Exemplar COPD Presentation
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is COPD?
A progressive disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible, caused by abnormal inflammatory response of the lungs primarily due to cigarette smoking and exposure to noxious particles or gases.
Which are common complications of COPD?
Cor pulmonale (right heart failure), acute respiratory failure, respiratory infections, peptic ulcer disease, and depression/anxiety.
What are the main risk factors for developing COPD?
Cigarette smoking, occupational chemicals and dust, air pollution, severe recurring respiratory infections, and α1-antitrypsin deficiency.
How does COPD typically affect breathing patterns in patients?
Patients may have dyspnea upon exertion, use accessory muscles for breathing, and develop a barrel chest due to lung hyperinflation.
What is the significance of COPD in the United States?
Third leading cause of death,
killing more than 133,000 Americans each year.
What diagnostic study is key for confirming a diagnosis of COPD?
Confirmed by Spirometry, which measures the FEV1/FVC ratio, typically revealing a ratio less than 70%.
Chest x-ray-reveals hyperinflation of alveoli & flattened diaphragm in late stages.
Alpha1 antitrypsin levels.
What is the significance of using pursed-lip breathing for COPD patients?
It prolongs exhalation, prevents airway collapse, decreases dyspnea, and improves oxygenation.
What symptoms indicate an exacerbation of COPD?
Changes in usual dyspnea, cough, and sputum, often caused by bacterial or viral infections.
What dietary recommendations are suggested for a COPD patient?
A high-calorie, high-protein diet with six small meals a day to prevent weight loss and conserve energy.
What environmental measures can help prevent COPD exacerbations?
Evaluating and reducing exposure to environmental or occupational irritants, and getting the influenza and pneumococcal vaccines.
What is a common diagnostic finding in a chest x-ray of a COPD patient?
Hyperinflation of the alveoli and a flattened diaphragm, & barrel chest appearance are common.
What is the recommended oxygen saturation range for COPD patients?
The expected reference range for oxygen saturation levels is 88% - 92%, although some older adults may have slightly lower levels.
How should nursing management prioritize care for a patient with COPD?
Recognize cues of ineffective breathing pattern, ineffective airway clearance, impaired gas exchange, imbalanced nutrition, and risk for infection.
In COPD patients, what new learning is crucial for managing daily activities?
Modification of activities to conserve energy, including pacing during personal care and exercise conditioning.
What is the role of α1-antitrypsin in the lungs, and why is its deficiency significant?
α1-antitrypsin deficiency is one of the most common genetic disorders among those w/ European ancestry. It protects the lungs from damage caused by enzymes like elastase, which can lead to emphysema and other lung diseases when deficient.
COPD clinical manifestations include:
Increased hematocrit level (due to low oxygenation level)
Increased levels of Hgb - may reach 20 g/dL or greater.
Nursing management that should be prioritized for COPD patients include:
Ineffective breathing pattern
ineffective airway clearance
Impaired gas exchange
Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements
Risk for infection
Solutions and or Goals for the COPD patient include:
Prevention of disease progression
ability to perform ADLs
Relief from symptoms
No complications related to COPD
Oxygen therapy for COPD patients:
Nasal cannula O2 sats: 88-92%
Venturi mask: 40 %
What is the primary stimulus for breathing in COPD patients?
A decrease in blood oxygen levels is the main drive for COPD patients.
COPD nutritional therapy includes:
Encourage fluids to promote adequate hydration and thin secretions (2-3 L/day to liquefy mucus)
High calorie, high protein diet to maintain energy and weight
Eat 5-6 small meals to avoid bloating
avoid foods that require great deal of chewing
No exercise 1 hrs before & after mealsto prevent shortness of breath.
How often should COPD patients should exercise for to improve conditioning?
Walk 20 min/day at least 2 to 3 times a week. This helps enhance overall lung function and physical endurance.
How can goals be evaluated for COPD patients?
Prevention of disease progression
Ability to perform ADLs
Relief from symptoms
No complications related to COPD
The nurse is caring for a client with COPD who complains of poor quality of sleep. Which question should the nurse ask next?
How many pillows do you sleep on? Asking the client how many pillows she sleeps on evaluates the client for orthopnea, which is shortness of breath caused by lying down.
The patient with COPD who has difficulty breathing should be given?
Low levels of oxygen & closely observed for quality & rate of ventilation.
Giving glucocorticoids will NOT fix his immediate needs.
Encouraging coughing & deep breathing does NOT meet his needs as giving low-level oxygen does.
How does a large meal affect patients with COPD?
It impairs the ability of the diaphragm to descend during inspiration, thus interfering w/ the work of breathing.
How does pursed-lip breathing help patients with COPD?
Helps to slow down the exhalation phase, which decreases bronchial collapse and subsequent air trapping in the lungs during exhalation.
How does smoking affect patients with COPD and their ability to fight infections?
Smoking damages the airways and lungs, reducing their ability to clear mucus and pathogens, which increases susceptibility to respiratory infections.
The tiny hair-like structures (cilia) that normally sweep away mucus and bacteria get damaged, and the immune cells in the lungs don’t work as well.
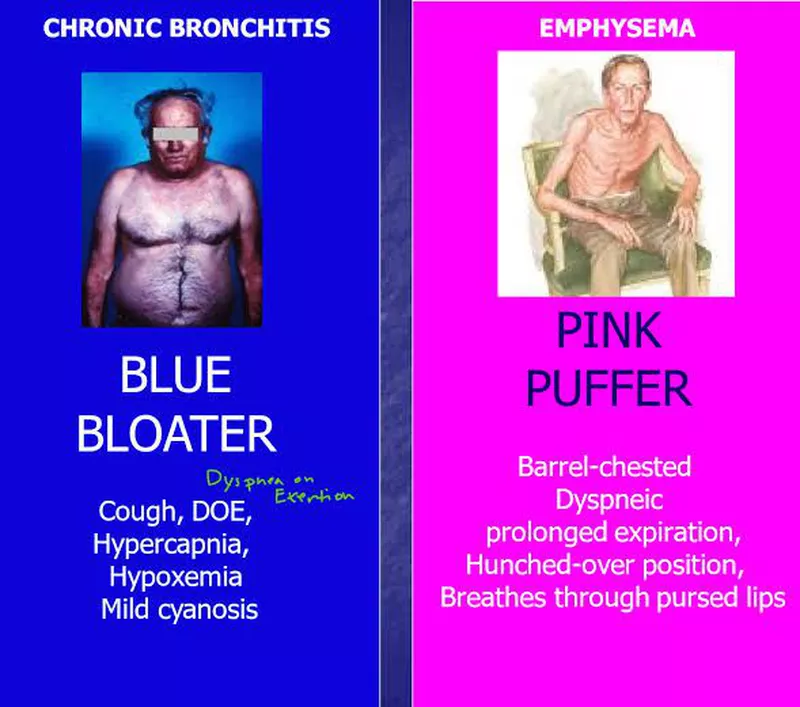
Main differences between chronic bronchitis vs emphysema:
Chronic bronchitis (blue bloaters): chronic cough, excessive mucus production, and airway obstruction, mild cyanosis.
Emphysema (pink puffers): destruction of alveoli, leading to decreased gas exchange and shortness of breath. Skinny appearance, increased respiratory rate, and pursed-lip breathing.
Leaning forward with arms outstretched and supported (tripoding) is more common in which type of patients?
COPD patients.
This position helps to optimize lung expansion and improve breathing efficiency by using gravity and supporting muscles.