Econ sample final exam
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
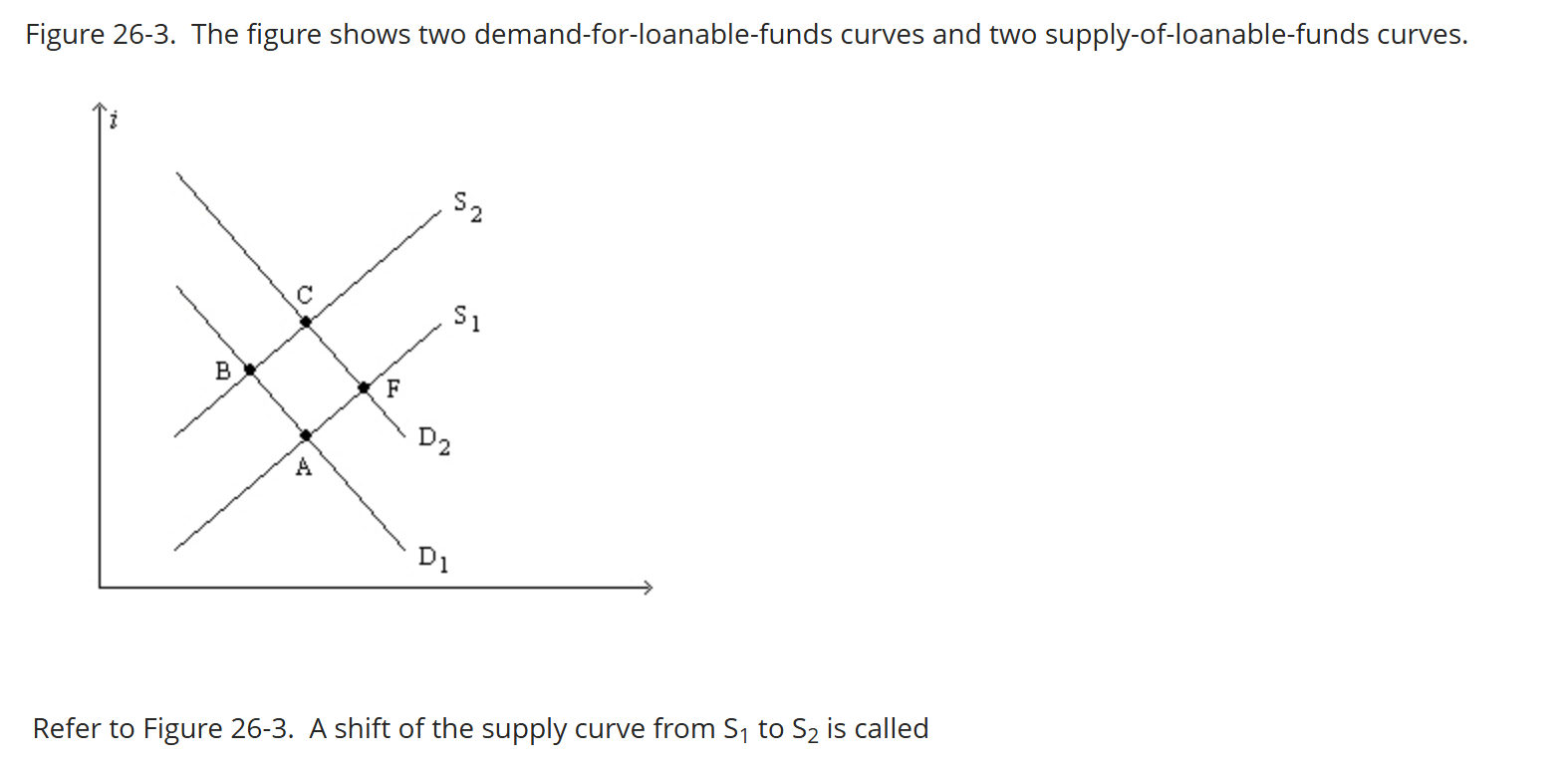
The figure shows two demand-for-loanable-funds curves and two supply-of-loanable-funds curves.
A shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2 is called
a. an increase in the supply of loanable funds.
b. an increase in the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
c. a decrease in the supply of loanable funds.
d. a decrease in the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
a decrease in the supply of loanable funds
Institutions that help to match one person's saving with another person's investment are collectively called the
financial system
Which of the following is not correct?
A. If you buy a bond from a corporation, you can sell the bond to someone else before it matures.
B. Term refers to the scheduling of periodic interest rate payments on a bond.
C. A bond is an IOU.
D. There are millions of different bonds in the U.S. economy
Term refers to the scheduling of periodic interest rate payments of a bond
Bond definition
a certificate of indebtedness
stock definition
a claim to partial ownership in a firm
Which of the following events could explain a decrease in interest rates together with an increase in investment?
A. The government instituted an investment tax credit.
B. The government went from surplus to deficit.
C. The government reduced the tax rate on savings.
D. None of the above is correct.
The government reduced the tax rate on savings
If an economy is closed and if it has no government, then
A. national saving = private saving.
B. total income = consumption + investment.
C. saving = total income - consumption.
D. All of the above are correct
all the above are correct
In a closed economy, national saving equals
A. income minus the sum of consumption and government purchases.
B. private saving plus public saving.
C. investment.
D. All of the above are correct.
All the above are correct
Which bond is most likely to default
A. Junk Bond
B. municipal bond
C. U.S Government bond
D. corporate bond issues by Proctor & Gamble Corporation
Junk bond
An increase in the price level and a reduction in output would result from
A. declining government expenditures.
B. a fall in stock prices.
C. tax rebates.
D. natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
Natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts
Most economists believe that fiscal policy
A. only affects aggregate demand and not aggregate supply.
B. primarily affects aggregate demand.
C. primarily effects aggregate supply.
D. only affects aggregate supply and not aggregate demand
primarily affects aggregate demand.
Historical evidence for the U.S. economy indicates that
A. recessions have occurred roughly once every six years since the 1960s.
B. the unemployment rate usually decreases during a recession and increases shortly after the recession ends.
C. real GDP usually remains roughly constant during a recession and decreases shortly after the recession ends.
D. changes in real GDP over the business cycle are largely attributable to changes in investment over the business cycle.
Changes in real GDP over the business cycle are largely attributable to changes in investment over the business cycle
In which of the following cases would the quantity of money demanded be largest?
A. r and P are the lowest
B. r the highest and P the lowest
C. r lowest and P the highest
D. r and P the highest
r is the highest and P is the lowest
In the graph of the money market, the money supply curve is
A. vertical. It shifts rightward if the Fed buys bonds.
B. vertical. It shifts rightward if the Fed sells bonds.
C. upward sloping. It shifts rightward if the Fed buys bonds.
D. upward sloping. It shifts rightward if the Fed sells bonds.
vertical. it shifts rightward if the Fed buys bonds
Tax cuts
A. shift aggregate demand right while increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand left.
B. shift aggregate demand left while increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand right.
C. and increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand left.
D. and increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand right.
and increases government expenditures shifts aggregate demand right
Economists use the word "money" to refer to
A. financial assets such as stocks and bonds.
B. any type of wealth.
C. those assets regularly used to buy goods and services.
D. income generated by the production of goods and services
those assets regularly used to buy goods and services
When the price level falls
A. people want to hold less money.
B. the interest rate falls.
C. investment spending rises.
D. All of the above are correct.
All of the above are correct
Which of the following Fed actions would both increase the money supply?
A. buy bonds and raise the reserve requirement
B. buy bonds and lower the reserve requirement
C. sell bonds and raise the reserve requirement
D. sell bonds and lower the reserve requirement
buy bonds and lower the reserve requirement
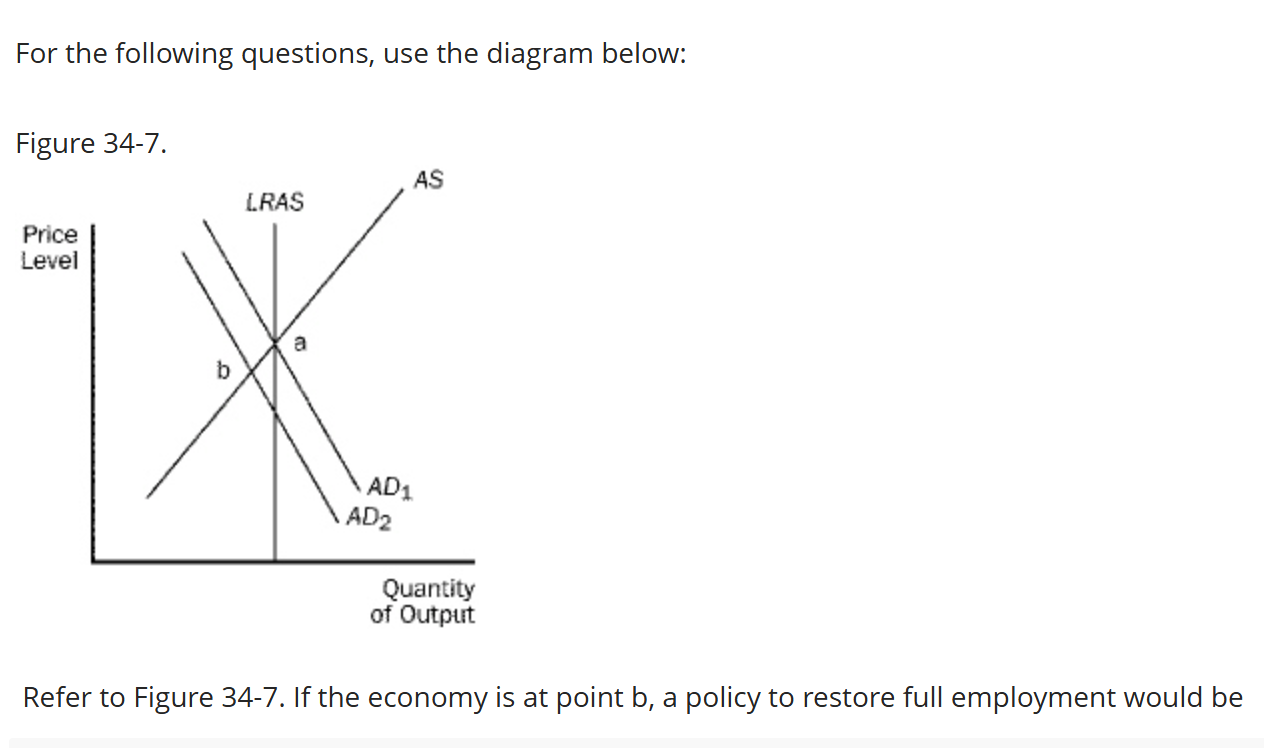
Refer to Figure 34-7. If the economy is at point b, a policy to restore full employment would be
A. an increase in the money supply
B. a decrease in government purchases.
C. an increase in taxes. ‘
D. All of the above are correct.
An increase in the money supply
Suppose a shift in aggregate demand creates an economic contraction. If policymakers can respond with sufficient speed and precision, they can offset the initial shift by shifting
A. aggregate supply right
B. aggregate demand right.
C. aggregate demand left.
D. aggregate supply left.
aggregate demand right
Which of the following does the Federal Reserve not do?
A. conduct monetary policy
B. act as a lender of last resort
C. convert Federal Reserve Notes into gold
D. serve as a bank regulator
Convert federal notes into gold
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A. The price level rises.
B. The price level falls.
C. The Fed purchases government bonds on the open market.
D. None of the above is correct
The Fed purchases government bonds and the open market
Supply-side economists believe that a reduction in the tax rate
A. always decrease government tax revenue.
B. shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.
C. provides no incentive for people to work more.
D. would decrease consumption.
shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A. an increase in the price level
B. an increase in the money supply
C. a decrease in the price level
D. a decrease in the money supply
increase in the money supply
Liquidity refers to
A. the relation between the price and interest rate of an asset.
B. the risk of an asset relative to its selling price.
C. the ease with which an asset is converted into a medium of exchange.
D. the sensitivity of investment spending to changes in the interest rate.
the ease with which an asset is converted into a medium of exchange
Which of the following shifts short-run, but not long-run aggregate supply right?
A. a increase in the nominal wage
B. a decrease in the nominal wage
C. a decrease in the capital stock
D. an increase in the money supply
decrease in nominal wage
The multiplier effect
A. and the crowding-out effect both amplify the effects of an increase in government expenditures.
B. and the crowding-out effect both diminish the effects of an increase in government expenditures.
C. diminishes the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while the crowding-out effect amplifies the effects.
D. amplifies the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while the crowding-out effect diminishes the effects.
amplifies the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while crowding out effect diminished the effects
If expected inflation is constant and the nominal interest rate increases by 3.5 percentage points, then the real interest rate
A. increases by 3.5 percentage points.
B. increases, but by less than 3.5 percentage points.
C. decreases, but by less than 3.5 percentage points.
D. decreases by 3.5 percentage points.
increase by 3.y percentage points
The primary argument against active monetary and fiscal policy is that
A. attempts to stabilize the economy do not constitute a proper role for government in a democratic society.
B. these policies affect the economy with a long lag.
C. these policies affect the economy too quickly and with too much impact.
D. history demonstrates that interest rates respond unpredictably to active policies, leading to unpredictable effects on income
these policies affect the economy with a long lag
Which of the following is not included in M1?
A. savings deposits
B. traveler's checks
C. currency
D. demand deposits
Savings deposits
Some economists argue that
A. monetary policy should actively be used to stabilize the economy.
B. fiscal policy should actively be used to stabilize the economy.
C. fiscal policy can be used to shift the AD curve.
D. All of the above are correct.
All of the above
The government builds a new water-treatment plant. The owner of the company that builds the plant pays her workers. The workers increase their spending. Firms from which the workers buy goods increase their output. This type of effect on spending illustrates
A. the multiplier effect.
B. the crowding-out effect.
C. the Fisher effect.
D. the wealth effect.
The multiplier effect
Which of the following would raise the price level in both the short and long run?
A. an increase in taxes
B. an increase in government expenditures
C. a decrease in the minimum wage
D. an increase in the capital stock
an increase in government expenditures
The wealth effect stems from the idea that a higher price level
A. increases the real value of households’ money holdings.
B. decreases the real value of households’ money holdings.
C. increases the real value of the domestic currency in foreign-exchange markets.
D. decreases the real value of the domestic currency in foreign-exchange markets.
decreases the real value of households money holdings
When the dollar depreciates, U.S.
A. exports decrease, while imports increase.
B. exports and imports decrease.
C. exports and imports increase.
D. exports increase, while imports decrease.
exports increase while imports decrease
In response to the sharp decline in stock prices in October 1987, the Federal Reserve
A. increased interest rates, and the economy avoided a recession.
B. increased interest rates, but the economy was unable to avoid a recession.
C. decreased interest rates to avoided a recession.
D. decreased interest rates to avoid a boom.
decreased interest rates to avoid a recession
Suppose stock prices rise which shifts AD to the right. To offset the resulting change in output the Federal Reserve could
A. increase the money supply. This increase would also move the price level closer to its value before the rise in stock prices.
B. increase the money supply. However, this increase would move the price level farther from its value before the rise in stock prices.
C. decrease the money supply. This decrease would also move the price level closer to its value before the rise in stock prices.
D. decrease the money supply. However, this decrease would move the price level farther from its value before the rise in stock prices
decrease the money supply. this decrease would also move the price level closer to its value before the rise in stock prices
Other things the same, when the price level falls, interest rates
A. rise, so firms increase investment.
B. rise, so firms decrease investment.
C. fall, so firms increase investment.
D. fall, so firms decrease investment.
falls so firms increase investment
The (equilibrium) interest rate falls if
A. either money demand or money supply shifts right.
B. money demand shifts right or money supply shifts left.
C. either money demand or money supply shifts left.
D. money demand shifts left or money supply shifts right.
money demand shifts left or money supply shifts right
From 2001 to 2005 there was a dramatic rise in the price of houses. If this rise made people feel wealthier, then it would have shifted
A. aggregate demand left.
B. aggregate supply left.
C. aggregate demand right.
D. aggregate supply right.
aggregate demand right
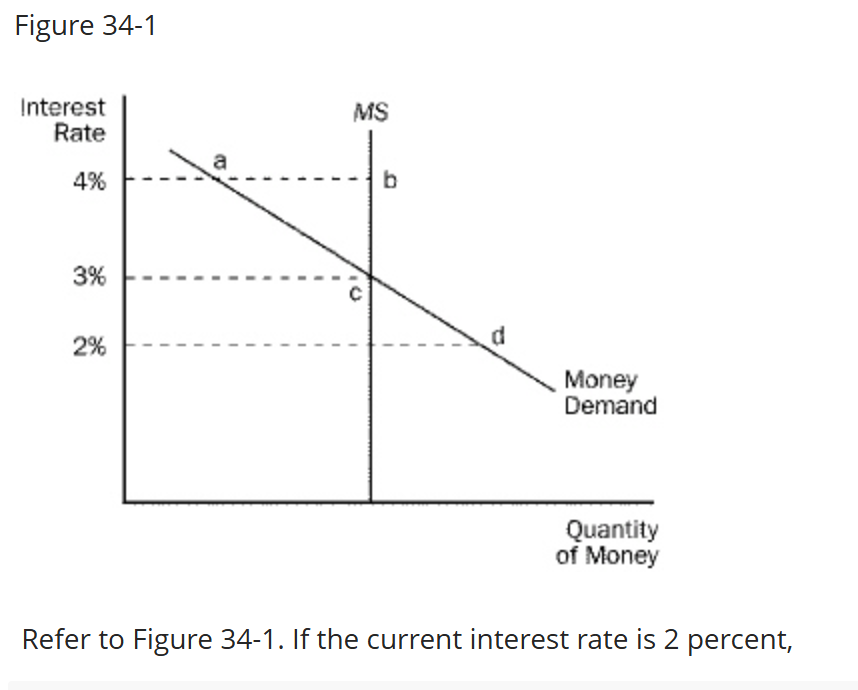
Refer to Figure 34-1. If the current interest rate is 2 percent,
A. there is an excess supply of money.
B. people will sell more bonds, which drives interest rates up.
C. as the money market moves to equilibrium, people will buy more goods.
D. All of the above are correct.
people will sell more bonds which drives interest rates up
If the dollar appreciates because of speculation or government policy U.S.
A. aggregate demand shifts left. U.S. aggregate demand also shifts left if other countries experience recessions.
B. aggregate demand shifts left. U.S. aggregate demand shifts right if other countries experience recessions.
C. aggregate demand shifts right. U.S. aggregate demand also shifts right if other countries experience recessions.
D. aggregate demand shifts right. U.S. aggregate demand shifts left if other countries experience recessions
aggregate demand shifts left U.S aggregate demand also shifts left if other countries experience recessions
The country of Cedarland does not trade with any other country. Its GDP is $17 billion. Its government purchases $5 billion worth of goods and services each year and collects $6 billion in taxes. Private saving in Cedarland is $5 billion. For Cedarland, investment is…
6 billion and consumption is 6 billion
In a closed economy, if Y, C, and T remained the same, a decrease in G would
increase public saving but not private saving.
In a closed economy, what does (Y − T − C) represent?
private savings
Consider the expressions T − G and Y − T − C. Which of the following statements is correct?
The first of these is public saving; the second one is private saving.
In a closed economy, what does the difference between the tax revenue and government purchases, (T − G), represent?
public saving
If the government instituted an investment tax credit, then which of the following would be higher in equilibrium?
saving and the interest rate
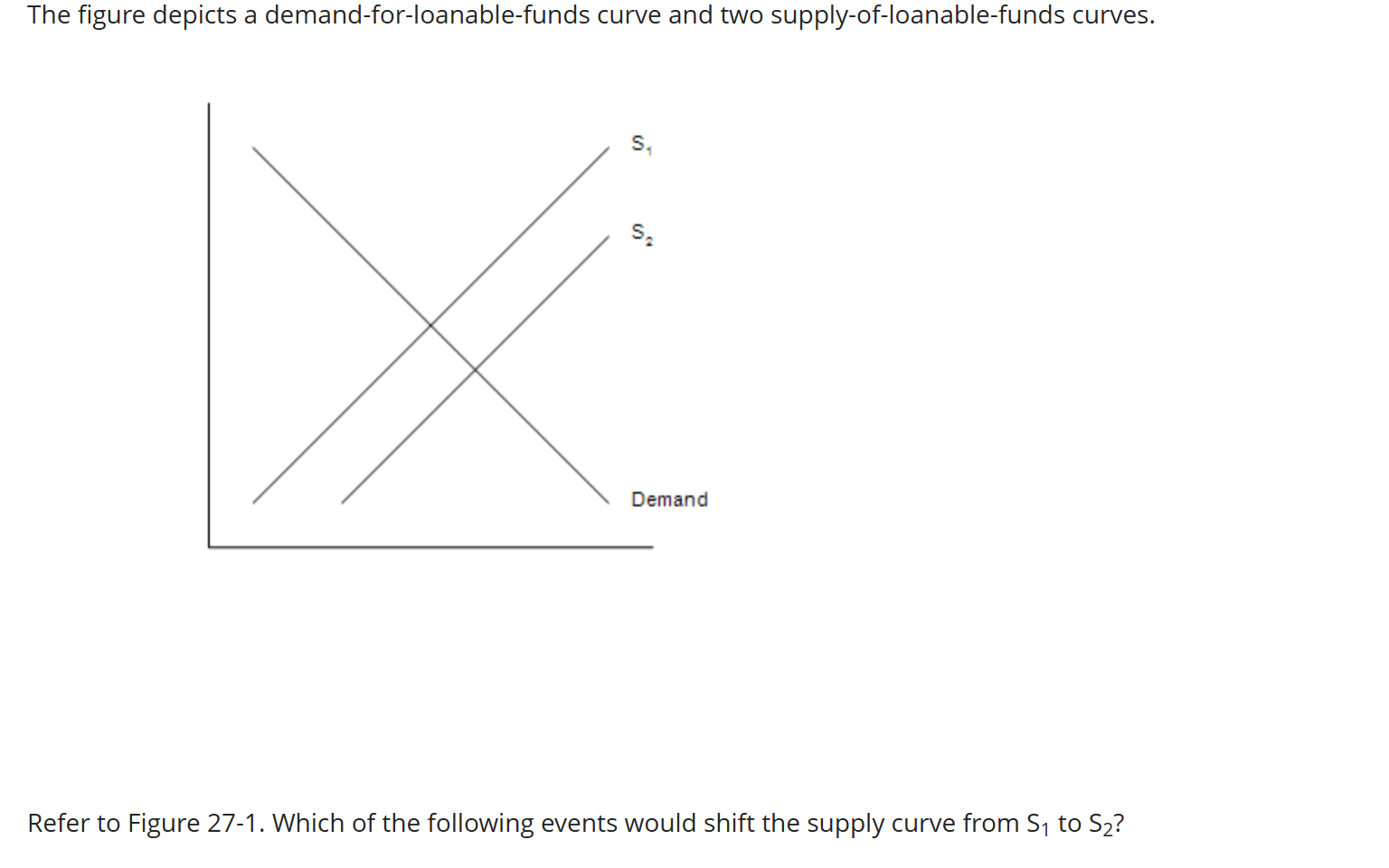
Which of the following events would shift the supply curve from S1 to S2?
In response to tax reform, households are encouraged to save more than they previously saved.
Suppose the U.S. offered a tax credit for firms that built new factories in the U.S. Then the
demand for loanable funds would shift rightward, initially creating a shortage of loanable funds at the original interest rate.
Suppose a country has only a sales tax. Now suppose it replaces the sales tax with an income tax that includes a tax on interest income. This would make equilibrium
interest rates rise and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds fall
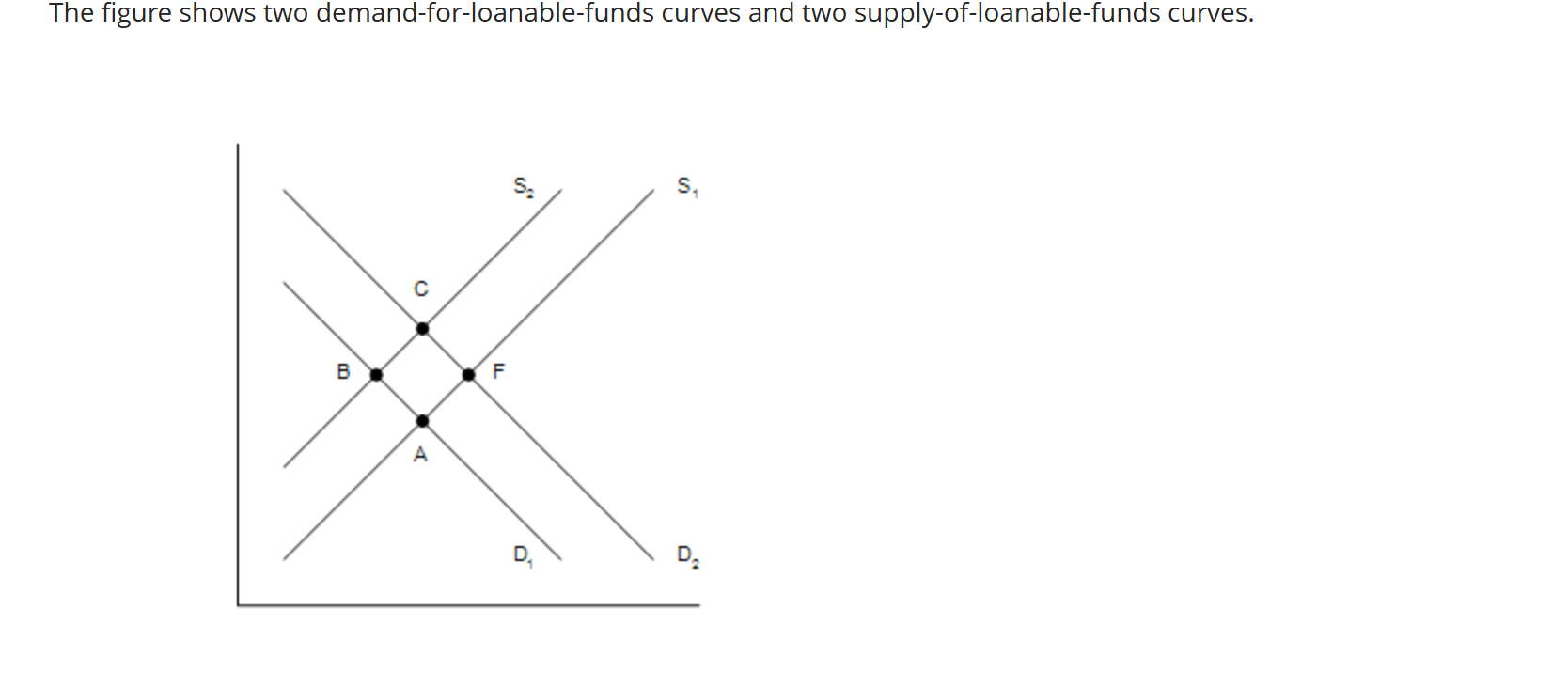
Which of the following movements would be consistent with the government budget going from deficit to surplus and the simultaneous enactment of an investment tax credit?
A movement from Point B to Point F
Which of the following would necessarily create a surplus at the original equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market?
An increase in the supply of or a decrease in the demand for loanable funds
Other things the same, the higher the rate of saving and investment in a country, the higher will be the standard of living in the future.
true