Unit 3: Social-Emotional Development
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Ecological Systems Theory
Theory of how we grow our social and emotional developments over time based on our connections with what is around us
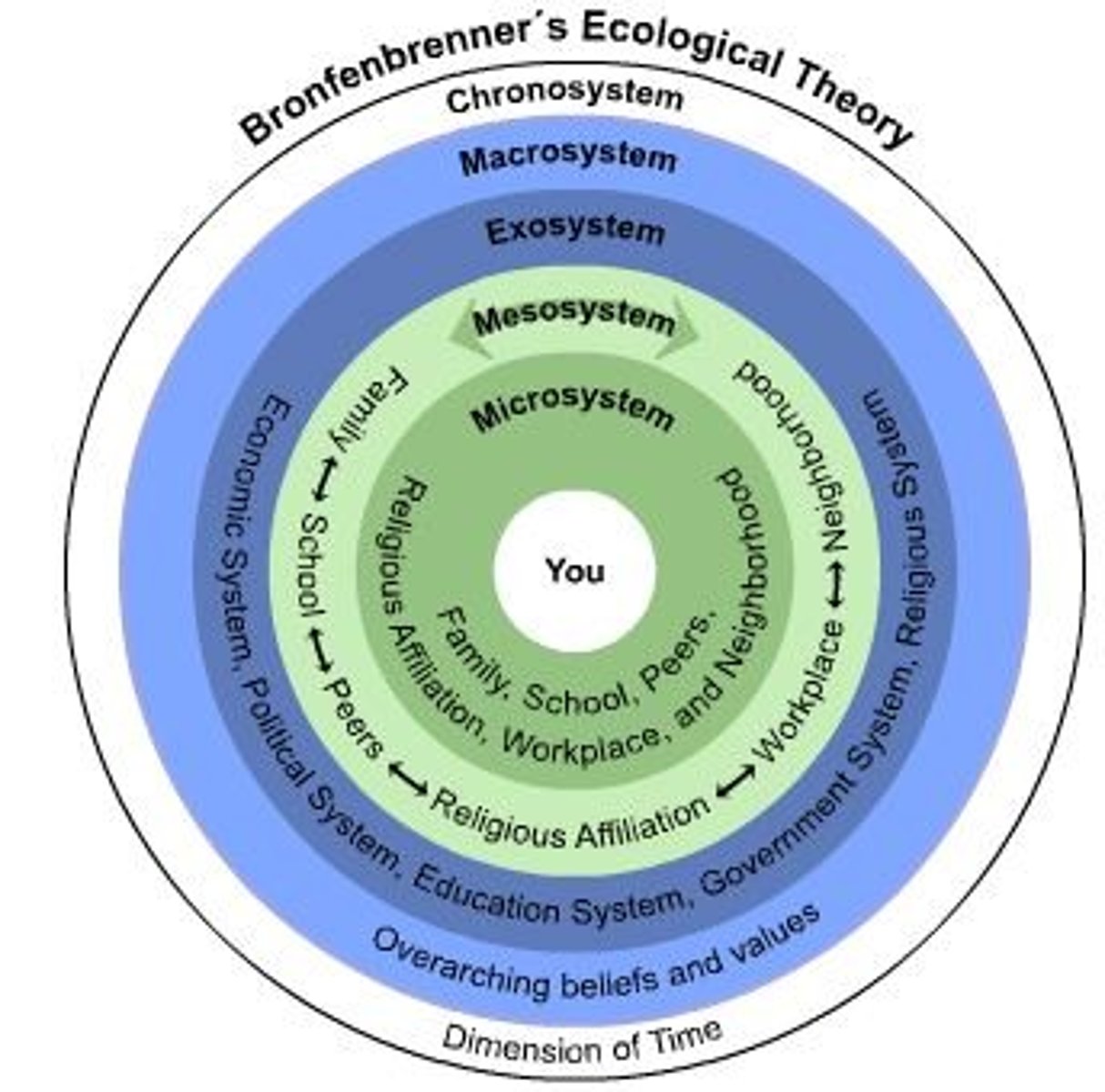
Individual
your individual characteristics that affect your socio-emotional development
-Age, gender, health, ability, temperament
Microsystem
the individual's most immediate environment and their direct interactions within these relationships that impact their daily socio-emotional development
-Family, friends, teachers, coaches
Mesosystem
the connections and interactions between different microsystems in an individual's life
-Parents and teachers meet, boy/girlfriend and parents
Exosystem
external environments that indirectly affect an individual
-Religion, media, education, community resources
Macrosystem
societal and cultural influences that shape an individual's social-emotional development
-Societal norms, laws, politics, economic conditions
Chronosystem
dimension of time and how things change over time
-Life transitions, historical events, personal experiences
Psychosocial Stages Theory
suggest that socio-emotional development requires individuals to resolve psychosocial conflicts at each stage of their lifespan. Unresolved conflicts can impact later development and may resurface later in life if not addressed properly
Trust v. Mistrust
If basic needs are met, infants develop trust (>1 year old)
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
Toddlers learn to exercise their free will and do things for themselves, or they begin to doubt their abilities (1-3 years old)
Initiative v. Guilt
Preschoolers learn to initiate tasks or feel guilty trying to be independent (3-6 years old)
Competence v. Inferiority
Learn pleasure of applying themselves, or feel inferior for not applying themselves (6-puberty)
Identity v. Role Confusion
Refining sense of self to form an identity, or become confused about who they are (teen-20s)
Intimacy v. Isolation
Struggle to form close relationships/intimate love, or feel socially isolated (20s-40s)
Generativity v. Stagnation
Discover sense of giving to the world or may develop a lack of purpose in life (40s-60s)
Integrity v. Despair
Reflecting on life, an older adult may feel a sense of satisfaction or failure with their life (60s-+)
Attachment
Emotional tie with others, seeking closeness to caregivers and showing distress upon separation. Inborn instinct for evolutionary survival; physical contact is crucial (Harlow's Monkeys)
Secure Attachment
infants who comfortably explore environments in the presence of a caregiver; show a temporary sign of distress when the caregiver leaves, comfort when they return
Separation anxiety
fear when away from a caregiver or in the presence of a stranger; normal unless present after 3 years old
Insecure Attachment (Avoidant)
resists closeness to caregiver, common in autistic kids
Insecure Attachment (Anxious)
fear of abandonment or rejection, can act clingy, dependent, or constantly seek reassurance
Insecure Attachment (Disorganized)
no consistent behavior when separated or reunited, typical in kids with trauma
Temperament
linked to attachment styles; largely biologically based but influenced by a person's environment
Adolescent identity
sense of self, including physical, psychological, and interpersonal characteristics (race, gender, sexual orientation, religion, etc.) derived from one's bodily sensations; body image, memories, goals, values, expectations, etc.
Diffusion
little sense of who they are; no commitment to identity aspects
Foreclosure
premature commitment without exploration
Moratorium
actively seeking a meaningful identity
Achievement (identity)
a committed sense of self
Social clock
the culturally preferred time of social events (marriage, parenthood, retirement, etc.)
Components of Adulthood
-Independence
-Love, intimacy, committed relationships
-Family
-Work/retirement
Secure attachment later in life
more readily able to form long-lasting relationships, more likely to trust partners and be emotionally available
Avoidant attachment later in life
seen as self-reliant and emotionally guarded, unlikely to seek emotional comfort or know how to comfort others
Anxious attachment later in life
may be "clingy" or not trusting, concerned that people will abandon them, seek constant reassurance
Disorganized attachment later in life
likely have mental health disorders that prevent healthy relationships
Secure attachment's impact with your kids
intuitive understanding of kid's needs
Anxious attachment's impact with your kids
overly concerned with kid's needs, hover or make anxious attachment with kid
Avoidant attachment's impact with your kids
struggle with emotional intimacy, distance themself from kid
Authoritarian parenting
strict, obedience, control, low response/high demand
Authoritative parenting
"Goldilocks zone," high response/high demand
Permissive parenting
few limits and rules, low response/low demand
Neglectful parenting
uninvolved, no limits, no demand
Parallel play
playing within the vicinity of peers but with no interaction
Pretend play
alone or together, use imagination to play
Associative play
sharing toys and interacting, minimal coordination
Cooperative play
playing together with increased coordination, taking turns, or following rules
Pros in Adolescence
-new social skills
-romance
-expanded friend groups
Cons in Adolescence
-cliques and enemies
-isolation or loneliness
-breakups
-new egocentricism develops
Imaginary audience
belief everyone is watching you and judging (anxiety and phobias)
Personal fable
belief you are completely unique, invulnerable, and special; can lead to risky behaviors and feelings of being misunderstood
Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE)
disruptions to the promotion of safe, stable and nurturing relationships; characterized by stressful and traumatic events (neglect, poverty, bullying, war, abuse)
Difficulty regulating emotions (ACE)
risk of mood disorders
Low self-esteem/self-worth (ACE)
internalize negative beliefs
Insecurity and trust issues (ACE)
less stable relationships
Withdrawal or isolation (ACE)
avoid interactions that can lead to loneliness
Aggression (ACE)
defensive behavior, copes with instability
Substance abuse (ACE)
turn to this as a form of self-medication
Repeating trauma (ACE)
continuing cycles of abuse, 30% of kids who were abused abuse their kids
Collectivism v. Individualism (Cultural Perspective)
Western: emphasize independence and expression
Eastern: focus on respect, discipline, community, responsibility
Discipline styles (Cultural Perspective)
Western: guidance-based concepts, work to make better
Eastern: strict discipline and punishments
Emotional expression (Cultural Perspective)
Western: encourages verbal affirmations
Eastern: discourages emotional displays
Education approach (Cultural Perspective)
Western: values education; more experiential learning
Eastern: values education; more academic achievements
Family structure (Cultural Perspective)
Western: individualist self-growth
Eastern: collectivist, heavy family bonds
Discipline and punishment (Cultural Perspective)
Western: physical punishment is seen as traumatic
Eastern: physical punishment is a normal aspect of discipline
Child labor (Cultural Perspective)
Western: don't allow neglect or exploitation
Eastern: cultural norm and a necessity to contribute
Exposure to violence (Cultural Perspective)
Western: witnessing domestic or community violence is traumatic
Eastern or unstable nations: violence may be normalized
Divorce (Cultural Perspective)
Western: recognized as traumatic due to emotional impact
Eastern: rarer and stigmatized but family conflict within marriages may be normalized
Adulthood (Cultural Perspective)
Defined differently through mix of legal, emotional, and economic milestones
Western: self-sufficiency and emotional independence
Eastern: social responsibility, cultural traditions