wk 1-3 CVS100
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Body Scan Planes, Terminology, How to obtain the images.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
medial
toward the middle/midline of the body
lateral
away from the midline
proximal
closer to the point of origin
closer to the heart
distal
farther from the point of origin
farther from the heart
cephalad
superior,above, towards the head
caudal
inferior, below, towards the feet
superficial
closer to the surface/skin
deep
farther down from the surface/skin
anterior
towards the front of the body
posterior
towards the back of the body
supine
lying on the back
prone
laying on the stomach
right lateral recumbent
lying on right side with the right arm extended and the left arm bent
aka right lateral decubitus
left lateral recumbent
lying on left side with the left arm extended and the right arm bent
aka left lateral decubitus
Fowler’s
sitting
Trendelenberg
feet higher than head
Reverse trendelenberg
head higher than feet
ultrasound
Very high frequency sound waves-millions of Hertz
they bounce off of structures and blood inside the body to obtain images and flow signals.
used for diagnostic purposes
transducer
Any device that changes energy from one form into another
Ultrasound probes turn electrical energy into mechanical vibrations of the crystals, producing ultrasound waves, and which also changes the echoes back into electrical energy for display on the screen.
ultrasound probes turn ______ into __________ producing _____, and which also changes the ____ back into _____ for display on the screen.
electrical energy
mechanical vibrations of the crystals
ultrasound waves
echoes
electrical energy
Beam
ultrasound emitting from the transducer
whatever the _____ will appear on your image.
beam transects
lower frequency is used to scan _____ structures.
deeper
higher frequency is used to scan _____ structures.
more superficial
lower frequency resolution
2.5 - 4 MHz
echo and abdominal
loss of some resolution (reduced image resolution, less detail)
higher frequency resolution
vascular
better resolution (5-10 MHz)
Linear array
4cm wide
rectangle field of view
created by a line of many crystals
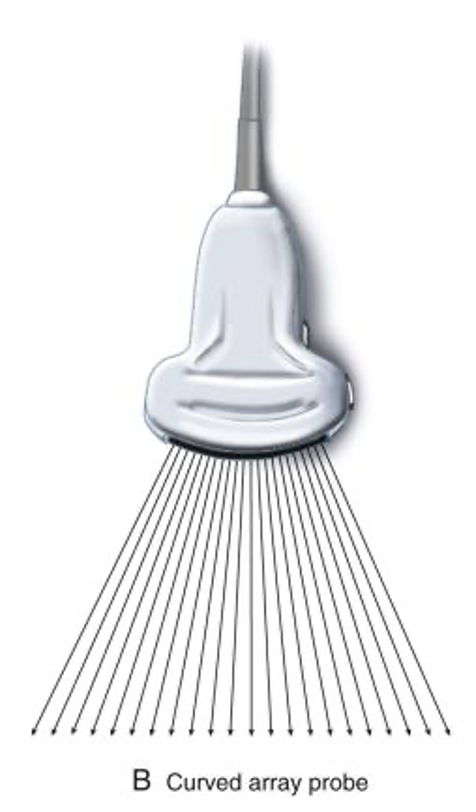

curved linear
line of crystals, but it is curved to create a sector (pie) shaped field of view

phased array
pie-shaped sector; smaller probe face and creates a wider sector than the curved
nearfield on your ultrasound image is the area…
closest to the transducer
More superficial part of neck.
Strongest signals are in the nearfield
midfield on your image is the
center of the image
farfield on your image is the
area farther away from the transducer
the more deeper part of your neck or body
Weakest signals are in farfield (bottom)
Time Gain Compensation and Lateral Gain Compensation
•Adjusts the brightness of the image in specific sections.
•Compensate for weaker signals
Overall Gain/ 2D Gain
Adjusts the brightness of the entire image.
Makes the entire image brighter or darker.
depth
•Describes the maximum distance into the body that an ultrasound system is imaging.
•Adjusts how far or how close we see into the body.

focal zone: focus/trans zone
• enhances the focus and resolution to a specific anatomical structure
•Always adjust to the area of interest
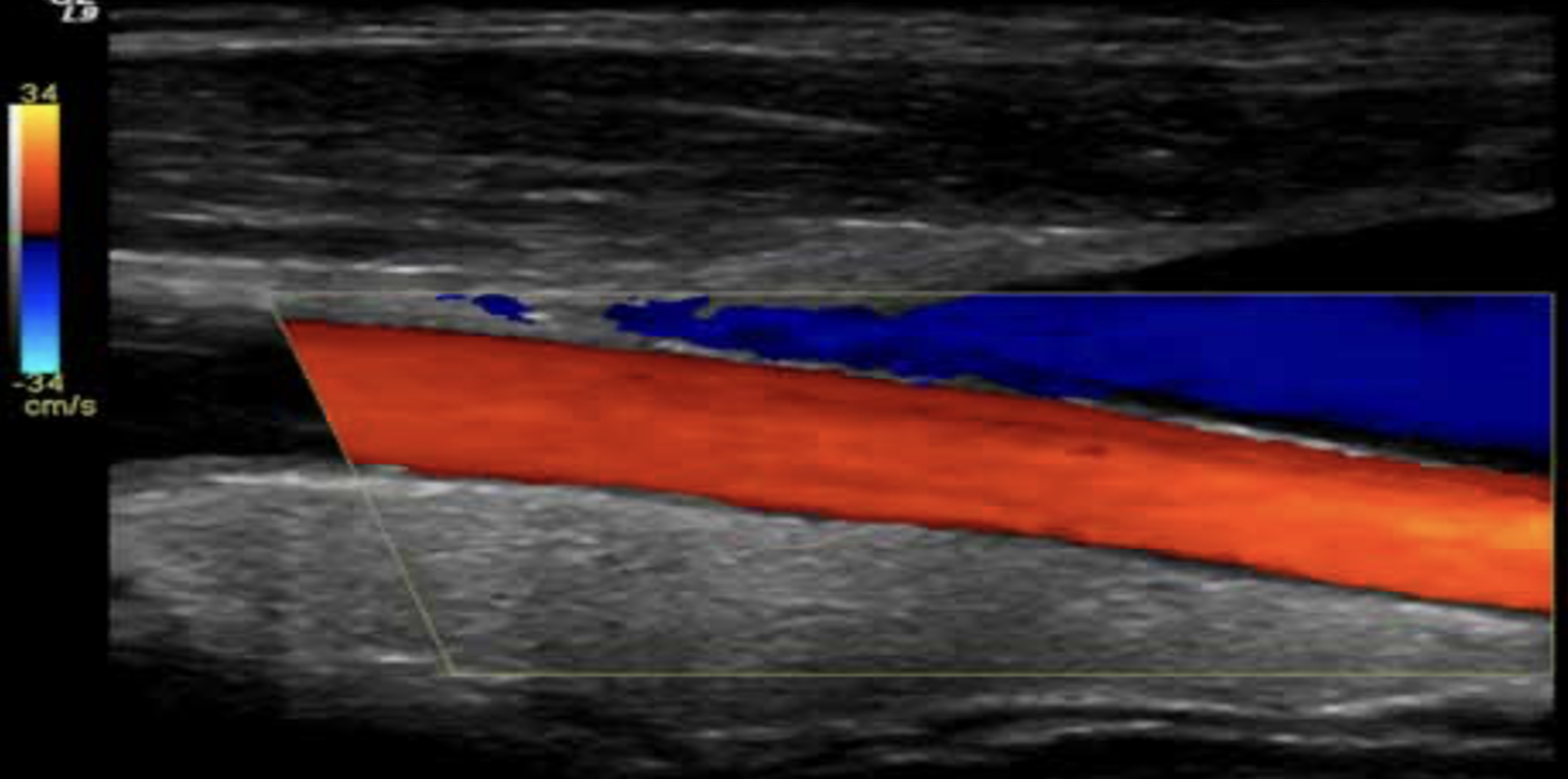
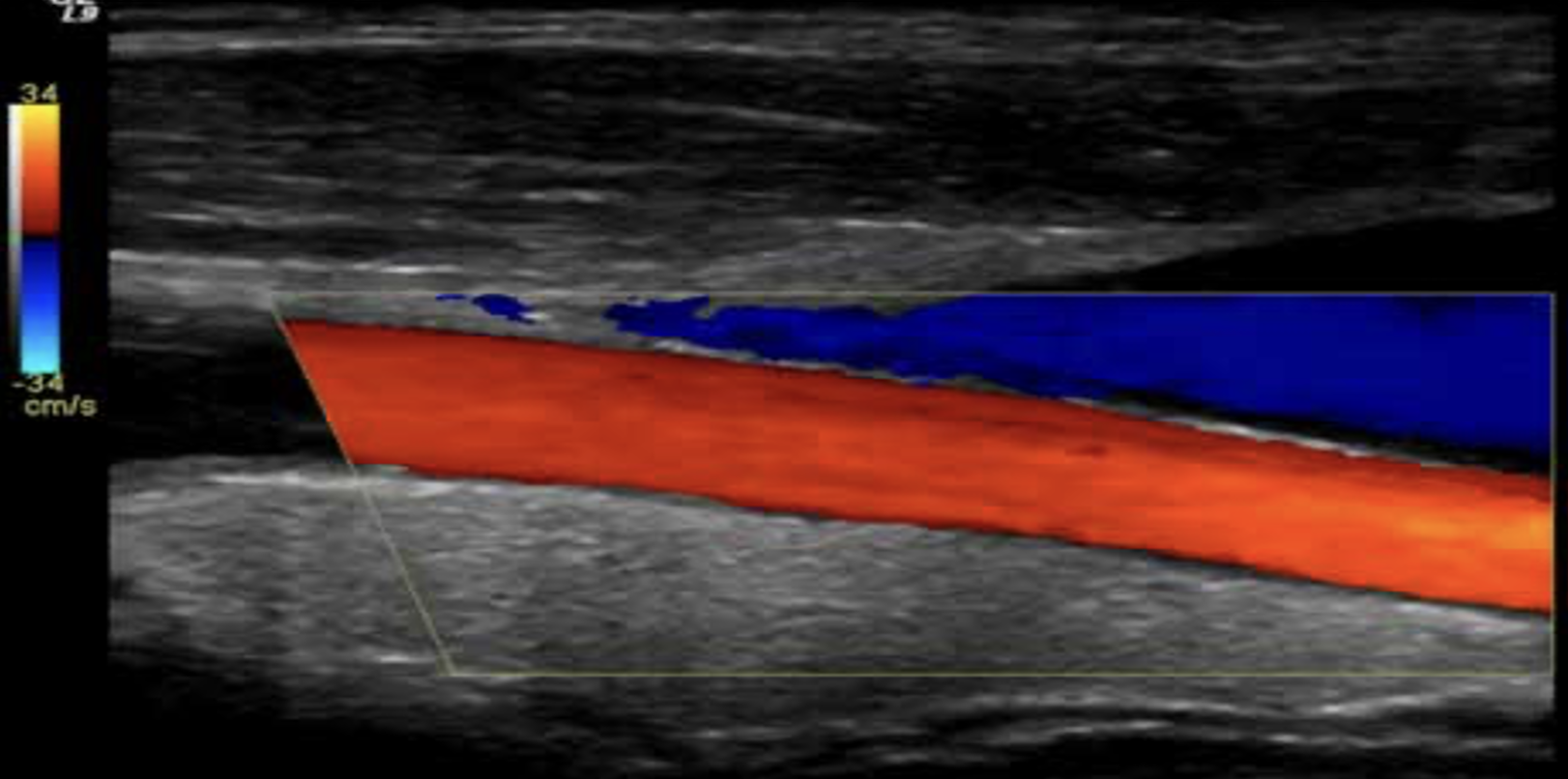
color flow doppler
shows blood flow motion in a selected two-dimensional area.
shows Direction and velocity blood flow.
direction and blood flow are color coded and superimposed on the corresponding B-mode image
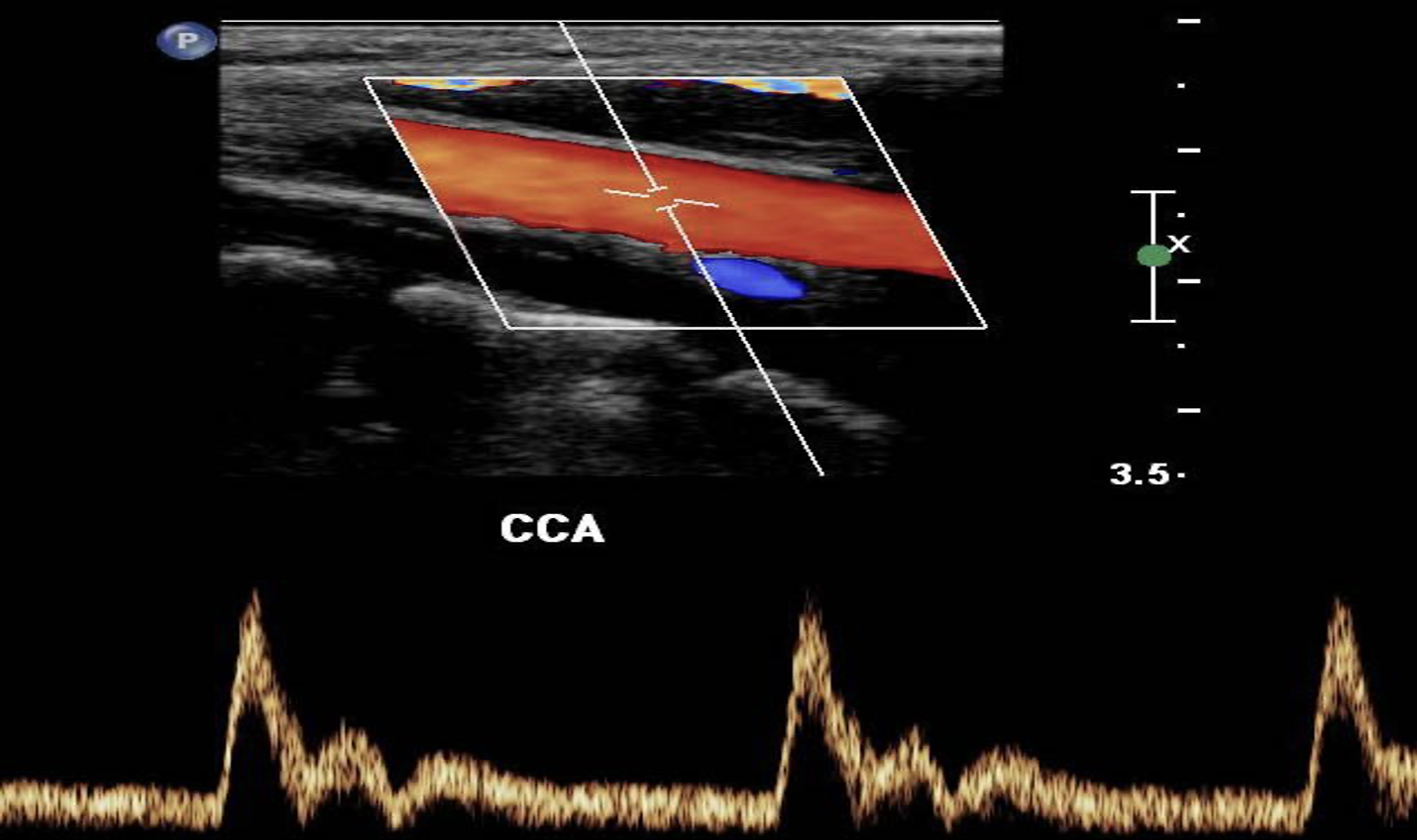
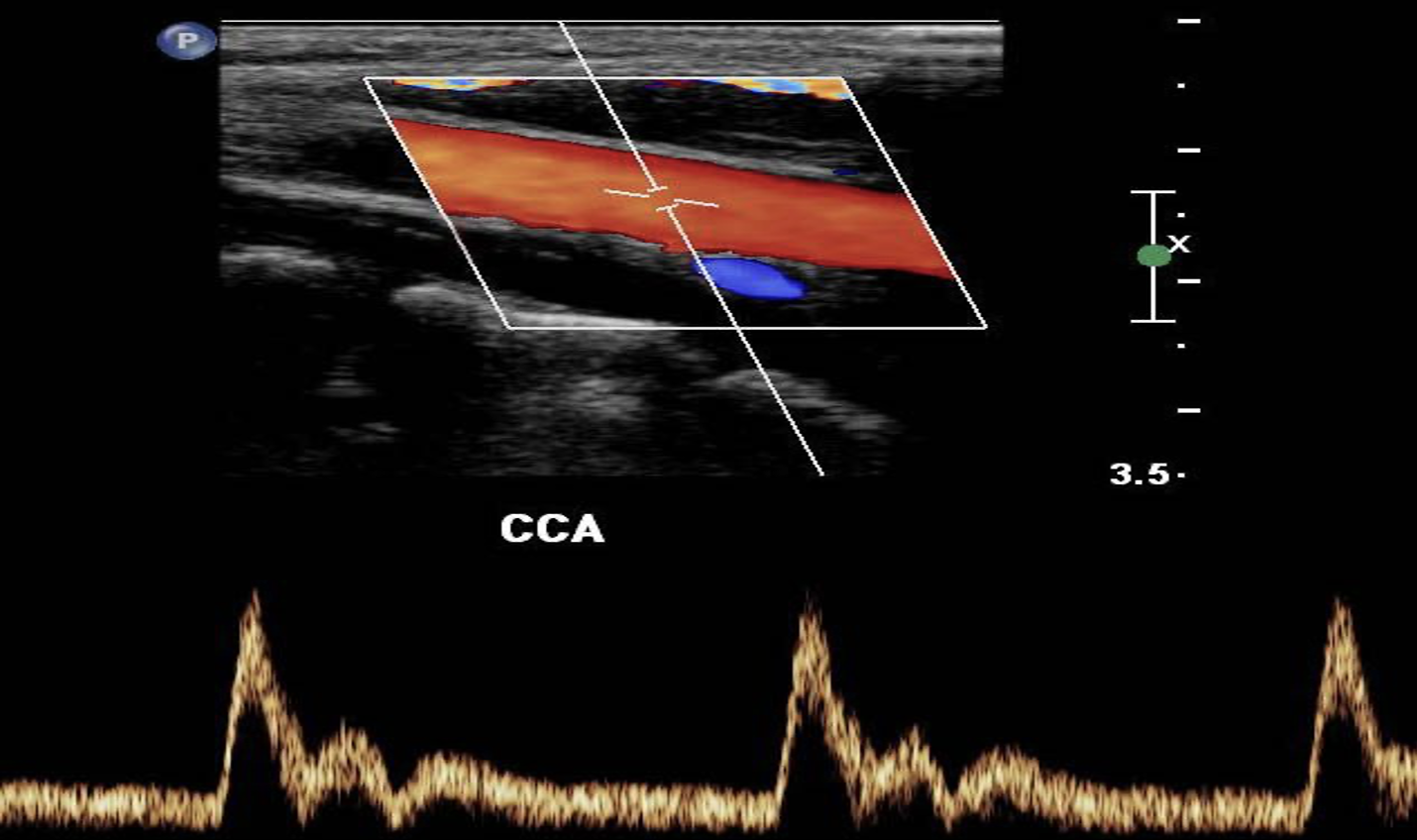
spectral doppler
consists of a continuous pulsed-wave form.
Shows the velocities of moving RBCs
shown to you as a Spectral Waveform.
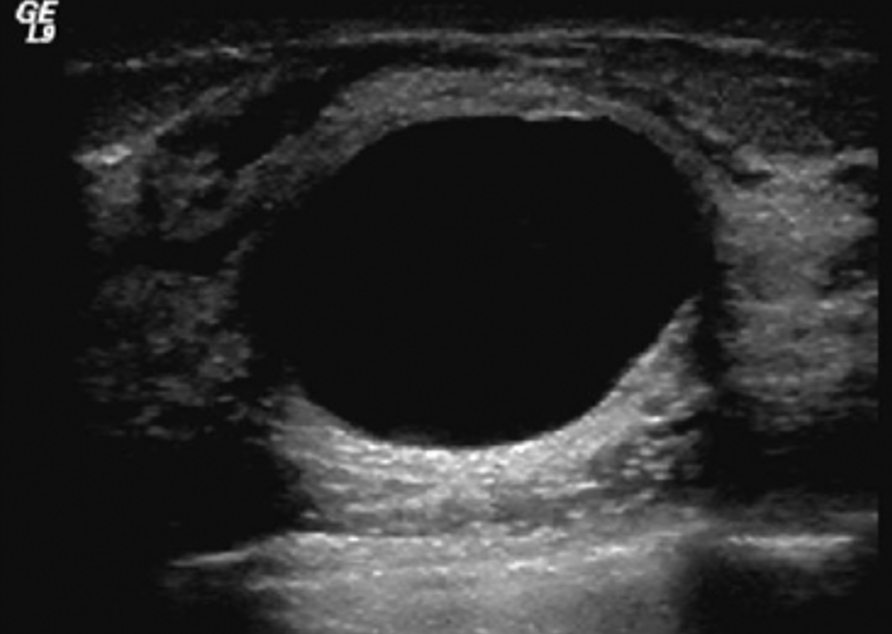
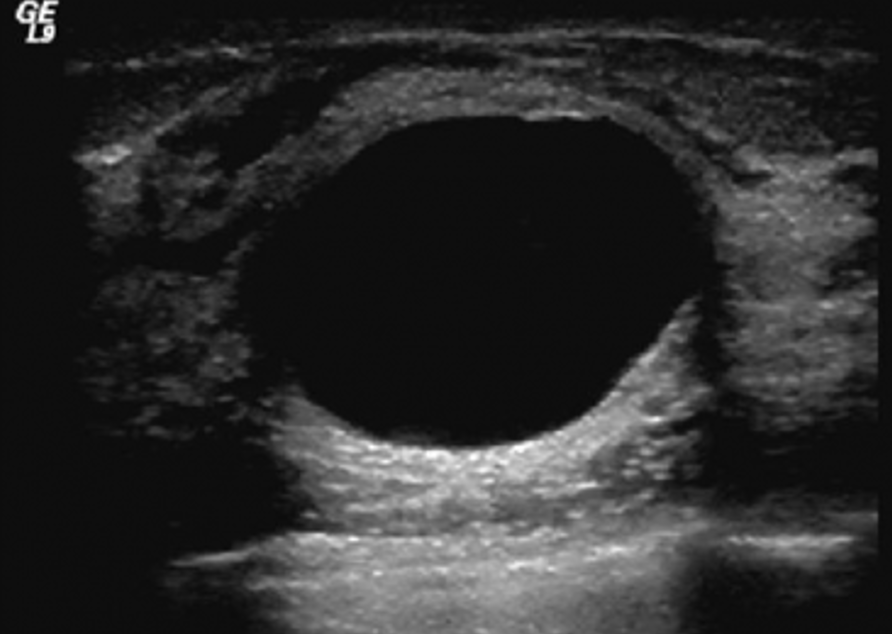
anechoic
being without echo (black) appearance on image
echogenic
The ability to create an ultrasound echo
hyperechoic
Producing echoes of higher amplitude than normal for the surrounding medium
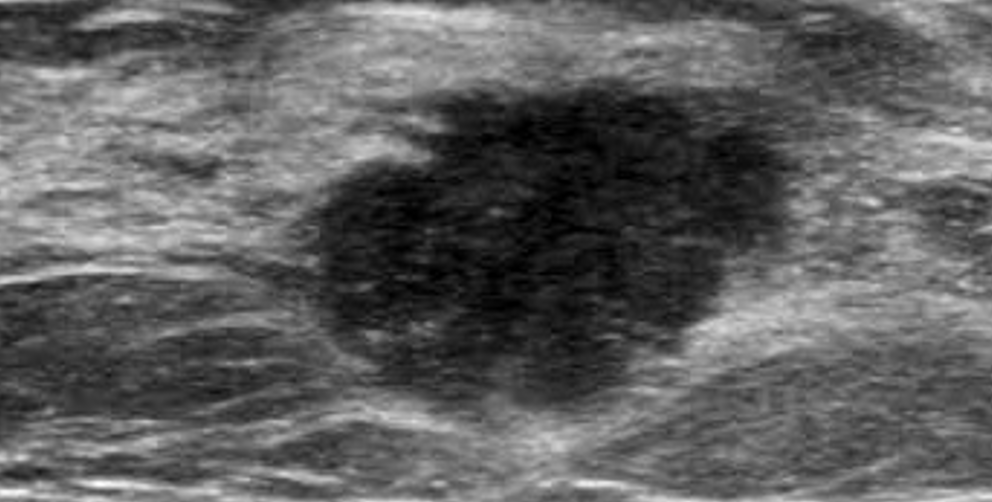
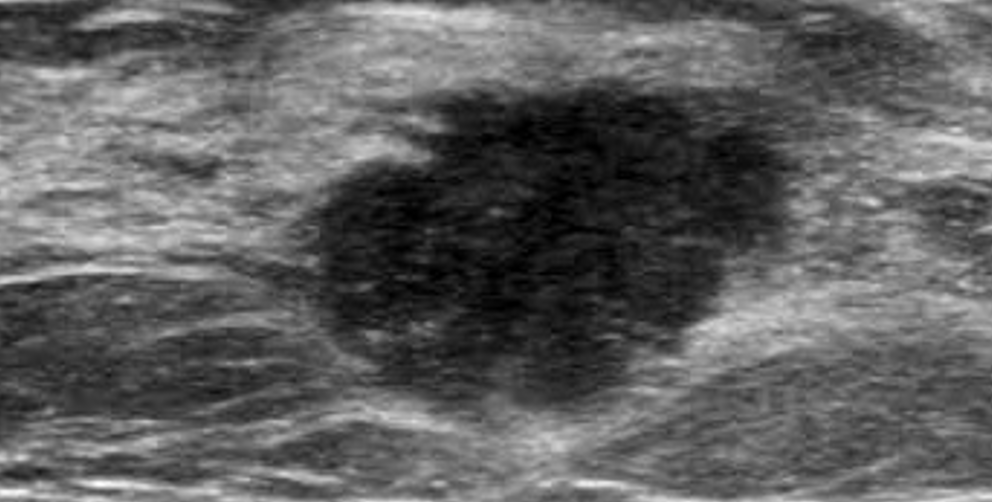
hypoechoic
Producing echoes of lower amplitude than normal for the surrounding medium
homogeneous
•Completely uniform in texture or composition.
•Same grayscale

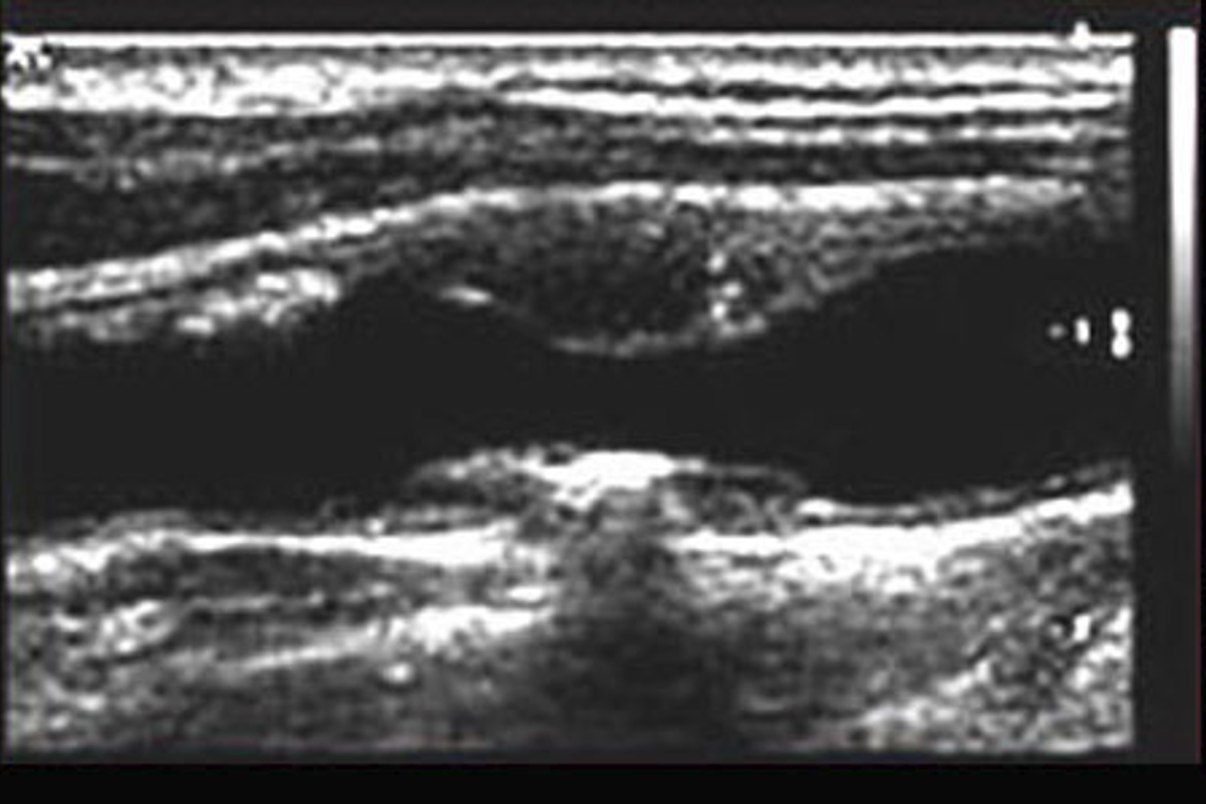
heterogeneous
an uneven echo pattern
reflections of varying grayscale
not uniform in texture or composition.
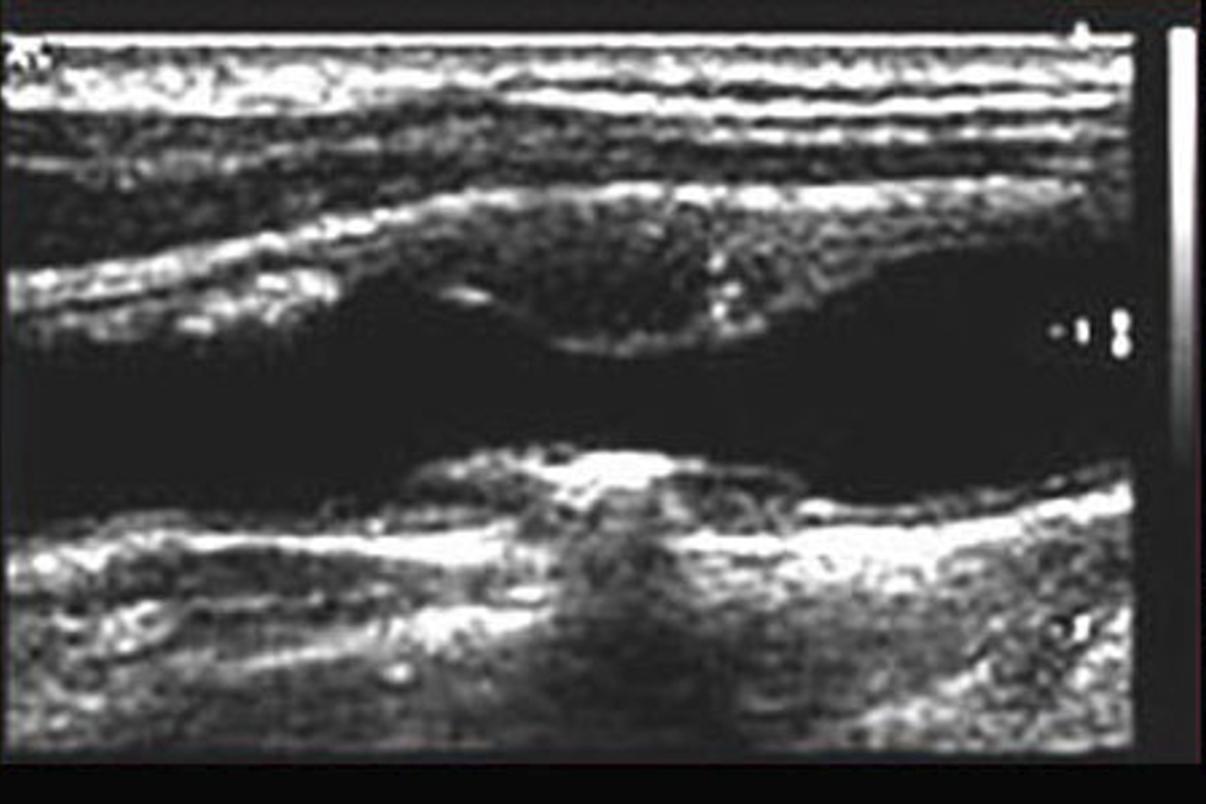
acoustic enhancement
•When ultrasound passes through a fluid medium, the intensity of the sound energy is not diminished.
•tissues behind the fluid collection are more echogenic (brighter because there is more acoustic power to reflect back to the transducer).

For acoustic enhancement, tissues behind the ___ ___ are more ___ (brighter).
fluid collection
Echogenic
acoustic shadowing
When ultrasound hits a dense object the ultrasound beam can not propagate(travel) through the dense object. The beam will be completely reflected, a posterior acoustical shadow is formed.