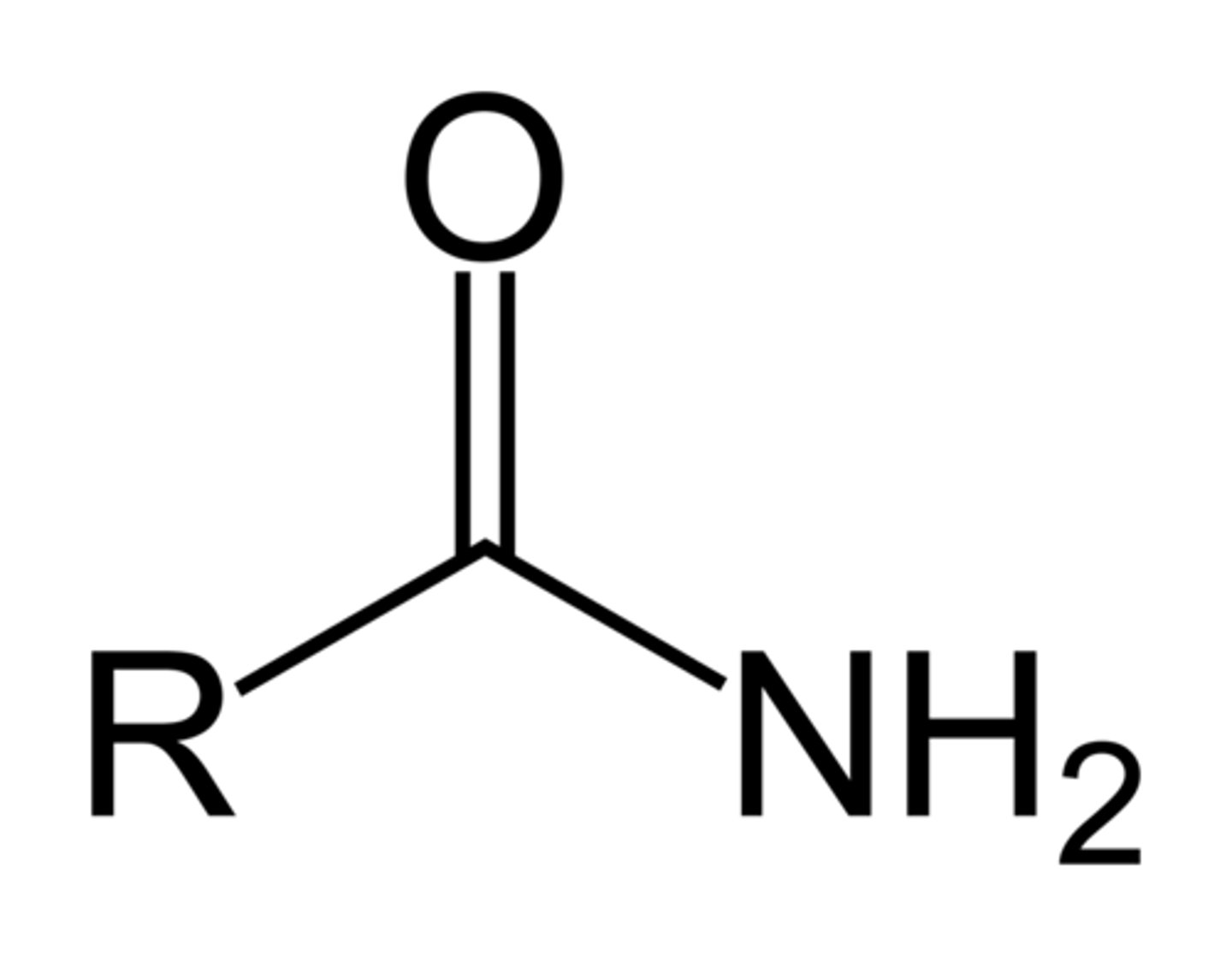
amide
=O NH2
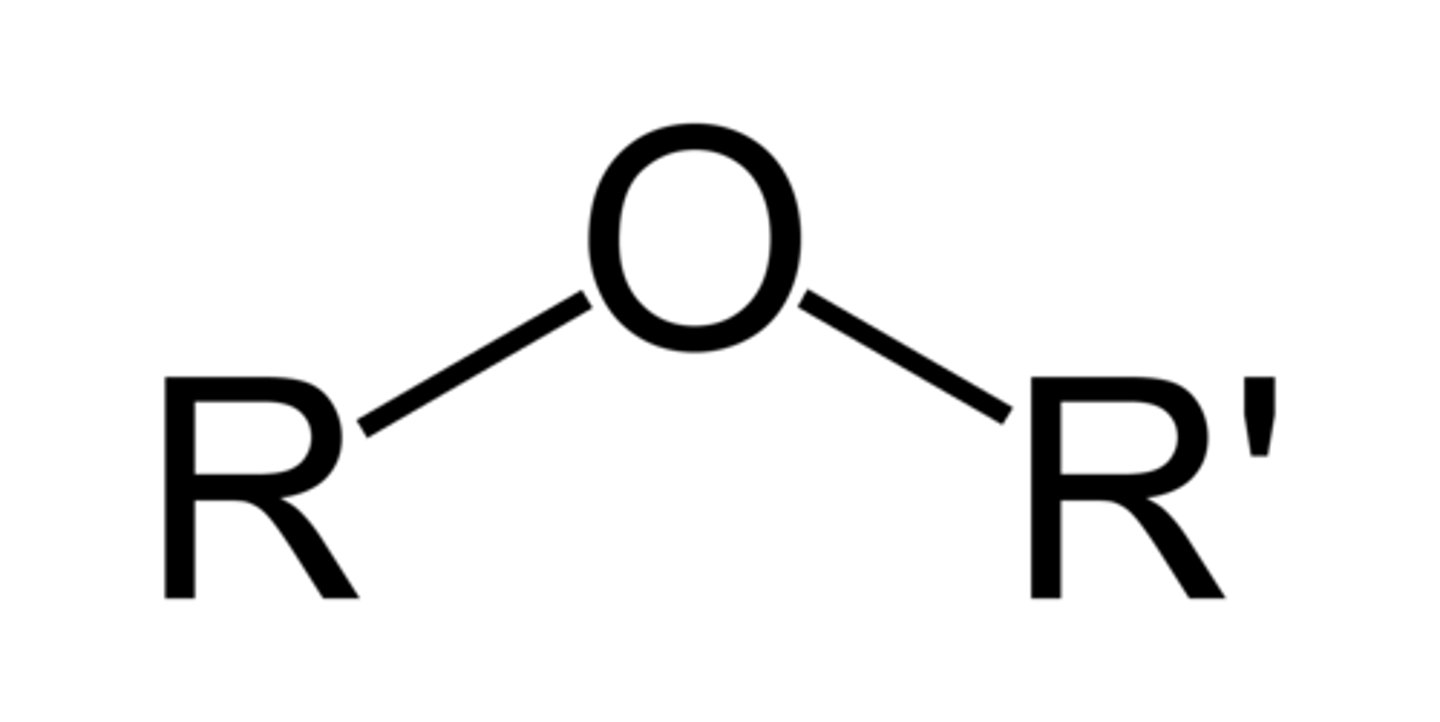
ether
C-O-C
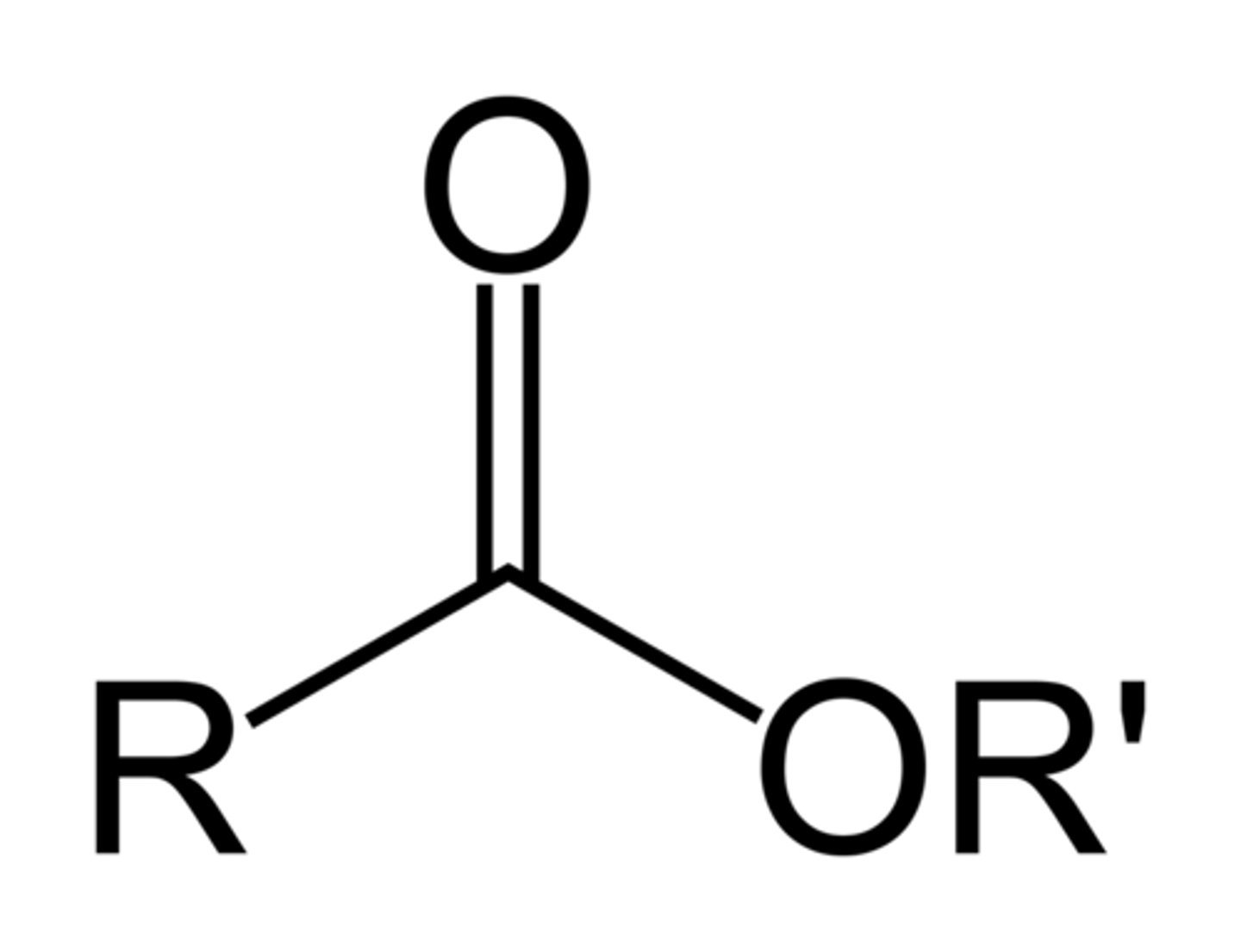
Ester
RCOOR
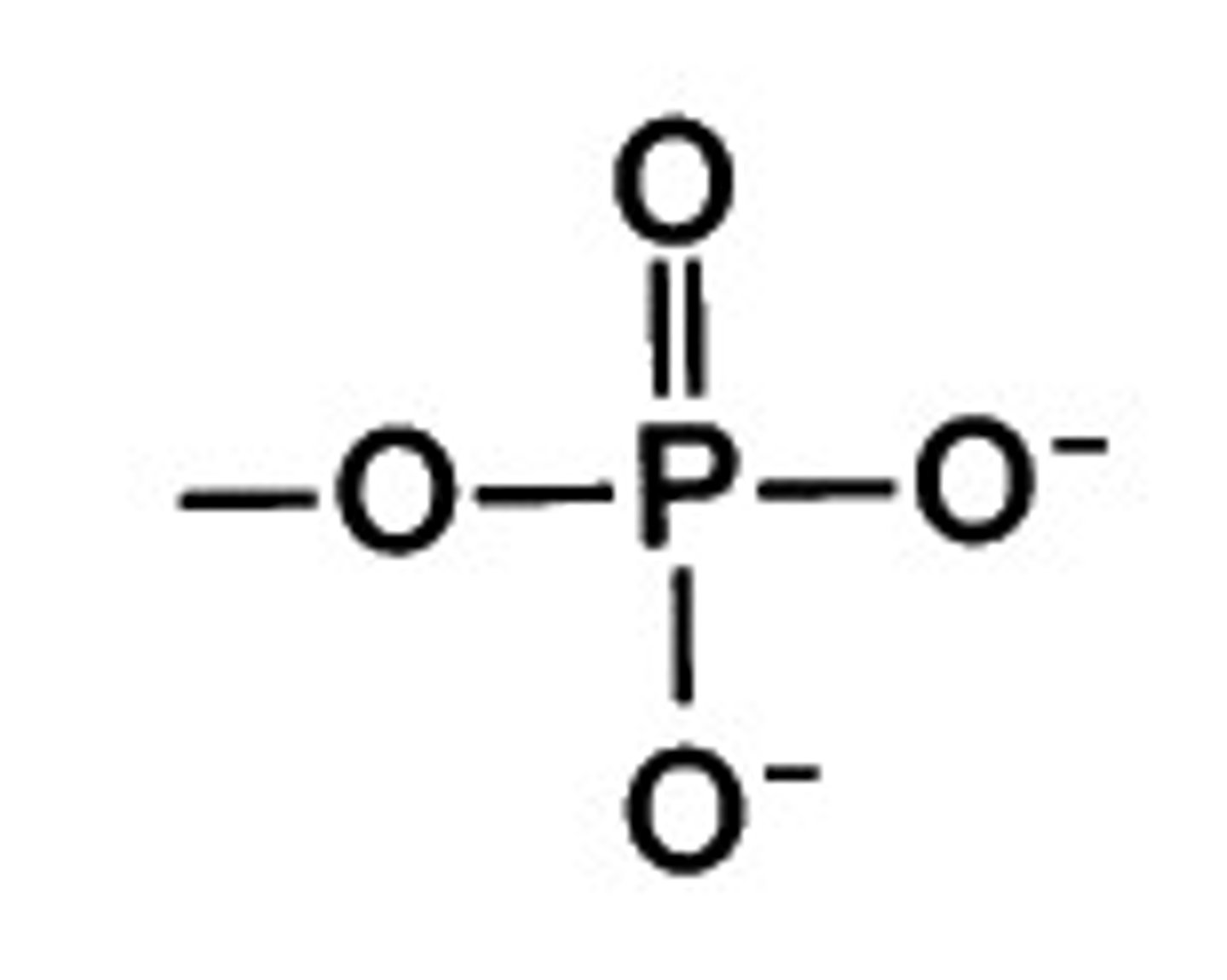
phosphate
PO4 3-
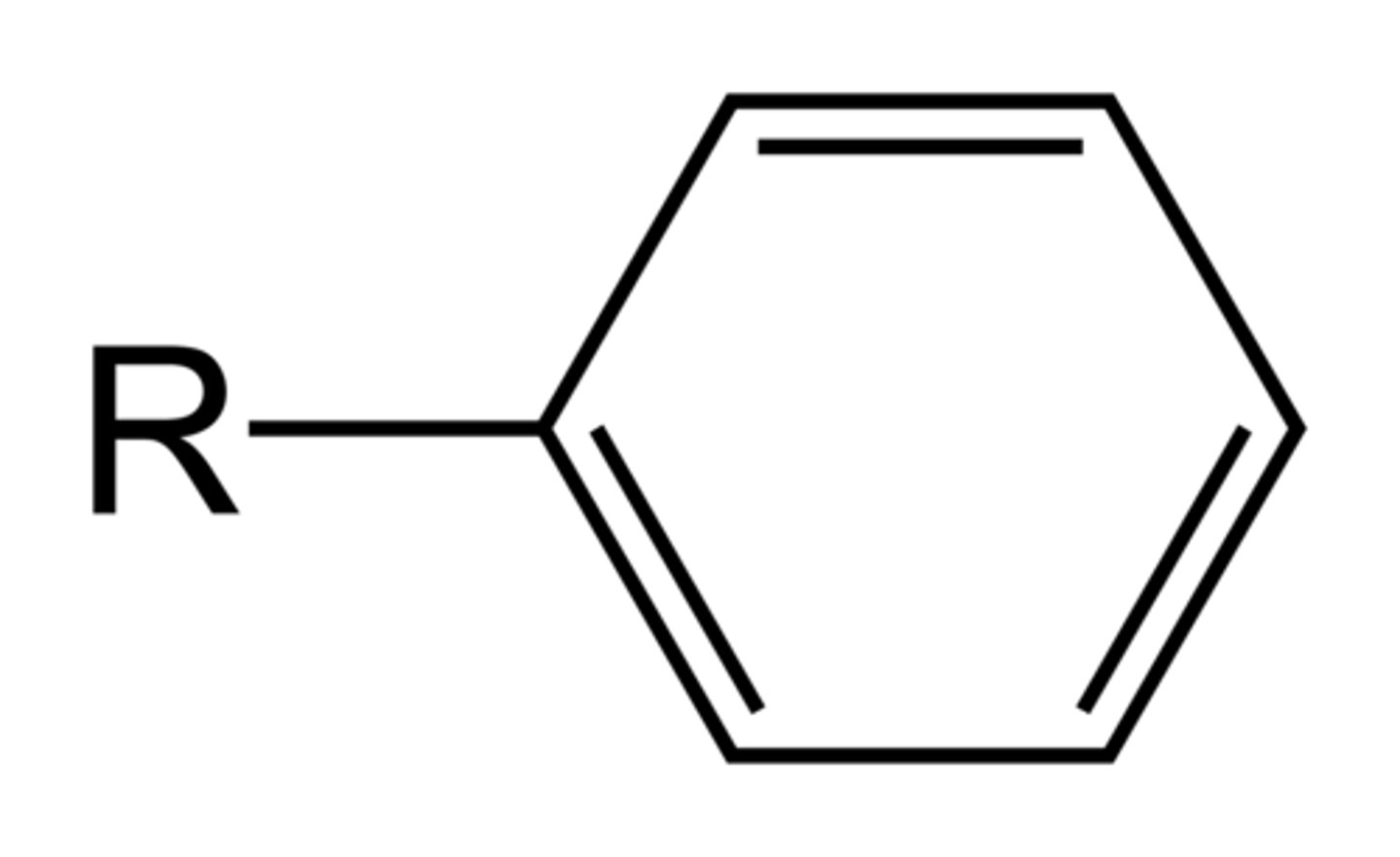
phenyl
C6H5
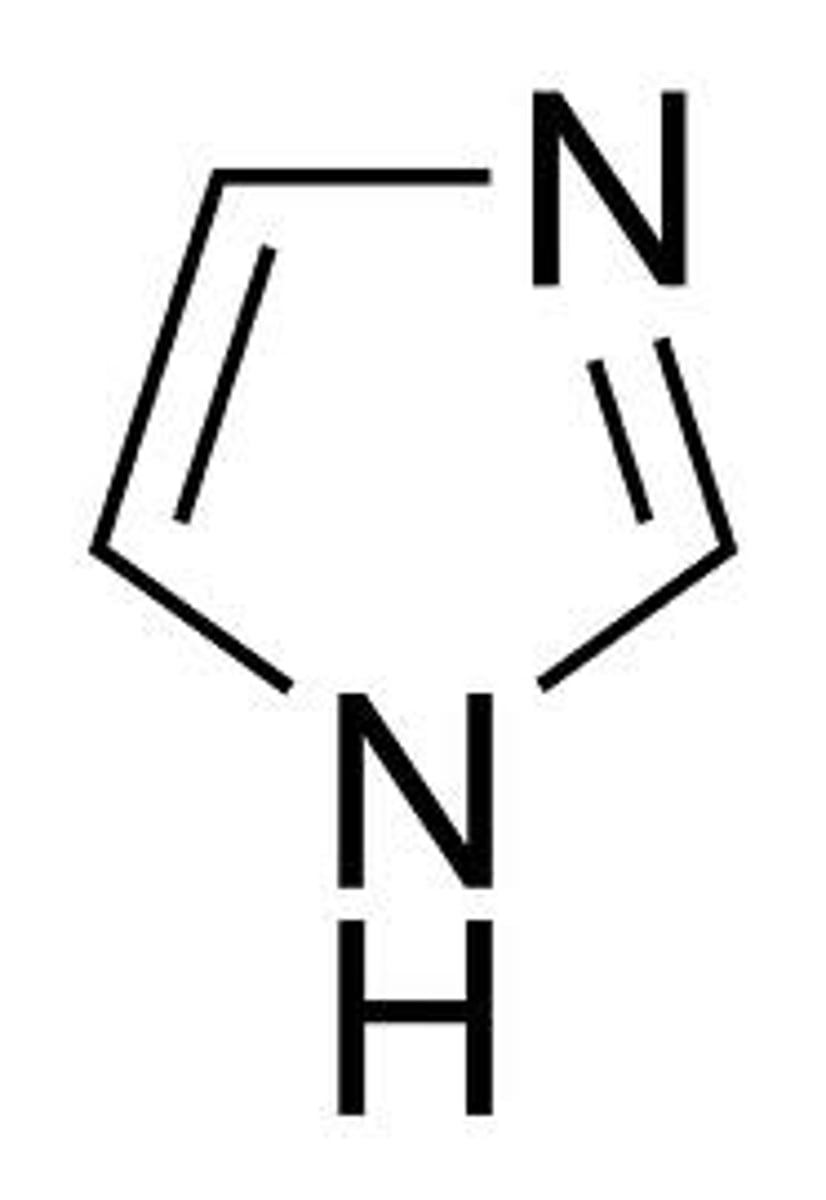
imidazole
how many h bonds can water form
- up to 4 transient h bonds due to unequal sharing of electrons
what kind of molecules can solubilize in water
- molecules that have polar and hydrophilic functional groups
what are amphipathic molecules
molecules that contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
what is the hydrophobic effect
- non polar molecules will aggregate in an aqueous solution, excluding water molecules
- main driving force behind formation of macromolecular structure
nucleophile
electron pair donor
electrophile
electron pair acceptor
why is water an excellent nucleophile
can donate the lone pairs on the oxygen
hydrolysis vs condensation reactions
hydrolysis: larger molecule forms two smaller ones and consumes water
condensation: two molecules combine to form one molecule and a water molecule
why might macromolecules fold to exclude water
- prevents reactions from occurring
- maximizes number of interactions of hydrophilic groups w water for solubility
what links AAs in polypeptide chains
peptide/amide bonds
carboxyl and amino group bond and release water (condensation rxn)
what is the alpha carbon
central carbon
what are essential amino acids
Amino acids that must be consumed because they cannot be created by the body
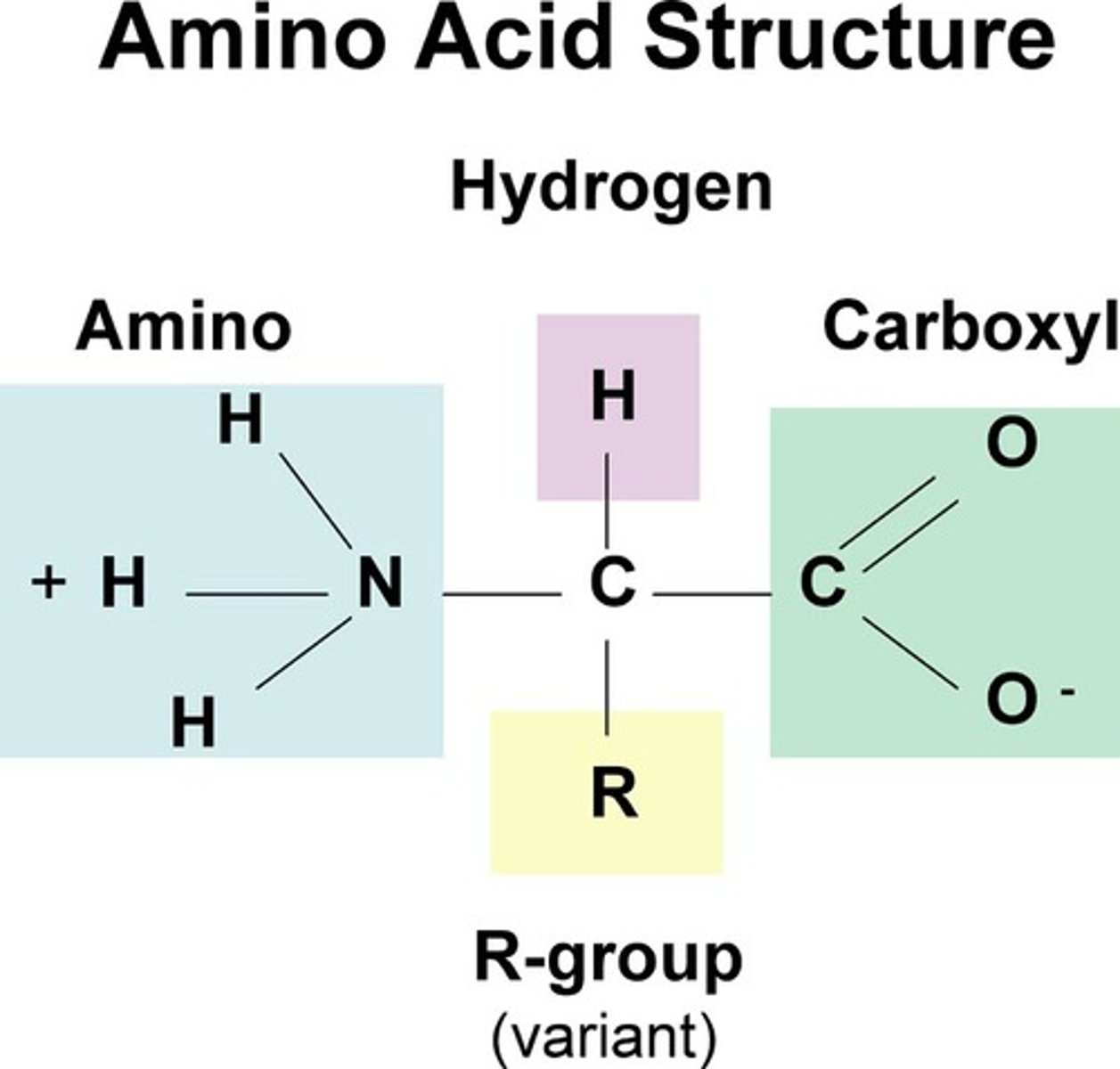
amino acid structure
carboxyl carbon is carbon 1 and covalently bonded to alpha carbon (carbon 2)
chirality
- non superimposable
- mirror images are called enantiomers
- isomers exhibit optical activity
- L AAs are physiologically relevant in plant & animal proteins
how to know if an amino acid is the L or Disomer
put H at back
L isomer:
- get RCN clockwise
- get RNC counterclockwise
what is a zwitterion
- a zwitterion is a species with both a positive and a negative charge, gives a net neutral charge
- when the side chain is uncharged, amino acids can be zwitterions
which letters are not used in the amino acid alphabet
JUZBOX
which amino acid is not chiral
Glycine
which amino acids are beta branched
valine, isoleucine, threonine
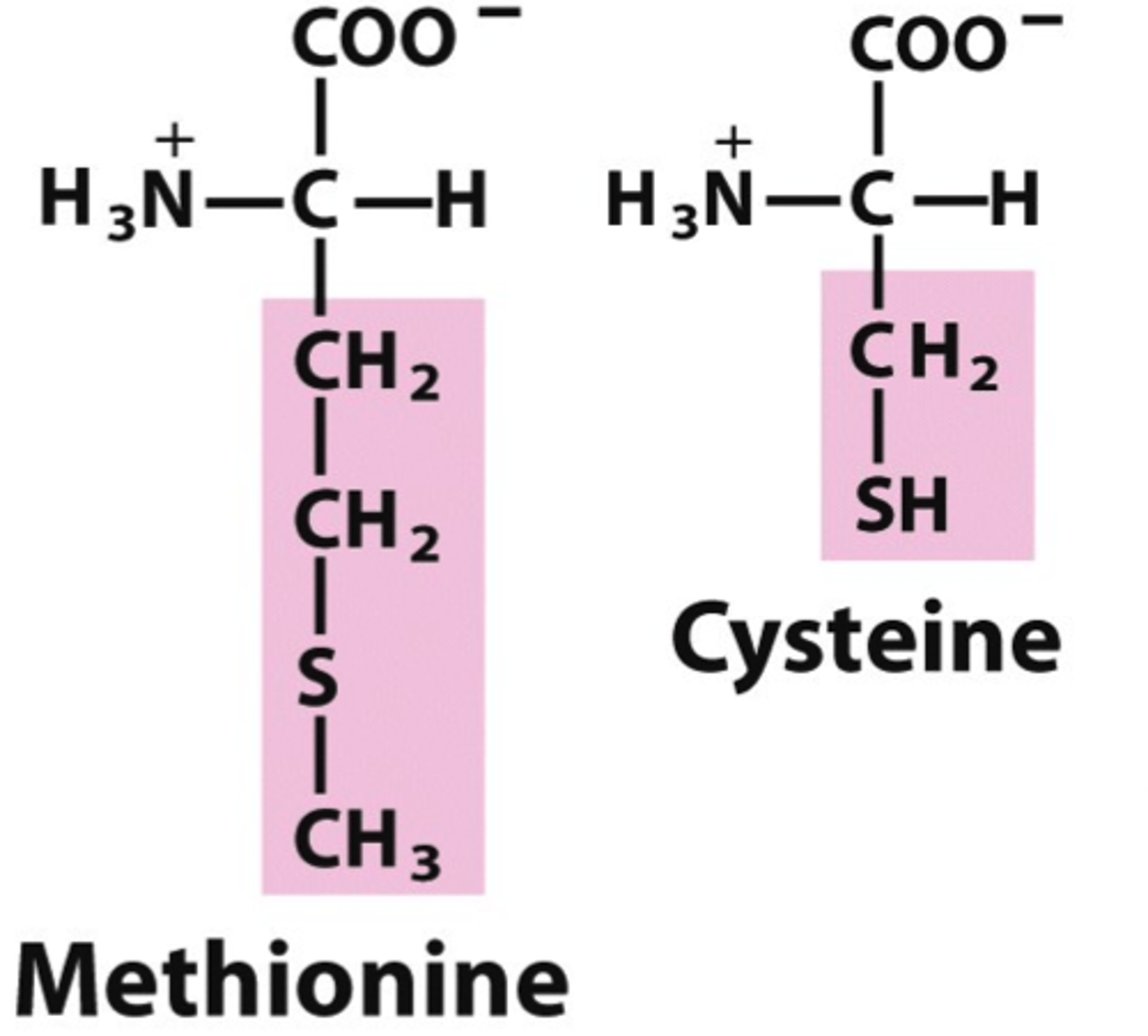
which amino acids contain sulfur
cysteine and methionine
which amino acids contain carboxylic acid in their side chain
aspartate and glutamate
which amino acids contain hydroxyls in their side chains
serine, threonine, tyrosine
which amino acids contain nitrogen in their side chains
histidine, lysine, arginine, tryptophan
which amino acids contain nitrogen and oxygen in their side chains
asparagine and glutamine
what can amino acids also be metabolized to form
- hormones
- neurotransmitters
- nitrogenous bases
- energy producing intermediates
what is a salt bridge
form between +vely and -vely charged amino acids
which amino acids form disulfide bonds
Cysteines covalently interact with each other
What is an oxidation reaction?
loss of electrons
What is a reduction reaction?
gain of electrons
cysteine vs cystine
cysteine = reduced form of the a.a.
(remember: the e is for electrons... which you still have in reduced form)
cystine = oxidized form of the a.a.
(remember: the absence of the e means loss of electrons, which is what you face in oxidation)
Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI)
An enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation rxn to produce cystine
B-mercaptoethanol
reducing agent that breaks disulfide bonds
why do cytosolic proteins usually contain cysteines
due to the reducing nature of the cytosol
which amino acids are positively charged (basic) at physiological pH
lysine, arginine, histidine
which amino acids are negatively charged (acidic) at physiological pH
aspartate, glutamate
which amino acids are polar
serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, glutamine
which amino acids are non polar
glycine, leucine, isoleucine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, alanine, valine, proline, and methionine
amino acid hydrophobicity
most to least hydrophobic
non polar to charged
where are hydrophobic amino acids usually found on proteins
for soluble proteins, the interior
but can still be found on the surface to allow for non covalent interactions
covalent modifications
- phosphorylation
- ubiquitination
- glycosylation
- acetyl, methyl, hydroxyl, carboxyl
post-translational modification
- addition/removal of functional groups
- disulfide bonds
- covalent modifications
- cofactor/ligand binding
can affect structure and function
GFP (green fluorescent protein)
- AAs buried at center of protein
- nucleophilic attack of amide nitrogen found in glycine by serine's carbonyl forms a heterocyclic structure that is important for its fluorescence
- changing these key AAs or the AAs nearby can affect properties like colour or brightness
equation for pH
pH=-log[H+]
ie. lower pH means more H+ present to protonate functional groups
pKa
used to measure the strength of an acid
pka = -logKa
tells you the value of pH at which a functional group loses or gains its H+
acid dissociation constant
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
what kind of Ka and pKa do strong acids have
high Ka (high dissociation) and low pKa
weak acid and conjugate base
protonated HA and deprotonated A-
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
used to determine the pH of a solution depending on the amount of ionization of a weak acid
relationship between pka and ph
pka is the ph at which a weak acid or functional group is 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated
what do buffers do
- solutions of weak acids and conjugate bases that can resist changes in pH (neutralizes small changes)
- maintain the pH +/- 1 pH unit around the pKa
how do you choose the right buffer
- has a pKa closes to the pH you require at a given temp
- consider chemical stability ex side rxns that interfere
- cost/availability
physiological pH
7.4
Aspartate vs aspartic acid
aspartate: conjugate base
aspartic acid: protonated form
What is the buffering region?
- lots of molecules that are buffering or binding to the protons (resist the change in ph)
- around 1 ph unit of the pka value
- flat portion of titration graph
isoelectric point
- The pH value at which the amino acid exists as a zwitterion (charge of molecule is zero)
- average pka values on either side of zwitterion
buffering species of blood
bicarbonate accepts or donates protons
how does blood buffer using bicarbonate
if the [H+] increases, bicarbonate (HCO3-) binds and produces carbonic acid (H2CO3)
carbonic acid breaks down to water and CO2
CO2 exhaled to remove excess H+
what is the bohr effect
- ph can affect O2 carrying ability of hemoglobin
- CO2 made in tissues combines with H2O to make HCO3- (bicarbonate) and a H+
- this helps with O2 release
- at lower ph, his146 is protonated and creates a salt bridge to asp94
- this favours the deoxygenated structure of hemoglobin
levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary protein structure
periodic regular structures (a-helix, beta strands, sheets, and turns)
tertiary structure
folding of secondary structures into defined protein motifs and domains
quaternary structure
assembly of distinct chains (many pp chains) into multi subunit structures
what is the backbone of a polypeptide chain
consists of the peptide bonds and alpha carbons while the variable parts are the distinct R side chains
nature of peptide bonds
- peptide bonds are polar but uncharged
- partial double bond character due to resonance, preventing rotation of the peptide bond
where is rotation allowed in a polypeptide chain
- the bonds linking the amide and carbonyl to the alpha carbon
- amide to alpha is phi
- carbonyl to alpha is psi
- range from -180 to 180
- not all angles permitted due to steric clashes
- clash minimized when side chains are trans to one another
a-helix
- right handed helix
- side chains point out
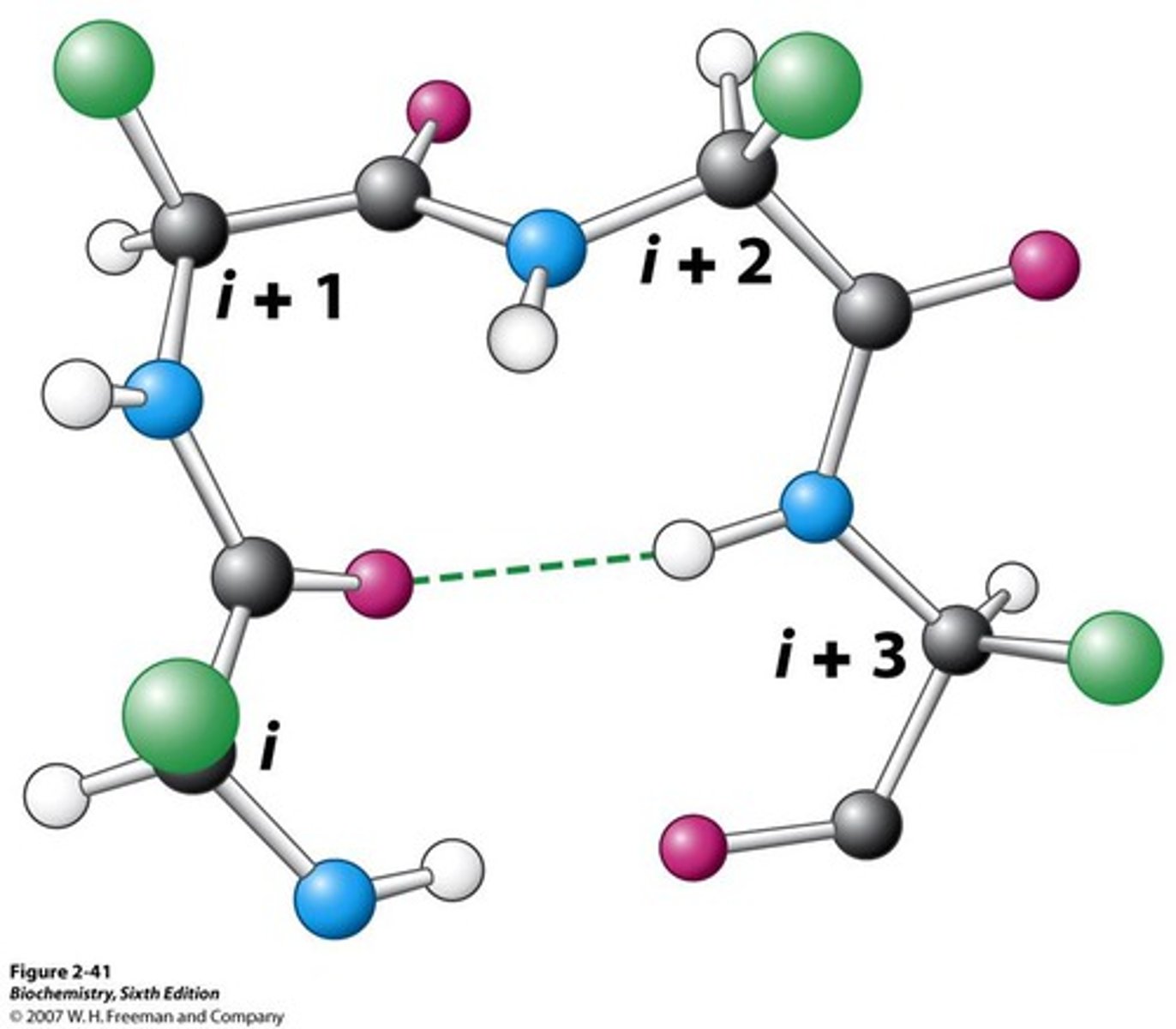
- intra strand h bonds between C=O (h bond acceptor) and N-H (h bond donor) 4 AA along the sequence (1 bonded to 5)
how many residues per 360 turn in alpha helix
3.6 residues (100 degrees between adjacent amino acids) and each residue is 1.5A high
3 types of alpha helices
- polar/hydrophilic
- hydrophobic
- amphipathic
how are beta sheets formed
- intermolecular h bonds link 2 or more beta strands
- h bonds occur between carbonyls and amines
types of beta sheets
- parallel, antiparallel, mixed
- strands alternate pointing above and below the sheet
- different sides of the sheet can have different properties
what are beta turns (reverse turns)
- 4 residue segment that allows the peptide chain to turn 180
- found on surface of globular proteins connecting secondary structures
- h bonds form btwn carbonyl O and amine H
- Pro common at position 2 (structure helps start the turn)
- Gly (small) Asn Ser (side chains can be modified at the surface of the protein) also frequently seen in turns