electron transport chain
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
NADH 1. 5 e
NAD+ H+
FADH
FAD+ H+
O2 +4H+
H2O
ADP+ Pi
ATP
ATP synthase
the more H+ ions = charge and PH (H+ acidic) gradient
step 1
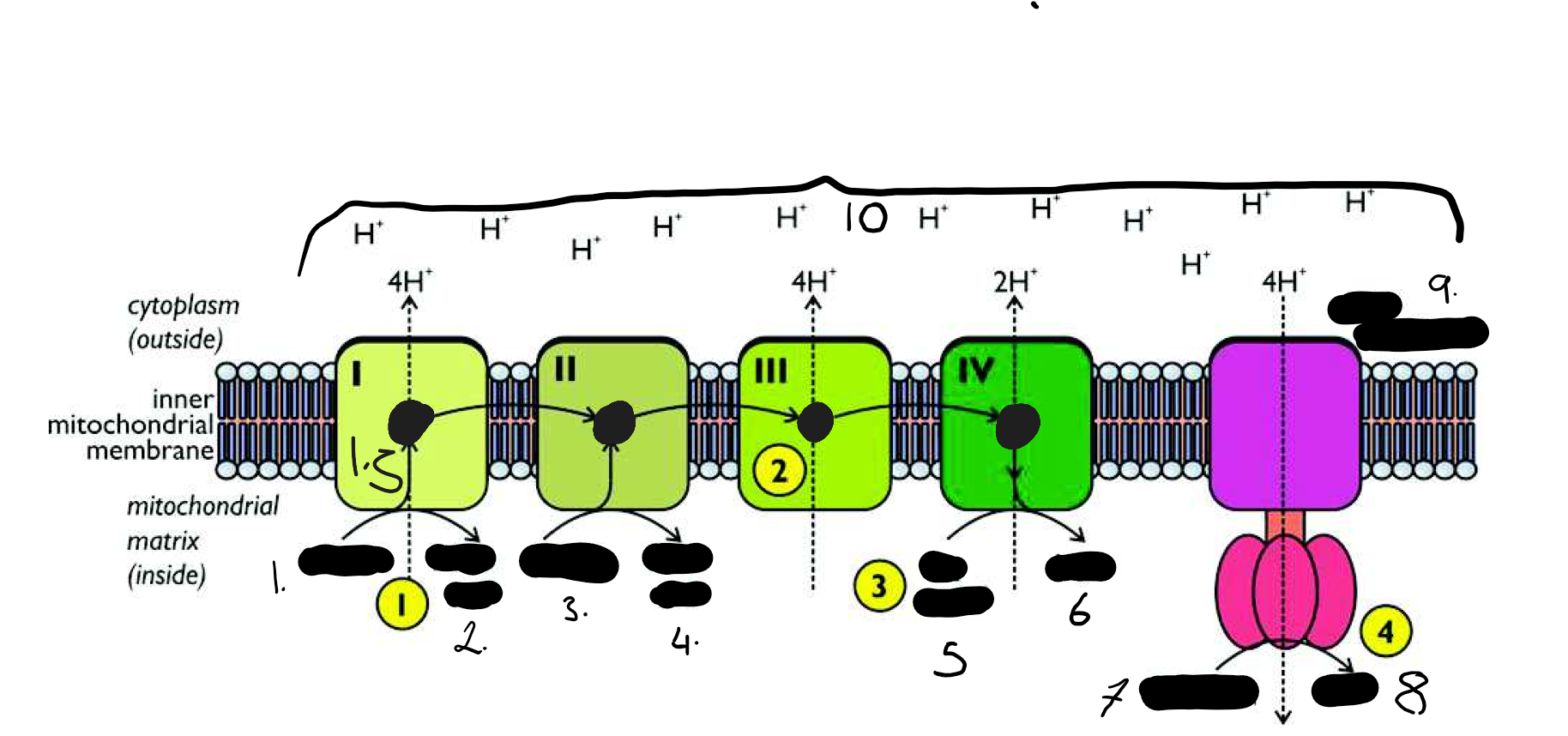
NADH molecules bind to protein I and release their hydrogen atoms as protons (H+) and electrons (e-). FADH binds to complex II rather than complex I to release its hydrogen. The NAD and FAD molecules then return to the Krebs Cycle to collect more hydrogen, so these coenzymes are constantly shuttling between their oxidised and reduced forms
Step 2
The electrons are passed along the chain of proteins via a series of redox reactions . Each protein is at a slightly lower energy level than the previous one so energy is transferred at each stage. The energy of the electrons is used to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane in the intermembrane space by active transport through the proteins, forming a proton gradient across the membrane.
step 3
This process ensures that there is a proton gradient across the membrane. There is a charge and PH gradient as protons (H+) are positive and they are acidic
Step 4
The energy of the electrons is now stored in the form of the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. It’s a bit like using energy to pump water uphill into a high reservoir, where it is stored as potential energy. And just as the potential energy in the water can be used to generate electricity in a hydroelectric power station, so the potential energy in the proton gradient can be used to generate ATP in the ATP synthase enzyme. The H+ diffuses across into the matrix as the inner membrane isn’t permeable to proton they diffuse they pass though stalked particles which contain ATP synthetase which uses the energy from the proton moving down the gradient to allow the condensation reaction between ADP +Pi to from ATP
Step 5
When the electrons reach the end of the transport chain they combine with hydrogen ions and oxygen to form water.
2H+ +2e + 1O
what is oxygen called in the electron transport chain
The terminal electron acceptor
What is the synthesis of ATP called and why
This synthesis of ATP is called oxidative phosphorylation because it uses oxygen to phosphorylate ADP.
what is the method of storing energy across a proton gradient called
The method of storing energy by creating a proton gradient across a membrane is called chemiosmosis, and was discovered by Peter Mitchell in the 1960s
why is oxygen ( terminal electron acceptor) so key
process would stop
In the absence of oxygen there will be no terminal electron acceptor. Electrons will be unable to off load their electrons. The carriers will all become reduced and the flow of electrons will stop. This means there will be no energy to pump H+ to create the conc gradient. NADH will be unable to off load its hydrogen and e at the start of the ETC. The NAD will not be regenerated. without regenerated NAD the enzymes in the Krebs cycle will not work. This means were only generating ATP from glycolysis in aerobic respiration where a step is added to regenerate NADH to NAD
What is a hydrogen acceptor
Molecules that pick up a hydrogen including the electron therefore them selves becoming reduced and what ever they take the oxygen off becomes oxidised.
Dehydrogenase
enzymes that remove hydrogen (carry out oxidation)
cytochromes
members of the electron transport chain. They are protein pigments with an ion group.
cytochromes oxides
An enzyme in the ETC which receives electrons from the cytochromes and is reduced as the cytochromes are oxidised
structure X = a stalked particle reference to H+ ions diffuse/ flow through (chemiosmosis) down the electrochemical gradient this process releases sufficient or enough energy is released to allow ADP +pi to from ATP.
where are the H+ ions pumped to
H+ pumped into intermembrane space
The idea of a difference enzymes between steps
which converts one intermediate( substrate) into the next eg enzyme 1 converts DHAP to 2 -P
The idea that this product becomes the next substrate of the next stage in the enzyme
idea of specificity (complimentary)
controls regulating the conversation
speeds up catalyses the conversation
by lowering the activation energy
idea that pyruvate only produced if all enzymes active
describe what happens to oxygen at the end of the electron transport chain
acts as an electron electron acceptor it also accepts a proton to become reduced and form water